Submitted:
26 October 2024
Posted:
28 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
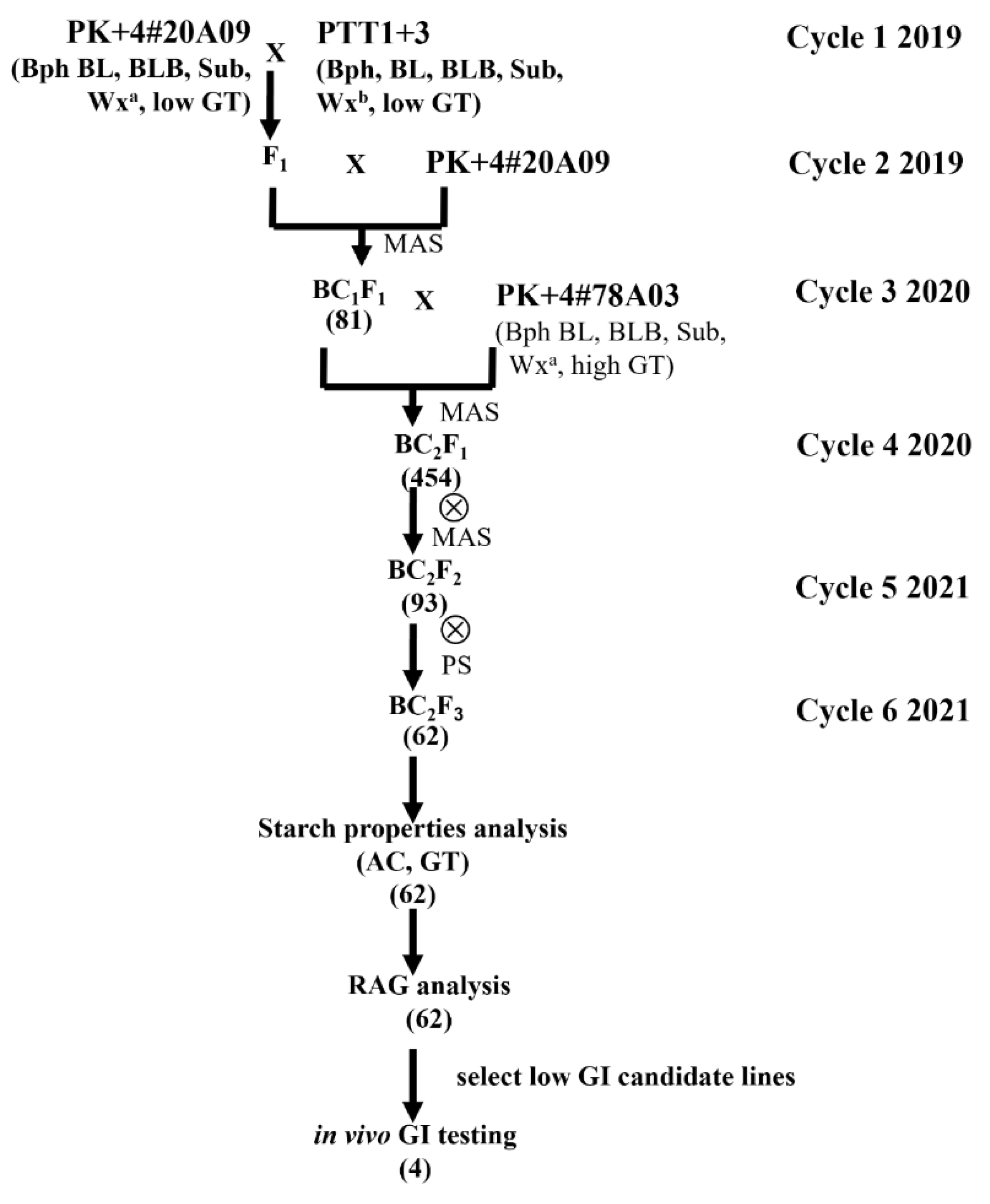
2.1. Plant Materials and Breeding Scheme
2.2. Starch Properties Analysis
2.2.1. Starch and Amylose Determination
2.2.2. Alkali Spreading Value (ASV) and Gelatinization Temperature (GT)
2.2.3. Paste Properties
2.2.4. Starch Digestibility and In Vitro Starch Digestion Kinetics
2.2.5. Proximate Analysis of Whole Grain Rice
2.2.6. Dietary Fiber Content Analysis
