Submitted:
13 August 2025
Posted:
14 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cat Samples
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Design Primer, Polymerase Chain Reaction, and DNA Sequencing
2.4. Coat Color Gene Evaluation
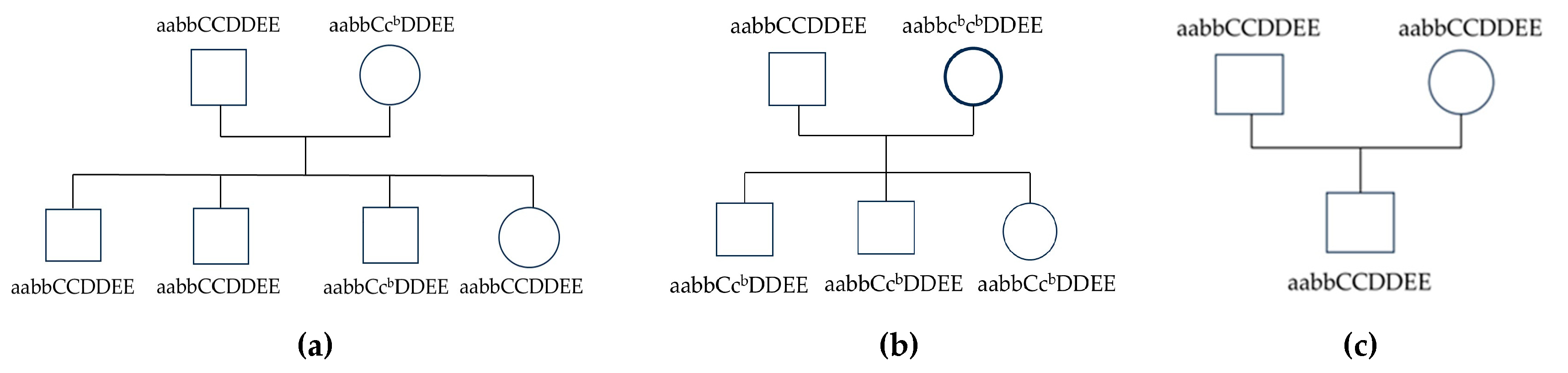
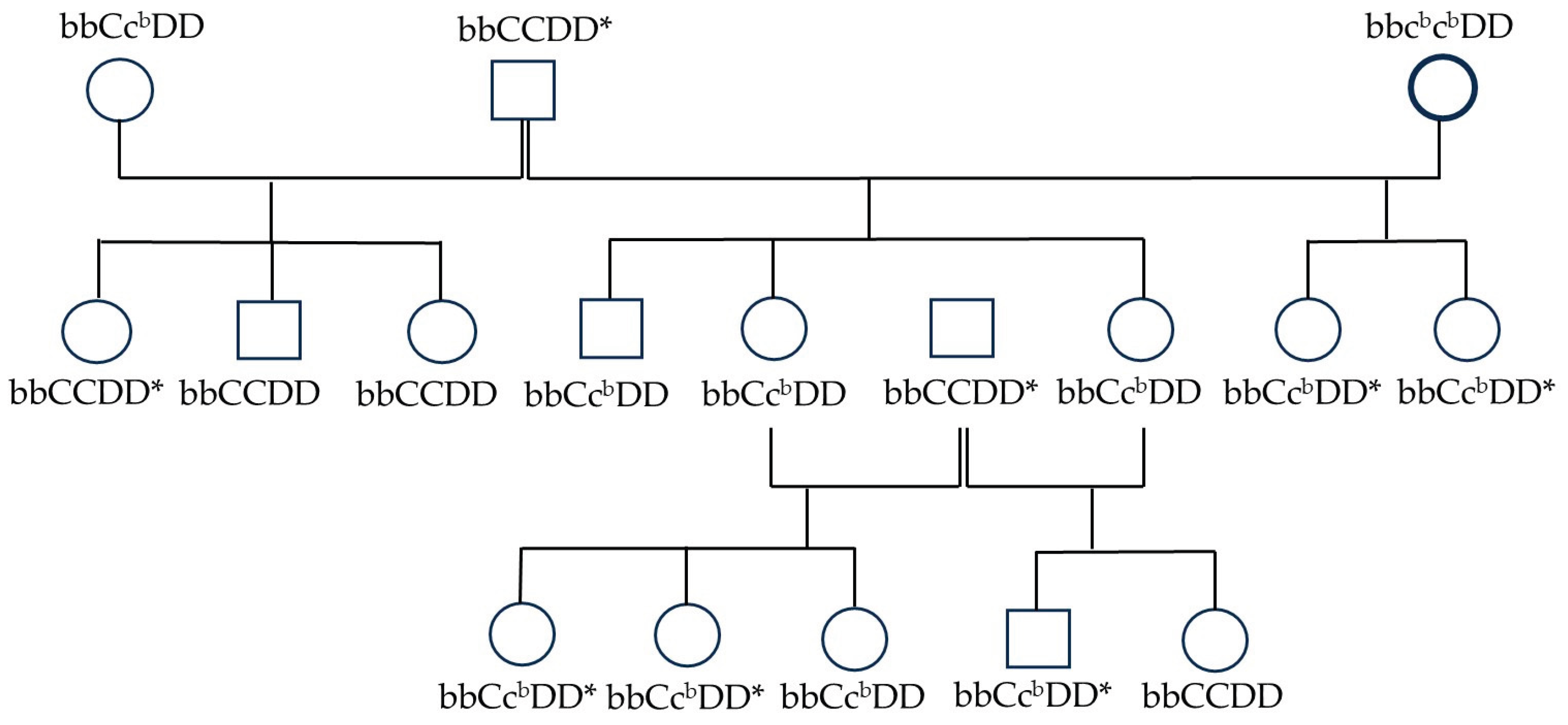
2.5. The Use of Coat Color Gene for Selection and Breeding Test in Suphalak Cats
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Coat Color Genetic Results
3.2. Application of the Coat Color Genes for Selective Breeding
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASIP | Agouti Signaling Protein |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid |
| TYRP1 | Tyrosinase-Related Protein 1 |
| TYR | Tyrosinase |
| MLPH | Melanophilin |
| MC1R | Melanocortin 1 Receptor |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| ºC | Degrees Celsius |
References
- Clutterbuck, M.R. Siamese Cats: Legends and Reality; White Lotus Co., Ltd: Bangkok, Thailand, 2004; pp. 1–244. [Google Scholar]
- Vella, C.M.; Shelton, L.M.; McGonagle, J.J.; Stanglein, T.W. Robinson’s Genetics for Cat Breeders and Veterinarians, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 1–496. [Google Scholar]
- Ubolrat, K.; Sudtisa, L.; Kavil, N.; Janjira, P. Genetic diversity and inbreeding situation of Korat and Siamese cats based on microsatellite markers. Vet. Integr. Sci. 2019, 17, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Barsh, G. S. The genetics of pigmentation: from fancy genes to complex traits. Trends Genet. 1996, 12, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieslak, M.; Reissmann, M.; Hofreiter, M.; Ludwig, A. Colours of domestication. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2011, 86, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearing, V.J.; Tsukamoto, K. Enzymatic control of pigmentation in mammals. FASEB J. 1991, 5, 2902–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, I.J. Colour-coded switches. Nature. 1993, 362, 587–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yongdong, P.; Xinhao, Z.; Xinrui, W.; Wenting, C.; Xiyan, K.; Huili, L.; Wei, R.; Muhammad, Z.K.; Changfa, W. Coloration in Equine: Overview of Candidate Genes Associated with Coat Color Phenotypes. Animals 2024, 14, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, S.; Taourit, S.; Mariat, D.; Langlois, B.; Guerin, G. Mutations in the agouti (ASIP), the extension (MC1R), and the brown (TYRP1) loci and their association to coat color phenotypes in horses (Equus caballus). Mamm. Genome 2001, 12, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eizirik, E.; Yuhki, N.; Johnson, W.E.; Menotti-Raymond, M.; Hannah, S.S.; O’Brien, S.J. Molecular genetics and evolution of melanism in the cat family. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; David, V.A.; Johnson, W.E.; O’Brien, S.J.; Barsh, G.S.; Menotti-Raymond, M.; Eizirik, E. How the leopard hides its spots: ASIP mutations and melanism in wild cats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershony, L.C.; Penedo, M.C.; Davis, B.W.; Murphy, W.J.; Helps, C.R.; Lyons, L.A. Who’s behind that mask and cape? The Asian leopard cat’s Agouti (ASIP) allele likely affects coat colour phenotype in the Bengal cat breed. Anim. Genet. 