Submitted:
27 October 2025
Posted:
29 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Related Works
1.3. Contribution
2. Methodology
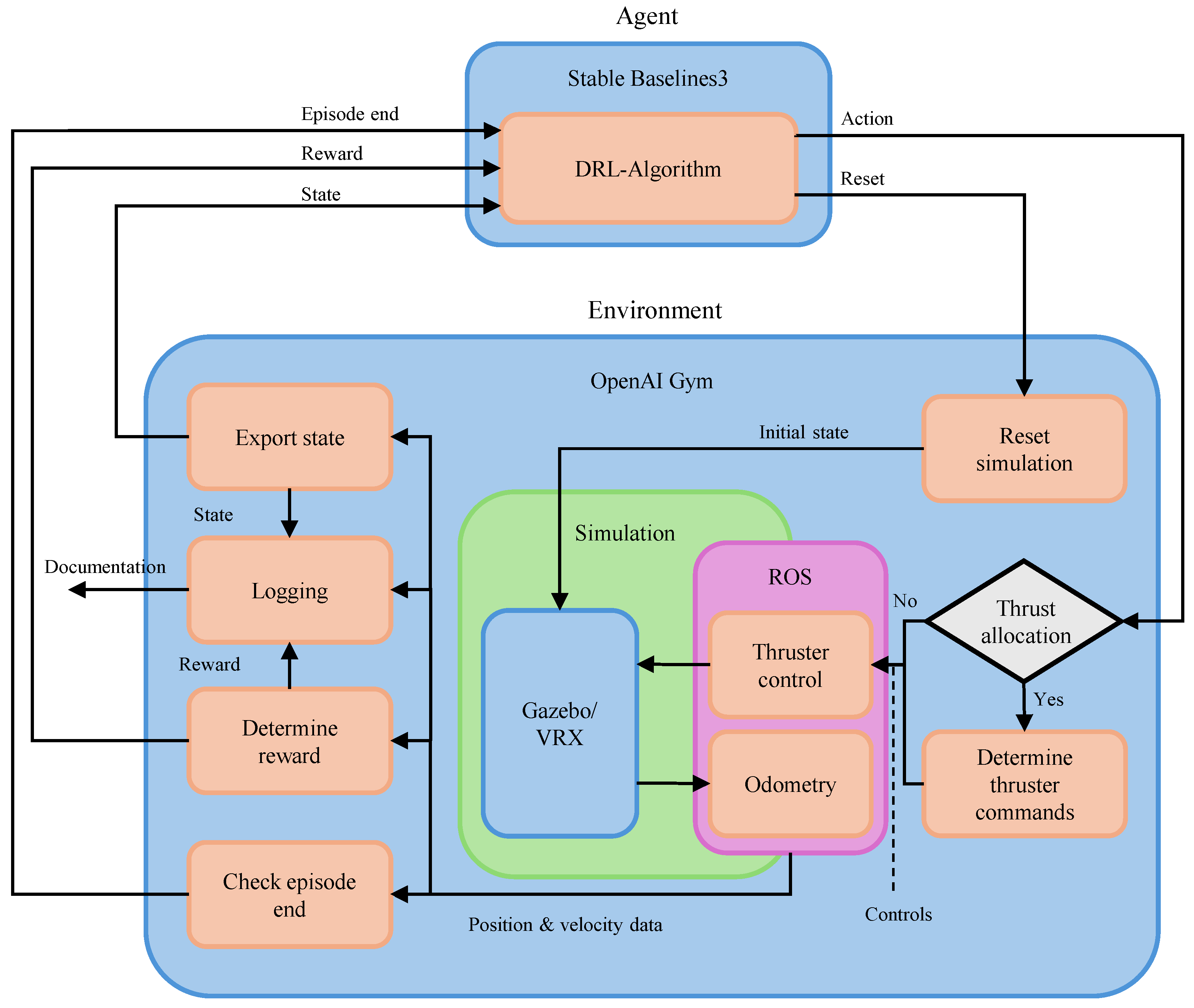
2.1. Framework Architecture
2.2. Scenario Overview and Definition of the Reinforcement Learning Problems
-
Collision Avoidance (CA)
- -
-
CA1 – Static Obstacle Avoidance:The USV is tasked with navigating towards a target destination while safely maneuvering around one or more stationary obstacles.
- -
-
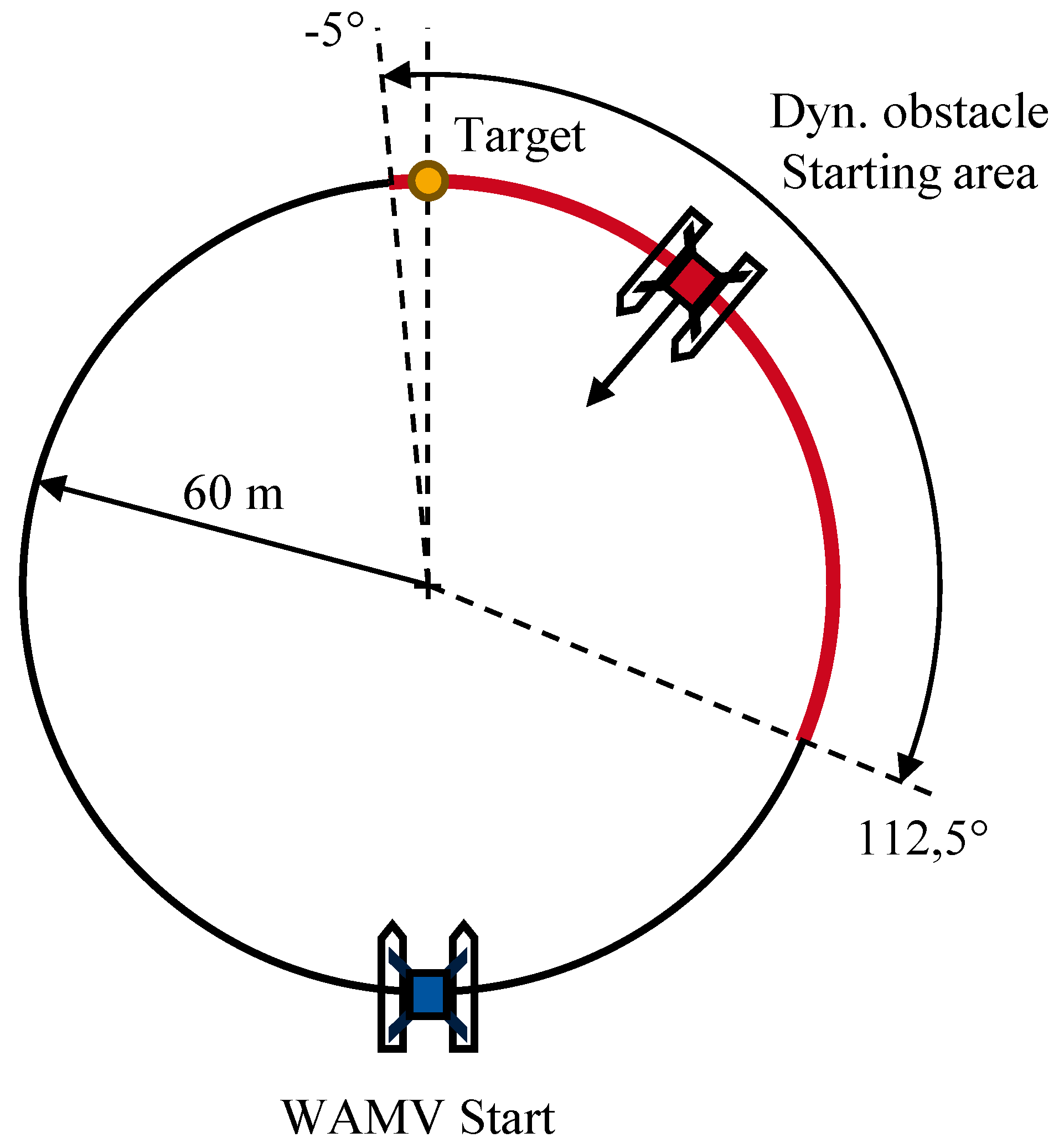
CA2 – Dynamic Obstacle Avoidance:This scenario involves the safe avoidance of a single, moving obstacle, requiring the USV to anticipate the obstacle’s future path.
