Submitted:
23 August 2025
Posted:
25 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
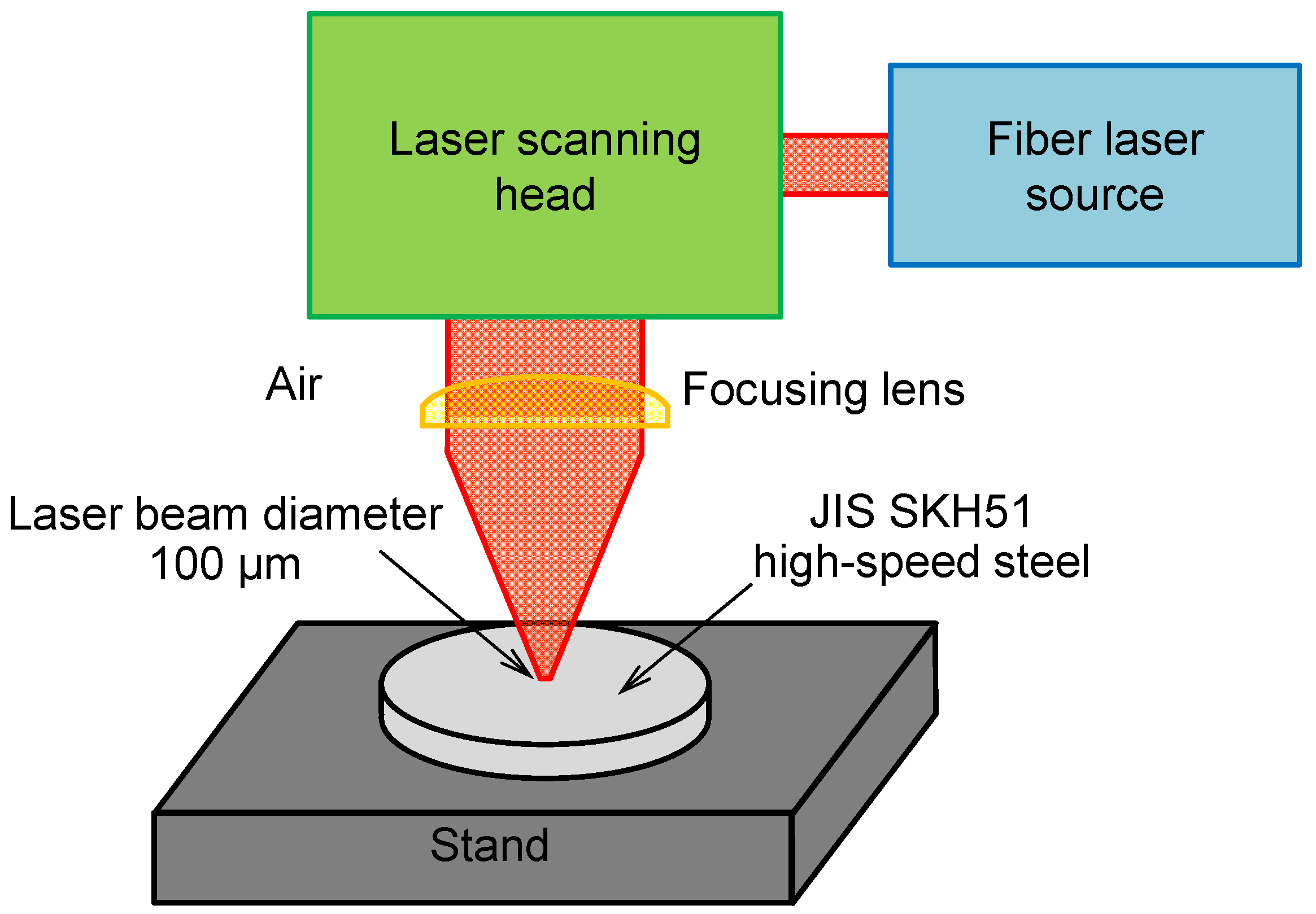
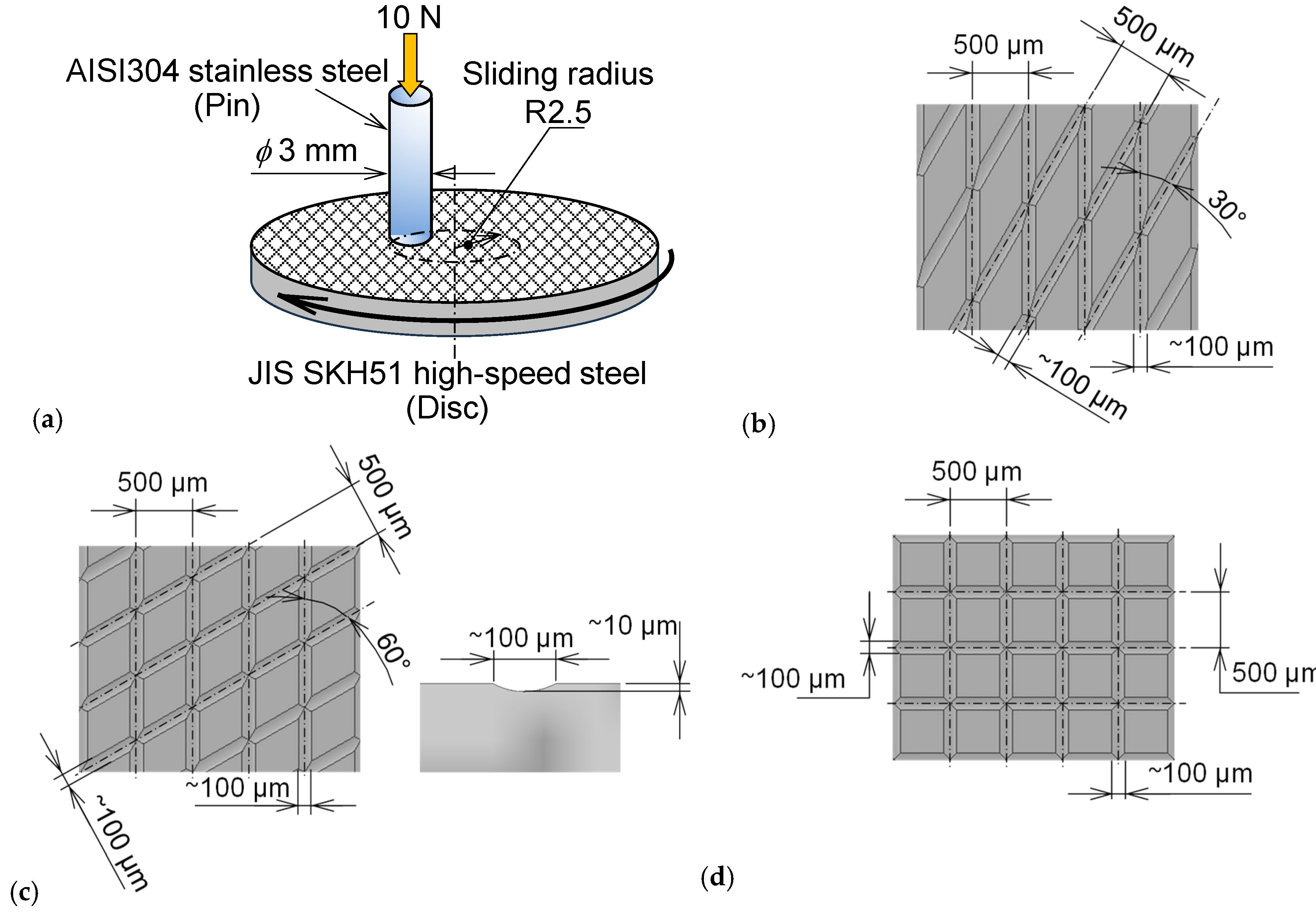
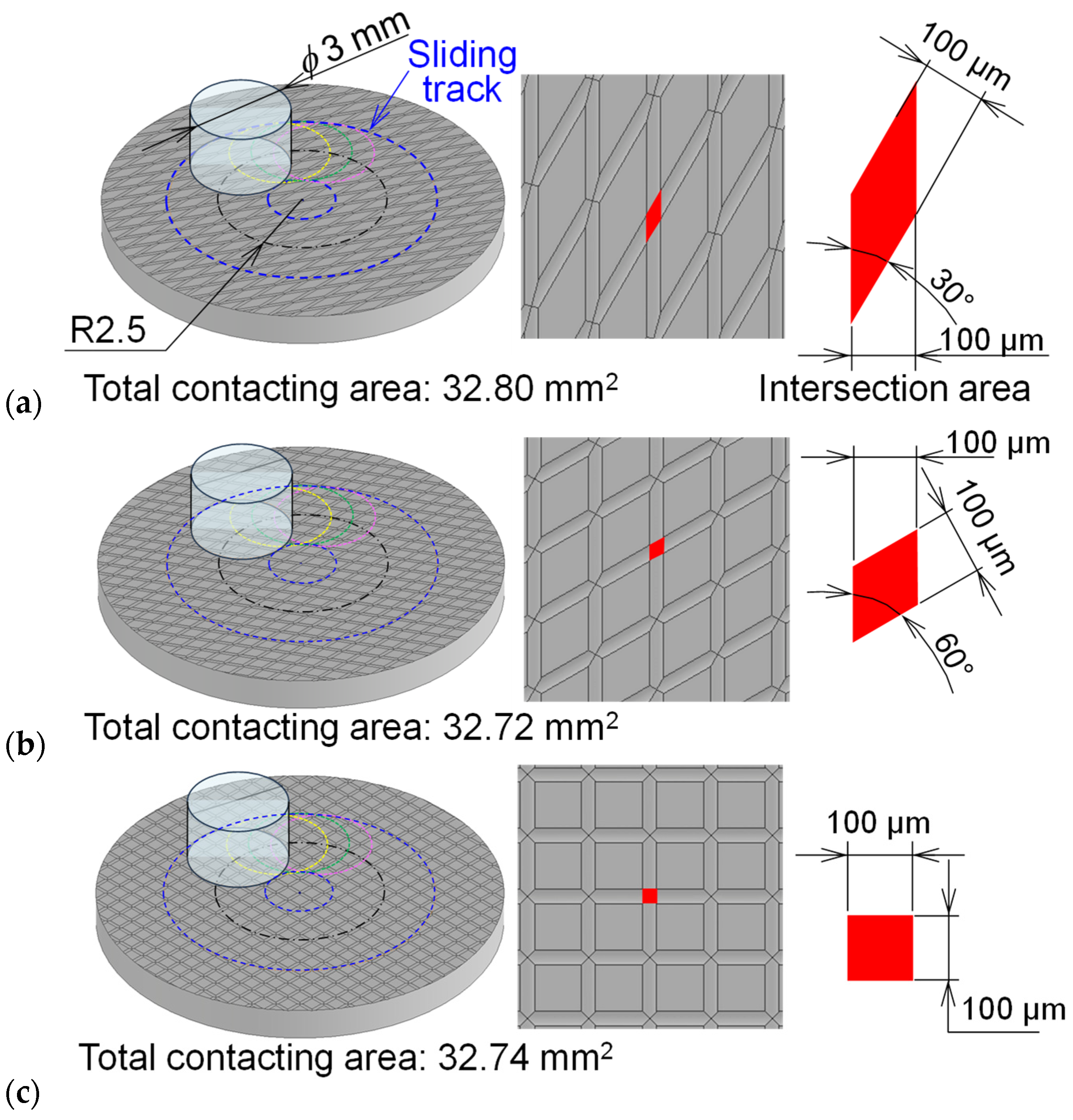
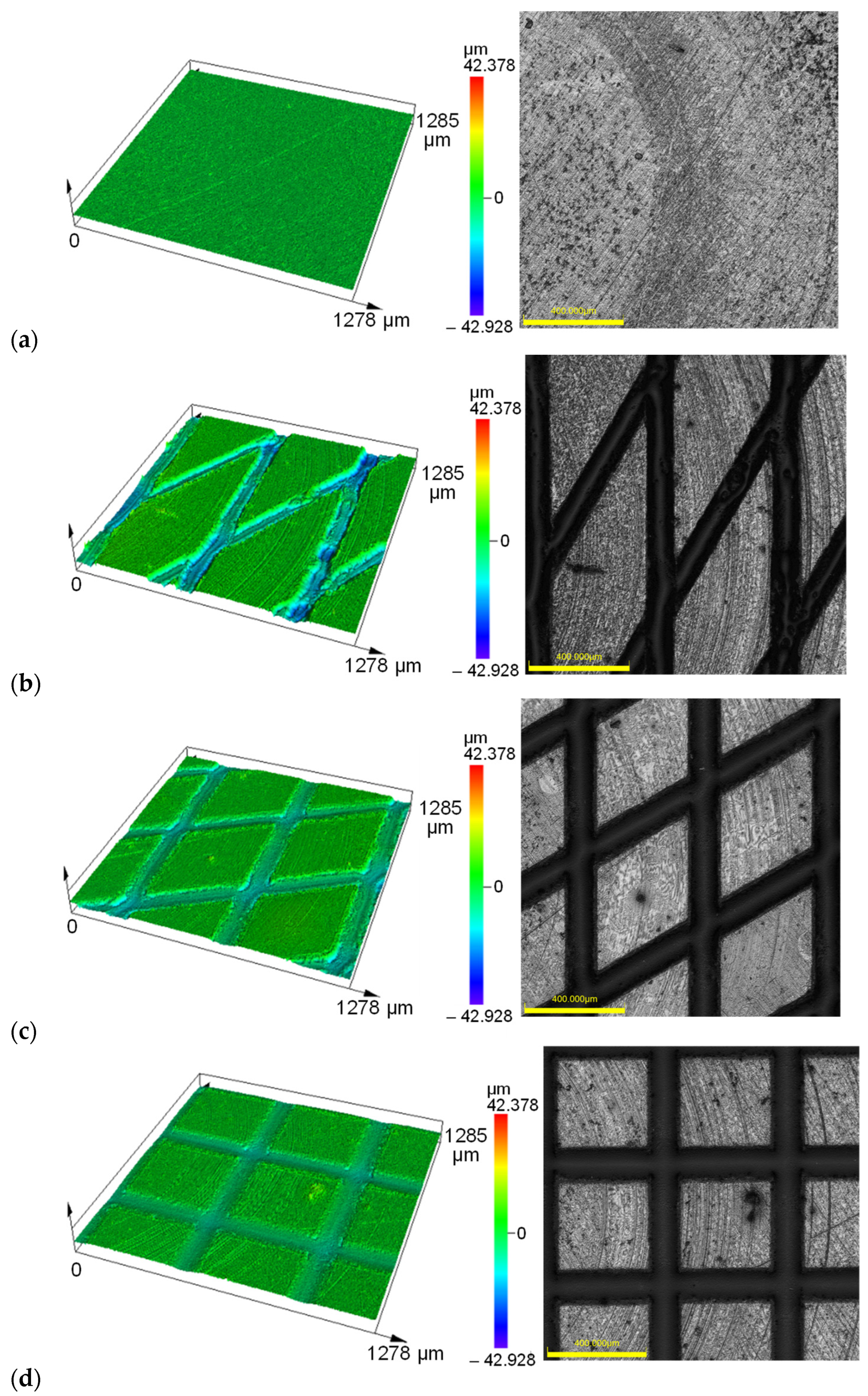
2.1. Micro-Groove Fabrication
2.2. Friction Test
2.3. Numerical Simulation of Pin-on-Disc Test
- Pin constraints: The movement of the pin was allowed in all directions, and the rotational displacement was restricted about the Z- and X- axes while allowing rotation around the disc axis (Y-axis) to simulate the circular sliding motion.
