2. The Falling Frame in Kruskal-Szekeres Coordinates
The Schwarzschild metric is the simplest non-trivial solution to Einstein’s field equations. It is the metric that describes every spherically symmetric vacuum spacetime. The the external form of the metric can be expressed as:
Equation
1 is the external metric with
t being the timelike coordinate and
r being the spacelike coordinate. The Schwarzschild radius of the metric is given by
in units with
. The external metric is the metric for an eternally spherically-symmetric vacuum centered in space.
We can see in equation
1 that as
, the basis vector
goes to zero while
goes to infinity. This location is called the ’Event Horizon’ of the metric. The behaviour of the basis vectors at this location seem to imply that there is a coordinate singularity at this location since the spacetime curvature is not infinite there.
In order to overcome the behaviour of the basis vectors at this location, different coordinate systems have been developed which do not have degenerate behaviour at the Event Horizon. The most important of these coordinate systems are the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates, which are the maximally extended coordinates for the Schwarzschild metric. The coordinate definitions and metric in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates are given below (derivation of the coordinate definitions and metric can be found in reference [
1] where
and
).
With the full metric in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates given by:
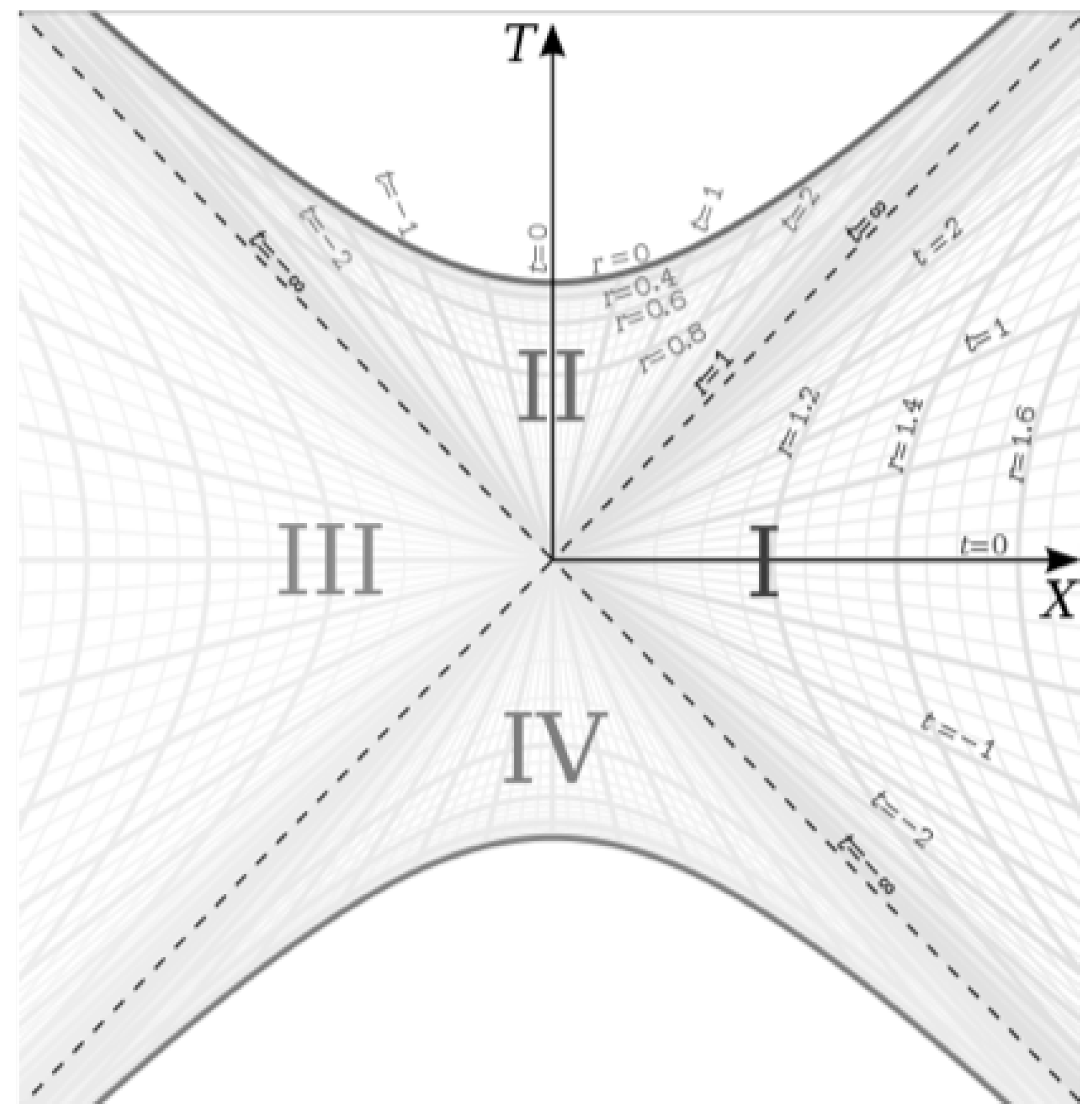
Finally, we plot the metric on the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinate chart [
2] in
Figure 1:
In this paper, we will be focusing on region I in this chart, which is the spherically symmetric spacetime around a spherically symmetric source in space.