- -
-
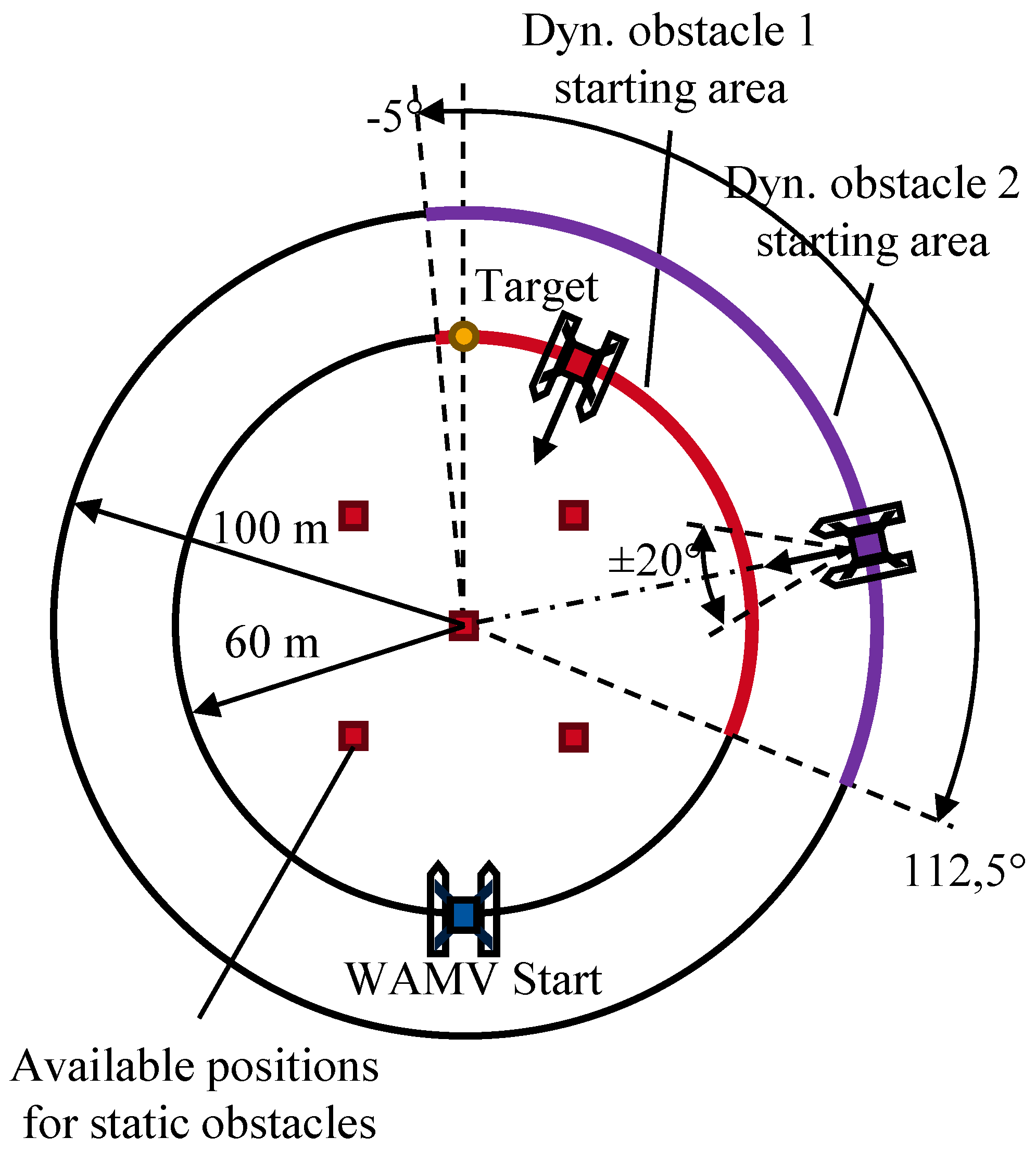
CA3 – Multi-Hindrance Environment:A complex scenario requiring the USV to navigate safely through an environment containing a combination of both static and dynamic obstacles.
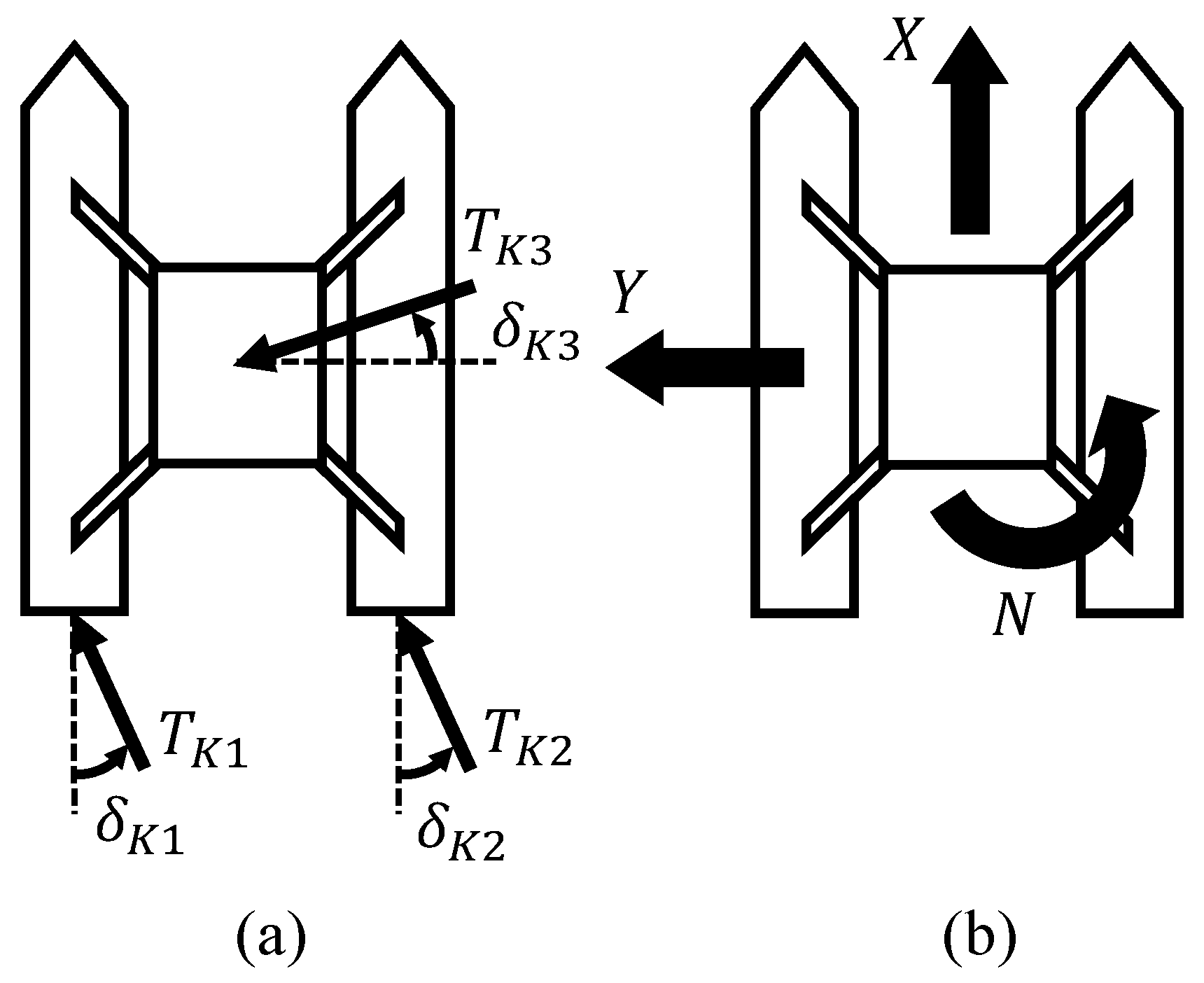
2.2.1. Action Space
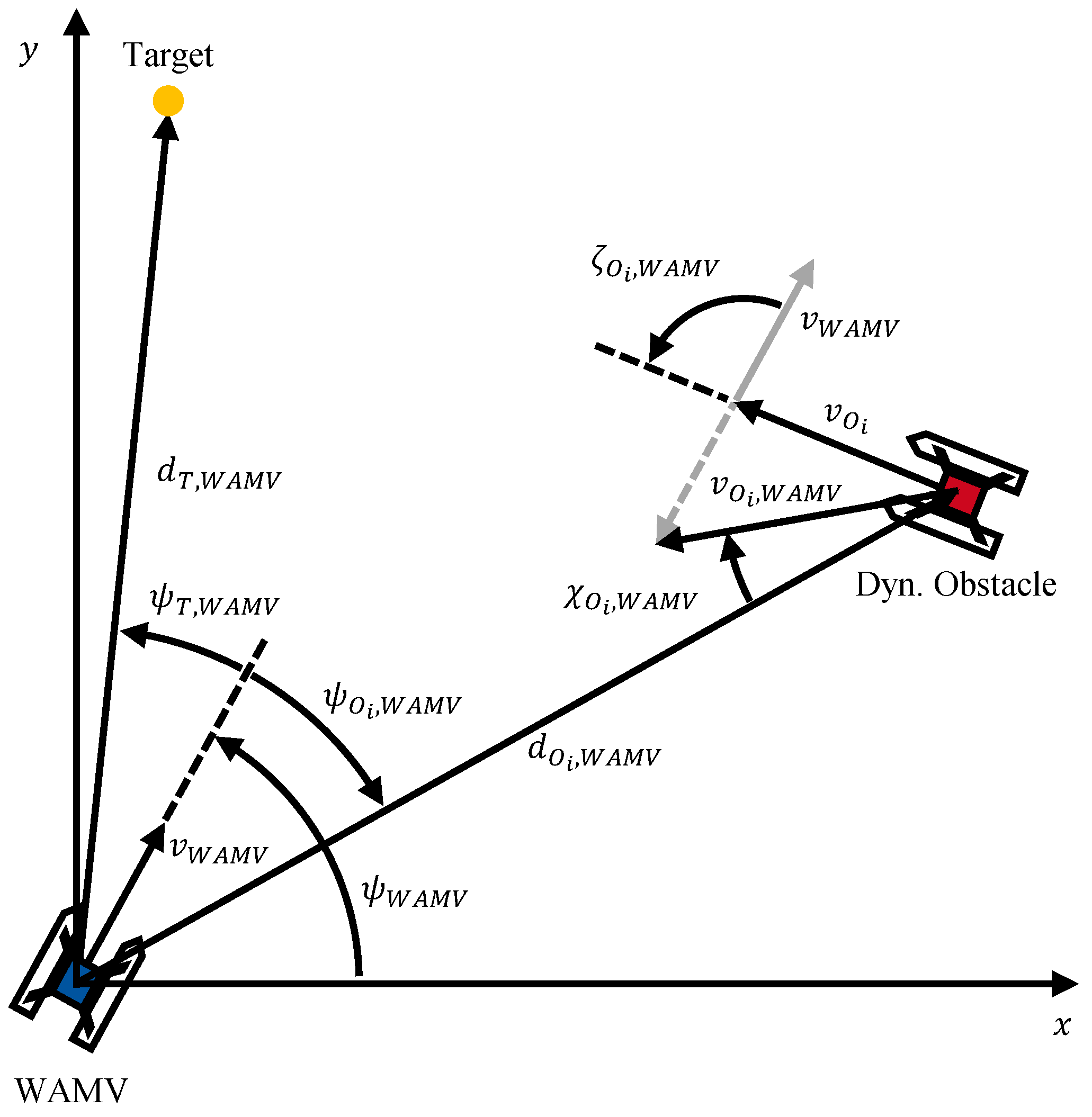
2.2.2. Observation Space
2.2.3. Reward Function
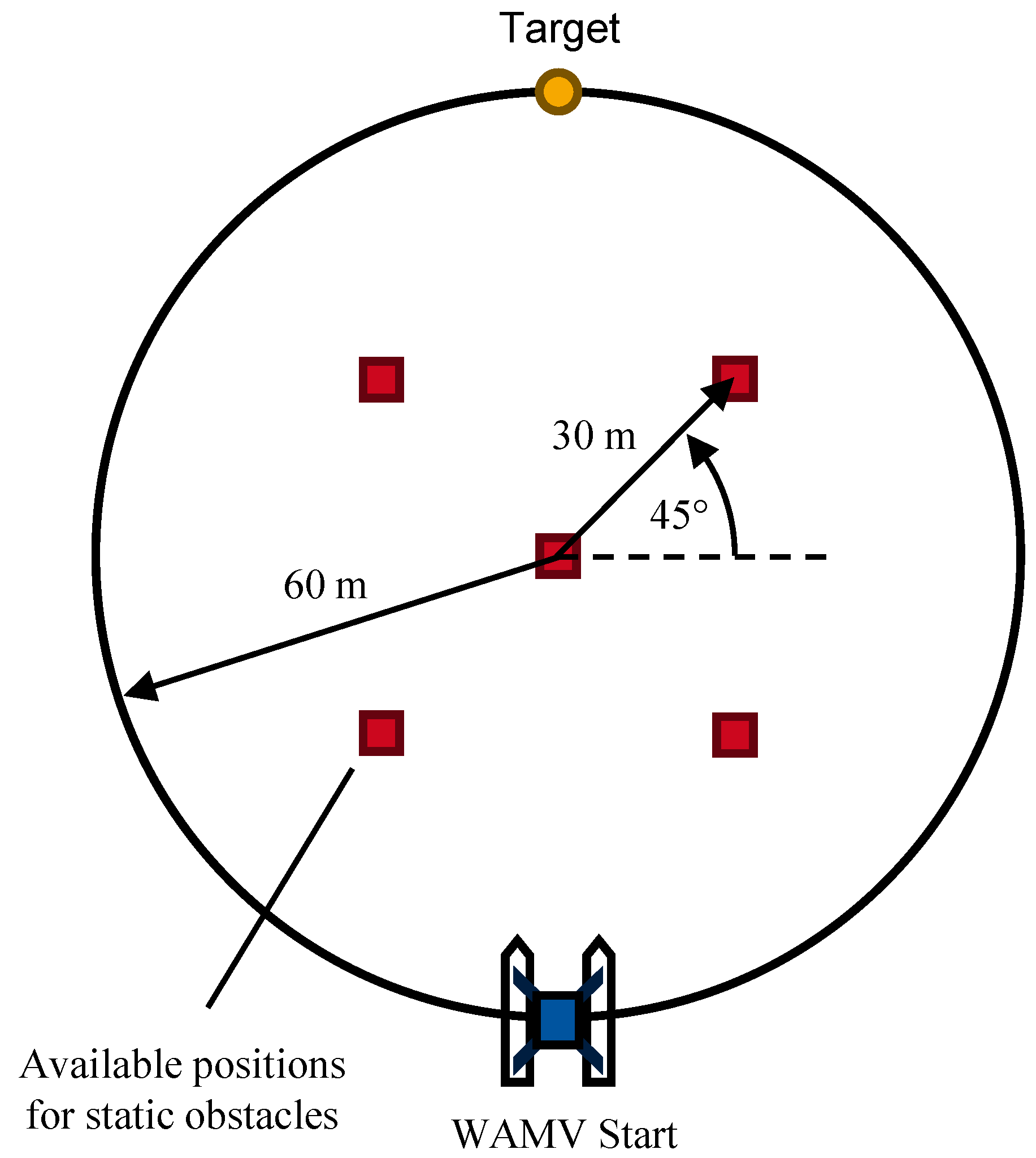
2.2.4. Scenario Generation
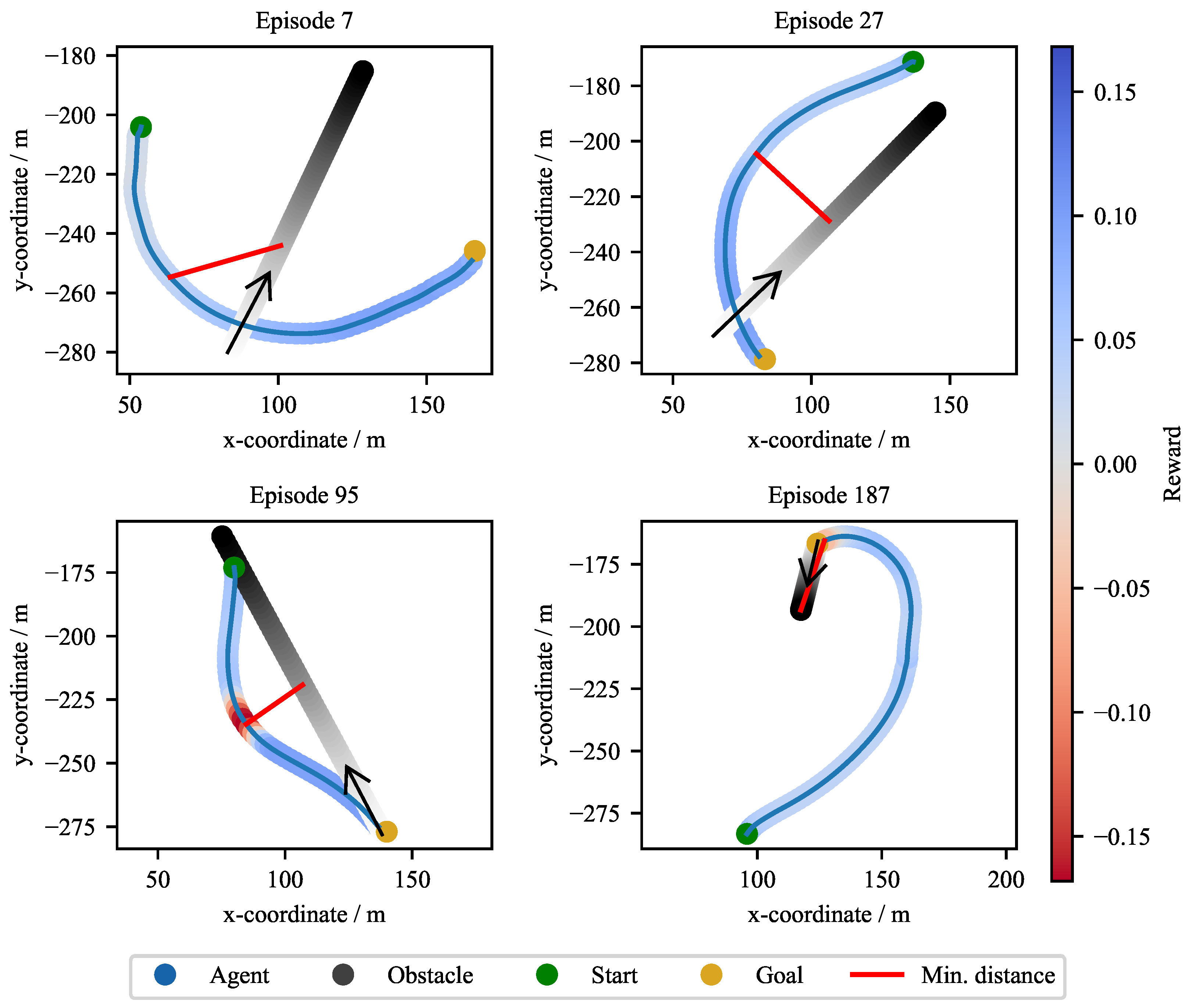
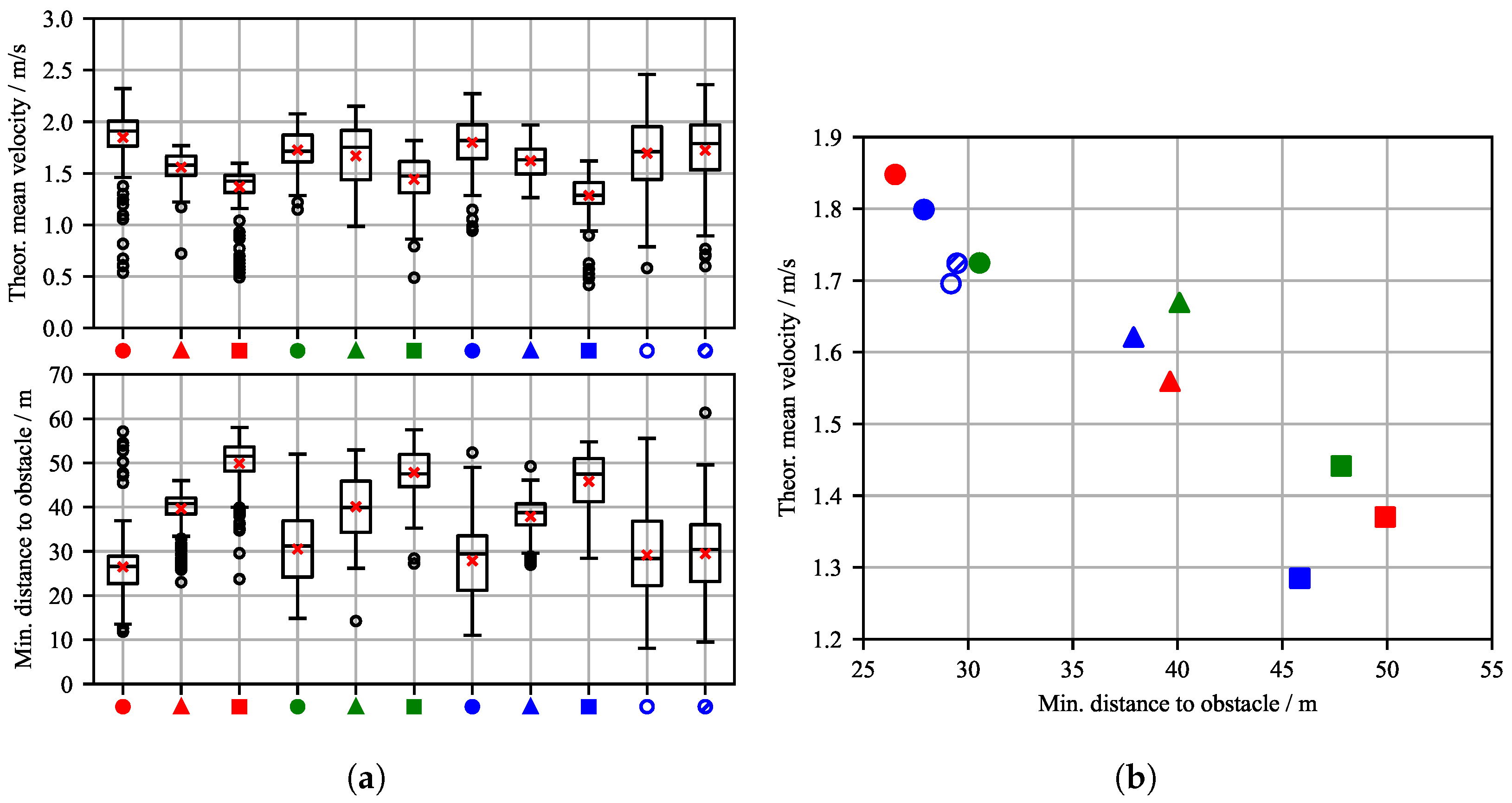
CA1 – Static Obstacle Avoidance
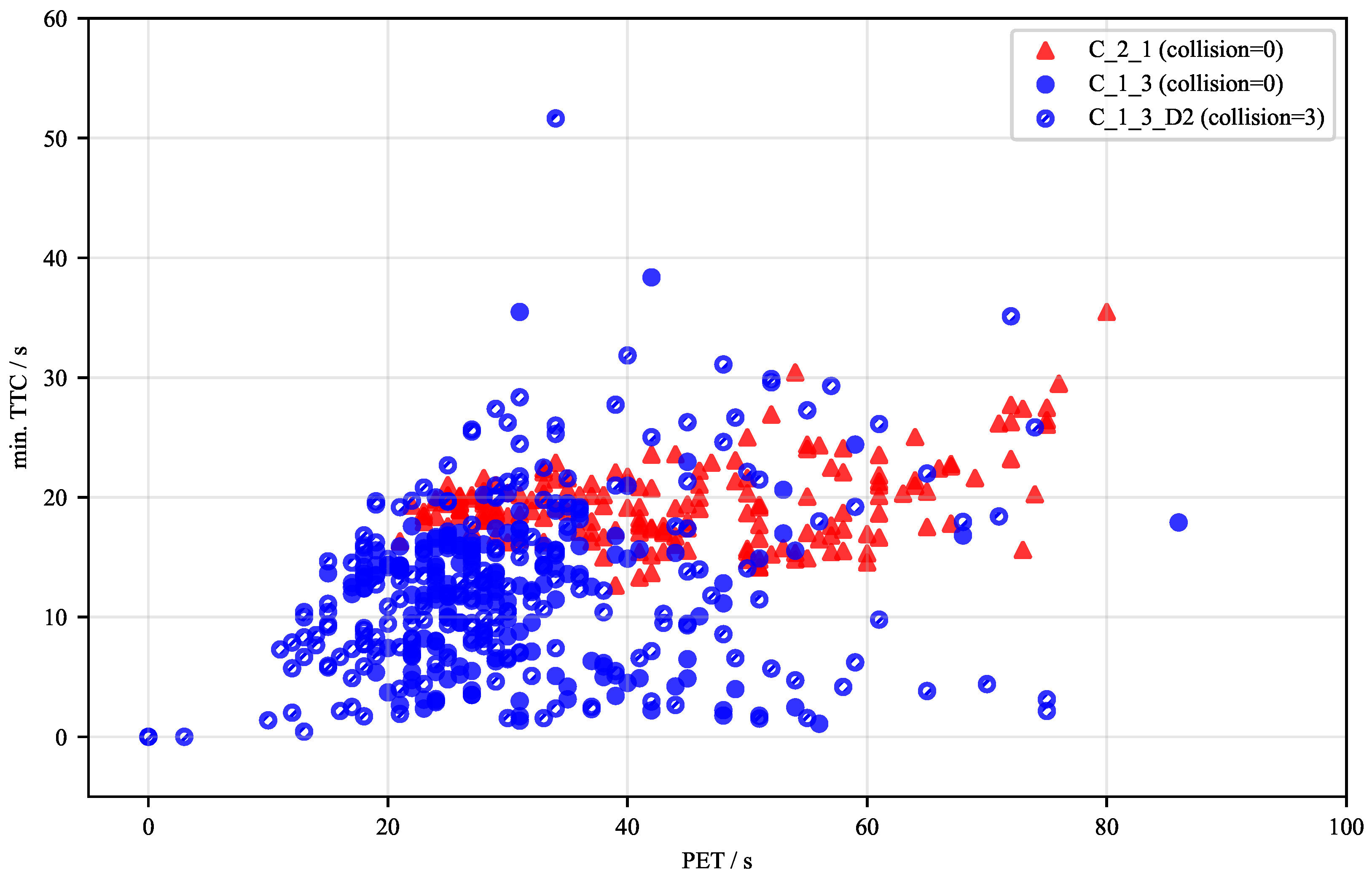
CA2 – Dynamic Obstacle Avoidance
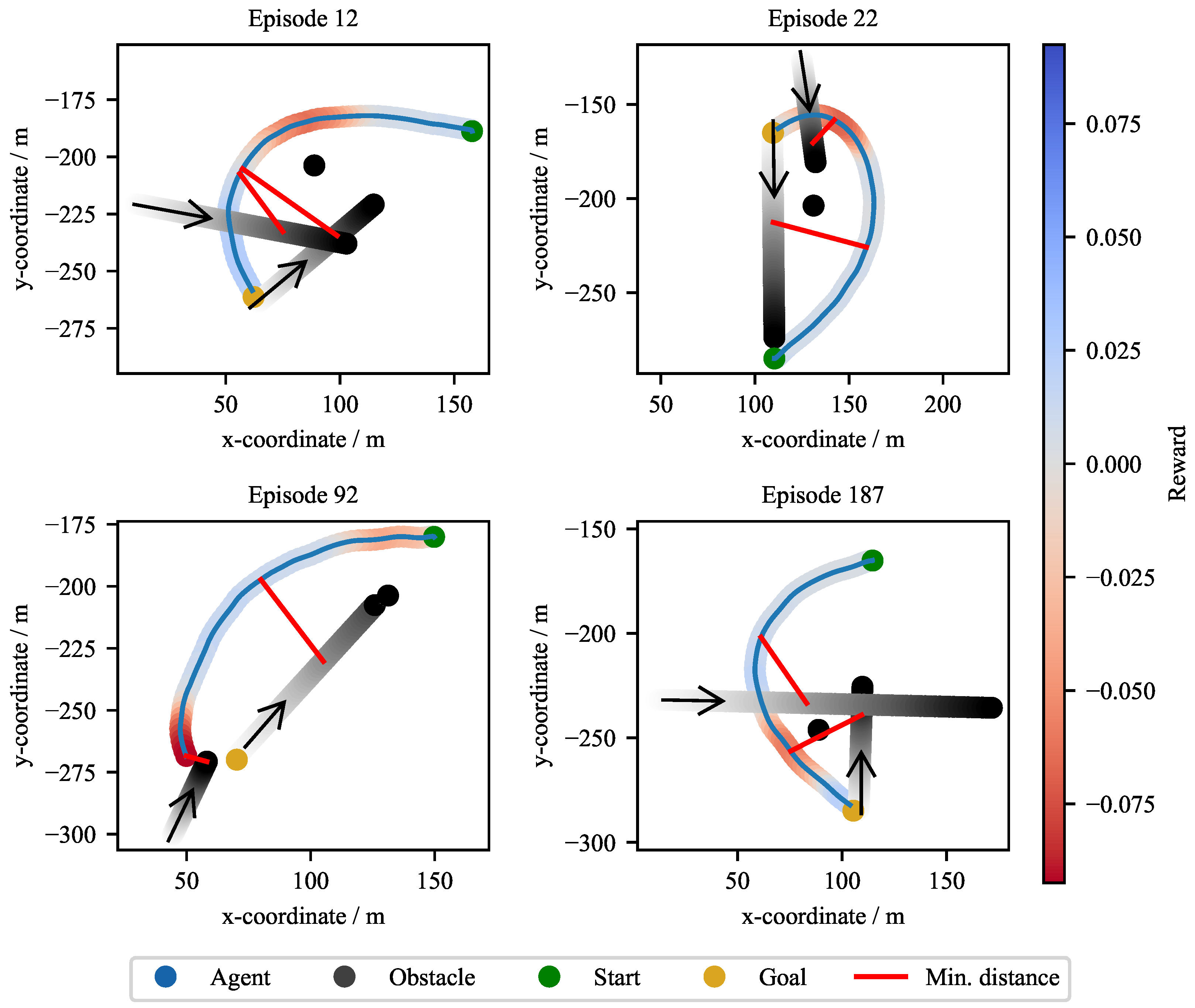
CA3 – Multi-Hindrance Scenario
3. Results and Discussion
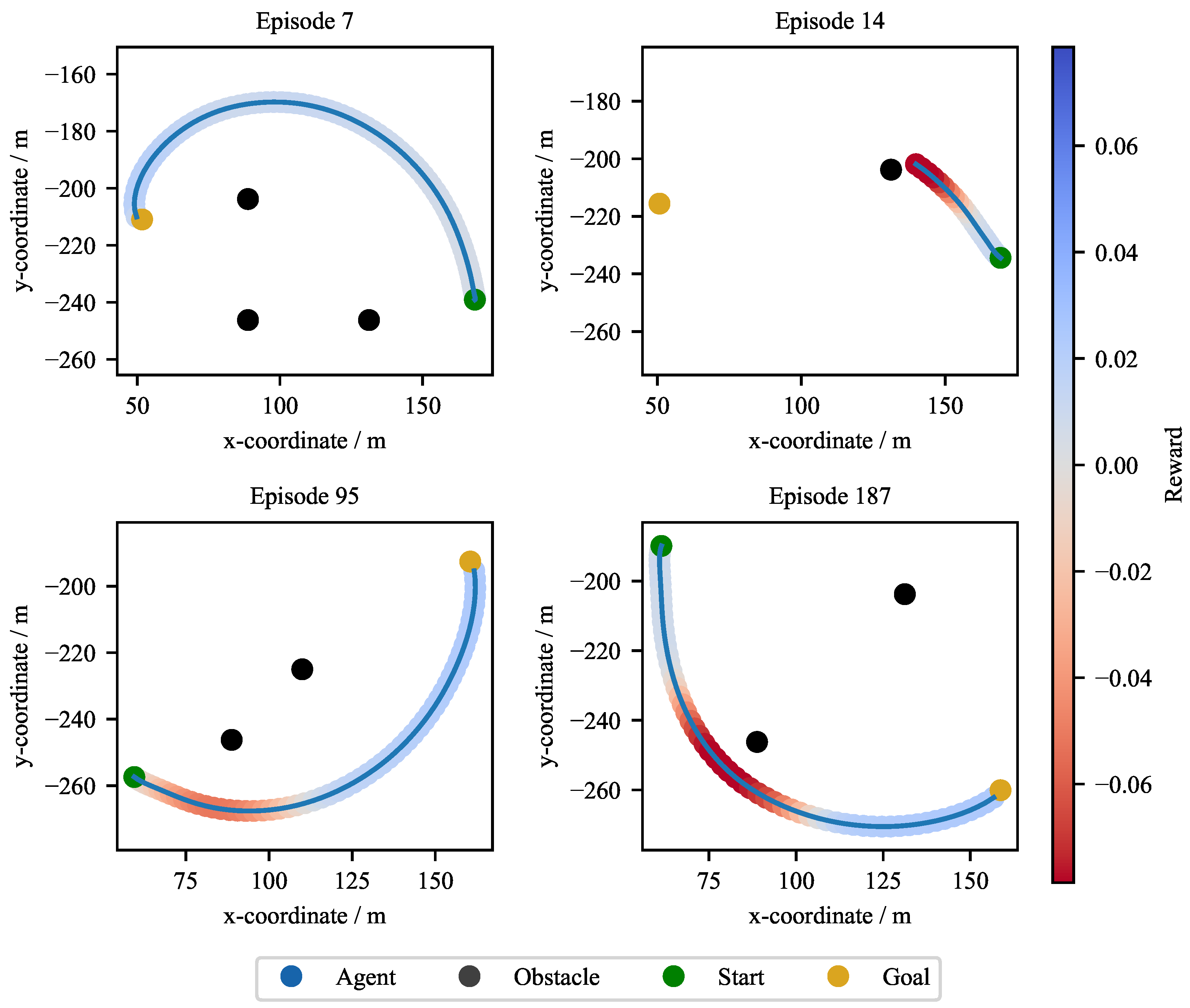
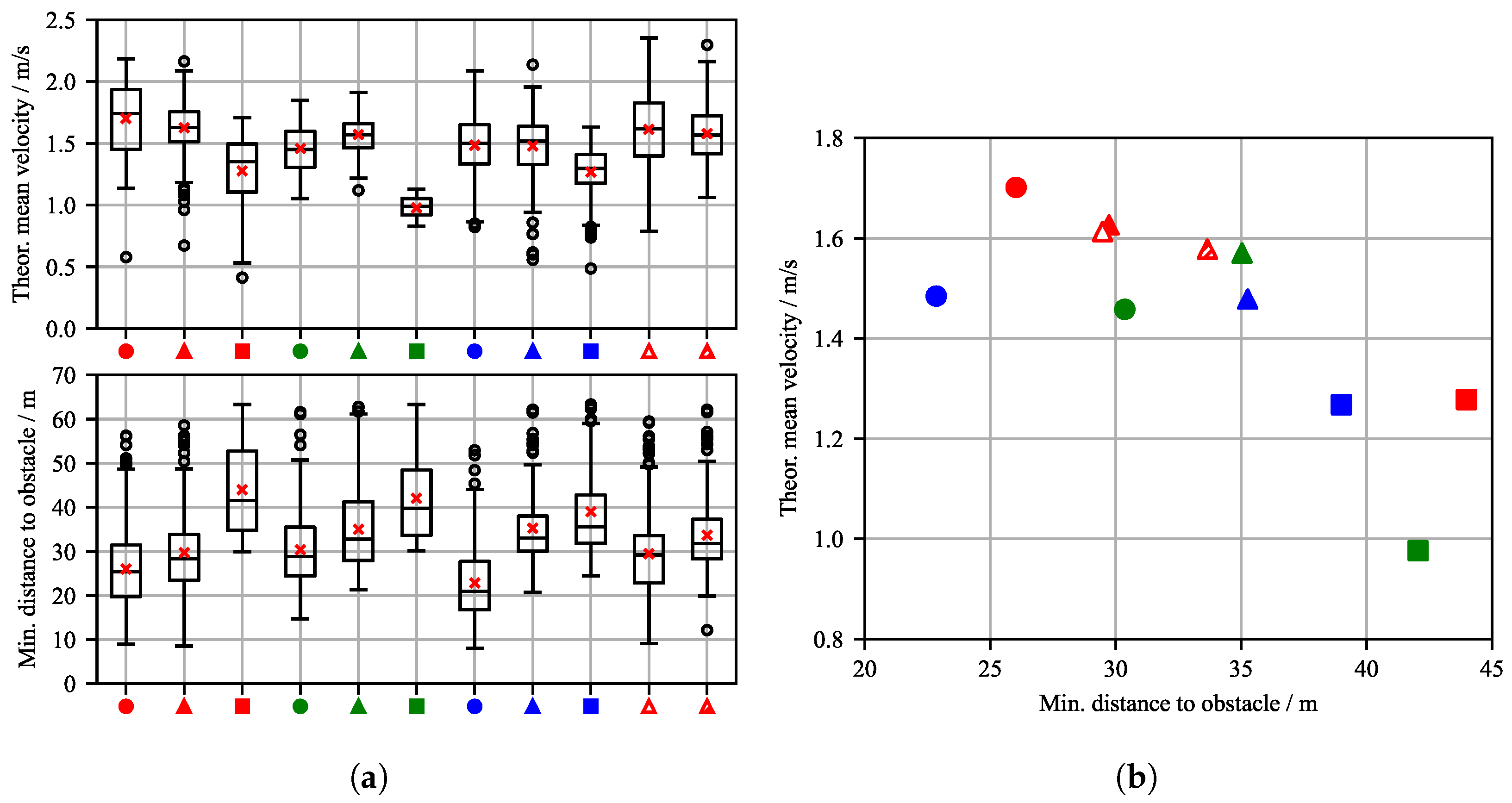
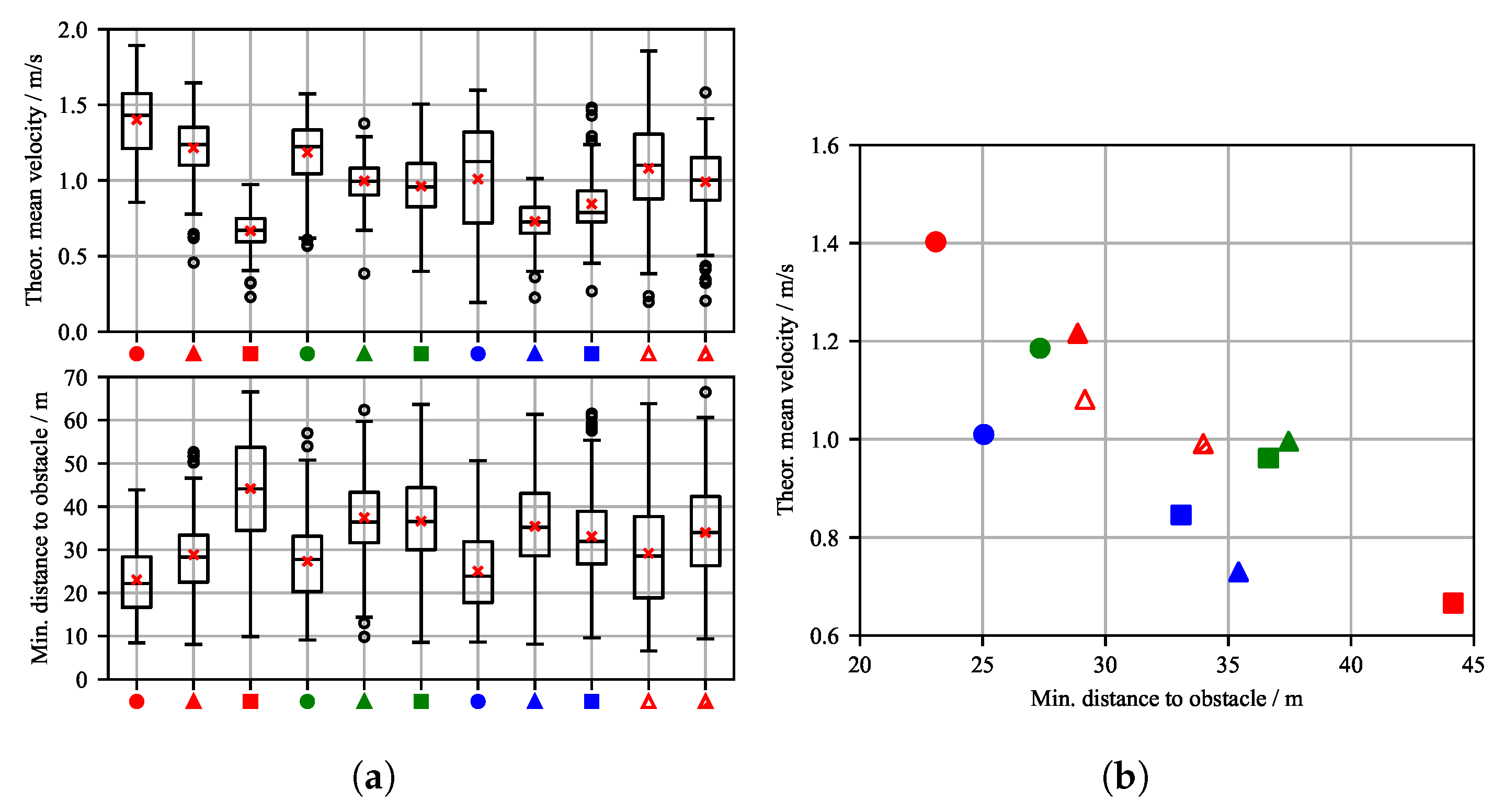
3.1. Scenario CA1 – Static Obstacle Avoidance
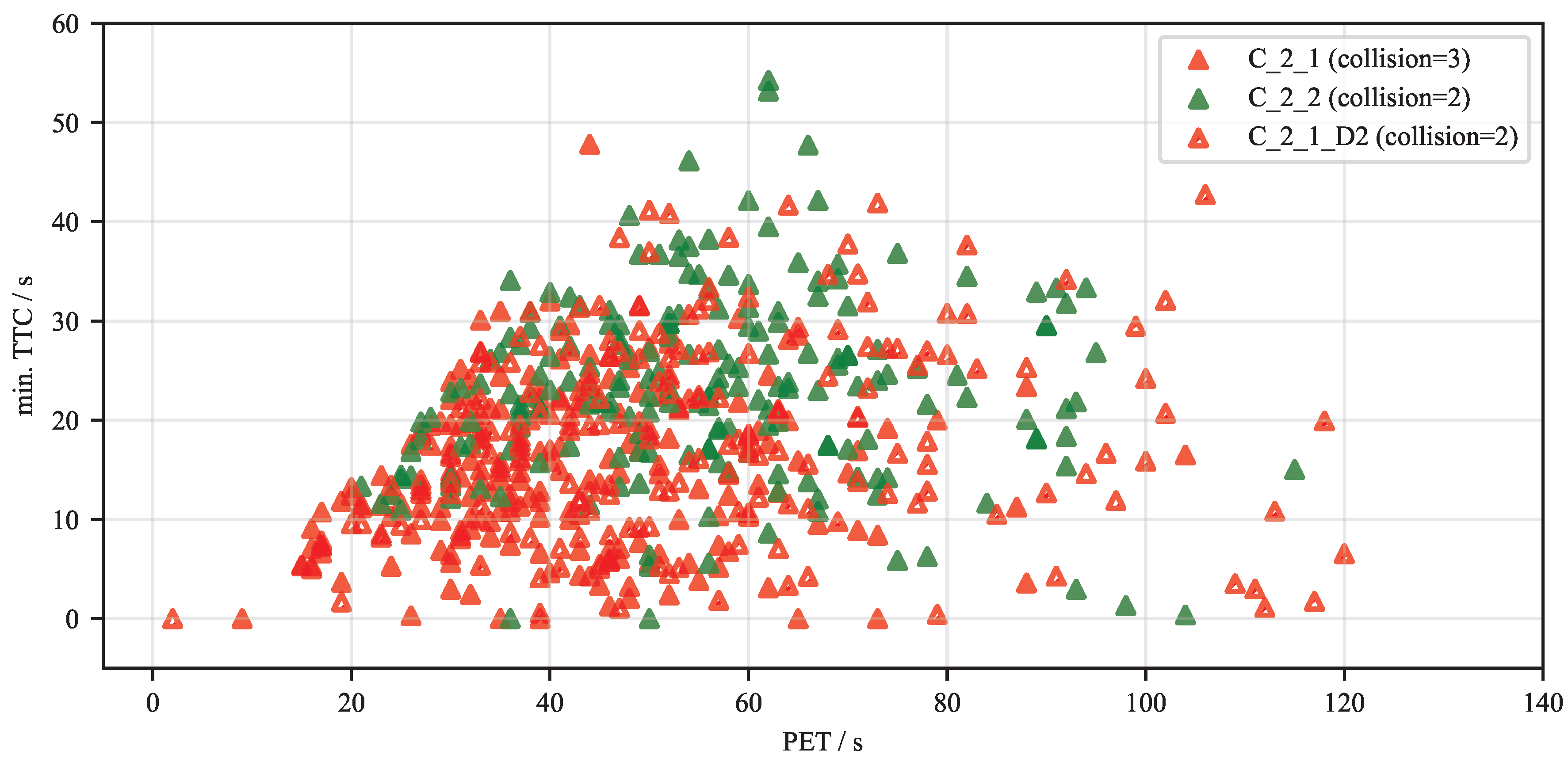
3.2. Scenario CA2 – Dynamic Obstacle Avoidance
3.3. Scenario CA3 – Multi-Hindrance Scenario
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| APF | Artificial Potential Fields |
| CA | Collision Avoidance |
| COLREGS | Collision Regulations |
