1. Introduction
The Schwarzschild metric is the simplest non-trivial solution to Einstein’s field equations. It is the metric that describes every spherically symmetric vacuum spacetime. The the external and internal forms of metric can be expressed as (coordinates in the internal metric are primed to distinguish them from the internal metric coordinates):
Equation
1 is the external metric with
t being the timelike coordinate and
r being the spacelike coordinate. The Schwarzschild radius of the metric is given by
in units with
. We use the prime notation for the coordinates here to distinguish the external coordinates from the internal coordinates. The external metric is the metric for an eternally spherically-symmetric vacuum centered in space. This metric is also used to describe the vacuum outside a spherically symmetric object occupying a finite amount of space with a finite mass (like a star or planet). This metric as written in Equation
1 becomes the Minkowski metric as
.
Equation
2 is the internal metric with
being the spacelike coordinate and
being the timelike coordinate. Instead of using
in the internal metric, we use the variable
u for the internal metric in this paper. The reason will become more apparent later on, but it is important to note that
is a length while
u is a time. This metric is currently believed to describe the interior of a Black Hole. We can see in Equations
1 and
2 that as
or
, the basis vectors
and
go to zero while the
and
go to infinity. This location is called the ’Event Horizon’ of the metric. The behaviour of the basis vectors at this location seem to imply that there is a coordinate singularity at this location since the spacetime curvature is not infinite there.
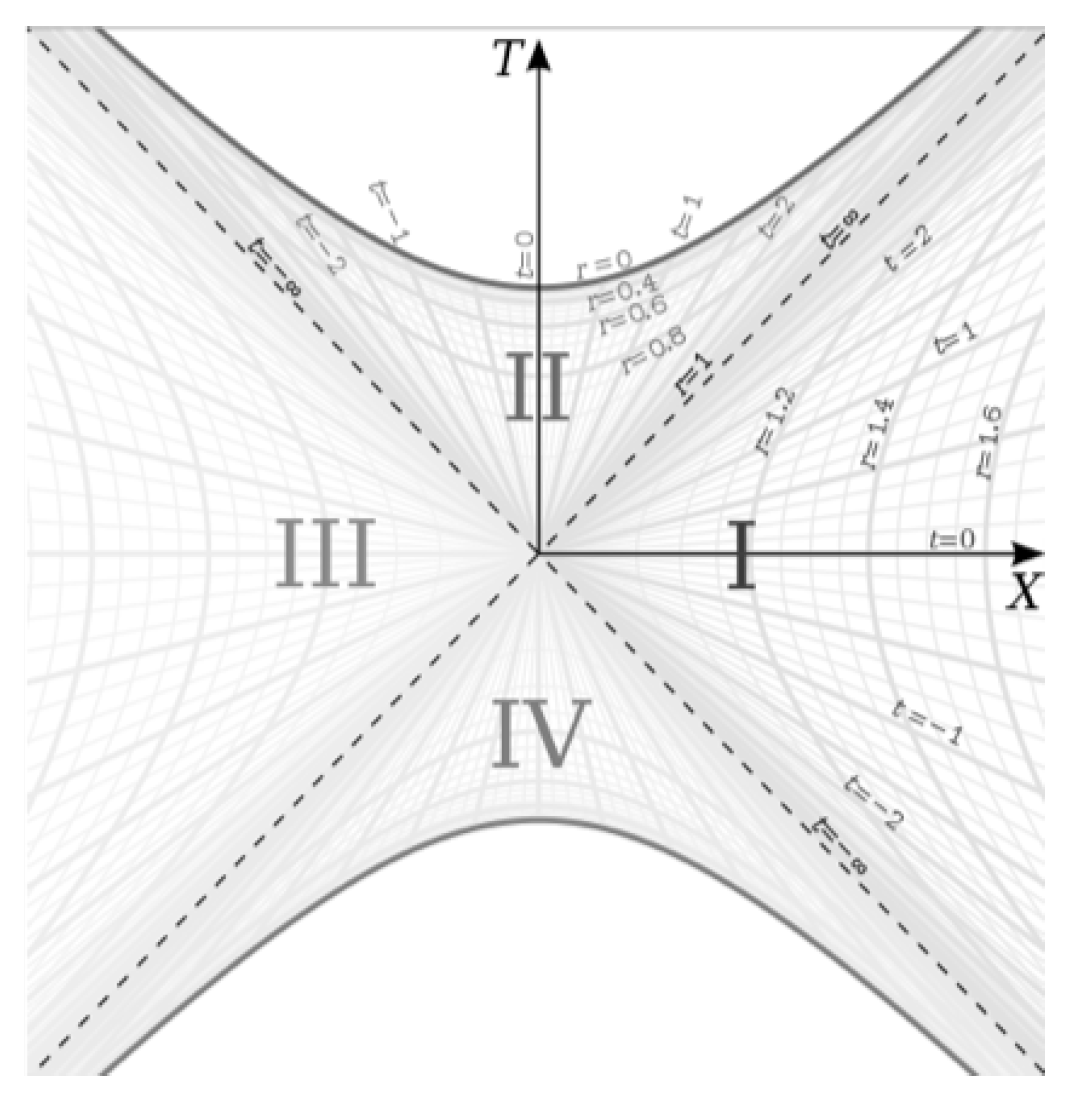
In order to overcome the behaviour of the basis vectors at this location, different coordinate systems have been developed which do not have degenerate behaviour at the Event Horizon. The most important of these coordinate systems are the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates, which are the maximally extended coordinates for the Schwarzschild metric. The coordinate definitions and metric in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates are given below (derivation of the coordinate definitions and metric can be found in reference [
1] where
and
).
For the external metric:
And for the internal metric:
With the full metric in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates given by:
Where
R represents either
for the external metric or
u for the internal metric. Given the coordinate definitions, we get the following relationship between the
T and
X coordinates:
Finally, we plot the metric on the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinate chart [
2] in
Figure 1:
In this paper, we will be focusing on regions I and II in this chart. Region I represents the external metric, and region II represents the internal metric.
