Submitted:
17 April 2024
Posted:
18 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Plasmids and Rice Transformation
2.3. Observation of Grain Transparency
2.4. Examination of Cavities within Starch Granules
2.5. Grain Quality Analyses
2.6. Measurement of the Gelatinization and Pasting Properties of Rice
2.7. Gel Permeation Chromatograms
2.8. Crystalline Structure Analysis
2.9. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase PCR Analysis
2.10. Enzyme Activity Assays
2.11. Western Blot Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
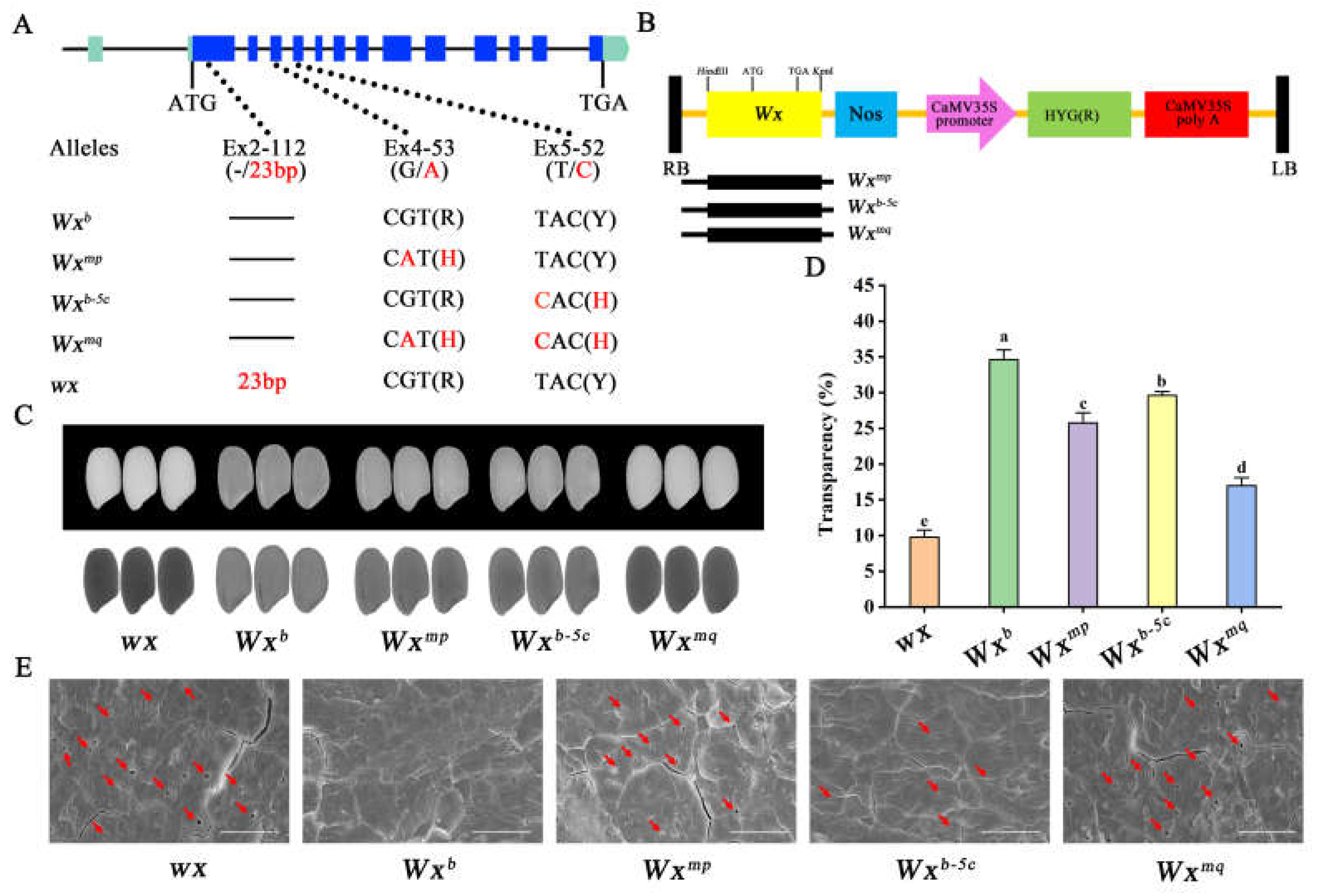
3.1. Effects of Two Functional Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms on Seed Transparency
3.2. Effect of the Distinct Transgenic Rice Lines on Rice Eating Quality
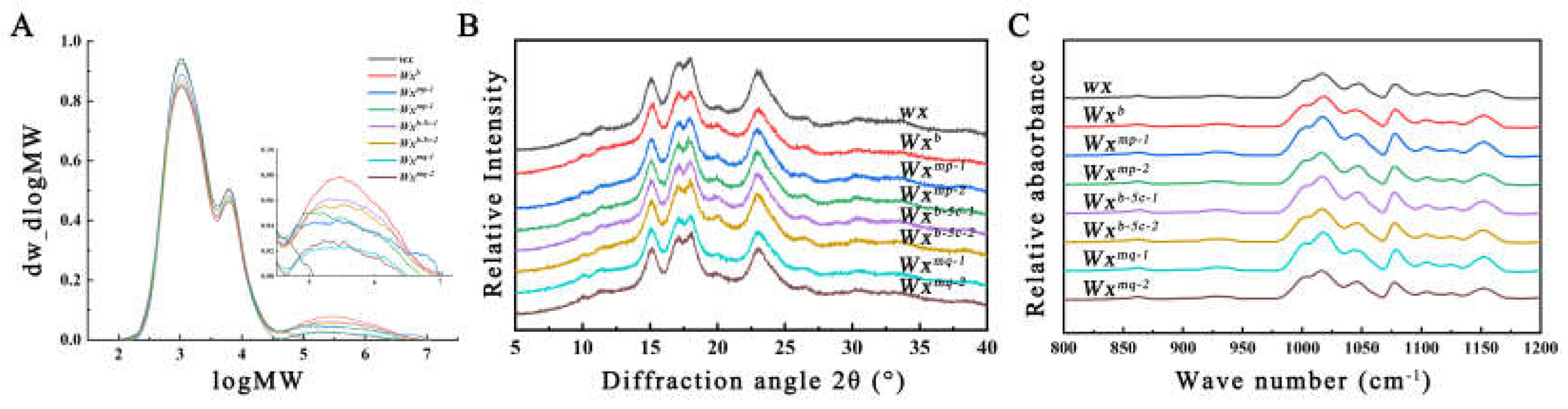
3.3. Comparison of Starch Crystalline Structure in Transgenic Rice
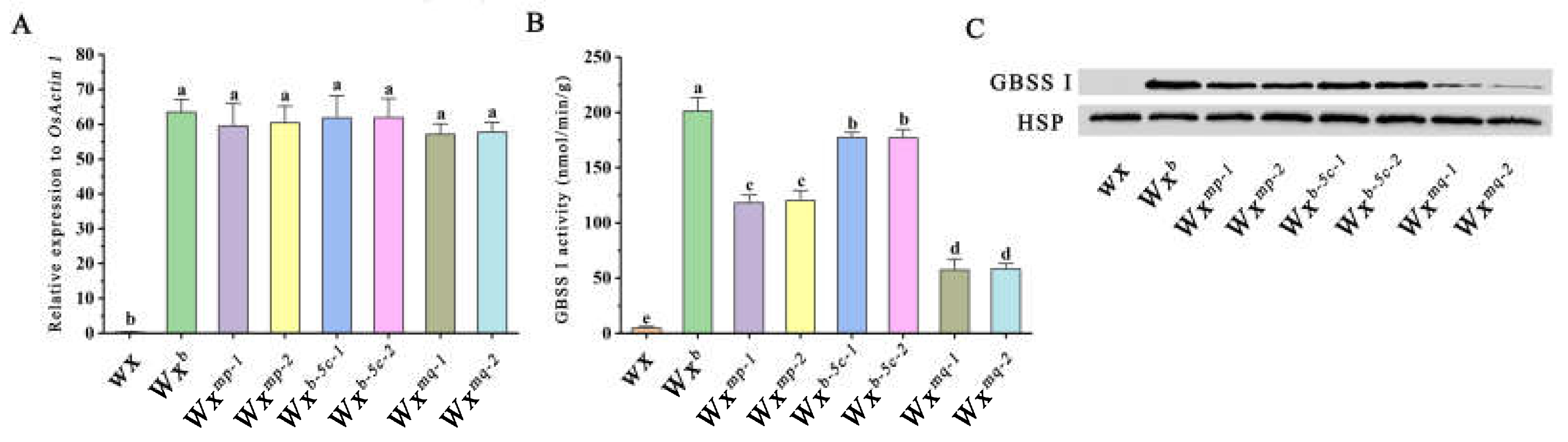
3.4. Effects of Two Functional SNPs on Wx Gene Expression and GBSSI Enzyme Activity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeon, J.S.; Ryoo, N.; Hahn, T.R.; Walia, H.; Nakamura, Y. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperm. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010, 48, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.H.; Zhang, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.D.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, Q.Q. Genetic manipulation of endosperm amylose for designing superior quality rice to meet the demands in the 21st century. Journal of Cereal Science. 2022, 105, 103481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Gilbert, R.G. Starch molecular structure: The basis for an improved understanding of cooked rice texture. Carbohydr Polym. 2018, 195, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.L.; Zhang, Y.D.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, T.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Zhong, W.G.; Yang, J.; Yao, S.; Zhou, L.H.