1. Introduction
The Schwarzschild metric described in Schwarzschild coordinates, exhibits a well-recognized coordinate singularity at the event horizon. This singularity is addressed through coordinate transformations, with the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates being the predominant choice, offering regularity at the horizon. However, the interpretation of Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates in terms of spacelike and timelike basis vectors remains ambiguous. Throughout much of the spacetime, Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates are a blend of spatial and temporal components, obscuring the significance of the slope of a worldline in these coordinates. Nevertheless, these coordinates have been utilized to argue that the event horizon permits traversal by falling observers, as no coordinate singularity arises in the Kruskal-Szekeres system. Consequently, this understanding has led to the recognition of Black Holes as entities into which objects can plunge irreversibly, precluding any possibility of escape back into the external Universe.
In the seminal text ’Gravitation’ by Misner, Thorne, and Wheeler [
1], the depiction of a falling worldline crossing the event horizon in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates (Figure 32.1(b)) is presented, yet lacks an accompanying calculation of the worldline in these coordinates. The sole comprehensive calculation found in the literature is outlined in [
2], where the author asserts the universality of worldlines being light-like at the horizon in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates, irrespective of their initial states of motion. However, it is noted in that work that the proof merely establishes the undefined nature of the Kruskal-Szekeres derivative of the falling worldline at
in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates. Nevertheless, the author concludes that for the extended spacetime to maintain coherence, the geodesic must indeed be light-like at the horizon.
In this study, employing modified Schwarzschild coordinates and Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates, it is established that infalling observers reach light-like states at the horizon, exhibiting zero velocity in Schwarzschild coordinates. To understand the transition from timelike to light-like behavior at the horizon, we demonstrate, utilizing these coordinate systems, that the black hole geometry encapsulates two PT-symmetric spacetimes, construed as a Universe and an anti-Universe. It is further revealed that if the anti-Universe encompasses all anti-particles of the Universe, it manifests as a CPT symmetric mirror Universe. The interface between these Universes is the event horizon, where a falling particle and its mirror antiparticle converge, annihilating each other and leaving outward-directed photons trapped at the horizon.
The connection between the Universe and its anti-Universe counterpart at the event horizon, along with the mathematical framework supporting this concept, fundamentally entails a reinterpretation of the Einstein-Rosen bridge. In this reinterpretation, rather than a wormhole linking two events within our Universe, the wormhole serves as the demarcation separating the Universe from the anti-Universe. Additionally, we elucidate the construction of black hole geometry by distorting a point in Minkowski space to form a hole. Furthermore, we demonstrate how the anti-Universe can be comprehended as the Universe phase-shifted in time by 180 degrees.
2. Modification of the Schwarzschild Coordinate Chart
The distinguishing feature of Minkowski spacetime within Special Relativity lies in its geometric uniformity, devoid of intrinsic landmarks or preferred reference points. Consequently, the establishment of a universal rest frame within Minkowski spacetime is unattainable. In this spacetime, all inertial reference frames, moving at constant velocity relative to each other, are equally valid. As a result, the selection of a specific rest frame is entirely arbitrary due to the absence of inherent distinctions within the geometry.
This is in contrast to the Schwarzschild metric of General Relativity, which is the simplest non-trivial solution to Einstein’s field equations. It is the metric that describes every spherically symmetric vacuum spacetime. The the external form of the metric can be expressed as:
Equation (
1) is the external metric (where
with
t being the timelike coordinate and
r being the spacelike coordinate. The Schwarzschild radius of the metric is given by
in units with
and is commonly known as the Event Horizon. The external metric is the metric for an eternally spherically-symmetric vacuum centered in space.
The Schwarzschild manifold possesses an inherent center, setting it apart from the Minkowski metric. This property allows for the establishment of a unique universal rest frame within the Schwarzschild metric. This frame corresponds to the state of rest relative to the gravitational source located at the singularity. Within this frame, observers experience a proper acceleration determined by their distance from the source. Consequently, the rest frame of the Schwarzschild metric serves as a crucial reference point for analyzing the characteristics of other frames within the spacetime, including inertial frames, all of which are in motion relative to the gravitational source.
The metric exhibits a recognized coordinate singularity at
, characterized by the divergence of the
component and the vanishing of the
component when
. To mitigate the issue associated with the
component, we implement the following trivial coordinate transformation:
This puts the metric in the following form (ignoring the angular term):
If we take the square root of Equation (
2) and integrate, we obtain
s as a function of
r:
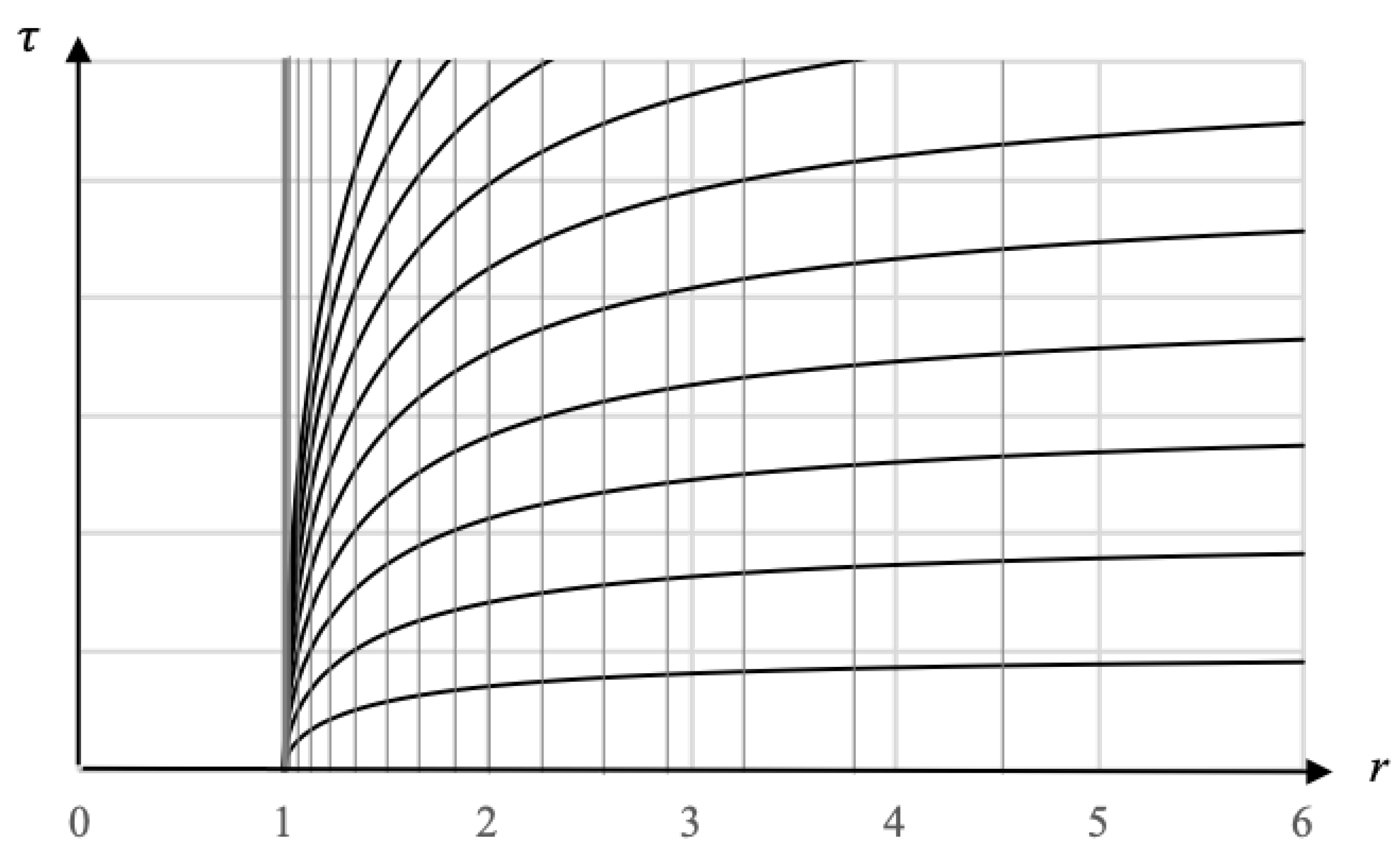
In the conventional depiction of the Schwarzschild coordinate chart, the
r and
t coordinate lines are commonly illustrated as a planar grid. However, for a more insightful examination, let us endeavor to envisage the geometric configuration from the vantage point of observers at rest as well as observers commencing free fall from rest at
.