2. The Symmetries of the Schwarzschild Metric
Historically, when the Schwarzschild metric was derived, it was derived under the assumptions of a static spherically-symmetric vacuum. Birkhoff’s theorem later showed that the static assumption is not necessary and that the Schwarzschild metric is the description for all spherically-symmetric vacua in General Relativity. This makes sense because while the assumption of a static metric applies to the external solution, it is well-known that the internal solution is not static due to the fact that r becomes the timelike coordinate and t becomes the spacelike coordinate in the internal metric.
The assumption of a static condition in the case of the Schwarzschild metric turns out to be the assumption that the metric is symmetric under hyperbolic rotation. We can see this in
Figure 1, where in both the external and internal cases, the
t coordinate is a hyperbolic angle. Since the metric coefficients are independent of
t, this means that performing a hyperbolic rotation of the spacetime does not change the physics just as doing a spherical rotation of the spacetime does not change the physics.
Regions I and II of
Figure 1 represent 1+1 dimensions of the external and internal metric. Therefore, for example, region I represents a radial line at fixed angles
and
in space at all times. So all worldlines in region I represent particles on the same radial line at different times. We can extend
Figure 1 to 2+1 dimensions by adding a
Y coordinate perpendicular to both
X and
T to equation
6 as follows:
We can do this because of the spherical symmetry of the metric if we assert that
is the center of the source of the metric. Next, let us compare equation
7 to the equation for a hyperboloid of revolution given below:
These equations are equivalent if we set
,
,
, and
. We can see that
for the external metric and
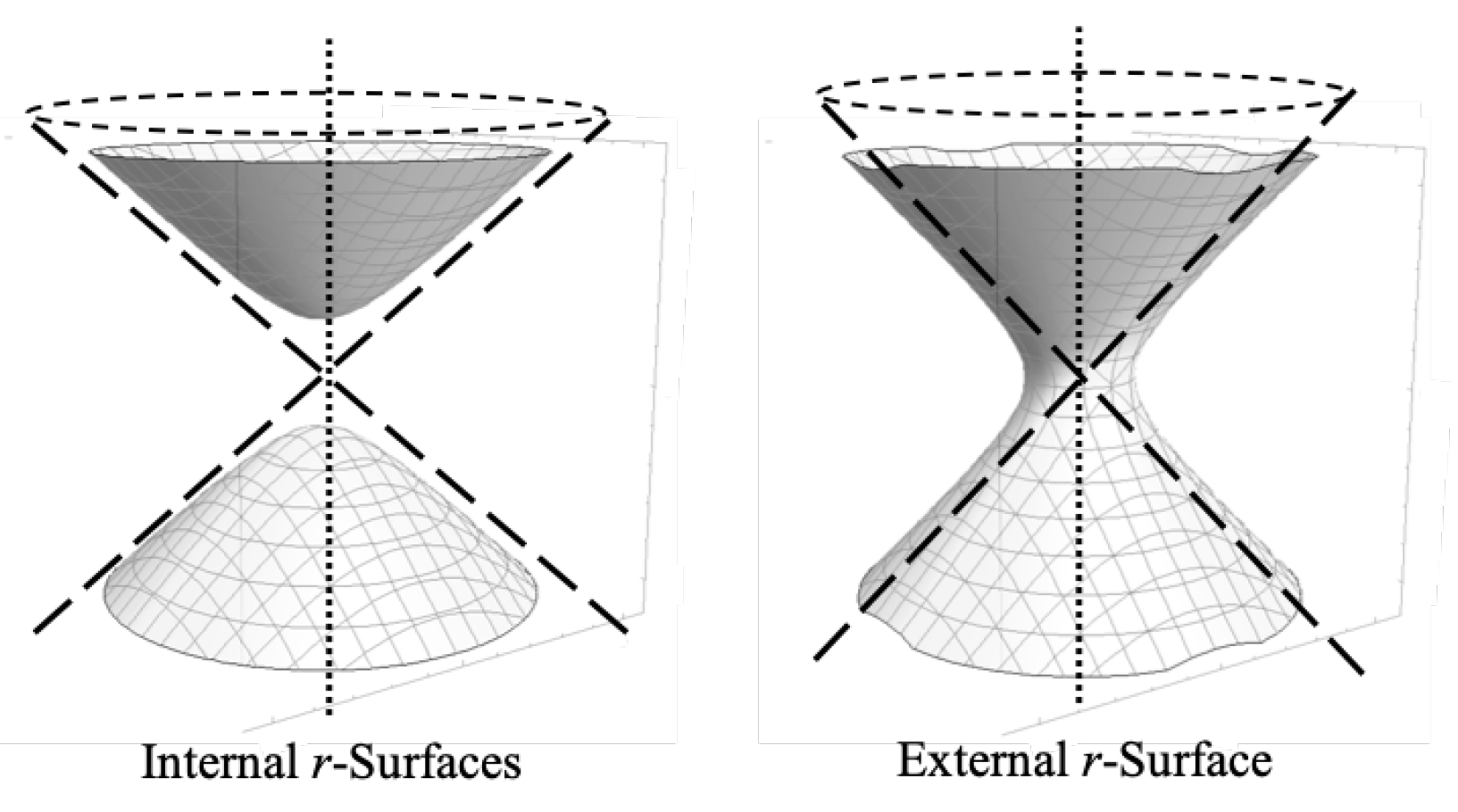
for the internal metric. We can plot both cases for fixed
r (
for the external case,
for the internal case) to see what surfaces of constant
r look like in both the external and internal solutions:
Note that in the external case shown in
Figure 2, the
t coordinates are radial lines emanating out of the center of the diagram on the outside of the light cone representing the event horizon (dashed lines). This is clear by imagining you revolve region I in
Figure 1 around the
T axis (the
T axis is represented by the vertical dotted line). All
r surfaces in the external metric lie outside of the event horizon light cone depicted. Likewise, for the internal case, the
t coordinates are radial lines emanating out of the center of the diagram on the inside of the event horizon light cone and all
r surfaces of the internal metric lie inside the event horizon light cone. This can also be visualized by revolving region II in
Figure 1 around the
T axis.