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.S. Research progress on the breeding of japonica super rice varieties in Jiangsu Province, China. J integr agr. 2017, 16, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Q.; Zhu, J.H.; Chen, S.J.; Fan, X.L.; Li, Q.F.; Lu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, H.X.; Yi, C.D.; Tang, S.Z.; Gu, M.H.; Liu, Q.Q. Wxlv, the ancestral allele of rice Waxy gene. Mol Plant. 2019, 12, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.C.; Tan, H.Y.; Zhang, C.Q.; Li, Q.F.; Liu, Q.Q. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperms: An updated review over the last decade. Plant Communications. 2021, 2, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, F.J.; Zhu, J.Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, C.L; Zheng, T.Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, W.G.; Xu, J.L. Development of AS-PCR marker based on a key mutation confirmed by resequencing of Wx-mp in Milky Princess and its application in japonica soft rice (Oryza sativa L.) breeding. Plant Breeding. 2013, 132, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Sakai, M.; Imbe, T. Molecular characterization of Wx-mq, a novel mutant gene for low-amylose content in endosperm of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed. Sci. 2002, 52, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Hong, M.M.; Gu, M.H. A highly efficient transformation system mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Phytophysiol. Sin. 1998, 24, 259–271. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.Y.; Jia, J.W.; Yang, L.T.; Wen, H.B.; Zhang, C.M.; Liu, W.X.; Zhang, D.B. Validation of a rice specific gene, sucrose phosphate synthase, used as the endogenous reference gene for qualitative and real-time quantitative PCR detection of transgenes. J Agric Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3372–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.L.; Zhang, J.; Cai, X.L.; Liu, Q.Q.; Wei, C.X. Relationships between transparency, amylose content, starch cavity, and moisture of brown rice kernels. J Cereal Sci. 2019, 90, 102854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Q.; Chen, S.J.; Ren, X.Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, D.R.; Cai, X.L.; Li, Q.Q.; Gao, J.P.; Liu, Q.Q. Molecular structure and physicochemical properties of starches from rice with different amylose contents resulting from modification of OsGBSSI activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2222–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.W.; Man, J.M.; Huang, J.; Liu, Q.Q.; Wei, W.X.; Wei, C.X. Relationship between structure and functional properties of normal rice starches with different amylose contents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 125, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.R.; Wang, W.; Cai, X.L. Modulation of amylose content by structure-based modification of OsGBSS1 activity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Biotech. J. 2014, 12, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Lv, D.J.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Y.; Hao, W.Z.; Huang, L.C.; Fan, X.L.; Zhao, D.S.; Li, Q.F.; Zhang, C.Q.; Liu, Q.Q. Combined effects of SSII-2RNAi and different Wx alleles on rice grain transparency and physicochemical properties. Carbohydr Polym. 2023, 15, 120651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeputte, G.E.; Vermeylen, R.; Geeroms, J.; Delcour., J.A. Rice starches. I. Structural aspects provide insight into crystallinity characteristics and gelatinization behavior of granular starch. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 38, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Q.; Zhou, L.H.; Zhu, Z.B.; Lu, H.W.; Zhou, X.Z.; Qian, Y.T.; Li, Q.F.; Lu, Y.; Gu, M.M.; Liu, Q.Q. Characterization of grain quality and starch fine structure of two japonica rice (Oryza Sativa) cultivars with good sensory properties at different temperatures during the filling stage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4048–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, D.; Gidley, M.J. Loss of crystalline and molecular order during starch gelatinisation: origin of the enthalpic transition. Carbohyd Polym. 