1. Introduction
Tourism is one of the important sectors in regional economic development because it provides a direct impact on community income, job creation, and infrastructure improvement. Mentawai Islands, as one of the mainstay tourist destinations in Indonesia, has great potential in attracting domestic and foreign tourists. Various tourist attractions such as the unique culture of the Mentawai tribe, breathtaking natural beauty, and world-class surfing activities make the Mentawai Islands a desirable destination. However, despite the significant potential, tourist loyalty is still a major challenge in an effort to increase tourist visits in a sustainable manner. Destination image plays an important role in building tourist loyalty. According to Kotler and Keller (2012), destination image is a collective perception formed in the minds of tourists based on the experience or information received. A positive destination image can increase tourists' intention to return to visit and recommend destinations to others (Prayag & Ryan, 2012). Destination image is a perception formed in the minds of tourists about a place that is influenced by various factors, including personal experience, media, and information received. The Mentawai people, with their unique culture, nature, and traditions, offer a destination that has a strong image, both domestically and internationally. This distinctive Mentawai destination image is closely related to its customs, natural beauty, and the growing development of the tourism sector. Destination image is the perception or picture that tourists have of a tourist destination, which is formed from personal experience, information received, and socio-cultural influences. Meanwhile, tourist attraction includes various elements that make the destination attractive to tourists, whether in the form of natural beauty, local culture, or facilities provided.
Mentawai's destination image is shaped by its natural wealth and unique culture. Rapidly growing tourism in Mentawai provides a positive impact in terms of economy, but also presents challenges to the preservation of local culture. Therefore, sustainable tourism management needs to be considered by prioritizing cultural and environmental preservation. Recommendations for tourism management in Mentawai are to increase the involvement of local communities in every aspect of tourism management, as well as maintaining a balance between economic development and cultural preservation. In addition to destination image, tourism attraction is also an important element that influences the tourist experience. According to Gunn (2011), tourist attractions include the physical, cultural, and unique experience aspects that destinations provide. Attractions that are authentic and maintained in quality can strengthen the emotional connection between tourists and destinations, which ultimately impacts tourist loyalty (Kim et al., 2013). The Mentawai Islands Regency, located in West Sumatra, is one of the growing tourist destinations in Indonesia. With its natural beauty, exotic beaches, and unique culture, Mentawai has great potential in attracting domestic and international tourists. However, to maintain and increase tourist visits, a deep understanding of the factors that influence tourist loyalty is required. The two main factors of concern in this research are destination image and tourist attraction.
Mentawai has a very strong appeal, both in terms of nature and culture. Its natural beauty, including its famous beaches and surf breaks, and the cultural life that is still strongly maintained by the local community, make Mentawai a unique tourist destination. Nonetheless, sustainable tourism management is essential to maintain these attractions. In Mentawai Islands, the development of destination image and tourist attraction faces several challenges, such as limited infrastructure, lack of promotion, and accessibility constraints. This study aims to analyze the influence of destination image and tourist attraction on tourist loyalty, with the hope of providing strategic recommendations for more effective tourism management. Mapping the current state of knowledge about the emerging synthetic world in the hospitality sector, this research aims to do the following:
RO1: Analyzing the effect of destination image on tourist loyalty in the Mentawai Islands Regency.
RO2: Identifying the effect of tourist attraction on tourist loyalty in the Mentawai Islands Regency.
RO3: Examine the simultaneous relationship between destination image and tourist attraction with tourist loyalty in the Mentawai Islands Regency.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Destination Image
The Role of Culture in Destination Image Formation Local culture has an important role in shaping destination image. According to Harrison & Dube (2012), cultural experiences, such as local customs and traditions, serve as one of the factors that attract tourists to visit a place. In Mentawai, the rich indigenous culture, including the kinship system and traditional ceremonies, becomes an important element that influences the image of the destination. This is in accordance with the findings of Cohen (2012) who emphasized that destinations with authentic culture often attract more tourists who seek an immersive cultural experience. Alcocer and Ruiz (2020) discussed the cognitive and affective components shaping destination image perceptions. Tourism Development in Mentawai Mentawai tourism has grown rapidly in recent decades, particularly since the discovery of Mentawai's islands as world-renowned surfing locations. According to Borchers & Schott (2017), nature-based tourism, such as surfing and ecotourism, contributes greatly to Mentawai's image as a tourist destination. However, this development cannot be separated from the challenges of preserving local culture and the impact on the socio-economy of the local community. Tourism's Impact on Destination Image Tourism in Mentawai, although giving positive impacts in terms of economy, also brings challenges to the destination image, especially in the context of cultural preservation. Jenkins & McCarthur (2020) argue that poorly managed tourism can lead to cultural erosion, where traditional elements may lose their original meaning to meet the demands of tourists. Therefore, it is important for governments and local communities to manage tourism sustainably.
2.2. Tourist Attractions
Tourist attractions, both natural and man-made, are an important factor in attracting visitors. Unique attractions, such as natural beauty, cultural diversity, or recreational facilities, provide a more memorable experience and influence tourists' decision to return to a particular destination. Research shows that tourist attractions have a significant impact on visiting decisions and tourist satisfaction (Dayrobi & Raharjo, 2020). Natural Attractions and Nature-Based Tourism Mentawai's natural attractions, especially in terms of beaches and surf waves, make the islands one of the main destinations for international surfers. According to Dawson et al. (2013), destinations with unique natural attractions often attract travelers seeking unspoiled nature experiences. Kim and Kim (2018) emphasized the role of perceived value and destination experience as antecedents of loyalty. The surf breaks in Mentawai, such as in Sipora Island, are already known among the world's surfers as one of the best. This phenomenon is matched by the unindustrialized natural beauty, which gives a natural and pristine impression. Local Culture as an Attraction In addition to the natural attraction, the cultural richness of the Mentawai people is also a major factor in shaping the attractiveness of the destination. Tung et al. (2020) argue that local culture, especially with regard to customs and social systems, provides an additional dimension of interest for tourists seeking authentic cultural experiences. In Mentawai, traditions such as a strict kinship system, traditional rituals such as Arat Sabulungan, and daily life that is still connected to nature, provide a very distinctive experience for tourists. According to Richards & Wilson (2014), local culture often attracts tourists who seek depth in understanding the traditions and way of life of local communities.
Sustainable Tourism Management and its Impact on Attractiveness where the good management of natural resources and local culture becomes very important in maintaining the attractiveness of Mentawai as a tourist destination. Sharpley (2014) revealed that community-based and sustainable tourism management can help maintain existing natural and cultural attractions without damaging the environment or culture itself. In Mentawai, nature-based tourism such as surfing and ecotourism, which prioritizes environmental preservation, is a growing model. However, this must be balanced with an awareness of the importance of maintaining a balance between economic development and cultural and environmental preservation. Mentawai's Attractiveness in the Context of International Tourism Mentawai's attractiveness is also reflected in the international recognition of its natural beauty. According to Kusumaningrum (2018), Mentawai tourism has become part of the global trend in terms of ecotourism and adventure. Besides surfing, the biodiversity in Mentawai, including tropical forests and distinctive fauna, adds to the attraction of tourists who come to explore the rich ecosystem.
2.3. Traveler Loyalty
Tourist loyalty is defined as tourists' loyalty to a destination or service provider, which is reflected in their repeated behavior to visit or use the service. Kim et al. (2010) stated that tourist loyalty consists of two main dimensions: affective loyalty (positive feelings towards the destination or service) and conative loyalty (desire to return or recommend the destination or service to others). Factors Affecting Tourist Loyalty can be with several influencing factors that have been identified in the literature. According to Jang & Feng (2012), the main factors that influence traveler loyalty include customer satisfaction, enjoyable travel experiences, service quality, and competitive prices. Traveler satisfaction is the dominant factor in creating loyalty, because when travelers are satisfied with their experience, they are more likely to return. Lee et al. (2014) also emphasized the importance of experience quality that includes aspects of natural beauty, adequate facilities, and positive social interactions during the trip. Traveler Loyalty Model In the loyalty model, Oliver (2010) developed a model that distinguishes three stages in the formation of loyalty: cognitive, affective, and conative. The cognitive stage includes the initial assessment of the tourist experience, the affective stage is the emotional evaluation formed based on the experience, and the conative stage is the behavior that reflects the intention to return or recommend the destination. This research shows that the stronger the positive feelings towards the destination, the higher the likelihood of tourists becoming loyal. Stylidis et al. (2017) proposed that cognitive and affective image components jointly predict tourist attitudes. Loyalty and Social Media In today's digital era, social media has a very important role in shaping traveler loyalty. Xie & Chen (2016) showed that tourist recommendations or testimonials posted on social media can influence other tourists' decisions in choosing a destination. In addition, direct interaction with destination managers through digital platforms can also strengthen tourist loyalty. Social media allows travelers to share their experiences, which can improve the destination's image and influence loyalty.