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.3. In Vivo Glycemic Index (GI) Analysis
2.3.1. Experimental Design
2.3.2. Reference and Test Foods
2.3.3. Measuring Blood Sugar Levels, GI Calculation, and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Development of the Low Amylose Content Progeny of the PK+4#20A09
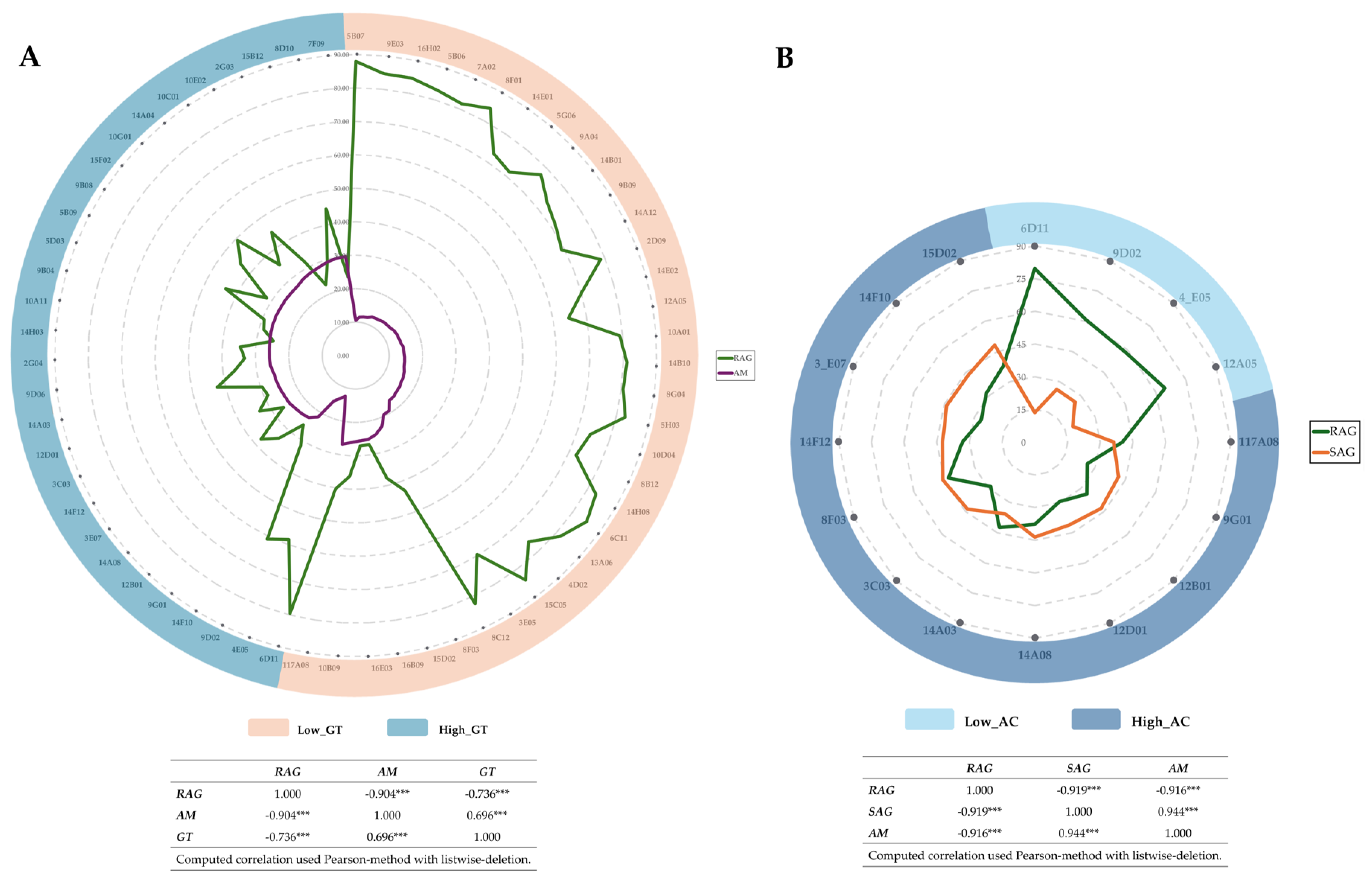
3.2. Amylose Content and Alkali Spreading Value Analysis
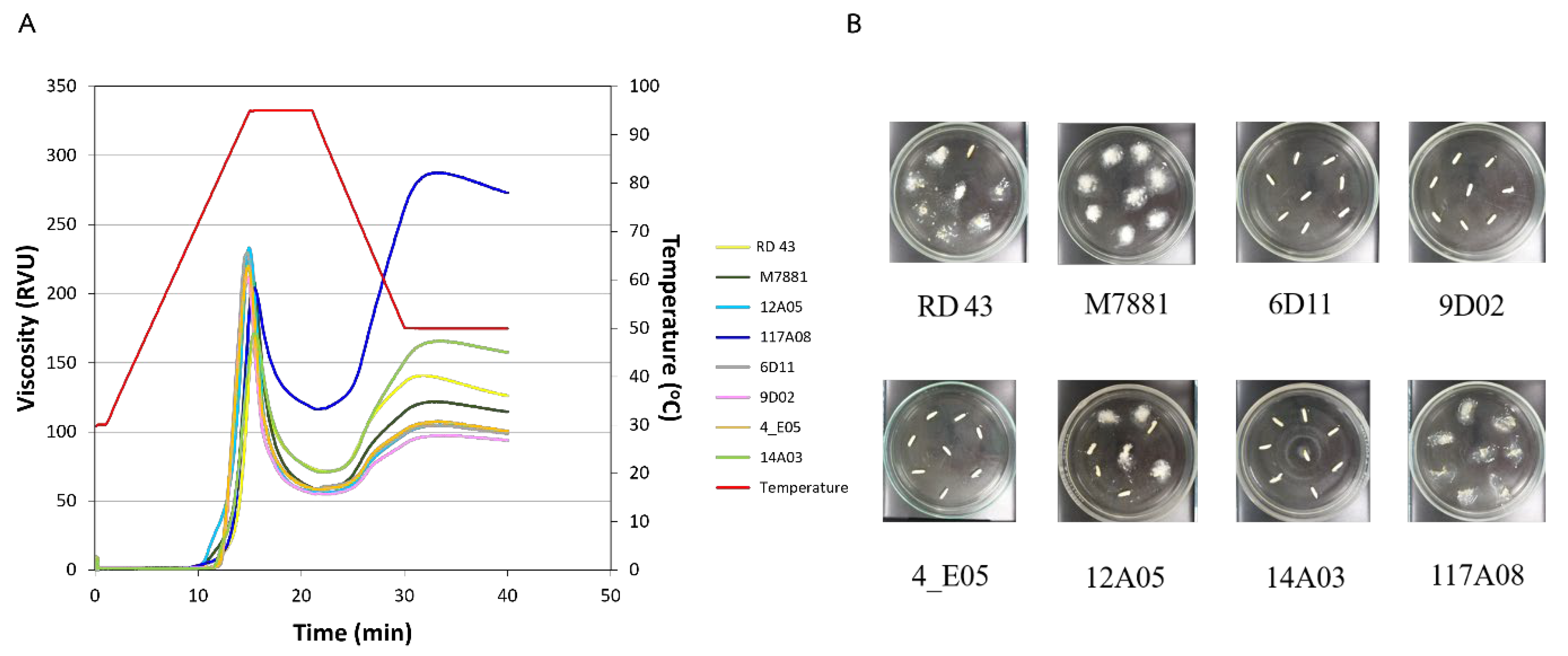