2014, 45, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Li, S.; Xia, X.; Ji, C.; Zhang, G.; Yu, J.; Jiang, G.; Dang, R.; Lei, C. ASIP gene variation in Chinese donkeys. Anim. Genet. 2017, 48, 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javerzat, S. , Jackson, I.J. White-based brown (Tyrp1B-w) is a dominant mutation causing reduced hair pigmentation owing to a chromosomal inversion. Mamm. Genome. 1998, 9, 469–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmutz, S.M.; Berryere, T.G.; Goldfinch, A.D. TYRP1 and MC1R genotypes and their effects on coat color in dogs. Mamm. Genome. 2002, 13, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, L.A.; Foe, I.T.; Rah, H.C.; Grahn, R.A. Chocolate-coated cats: TYRP1 mutations for brown color in domestic cats. Mamm. Genome. 2005, 16, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Kuntzel, A.; Eizirik, E.; O’Brien, S.J.; Menotti-Raymond, M. Tyrosinase and tyrosinase related protein 1 alleles specify domestic cat coat color phenotypes of the albino and brown loci. J. Hered. 2005, 96, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, L.A.; Imes, D.L.; Rah, H.C.; Grahn, R.A. Tyrosinase mutations associated with Siamese and Burmese patterns in the domestic cat (Felis catus). Anim. Genet. 2005, 36, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imes, D.L.; Geary, L.A.; Grahn, R.A.; Lyons, L.A. Albinism in the domestic cat (Felis catus) is associated with a tyrosinase (TYR) mutation. Anim. Genet. 2006, 37, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utzeri, V.J.; Bertolini, F.; Ribani, A.; Schiavo, G.; Dall’Olio, S.; Fontanesi, L. The albinism of the feral Asinara white donkeys (Equus asinus) is determined by a missense mutation in a highly conserved position of the tyrosinase (TYR) gene deduced protein. Anim. Genet. 2016, 47, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Grahn, R.A.; Lyons, L.A. Mocha tyrosinase variant: a new flavour of cat coat coloration. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; David, V.A.; Eizirik, E.; Schaffer, A.A.; Neelam, B.A.; Roelke, M.E.; Hannah, S.S.; O’Brien, S.J.; Menotti-Raymond, M. A homozygous single-base deletion in MLPH causes the dilute coat color phenotype in the domestic cat. Genomics 2006, 88, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drögemüller, C.; Ute, P.; Bianca, H.; Anne-Rose, G.-A.; Tosso, L. A Noncoding Melanophilin Gene (MLPH) SNP at the Splice Donor of Exon 1 Represents a Candidate Causal Mutation for Coat Color Dilution in Dogs. J. Hered. 2007, 98, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterschmitt, M.; Grain, F.; Arnaud, B.; Deleage, G.; Lambert, V. Mutation in the melanocortin 1 receptor is associated with amber colour in the Norwegian Forest Cat. Anim. Genet. 2009, 40, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, L.; Nadeau, J.; Johnson, K.R.; Kelly, M.; Roselli-Rehfuss, L.; Baack, E. Pigmentation phenotypes of variant extension locus alleles result from point mutations that alter MSH receptor function. Cell 1993, 72, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, P.; Healy, E.; Jackson, I.; Rees, J.; Thody, A. Variants of the melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor gene are associated with red hair and fair skin in humans. Nat. Genet. 