If we assume the surfaces in
Figure 2 are depicting the case where
, then the two Killing vectors of the spacetime are
and
. The
Killing vector tells us that if we rotate the surface along with all the worldline points on it in the
direction (revolve all the points on the surface around the
T axis by some amount), there is no change to the physics. This is true for both surfaces.
The
Killing vector tells us that if we hyperbolically rotate the surface along with all the worldline points on it, the physics also remains unchanged. For the external case, this hyperbolic rotation is essentially 1-dimensional in that you can only hyperbolically rotate the external surface in the ’vertical’ (
T) direction (looking at region I of
Figure 1, this means you move all the points up or down along their respective hyperbolas). But in the internal case, we can see that the surface can be hyperbolically rotated in 2 dimensions either along the
X or
Y directions, or in a direction whose vector is some linear combination of the
X and
Y directions. Again, looking at
Figure 1, the hyperbolic rotation would mean you move all the points left or right along their respective hyperbolas. But since the axis of rotation is
T, this means that we have two degrees of freedom for hyperbolic rotation in the internal case.
We can extend this to 3 spatial dimensions by adding a
term to equation
9 as follows:
This cannot be visualized as it requires four dimensions to do so, but we can just imagine that each circle around the
T axis shown on the surfaces in
Figure 2 represents the surface of a sphere in 3D.
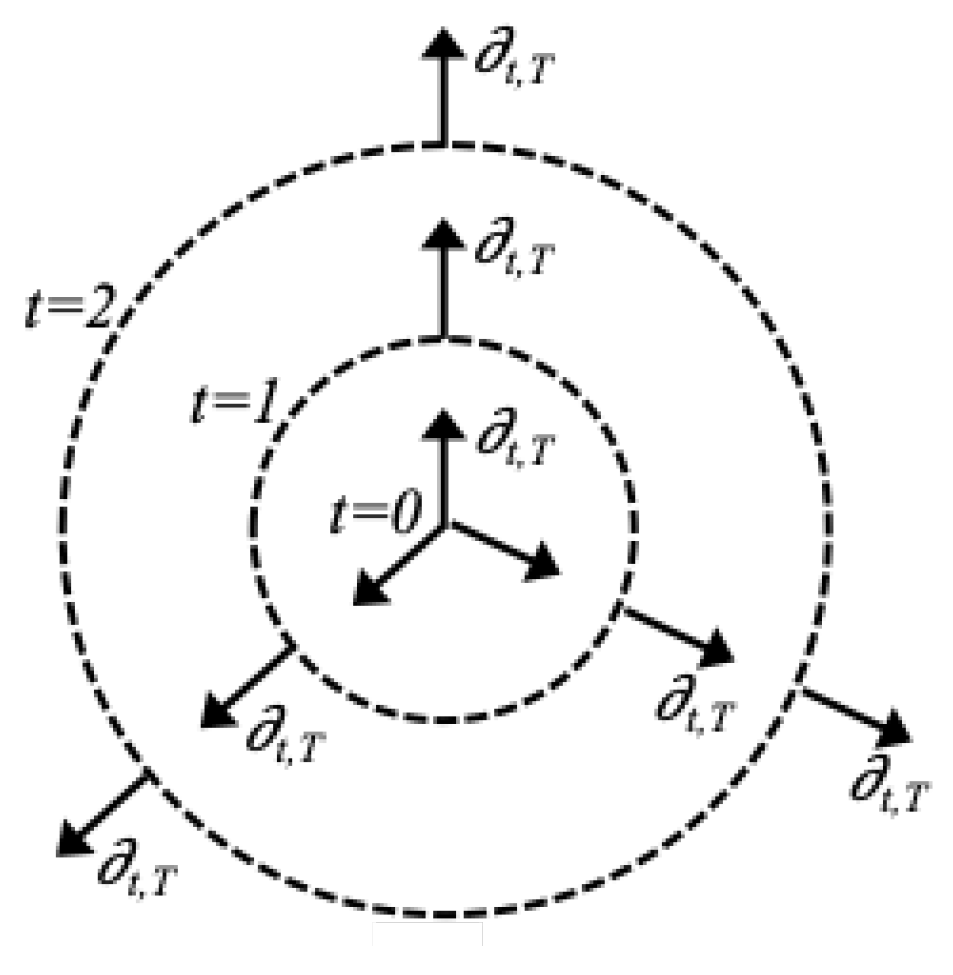
So with the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates, we can call the
t Killing vector
since it involves hyperbolic rotation exclusively in the
T direction. We can even imagine it as having a radial-type structure as shown in
Figure 3 below, where the vectors are the same in all directions and at all times:
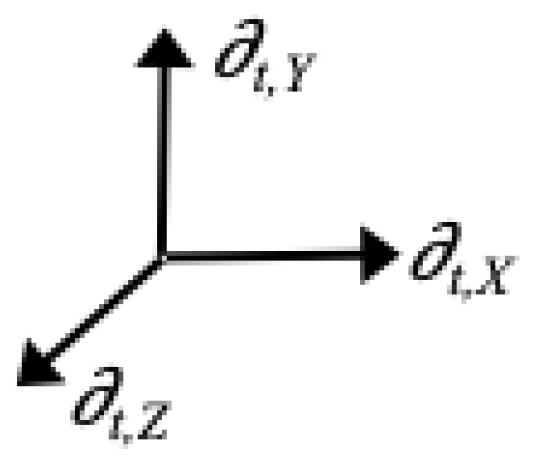
For the internal metric, we essentially have t Killing vectors in each of the 3 spatial Kruskal-Szekeres directions called , , and . These form a Cartesian basis for the 3D space of the internal solution at a given time (r is the timelike coordinate in the internal solution):
So for the 2 sheets on the left side of
Figure 2, the
and
coordinates can be interpreted as the hyperbolas on the surface running perpendicular to each other in the
X and
Y directions (in this paper, we are only concerned with the upper hyperboloid on the left side of
Figure 2, but the
X and
Y oriented hyperbolas are more easily seen as the mutually perpendicular hyperbolas on the low hyperboloid. The upper sheet has the same hyperboloids, but it is more difficult to see them in the figure). Again,
Figure 2 is only depicting 2 spatial dimensions, but the spherical symmetry tells us that there is a 3rd spatial dimension
Z that behaves identically to the
X and
Y dimensions.
