Submitted:
25 August 2023
Posted:
25 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Data Description
Main Content
Context
Methods
Samples and Ethics Statement
Nucleic Acid Isolation, Library Preparation, and Sequencing
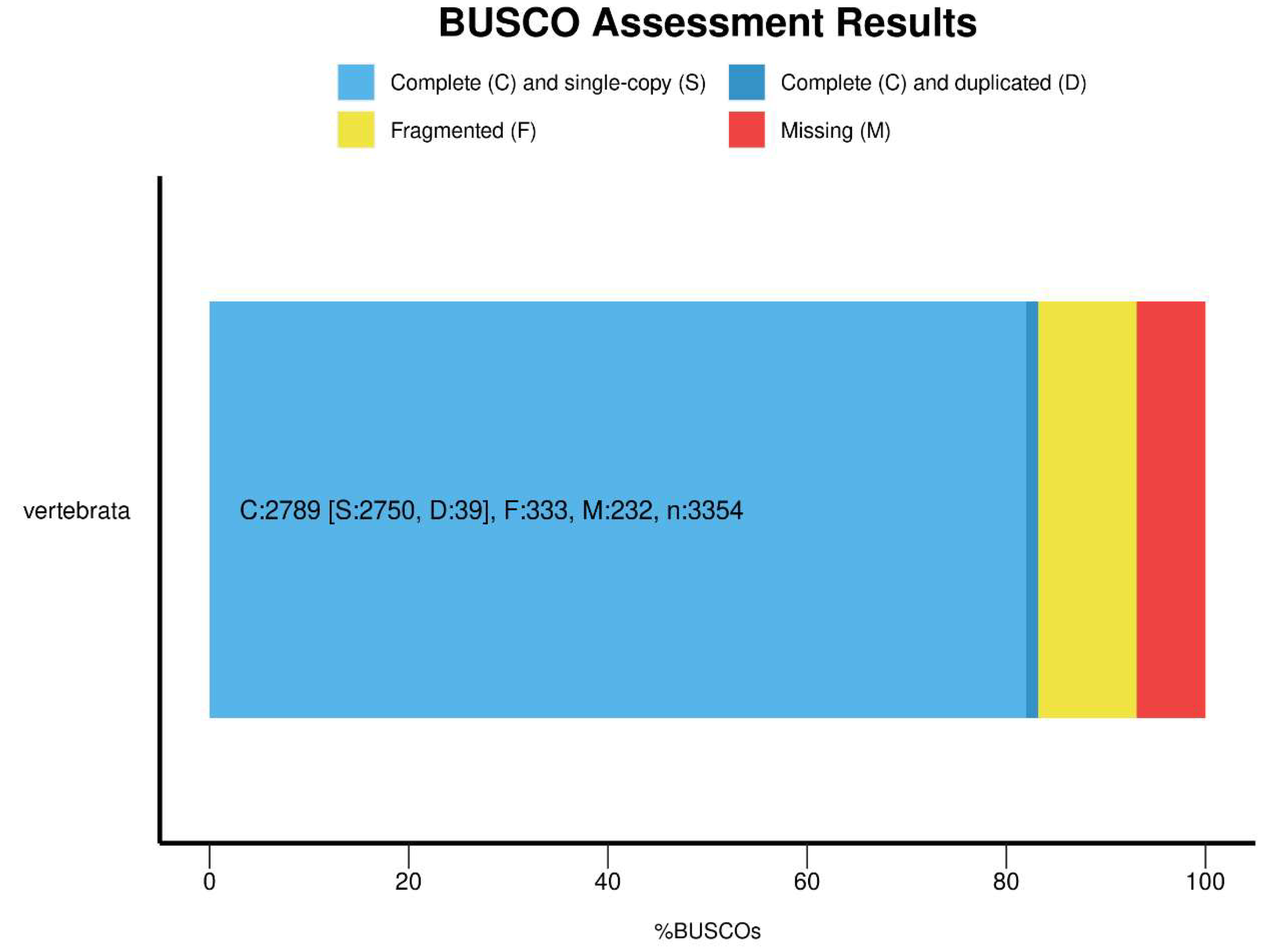
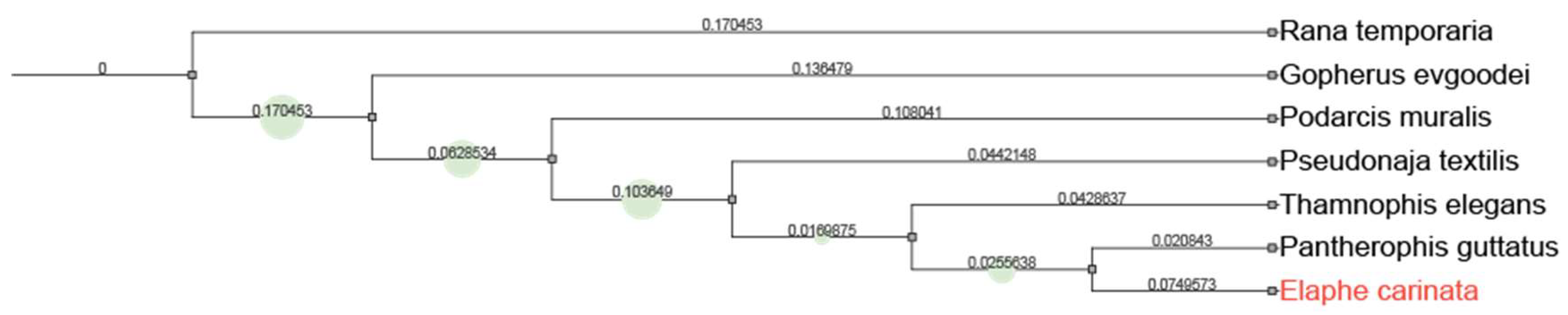
Genome Assembly, Annotation and Assessment
Results
Data Validation and Quality Control
Reuse Potential
Data Availability
Competing Interests
Consent for Publication
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Zhao, E.; Huang, M.; Zong, Y. 中国动物志: 爬行纲. 第三卷, 有鳞目 蛇亚目 [Fauna Sinica. Reptilia Vol. 2. Squamata. Ophidia]. Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999.
- Xiang, J.; Pingyue, S.; Xuefeng, X.; Weiguo, D. Relationships among body size, clutch size, and egg size in five species of oviparous colubrid snakes from Zhoushan Islands, Zhejiang, China. Dong Wu Xue Bao [Acta Zool. Sin. ] 2000, 46, 138–145. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, L.-L.; Hsieh, C.-K.; Shih, C.-M. First report of Amblyomma helvolum (Acari: Ixodidae) from the Taiwan stink snake, Elaphe carinata (Reptilia: Colubridae), collected in southern Taiwan. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2013, 4, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; He, J.; Deng, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, G.; Li, S.; et al. Integrated analysis of mRNA and miRNA expression profiles reveals muscle growth differences between fast-and slow-growing king ratsnakes (Elaphe carinata). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 248, 110482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, E.; Wang, S. China red data book of endangered animals: Amphibia and Reptilia; Science Press: 1998.