3.3. Starch Properties Analysis
3.4. In Vitro Analysis of Starch Digestion Kinetics
3.5. Nutrition Analysis of Tested Rice Samples
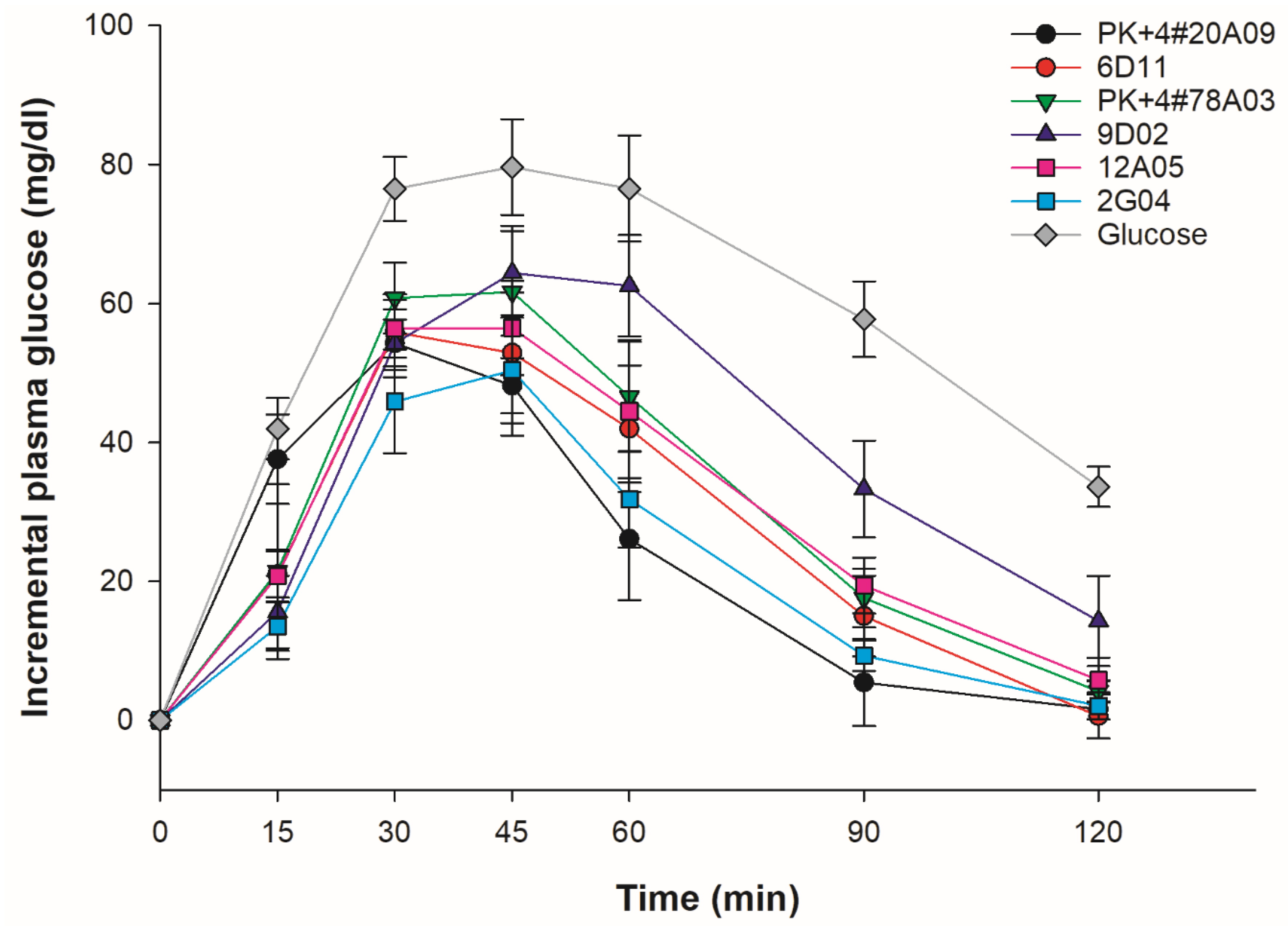
3.6. In Vivo GI Analysis of Cooked Whole-Grain Rice
3.7. Dietary Fiber Content Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabral D, Fonseca SC, Moura AP, Oliveira JC, Cunha LM. Conceptualization of Rice with Low Glycaemic Index: Perspectives from the Major European Consumers. Foods. 2022 Jul 21;11(14):2172.