- Disc constraints: The disc was fully constrained in all translational and rotational directions to remain fixed during the simulation, reflecting its stationary role in the model.
- Contact definition: A surface-to-surface contact interaction was defined between the pin and disc using an elastic contact condition and a penalty-based tangential contact model to allow frictional sliding. A constant friction coefficient of 0.25 was assigned, although the friction force was not the primary focus of the simulation.
3. Results and Discussion
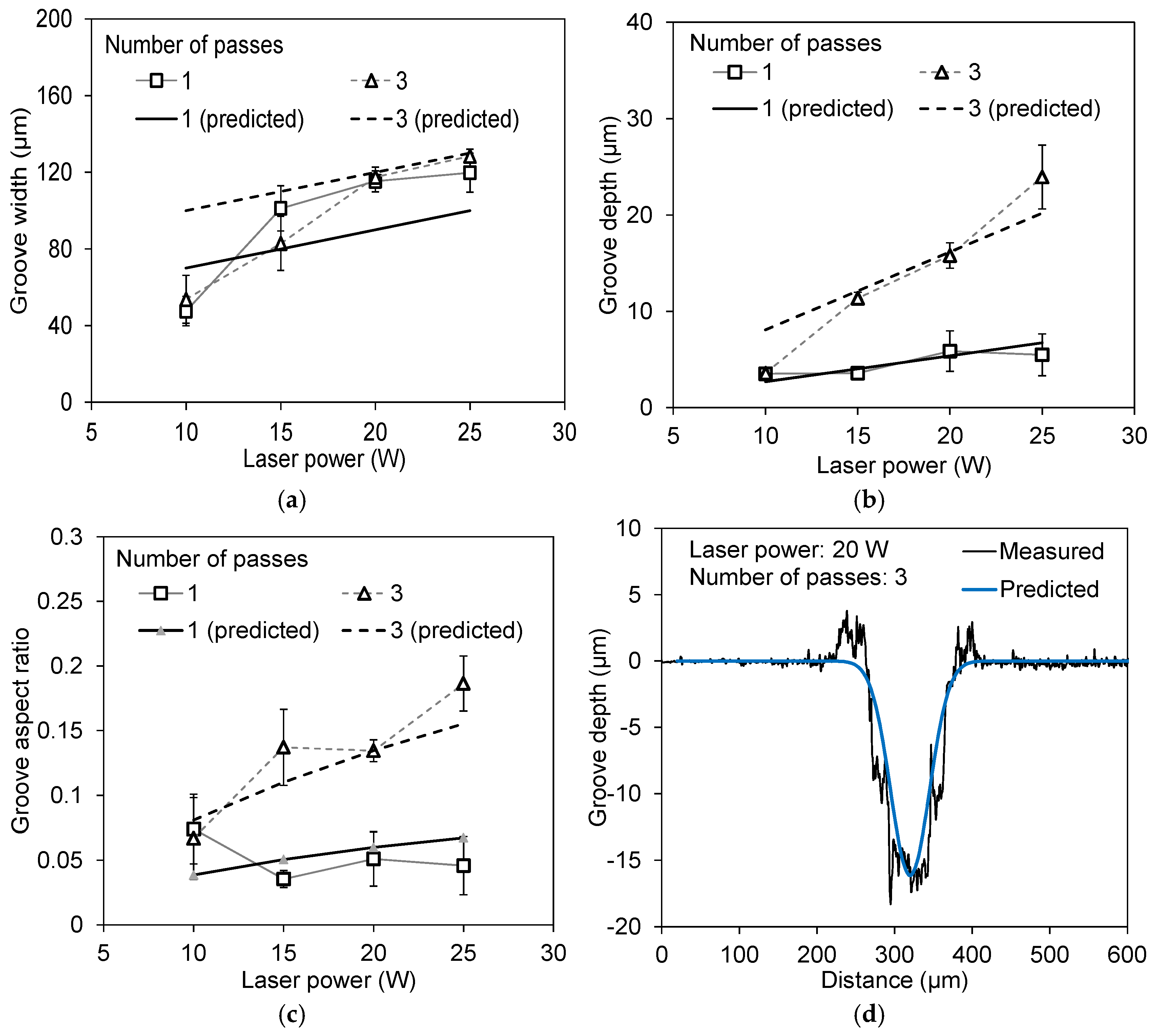
3.1. Effect of Laser Power and Number of Passes on Width and Depth of Micro-Grooves
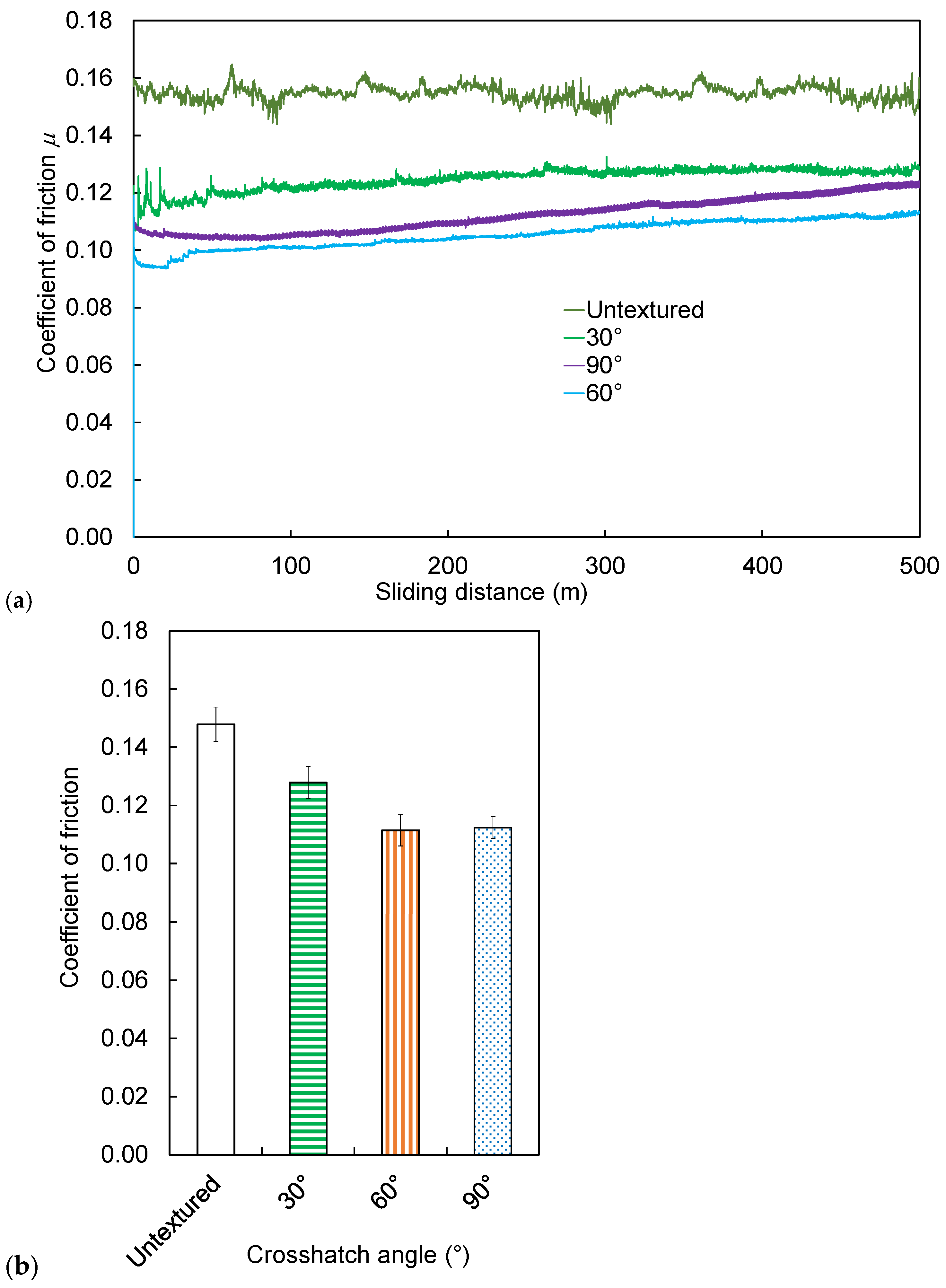
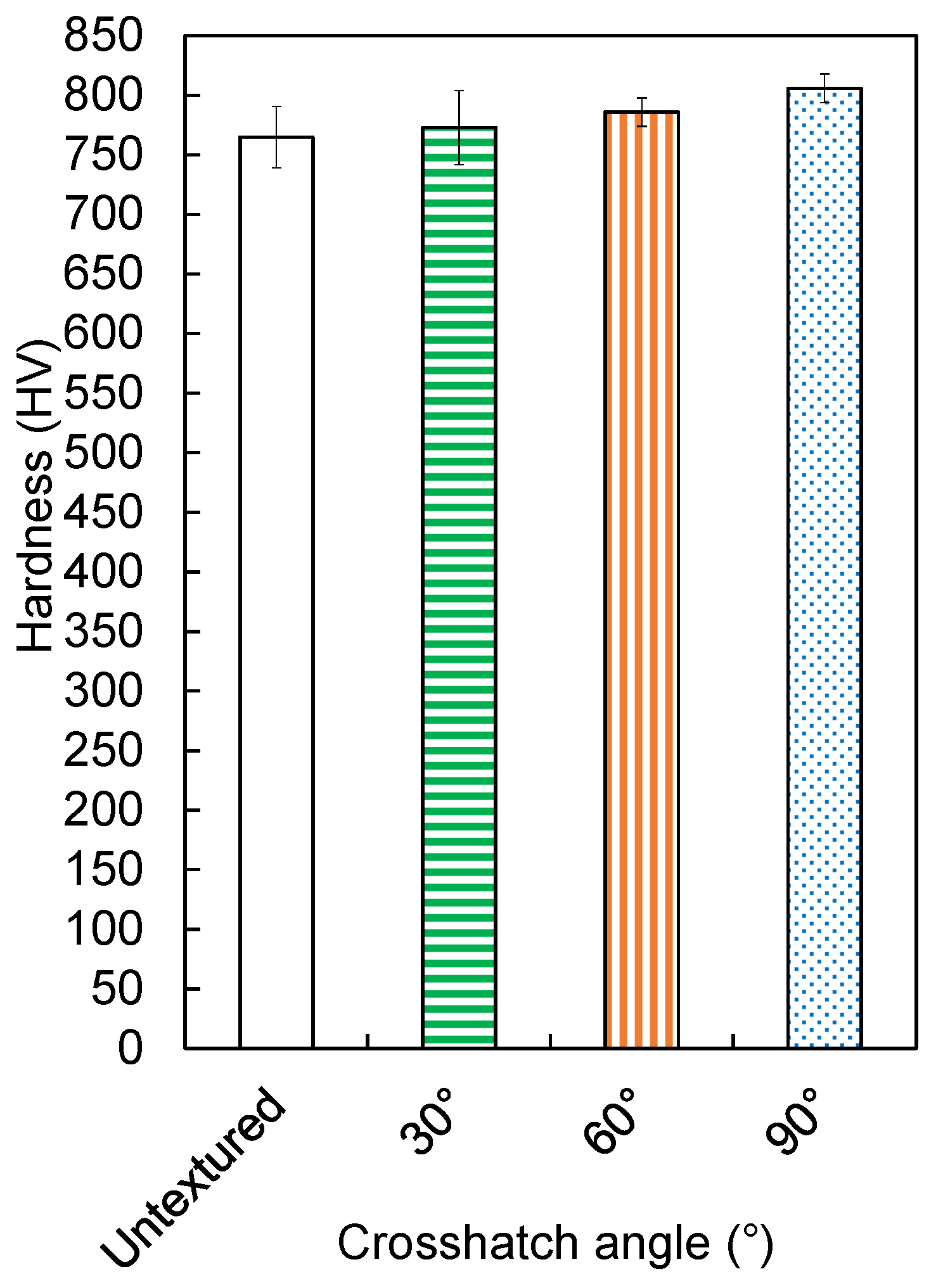
3.2. Effect of Groove Crosshatch Angles on Friction and Wear of High-Speed Steel Surfaces
3.3. Numerical Simulation of Contact Behavior