Loyalty in the Context of Sustainable Tourism Tourist loyalty is also influenced by awareness of the sustainability and environmental impacts of tourism. According to Hsu et al. (2020), tourists who are aware of environmental issues tend to be more loyal to destinations that implement sustainable tourism practices, such as waste management, nature conservation, and preservation of local culture. This also relates to the Green Loyalty theory, which states that tourists who care about the environment will be more supportive of environmentally friendly destinations. Previous studies have also demonstrated that destination image significantly influences tourist loyalty, as highlighted by Kim et al. (2019). The Role of Travel Experience in Loyalty, Chen & Chen (2015) suggest that memorable experiences during travel can increase traveler loyalty. The experience is not only limited to physical or material aspects, but also includes emotional and psychological experiences that make tourists feel connected to the destination. The deeper the emotional experience felt, the more likely tourists are to become loyal.
2.4. Conceptual Framework
Independent Variable: Destination Image, Dimensions: Reputation, beauty, safety, hospitality, and infrastructure. Theory: Echtner and Ritchie's (1991) destination image model and development by Kavaratzis and Ashworth (2010). Tourism Attraction, Dimensions: Uniqueness of local culture, natural beauty, tourism facilities, and tourism experience. Theory: The concept of tourist attraction by Gunn (1988) refined by Chon (2010). Dependent Variable: Tourist Loyalty, Dimensions: Repeat visit intention, recommendation to others, and satisfaction level. Theory: Customer loyalty model by Oliver (1999) and development in the context of tourism by Oppermann (2000). Destination image influences traveler loyalty directly through positive perceptions of the destination. Tourist attractions contribute to satisfaction and experiences, which strengthen traveler loyalty. The combination of these two independent variables has a synergistic effect on traveler loyalty.
Destination Image: Kavaratzis & Ashworth (2010): The role of branding in enhancing destination image. Qu et al. (2011): The relationship between destination image and tourist loyalty. Xu & Pratt (2018): The impact of emotional and functional image on repeat visit intentions. Tourist Attraction: Chon (2010): Tourist attraction factors in influencing tourist satisfaction. Prayag et al. (2013): Destination uniqueness as an important factor in tourist attraction. Wijaya et al. (2022): Integration of tourist experience and attractiveness as predictors of tourist loyalty. Tourist Loyalty: Oppermann (2000): A repeat visit-based traveler loyalty model. Yoon & Uysal (2015): Satisfaction factor as a mediator between destination image and tourist loyalty. Song et al. (2023): A case study of a remote island destination in building tourist loyalty.
H1: Destination image has a positive and significant effect on tourist loyalty in the Mentawai Islands Regency.
H2: Tourist attraction has a positive and significant effect on tourist loyalty in the Mentawai Islands Regency.
H3: Destination image and tourist attraction together have a positive and significant effect on tourist loyalty in the Mentawai Islands Regency.
Methode
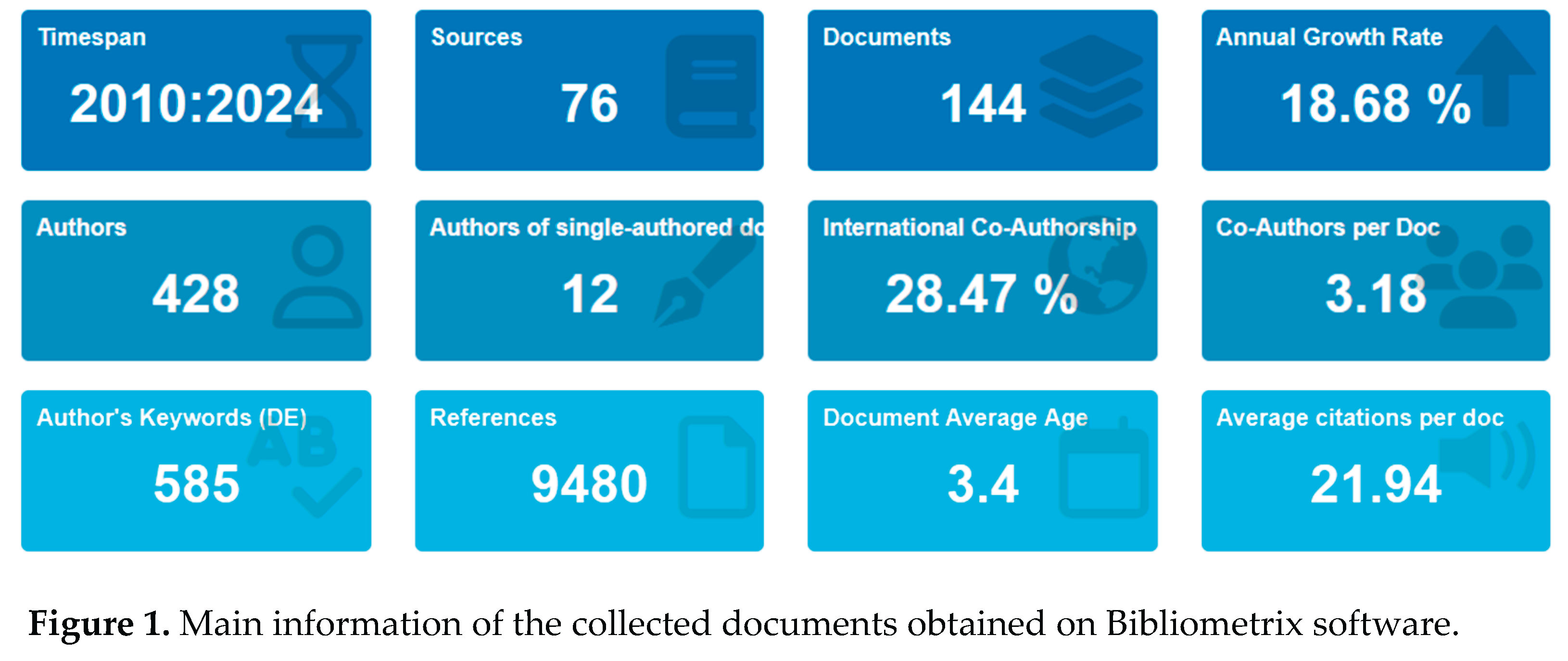
In this study, a total of 144 documents were retrieved from the Scopus database using the keywords "destination image", "tourist attraction", and "loyalty" during the period of 2010 to 2024. These documents originated from 76 different journals, authored by 428 authors, and included 585 keywords. The total number of references analyzed was 9,480. The average age of the documents was 3.4 years, with an average of 21.94 citations per document and 3.18 authors per document. The annual scientific publication growth rate was 18.68%, and the international collaboration ratio (MCP) reached 28.47%.
Data collection was conducted using advanced organizational searches on Scopus indexed journals using the keywords “Destination image” or “Tourist attraction”. This made it possible to narrow the search to article abstracts, titles, and keywords. The studies included in this review were conducted between 2010-2024. In addition, we restricted the inclusion to only final papers (in the publication stage). Data was collected on December 11, 2024; any changes made after that date were not considered in this review. Figure 0 shows an overview of the collected data, which includes 144 documents from 76 sources. Based on the bibliometric data given in the figure, here is a brief explanation, in the Timespan section (2010-2024) this analysis covers data from 2010 to 2024, providing insight into trends over the last 14 years, with 76 unique sources used in this analysis, such as journals, books, or conferences. Documents obtained as many as 144 documents have been analyzed. Then, in terms of Annual Growth Rate (18.68%) as the growth rate of publications each year reached 18.68%, indicating an increase in interest or research activity in this topic. Furthermore, with Authors there are 428 authors who contribute to these works. Authors of Single-Authored there are only 12 documents written by a single author, showing the dominance of collaboration in research. International Co-Authorship (28.47%) where almost 28.5% of the documents involved collaboration of authors from different countries, indicating the international scale of the research. Co-Authors per Doc averaged 3.18 authors per document, indicating a trend towards collaboration in research. Author's Keywords totaling 585 keywords were used, illustrating the main topics and issues that were the focus of this research. References with analysis involved a total of 9,480 references, indicating the scope and depth of the literature review. Document Average Age (3.4 years) as the average document analyzed was 3.4 years old, indicating a focus on current research. Finally, Average Citations per Doc (21.94) where each document averaged 21.94 citations, signifying the significant impact of these works.