| DDPG | Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient |
| DQN | Deep Q-Network |
| DRL | Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| DWA | Dynamic Window Approach |
| EKF | Extended Kalman Filter |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GNC | Guidance Navigation and Control |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Units |
| KPI | Key Performance Indicators |
| LOS | Line-of-Sight |
| LQR | Linear Quadratic Regulator |
| MPC | Model Predictive Controller |
| PER-DDQN | Prioritized Experience Replay-enhanced Double Deep Q-Network |
| PET | Post Encroachment Time |
| PPO | Proximal Policy Optimization |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| RLCA | Reinforcement Learning-based Collision Avoidance |
| ROS | Robot Operating System |
| SLAM | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping |
| SLSQP | Sequential Least Squares Programming |
| TTC | Time To Collision |
| USV | Unmanned Surface Vehicle |
| VRX | Virtual RobotX |
| WAMV | Wave Adaptive Modular Vehicle |
Appendix A
| Parameter | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 1 | 0.001 | 250 N | -100 N | rad | rad |
References
- de Andrade, E.M.; Sales, J.S.; Fernandes, A.C. Operative Unmanned Surface Vessels (USVs): A Review of Market-Ready Solutions. Automation 2025, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Li, B.; Xu, X.; Xiao, Y. A Review of Current Research and Advances in Unmanned Surface Vehicles. Journal of Marine Science and Application 2022, 21, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Bao, T.; Zhang, B.; Wu, T.; Chu, X.; Zhou, Z. Deep Reinforcement Learning Methods for USV Control: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2023 China Automation Congress (CAC). IEEE; 2023; pp. 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Yuan, C. Unmanned surface vehicles: An overview of developments and challenges. Annual Reviews in Control 2016, 41, 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Yang, P.; Li, Q.; Song, Y.; Gelder, P.H.A.J.M.v.; Papadimitriou, E.; Hu, H. Machine Learning in Maritime Safety for Autonomous Shipping: A Bibliometric Review and Future Trends. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2025, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Mostafa, M.; Jnadi, A.; Salloum, H.; Osinenko, P. 2024; arXiv:cs.LG/2408.10215.