1992, 227, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Q.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.J.; Liu, X.J.; Zhu, J.H.; Zhou, L.H.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q.F.; Fan, X.L.; Tang, S.Z.; Gu, M.H.; Liu, Q.Q. A rare Waxy allele coordinately improves rice eating and cooking quality and grain transparency. J Integr Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.L.; Ma, X.D.; Liu, S.J.; Zhu, C.L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Shen, Y.; Ren, Y.L.; Dong, H.; Chen, L.M.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.G.; Zhai, H.Q.; Wan, J.M. Identification and characterization of a novel Waxy allele from a Yunnan rice landrace. Plant Mol Biol, 2009, 71, 609–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.C.; Li, Q.F.; Zhang, C.Q.; Chu, R.; Gu, Z.W.; Tan, H.Y.; Zhao, D.S.; Fan, X.L.; Liu, Q.Q. Creating novel Wx alleles with fine-tuned amylose levels and improved grain quality in rice by promoter editing using CRISPR/Cas9 system. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2164–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.C.; Liu, T.L.; Ma, X.L.; Wang, B.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xie, X.R.; Yang, B.W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, Q.L.; Liu, Y.G. Quantitative regulation of Waxy expression by CRISPR/Cas9–based promoter and 5’UTR–intron editing improves grain quality in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2385–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, Q.P.; Li, X.F.; Wang, F.Q.; Chen, Z.H.; Wang, J.; Li, W.Q.; Fan, F.J.; Tao, Y.J.; Jiang, Y.J.; Wei, X.D.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, Q.H.; Bu, Q.Y.; Yang, J.; Gao, C.X. Fine-tuning the amylose content of rice by precise base editing of the Wx gene. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.D.; Ding, Q.; Wang, W.S.; Pan, Y.L.; Tan, C.; Qiu, Y.B.