We can see in
Figure 1 that for a rest frame (
), that
depends on the value of
t we evaluate the derivative at since the derivative for the rest frame is the tangent to the hyperbola at
t. Since the metric is time-symmetric, we now that the actual physics does not depend on the value of
t and therefore, we need a deeper understanding of the meaning of the changing
in the rest frame and how it relates to the falling frame at the same point.
Let us first take the differentials of
T and
X in equations
2:
Calculating the partial derivatives, rearranging and defining
:
Next, we need to calculate
from equations
5 by factoring out
from each equation and dividing:
Next, we make the following definitions:
This is the derivative of the rest frame at
t since plugging
into equation
6, we get
. And we define the relative velocity of the frame in motion relative to the rest frame as:
This is the relative velocity in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates between the frame in motion and the rest frame at
r. This derivative is 0 for the rest frame since
in that frame.
Plugging these definitions into equation
6, we get:
We recognize that equation
9 is the relativistic velocity addition formula giving us the total velocity as the relativistic sum of the rest frame velocity and the relative velocity between the moving frame and the rest frame. We can solve for
to get an expression for the relative velocity between a frame in motion and the rest frame in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates:
Assuming
, we see that the relative velocity approaches -1 for all
as the horizon is approached since the horizon is at
, such that
there. Equation
10 is also constant along a given hyperbola, meaning it is independent of
t. In fact, it is the
we get when setting
in equation
6 which makes sense because at
, the Schwarzschild basis vectors and Kruskal-Szekeres basis vectors are aligned there, meaning that the
X and
T in
are pure spacelike and timelike basis vectors and thus the derivative gives a true velocity. This is in contrast to the general
which is a derivative without a clear spacetime meaning since the
X and
T coordinates are mixtures of space and time everywhere else.
We will now get an expression for the Lorentz boosts of frames in motion relative to the rest frame. We can solve for
in equation
1 as follows:
We get the time dilation for the rest frame by setting
. We can define the Lorentz boost of the moving frame by dividing
in equation
11 by
, which is the time dilation in the rest frame at
r:
The rapidity
relative to the local rest observer in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates is given by:
Finally, we can combine these to get the Lorentz factor as a function of rapidity:
We can begin to see that the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates are similar to Minkowski coordinates for an inertial frame. For an inertial observer in freefall, the local speed of light is always 1, and in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates, the speed of light is 1 everywhere. The difference here is, of course, that we have a curved spacetime such that the speed of light observed by rest frames will vary depending on the location relative to the black hole.
The Kruskal-Szekeres coordinate axes in
Figure 1 represent the spacetime in the frame of the source of the metric. In this frame, rest frames accelerate away from the source, such that those lines are hyperbolas in the source frame. So
is the velocity of the falling frame as seen from the rest frame. But a falling frame will have an increasing velocity relative to the rest observers, and therefore, their reference frames will be Lorentz boosted relative to the rest frame per equation
12.