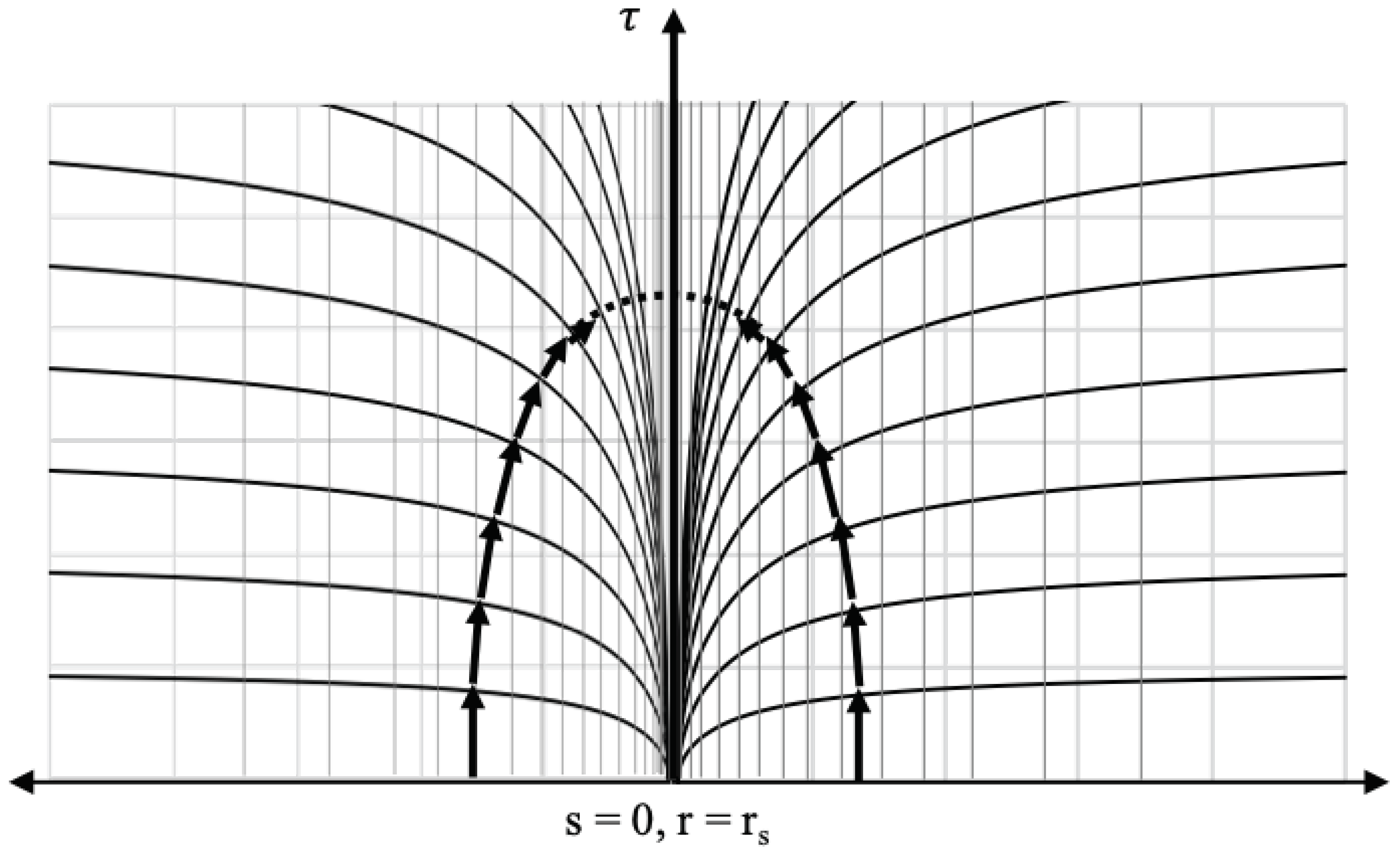
Figure 1 shows a modified coordinate chart that better captures the nature of the Schwarzschild geometry.
On this chart, the
t coordinate lines are the curved lines and they come from solving the metric for rest observers (
) and integrating to get the following equation:
Where each line corresponds to a fixed value of
t, with
being the flat line on the
r axis. Vertical worldlines on this coordinate chart are the worldlines of observers at rest and their height is the proper time elapsed. We can see that for a given
, less proper time passes for rest observers the closer they are to the horizon. Also plotted on this chart are the
s coordinate lines from Equation (
4) (we are currently plotting only the positive solution). We see that the density of these coordinate lines goes to infinity as the horizon is approached, reflecting the fact that
at the event horizon.