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.J.; Li, Y.L.; Ye, N.Z.; Xu, N.; Wu, X.; Ye, R.J.; Liu, J.F.; Ma, C.L. Targeted deletion of the first intron of the Wxb allele via CRISPR/Cas9 signifcantly increases grain amylose content in rice. Rice. 2022, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.S.; Zhang, C.Q.; Li, Q.F.; Liu, Q.Q. Genetic control of grain appearance quality in rice. Biotechnol Adv. 2022, 108014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isshiki, M.; Matsuda, Y.; Takasaki, A.; Wong, H.L.; Satoh, H.; Shimamoto, K. Du3, a mRNA cap-binding protein gene, regulates amylose content in Japonica rice seeds. Plant Biotechnol, 2008, 25, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, H.; Ito, H.; Shimada, T.; Kang, D.J.; Hamada, S. A novel rice dull gene, LowAC1, encodes an RNA recognition motif protein affecting Waxyb pre-mRNA splicing. Plant Physiol Biochem, 2021, 162, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, W.W.; Fu, Y.S.; Shan, Z.Z.; Xu, J.H.; Wang, P.; Kong, F.; Jin, J.; Yan, H.G.; Ge, X.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; You, X.M.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Chen, W.W.; Chen, X.G.; Ma, J.; Tang, X.J.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Y.Q.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.Y.; Wan, J.M. Du13 encodes a C2 H2 zinc-finger protein that regulates Wxb pre-mRNA splicing and microRNA biogenesis in rice endosperm. Plant Biotechnol J. 2022, 20, 1387–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
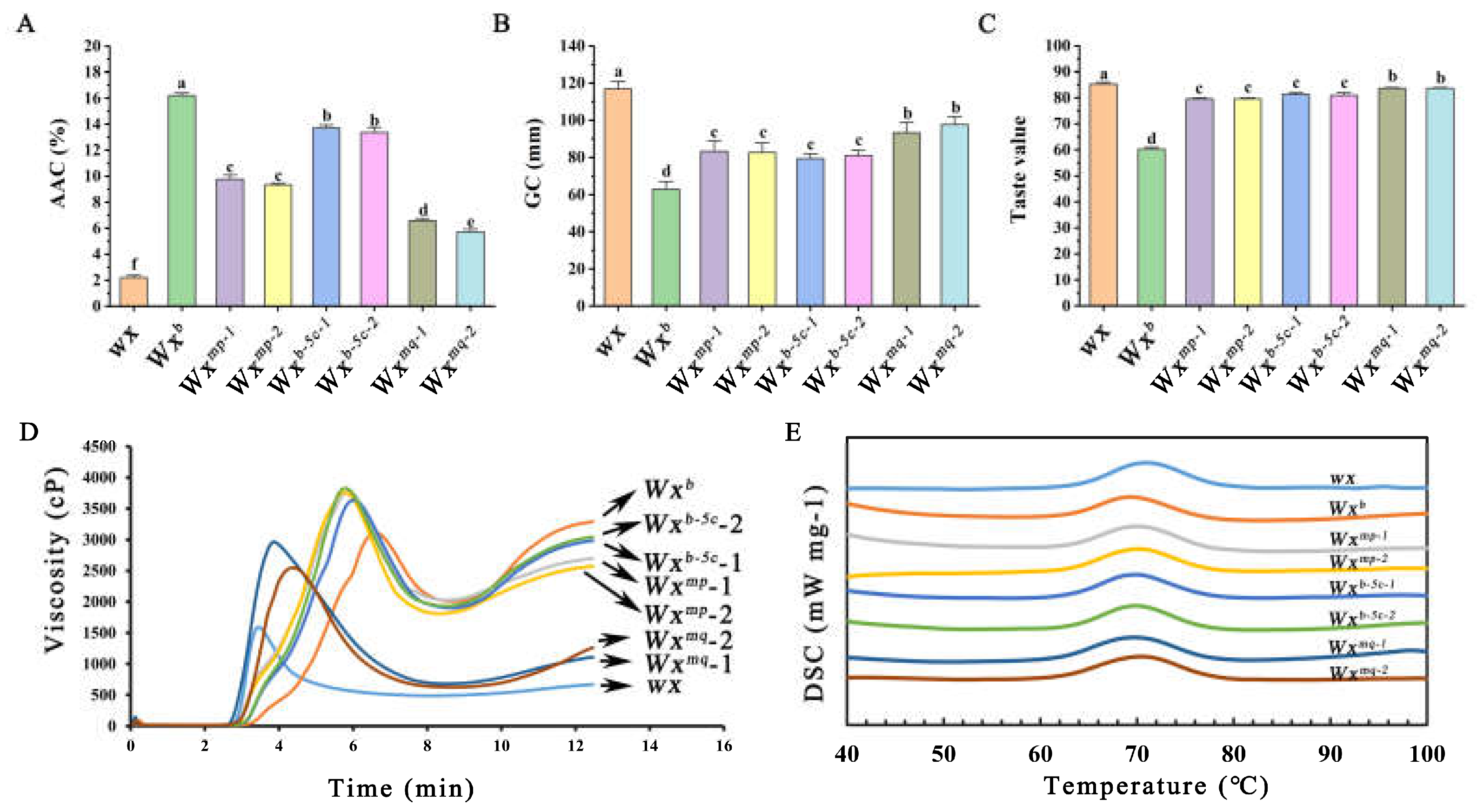
| Line | Peak Visco (cP) |
Trough Visco (cP) |
Breakdown (cP) |
Final Visco (cP) |
Setback (cP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nip(wx) | 1575.50±17.68 g | 495.00±9.90 f | 1116.00±22.63 f | 660.00±9.90 g | -927.50±9.19 b |
| Nip(Wxb) | 3109.00±11.31 d | 1792.50±6.36 c | 1307.00±18.38 e | 3235.00±16.97 a | 135.50±7.78 a |
| Nip(wx)-Wxmp-1 | 3774.00±18.38 a | 1815.50±10.60 c | 1963.00±14.14 b | 2558.50±14.85 d | -1185.00±9.90 e |
| Nip(wx)-Wxmp-2 | 3762.50±10.61 a | 2014.50±19.09 a | 1954.00±16.97 bc | 2680.50±19.09 c | -1089.50±19.09 d |