1995, 11, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerg, H.; Fries, H.; Meijerink, E.; Stranzinger, G. Red coat color in Holstein cattle is associated with a deletion in the MSHR gene. Mamm. Genome 1996, 7, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklund, L.; Moller, M.; Sandberg, K.; Andersson, L. A missense mutation in the gene for melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor (MC1R) is associated with the chestnut coat color in horses. Mamm. Genome 1996, 7, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Våge, D.I.; Lu, D.; Klungland, H.; Lien, S.; Adalsteinsson, S.; Cone, R.D. A non-epistatic interaction of agouti and extension in the fox, Vulpes vulpes. Nat. Genet. 1997, 15, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijas, J.M.H.; Wales, R.; Törnsten, A.; Chardon, P.; Moller, M.; Andersson, L. Melanocortin receptor 1 (MC1R) mutations and coat color in pigs. Genetics. 1998, 150, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Våge, D.I.; Klungland, H.; Dongsi, L.; Cone, R.D. Molecular and pharmacological characterization of dominant black coat color in sheep. Mamm. Genome 1999, 10, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, R.E.; Rothuizen, J.; Van Oost, B.A. Identification of a premature stop codon in the melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor gene (MC1R) in Labrador and Golden retrievers with yellow coat colour. Anim. Genet. 2000, 31, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzaud, F.; Martin, J.; Gallet, P.F.; Delourme, D.; Goulemont-Leger, V.; Amigues, Y.; Ménissier, F.; Levéziel, H.; Julien, R.; Oulmouden, A. A first genotyping assay of French cattle breeds based on a new allele of the extension gene encoding the melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R). Genet. Sel. Evol. 2000, 32, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abitbol, M.; Legrand, R.; Tiret, L.A. Missense mutation in melanocortin 1 receptor is associated with the red coat color in donkeys. Anim. Genet. 2014, 45, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, N. A.; Gandolfi, B.; Lyons, L. A. Not another type of potato: MC1R and the russet coloration of Burmese cats. Anim. Genet. 2016, 47, 704–705. [Google Scholar]
- Becerril, C.M.; Wilcox, C.J.; Lawlor, T.J.; Wiggans, G.R.; Webb, D.W. Effects of percentage of white coat color on Holstein production and reproduction in a subtropical climate. J. Dairy Sci. 1993, 76, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.; Pielberg, G.; Andersson, L.; Edfors – Lilja, I. Polymorphism at the porcine dominant white/KIT locus influences coat color and peripheral blood cell measures. Anim. Genet. 