Submitted:
19 October 2023
Posted:
23 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
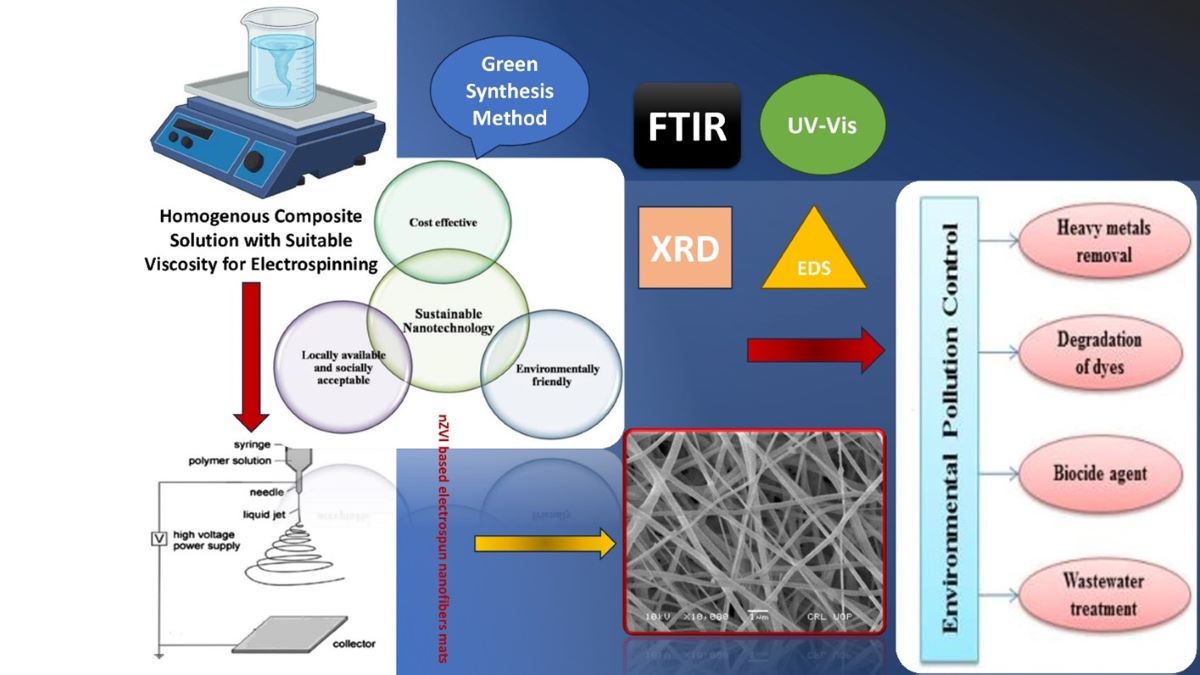
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Synthesis
2.2. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological and Thermal Analysis