It is important to recall here that the
t coordinate and therefore the
basis/Killing vectors are spacelike in the internal metric and
r is the timelike coordinate. Therefore, since the Cartesian basis of the spatial part of the internal metric depicted in
Figure 4 are also Killing vectors, we see that at a given time, the space of the internal metric is homogeneous and isotropic. Thus, the hyperbolic rotation symmetry of the Schwarzschild metric results in a static solution for the external metric and homogeneous space at fixed time for the internal solution.
3. The Presentist Perspective
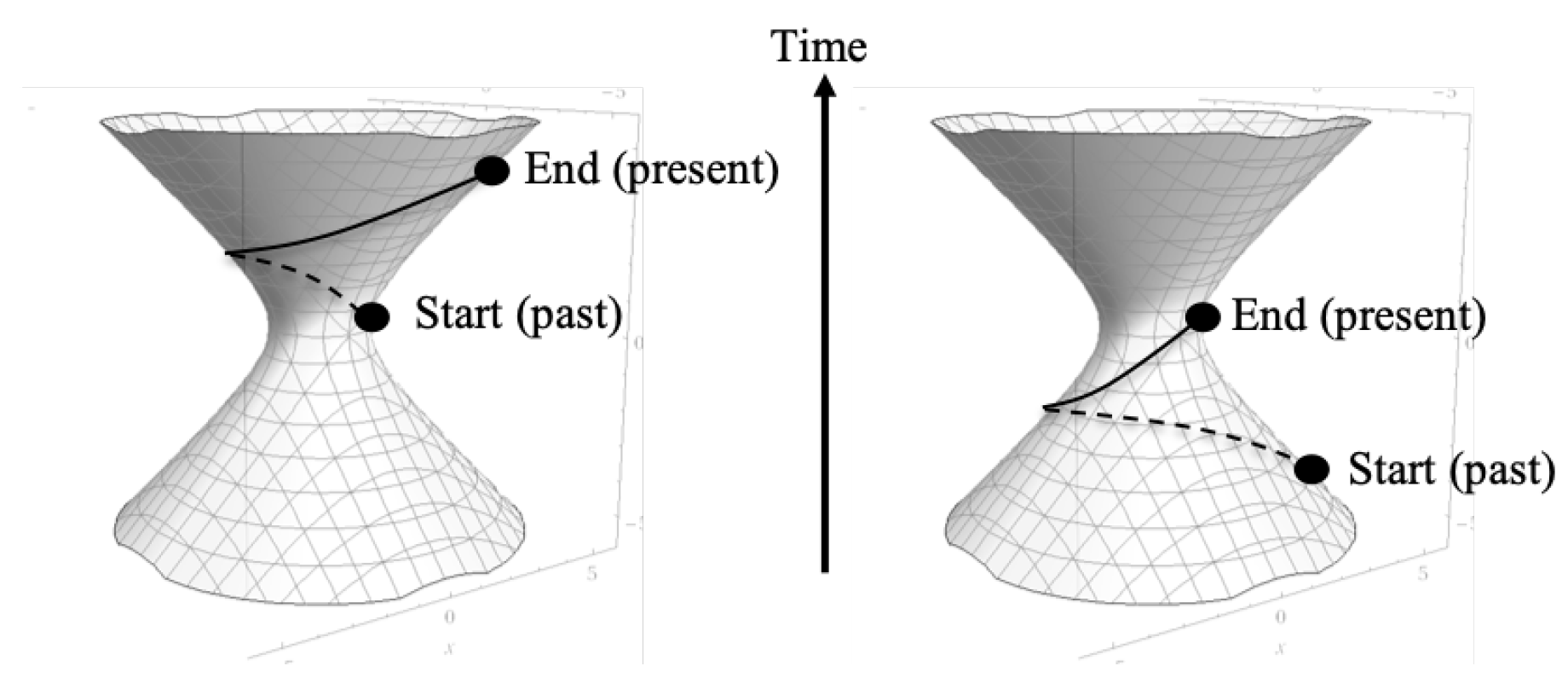
Given the circular and hyperbolic rotational symmetries of the Schwarzschild metric, we can now examine the worldlines for particles in circular orbit as well as in radial freefall from a presentist perspective. To define the meaning of a ’presentist perspective’, consider
Figure 5 below:
In this figure, we see the sheet for the external solution at some fixed r. Drawn on the sheet is the worldline of a particle in inertial circular orbit around the source of the metric for one revolution of the orbit. Time increases vertically as shown in the figure. On the left side, the worldline starts at the center () and spirals up the surface counter-clockwise until in returns to the same angular position at which it started at some later time t.
On the left side, we have the same worldline, but hyperbolically rotated down so that the end point is at and the starting point is at some . Because of the hyperbolic symmetry, these two worldlines are identical because they are on the same surface with the only difference being that they have been hyperbolically rotated relative to each other. This is equivalent to saying that since the external metric is static, it doesn’t matter what time t at which you choose to start (or end) the worldline, as long as (in this case) the and are the same in both cases.