2005, 36, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charon, K.M.; Lipka, K.R. The effect of a coat colour-associated gene polymorphism on animal health review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2015, 15, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennah, J.L.; Peers, M.J.L.; Wal, E.V.; Majchrzak, Y.N.; Menzies, A.K.; Studd, E.K.; Boonstra, R.; Humphries, M.M.; Jung, T.S.; Kenney, A.J.; Krebs, C.J.; Boutin, S. Coat color mismatch improves survival of a keystone boreal herbivore: Energetic advantages exceed lost camouflage. Ecology 2023, 104, e3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oli, M.K.; Kenney, A.J.; Boonstra, R.; Boutin, S.; Murray, D.L.; Peers, M.J.L.; Gilbert, B.S.; Jung, T.S.; Chaudhary, V.; Hines, J.E.; Krebs, C.J. Does coat colour influence survival? A test in a cyclic population of snowshoe hares. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2023, 290, 20221421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, C.C. Color inheritance in cats, with special reference to the colors black, yellow, and tortoise-shell. Genetics. 1919, 8, 279–290. [Google Scholar]
- Kurushima, J.D.; Lipinski, M.J.; Gandolfi, B.; Froenicke, L.; Grahn, J.C.; Grahn, R.A.; Lyons, L.A. Variation of cats under domestication: genetic assignment of domestic cats to breeds and worldwide random-bred populations. Anim Genet. 2012, 44, 311–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montague, M.J.; Li, G.; Gandolfi, B.; Khan, R.; Aken, B.L.; Searle, S.M.J.; Warren, W.C. Comparative analysis of the domestic cat genome reveals genetic signatures underlying feline biology and domestication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014, 111, 17230–17235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.C.; Virginia, C.C.; Clyde, E.K.; Madeleine, D. Genetics of the Burmese cat. J. Hered. 1943, 34, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, H. Siamese cats. In: Our cats. In Our cats and all about them, Weir, H. ed.; Boston and New York: Houghton, Mifflin, 1889; pp. 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Abitbol, M.; Gache, V. Copal, a new MC1R allele in the domestic cat. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phavaphutanon, J.; Laopium, S.; Nanklang, K.; Sirinarumitr, K.; Kornkaewrat, K.; Pinyopummin, A.; Viriyarumpa, J.; Suthanmapinunt, P.; Vorawattanatham, N. Buccal Swab as a Source of Noninvasive Technique for Genomic DNA Collection in Felidae. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2013, 43, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hustad, C.M.; Perry, W.L.; Siracusa, L.D.; Rasberry, C.; Cobb, L.; Cattanach, B.M.; Kovatch, R.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A. Molecular genetic characterization of six recessive viable alleles of the mouse agouti locus. Genetics. 1995, 140, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuramoto, T.; Nomoto, T.; Sugimura, T.; Ushijima, T. Cloning of the rat agouti gene and identification of the rat nonagouti mutation. Mamm. Genome 2001, 12, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CFA. The Cat Fanciers’ Association Cat Encyclopedia; Simon & Schuster, USA: New York, 1993; pp. 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Serina, F.; Hasan, A.; Barbara, G.; Jennifer, D.K.; Alejandro, C.; Christine, V.; Leslie, A. L.; Gottfried, B. Selkirk Rex: Morphological and genetic characterization of a new cat breed. J. Hered. 2012, 103, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WCF. World Cat Federation. Available online: http://wcf.de/en (accessed on 18 July 2025).