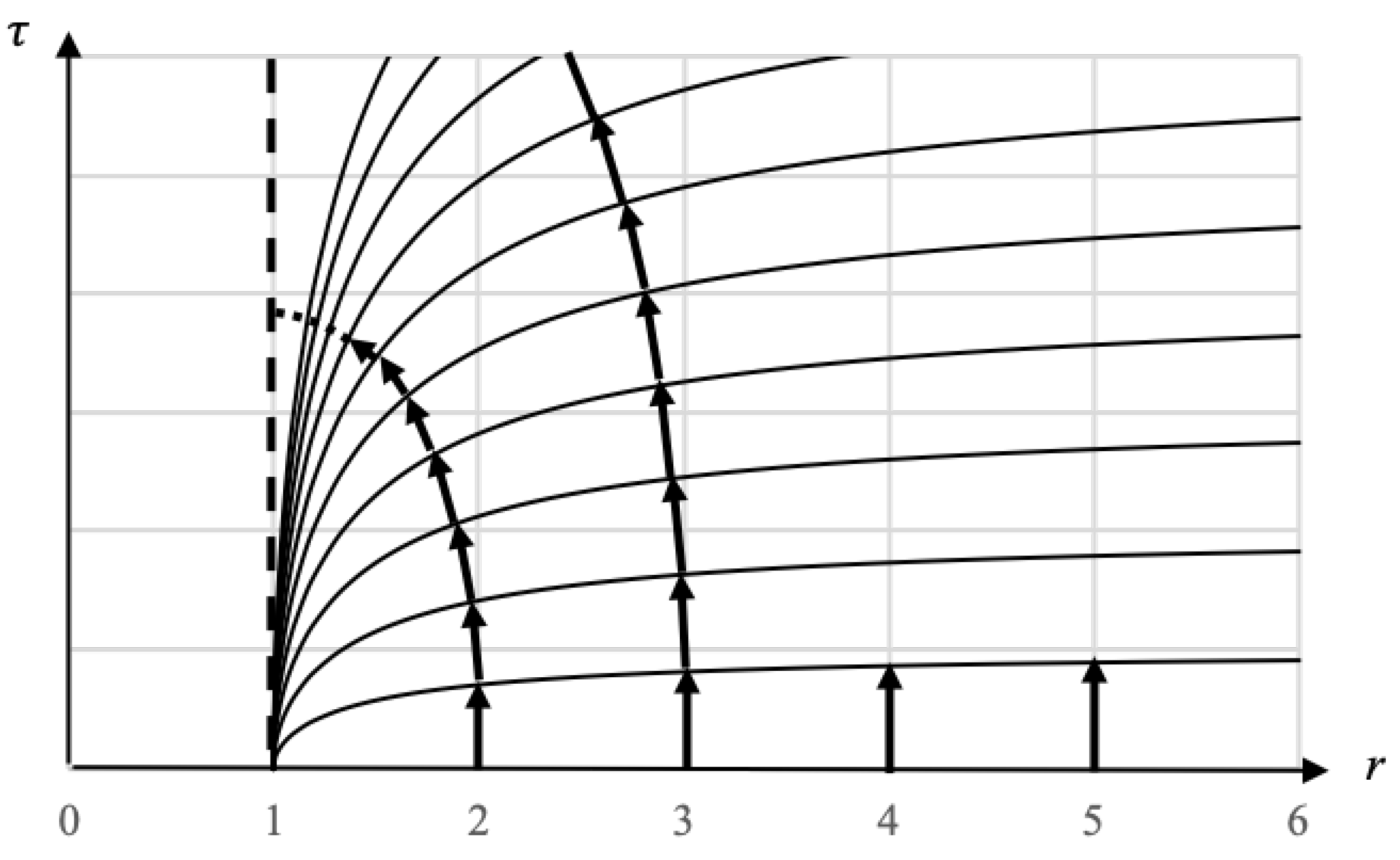
Now let us examine the inertial worldlines of falling observers falling from rest at
at different radii. The worldlines of observers falling from two different radii are shown in
Figure 2.
We can conceptualize the t coordinate lines as analogous to isocontours on a contour chart, where represents the highest level and represents the lowest level. The trajectory of a falling observer follows the geodesic of shortest distance from the highest level to the lowest level, ensuring their worldline remains perpendicular to the t coordinate lines at every point. Consequently, the worldlines of all falling observers start vertically at , gradually curving to maintain orthogonality to the t coordinate lines at each point, and eventually becoming horizontal at , .
Figure 2 additionally depicts the acceleration experienced by the rest observers situated at
r. Differentiating Equation (
5) with respect to
r for constant
t yields the slope of the curve at a given point
:
We recognize Equation (
6) for constant
r as a constant acceleration equation where the bracketed expression is the proper acceleration of the rest observer. Since
is the slope of the
t coordinate line at
, we know that the slope of the inertial worldline at the same point is
. For an observer at rest,
r is constant and
t increases and we can therefore interpret
in Equation (
6) as a pseudo-velocity relative to inertial frames that increases with increasing
t at a constant acceleration defined by the bracketed expression.
We can see from
Figure 2 the first evidence that the falling worldlines are light-like at the horizon since
for the worldlines are zero there. But we can make this claim more concrete by re-expressing the metric in Equation (
3) as follows:
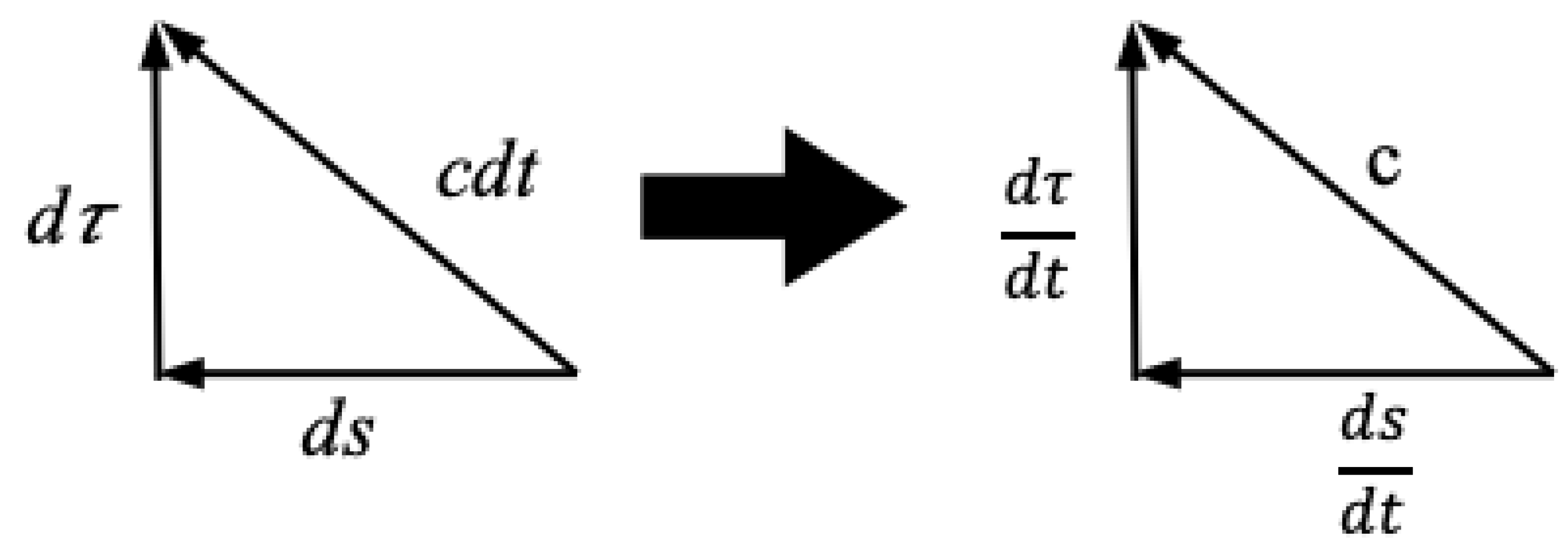
Where
. We can understand this expression geometrically with
Figure 3 below:
The hypotenuse of the triangle represents the tangent vector of the falling worldline, aligned with the
direction at each point along the trajectory. Initially, at
, the falling observer positioned at
is at rest, leading to
. Consequently,
is equivalent to the speed of light at
. However, due to the curvature of the
t coordinate lines, the
vector undergoes rotation as the fall progresses, resulting in an augmented
component and a decreased magnitude of the
component.