This research adopts a bibliometric analysis methodology based on a quantitative approach with a descriptive research design that aims to analyze the influence of destination image and tourist attraction on tourist loyalty in the Mentawai Islands Regency. This research will be conducted by utilizing secondary data obtained from various trusted sources, such as tourism reports, statistical data, academic articles, and previously published surveys Secondary Data Source: Government Tourism Report: Data from the Ministry of Tourism or the local Tourism Office that includes statistics on the number of tourists, tourist profiles, and visitation rates to tourist destinations in the Mentawai Islands Regency. Case Studies and Academic Articles: Research and articles that discuss destination image, tourist attraction, and tourist loyalty in various places relevant to the Mentawai Islands Regency. Tourist Surveys and Polls: Surveys that have been conducted by research institutions or tourism organizations that measure tourist satisfaction and loyalty to the Mentawai Islands destination. Social Media and Online Reviews: Data from review platforms such as TripAdvisor, Google Reviews, and social media that provide information about travelers' perceptions of Mentawai destinations, the image they form, and the attractions they enjoy. The next stage is keyword selection. To select the final keywords to be used, search terms were created based on the research scope of the study as well as based on previous reviews. Therefore, we considered “Destination image,” “Destination image,” “Tourism attraction,” combined with “Loyalty” as the main keywords to search for the required journal data.
Destination Image: Measuring tourists' perception of Mentawai image based on the dimensions of natural beauty, cleanliness, ease of access, and facilities. Tourist Attraction: Assessing factors that influence destination attractiveness, such as beach quality, cultural diversity, adventure activities, and other tourism experiences. Tourist Loyalty: Measuring tourist loyalty through intention to return, recommending the destination, and willingness to try other activities offered in Mentawai. In this research, secondary data will be collected through two main steps: Literature Search: Collecting journal articles, research reports, books, and other sources related to destination image, tourist attraction, and tourist loyalty. Articles and journals relevant to this topic will be selected, particularly those published between 2010 and 2024. Statistical Data Collection: Accessing secondary data available through official reports from the government or research institutions that present statistical information on tourists visiting the Mentawai Islands Regency, as well as survey and poll results related to tourist satisfaction and loyalty.
The data collected was analyzed using bibliometric analysis techniques, vosviewer and descriptive statistical analysis to describe the findings of existing secondary data. The steps taken in data analysis are: Descriptive Analysis: Describes data related to destination image, tourist attraction, and tourist loyalty, including statistics such as the number of tourists, level of satisfaction, and number of positive or negative reviews given. Correlation Analysis: Analyzes the relationship between destination image, tourist attraction, and tourist loyalty based on existing data. This analysis can be done using bibliometric statistical tools to test the correlation between these variables. Trend Analysis: Identifying trends in the data regarding tourist loyalty from year to year, as well as how destination image and tourist attraction play a role in creating tourist loyalty.
Disclaimer : "All bibliometric data were retrieved from Scopus database and were used solely for academic review purposes."
3. Results
In this section, the results regarding the influence of Destination Image and Tourism Attraction on Tourist Loyalty in Mentawai Islands Regency. The most productive countries, journals, and institutions are then analyzed. Finally, important topics are extrapolated from the 144 selected articles using keyword co-occurrence analysis.
3.1. The evolution of Annual Scientific Production
Figure 1 illustrates the evolution of the 144 selected articles retrieved from Scopus. The linear trend shows that, in the last 15 years from 2010 to 2024, scientific production on the topic of Destination Image and Tourist Attraction has increased at a constant pace. To understand the importance of this research topic in recent years, it is imperative to note that 86.80% of all articles (i.e., 125 out of 144 articles) were published in the last seven years i.e. in 2018 to 2024. It is also important to note that 2021 was the most productive year in terms of the number of publications (i.e., 25 articles, representing 17.36% of the total publications) and further growth is expected in 2022 given that 23 articles were published. These findings suggest Destination Image and Tourist Attraction in the context of tourism has recently gained prominence as a topic among academics.
3.2. Most Productive Countries
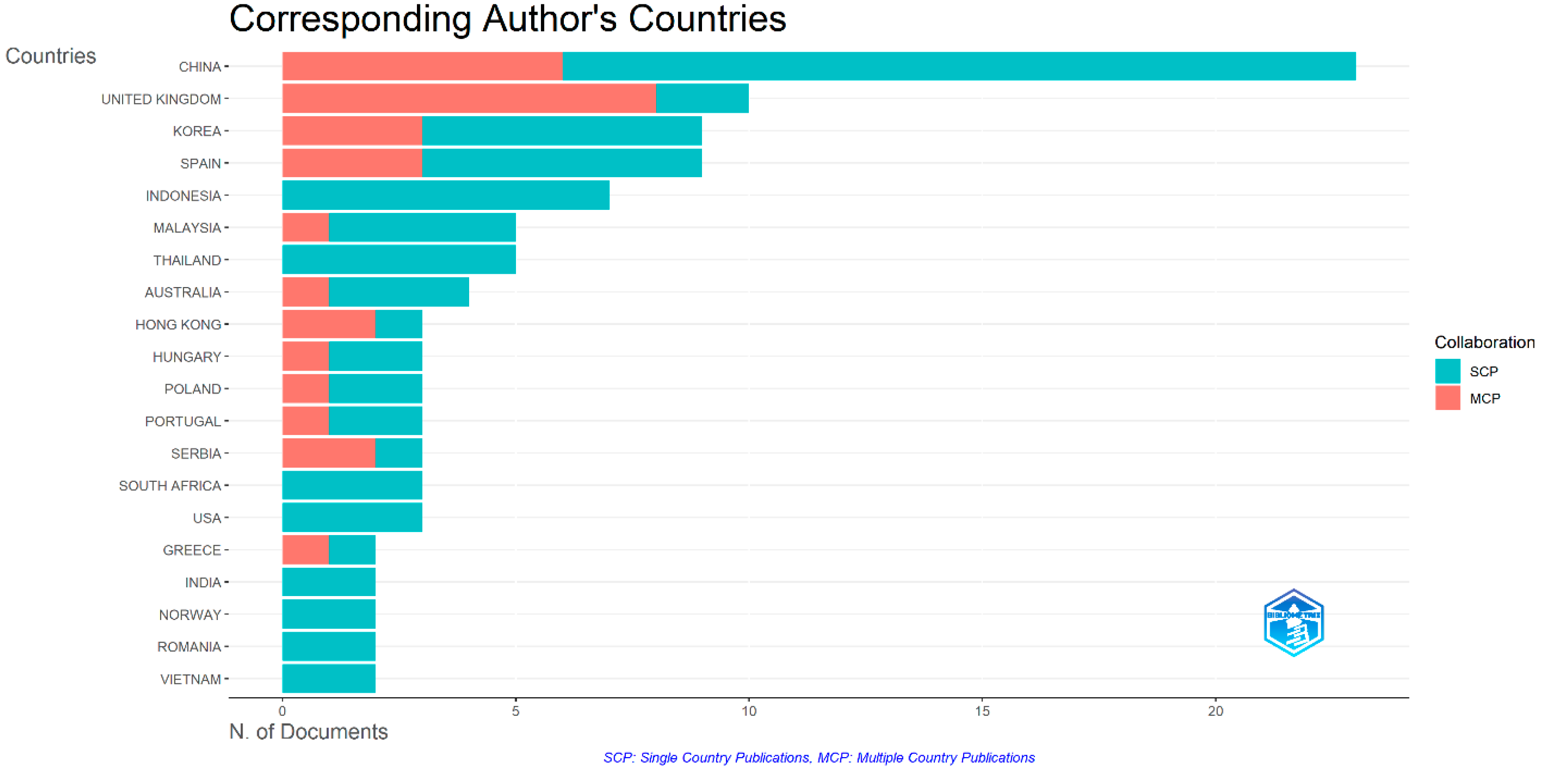
Based on the country of the corresponding author, the total number of articles published per country is shown in
Figure 2. The multiple country publication (MCP) value, represented by the red horizontal column next to each country in the figure, indicates the number of publications produced by authors from that country jointly with their colleagues from different countries. The single country publication (SCP) value, which represents the number of papers published by authors in collaboration with their nationals, is shown in the blue horizontal column. The total number of articles for each country considers both the SCP and MCP values. China is the country that contributed the most articles in this area (23 articles with 16%), followed by the United States (10 articles with 6.9%), Korea (9 articles with 6.3%), and Spain (9 articles with 6.3%), respectively. Further details on these findings are presented in
Table 1.