But on the right side of
Figure 5, instead of interpreting the figure as saying that the worldline runs from some
to
, we can look at it as the present point always remaining at
and
while the surface rotates about the vertical axis and hyperbolically rotates downward as time goes on. So we need to imagine a dynamic picture where we fix a pen to the
,
point on the surface and then circularly and hyperbolically rotate the surface such that the past worldline grows out of the point in the
direction as time passes. Since the end of the worldline, which always represents the present is always at the
coordinate, this is what is meant by the presentist perspective. In this perspective the present worldline point is always at
and the past worldline points are hyperbolically rotated downward to increasing
coordinates as time passes. This is still equivalent to drawing the line as described for the left side of the figure, where the past worldline points have fixed
t coordinates and as time passes, new worldline points are fixed to increasing
t coordinates.
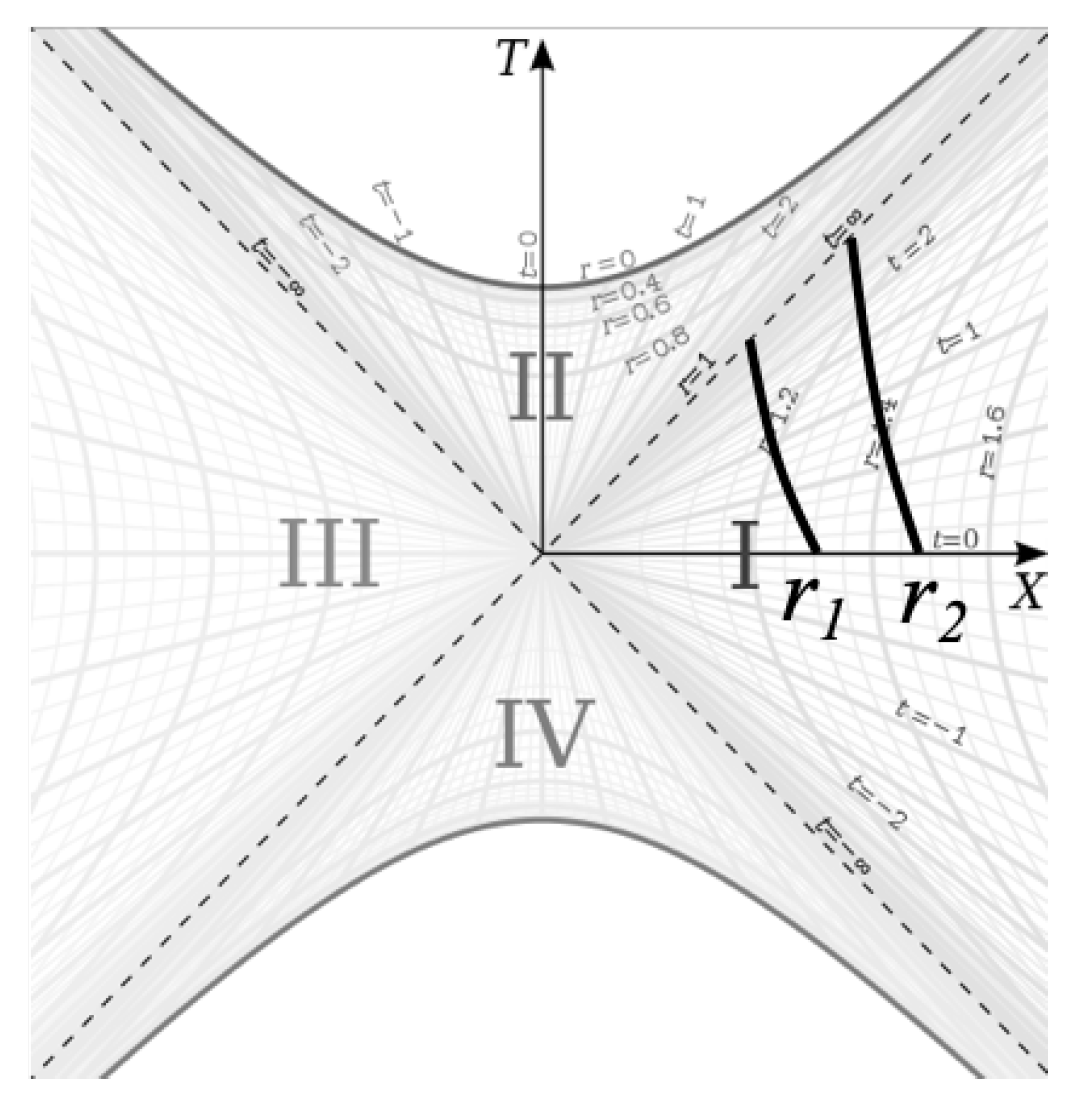
Now let us consider particles in radial freefall as seen on the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinate chart.
Figure 6 shows the worldlines for two different particles falling toward the event horizon. They both start at time
but one starts the fall from some radius
and the other from some greater radius
.
If we were to extend the worldlines to , we are given the impression that the particles never meet at any point in the spacetime where since the worldlines never intersect each other. But let us look more closely at the event horizon, represented by the dashed line on the diagram. That line is a null geodesic in the spacetime meaning the proper distance s between any two points on the line is zero. Furthermore, the coordinate position for all points on that line is the same (). Therefore, the points where the two worldlines intersect the horizon are at the same coordinate position separated by zero proper distance. By definition, this means that the two particles are coincident at the horizon. This tells us that no matter how far apart any two particles are when they start to fall, they will meet each other at the event horizon.