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 provide a comprehensive depiction of the mechanism through which the falling observer experiences acceleration relative to rest observers. This acceleration arises from the varying alignment between the
basis vector and the
basis vector across different spatial locations, thereby inducing inertial acceleration in the falling frame.
Reference [
3] tells us that
for an observer falling from rest at
is given by:
Combining equations
8 and
2, we get the needed derivative:
In Equation (
9), we observe that the expression
, where
and
. Moreover, at the horizon,
, indicating a light-like worldline. This is evident in
Figure 2, where the worldline becomes horizontal, implying zero proper time elapses at the horizon.
Equation (
9) attains a value of 0 at
, achieves a maximum magnitude at some
, and then returns to 0 at
.
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 aid in understanding this behavior. Notably, the hypotenuse in
Figure 3 both rotates and contracts as the falling observer approaches the horizon.
The rotation of the vector corresponds to the
term in Equation (
9). When the vector is vertical, the observer is at rest, resulting in
. Conversely, at the horizon where the vector is horizontal, the observer becomes light-like due to
.
The magnitude of the vector corresponds to
, representing the speed of light
c at
r. Consequently, this magnitude reaches its maximum at the start of the fall and diminishes to zero at the horizon. This phenomenon is illustrated in
Figure 2, where the vectors between successive lines of
t and
s along the worldline gradually diminish as the horizon is approached, attributable to the compression of coordinates in that region. Hence, the magnitude of
increases up to a point, wherein the contribution from the rotation of the hypotenuse exceeds that from its decreasing length, reaching a maximum. Subsequently, the dominance of the shrinking length of the hypotenuse causes
to decline, eventually converging to zero at the horizon.
Careful examination of the Schwarzschild geometry in Schwarzschild coordinates has shown that free-falling worldlines transition to light-like trajectories at the event horizon. However, the mechanism by which an inertial, timelike worldline undergoes this sudden transformation to a light-like state remains ambiguous and warrants further exploration.
Section 4 will delve into this inquiry; nonetheless, before delving into that, let us scrutinize the identical scenario through the lens of Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates.
3. The Falling Frame of the External Metric in Kruskal-Szekeres Coordinates
The Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates are the maximally extended coordinates for the Schwarzschild metric. The coordinate definitions and metric in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates are given below (derivation of the coordinate definitions and metric can be found in reference [
4] where
and
).
With the full metric in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates given by:
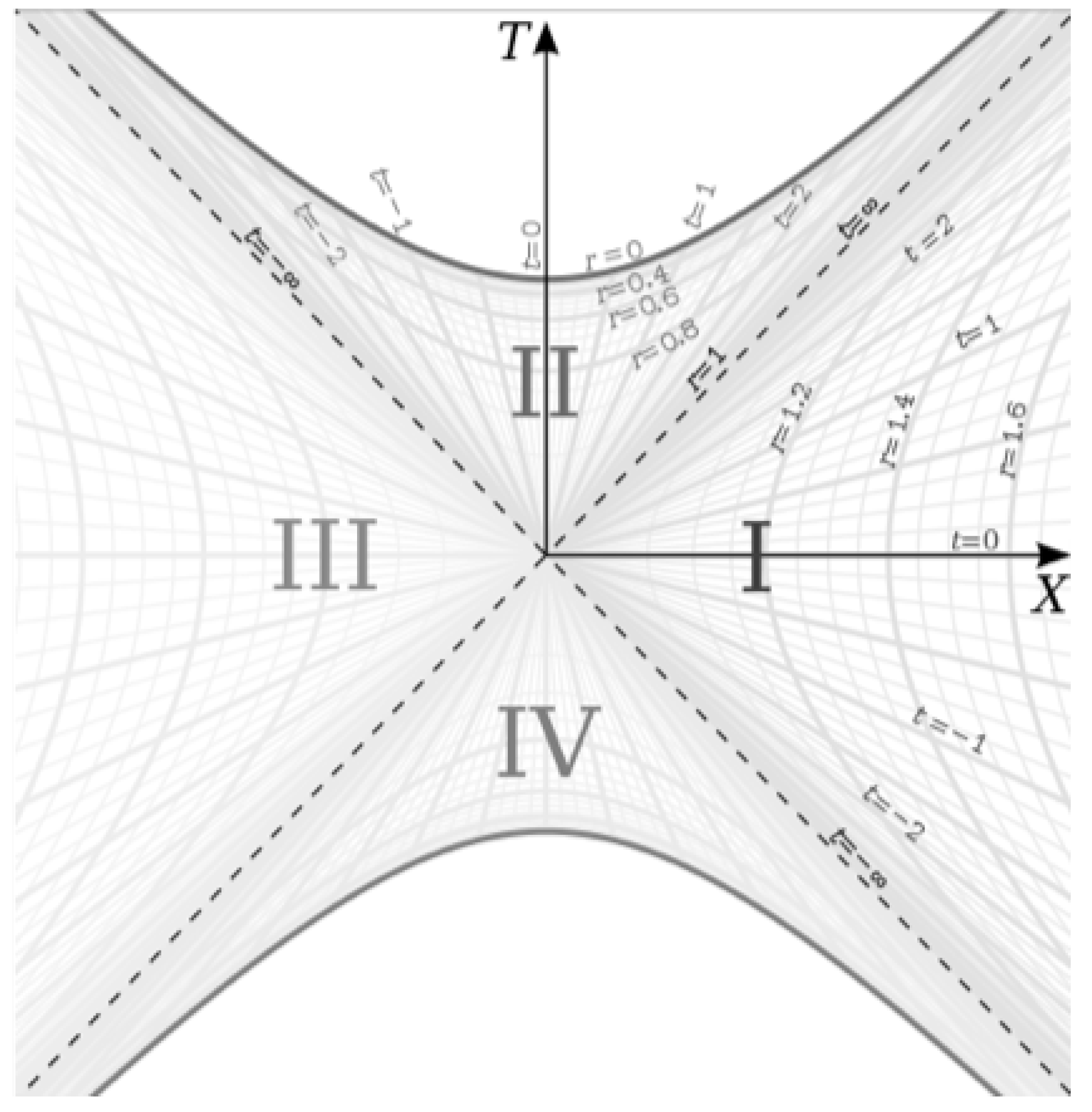
Finally, we plot the metric on the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinate chart [
5] in
Figure 4:
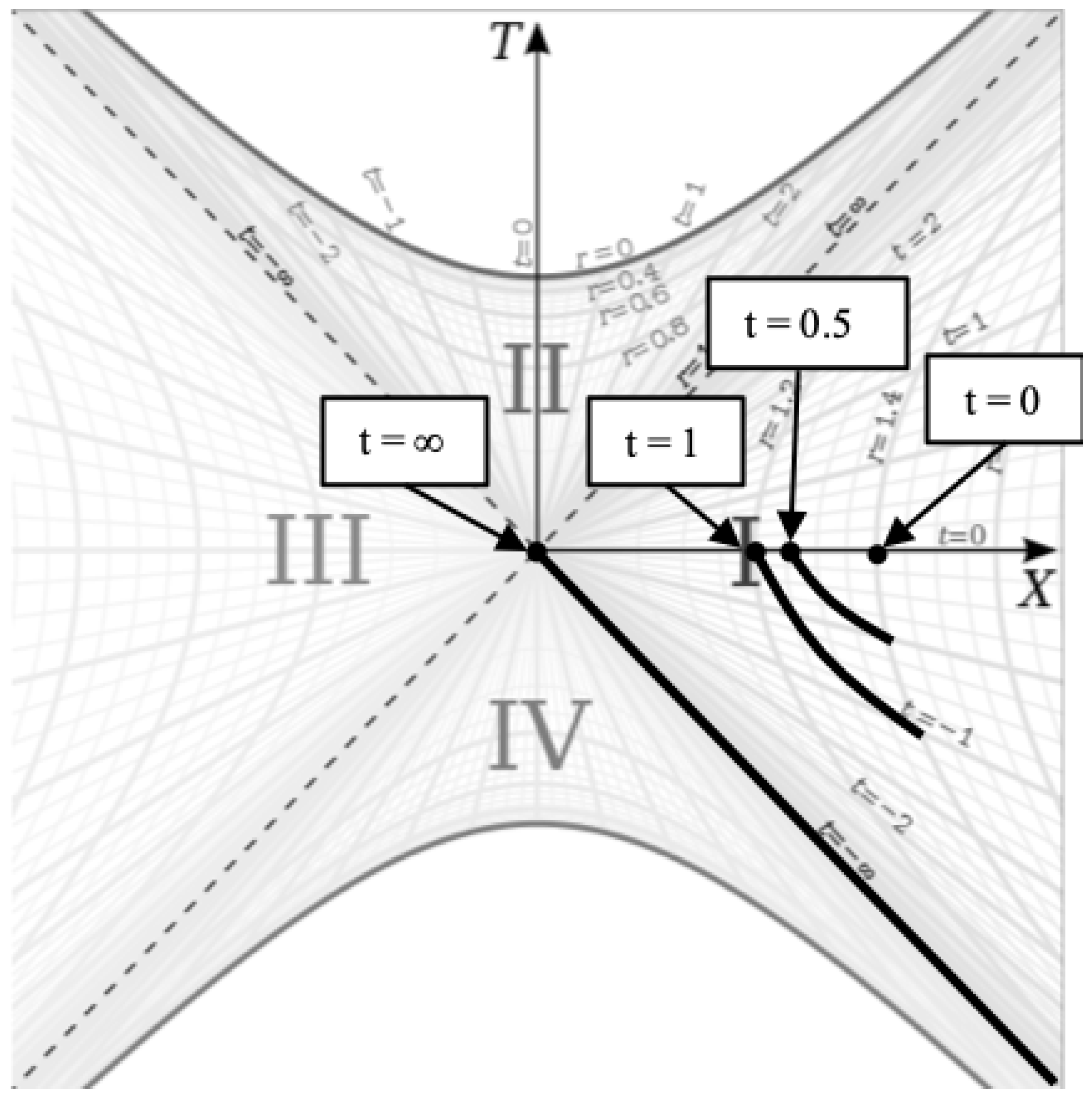
Presently, we will be focusing on region I in this chart, which is the spherically symmetric spacetime around a spherically symmetric source in space.