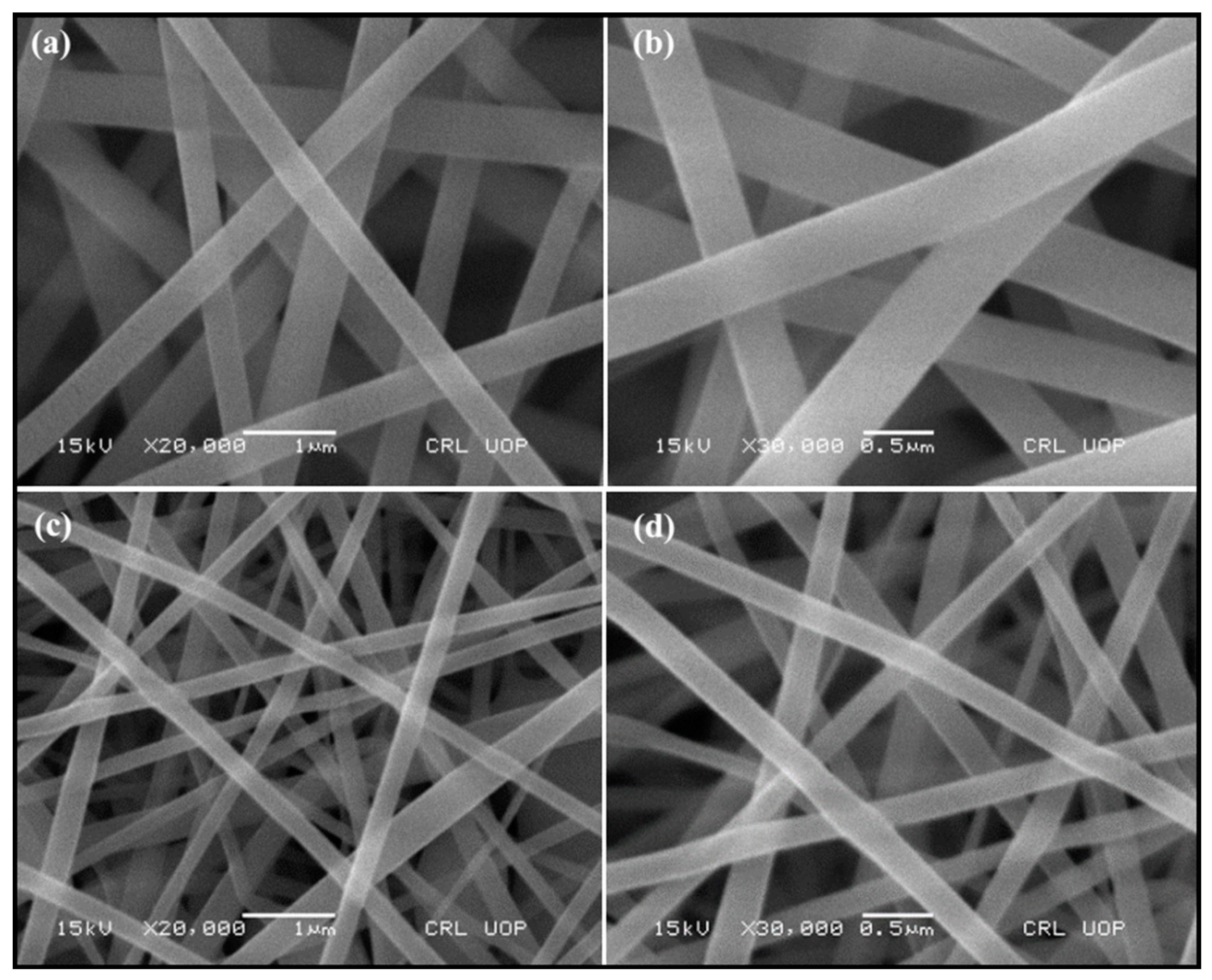
3.1.1. SEM Analysis of Composite and Carbonized Nanofibers
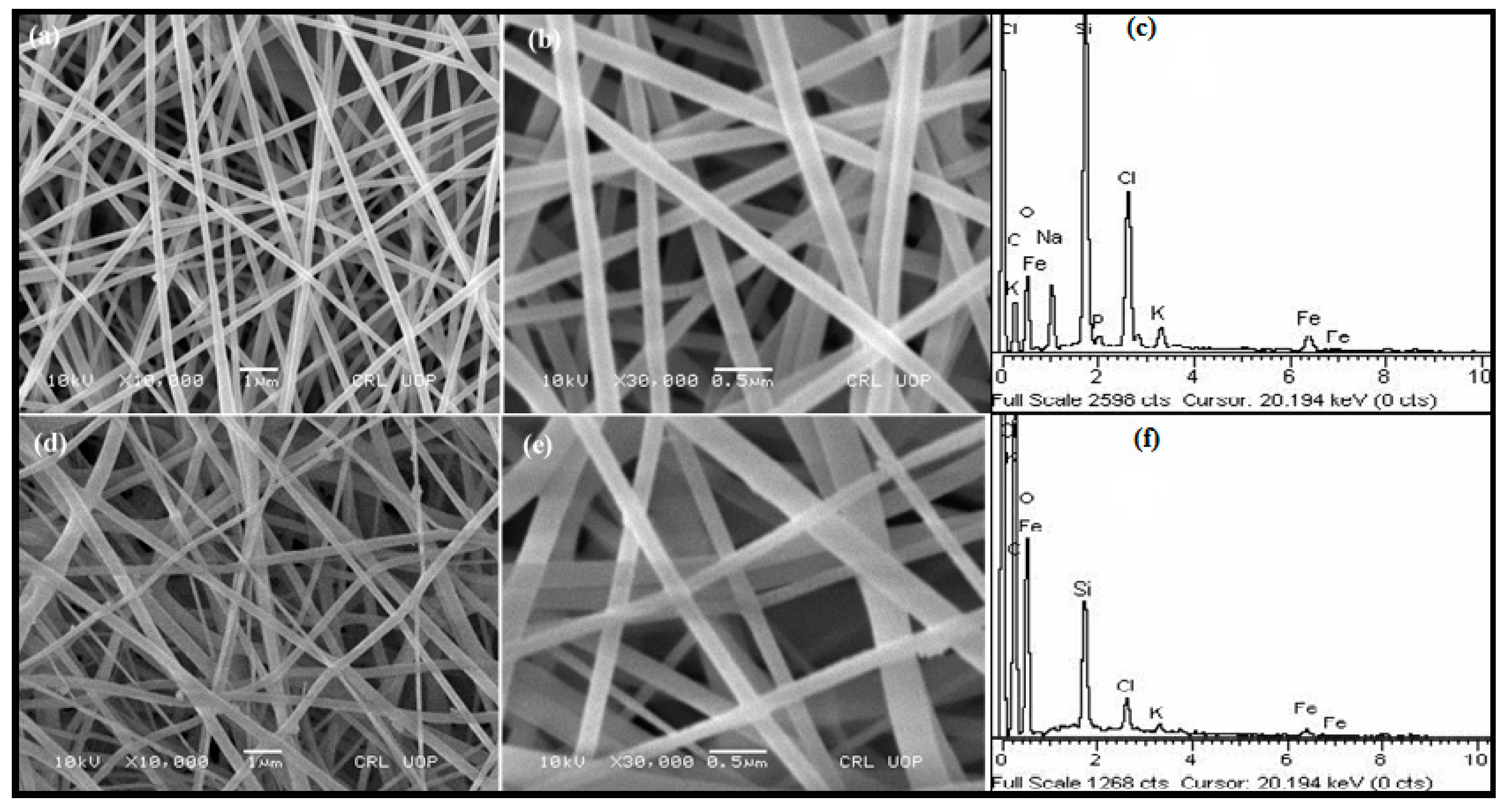
3.1.2. SEM and EDX Analysis of nZVI-Based Composite and Carbonized Nanofibers
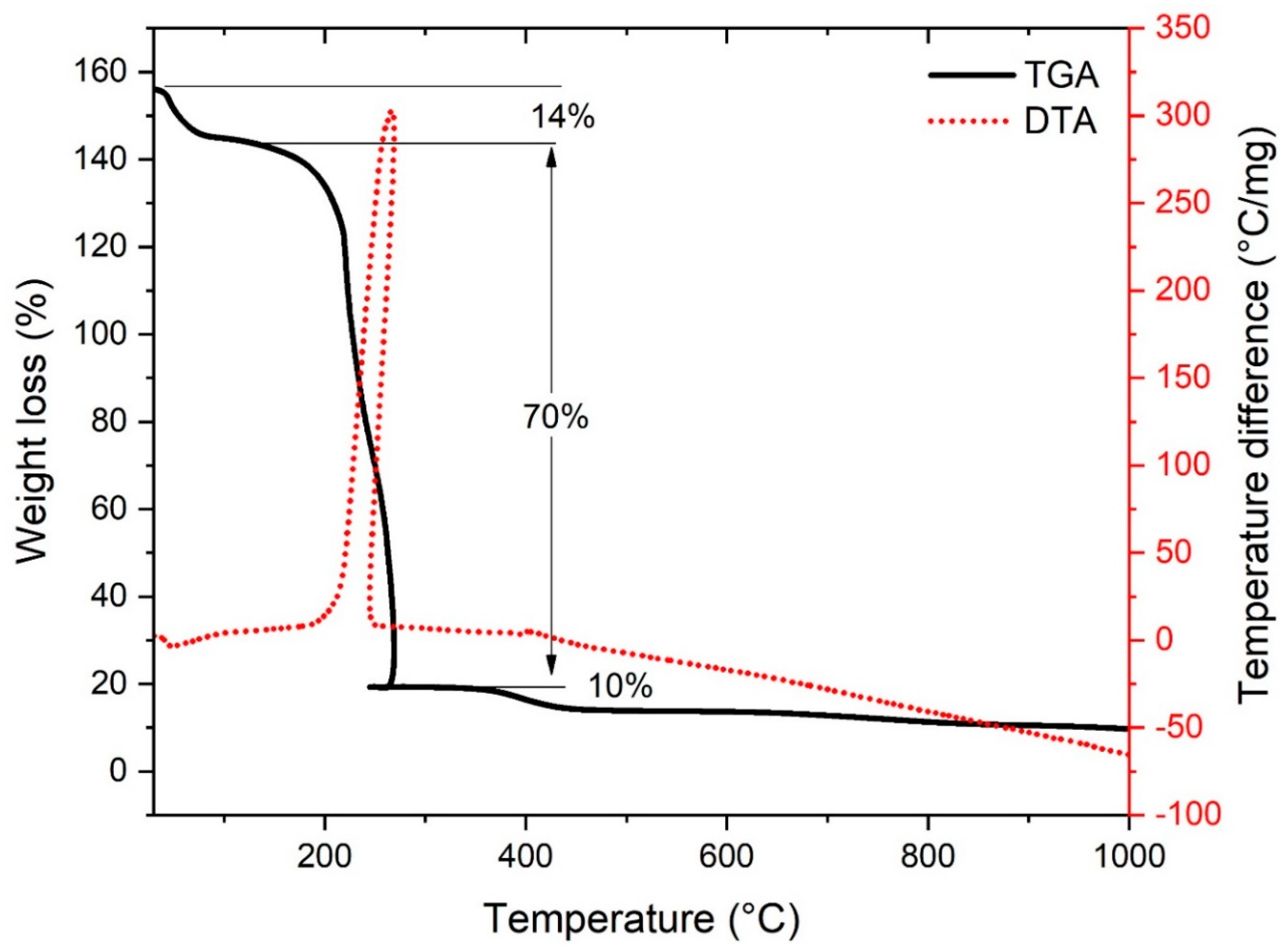
3.1.3. TG / DT Analysis of nZVI-Based Composite Nanofibers
3.2. Phase and Structural Analysis.
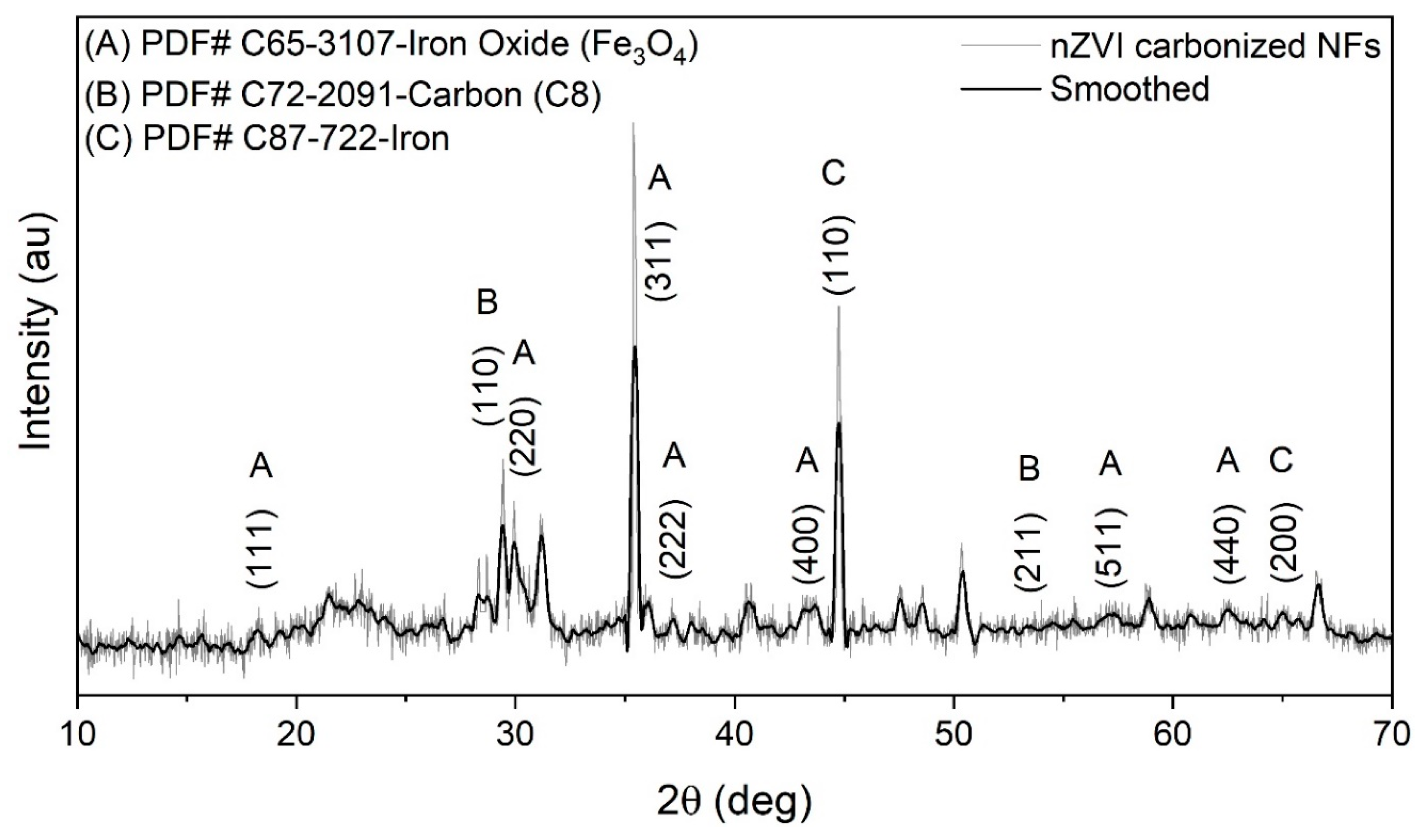
3.2.1. XRD Analysis of nZVI-based Carbonized Nanofibers
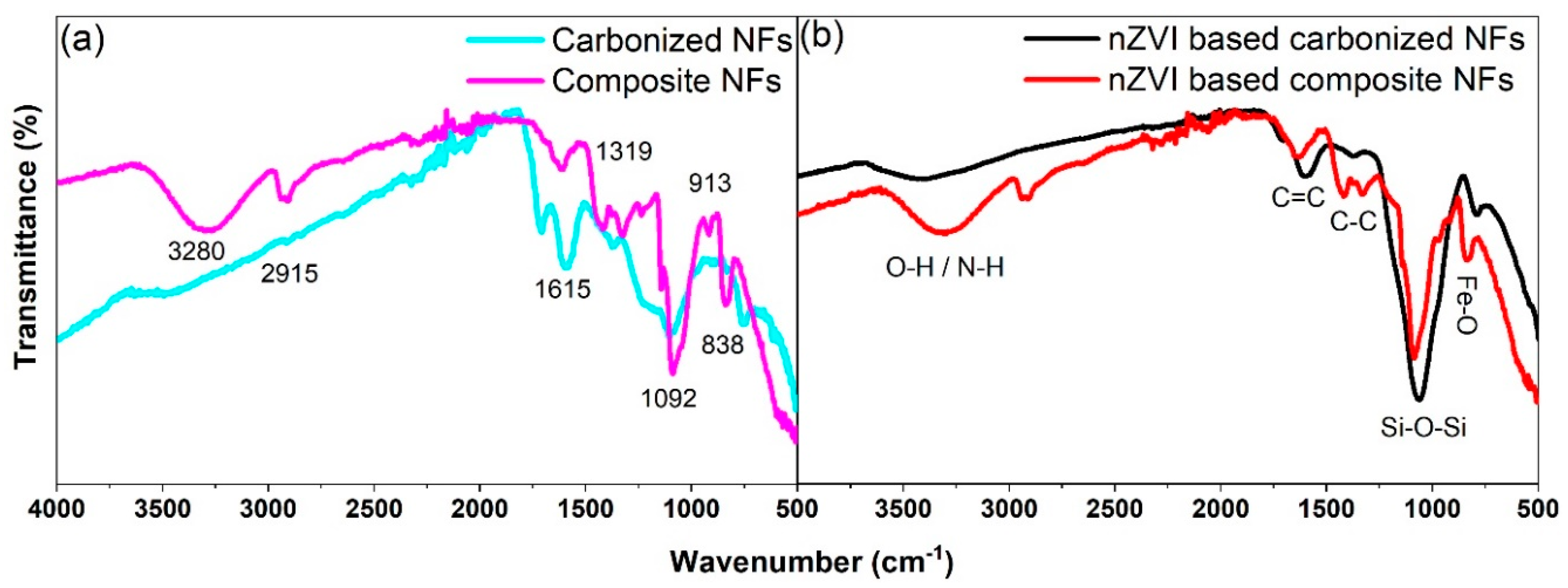
3.2.2. FTIR Analysis of Composite and Carbonized Nanofibers
3.2.3. FTIR Analysis of nZVI-based Composite and Carbonized Nanofibers
3.3. Absorption Spectroscopy Analysis
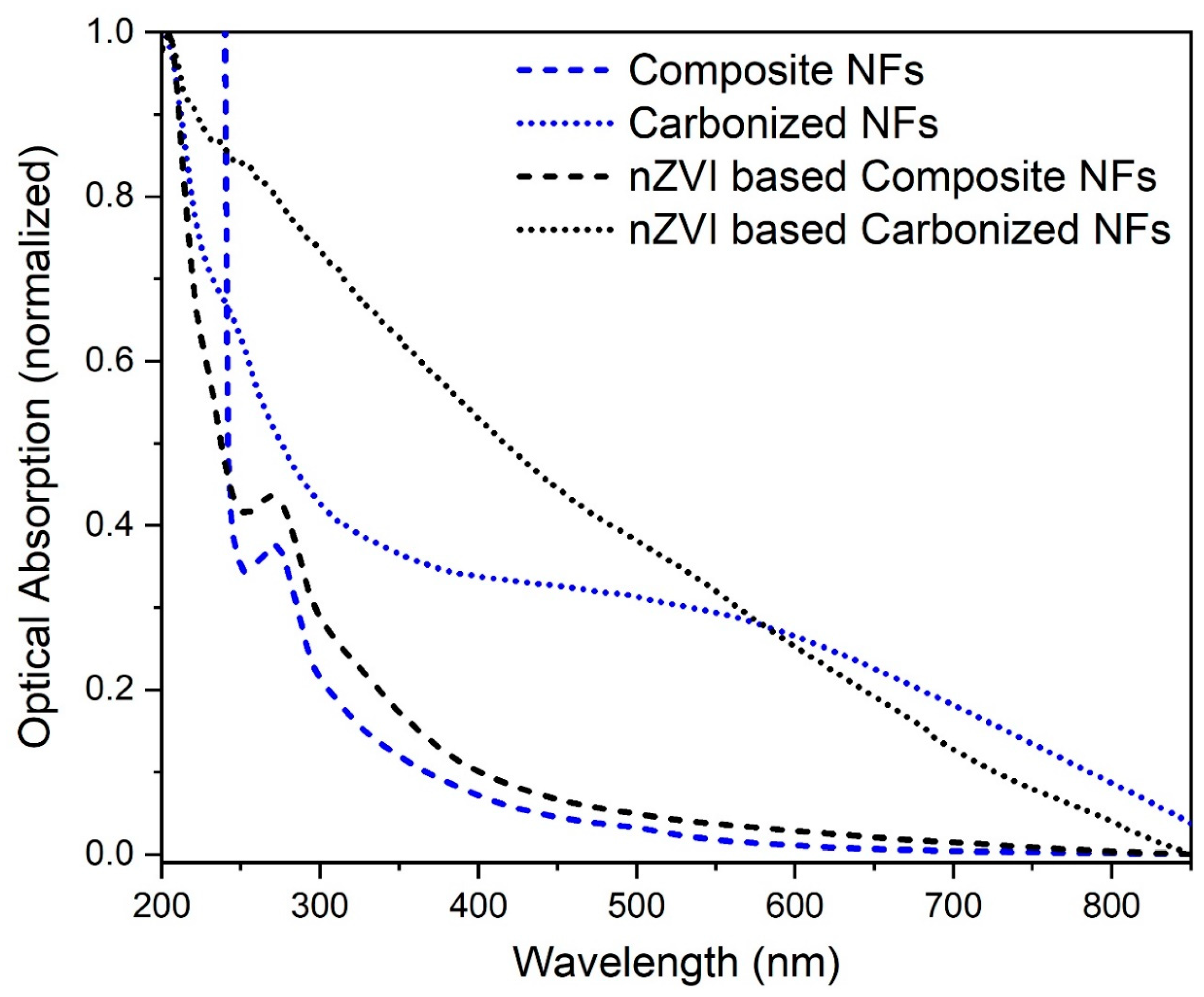
3.3.1. UV-Vis Analysis of Composite, Carbonized Nanofibers and nZVI-based Composite, Carbonized Nanofibers
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Ponder, S.M.; Darab, J.G.; Mallouk, T.E. Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) Aqueous Solutions Using Supported, Nanoscale Zero-valent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2564–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, J.; Liu, H.; Tong, Y. Aqueous Cr(VI) reduction by electrodeposited zero-valent iron at neutral pH: Acceleration by organic matters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-B.; Zhang, W.-X. Synthesizing Nanoscale Iron Particles for Rapid and Complete Dechlorination of TCE and PCBs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2154–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Phenrat, T.; Lowry, G.V. Effect of TCE Concentration and Dissolved Groundwater Solutes on NZVI-Promoted TCE Dechlorination and H2 Evolution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7881–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatisson, J.; Ghoshal, S.; Tufenkji, N. Deposition of Carboxymethylcellulose-Coated Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles onto Silica: Roles of Solution Chemistry and Organic Molecules. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12832–12840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharisov, B.I.; Dias, H.V.R.; Kharissova, O.V.; Vázquez, A.; Peña, Y.; Gómez, I. Solubilization, dispersion and stabilization of magnetic nanoparticles in water and non-aqueous solvents: recent trends. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45354–45381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.C.; Wang, J.; Gao, B.; Sato, S.; Feng, K.; Yin, W.; Igalavithana, A.D.; et al. Biochar-supported nZVI (nZVI/BC) for contaminant removal from soil and water: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 820–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Dai, Y.; Shi, L.; Wei, Y.; Xiu, Q.; Sun, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, S. Humic acid addition sequence and concentration affect sulfur incorporation, electron transfer, and reactivity of sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mu, Y.; Shang, H.; Mao, C.; Cao, S.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, L. Phosphate modification enables high efficiency and electron selectivity of nZVI toward Cr(VI) removal. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2019, 263, 118364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasinszki, T.; Krebsz, M. Synthesis and Application of Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles in Water Treatment, Environmental Remediation, Catalysis, and Their Biological Effects. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Li, X.-Q.; Zhang, W.-X.; Wang, H.P. A method for the preparation of stable dispersion of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 308, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Zhao, D. Manipulating the Size and Dispersibility of Zerovalent Iron Nanoparticles by Use of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Stabilizers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6216–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoag, G.E.; Collins, J.B.; Holcomb, J.L.; Hoag, J.R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Varma, R.S. Degradation of bromothymol blue by ‘greener’ nano-scale zero-valent iron synthesized using tea polyphenols. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8671–8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponder, S.M.; Darab, J.G.; Bucher, J.; Caulder, D.; Craig, I.; Davis, L.; Edelstein, N.; Lukens, W.; Nitsche, H.; Rao, L.; et al. Surface Chemistry and Electrochemistry of Supported Zerovalent Iron Nanoparticles in the Remediation of Aqueous Metal Contaminants. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Park, H.; Lee, S.-H.; Sigmund, W.M. Poly(acrylic acid) nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Sorbo, G.R.; Truda, G.; Bifulco, A.; Passaro, J.; Petrone, G.; Vitolo, B.; Ausanio, G.; Vergara, A.; Marulo, F.; Branda, F. Non Monotonous Effects of Noncovalently Functionalized Graphene Addition on the Structure and Sound Absorption Properties of Polyvinylpyrrolidone (1300 kDa) Electrospun Mats. Materials 2018, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Ma, H.; Shen, M.; Wang, S.; Huang, Q.; Shi, X. Excellent copper(II) removal using zero-valent iron nanoparticle-immobilized hybrid electrospun polymer nanofibrous mats. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 381, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Shen, M.; Guo, R.; Wang, S.; Shi, X. Immobilization of Zerovalent Iron Nanoparticles into Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers: Synthesis, Characterization, and Potential Environmental Applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 18062–18068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, M.; Smuleac, V.; Ormsbee, L.E.; Sedlak, D.L.; Bhattacharyya, D. Iron oxide nanoparticle synthesis in aqueous and membrane systems for oxidative degradation of trichloroethylene from water. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, K.; Vali, H.; Orsat, V. Value-adding to grape waste: Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles. J. Food Eng. 2014, 142, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, V.; Iannotti, V.; Ausanio, G.; Ambrosio, L.; Lanotte, L. Elastomagnetic nanofiber wires by magnetic field assisted electrospinning. Express Polym. Lett. 2019, 13, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, V.; Iannotti, V.; Ausanio, G.; Ambrosio, L.; Lanotte, L. Nanocomposite tubes for magneto-active devices. Express Polym. Lett. 2020, 14, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, M.H.; Gao, P.; Tan, B.Y.L.; Sun, D.D.; Leckie, J.O. Highly Efficient and Flexible Electrospun Carbon–Silica Nanofibrous Membrane for Ultrafast Gravity-Driven Oil–Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 9393–9401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, X.; Khan, A.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Environmental Remediation and Application of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and Its Composites for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7290–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefănescu, M.; Stoia, M.; Stefănescu, O.; Davidescu, C.; Vlase, G.; Sfîrloagǎ, P.J.R.R.C. Synthesis and caracterization of poly (vinylalcohol)/ethylene glycol/silica hybrids. Thermal analysis and FT-IR study 2010, 55, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Fatema, U.K.; Uddin, A.J.; Uemura, K.; Gotoh, Y. Fabrication of carbon fibers from electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers. Text. Res. J. 2010, 81, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, B.D.; Garimella, S.V. Recent advances in microscale pumping technologies: a review and evaluation. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2008, 5, 145–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-F.; Li, H.