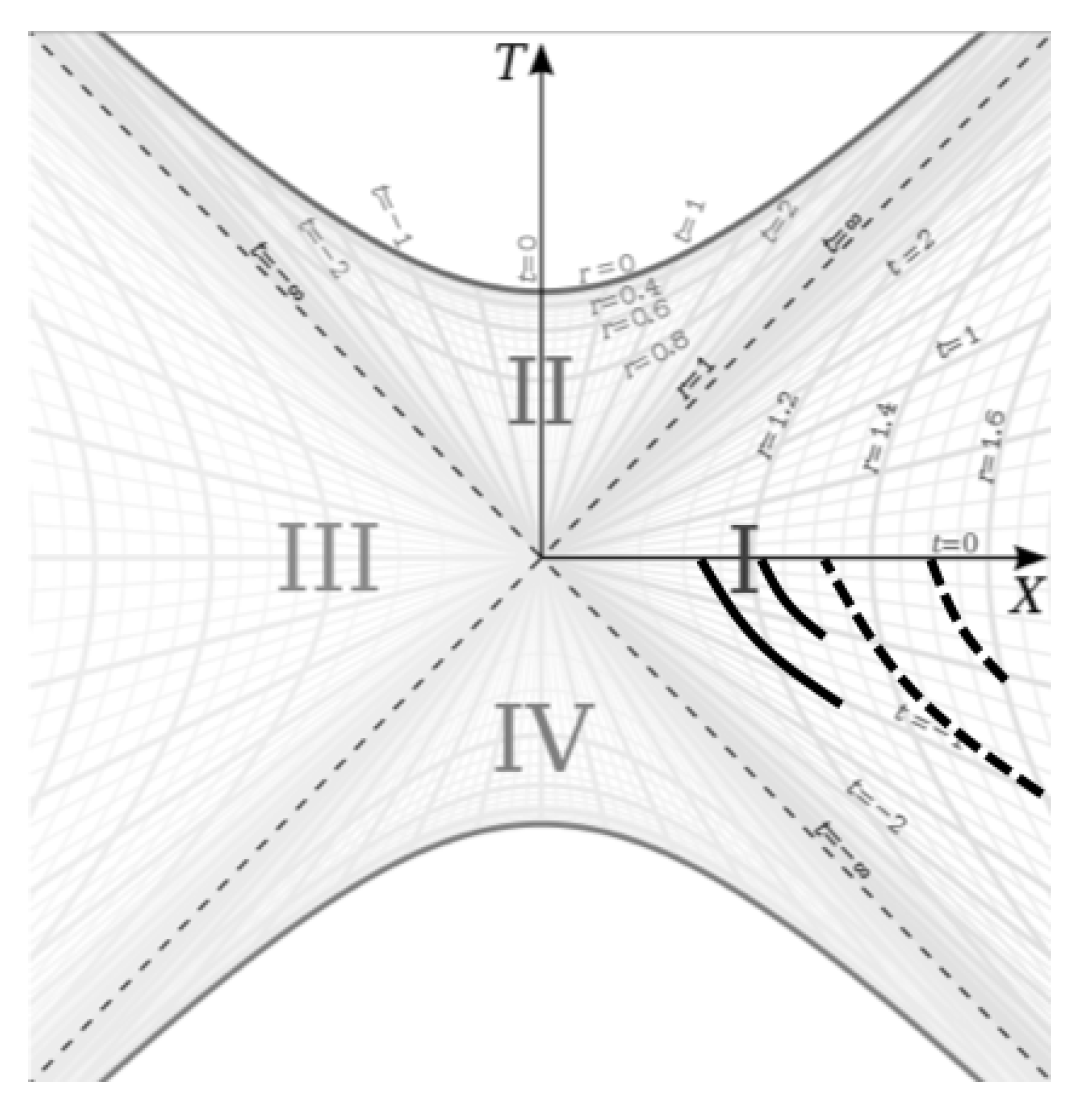
This becomes more obvious if we construct the worldlines in the presentist perspective. In
Figure 7, we see the worldlines for each particle drawn at two different ’present’ moments. The solid worldlines represent the the particle that started falling closer to the source and the dashed worldlines represent that particle that started falling from farther away.
Since, in this construction, the present time coordinate of the particles is always at the (X axis) line, both particles fall along the line. The past worldlines grow longer over time as the past worldline points are hyperbolically rotated downward during the fall. We can see therefore that they will both reach the horizon at the point on the coordinate chart, and from the perspective of the infinite observer, they will reach that point simultaneously. We know this because for each interval , the change in radius for each particle will go down the closer the particle is to the horizon (the amount of proper time elapsed in that period for each particle will also go down the closer the particle is to the horizon) and an infinite amount of is needed for all particles to reach . Therefore, all particles will become asymptotically closer to the particles closer to the horizon than them and the distance will shrink to zero as .
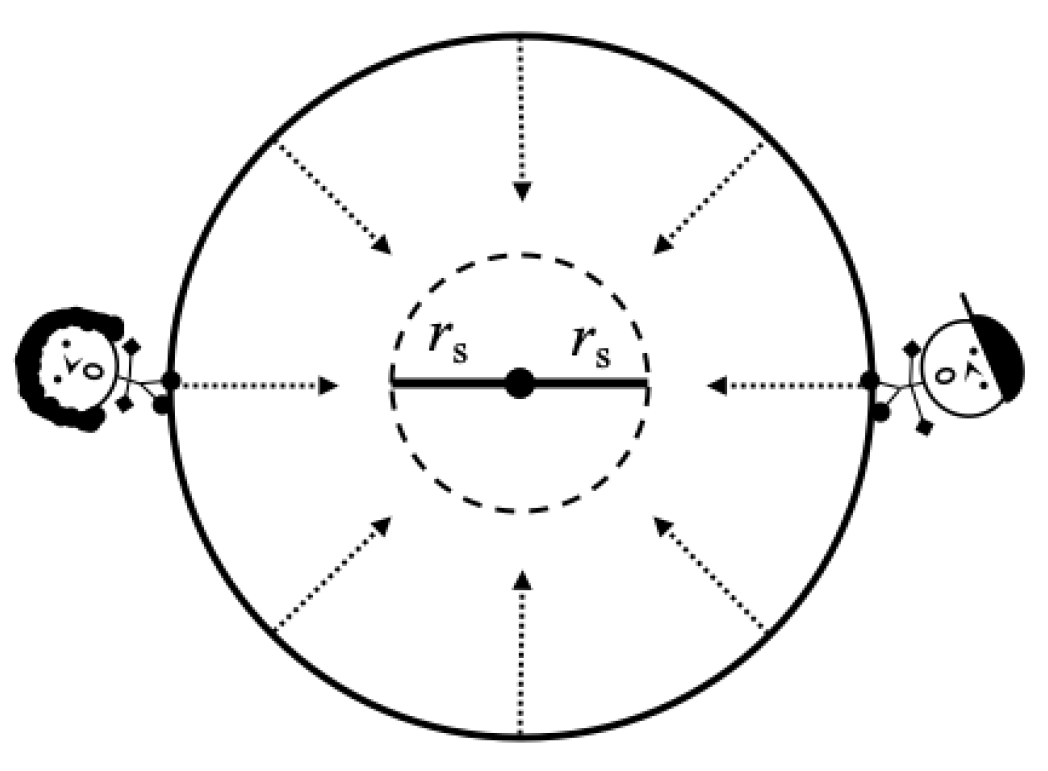
But what about from the perspective of the freefaling particles? Consider a spherically symmetric shell collapsing toward its Schwarzschild radius. At the beginning of collapse, the radius of the shell is greater than the Schwarzschild radius and we place two rods inside the shell whose rest lengths are the Schwarzschild radius of the shell with one end of each rod placed at the center of the shell. Let us place two observers, Scout and Jem, on opposite sides of the shell in free fall with it as depicted in
Figure 8.