| Gene |
5’-3’ Forward and reverse primers |
Product size (bp) | Sequence variants | Identify color |
| ASIP | F- CTTTCTGGTCCTCTGGCTCCAC R- GGTGGTATGCAGAGCTTTTCCAA |
500 | 41G>C | Wild type (A; agouti) Non-agouti (a; solid) ALC agouti (APbe), |
| 123-124 2bp del | Non-agouti (a; solid) | |||
| 142T>C | ALC agouti (APbe) | |||
| TYRP1 | F- AACCAGAGATCTGTTCTTCACTCTT R- CTATGAGAACTCTCTGGTCACAAGC |
428 | 8C>G 298C>T |
Wild type (B; black) Chocolate (b) Cinnamon (bl) |
| TYR | F- TTTATAATCGGACCTGCCAGTG R- TCTGATATTGTATGTCCAGGATGTCTT |
598 | 679G>T | Wild type (C; full color) Burmese (cb) |
| F- CGAAGCCACAAACTGCGAGA R- CCTGAGGCTGCCAACCATCT |
700 | 901G>A 975delC 6delinsAATCTC |
Siamese (cs) Albino (c) Mocha (cm) |
|
| MLPH | F- GTGTGATCCTGACAGGCAGAG R- GGCTCGGCCTCATACACTC |
152 | 83delT | Wild type (D; full color) Dilute (d) |
| MC1R | F- TGCTGGGCTCCCTCAACTC R- GTACCGCAGCGCGTAGAAGA |
500 | 250G>A 15del (Jaguar-Mel) 24del (Jaguarundi-Dark) 439-441del |
Wild type (E; extension) Amber (e) Melanistic jaguar (e*) Dark-brown jaguarundi (e**) Russet (er) |
| Gene | Sequence variants | Thai cat conservation center | Thai cat breeders | |||||
| ASIP | c.41G>C | Agouti | Agouti | ALC agouti | Agouti | Agouti | ALC agouti | |
| G/G | G/C | C/C | G/G | G/C | C/C | |||
| 61 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Agouti | Agouti | Solid | Agouti | Agouti | Solid | |||
| c.123-124 2bp del | CA/CA | CA/- | -/- | CA/CA | CA/- | -/- | ||
| 0 | 0 | 61 | 0 | 0 | 66 | |||
| Agouti | Agouti | ALC agouti | Agouti | Agouti | ALC agouti | |||
| c.142T>C | T/T | T/C | C/C | T/T | T/C | C/C | ||
| 61 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 0 | 0 | |||
| TYRP1 | c.8C>G | Black | Black | Chocolate | Black | Black | Chocolate | |
| C/C | C/G | G/G | C/C | C/G | G/G | |||
| 31 | 22 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 62 | |||
| c.298C>T | Black | Black | Cinnamon | Black | Black | Cinnamon | ||
| C/C | C/T | T/T | C/C | C/T | T/T | |||
| 61 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 0 | 0 | |||
| TYR | c.679G>T | Full color | Full color | Burmese | Full color | Full color | Burmese | |
| G/G | G/T | T/T | G/G | G/T | T/T | |||