As shown in
Table 1, China ranks first with the most articles published (i.e., 17 SCPs and 6 MCPs for a total of 23 articles), however, its MCP ratio is not very high. This suggests that academics from China usually prefer to work with colleagues from their own country. The same is true for Indonesia and Thailand, which show the lowest MCP ratio (0). On the other hand, the country with the highest MCP ratio (0.80) is the United States, which comes second in terms of the number of articles. Similarly, Hong Kong appears to have the second highest MCP ratio (0.66), despite being ninth overall based on the number of articles published. Based on their MCP ratios, therefore, authors in the United States and Hong Kong often collaborate with scholars across countries.
3.3. Most Productive Journals
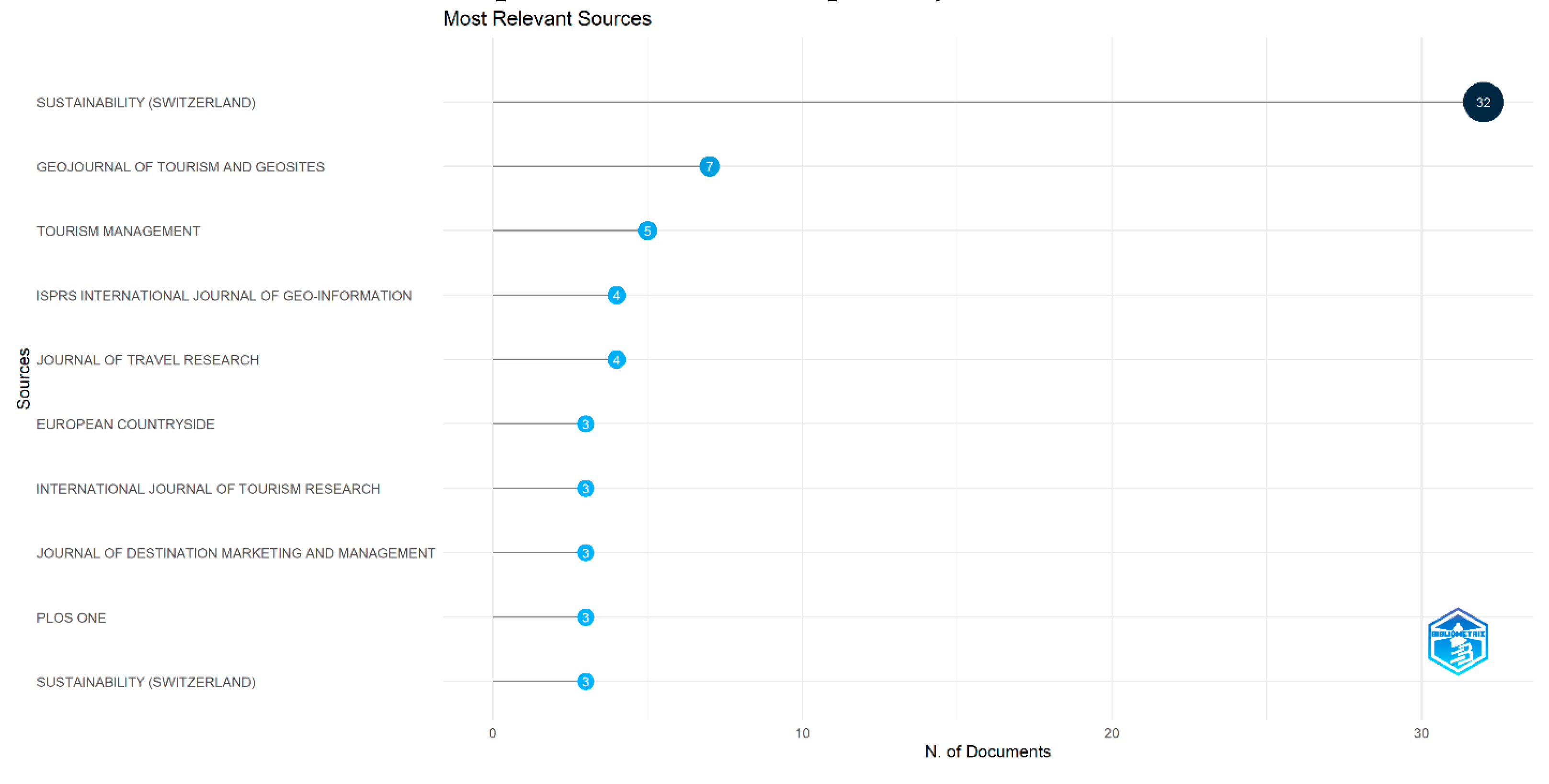
Based on the number of articles published on the topic of Destination Image and Tourism Attraction in tourism, the 10 most productive journals are shown in
Figure 3. After taking a closer look at each of these journals individually, it is clear that the Journal of Sustainability has the most articles published on the subject, with 32 articles in total. The journals with the next highest number of publications are Geojournal of Tourism and Geosites (7 articles); Tourism Management (5 articles). ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information and Journal of Travel Research (4 articles each); European Countryside, International Journal of Tourism Research, Journal of Destination Marketing and management, Plos One had (3 articles each); It is evident that 77.61% of the articles on Destination Image and Tourism Attraction were published in the top five journals.
3.4. Most Productive Authors
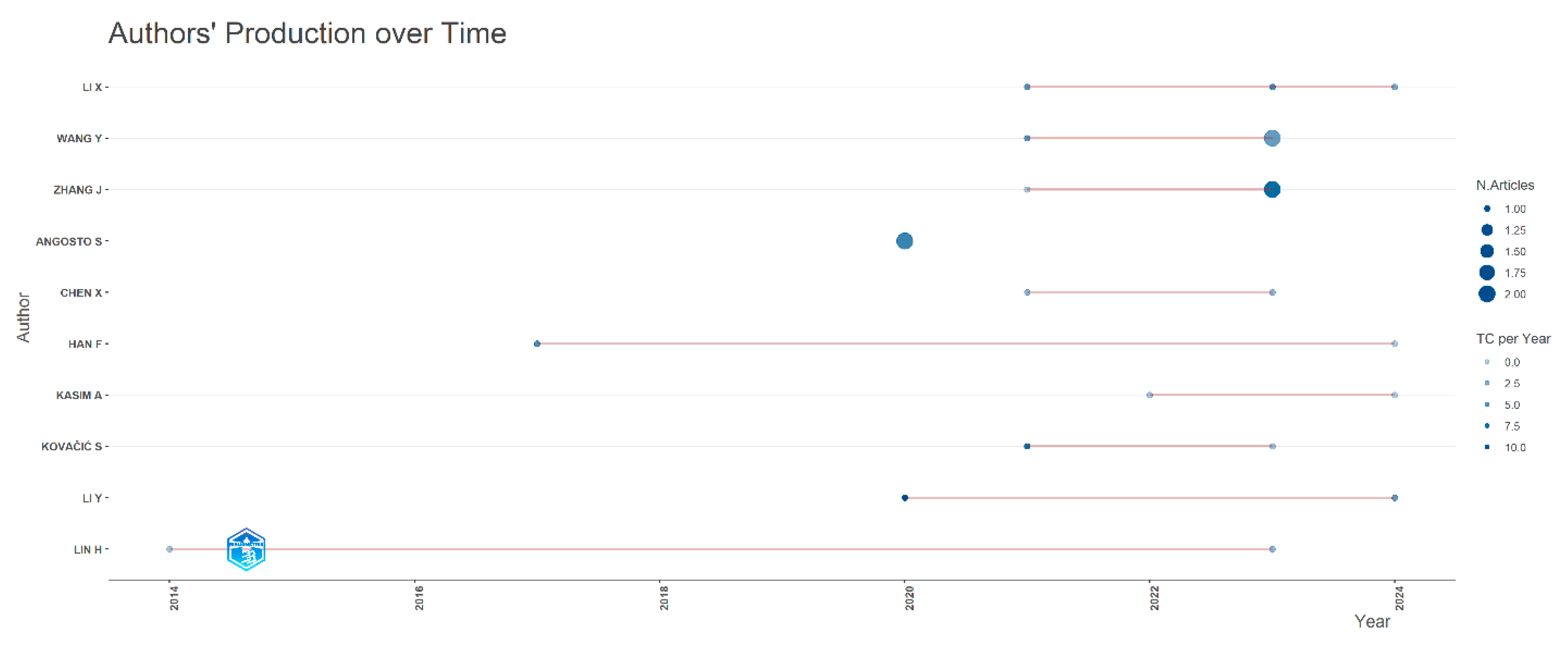
The top 10 authors with the most articles published over time are identified in
Figure 4. The size of the circle reflects the number of articles published in the year, and the darker the circle, the more citations received per year. Thus, it can be seen that the most prolific author in the field of Destination Image and Tourist Attraction in tourism is Zhang J, who contributed 10 articles over time, 6 of which were published in 2023, receiving 10 total citations per year. The next most prolific author is Wang Y, with six articles.