Light-like geodesics are 45 degree lines on this diagram. We can derive the fact that falling worldlines become light-like at the horizon mathematically as follows. Let us first take the differentials of
T and
X in equations
10:
Calculating the partial derivatives, rearranging and defining
we get:
Next, we need to calculate
from equations
13 by factoring out
from each equation and dividing:
This equation is the same equation derived in [
2] but put in a slightly different form. Next, we make the following definitions:
This is the derivative of the rest frame at
t since plugging
into Equation (
14), we get
. Since we know the Schwarzschild metric is independent of
t, this derivative must be a non-physical artifact of the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates at fixed
r and is not related to any actual change in motion through space and time.
And we define the relative velocity of the frame in motion relative to the rest frame as:
This is the relative velocity in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates between the frame in motion and the rest frame at
r. This derivative is 0 for the rest frame since
in that frame. If we combine Equations (
16) and (
8) we get:
Which is well behaved and equal to -1 when
. Plugging these definitions into Equation (
14), we get:
We recognize that Equation (
18) is the relativistic velocity addition formula giving us the total velocity as the relativistic sum of the rest frame velocity and the relative velocity between the moving frame and the rest frame. We can solve for
to get an expression for the relative velocity between a frame in motion and the rest frame in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates:
Assuming that
ranges from -1 to 1 and
, we see that the relative velocity approaches 1 or -1 for all
as the horizon is approached since the horizon is at
, such that
there. Equation (
19) is also constant along a given hyperbola (i.e it is independent of
t) since it represents the relative velocity between the moving and rest frames.
It is notable that Equation (
18) is undefined when
because since
there and
there, we get:
This is also what was demonstrated in [
2]. Therefore, under these conditions,
and
are undefined at the horizon when
T and
X are greater than 0. However, it is notable that if
and
, then
, indicating that under that condition, the worldline is not undefined, but clearly light-like at the horizon.
To understand the undefined nature of the worldline at the horizon in these coordinates, let us examine the rest observer. In these coordinates, rest observers accelerate over time as evidenced by the fact that their worldlines are hyperbolas in these coordinates. If we consider the
X position of a rest observer at some
, we see that its
X-coordinate is given by
where
is the
X coordinate of the rest observer at
r when
. At
, the rest observer is moving with some velocity relative to itself at
on this coordinate chart. Therefore, we should expect that the
X coordinate will be length contracted as
t increases in the rest frame in Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates. The length contracted value of
X in the rest frame at
r and
is given by:
We use
in the equation because we are looking at rest observers, so according to Equation (
18),
in this case.