- Suryamohan, K.; Krishnankutty, S.P.; Guillory, J.; Jevit, M.; Schröder, M.S.; Wu, M.; et al. The Indian cobra reference genome and transcriptome enables comprehensive identification of venom toxins. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullate-Agote, A.; Milinkovitch, M.C.; Tzika, A.C. The genome sequence of the corn snake (Pantherophis guttatus), a valuable resource for EvoDevo studies in squamates. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2015, 58, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.-F.; Li, H.; Gao, J.-F.; Ji, X. Geographical variation in reproductive traits and trade-offs between size and number of eggs in the king ratsnake, Elaphe carinata. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2011, 104, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, X.; Chen, Q.; Ji, J.; Kan, Y.; Yao, L.; et al. Genetic analysis of avian gyrovirus 2 variant-related Gyrovirus detected in farmed king ratsnake (Elaphe carinata): The first report from China. Pathogens 2019, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisenfeld, N.I.; Kumar, V.; Shah, P.; Church, D.M.; Jaffe, D.B. Direct determination of diploid genome sequences. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 2012, 1, 2047–2217X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryszcz, L.P.; Gabaldón, T. Redundans: An assembly pipeline for highly heterozygous genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Hao, W. LTR_FINDER: An efficient tool for the prediction of full-length LTR retrotransposons. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 265–268. [Google Scholar]
- Smit, A.; Hubley, R.; Green, P. RepeatModeler Open-1.0; Institute for Systems Biology: Seattle, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tarailo-Graovac, M.; Chen, N. Using RepeatMasker to Identify Repetitive Elements in Genomic Sequences. Current protocols in bioinformatics / editoral board, Andreas D Baxevanis [et al]. 2009.