- Eleazu, CO. The concept of low glycemic index and glycemic load foods as panacea for type 2 diabetes mellitus; prospects, challenges and solutions. Afr Health Sci. 2016 Jun;16(2):468-79.
- Peres M, Costa HS, Silva MA, Albuquerque TG. The Health Effects of Low Glycemic Index and Low Glycemic Load Interventions on Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Literature Review of RCTs. Nutrients. 2023 Dec 10;15(24):5060.
- Ngo TV, Kunyanee K, Luangsakul N. Insights into Recent Updates on Factors and Technologies That Modulate the Glycemic Index of Rice and Its Products. Foods. 2023 Oct 4;12(19):3659.
- Jukanti AK, Pautong PA, Liu Q, Sreenivasulu N. Low glycemic index rice—a desired trait in starchy staples. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2020 Dec 1;106:132-49.
- Srikaeo K, Sangkhiaw J. Effects of amylose and resistant starch on glycaemic index of rice noodles. LWT-Food Science and Technology. 2014 Dec 1;59(2):1129-35.
- Pereira CL, Sousa I, Lourenço VM, Sampaio P, Gárzon R, Rosell CM, Brites C. Relationship between Physicochemical and Cooking Quality Parameters with Estimated Glycaemic Index of Rice Varieties. Foods. 2023 Dec 30;13(1):135.
- Srinang P, Khotasena S, Sanitchon J, Chankaew S, Jogloy S, Monkham T. New Source of Rice with a Low Amylose Content and Slow In Vitro Digestion for Improved Health Benefits. Agronomy. 2023; 13(10):2622.
- Magallanes-Cruz PA, Flores-Silva PC, Bello-Perez LA. Starch structure influences its digestibility: a review. Journal of food science. 2017 Sep;82(9):2016-23.
- Li E, Yang X, Li C. Combined effects of starch fine molecular structures and storage temperatures on long-term rice amylopectin retrogradation property. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 Mar 15;201:458-467.
- Dipnaik K, Kokare P. Ratio of Amylose and Amylopectin as indicators of glycaemic index and in vitro enzymatic hydrolysis of starches of long, medium and short grain rice. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017; 5: 4502-5.
- Giuntini EB, Sardá FAH, de Menezes EW. The Effects of Soluble Dietary Fibers on Glycemic Response: An Overview and Futures Perspectives. Foods. 2022 Dec 6;11(23):3934.
- Khalid W, Arshad MS, Jabeen A, Muhammad Anjum F, Qaisrani TB, Suleria HAR. Fiber-enriched botanicals: A therapeutic tool against certain metabolic ailments. Food Sci Nutr. 2022 Aug 26;10(10):3203-3218.
- Chang UJ, Hong YH, Jung EY, Suh HJ. Rice and the glycemic index. In Wheat and rice in disease prevention and health 2014 Jan 1 (pp. 357-363). Academic Press.
- Cheng Z, Qiao D, Zhao S, Zhang B, Lin Q, Xie F. Whole grain rice: Updated understanding of starch digestibility and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety. 2022 Jul;21(4):3244-73.
- Yao F, Li C, Li J, Chang G, Wang Y, Campardelli R, Perego P, Cai C. Effects of Different Cooking Methods on Glycemic Index, Physicochemical Indexes, and Digestive Characteristics of Two Kinds of Rice. Processes. 2023; 11(7):2167.
- Mohan V, Anjana RM, Gayathri R, Ramya Bai M, Lakshmipriya N, Ruchi V, Balasubramaniyam KK, Jakir MM, Shobana S, Unnikrishnan R, Krishnaswamy K. Glycemic index of a novel high-fiber white rice variety developed in India—A randomized control trial study. Diabetes technology & therapeutics. 2016 Mar 1;18(3):164-70.
- Wattanavanitchakorn S, Wansuksri R, Chaichoompu E, Kamolsukyeunyong W, Vanavichit A. Dietary Fibre Impacts the Texture of Cooked Whole Grain Rice. Foods. 2023; 12(4):899.
- Selvaraj R, Singh AK, Singh VK, Abbai R, Habde SV, Singh UM, Kumar A. Superior haplotypes towards development of low glycemic index rice with preferred grain and cooking quality. Sci Rep. 2021 ;11(1):10082. 12 May.
- Singh RK, Prasad A, Muthamilarasan M, Parida SK, Prasad M. Breeding and biotechnological interventions for trait improvement: status and prospects. Planta. 2020 Sep 18;252(4):54.
- Sitaresmi T, Hairmansis A, Widyastuti Y, Susanto U, Wibowo BP, Widiastuti ML, Rumanti IA, Suwarno WB, Nugraha Y. Advances in the development of rice varieties with better nutritional quality in Indonesia. Journal of Agriculture and Food Research. 2023 Jun 1;12:100602.