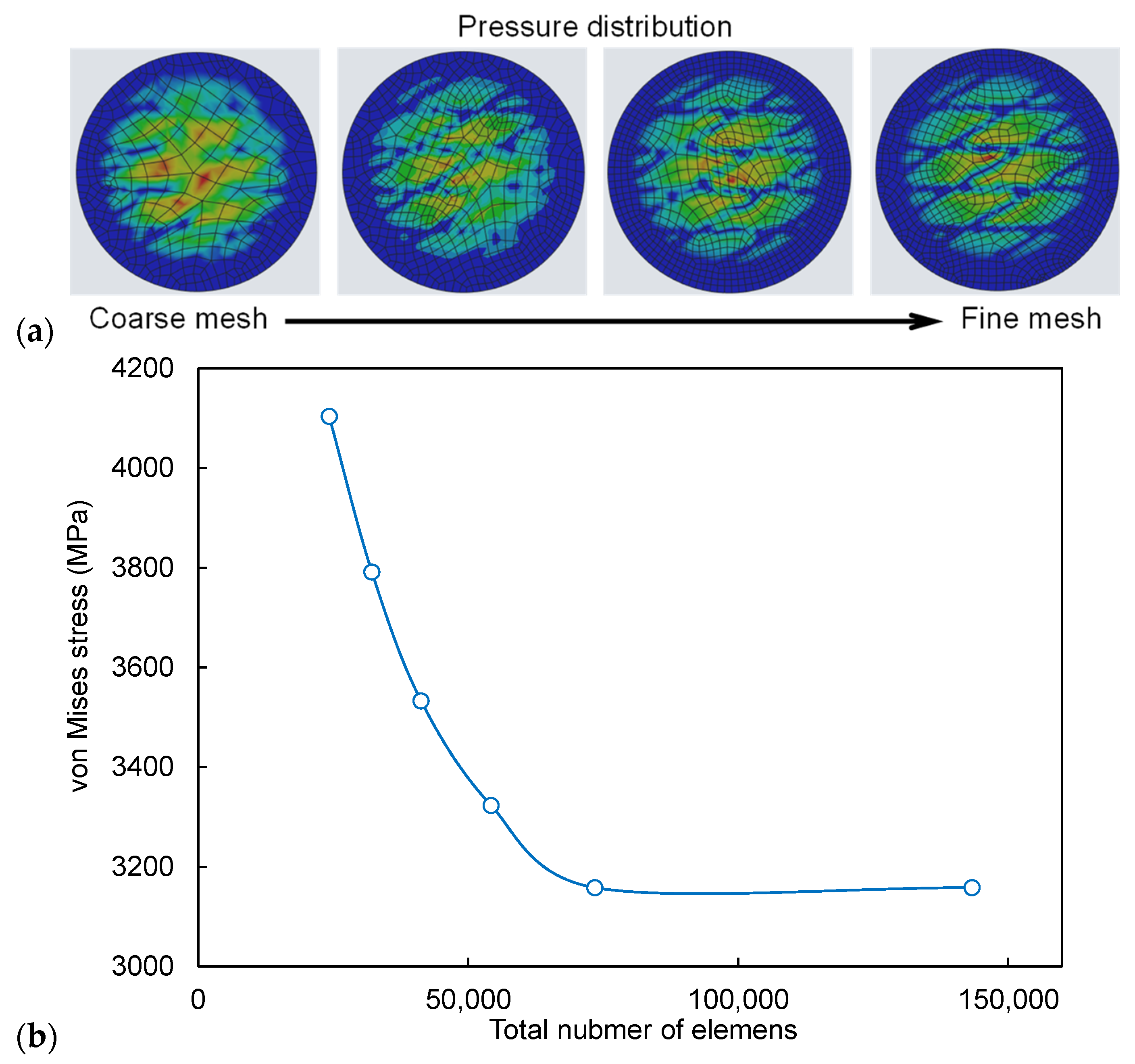
3.3.1. Mesh Independence Study
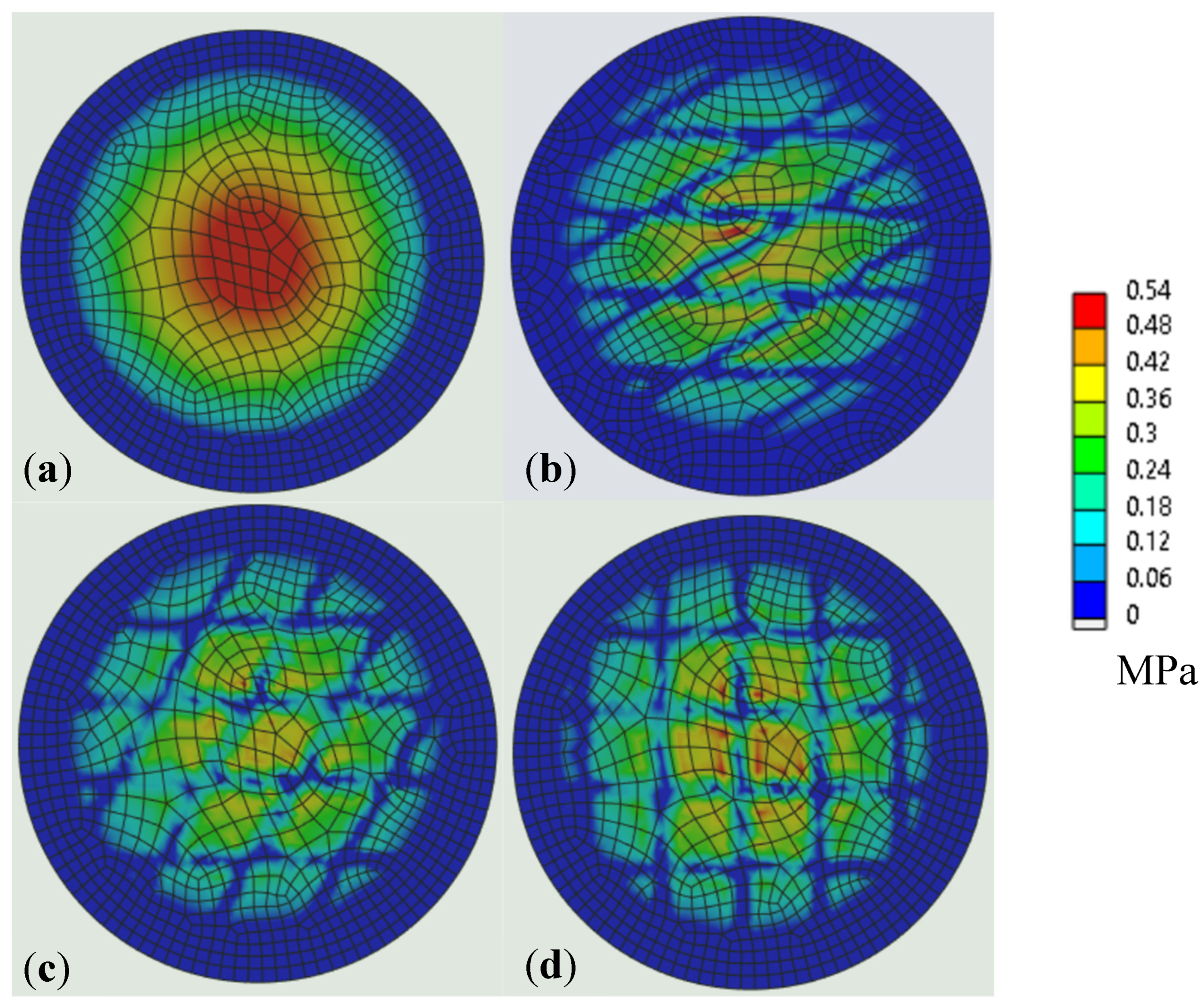
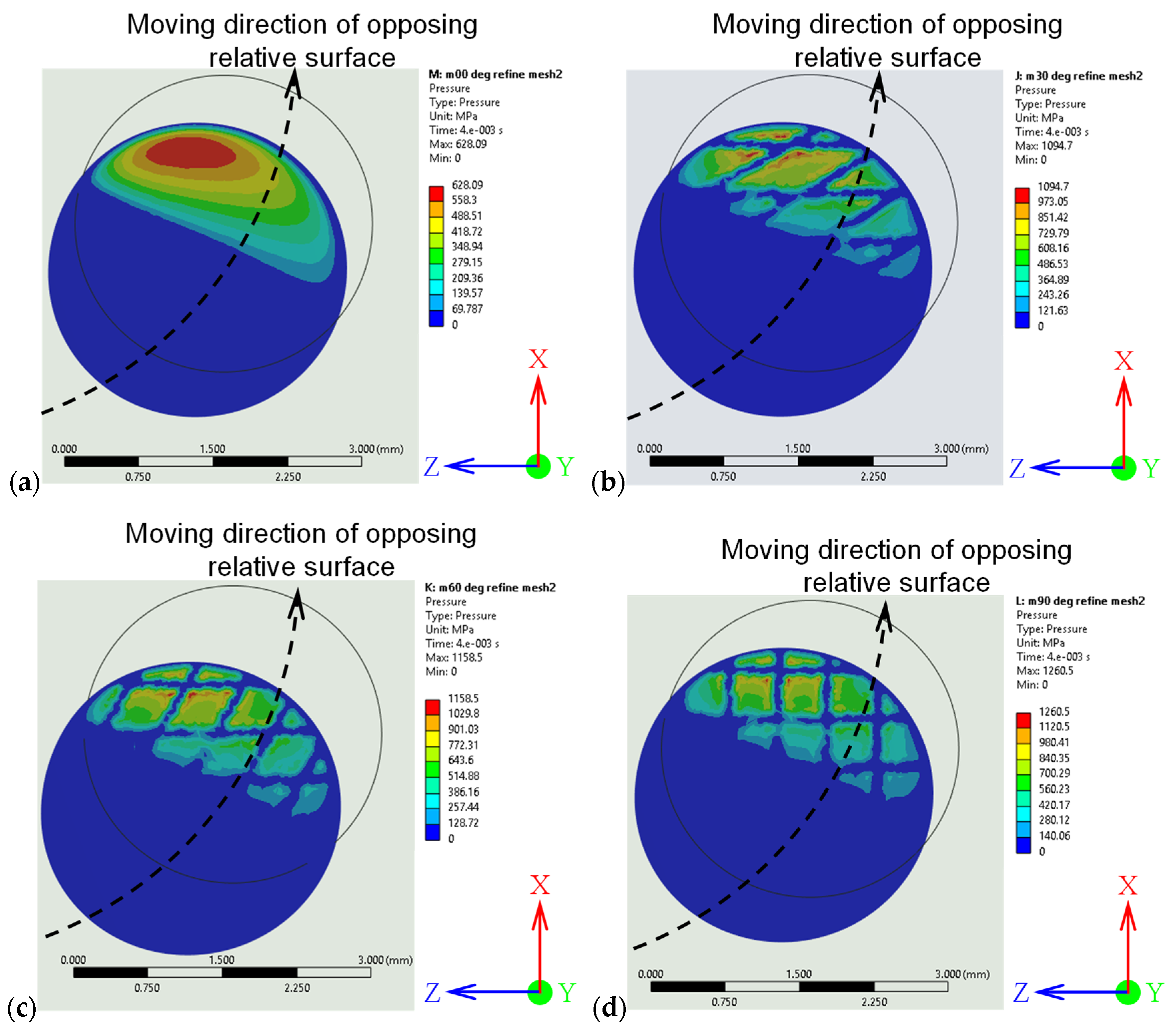
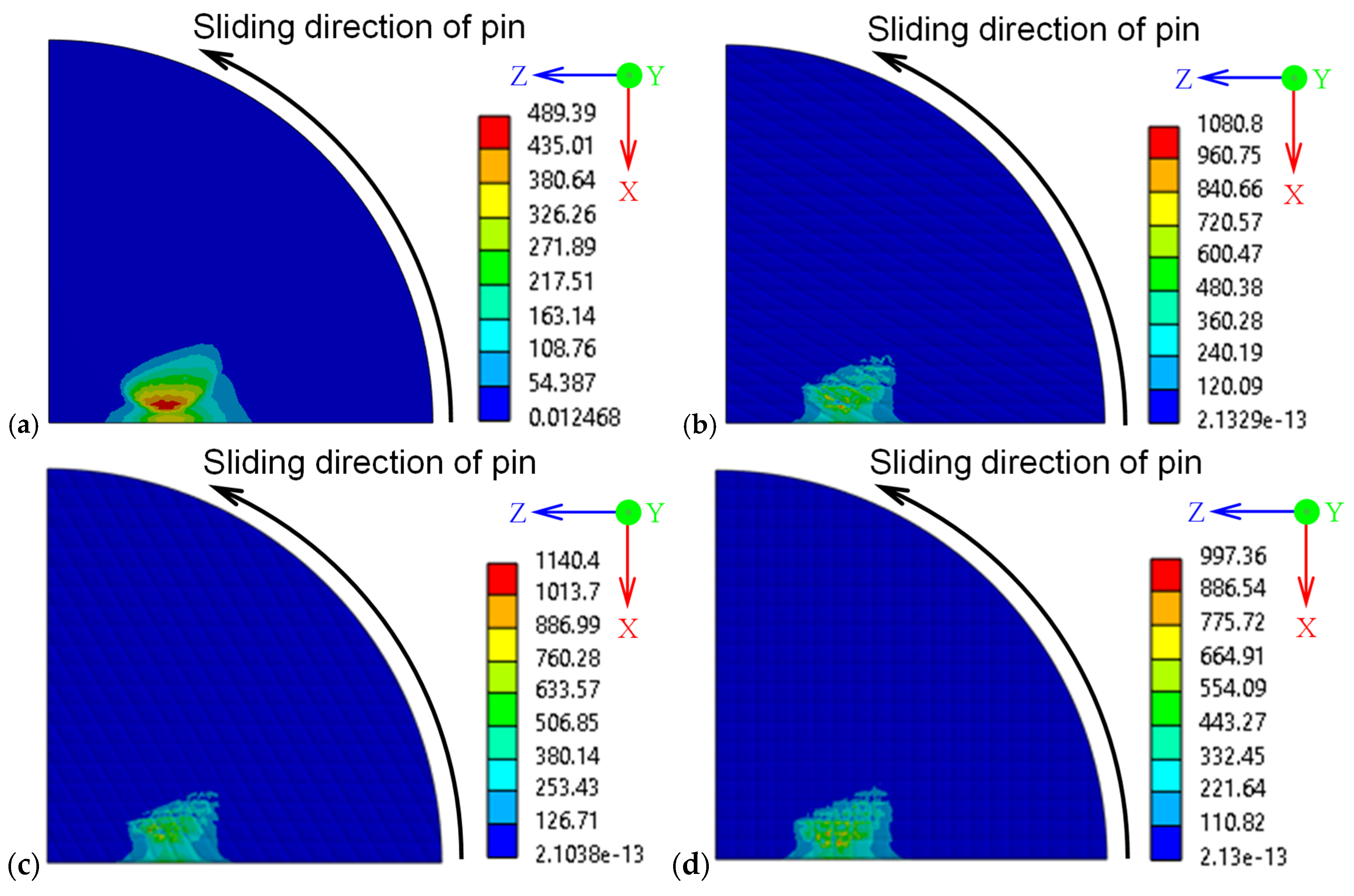
3.3.2. Contact Pressure Distribution and Stress Concentration
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- A higher laser power led to a simultaneous increase in the groove width and depth, whereas increasing the number of passes primarily increased the groove depth with minimal influence on the groove width. The numerical predictions closely matched the experimental measurements, confirming the reliability of the predictive model for the groove geometry.
- (2)
- Laser processing at 20 W with three passes produced grooves with an average width of 115.62 μm and a depth of 15.07 μm, resulting in an aspect ratio of 0.13, which is close to the target value of 0.1 with minimal variation.