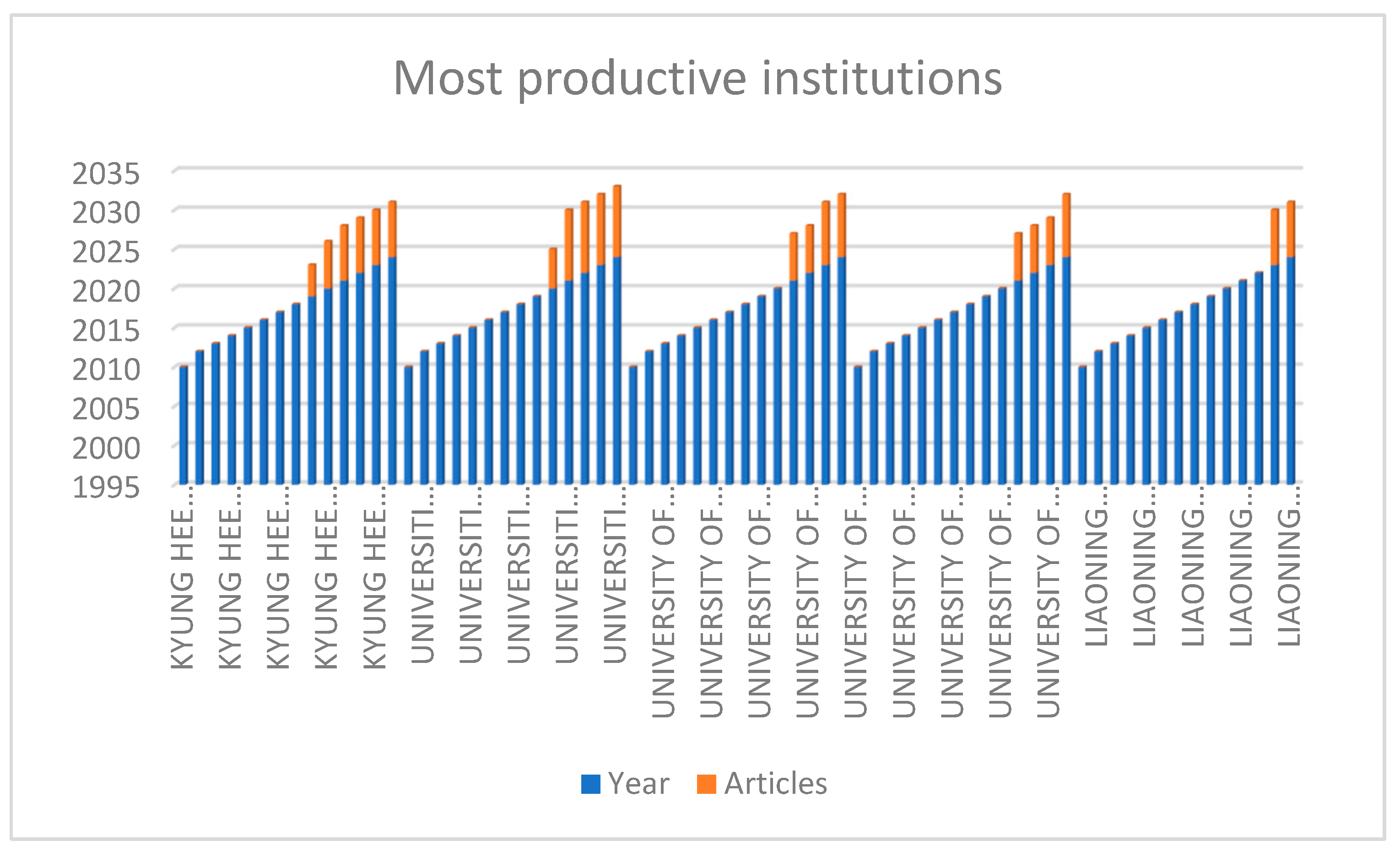
3.5. Most Productive Institutions
Figure 5 shows the number of publications associated with the 10 most productive universities. With 8 and 9 publications respectively, Kyung Hee University and Universiti Malaysia Sarawak lead the way among institutionally affiliated authors. Following closely behind, University of novi sad, University of Oradea, Liaoning University have published a total of 24 articles on Destination Image and Tourist Attractions in the context of tourism.
3.6. Sankey Diagram
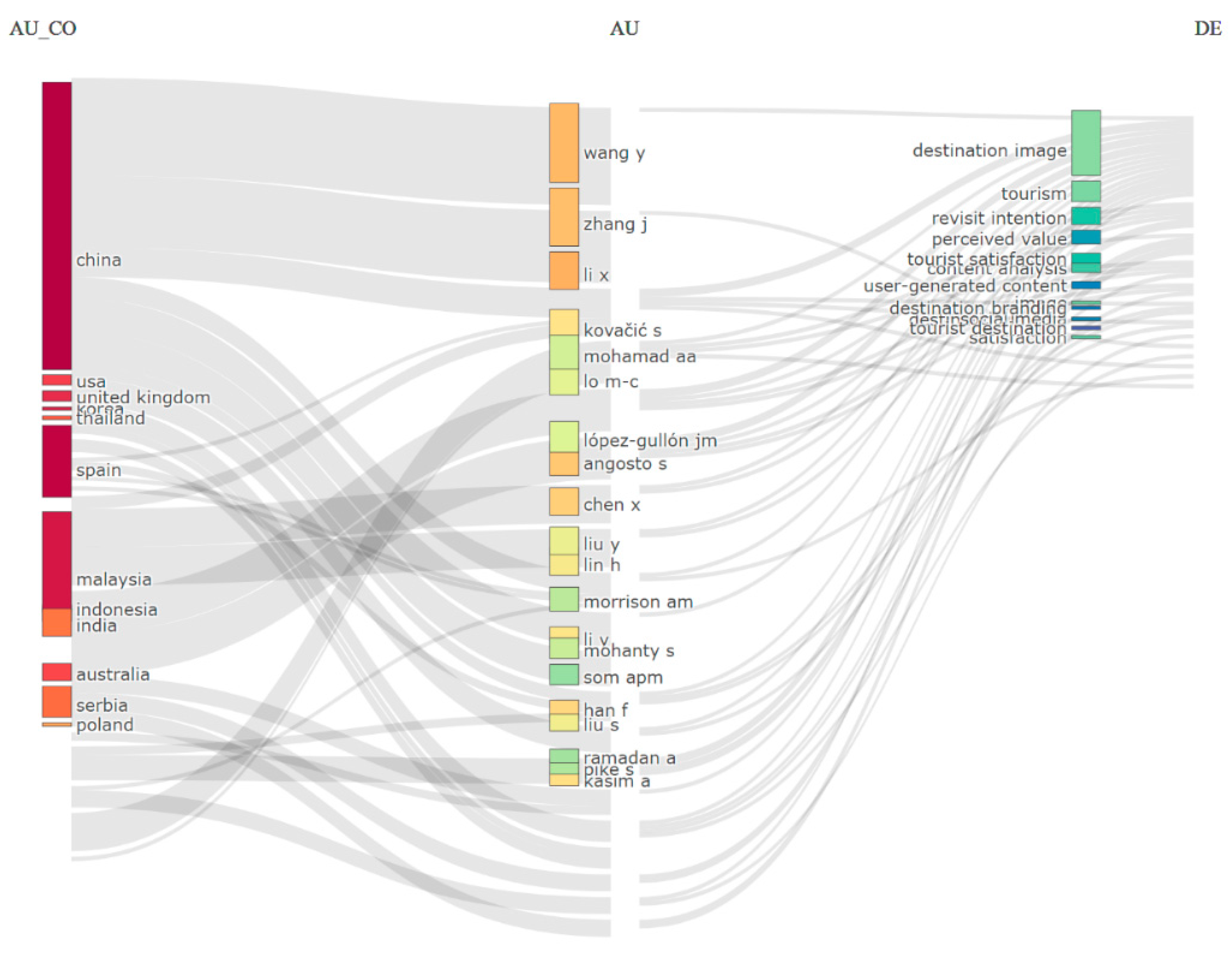
The linkages among the main keywords (or topics), countries, and authors can provide in-depth information.