- Huang L, Xiao Y, Zhao W, Rao Y, Shen H, Gu Z, Fan X, Li Q, Zhang C, Liu Q. Creating high-resistant starch rice by simultaneous editing of SS3a and SS3b. Plant Biotechnol J. 2024 Apr;22(4):787-789.
- Pathiraje PM, Madhujith WM, Chandrasekara A, Nissanka SP. The effect of rice variety and parboiling on in vivo glycemic response. Tropical Agricultural Research. 2011 Jan 10;22(1).
- Kale SJ, Jha SK, Jha GK, Sinha JP, Lal SB. Soaking induced changes in chemical composition, glycemic index and starch characteristics of basmati rice. Rice Science. 2015 Sep 1;22(5):227-36.
- Ruengphayak S, Chaichumpoo E, Phromphan S, Kamolsukyunyong W, Sukhaket W, Phuvanartnarubal E, Korinsak S, Korinsak S, Vanavichit A. Pseudo-backcrossing design for rapidly pyramiding multiple traits into a preferential rice variety. Rice (N Y). 2015 Feb 5;8:7.
- Nounmusig J, Kongkachuichai R, Sirichakwal PP, Yamborisut U, Charoensiri R, Vanavichit A. The effect of low and high glycemic index based rice varieties in test meals on postprandial blood glucose, insulin and incretin hormones response in prediabetic subjects. International Food Research Journal. 2018 Apr 1;25(2).
- Mungkung, Rattanawan, Saruda Sitthikitpanya, Ratcha Chaichana, Krisada Bamrungwong, Yuwanan Santitaweeroek, Napat Jakrawatana, Thapat Silalertruksa, and Shabbir H. Gheewala. 2022. "Measuring Sustainability Performance of Rice Cultivation in Thailand Using Sustainable Rice Platform Indicators." International Journal of Agricultural Sustainability 20 (7): 1278–93.
- Juliano, BO. A simplified assay for milled-rice amylose. Cereal Sci. Today. 1971;12:334-60.
- Little RR, Hilder GB, Dawson EH. Differential effect of dilute Alkali on 25 varieties of milled white rice. Cereal Chemistry. 1958;35:111–26.
- Goñi I, Garcia-Alonso A, Saura-Calixto F. A starch hydrolysis procedure to estimate glycemic index. Nutrition research. 1997 Mar 1;17(3):427-37.
- Pautong PA, Añonuevo JJ, de Guzman MK, Sumayao Jr R, Henry CJ, Sreenivasulu N. Evaluation of in vitro digestion methods and starch structure components as determinants for predicting the glycemic index of rice. LWT. 2022 Oct 1;168:113929.
- Wolever TM, Jenkins DJ, Jenkins AL, Josse RG. The glycemic index: methodology and clinical implications. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991 Nov;54(5):846-54. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama M, Tang AC, Wakaki Y, Koyama W. Glycemic index of single and mixed meal foods among common Japanese foods with white rice as a reference food. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2003 Jun;57(6):743-52. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouns F, Bjorck I, Frayn KN, Gibbs AL, Lang V, Slama G, Wolever TM. Glycaemic index methodology. Nutr Res Rev. 2005 Jun;18(1):145-71.
- FAO/WHO. 1998. Carbohydrates in human nutrition: report of a joint FAO/WHO expert consultation, Rome, 14-. In Carbohydrates in human nutrition: report of a joint FAO/WHO expert consultation, Rome, 14-. 18 April.
- Wolever, TM. Aspects of some vitamins, minerals and enzymes in health and disease. The Glycaemic Index. Basel: Karger. 1990:120-85.
- Suklaew PO, Chusak C, Wang CK, Adisakwattana S. RD43 rice flour: the effect on starch digestibility and quality of noodles, glycemic response, short-acting satiety hormones and appetite control in humans. Food Funct. 2021 Sep 7;12(17):7975-7985.
- Xu Y, Ma K, Zhao Y, Wang X, Zhou K, Yu G, Li C, Li P, Yang Z, Xu C, Xu S. Genomic selection: A breakthrough technology in rice breeding. The Crop Journal. 2021 Jun 1;9(3):669-77.
- Hasan MM, Rafii MY, Ismail MR, Mahmood M, Rahim HA, Alam MA, Ashkani S, Malek MA, Latif MA. Marker-assisted backcrossing: a useful method for rice improvement. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2015 Mar 4;29(2):237-254.
- Ge J, Chen X, Zhang X, Dai Q, Wei H. Comparisons of rice taste and starch physicochemical properties in superior and inferior grains of rice with different taste value. Food Research International. 2023 Jul 1;169:112886.
- Okello JJ, Swanckaert J, Martin-Collado D, Santos B, Yada B, Mwanga ROM, Schurink A, Quinn M, Thiele G, Heck S, Byrne TJ, Hareau GG, Campos H. Market Intelligence and Incentive-Based Trait Ranking for Plant Breeding: A Sweetpotato Pilot in Uganda. Front Plant Sci. 8: 2022 Mar 4;13, 2022.