| 0 | 3 | 58 | 28 | 34 | 4 | |||
| c.901G>A | Full color | Full color | Siamese | Full color | Full color | Siamese | ||
| G/G | G/A | A/A | G/G | G/A | A/A | |||
| 58 | 3 | 0 | 54 | 9 | 3 | |||
| c.975delC | Full color | Full color | Albino | Full color | Full color | Albino | ||
| 61 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 6delinsAATCTC | Full color | Full color | Mocha | Full color | Full color | Mocha | ||
| 61 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 0 | 0 | |||
| MLPH | c.83delT | Dense color | Dense color | Dilute | Dense color | Dense color | Dilute | |
| T/T | T/- | -/- | T/T | T/- | -/- | |||
| 47 | 14 | 0 | 54 | 11 | 1 | |||
| MC1R | c.250G>A | Extension | Extension | Amber | Extension | Extension | Amber | |
| G/G | G/A | A/A | G/G | G/A | A/A | |||
| 61 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 15del | Extension | Extension | Jaguar-Mel | Extension | Extension | Jaguar-Mel | ||
| (Jaguar-Mel) | WT/WT | WT/15del | 15del/15del | WT/WT | WT/15del | 15del/15del | ||
| 61 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 24del | Extension | Extension | Jaguarundi-Dark | Extension | Extension | Jaguarundi-Dark | ||
| (Jaguarundi-Dark) | WT/WT | WT/24del | 24del/24del | WT/WT | WT/24del | 24del/24del | ||
| 61 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 0 | 0 | |||
| c.439-441del | Extension | Extension | Russet | Extension | Extension | Russet | ||
| WT/WT | WT/- | -/- | WT/WT | WT/- | -/- | |||
| 61 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Gene | Allele | Predicted Phenotype |
Thai Cat Conservation Center (n = 61) |
Thai Cat breeders (n = 66) |
Total (n = 127) |
| ASIP | A | Agouti | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) |
| a | Solid | 122 (100) | 132 (100) | 254 (100) | |
| APbe | AAPbe(Agouti), APbea(Charcoal) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| TYRP1 | B | Black | 84 (68.85) | 3 (2.27) | 87 (34.25) |
| b | Chocolate | 38 (31.15) | 129 (97.73) | 167 (65.75) | |
| bl | Cinnamon | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| TYR | C | Full color | 0 (0.00) | 75 (56.82) | 75 (29.53) |