Figure 6 displays a Sankey diagram (plot analysis of three fields) of literature related to Destination and Attraction Image in the tourism industry. This diagram illustrates the most relevant relationships between the author's country of affiliation (on the left), author (in the center), and article keywords (right). The investigation revealed that the most popular keywords used by authors and relevant countries in the field of Destination Image and Tourism Attraction in the tourism industry. According to
Figure 6, the most popular topics in this field are “Destination image,” “Tourism,” “revisit Intention,” 'perceived value,' 'content analysis,' 'tourist satisfaction,' and 'user-generated content.” The Sankey diagram shows that most of the articles covering these topics were published by authors from China, followed by authors from Spain, and Malaysia, thus confirming the results shown in
Figure 2 and
Table 1.
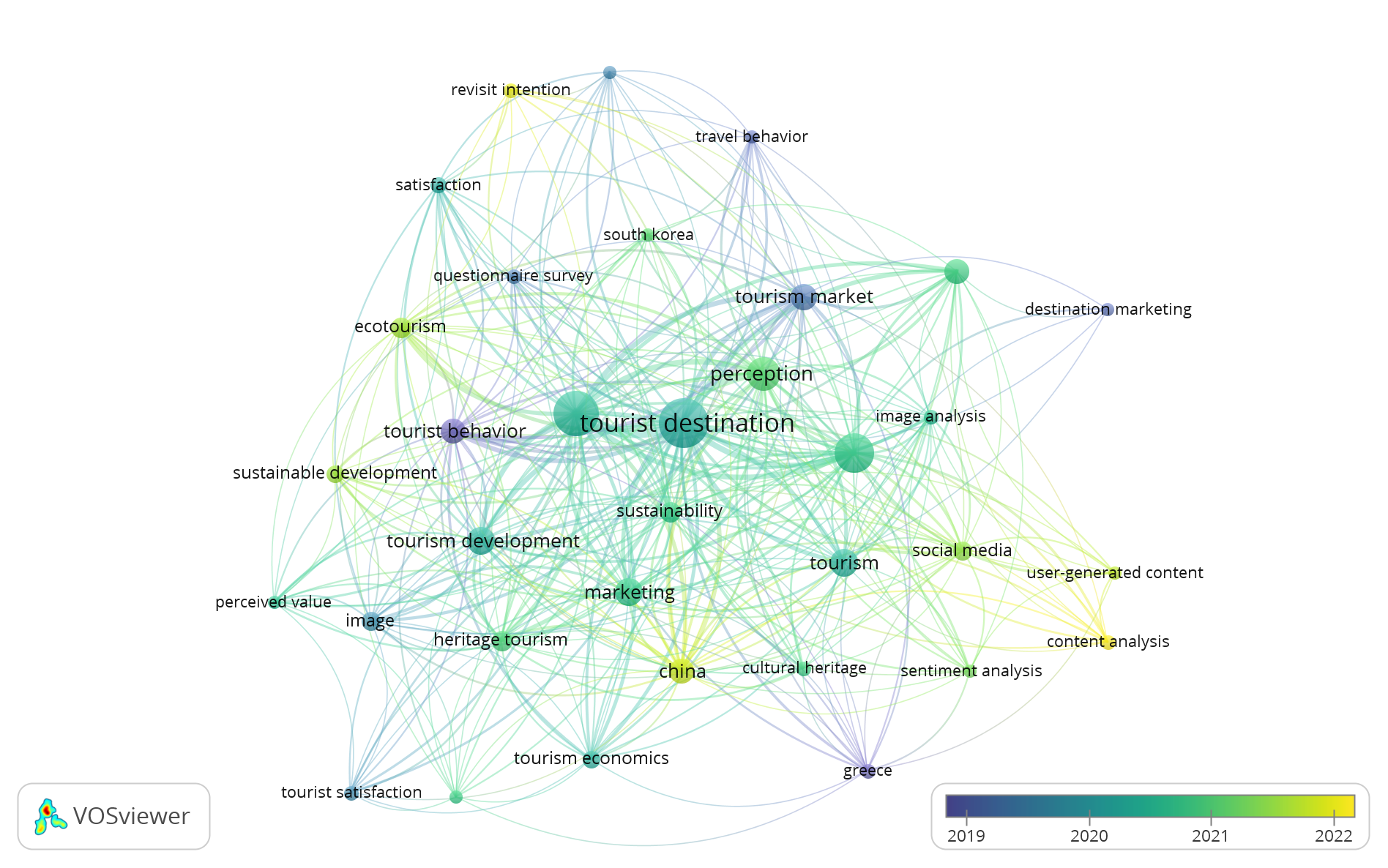
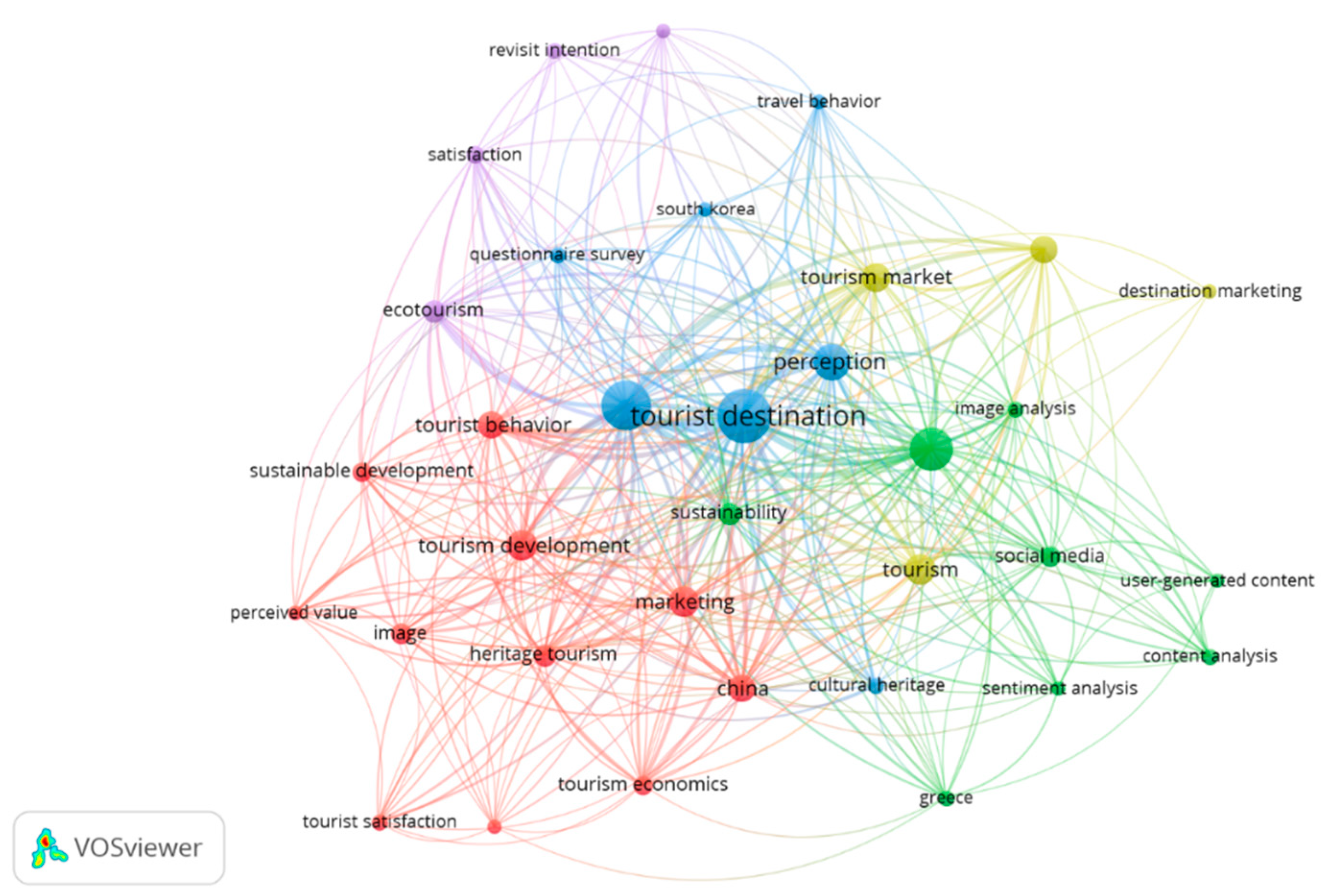
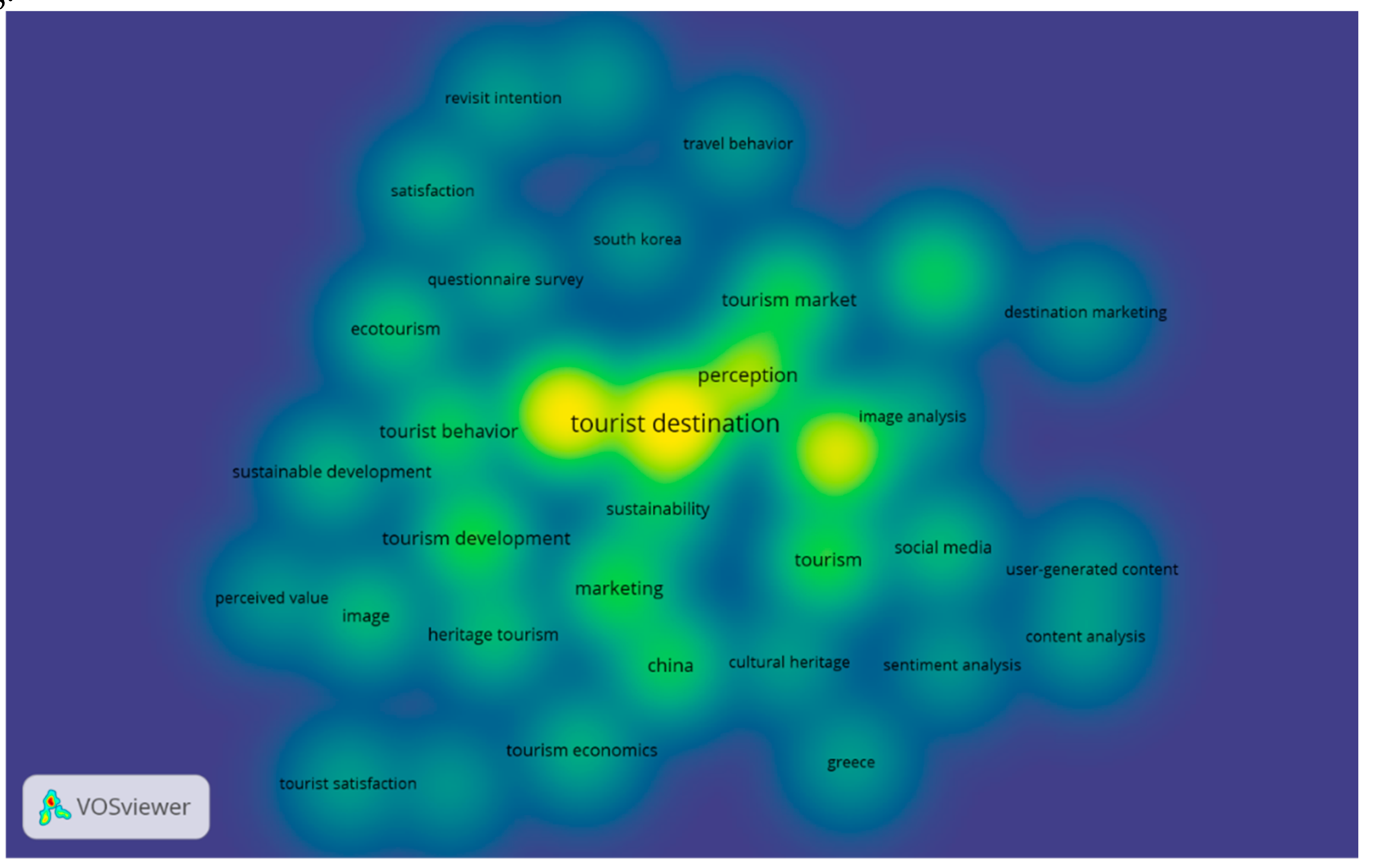
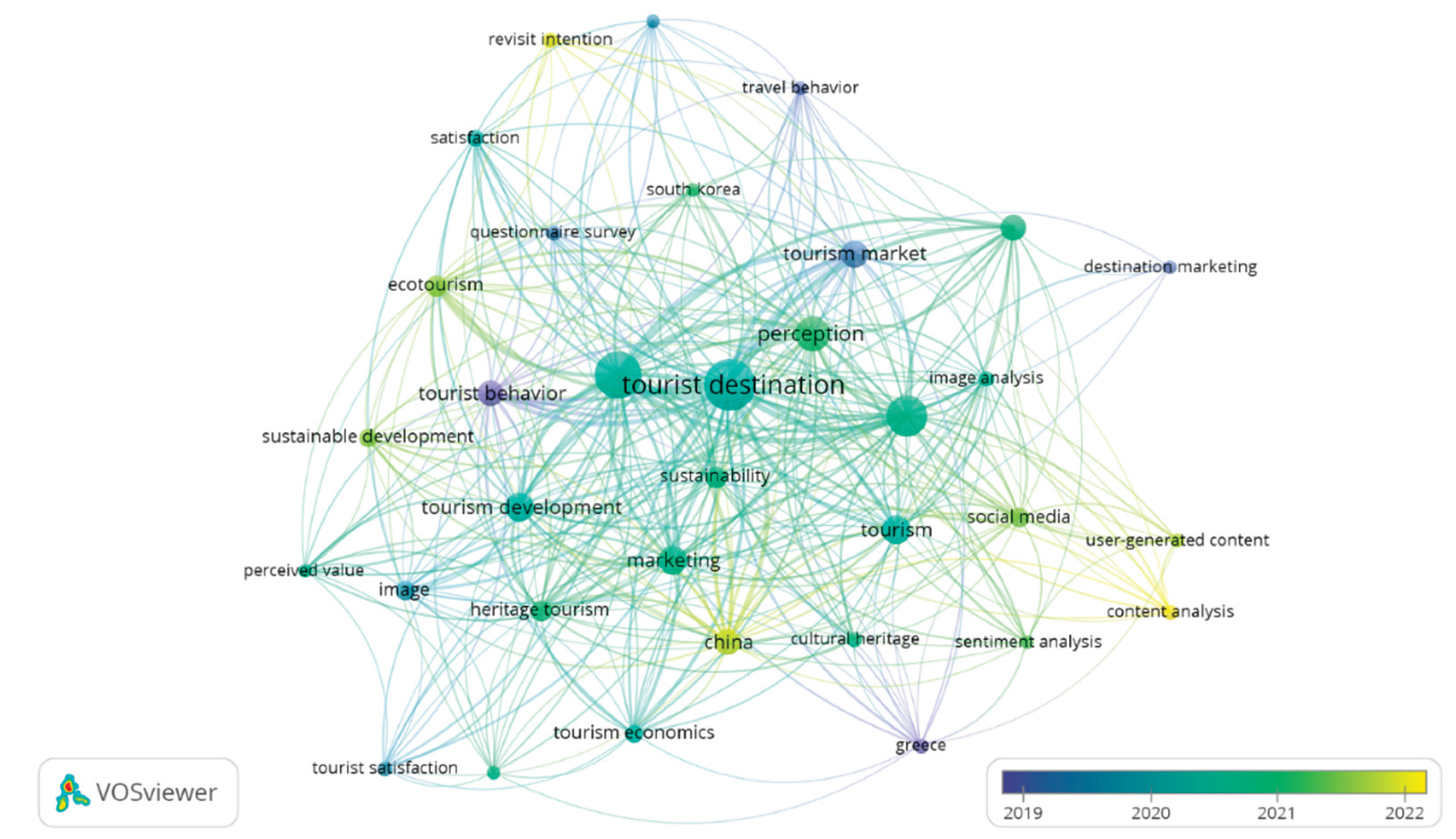
Figure 8 provides a visualization of the same network density of the 30 keywords or topics shown in
Figure 7. It highlights the densest areas in the network in bright yellow (dark yellow), allowing for immediate identification of the most prominent topics in Tourism Destinations and Attractions Image Research in the context of tourism. According to
Figure 8, the central area of the network is the most significant and contains topics such as “tourist destination,” “perception,” “image analysis,” “tourism development,”.” In contrast, the less brightly colored areas (light yellow or blur) indicate topics that have received less attention in the literature, including “marketing,” “ecotourism,” “heritage tourism,” among others. The fact that the term “destination” is highlighted in bright light yellow, while “image analysis” is in dark yellow - and the former is also less centralized in the network than the latter - may indicate a lower concentration of studies on “destination image” compared to “image analysis”. However, as illustrated in the co-occurrence network of the keyword network in
Figure 9, which depicts the temporal distribution of topics with colors ranging from blue to yellow, the term “destination image” started to appear around 2019.