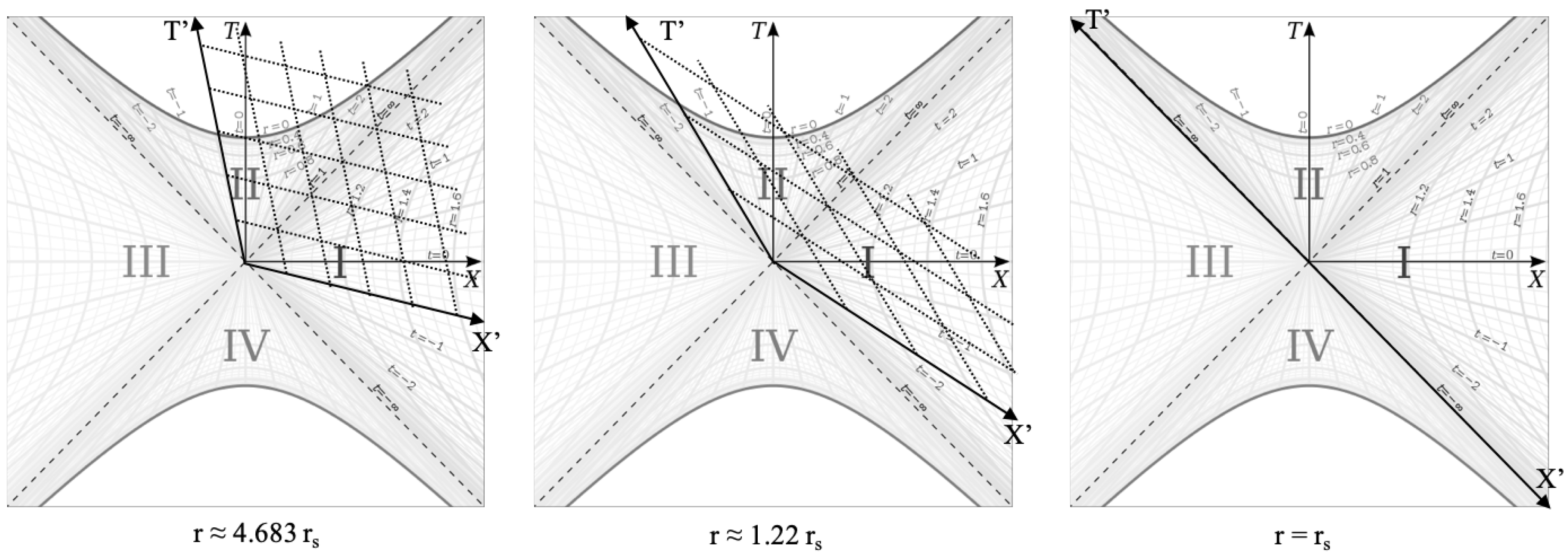
Figure 2 shows three snapshots of boosted falling frames that started falling from infinity with the frame’s
r coordinate (the
r the frame had fallen to when the boost is being depicted) labelled below each snapshot.
In this figure, we can see that the basis vectors of the boosted frames are rotated relative to the rest frame (the and axes represent the boosted frames).
From this, we can also get a sense of length contraction in the falling frame. Firstly, we must note that the
term of the metric really should be
since it represents a change in the radial position of a particle. This means the Lorentz boost the falling frame experiences when it falls is radial in all directions, with the origin of the frame at the horizon (it is the radial
basis vector that rotates in
Figure 2). The planar surfaces perpendicular to a Cartesian coordinate axis in the Minkowski metric become spherical surfaces centered on the metric source in the Schwarzschild metric. So when we talk about length contraction in a radially falling frame, we are saying that circumferences around the source of the metric are length contracted in that frame and remain circular. This radial contraction is necessary for all inertial observers to see the spacetime as spherically symmetric. If the length contraction was dependant on the direction of the radial fall, then inertial observers would disagree on the spherical symmetry of the metric.