- Yu, R.; Wan, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, C.X.; Gan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhan, D.C. A: Models in Deep Reinforcement Learning, 2025; arXiv:cs.LG/2506.15421.
- Schumacher, M.; Adriano, C.M.; Giese, H. Challenges in Reward Design for Reinforcement Learning-based Traffic Signal Control: An Investigation using a CO2 Emission Objective. SUMO Conference Proceedings 2023, 4, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Design of Reward Functions for Autonomous Driving Based on Reinforcement Learning: Balancing Safety and Efficiency. Applied and Computational Engineering 2025, 146, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osika, Z.; Zatarain-Salazar, J.; Oliehoek, F.A.; Murukannaiah, P.K. Navigating Trade-offs: Policy Summarization for Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning. In ECAI 2024; IOS Press, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockman, G.; Cheung, V.; Pettersson, L.; Schneider, J.; Schulman, J.; Tang, J.; Zaremba, W. Openai gym. arXiv preprint 2016, arXiv:1606.01540 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bingham, B.; Agüero, C.; McCarrin, M.; Klamo, J.; Malia, J.; Allen, K.; Lum, T.; Rawson, M.; Waqar, R. Toward Maritime Robotic Simulation in Gazebo. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2019 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE; 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer Handbook of Robotics; Siciliano, B., Khatib, O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Lin, C.J.; Lai, C.C.; Lin, S.Y. Velocity Estimation and Cost Map Generation for Dynamic Obstacle Avoidance of ROS Based AMR. Machines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.; Likhachev, M. Efficiently Using Cost Maps For Planning Complex Maneuvers. 2008.
- Racinskis, P.; Arents, J.; Greitans, M. Constructing Maps for Autonomous Robotics: An Introductory Conceptual Overview. Electronics 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrun, S. Robotic mapping: a survey. In Exploring Artificial Intelligence in the New Millennium; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, C.; Jeong, S.; Cho, J. Map Representation for Robots. Smart Computing Review 2012, 2, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macenski, S.; Moore, T.; Lu, D.V.; Merzlyakov, A.; Ferguson, M. From the desks of ROS maintainers: A survey of modern & capable mobile robotics algorithms in the robot operating system 2. Robotics and Autonomous Systems 2023, 168, 104493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.; Morales, J.; Martínez, J.; Fernández-Lozano, J.; Garcia, A. Automatically Annotated Dataset of a Ground Mobile Robot in Natural Environments via Gazebo Simulations. Sensors 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souissi, O.; Benatitallah, R.; Duvivier, D.; Artiba, A.; Belanger, N.; Feyzeau, P. Path planning: A 2013 survey. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of 2013 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Systems Management (IESM); 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- LaValle, S.M. Planning algorithms, cop. 2006, reprinted. ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York (NY), 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Karaman, S.; Frazzoli, E. Sampling-based algorithms for optimal motion planning. The International Journal of Robotics Research 2011, 30, 846–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loe, . Collision Avoidance Concepts for Marine Surface Craft 2007.