- Tempel, S. Using and understanding RepeatMasker. In Mobile Genetic Elements; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 29–51. [Google Scholar]
- Stanke, M.; Steinkamp, R.; Waack, S.; Morgenstern, B. AUGUSTUS: A web server for gene finding in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W309–W312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Zhu, W.; Pertea, M.; Allen, J.E.; Orvis, J.; et al. Automated eukaryotic gene structure annotation using EVidenceModeler and the Program to Assemble Spliced Alignments. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, D.W. Using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). CSH Protocols 2007, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birney, E.; Clamp, M.; Durbin, R. GeneWise and Genomewise. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.S.; Holt, C.; Moore, B.; Yandell, M. Genome Annotation and Curation Using MAKER and MAKER-P. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, B.; Rolf, A. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence database and its supplement TrEMBL in 2000. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 1, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Pitk, E. KEGG database. Novartis Found. Symp. 2006, 247, 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.-Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.R.; Holt, K.E. Benchmarking of long-read assemblers for prokaryote whole genome sequencing. F1000Research 2019, 8, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emms, D.M.; Kelly, S. OrthoFinder: Solving fundamental biases in whole genome comparisons dramatically improves orthogroup inference accuracy. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, T.; Fang, D.; Li, H.; Sahu, S.K.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, H.; et al. Chromosome-Scale Genome of Masked Palm Civet (Paguma larvata) Shows Genomic Signatures of Its Biological Characteristics and Evolution. Front. Genet. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, N.; Hedges, S.B. The molecular evolutionary tree of lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2009, 332, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Du, W.-G.; Li, H.; Lin, L.-H. Experimentally reducing clutch size reveals a fixed upper limit to egg size in snakes, evidence from the king ratsnake, Elaphe carinata. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2006, 144, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Gao, H.; Lian, L.; Zhang, Z. Variation pattern and adaptive significance of different subtypes of leukocytes in the king ratsnakes (Elaphe carinata) from birth to 30 days of postembryonal period. Chin. J. Ecol. 2017, 36, 2246. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Chen, F.; Gao, F.; Li, L.; Liu, K.; You, L.; et al. CNSA: A data repository for archiving omics data. Database 2020, 2020, baaa055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.C.; Li, J.Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, N.W.; Xiao, F.W. CNGBdb: China National GeneBank DataBase. Hereditas 2020, 42, 799–809. [Google Scholar]


| Contig | Scaffold | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximal length(bp) | 657733 | 52164798 |
| N90(bp) | 3039 | 4090 |
| N50(bp) | 45108 | 6847971 |
| number>=500bp | 187253 | 134573 |
| Ratio of Ns | 0.059 | 0.059 |
| GC content(%) | 40.25 | 40.25 |