| cb | Burmese colorpoint | 119 (97.54) | 42 (31.82) | 161 (63.39) | |
| cs | Siamese colorpoint | 3 (2.46) | 15 (11.36) | 18 (7.09) | |
| c | Albino | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| cm | Mocha | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| MLPH | D | Dense pigment | 108 (88.52) | 119 (90.15) | 227 (89.37) |
| d | Dilute | 14 (11.48) | 13 (9.85) | 27 (10.63) | |
| MC1R | E | Extension | 122 (100) | 132 (100) | 254 (100) |
| e | Amber | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| e* | Melanistic jaguar | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| e** | Dark-brown jaguarundi | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| er | Russet | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) |
| Gene | Genotype | Predicted Phenotype |
Thai Cat Conservation Center (n = 61) |
Thai Cat breeders (n = 66) |
Total (n = 127) |
| ASIP | AA | Agouti | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) |
| Aa | Agouti | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| AAPbe | Agouti | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| APbea | Charcoal | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| aa | Solid | 61 (100) | 66 (100) | 127 (100) | |
| TYRP1 | BB | black | 31 (50.82) | 1 (1.52) | 32 (25.20) |
| Bb | black (carrier of chocolate) | 22 (36.07) | 1 (1.52) | 23 (18.11) | |
| bb | chocolate | 8 (13.11) | 64 (96.97) | 72 (56.69) | |
| TYR | CC | full color | 0 (0.00) | 20 (30.30) | 20 (15.75) |
| Ccb | full color (carrier of Burmese point | 0 (0.00) | 30 (45.45) | 30 (23.62) | |
| Ccs | full color (carrier of Siamese point | 0 (0.00) | 5 (7.58) | 5 (3.94) | |
| cbcb | Burmese (colorpoint) | 58 (95.08) | 6 (9.10) | 64 (50.39) | |
| cbcs | Tonkinese (colorpoint) | 3 (4.92) | 2 (3.03) | 5 (3.94) | |
| cscs | Siamese (colorpoint) | 0 (0.00) | 3 (4.54) | 3 (2.36) | |
| MLPH | DD | dense | 47 (77.05) | 54 (81.82) | 101 (79.53) |
| Dd | dense (carrier of dilute) | 14 (22.95) | 11 (16.67) | 25 (19.69) | |
| dd | dilute | 0 (0.00) | 1 (1.52) | 1 (0.79) | |
| MC1R | EE | extension | 61 (100) | 66 (100) | 127 (100) |
