Submitted:
24 July 2025
Posted:
24 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
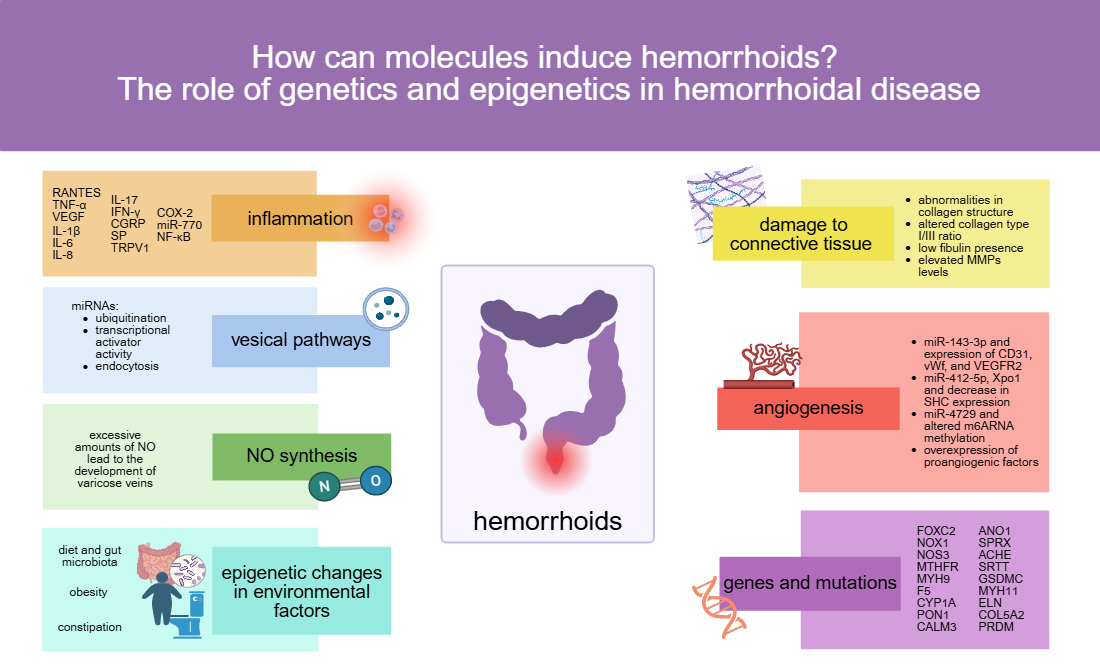
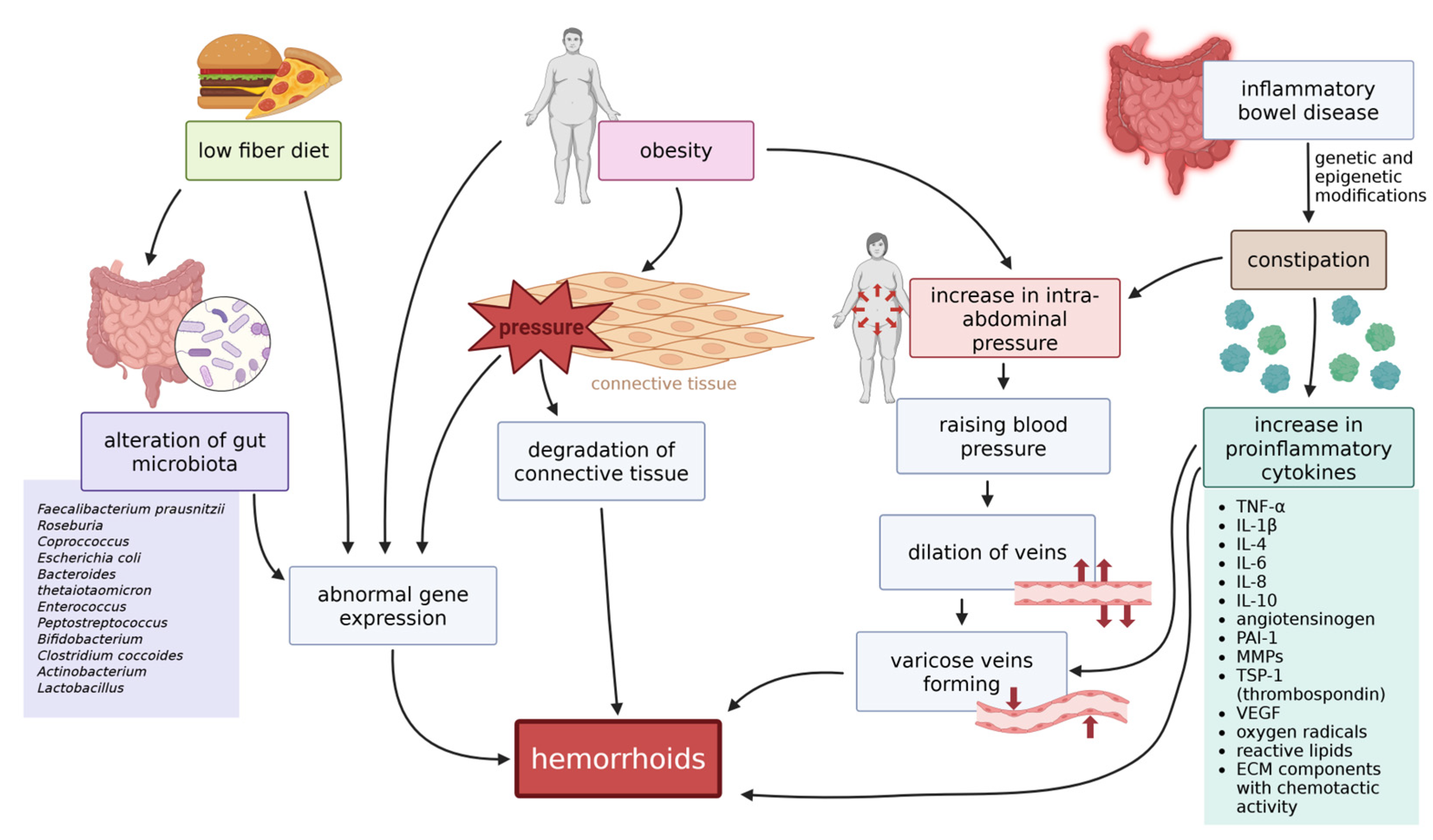
2.1. How do Hemorrhoids Develop?
2.2. Inflammation
2.3. The Role of Vesicles