So even though the X coordinate grows for an observer at rest in the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinate chart, when we shift to the frame of the rest observer by taking into account the length contraction of the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates in that frame, we see that we end up back at . This is a very important finding. It means that region II in the coordinate chart, which only exists for cannot actually be reached as a result of the length contraction.
If the rest frame has the length contraction, then the falling frame, which is moving relative to the rest frame will have an even greater contraction. So the rest frame at
r sees their distance from
in their frame as
. This distance in the falling frame will become:
We can use these facts to change how we visualize the worldline of an observer falling toward the horizon. Rather than drawing the line from
at some
r to
at the horizon, we can continuously hyperbolically rotate the space as the observer falls such that the ’present’ state of the falling frame is always at
. An example of this is given in
Figure 5.
In
Figure 5, the observer begins falling at
. This is represented by the rightmost point on the
X axis in the diagram. After
, the observer has fallen to a lower radius represented by the point to the left of the rightmost point. So rather than having the worldline grow up from
as time passes, we hyperbolically rotated the worldline points down as time passes to keep the present point of the worldline on the
X axis (accounting for the length contraction of the rest frame). This is a valid way of visualizing the worldline as a result of the time symmetry of the metric (the geometry has a Killing vector in the
direction, meaning that we can hyperbolically rotate the space as much as we like without changing any of the physics).
When using this construction, we see that the falling worldline reaches the point on the diagram. And if the worldline does indeed become light-like at the horizon, this means the worldline remains on the line since that is the light-like geodesic representing the horizon.
Now let’s calculate the situation described in
Figure 5 where we calculate the worldline falling along the
X axis as the past worldline is hyperbolically rotated down. For this construction, we set
in the equations since the derivative is always taken on the
X axis. For this calculation, we put the metric in the following form (we will be examining radial infall so
):
Since we are keeping
, we can use the inverse of Equation (
17) for
in the equation. We can solve for
r in terms of
X by setting
for the
X equation in Equation (
10) and solving for
r:
Where
W is the Product Log function. Substituting Equations (
24) and (
17) into Equation (
23) gives us an equation for the falling worldline along the
X axis:
Which goes to 0 as
X goes to 0, meaning, once again, the worldline becomes light-like at the horizon. But we can now show that this is exactly equivalent to falling in Schwarzschild coordinates by first using Equation (
13) to solve for
when
:
Substituting Equations (
26) and the inverse of
16 into Equation (
23) gives:
And we can see that Equation (
27) is in fact the Schwarzschild metric in Schwarzschild coordinates.
Therefore it has been proven that the worldline construction shown in
Figure 5 is equivalent to falling in Schwarzschild coordinates and it has been demonstrated that the worldline in that construction is light-like at the horizon. When we couple this finding with the fact that the Kruskal-Szekeres derivative is undefined at the horizon for any construction in which the worldline reaches the horizon at
, we can conclude that the event horizon is length contracted to a point in a falling frame approaching the horizon as a result of the fact that the worldline becomes light-like there.
Furthermore, we see from Equation (
26) that
is zero at
. Therefore, the falling frame remains at the horizon in the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinate chart when it reaches the horizon.
4. Anti-Matter Annihilation at the Event Horizon
It has been shown using both Schwarzschild and Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates that falling worldlines become light-like at the event horizon. Furthermore, there is the problem of the speed of infalling particles going to zero at the horizon. This is puzzling particularly when looking at
Figure 2, where the worldline is parallel to the space dimension, suggesting the particle should continue falling past the horizon.
The question now becomes: how can an inertial time-like particle become light-like and at rest at the horizon? This seems to be a violation of Special Relativity which suggests that an infinite amount of energy would be required to accelerate a time-like particle to a light-like state. But there is a known mechanism through which time-like particles can become light-like: matter/antimatter annihilation.
In
Figure 5, it was shown that falling particles can reach the
point on the coordinate chart. Let us now revisit the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinate chart and consider the directions of time and space for all four regions on the chart:
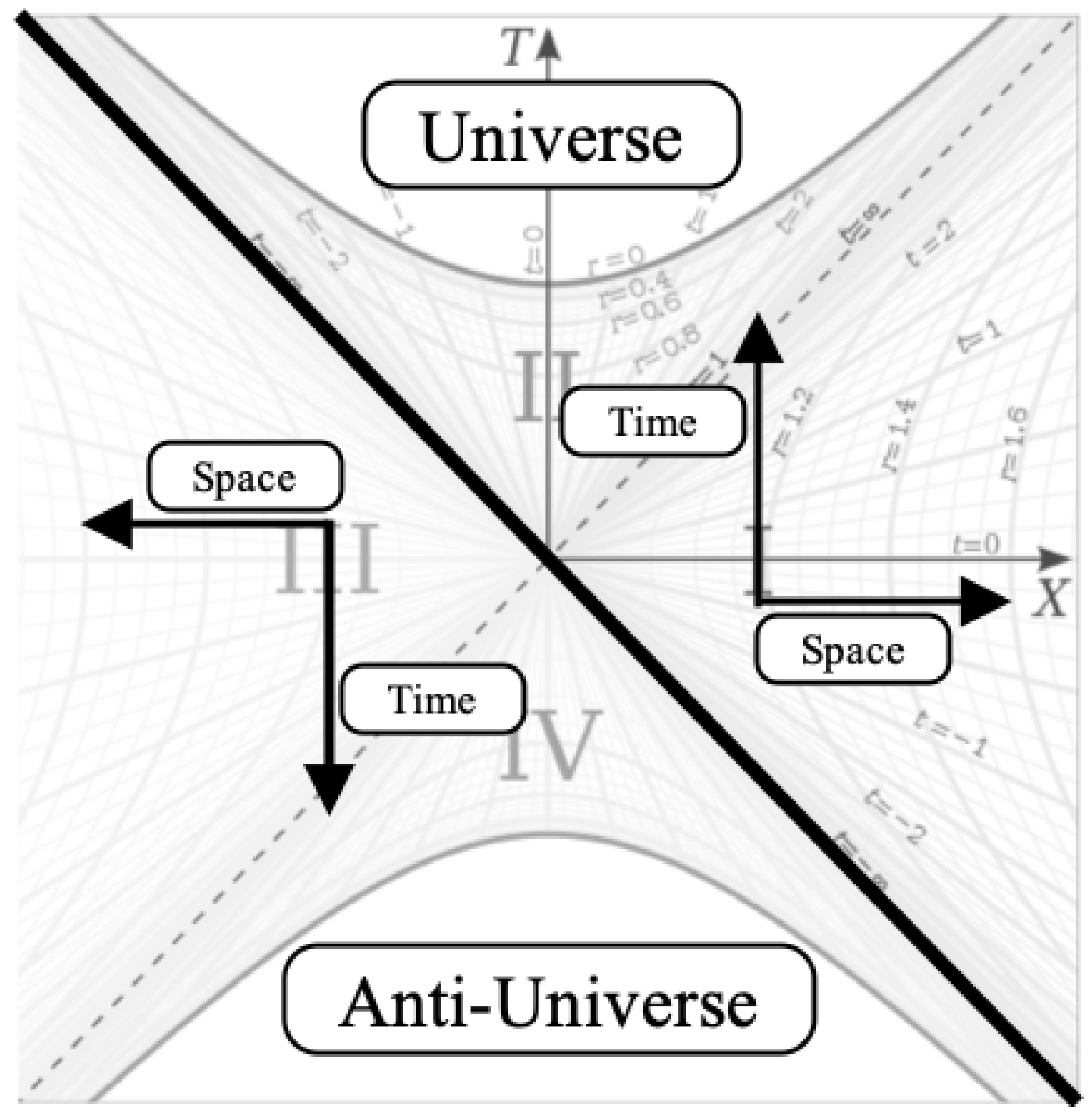
As we can see from
Figure 6, the directions of time and space in regions III and IV are opposite to the directions of time and space in regions I and II (because
r increases to the right and
t increases upward in region I, while
r increases to the left and
t increases downward in region III). Another way to say this is that regions are time and parity reversed. If we therefore conjecture that regions I and II represent a ’matter dominant’ Universe, and regions III and IV represent an ’anti-matter dominant’ Universe, then what we have are two mirror Universes that are CPT symmetric.