- (3)
- Among the tested geometries, the 60° crosshatch pattern achieved the lowest average coefficient of friction of 0.111, representing a 25% reduction compared with the untextured surface, which had a coefficient of 0.148. It was also superior to the 30° pattern, which had a coefficient of 0.127, and the 90° pattern, which recorded a coefficient of 0.112.
- (4)
- Variations in the crosshatch angle produced small differences in the total contact area but significantly affected the distribution of flat contact zones. A more uniform and well-distributed flat contact area contributed to the improved friction performance.
- (5)
- Pin-on-disc testing over a sliding distance of 500 m showed no measurable material loss from the SKH51 surface, with only minor surface scratching observed.
- (6)
- Finite element analysis revealed that laser-textured surfaces disrupted the uniform pressure distribution of the untextured surfaces, producing heterogeneous, localized high-pressure zones along the groove edges. Increasing the crosshatch angle from 30° to 90° progressively reduced mean contact pressure (118.38 MPa to 109.76 MPa) while maintaining similar overall von Mises stress levels (3156.9–3158.0 MPa). This indicates enhanced load redistribution without compromising the global load-bearing capacity. The 60° and 90° crosshatch patterns provided the most balanced combination of reduced mean pressure and controlled stress localization, which may reduce the friction in service.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nielsen, C.V.; Bay, N. Review of Friction Modeling in Metal Forming Processes. Journal of materials processing technology 2018, 255, 234–241, . [CrossRef]
- Tamaoki, K.; Manabe, K.; Kataoka, S.; Aizawa, T. Continuous Dry Cylindrical and Rectangular Deep Drawing by Electroconductive Ceramic Dies. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering 2013, 135, . [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Mori, K.; Hatashita, F.; Shiba, T.; Daodon, W.; Osakada, K. Improvement of Seizure Resistance in Ironing of Stainless Steel Cup with Cermet Die Having Fine Lubricant Pockets. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2016, 234, 195–207, . [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Bai, L.; Zhou, R.; Fan, X.; Kang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, K. Recent Progress on Wear-Resistant Materials: Designs, Properties, and Applications. Advanced Science 2021, 8, 2003739, . [CrossRef]
- Hacisalihoglu, I.; Yildiz, F.; Alsaran, A. Wear Performance of Different Nitride-Based Coatings on Plasma Nitrided AISI M2 Tool Steel in Dry and Lubricated Conditions. Wear 2017, 384-385, 159–168, . [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kaur, M.; Joseph, A.; Jhala, G. Surface Engineering Analysis of Plasma-Nitrided Die Steels. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology 2019, 234, 917–931, . [CrossRef]
- Podgornik, B.; Hogmark, S.; Sandberg, O. Proper Coating Selection for Improved Galling Performance of Forming Tool Steel. Wear 2006, 261, 15–21, . [CrossRef]
- Daodon, W.; Premanond, V.; Wongpisarn, W.; Niranatlumpong, P. Vanadium Nitride and Titanium Nitride Coatings for Anti-Galling Behavior in Ironing of Aluminum Alloy Cups. Wear 2015, 342-343, 279–287, . [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T. Approaches for Preventing Tool Wear in Sheet Metal Forming Processes. Machines 2023, 11, 616–616, . [CrossRef]
- Bay, N.; Azushima, A.; Groche, P.; Ishibashi, I.; Merklein, M.; Morishita, M.; Nakamura, T.; Schmid, S.; Yoshida, M. Environmentally Benign Tribo-Systems for Metal Forming. CIRP Annals 2010, 59, 760–780, . [CrossRef]
- Adamus, J.; Więckowski, W.; Lacki, P. Analysis of the Effectiveness of Technological Lubricants with the Addition of Boric Acid in Sheet Metal Forming. Materials 2023, 16, 5125, . [CrossRef]
- Gachot, C.; Rosenkranz, A.; Hsu, S.M.; Costa, H.L. A Critical Assessment of Surface Texturing for Friction and Wear Improvement. Wear 2017, 372-373, 21–41, . [CrossRef]
- Dhage, S.; Jayal, A.D.; Sarkar, P. Effects of Surface Texture Parameters of Cutting Tools on Friction Conditions at Tool-Chip Interface during Dry Machining of AISI 1045 Steel. Procedia Manufacturing 2019, 33, 794–801, . [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Wang, D.; Wu, S.; Qi, H.; Saetang, V. Investigation on Turning of Inconel 718 Using Differently Coated Microtextured Tools. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part E Journal of Process Mechanical Engineering 2023, . [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I. State of the Art in Laser Surface Texturing. Journal of Tribology 2005, 127, 248, . [CrossRef]
- Costa, H.L.; Hutchings, I.M. Effects of Die Surface Patterning on Lubrication in Strip Drawing. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2009, 209, 1175–1180, . [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yang, H. The Effect of Surface Texturing on Reducing the Friction and Wear of Steel under Lubricated Sliding Contact. Applied Surface Science 2013, 273, 199–204, . [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.W.; Shin, H.S.; Kwon, M.H.; Kim, B.H.; Chu, C.N. Surface Texturing by Micro ECM for Friction Reduction. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing 2010, 11, 747–753, . [CrossRef]
- Costa, H.; Hutchings, I. Some Innovative Surface Texturing Techniques for Tribological Purposes. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology 2014, 229, 429–448, . [CrossRef]
- Mankeekar, T.; Bähre, D.; Durneata, D.; Hall, T.; Lilischkis, R.; Natter, H.; Saumer, M. Fabrication of Micro-Structured Tools for the Production of Curved Metal Surfaces by Pulsed Electrochemical Machining. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2021, 119, 2825–2833, . [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Han, J.; Saetang, V.; Xu, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhou, J. Fabrication of Oxide-Free Dimple Structure on Germanium via Electrochemical Jet Machining Enhanced by Opposing Laser Irradiation. Journal of Manufacturing Processes 2022, 85, 623–635, . [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Jain, V.K.; Ramkumar, J. Micro-Texturing on Flat and Cylindrical Surfaces Using Electric Discharge Micromachining. Journal of Micromanufacturing 2020, 4, 127–137, . [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Shi, L.; Huang, W.; Wang, X. A Multi-Phase Micro-Abrasive Jet Machining Technique for the Surface Texturing of Mechanical Seals. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2016, 86, 2047–2054, . [CrossRef]
- Kasem, H.; Stav, O.; Grützmacher, P.; Gachot, C. Effect of Low Depth Surface Texturing on Friction Reduction in Lubricated Sliding Contact. Lubricants 2018, 6, 62–62, . [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Siddaiah, A.; Liao, Y.; Menezes, P.L. Laser Surface Texturing and Related Techniques for Enhancing Tribological Performance of Engineering Materials: A Review. Journal of Manufacturing Processes 2020, 53, 153–173, . [CrossRef]
- Daodon, W.; Saetang, V. Improvement of Frictional Property of AISI D2 Tool Steel Surface against JIS SPFC 980Y Advanced High-Strength Steel by Using Laser Texturing Process. Lubricants 2023, 11, 68–68, . [CrossRef]
- Kovalchenko, A.; Ajayi, O.; Erdemir, A.; Fenske, G.; Etsion, I. The Effect of Laser Surface Texturing on Transitions in Lubrication Regimes during Unidirectional Sliding Contact. Tribology International 2005, 38, 219–225, . [CrossRef]