-Y.; Pan, K.-L.; Si, C.-Y. Green synthesis of nanoscale zero-valent iron using a grape seed extract as a stabilizing agent and the application for quick decolorization of azo and anthraquinone dyes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 22526–22537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Rao, D.S.; Vankar, V. Growth of nanocrystalline β-silicon carbide and nanocrystalline silicon oxide nanoparticles by sol gel technique. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3174–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Green synthesis of Fe nanoparticles using eucalyptus leaf extracts for treatment of eutrophic wastewater. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 466-467, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, G.; Fontenla, E.; Santos, J.; Freire, M.; González-Álvarez, J.; Antorrena, G. Antioxidant activity and phenolic content of chestnut (Castanea sativa) shell and eucalyptus (Eucalyptus globulus) bark extracts. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2008, 28, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunalan, S.; Sivaraj, R.; Rajendran, V. Green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2012, 22, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrona, M.; Cran, M.J.; Nerín, C.; Bigger, S.W. Development and characterisation of HPMC films containing PLA nanoparticles loaded with green tea extract for food packaging applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadokoro, H.; Kǒzai, K.; Seki, S.; Nitta, I. On the crystalline band in the infrared absorption spectrum of polyvinyl alcohol. J. Polym. Sci. 1957, 26, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Fong, H. Hierarchical electrospun SiO2 nanofibers containing SiO2 nanoparticles with controllable surface-roughness and/or porosity. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wu, Z.; Wei, W.