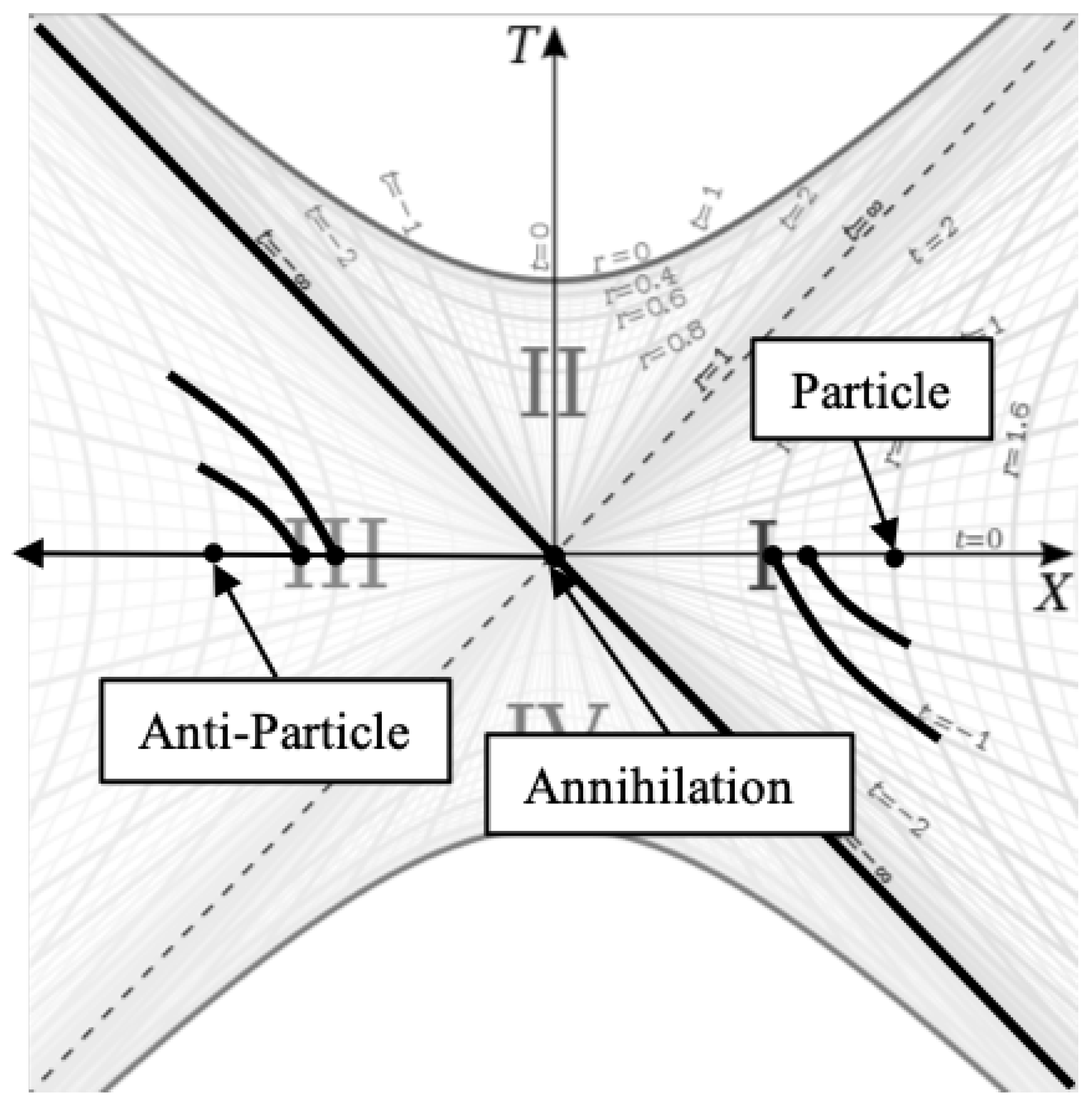
So if region III is a CPT symmetric mirror of region I, then we can imagine that every particle falling toward the horizon in region I has a partner antiparticle falling toward the same point on the horizon in region III. We can depict this by modifying
Figure 5 as follows:
We see in
Figure 7 a particle falling from rest at
in region I and its partner antiparticle falling from rest at
in region III. These particles will collide at the horizon at
and annihilate one another. Since the particles have
when they annihilate at the horizon, the photons produced after annihilation will also need to remain at the horizon. Therefore, the photons produced at the horizon will be outward-directed such that they remain on the horizon along the
line in order to conserve momentum. Thus, the mass of the particles is converted to the energy of photons ’trapped’ at the horizon. This trapped energy manifests as in increase in the mass of the Black Hole. The fact that the Schwarzschild radius of a Black Hole is
as opposed to just
may be due to the fact that it incorporates the mass from both the matter and anti-matter Universes.
We can show the same using the modified Schwarzschild coordinates from
Section 2. When solving for the
s coordinate in Equation (
4), we only used the positive solution. If we use both the positive and negative solutions for
s and modify
Figure 2 such that we represent space using the
s-coordinate, we get another visualization of the Universe/Anti-Universe:
Since at , both Universes meet at in these coordinates. Note that in this coordinate chart, infalling light-like geodesics are horizontal and outgoing light-like geodesics are vertical at the horizon. Therefore, the photons produced by the annihilation will have vertical trajectories along the line on this coordinate chart.
Note that the s coordinate transformation is very similar to the transformation used to describe the geometry of Einstein-Rosen bridges. What we have effectively shown here is that the E-R geometry is not describing wormholes connecting different events in spacetime within our Universe as is currently believed, but rather it was always describing the boundary between our Universe and Anti-Universe as described in the present paper.