- Seder, M.; Petrovic, I. Dynamic window based approach to mobile robot motion control in the presence of moving obstacles. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation; 2007; pp. 1986–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiberg, A.; Larsen, T.N.; Meyer, E.; Rasheed, A.; San, O.; Varagnolo, D. Risk-based implementation of COLREGs for autonomous surface vehicles using deep reinforcement learning. Neural Networks 2022, 152, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagale, A.; Oucheikh, R.; Bye, R.T.; Osen, O.L.; Fossen, T.I. Path planning and collision avoidance for autonomous surface vehicles I: a review. Journal of Marine Science and Technology 2021, 26, 1292–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamini, C.; Benhlima, S.; Elbekri, A. Genetic Algorithm Based Approach for Autonomous Mobile Robot Path Planning. Procedia Computer Science 2018, 127, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tan, D.; Liu, L. Particle swarm optimization algorithm: an overview. Soft Computing 2018, 22, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Cruz, M.A.; Ayala-Ramirez, V.; Hernandez-Belmonte, U.H. Mobile robot path planning using artificial bee colony and evolutionary programming. Applied Soft Computing 2015, 30, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. VoxelNet: End-to-End Learning for Point Cloud Based 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2018; pp. 4490–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.; Naeem, W.; Irwin, G.W. A review on improving the autonomy of unmanned surface vehicles through intelligent collision avoidance manoeuvres. Annual Reviews in Control 2012, 36, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsardoulias, E.; Iliakopoulou, K.; Kargakos, A.; Petrou, L. A Review of Global Path Planning Methods for Occupancy Grid Maps Regardless of Obstacle Density. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems 2016, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.; Yu, M.; Liu, Z.; Tan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, B. A Review of Path Planning for Unmanned Surface Vehicles. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Gao, Q.; Yue, Y.; Lim, E.G.; Paoletti, P.; Ma, J.; Zhu, X. Evolution of Unmanned Surface Vehicle Path Planning: A Comprehensive Review of Basic, Responsive, and Advanced Strategic Pathfinders. Drones 2024, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandretti, A.; Aguiar, A.P.; Jones, C.N. Trajectory-tracking and path-following controllers for constrained underactuated vehicles using Model Predictive Control. In Proceedings of the 2013 European Control Conference (ECC); 2013; pp. 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyri, E.H.; Breivik, M. Collision avoidance for ASVs through trajectory planning: MPC with COLREGs-compliant nonlinear constraints. Modeling, Identification and Control: A Norwegian Research Bulletin 2022, 43, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, M.S.; Stastny, T.; Alexis, K.; Siegwart, R. Model Predictive Control for Trajectory Tracking of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Using Robot Operating System; 2017. [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.T.; Streetman, B.; Lessard, L. Model Predictive Planning: Trajectory Planning in Obstruction-Dense Environments for Low-Agility Aircraft, 2024, [arXiv:eess.SY/2309.16024].
- Li, Z.; Sun, J. Disturbance Compensating Model Predictive Control With Application to Ship Heading Control. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology 2012, 20, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, M.M.; Huang, M.; Abel, D. Model Predictive Control for Safe Path Following in Narrow Inland Waterways for Rudder Steered Inland Vessels*. In Proceedings of the 2023 European Control Conference (ECC); 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, H.; Fu, M. Line-of-sight guidance law for path following of amphibious hovercrafts with big and time-varying sideslip compensation. Ocean Engineering 2019, 172, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossen, T.I.; Breivik, M.; Skjetne, R. Line-of-sight path following of underactuated marine craft. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 2003, 36, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, A.; Platt, R.; Konidaris, G.; Kaelbling, L.; Lozano-Perez, T. LQR-RRT*: Optimal sampling-based motion planning with automatically derived extension heuristics. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation; 2012; pp. 2537–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Q. Research on Collision Avoidance Algorithm of Unmanned Surface Vehicle Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Sensors Journal 2023, 23, 11262–11273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, T.A.; Fossen, T.I.; Berge, S.P. Constrained Nonlinear Control Allocation With Singularity Avoidance Using Sequential Quadratic Programming. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology 2004, 12, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, U. Reinforcement Learning: Aktuelle Ansätze verstehen – mit Beispielen in Java und Greenfoot, 2th ed.; Springer Vieweg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ji, Y.; Liu, J.; Bai, Z.; Hu, J.; Gao, Q. Global Path Planning of Unmanned Surface Vehicles Based on Deep Q Network. In Proceedings of the 2024 43rd Chinese Control Conference (CCC); 2024; pp. 3827–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, P.; Li, B.; Bai, C. A DDPG-Based USV Path-Planning Algorithm. Applied Sciences 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Song, C.; Chen, L.; Cui, W. Image Based River Navigation System of Catamaran USV with Image Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 WRC Symposium on Advanced Robotics and Automation (WRC SARA). IEEE; 2022; pp. 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibo Zhong; Haodong Li.; Yizhen Meng.; Xiaofei Yang.; Youbing Feng.; Hui Ye.; Wei Liu. USV path following controller based on DDPG with composite state-space and dynamic reward function. Ocean Engineering 2022, 266, 112449. [CrossRef]
- Deraj, R.; Kumar, R.S.; Alam, M.S.; Somayajula, A. Deep reinforcement learning based controller for ship navigation. Ocean Engineering 2023, 273, 113937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhewen Cui; Wei Guan.; Xianku Zhang. Collision avoidance decision-making strategy for multiple USVs based on Deep Reinforcement Learning algorithm. Ocean Engineering 2024, 308, 118323. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wang, G. An Intelligent Algorithm for USVs Collision Avoidance Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach with Navigation Characteristics. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, G. A Novel Reinforcement Learning Collision Avoidance Algorithm for USVs Based on Maneuvering Characteristics and COLREGs. Sensors 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, P.; Sun, L. Motion Path Planning of Agent Based on Proximal Policy Optimization Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th International Conference on Industrial Artificial Intelligence (IAI); 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuanda Wang.; Jingyu Cao.; Jia Sun.; Xuesong Zou.; Changyin Sun. Path Following Control for Unmanned Surface Vehicles: A Reinforcement Learning-Based Method With Experimental Validation. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems 2023, PP. [CrossRef]
- Raffin, A.; Hill, A.; Gleave, A.; Kanervisto, A.; Ernestus, M.; Dormann, N. Stable-Baselines3: Reliable Reinforcement Learning Implementations. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2021, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Quigley, M.; Gerkey, B.; Conley, K.; Faust, J.; Foote, T.; Leibs Jeremy.; Berger, E.; Wheeler, B.; Ng Andrew. ROS: an open-source Robot Operating System. In Proceedings of the ICRA workshop on open source software, 2009, Vol. 3, p. 5.
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nature Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Z.G.; Yang, W.C.; Lu, Q.C. The role of traffic conflicts in roundabout safety evaluation: A review. Accident Analysis & Prevention 2024, 196, 107430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badalian, K.; Koch, L.; Brinkmann, T.; Picerno, M.; Wegener, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Andert, J. LExCI: A framework for reinforcement learning with embedded systems. Applied Intelligence 2024, 54, 8384–8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedei, J.; Koch, L.; Badalian, K.; Winkler, A.; Schaber, P.; Andert, J. Safe Reinforcement Learning for Real-World Engine Control, 2025, [arXiv:cs.LG/2501.16613].
| Configuration encoding | Parametrization |
|---|---|
| C_1_Y | |
| C_2_Y | |
| C_3_Y | |
| C_X_1 | |
| C_X_2 | |
| C_X_3 |
| Name | Target Reached % | Collision % | Step Limit Reached % | Exited Workspace % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
C_1_1
|
92.0 | 8.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_2_1
|
99.5 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 |
C_3_1
|
51.0 | 0.0 | 44.5 | 4.5 |
C_1_2
|
100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_2_2
|
67.5 | 0.0 | 30.5 | 2.0 |
C_3_2
|
22.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 78.0 |
C_1_3
|
86.5 | 5.5 | 8.0 | 0.0 |
C_2_3
|
99.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
C_3_3
|
89.0 | 0.0 | 10.5 | 0.5 |
C_2_1_D1
|
98.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 |
C_2_1_D2
|
100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Name | Target Reached % | Collision % | Step Limit Reached % | Exited Workspace % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
C_1_1
|
98.5 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 |
C_2_1
|
100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_3_1
|
100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_1_2
|
100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_2_2
|
100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_3_2
|
99.5 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_1_3
|
100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_2_3
|
100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_3_3
|
99.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
C_1_3_D1
|
95.5 | 4.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 |
C_1_3_D2
|
98.5 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Name | Target Reached % | Collision % | Step Limit Reached % | Exited Workspace % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
C_1_1
|
95.0 | 5.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_2_1
|
98.0 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.0 |
C_3_1
|
96.0 | 0.0 | 4.0 | 0.0 |
C_1_2
|
97.5 | 2.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_2_2
|
99.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_3_2
|
97.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
C_1_3
|
94.5 | 5.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 |
C_2_3
|
93.0 | 7.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
C_3_3
|
96.5 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
C_2_1_D1
|
91.0 | 8.5 | 0.0 | 0.5 |
C_2_1_D2
|
98.5 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