- Crofts N, Hareyama K, Miura S, Hosaka Y, Oitome NF, Fujita N. Effect of Heading Date on the Starch Structure and Grain Yield of Rice Lines with Low Gelatinization Temperature. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 15;23(18):10783.
- Naidu BN, Madhavilatha L, Maraskole SK, Panotra N, Singh OB, Kumar A, Devi OR, Laishram B, Anbarasan S. Enhancing the Genetic Understanding of Rice for Strategic Breeding of High Yielding and Superior Quality Varieties. J. Adv. Biol. Biotechnol. 2024 Aug. 9 ;27(8):1252-61.
- Obadi M, Li C, Li Q, Li X, Qi Y, Xu B. Relationship between starch fine molecular structures and cooked wheat starch digestibility. Journal of Cereal Science. 2020 Sep 1;95:103047.
- Hu L, Cao J, Liu Y, Xiao Z, Zhang M, Chen J, Cao F, Iqbal A, Abou-Elwafa SF, Huang M. Multidimensional Relationships of Starch Digestibility with Physicochemical, Pasting and Textural Properties of 30 Rice Varieties. Agronomy. 2022; 12(3):720.
- Li C, Ji Y, Zhang S, Yang X, Gilbert RG, Li S, Li E. Amylose Inter-Chain Entanglement and Inter-Chain Overlap Impact Rice Quality. Foods. 2022 ;11(10):1516. 23 May.
- Patel H, Royall PG, Gaisford S, Williams GR, Edwards CH, Warren FJ, Flanagan BM, Ellis PR, Butterworth PJ. Structural and enzyme kinetic studies of retrograded starch: Inhibition of α-amylase and consequences for intestinal digestion of starch. Carbohydr Polym. 2017 ;164:154-161. 15 May.
- Li C, Yu W, Gilbert RG. The Effects of Starch Molecular Fine Structure on Thermal and Digestion Properties of Rice Starch. Foods. 2022 Dec 11;11(24):4012.
- Baptista NT, Dessalles R, Illner AK, Ville P, Ribet L, Anton PM, Durand-Dubief M. Harnessing the power of resistant starch: a narrative review of its health impact and processing challenges. Front Nutr. 2024 Mar 20;11:1369950.
- Xie X, Qi L, Xu C, Shen Y, Wang H, Zhang H. Understanding how the cooking methods affected structures and digestibility of native and heat-moisture treated rice starches. Journal of Cereal Science. 2020 Sep 1;95:103085.
- Al-Rabadi GJ, Gilbert RG, Gidley MJ. Effect of particle size on kinetics of starch digestion in milled barley and sorghum grains by porcine alpha-amylase. Journal of Cereal Science. 2009 Sep 1;50(2):198-204.
- Soltani A, Golmakani MT, Fazaeli M, Niakousari M, Hosseini SM. Evaluating the effect of different physical pretreatments and cooking methods on nutritional (starch digestibility) and physicochemical properties of white rice grains (Fajr cultivar). LWT. 2023 Jul 15;184:115101.
- Colasanto A, Savastio S, Pozzi E, Gorla C, Coïsson JD, Arlorio M, Rabbone I. The Impact of Different Types of Rice and Cooking on Postprandial Glycemic Trends in Children with Type 1 Diabetes with or without Celiac Disease. Nutrients. 2023 Mar 29;15(7):1654.
- Shen M, Huang K, Guan X, Xia J, Sun Z, Yu Z, Fang Y. Effects of milling on texture and in vitro starch digestibility of oat rice. Food Chem X. 2023 Jul 6;19:100783.
- Badoni S, Pasion-Uy EA, Kor S, Kim SR, Tiozon RN Jr, Misra G, Buenafe RJQ, Labarga LM, Ramos-Castrosanto AR, Pratap V, Slamet-Loedin I, Steimker JV, Alseekh S, Fernie AR, Kohli A, Khush GS, Sreenivasulu N. Multiomics of a rice population identifies genes and genomic regions that bestow low glycemic index and high protein content. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Sep 3;121(36):e2410598121.
- Nieto-Ortega B, Arroyo JJ, Walk C, Castañares N, Canet E, Smith A. Near infrared reflectance spectroscopy as a tool to predict non-starch polysaccharide composition and starch digestibility profiles in common monogastric cereal feed ingredients. Animal Feed Science and Technology. 2022 Mar 1;285:115214.
- Chakraborty I, Das B, Govindaraju I, Yamamoto T, Noothalapati H, Managuli V, Mazumder N. Exploring Retrogradation Behavior of Commercial Rice Varieties and Physicochemical Properties of Respective Extracted Starch. ACS Food Science & Technology. 2024 Mar 21;4(4):947-62.
- Buenafe RJQ, Kumanduri V, Sreenivasulu N. Deploying viscosity and starch polymer properties to predict cooking and eating quality models: A novel breeding tool to predict texture. Carbohydr Polym. 2021 ;260:117766. 15 May.
- Kim HR, Hong JS, Choi SJ, Moon TW. Modeling of in vitro digestion behavior of corn starches of different digestibility using modified log of slope (LOS) method. Food Research International. 2021 Aug 1;146:110436.
- Wang Y, Ou X, Al-Maqtari QA, He HJ, Othman N. Evaluation of amylose content: Structural and functional properties, analytical techniques, and future prospects. Food Chemistry: X. 2024 Sep 11:101830.