- Ryk, G.; Etsion, I. Testing Piston Rings with Partial Laser Surface Texturing for Friction Reduction. Wear 2006, 261, 792–796, . [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Geng, P.; Ma, N. Effect of Nanosecond Pulsed Laser Parameters on Texturing Formation of Metallic Surface: Experiment and Modelling. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2023, 26, 7775–7788, . [CrossRef]
- Fouathiya, A.; Meziani, S.; Sahli, M.; Barrière, T. Experimental Investigation of Microtextured Cutting Tool Performance in Titanium Alloy via Turning. Journal of Manufacturing Processes 2021, 69, 33–46, . [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Braun, D.; Greiner, C. Laser Textured Surfaces for Mixed Lubrication: Influence of Aspect Ratio, Textured Area and Dimple Arrangement. Lubricants 2017, 5, 32, . [CrossRef]
- Geiger, M.; Popp, U.; Engel, U. Excimer Laser Micro Texturing of Cold Forging Tool Surfaces - Influence on Tool Life. CIRP Annals 2002, 51, 231–234, . [CrossRef]
- Wakuda, M.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kanzaki, S.; Yasuda, Y. Effect of Surface Texturing on Friction Reduction between Ceramic and Steel Materials under Lubricated Sliding Contact. Wear 2003, 254, 356–363, . [CrossRef]
- Popp, U.; Engel, U. Microtexturing of Cold-Forging Tools - Influence on Tool Life. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture 2006, 220, 27–33, . [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.; Völkl, R.; Engel, U. Tool Life Enhancement in Cold Forging by Locally Optimized Surfaces. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2008, 201, 2–8, . [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; zhou, R.; Davis, T.; Cao, J.; Wang, Q.Jane.; Hua, D.; Liu, J. Study on Effect of Dimples on Friction of Parallel Surfaces under Different Sliding Conditions. Applied Surface Science 2010, 256, 2863–2875, . [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Bai, F.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Q. Angle-Dependent Lubricated Tribological Properties of Stainless Steel by Femtosecond Laser Surface Texturing. Optics and Laser Technology 2016, 81, 60–66, . [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tian, L.; Zheng, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Z. The Synergetic Effects of Laser Texturing and Super-Hydrophobic Coatings on Improving Wear Properties of Steel. Tribology International 2022, 173, 107657–107657, . [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yuan, C.; Guo, Z.; Huang, Q. Effect of the Groove Parameters on the Lubricating Performance of the Water-Lubricated Bearing under Low Speed. Wear 2023, 522, 204708–204708, . [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Deng, J.; Duan, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G. Modifying Tribological Performances of AISI 316 Stainless Steel Surfaces by Laser Surface Texturing and Various Solid Lubricants. 2019, 109, 401–411, . [CrossRef]
- Segu, D.Z.; Chae, Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, C.-L. Synergistic Influences of Laser Surface Texturing and ZrO2-MoDTC Hybrid Nanofluids for Enhanced Tribological Performance. Tribology international 2023, 183, 108377–108377, . [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Pang, X.; Yue, S.; Shangguan, B.; Zhang, Y. The Friction and Wear Behavior of Laser Textured Surfaces in Non-Conformal Contact under Starved Lubrication. Wear 2021, 476, 203723–203723, . [CrossRef]
- Phun, C.; Daodon, W.; Septham, K.; Kumkhuntod, P.; Zhu, H.; Saetang, V. Laser-Fabricated Micro-Dimples for Improving Frictional Property of SKH51 Tool Steel Surfaces. Lubricants 2023, 11, 456–456, . [CrossRef]
- Online Materials Information Resource – MatWeb. Available online: http://www.matweb.com (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- Karunathilaka, N.; Tada, N.; Uemori, T.; Hanamitsu, R.; Kawano, M. Effect of Contact Pressure Applied on Tool Surface during Cold Forging on Fatigue Life of Tool Steel. Procedia Manufacturing 2018, 15, 488–495, . [CrossRef]
- Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels, and High-Performance Alloys, vol. 1 in: Metals Handbook, 10th Ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1990.
- Torres Pérez, A.; García-Atance Fatjó, G.; Hadfield, M.; Austen, S. A Model of Friction for a Pin-On-Disc Configuration with Imposed Pin Rotation. Mechanism and Machine Theory 2011, 46, 1755–1772, . [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I.; Halperin, G.; Brizmer, V.; Kligerman, Y. Experimental Investigation of Laser Surface Textured Parallel Thrust Bearings. Tribology Letters 2004, 17, 295–300, . [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Sugiura, M.; Ando, T.; Kumkhuntod, P.; Septham, K.; Daodon, W.; Mori, K. Improvement of Seizure Resistance in Ironing of Aluminum Alloy Sheets and Stainless Steel Cups by Utilizing Laser Textured Die Having Lubricant Pockets. Metals 2023, 13, 803–803, . [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Vorholt, J.; Yang, M. Lubrication Analysis of Micro-Dimple Textured Die Surface by Direct Observation of Contact Interface in Sheet Metal Forming. Metals 2019, 9, 917, . [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, X. Orientation Effects of Micro-Grooves on Sliding Surfaces. Tribology International 2011, 44, 1047–1054, . [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Huang, W. Design Principles for the Area Density of Dimple Patterns. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology 2014, 229, 538–546, . [CrossRef]

| Properties | JIS SKH51 | AISI 304 | ||||||||||
| Modulus of elasticity (GPa) | 207 | 193 | ||||||||||
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.29 | 0.29 | ||||||||||
| Densities (10-3g/mm3) | 8.14 | 8.00 | ||||||||||
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 2,302 | 505 | ||||||||||
| Yield strength (MPa) | 1,600 | 215 | ||||||||||
| Hardness (HV) | 783 | 129 | ||||||||||
| Chemical composition (wt.%) | ||||||||||||
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | W | V | Ni | |||
| JIS SKH51 | 0.80-0.88 | max 0.45 | max 0.40 | max 0.03 | max 0.03 | 3.8−4.5 | 4.7−5.2 | 5.9−6.7 | 1.7-2.1 | - | ||
| AISI 304 | 0.08 | 0.60 | 1.50 | - | - | 18.5 | - | - | - | 10 | ||
| Parameter | Value |
| Laser wavelength (nm) | 1064 |
| Laser pulse duration, τ (ns) | 100 |
| Laser pulse repetition rate, f (kHz) | 100 |
| Laser scanning speed, v (mm/s) | 10 |
| Laser beam diameter at 1/e2(μm) | 100 |
| Average laser power, P (W) | 10, 15, 20 and 25 |
| Number of passes, n | 1 and 3 |
| Friction test | |
| Disk material | JIS SKH51 |
| Pin material | AISI 304 |
| Sliding speed (mm/s) | 150 |
| Sliding distance (m) | 500 |
| Groove densities (%) | 36 |
| Crosshatch angle (°) | 30, 60 and 90 |
| Normal load (N) | 10 |
| Total number of elements | von Mises stress (MPa) | Error (%) |
| 24,231 | 4,103.28 | - |
| 32,120 | 3,791.26 | 8.230 |
| 41,234 | 3,532.67 | 7.320 |
| 54,231 | 3,322.68 | 6.320 |
| 73,425 | 3,157.84 | 5.220 |
| 143,294 | 3,157.80 | 0.001 |
| Crosshatch angles (°) | Average von Mises stress (MPa) | Average pressure (MPa) |
| Untextured | 3156.9 | 118.38 |
| 30 | 3157.8 | 114.39 |
| 60 | 3157.9 | 111.93 |
| 90 | 3158.0 | 109.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