5. Creating a Hole in the Minkowski Manifold
Equation (
1) is the external metric (where
with
t being the timelike coordinate and
r being the spacelike coordinate. The Schwarzschild radius of the metric is given by
in units with
and is commonly known as the Event Horizon. The external metric is the metric for an eternally spherically-symmetric vacuum centered in space.
But this metric comes from assuming a stress-energy tensor that is zero everywhere, meaning there is no mass anywhere in the manifold, even at the center. Therefore, this metric is describing a spherically symmetric vacuum manifold having only Weyl curvature. The question then becomes: how can the Minkowski manifold, which is massless everywhere, be intrinsically deformed to give us the Schwarzschild manifold?
Let us imagine Minkowski space-time which is flat everywhere in space and time. We choose a point in space (at all times) on the manifold and label it as the spatial origin . Thus we use spherical coordinates to describe the metric with r as the spacelike coordinate. For future clarity, we will label the Minkowski time coordinate , representing the proper time of observers at rest in their own frame.
Now we make a hole in the manifold by stretching the space-time at the point into a 4-sphere (because the hole is in space as well as in time at that location in space). In doing so, we have done two things:
We have given the manifold an intrinsically spherical shape with an intrinsic center
We have created a null space-time in the region inside the 4-sphere where space and time itself are absent (this would be the definition of creating a hole in the manifold)
So we assert that the Schwarzschild metric, which is the only spherically-symmetric solution to Einstein’s field equations describes 3 distinct, separate manifolds. When , we get the manifold described above where there is a hole in the Minkowski manifold. The spacetime is not flat anywhere in this metric. We cannot actually set r to infinity in this metric, as this is mathematically dubious. The best we can do is say that the spacetime approaches the Minkowski space-time as approaches zero. The Minkowski metric is only achieved when . Since , we might think that this means that the Minkowski metric is just the Schwarzschild metric when there is no mass present on the manifold. But this is false. As mentioned previously, the Schwarzschild metric comes from solving the field equations with a zero stress-energy tensor (and assuming spherical symmetry). So the Schwarzschild metric with non-zero already assumes no mass or energy anywhere on the manifold. Therefore, by setting , we are really saying is that there is no hole in the Minkowski manifold.
Returning our attention to the external metric with non-zero , we will now examine how the stretching of a point into a 4-sphere to create the hole in the manifold affects the Minkowski coordinates. Since the manifold is continuous, it is helpful to make an analogy here to true strain in a perfectly elastic material in continuum mechanics. Since we are stretching the center of the manifold from a point into a 4-sphere (as opposed to just ’cutting a hole out of the manifold’) with a finite radius, both the space and time will be strained by the stretch such that their strain is zero infinitely far from the hole.
We can characterize this strain as follows. We start with Minkowski space-time with a point designated
and a second point
r some distance away from that point such that the distance
r is greater than the radius of the hole being created. We now stretch the point at
into a hole with radius
. The true strain is defined as:
Where
is the final length and
is the initial length and the ratio:
is known as the "stretch factor". In this case, the initial length is the distance from
r to 0,
. The final length after the stretch is
. Substituting into Equation (
30) we get:
The strain goes to 0 as
and goes to negative infinity (infinite compressive strain) when
. The strain analogy is what was depicted in the coordinate chart of
Figure 2.
Note that the manifold density
at
r will be inversely proportional to the stretch factor
at
r. More formally, we can say:
Where
is the stretch factor infinitely far from the hole and
is the density infinitely far from the hole. We can define
, meaning we define the density of the Minkowski manifold as 1, which gives us the relationship:
Combining equations
32 and the fact that the speed of light
, we obtain the relationship between the speed of light and the manifold density:
Which is the same way in which the speed of sound is related to the density of an elastic material with a Young’s modulus of . This also tells us that where and are the vacuum permeability and permittivity.
So we can think of the Schwarzschild manifold as the Minkowski manifold with a hole in it such that the boundary of the hole is the event horizon. So this hole appears to us as a 2D spherical surface in 3D space. If we foliate the spacetime with a 2D space-like plane that passes through the center of the hole, this plane represents the 2D space surrounding an equator of the hole. So a particle falling radially would be a line on this plane and a particle in circular orbit around the equator of the hole will be a circle on the plane. We can think of the Universe and Anti-Universe as being on either side of this plane.
If we conceptualize the time dimension as an imaginary axis perpendicular to the spatial plane, with an origin coinciding with the plane, then the lower portion of the plane would undergo a phase shift of 180 degrees in the time dimension relative to the upper portion. This arises from the fact that the upper section represents , while the lower section represents .
Relating this notion to
Figure 8, the region corresponding to
would align with the upper side of the plane, while the region associated with
would align with the lower side of the plane (whereas the
r coordinate denotes the distance from the center of the hole for both regions). The convergence of particles and antiparticles occurs at the event horizon, which constitutes the boundary of the plane intersected by the black hole. Consequently, with this framework, the anti-Universe essentially mirrors the Universe, as it is reflected across orientable planes such as this.
6. A Short Note on the Internal Metric
In this study, our investigation has been confined to the external Schwarzschild metric. However, it’s imperative to acknowledge the existence of another spacetime governed by the Schwarzschild solution, applicable when , commonly referred to as the internal Schwarzschild metric. Based on the analyses presented in this paper, we deduce that the internal metric delineates a distinct spacetime entity, distinct from the external metric examined in this study.
A comprehensive examination of the internal metric, along with the two additional regions delineated in the Kruskal-Szekeres coordinate chart, will constitute the subject of a followup paper. It will be demonstrated that the internal metric characterizes a spatially homogeneous, spherically symmetric space, experiencing an initial phase of decelerated expansion followed by accelerated expansion over time. From the standpoint of an observer situated within this space, the metric’s source manifests as an infinite mass positioned at an infinite distance in space, albeit at a finite temporal interval in the past.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Conflicts of Interest
There are no competing interests.
References
- C. Misner, K. C. Misner, K. Thorne, and J. Wheeler, Gravitation, Gravitation No. pt. 3 (W. H. Freeman, 1973).
- Mitra, A. International Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics 2012, 2, 174. [CrossRef]
- A. Augousti, M. A. Augousti, M. Gawełczyk, A. Siwek, and A. Radosz, European Journal of Physics - EUR J PHYS 33, 1 (2012).
- Carroll, S.M. Lecture notes on general relativity. arXiv 1997, arXiv:arXiv:9712019v1. [Google Scholar]
- Figures 4, 5, 6, and 7 are modifications of: ’kruskal diagram of schwarzschild chart’ by dr greg. licensed under cc by-sa 3.0 via wikimedia commons, http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kruskal_diagram_of_Schwarzschild_chart.svg#/media/File:Kruskal_diagram_of_Schwarzschild_chart.svg (Accessed in 2017).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).