- Pan L, Chen F, Yang Y, Li Q, Fan X, Zhao D, Liu Q, Zhang C. The underlying starch structures of rice grains with different digestibilities but similarly high amylose contents. Food Chemistry. 2022 Jun 15;379:132071.
- Li J, Maruyama K, Minakuchi S, Toshimitu K, Kawamura R, Takata Y, Osawa H. Effect of high-amylose rice "Hoshinishiki" on postprandial glucose levels measured by continuous glucose monitoring in patients with diabetes. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2024 May;74(3):230-234.
- Li HT, Zhang W, Zhu H, Chao C, Guo Q. Unlocking the potential of high-amylose starch for gut health: Not all function the same. Fermentation. 2023 Jan 30;9(2):134.
- Qin Y, Xiao J, Wang Y, Dong Z, Woo MW, Chen XD. Mechanistic exploration of glycemic lowering by soluble dietary fiber ingestion: Predictive modeling and simulation. Chemical Engineering Science. 2020 Dec 31;228:115965.
- Bakar SK, Ahmad N, Jailani F. In vitro starch hydrolysis and estimated glycaemic index of biscuits from unripe banana peel flour. Journal of nutritional science and vitaminology. 2020;66(Supplement):S234-8.
- Raungrusmee S, Anal AK. Effects of lintnerization, autoclaving, and freeze-thaw treatments on resistant starch formation and functional properties of pathumthani 80 rice starch. Foods. 2019 Nov 7;8(11):558.

| Time | Activity | Blood Volume Drawn |
|---|---|---|
| 7:00 AM | Finger prick blood draw #1 after fasting for 10-12 hours | Approximately two drops |
| 7:05-7:20 AM | Eat the prepared food | No blood draw |
| 7:20 AM | Finger prick blood draw #2 after finishing the meal | Approximately two drops |
| 7:35 AM | Finger prick blood draw #3 | Approximately two drops |
| 7:50 AM | Finger prick blood draw #4 | Approximately two drops |
| 8:05 AM | Finger prick blood draw #5 | Approximately two drops |
| 8:35 AM | Finger prick blood draw #6 | Approximately two drops |
| 9:35 AM | Finger prick blood draw #7 | Approximately two drops |
| Rce varieties/ lines | wx_5UTR_G/T | ALK_ex8_SNPII_GC/TT | TBGI055578_TC_Chr1 | TBGI453598 | TBGI454717 | TBGI454800 | SNP_xa5 | Sub1C_loci5 | SNP_P100 Xa21 | Bph32_4_1223559 | OsSTPS2_ATHB-1_TF | OsLecRK3_QBPHR | Aroma_2-3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| check | PK+4#20A09 | G:G | TT:TT | C:C | C:C | A:A | C:C | T:T | T:T | G:G | C:C | T:T | G:G | Del: Del | |
| check | PK +4#78A03 | G:G | GC: GC | T:T | C:C | A:A | C:C | T:T | T:T | G:G | C:C | T:T | G:G | Del: Del | |
| check | PTT1+3 | T:T | TT:TT | C:C | T:T | T:T | G:G | T:T | T:T | G:G | C:C | T:T | G:G | Del: Del | |
| BC2F2 | Group 1: 41 plants | G:G | GC: GC | T:T | C:C | A:A | C:C | T:T | T:T | G:G | C:C | T:T | G:G | Del: Del | |
| BC2F2 | Group 2: 8 plants | T:T | GC: GC | T:T | C:C | A:A | C:C | T:T | T:T | G:G | C:C | T:T | G:G | Del: Del | |
| BC2F2 | Group 3: 5 plants | G:G | TT:TT | T:T | C:C | A:A | C:C | T:T | T:T | G:G | C:C | T:T | G:G | Del: Del | |
| BC2F2 | Group 4: 39 plants | T:T | TT:TT | T:T | C:C | A:A | C:C | T:T | T:T | G:G | C:C | T:T | G:G | Del: Del | |
| RiceVariety/ line | %Starch content | Pasting temperature(oC) | Viscosity (RVU) | |||||
| Peak viscosity | Trough viscosity | Breakdown | Final viscosity | Setback from trough* | Setback from Peak** | |||
| RD43 | 77.20 + 0.20cd | 70.5 | 171 | 71 | 100 | 126 | 55 | -45 |
| M7881 | 82.40 + 0.53a | 71.4 | 210 | 59 | 151 | 115 | 56 | -95 |
| 6D11 | 83.26 + 0.64a | 80.4 | 230 | 59 | 171 | 99 | 40 | -131 |