| Nip(wx)-Wxb-5c-1 | 3568.00±18.19 c | 1672.00±18.38 d | 1904.00±15.56 cd | 2577.00±14.14 d | -1004.00±24.04 c |
| Nip(wx)-Wxb-5c-2 | 3654.00±24.49 b | 1974.50±19.09 b | 1886.50±20.51 d | 2796.00±24.04 b | -1032.50±20.51 c |
| Nip(wx)-Wxmq-1 | 2970.50±10.60 e | 667.00±19.80 e | 2262.50±27.58 a | 1124.00±26.87 f | -1845.00±18.38 g |
| Nip(wx)-Wxmq-2 | 2532.50±16.26 f | 636.50±16.26 e | 1935.50±23.33 bcd | 1251.50±16.26 e | -1295.00±19.80 f |
| Line | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔH (J·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nip(wx) | 61.55±0.21 c | 69.30±0.14 c | 77.15±0.14 c | 7.45±0.05 a |
| Nip(Wxb) | 63.85±0.35 a | 71.05±0.21 a | 78.65±0.21 a | 5.90±0.10 d |
| Nip(wx)-Wxmp-1 | 62.95±0.35 b | 70.05±0.07 b | 77.55±0.21 bc | 6.48±0.08 c |
| Nip(wx)-Wxmp-2 | 63.00±0.28 b | 70.15±0.07 b | 77.30±0.14 c | 6.50±0.06 c |
| Nip(wx)-Wxb-5c-1 | 62.80±0.14 b | 70.00±0.28 b | 77.45±0.07 bc | 6.48±0.06 c |
| Nip(wx)-Wxb-5c-2 | 62.95±0.35 b | 70.00±0.14 b | 77.40±0.28 bc | 6.49±0.03 c |
| Nip(wx)-Wxmq-1 | 62.65±0.35 b | 70.05±0.35 b | 77.65±0.21 bc | 7.25±0.03 b |
| Nip(wx)-Wxmq-2 | 62.92±0.07 b | 70.30±0.14 b | 77.85±0.21 b | 7.24±0.04 b |
| Line | AP1 | AP2 | AM | relative crystallinity (%) | 1045/1022 cm-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nip(wx) | 74.22±0.29 a | 25.78±0.29 a | - | 29.6±0.13 a | 0.64±0.006 a |
| Nip | 63.52±0.3 e | 22.24±0.09 d | 14.24±0.21 a | 26.6±0.28 e | 0.55±0.004 e |
| Nip(wx)-Wxmp-1 | 69.42±0.23 c | 23.5±0.37 c | 7.08±0.13 c | 28.24±0.14 c | 0.6±0.002 c |
| Nip(wx)-Wxmp-2 | 69.22±0.28 c | 23.59±0.11 c | 7.19±0.17 c | 28.22±0.11 c | 0.6±0.004 c |
| Nip(wx)-Wxb-5c-1 | 66.39±0.01 d | 23.16±0.12 c | 10.46±0.11 b | 27.53±0.33 d | 0.57±0.003 d |
| Nip(wx)-Wxb-5c-2 | 65.82±0.4 d | 23.42±0.22 c | 10.76±0.18 b | 27.46±0.24 d | 0.58±0.004 d |
| Nip(wx)-Wxmq-1 | 71.82±0.35 b | 24.48±0.3 b | 3.7±0.05 d | 28.82±0.11 b | 0.63±0.004 b |
| Nip(wx)-Wxmq-1 | 72.17±0.42b | 24.52±0.33 b | 3.31±0.1 e | 28.82±0.2 b | 0.63±0.003 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