| E_ | extension | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| e* e* | Melanistic jaguar | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| e** e** | Dark-brown jaguarundi | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| er er | russet | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) |
| Gene | Genotype | Predicted coat color phenotype |
Thai Cat Conservation Center (n = 61) |
Thai Cat breeders (n = 66) |
Total (n = 127) |
|
Solid black (B_C_D_) |
BBCCDD | Solid black | 0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
0(0%) |
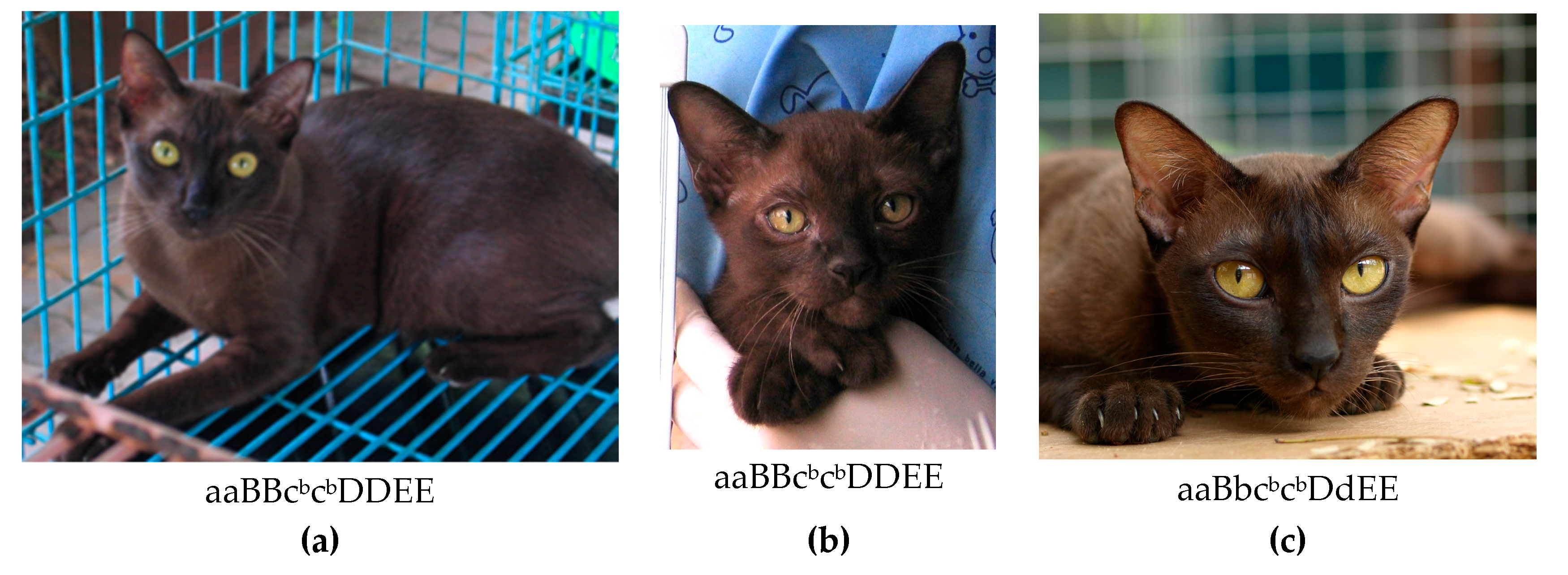
| Sable Burmese | BBcbcbDD | Sable Burmese | 26 | 26 | |
| (B_cbcbD_) | BBcbcbDd | Sable Burmese (carrier of dilute) | 5 | 1 | 6 |
| BbcbcbDD | Sable Burmese (carrier of chocolate) | 14 | 14 | ||
| BbcbcbDd | Sable Burmese (carrier of chocolate and dilute) | 6 | 1 | 7 | |
| Total | 53 | ||||
| Chocolate Burmese | bbcbcbDD | Chocolate Burmese | 6 | 2 | 8 |
| (bbcbcbD_) | bbcbcbDd | Chocolate Burmese (carrier of dilute) | 1 | - | 1 |
| Total | 9 | ||||
| Seal point Tonkinese | BbcbcsDd | Tonkinese point (carrier of chocolate and dilute) | 2 | - | 2 |
| (B_cbcsD_) | - | - | - | ||
| Total | 2 | ||||
| Chocolate point Tonkinese | bbcbcsDD | chocolate mink | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| (bbcbcsD_) | bbcbcsDd | chocolate mink (carrier of dilute) | - | 3 | 3 |
| Total | 5 | ||||
| Chocolate point | bbcscsDD | Siamese chocolate point | - | 1 | 1 |
| Siamese | bbcscsDd | Siamese chocolate point (carrier of dilute) | - | 1 | 1 |
| (bbcscsD_) | bbcscsdd | Siamese liac point | - | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 3 | ||||
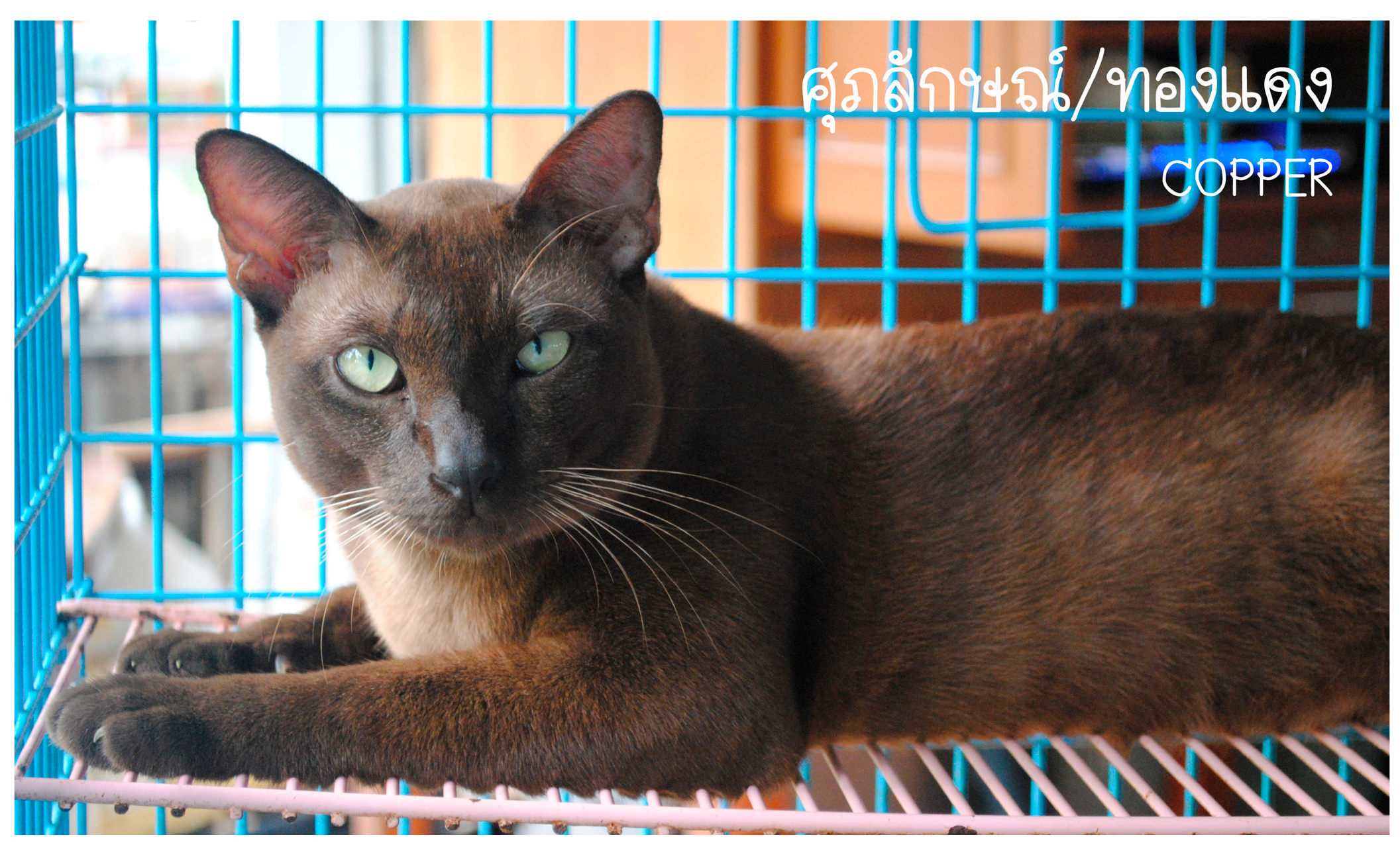
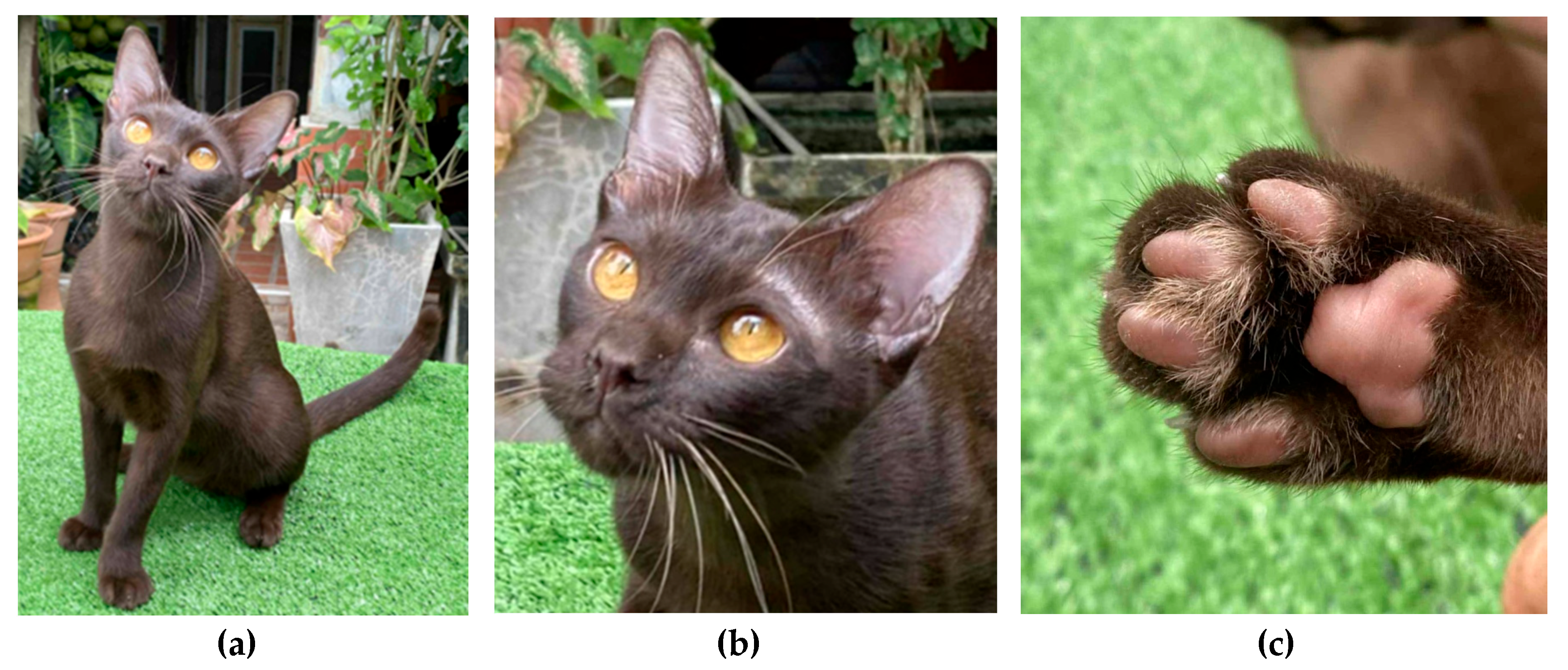
| Solid chocolate | bbCCDD | Solid chocolate | - | 18 | 18 |
| Suphalak | bbCCDd | Solid chocolate (carrier of dilute) | - | 2 | 2 |
| (bbC_D_) | bbCcbDD | Solid chocolate (carrier of Burmese point) | - | 29 | 29 |
| bbCcbDd | Solid chocolate (carrier of Burmese point and dilute) | - | 1 | 1 | |
| bbCcsDD | Solid chocolate (carrier of Siamese point) | - | 3 | 3 | |
| bbCcsDd | Solid chocolate (carrier of Siamese point and dilute) | - | 2 | 2 | |
| Total | 55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