| 9D02 | 77.85 + 0.17c | 76.3 | 212 | 55 | 157 | 94 | 39 | -118 |
| 4_E05 | 76.45 + 0.17d | 78.6 | 220 | 58 | 162 | 101 | 42 | -120 |
| 12A05 | 80.70 + 0.13b | 70.8 | 233 | 56 | 177 | 101 | 45 | -132 |
| 14A03 | 82.97 + 0.99a | 77.9 | 172 | 71 | 102 | 158 | 87 | -15 |
| PK+4#117A08 | 76.59 + 0.13d | 68 | 204 | 116 | 88 | 273 | 157 | 69 |
| Rice Variety/ line | In vitro kinetic of starch digestion | |||||||||
| Freeze dry (Fine powder) | Cutting, 0.3 mm | |||||||||
| Glycemic index |
H90exp | H90 | GI | Cα | k | Glycemic index |
H90exp | H90 | GI | |
| Basmati 370 | NA | intermediate | 23.0d | 30.1f | 63f | |||||
| PK+4#20A09 | NA | Low | 12.9e | 16.0g | 52g | |||||
| PK+4#78A03 | NA | Low | 13.5e | 16.5g | 52g | |||||
| RD 43 | High | 69.3bc | 89.7bc | 111bc | 73.43cd | 0.07ab | Low | 14.4e | 18.68g | 54g |
| M7881 | High | 73.2ab | 88.9bc | 111bc | 75.81abc | 0.06abc | High | 34.0b | 41.28de | 72de |
| 6D11 | High | 77.4a | 93.0ab | 114ab | 77.93a | 0.06ab | High | 42.5a | 51.1ab | 80ab |
| 9D02 | High | 68.9c | 88.5bc | 110bc | 72.14d | 0.06bc | High | 38.2ab | 49.09bc | 79bc |
| 4_E05 | High | 67.6c | 88.4bc | 110bc | 71.41d | 0.05c | High | 42.5a | 55.61a | 84a |
| 12A05 | High | 77.0a | 95.4a | 116a | 77.50ab | 0.07a | High | 36.1b | 44.76cd | 75cd |
| PK+4#117A08 | High | 65.8c | 85.9c | 108c | 74.92bc | 0.03d | intermediate | 27.7c | 36.14e | 68e |
| Rice Variety/ line | Energy (kcal) | Protein (g) | Fat (g) | Total Carbohydrate (g) | Dietary Fiber (g) | Available Carbohydrate (g) |
| PK+4#20A09 | 124.52 ± 0.75c | 2.57 ± 0.00c | 0.73 ± 0.01d | 27.85 ± 0.02d | 0.94 ± 0.18c | 26.91 ± 0.16b |
| PK+4#78A03 | 125.03 ± 0.25c | 2.78 ± 0.00a | 0.80 ± 0.01c | 27.82 ± 0.01d | 1.14 ± 0.08bc | 26.68 ± 0.08b |
| 6D11 | 124.73 ± 0.21c | 2.46 ± 0.01d | 0.84 ± 0.04c | 27.67 ± 0.11e | 1.38 ± 0.10ab | 26.83 ± 0.15b |
| 9D02 | 131.71 ± 0.15a | 2.76 ± 0.04a | 0.92 ± 0.01b | 29.24 ± 0.02b | 1.15 ± 0.04bc | 28.09 ± 0.06a |
| 12A05 | 131.24 ± 0.68a | 2.63 ± 0.02b | 1.00 ± 0.03a | 29.50 ± 0.04a | 1.57 ± 0.12a | 27.93 ± 0.08a |
| 2G04 | 129.40 ± 0.02b | 2.30 ± 0.01e | 0.91 ± 0.02b | 29.05 ± 0.02c | 1.07 ± 0.02c | 27.99 ± 0.03a |
| Rice Variety/ line | Total Carbohydrate (g) | Protein (g) | Fat (g) | Dietary Fiber (g) | Energy (kcal) | Amount of Cooked Rice (g) |
| PK+4#20A09 | 51.74 | 4.77 | 1.36 | 1.74 | 231.34 | 185.8 |
| PK+4#78A03 | 52.14 | 5.21 | 1.50 | 2.14 | 234.36 | 187.44 |
| 6D11 | 51.56 | 4.59 | 1.56 | 2.57 | 232.42 | 186.34 |
| 9D02 | 52.05 | 4.92 | 1.64 | 2.04 | 234.43 | 178 |
| 12A05 | 52.81 | 4.72 | 1.79 | 2.81 | 234.95 | 179.03 |
| 2G04 | 51.90 | 4.11 | 1.63 | 1.90 | 231.16 | 178.13 |
| Rice varieties/lines | %AC | GI values1,2 | P-values | |
| mean ± SD | Classification | |||
| PK+4#20A09 | 27.60 | 41.14 ± 10.97 | Low | <0.001 |
| PK+4#78A03 | 27.10 | 50.47 ± 10.29 | Low | <0.001 |
| 6D11 | 12.57 | 56.11 ± 14.10 | Intermediate | <0.001 |
| 9D02 | 15.15 | 74.35 ± 11.47 | High | <0.001 |
| 12A05 | 14.42 | 53.92 ± 14.87 | Low | <0.001 |
| 2G04 | 25.80 | 41.79 ± 9.54 | Low | <0.001 |
| Rice Variety/ line | SDF | IDF | SDF:IDF |
| PK+4#20A09 | 0.27 ± 0.02c | 2.71 ± 0.54b | 0.10b |
| PK+4#78A03 | 0.71 ± 0.00b | 2.86 ± 0.25ab | 0.25ab |
| 6D11 | 0.65 ± 0.06b | 3.65 ± 0.38a | 0.18ab |
| 9D02 | 0.25 ± 0.05c | 3.18 ± 0.07ab | 0.08b |
| 12A05 | 1.15 ± 0.01a | 3.51 ± 0.34a | 0.33a |
| 2G04 | 0.77 ± 0.41b | 2.49 ± 0.36b | 0.33a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