As the shell collapses, the velocities of both Scout and Jem will increase relative to the rods. But in the frame of Scout or Jem, it is the rods that are moving toward them. Therefore, the rods will become increasingly length contracted in both Scout and Jem’s frames as the shell collapses due to the relative velocities between the rods and the observers.
Let us consider a set of hovering observers which remain at rest relative to the rods. As the shell passes one of these observers, the hovering observer must accelerate to remain at
r with proper acceleration [
3]:
This is the acceleration that the hovering observer at
r will measure the shell having as it passes. When the shell is at
r, the proper time interval of the rods will equal that of the hovering observer at
r and the acceleration of the shell relative to the rods will therefore also be equal to Equation
10. Thus, as the shell approaches its Schwarzschild radius, the relative velocity of the shell with respect to the rods will approach the speed of light because the relative acceleration goes to infinity there. Thus, the lengths of the rods in Scout and Jem’s frames will contract to zero length as they reach the horizon.
Therefore, when the shell reaches the Schwarzschild radius, the space between Jem and Scout as observed by Scout and Jem will be relativistically contracted to zero and in their frames, and they will be coincident. What this tells us is that in the frame of the material falling to form a Black Hole, there is no spacetime beyond the Schwarzschild radius. In that frame, when the material reaches the Schwarzschild radius, then the material has been compressed to a point and there is nowhere else to fall. This also suggests that to reach the point, the massive particles would need to become light-like, but that it would take an infinite amount of coordinate time (though a finite proper time of the falling particle) for that to happen. The particles at the horizon would therefore become massless.
We can conclude from these arguments that the Schwarzschild radius represents the end point of collapse and that there is no physical space beyond that in which to continue falling. In the frame of observers approaching the Schwarzschild radius, all infalling material would become infinitely dense there. This also tells us that the source of the metric is not at the curvature singularity at , but at the event horizon. Anything that would reach the event horizon would do so simultaneously with all other particles reaching the event horizon, regardless of where they started falling from, or when they started falling.
This leaves us with the question of what the internal solution is describing as well as why the Schwarzschild metric in Kruskal-Szekeres does not treat the horizon as a special location/time.
4. Extrinsic vs. Intrinsic Coordinates and the Internal Solution
To answer the questions from the previous section, we must first understand the nature of the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates relative to the Schwarzschild coordinates.
Figure 2 shows the shape of the geometry at a given
r for both the internal and external solution. The fact that the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates can be used to visualize the objective shape of the spacetime indicates that these are extrinsic coordinates for the Schwarzschild metric. This is in contrast to the Schwarzschild coordinates
r and
t which are intrinsic coordinates, in that they are coordinates that run along the actual geometry. If we use the example of a sphere in 3D space, the Schwarzschild coordinates would be like lines of longitude and latitude on the sphere, whereas the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates would be equivalent to an
Cartesian basis whose origin is at the center of the sphere and the basis within which the spherical nature of the surface can be seen as though it is being viewed from ’outside’ the surface.
The important difference between the Schwarzschild and Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates is that at the horizon, all worldlines approach the the event horizon asymptotically in Schwarzschild coordinates, whereas, as we can see in
Figure 6, the worldlines in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates can approach the event horizon just like it approaches any other location. This lead to the belief that there is nothing special at the horizon and the problems with the Schwarzschild coordinates at the horizon are only the result of a coordinate singularity. But as we saw in
Section 3, when taking a presentist perspective, all infalling worldlines actually intersect there and from the perspective of infalling observers, space contracts infinitely as the fallers approach the horizon. The discrepancy in the coordinate systems can be understood by acknowledging the extrinsic nature of the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates and examining the analogy depicted in