Overall, this figure shows that thematic research directions in the study of Destination Image and Tourist Attractions in the context of tourism have been spread out from 2019 to 2022. Topics that appear in recent studies are represented with red circles, with the size of the circle indicating the frequency of occurrence. Thus, observing the green circles, it is interesting to conclude that recent articles also focus on “destination image” in addition to “tourist attraction” and “tourist attraction”, indicating that this research is an emerging and trending topic. Other topics related to this tourism, such as “tourist market,” “sustainable development,” “performance” and “heritage tourism,” are also trending.
4. Discussion
This research investigates research on Destination Image and Tourism Attraction, Destination image with tourists' perceptions of a place formed from experiences, information, and affective and cognitive impressions. Baloglu et al. (2015), tourist attraction includes elements such as the uniqueness of attractions, natural beauty, and facilities offered by a destination, Alcocer & Ruiz (2020). We conducted a bibliometric analysis, selecting and analyzing 144 relevant articles from Scopus published until 2024. First, we conducted a descriptive analysis using RStudio to identify the most productive countries, journals, authors and institutions. We also examined author keywords through Sankey diagrams. Second, we identified the most influential topics using keyword occurrence analysis in VOSviewer. This study sought to gain insights into the current state of the Destination Image and Tourist Attraction literature, which addresses related topics, such as tourist loylity, destination image, attractiveness, across various tourism industry domains. The findings offer valuable insights into recent research developments, with its focus covering the state and emerging trends of Destination Image and Tourist Attraction in the tourism sector.
The study identified a substantial increase in the number of scientific articles on Destination Image and Tourist Attraction technology in the tourism industry over the past fifteen years, with 86.80% of all articles (i.e., 125 out of 144 articles) of all articles published from 2018 to 2024. Notably, 2021 looks set to set a record peak in scholarly production, given the positive growth trend. In the first half of 2024 alone, 22 articles were published, compared to the previous peak of 18 articles reached in 2023. These results suggest that there is ongoing scientific interest in researching new Destination and Attraction Images in the tourism domain. Therefore, as our research has shown, Destination Image and Tourism Attractiveness research in the tourism sector is newer than other research as a whole, and has started to develop in recent years. More generally, a growing body of research is helping to shape a field of research-Destination Image and Tourism Attractiveness in the context of tourism-that is currently in a phase of rapid growth. One possible explanation for this significant growth can be attributed to the recent increase in tourists to various places, coupled with the fact that tourists, both foreign and local, can increase due to the Destination and Attraction Image. Tasci & Gartner (2020) point out that tourist attraction supports the formation of destination image. Destinations with clear and unique attractions tend to have a stronger image in the minds of tourists.
5. Conclusions
This bibliometric study provides an overview of the current state of Destination Image and Tourism Attractiveness research in the tourism industry through bibliometric analysis of literature data from the Scopus database. Previous reviews have explored this Destination Image and Tourism Attractiveness research landscape in the broader context of tourism, highlighting that this is a relatively new area of research. Indeed, there is an ongoing and lively debate in this area, and several recent studies have emphasized the important role played by Destination Image and Tourist Attraction, especially in the tourism sector. As such, this study contributes to the ongoing debate by outlining research trends in this particular sector and identifying related gaps in the literature and its continuation. Based on these results, we can conclude that the study of Destination Image and Attractiveness is still in its infancy but is beginning to develop, with further growth expected in the near future. Indeed, the analysis conducted on the data related to 144 articles selected from the Scopus database reveals a research activity that is still in its infancy but full of dynamism, involving different countries, authors, and institutions around the world. countries, authors, and institutions around the world. Compared to tourism destinations and attractions, Destination Image and Attractiveness are developed in various countries and have been researched by academics in the empirical data and data that they have carried out, and the shortcomings in this research of destination image and attractiveness on loyalty and only gained scientific interest recently. However, as the current research shows, there is still a lack of tourist development in the implementation of local excursions in their respective regions.
This research also has managerial implications. Its specific focus in discussing the literature of Destination Image and Attractiveness may raise awareness of sustainable tourism as an emerging range to improve competitiveness and tourism development in this sector. This increased awareness may inspire tourism practitioners to utilize this destination image and attractiveness for various purposes, such as developing the most dominant factor in influencing tourist loyalty in the Mentawai Islands is a positive experience during the visit. These factors indicate the importance of the government and destination managers' efforts in improving the quality of services and infrastructure in the Mentawai Islands so that tourists feel satisfied and loyal. In addition, accessibility and infrastructure also influence tourists' decision to return. Overall, this research shows that proper management of destination image and tourist attraction can contribute to increasing tourist loyalty in the Mentawai Islands Regency. Therefore, a marketing strategy that focuses more on the quality of the tourist experience is necessary to maintain and increase tourist visits to this area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.L.J. and Y.; methodology, R.L.J.; software, R.L.J.; validation, R.L.J. and Y.; formal analysis, R.L.J.; investigation, R.L.J.; resources, R.L.J.; data curation, R.L.J.; writing—original draft preparation, R.L.J.; writing—review and editing, R.L.J. and Y.; visualization, R.L.J.; supervision, Y.; project administration, R.L.J.; funding acquisition, Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Universitas Negeri Padang. The Article Processing Charge (APC) was funded by Universitas Negeri Padang.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to the Faculty of Tourism and Hospitality, Universitas Negeri Padang, for administrative and technical support during this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Alcocer, N., & Ruiz, P. (2020). Cognitive and affective characteristics of destination image. Journal of Tourism and Services, 11(21), 98–112. https://doi.org/10.29036/jots.v11i21.152. [CrossRef]
- Borchers, M., & Schott, J. (2017). The role of nature and surfing in developing sustainable tourism in Mentawai. Journal of Ecotourism, 16(2), 123–138. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C., & Chen, F. (2015). The influence of tourism experience on customer loyalty. Journal of Travel Research, 54(4), 511–523. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E. (2012). Tourism and cultural change: A global perspective. Routledge. ISBN: 9780415673463.
- Dawson, J. , Smith, R., & Taylor, L. (2013). Nature-based tourism and sustainability. Tourism Management, 35, 223–231. [CrossRef]
- Echtner, C. M., & Ritchie, J. R. B. (1993). The meaning and measurement of destination image. Journal of Tourism Studies, 31(4), 3–13. [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R., & Dube, L. (2012). Cultural tourism: A handbook for sustainable tourism development. Routledge. ISBN: 9780415522211.
- Hsu, C. H., Tsai, H., & Wang, Y. (2020). Sustainable tourism and its impact on tourist loyalty. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 28(6), 881–899. [CrossRef]
- Jang, S., & Feng, R. (2012). Investigating the role of experience and value in customer loyalty in the tourism industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 31(3), 927–937. [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, O., & McCarthur, N. (2020). Cultural tourism and local development. Oxford University Press. ISBN: 9780198790655.
- Kim, H. , & Kim, W. (2018). The effects of destination experience and perceived value on tourist loyalty. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 42(7), 1015–1031. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. , Lee, Y., & Koo, S. (2010). Tourism loyalty and destination image. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 34(3), 303–327. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H., Park, J., & Lee, C. (2019). The influence of destination image on tourist loyalty. Journal of Travel Research, 58(3), 442–457. [CrossRef]
- Kusumaningrum, E. (2018). Exploring ecotourism in Indonesia: The Mentawai case. Journal of Ecotourism Development, 10(1), 44–55. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H., Choi, Y., & Kang, M. (2014). Exploring the influence of quality and experience on customer loyalty in tourism. Tourism Management, 40, 359–368. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. , Lee, M., & Jang, S. (2017). The impact of attraction factors on tourists' loyalty. International Journal of Tourism Research, 19(4), 453–461. [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R. L. (2010). Satisfaction: A behavioral perspective on the consumer (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN: 9780765624182.
- Prideaux, B. (2000). The role of the tourist attraction in destination planning. Tourism Management, 21(1), 53–62. [CrossRef]
- Richards, G., & Wilson, J. (2014). Cultural tourism: A handbook for sustainable development. Routledge. ISBN: 9781138018980.
- Sharpley, R. (2014). Tourism and sustainable development: Reconsidering the role of culture. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 22(3), 469–485. [CrossRef]
- Stylidis, D., Shani, A., & Belhassen, Y. (2017). Measuring cognitive and affective components of destination images. Sustainability, 9(5), 1693. [CrossRef]
- Tung, A., Lin, P., & Wang, Y. (2020). Cultural tourism and its impact on local communities. Journal of Tourism and Culture, 12(3), 122–135. [CrossRef]
- Xie, K., & Chen, C. (2016). The impact of social media on tourism loyalty. Tourism Management, 53, 21–34. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).