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X.A.; Niu, M.; Wei, Q.; Rao, J. Hybrid composites of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/Si–Al for improving the properties of ultra-low density fiberboard (ULDF). RSC advances 2016, 6, 20706–20712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, H.S.; Sadahira, C.M.; Souza, A.N.; Mansur, A.A. FTIR spectroscopy characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel with different hydrolysis degree and chemically crosslinked with glutaraldehyde. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, N.; Lin, L.; Liu, F.; Pan, Q. Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Huang, L.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Synthesis of iron-based nanoparticles by green tea extract and their degradation of malachite. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 51, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, K.L.; Suh, S.; Keller, A.A. Assessing the Risk of Engineered Nanomaterials in the Environment: Development and Application of the nanoFate Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5541–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.; Kaur, M.; Dubey, K.A.; Bhardwaj, Y.K.; Jain, D.; Pillai, C.G.S.; Tyagi, A.K. Tyagi, Polyvinyl alcohol–In 2 O 3 nanocomposite films: synthesis, characterization and gas sensing properties. RSC Advances 2012, 2, 7180–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.H.; Wang, S.Y. Electrospun nanofibers from crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol) and its filtration efficiency. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2008, 109, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Weng, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles by various tea extracts: Comparative study of the reactivity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 130, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Chao, S.; He, X.; Li, M. Inorganic microencapsulated core/shell structure of Al–Si alloy micro-particles with silane coupling agent. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 6865–6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iram, M.; Guo, C.; Guan, Y.; Ishfaq, A.; Liu, H. Adsorption and magnetic removal of neutral red dye from aqueous solution using Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smuleac, V.; Varma, R.; Sikdar, S.; Bhattacharyya, D. Green synthesis of Fe and Fe/Pd bimetallic nanoparticles in membranes for reductive degradation of chlorinated organics. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basavaraja, S.; Balaji, S.D.; Lagashetty, A.; Rajasab, A.H.; Venkataraman, A. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium semitectum. Mater. Res. Bull. 2008, 43, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, M. SCG Kiruba Daniel, G. Vinothini, N. Subramanian, K. Nehru & M. Sivakumar. J Nanopart Res 2013, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, A.; Nangia, A.; Prasad, M.N.V. Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles from Selected Plant Materials of Peninsular India. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. A: Phys. Sci. 2017, 88, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Description | Brand | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | green tea, wt. = 90 | Locally available |
| 2 | PVA, Mw = 66,000 | Junsei |
| 3 | TEOS, 98% purity | Sigma Aldrich |
| 4 | FeCl3.6H2O, molar mass = 270.3 gm/mol |
Doejung |
| Element | Weight% | Atomic% |
|---|---|---|
| C | 41.31 | 56.69 |
| O | 24.39 | 25.12 |
| Na | 4.32 | 3.10 |
| Si | 14.43 | 8.47 |
| P | 0.69 | 0.37 |
| Cl | 9.84 | 4.57 |
| K | 1.58 | 0.66 |
| Fe | 3.44 | 1.02 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
| Element | Weight% | Weight% |
|---|---|---|
| C | 54.74 | 63.34 |
| O | 39.15 | 34.00 |
| Si | 3.76 | 1.86 |
| Cl | 1 1.25 | 0.49 |
| K | 0.34 | 0.12 |
| Fe | 0.77 | 0.19 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