Figure 9 below:
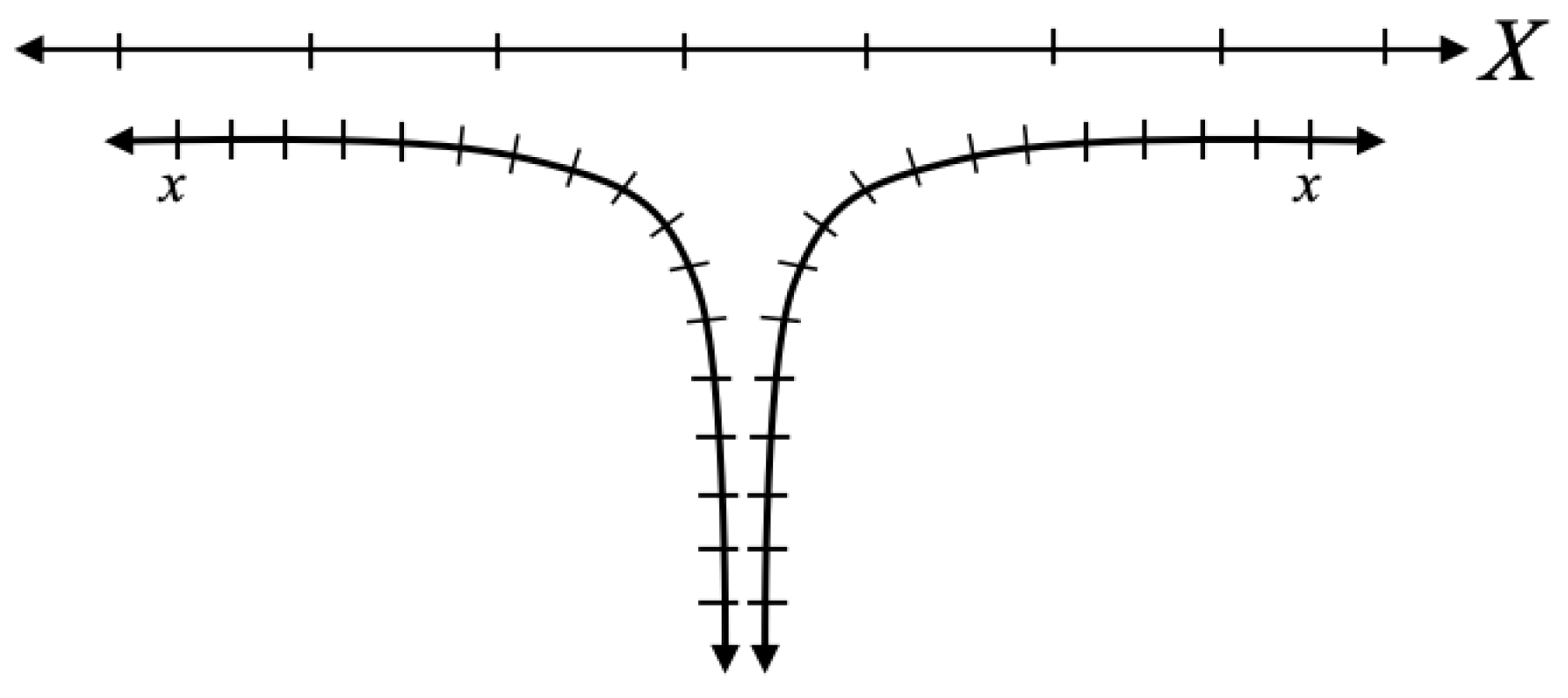
In
Figure 9, we see two lines depicting some space where each side of the space plunges downward infinitely so that the lines approach each other asymptotically. The lines don’t ever actually meet, they just get infinitesimally closer and closer to each other. The intrinsic coordinates are the
x coordinates that follow the actual geometry. The
x coordinate would therefore be analogous to the Schwarzschild coordinates. We also have an
X coordinate, which is an extrinsic coordinate that is essentially laid on top of the geometry. We can clearly see in the figure that in the intrinsic
x coordinate, the point directly between the two lines of the geometry is a special one. It is a discontinuity in the geometry separating the left and right lines of the geometry. But in the extrinsic
X coordinate, there is nothing special there at all. With this coordinate, you can move from one side of the discontinuity to the other the same way you can move between any other two points, and so if you treated the
X coordinate as being intrinsic, you would be led to believe that there is nothing special about the geometry at that point, even though we clearly see from
Figure 9 that the midpoint physically separates the two halves of the geometry.
We have an analogous situation with the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinate chart. The intrinsic Schwarzschild coordinates are telling us the geometry is discontinuous there. We know this because the worldlines from either side of the horizon approach it asymptotically. But the fact that the curvature is finite at the horizon is also an indication that the internal and external spacetimes are separate. In
Figure 9, if the lines approached each other asymptotically but actually connected, that connection would be infinitely sharp and therefore we would have infinite curvature there. But if they never connect and only approach each other asymptotically, then the curvature for each line will remain finite on approach to the separation point from either side. The Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates are giving us a coordinate system describing the geometry from the ’outside’ and just as in
Figure 9, it obscures the asymptotic separation of the two regions, making it appear that the horizon is not a special place when it has been clearly demonstrated to be a point of separation between spacetimes. And even though the metric in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates is regular at the horizon, it is also notable that the definitions of
T and
X need to be changed when going between regions (as demonstrated with equations
3 and
4), further supporting the fact that the horizon separates two different spacetimes.
The question then remains, what is region II of
Figure 1 describing. We know that the Schwarzschild solution describes all spherically symmetric vacua. In region I, the
t coordinate is spacelike while the
r coordinate is timelike. We see that the the horizon, the spatial
t coordinate density is infinite and the coordinate lines separate as one moves from the horizon to
. As discussed in
Section 2, the space of the metric at a given time is homogeneous and isotropic. It was also demonstrated in the case of the external solution that the source of the metric is at
. It stands to reason then that the source of the internal solution is also at that point. So the internal solution describes a spherically symmetric vacuum surrounded by a horizon which, from the perspective of an observer at some
r between the horizon and
, surrounds the vacuum infinitely far away in space and at some finite time in the past. And from the perspective of that observer, this horizon, which looks like a surrounding sphere, is a time where space is infinitely dense. A spacetime fitting this description would be any empty space in the Universe whose surrounding mass is spherically symmetric. Voids in the cosmic web would be an example of such a spacetime, and the horizon of the metric in this case would be the Big Bang, which is an event at some finite time in the past that surrounds all points in the Universe which has an infinite density. And an observer in the present Universe can never reach the Big Bang, no matter how far they travel through space, which is in alignment with the fact that the surface, from the perspective of a present observer, is infinitely far away from them in space. So we might think of the expanding Universe as baking bread where the air pockets that expand as the bread bakes give the bread a web-like structure over time, where the bread itself would be analogous to the cosmic filaments of matter in the Universe. A full cosmological analysis of the internal solution will be completed in a followup work which will also discuss all four regions of the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinate chart as well as the curvature singularity at
.