| Genome size(bp) | 1574091846 | 1674021862 |
| Type | Length(Bp) | % in genome |
|---|---|---|
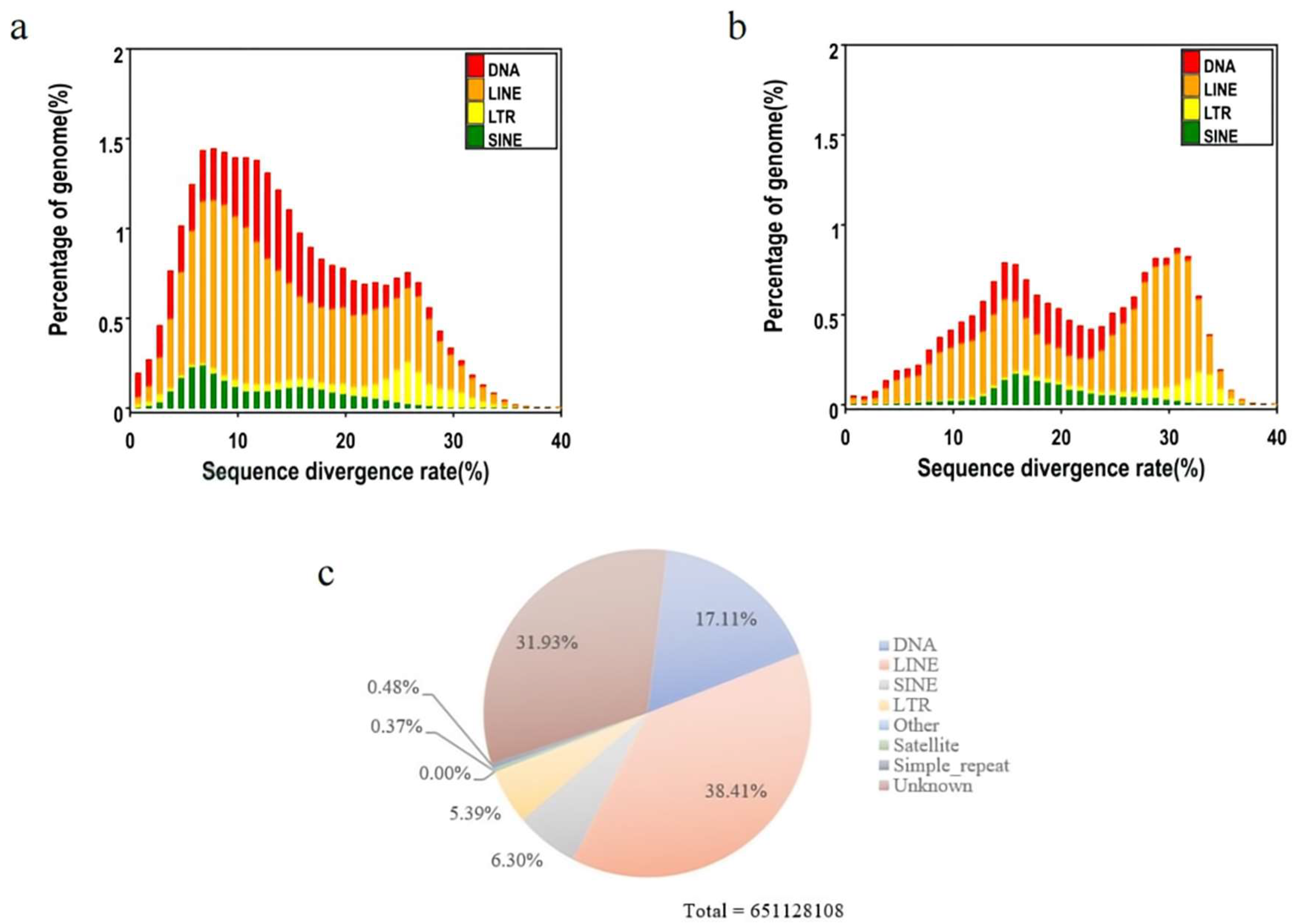
| DNA | 114900759 | 6.863755 |
| LINE | 257937611 | 15.408258 |
| SINE | 42327923 | 2.528517 |
| LTR | 36199886 | 2.16245 |
| Other | 0 | 0 |
| Satellite | 2487376 | 0.148587 |
| Simple_repeat | 3251656 | 0.194242 |
| Unknown | 214450953 | 12.810523 |
| Total | 651128108 | 38.896034 |
| Repbase TEs | TE protiens | De novo | Combined TEs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Length(Bp) | % in genome | Length(Bp) | % in genome | Length(Bp) | % in genome | Length(Bp) | % in genome |
| DNA | 44586593 | 2.663442 | 3037369 | 0.181441 | 114900759 | 6.863755 | 137315177 | 8.202711 |
| LINE | 172974640 | 10.332878 | 142896461 | 8.536117 | 257937611 | 15.408258 | 287262246 | 17.160006 |
| SINE | 27330057 | 1.632599 | 0 | 0 | 42327923 | 2.528517 | 52336172 | 3.126373 |
| LTR | 20332067 | 1.214564 | 26146398 | 1.561891 | 36199886 | 2.16245 | 48061022 | 2.870991 |
| Other | 28331 | 0.001692 | 291 | 0.000017 | 0 | 0 | 28622 | 0.00171 |
| Unknown | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 214450953 | 12.810523 | 214450953 | 12.810523 |
| Total | 252872307 | 15.105675 | 171980912 | 10.273516 | 645389076 | 38.553205 | 685733449 | 40.963231 |
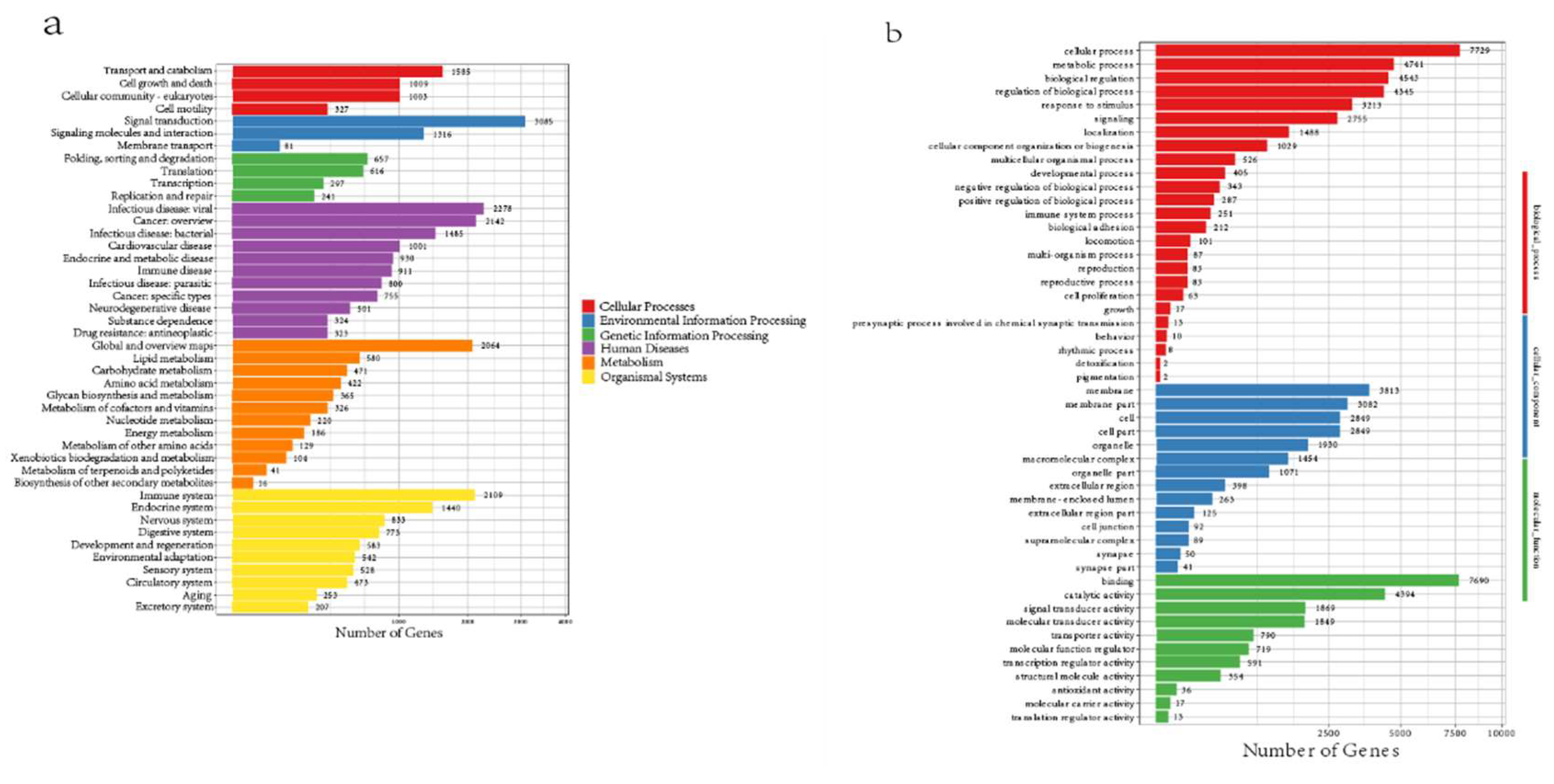
| Values | Total | Swissprot-Annotated | KEGG-Annotated | TrEMBL-Annotated | Interpro-Annotated | GO-Annotated | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 22,339 | 20,796 | 19,836 | 21,874 | 21,604 | 15,169 | 22,065 |
| Percentage | 100% | 93.09% | 88.80% | 97.92% | 96.71% | 67.90% | 98.77% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