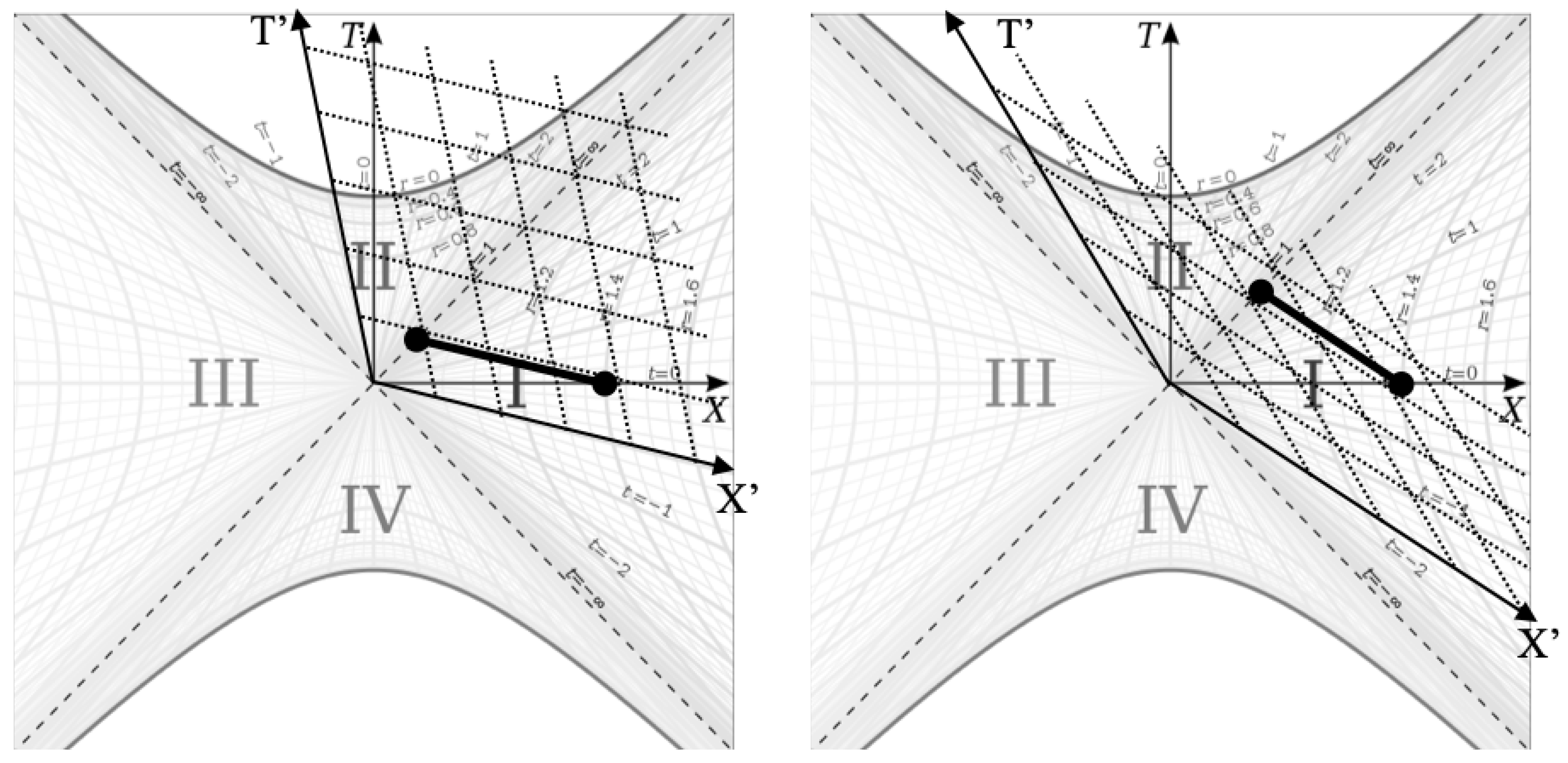
We can see the length contraction effect in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates by looking at the X distance from the horizon to some radius r along a line of constant T for two different cases where the observers started falling from a different radius in each case such that when when we look at the frame of each observer at some time after they started falling, the Lorentz factor and rapidity have different values for each case.
In the above figure, the left frame has a lower radial velocity and therefore a lower rapidity ( in this case) relative to the right frame, which has a rapidity of . We chose the same point in both frames for comparison to look at its distance from the event horizon in both frames. By comparing the dark lines in each picture, which represent the distance from the horizon to some r (the same r in both cases) measured in at constant in each frame, we clearly see that this distance is shorter in the frame on the right compared to the frame on the left.
We can calculate the actual ratio of the lengths in the two frames given the length contraction equation
. The ratio of the lengths of the lines on the left (
) and right (
) sides of
Figure 3 will be a ratio of Lorentz factors. We can see from the figure, that
and
. Using equation
14, we can solve for the ratio of the lengths in the falling frames as:
Note that we would get the same result regardless of which point on the
r hyperbola we draw the line to, as long as we use the same point in all frames being compared and draw the lines to the horizon along a line of constant
T in each frame.
As the rapidity increases further, we can see that this line will tend toward a null geodesic as the horizon is approached indicating that the spacetime contracts fully to the horizon in the falling frame, which is consistent with the argument that the falling frame becomes light-like at the horizon.
The contraction of the
r coordinate in these frames relative to the rest frame can be calculated by plugging the contracted
X length into equation
2 and solving for
r. By calculating the contracted
r coordinate, we can calculate the contracted circumferences around the metric source in the falling frame and we can see from the above analysis that these circumferences will contract to zero when the frame reaches the horizon.
Given the length contraction observed, the observer should also see the volume of the source contract in the falling frame. Applying the length contraction equation to the volume of the source:
Where
is the Schwarzschild radius. The mass of the source is related to its Schwarzschild radius by
If we assume the mass of the source is within the Schwarzschild radius, the density of the source in the falling frame is given by
So in the falling frame,
goes to infinity as the horizon is approached such that the density there also goes to infinity. This shows us that due to the length contraction, there is no space beyond the event horizon in the falling frame, indicating that the event horizon is the end point of gravitational collapse. At the horizon, the falling frame will see the entire Universe radially length contracted to the horizon as well due to length contraction. This is reflected in the rest frame by the fact that all hyperbolas intersect with the horizon when
, which is the horizon itself. We see therefore that the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates represent the spacetime in the frame of the source which is an infinitely dense point at
. This point looks like a surface to a distant observer, but is length contracted to a point when the horizon is approached. In a followup work, it will be demonstrated that reaching the horizon in is not possible in the actual Universe.
If the horizon is the endpoint of gravitational collapse, then the question then remains, what is region II of
Figure 1 describing. We know that the Schwarzschild solution describes all spherically symmetric vacua. In region I, the
t coordinate is spacelike while the
r coordinate is timelike. We see that at the the horizon, the spatial
t coordinate density is infinite and the coordinate lines separate as one moves from the horizon to
. It was also demonstrated that in the case of the external solution, the source of the metric is at
. It stands to reason then that the source of the internal solution is also at that point. So the internal solution describes a spherically symmetric vacuum surrounded by a horizon which, from the perspective of an observer at some
r between the horizon and
, surrounds the vacuum infinitely far away in space and at some finite time in the past. And from the perspective of that observer, this horizon, which looks like a surrounding sphere, is a time where space is infinitely dense. A spacetime fitting this description would be any empty space in the Universe whose surrounding mass is spherically symmetric. Voids in the cosmic web would be an example of such a spacetime, and the horizon of the metric in this case would be the Big Bang, which is an event at some finite time in the past that surrounds all points in the Universe which has an infinite density. And an observer in the present Universe can never reach the Big Bang, no matter how far they travel through space, which is in alignment with the fact that the surface, from the perspective of a present observer, is infinitely far away from them in space. So we might think of the expanding Universe as baking bread where the air pockets that expand as the bread bakes give the bread a web-like structure over time, where the bread itself would be analogous to the cosmic filaments of matter in the Universe. A full cosmological analysis of the internal solution will be completed in a followup work which will also discuss all four regions of the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinate chart as well as the curvature singularity at
.