2.4. Nitric Oxide and Varicose Veins
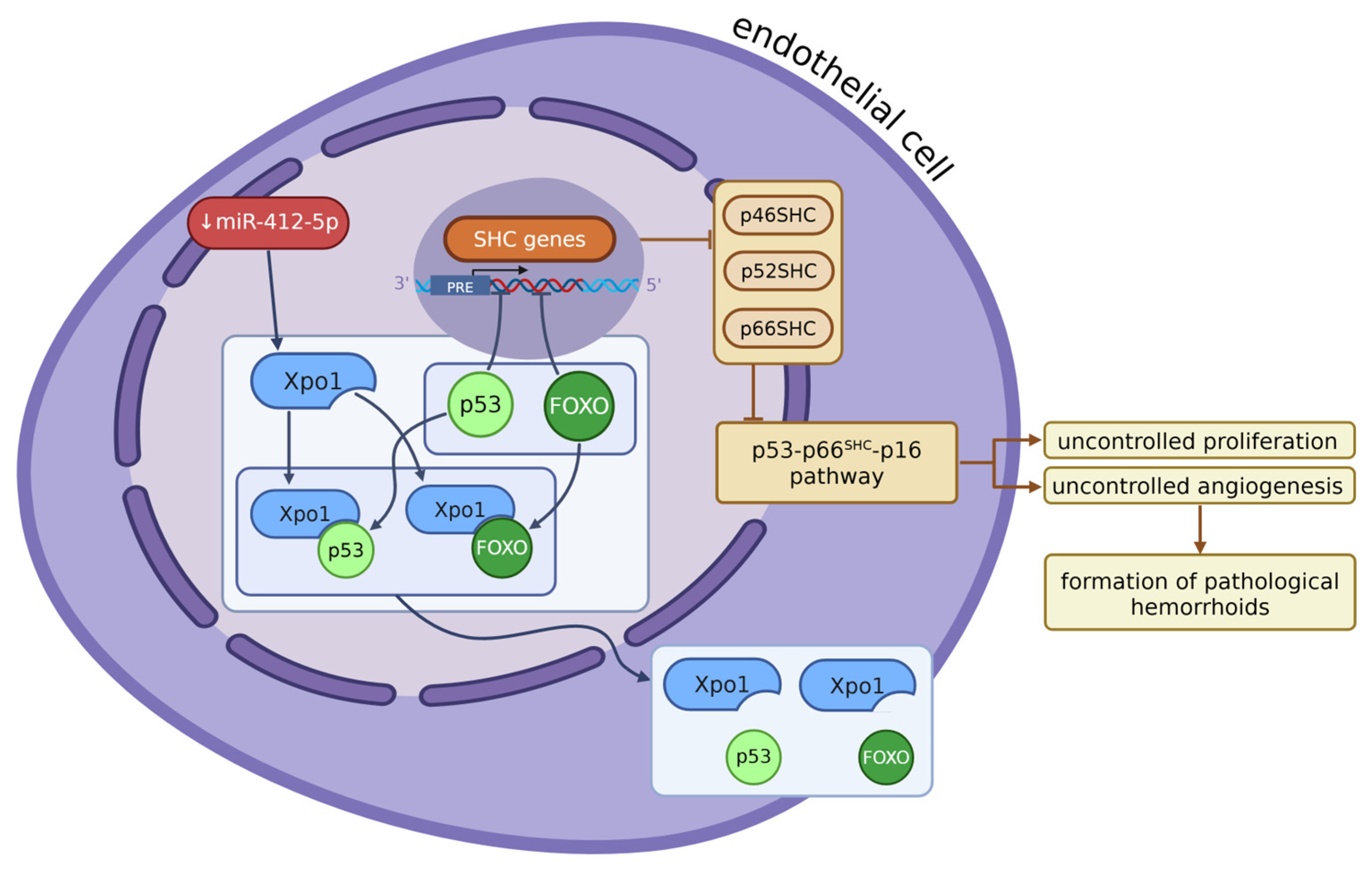
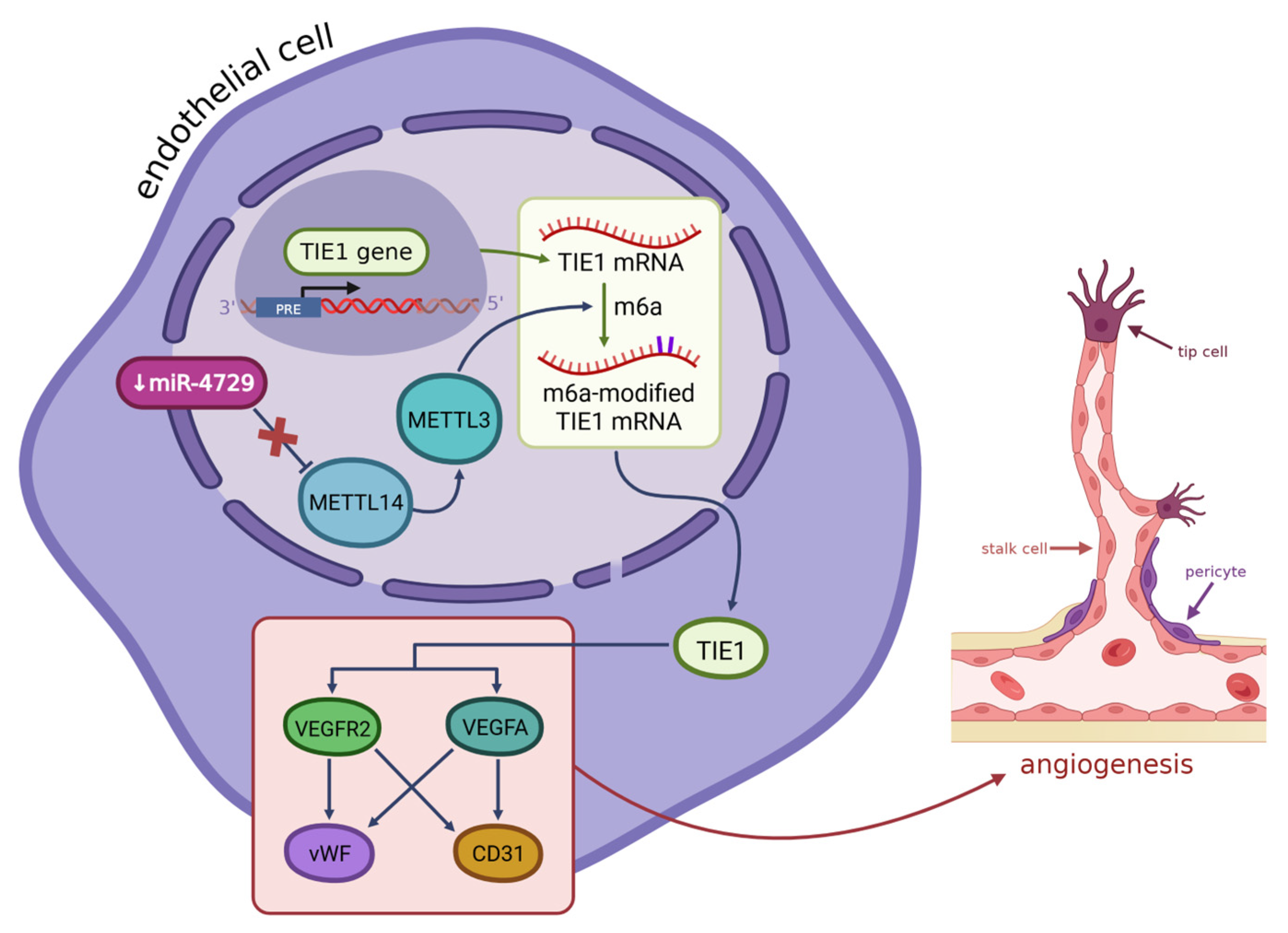
2.5. Angiogenesis
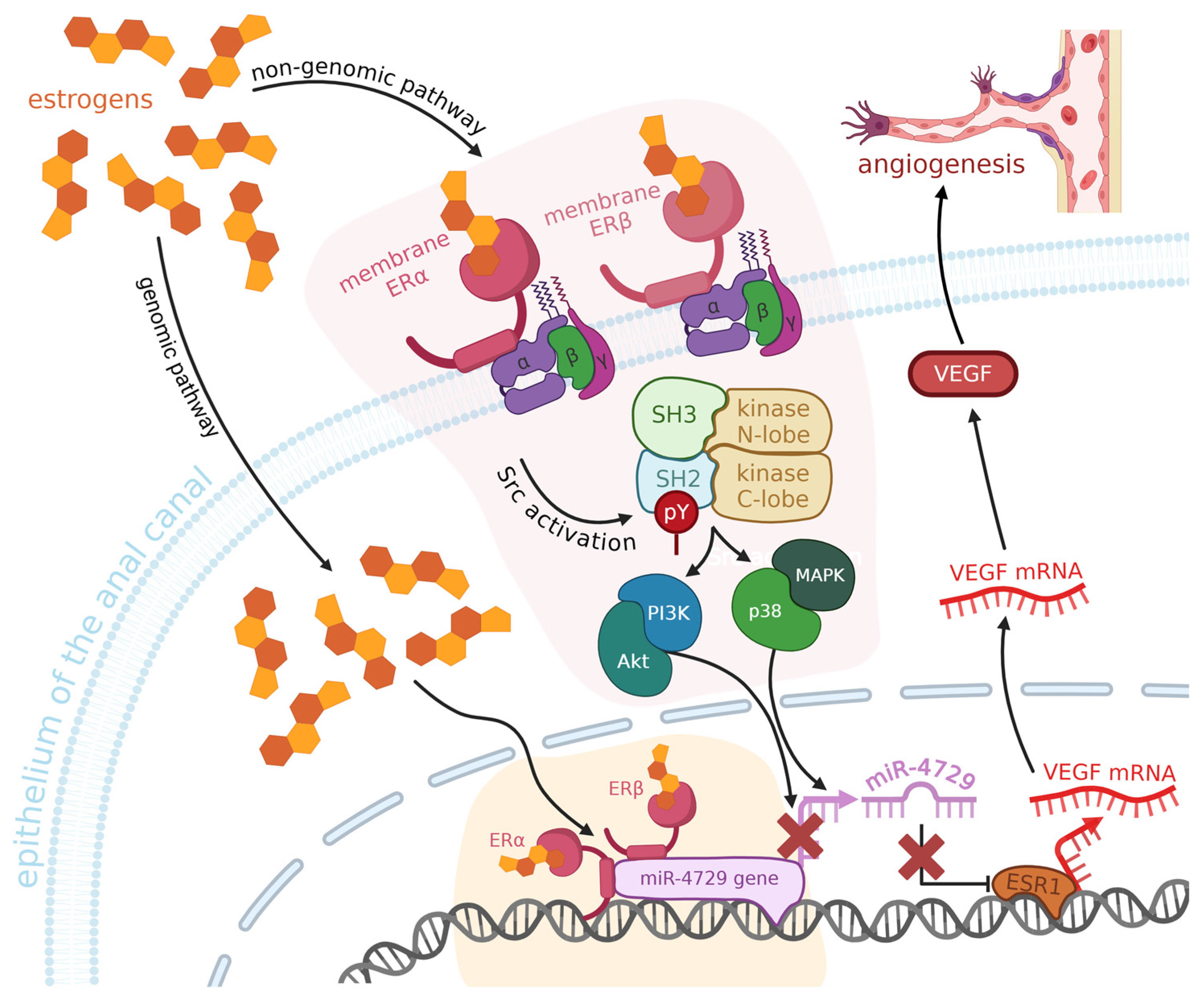
2.6. A Role of Estrogen in Angiogenesis?
2.7. Degeneration of Connective Tissue
2.8. Genes Significant in the Development of Hemorrhoids
2.9. Possible Epigenetic Factors in the Development of Hemorrhoids
2.9.1. Diet and Gut Microbiota
2.9.2. Obesity
2.9.3. Constipation
3. Discussion
| Molecular Components Altered in Hemorrhoids. | |||
| State | Upregulated | Downregulated | Mutated or Altered* Genes |
| Molecule | Pro-inflammatory cytokines, especially VEGF | Anti-inflammatory cytokines | FOXC2 |
| CGRP, SP, and TRPV1 | Inhibitory pathways of angiogenesis | MTHFR | |
| COX-2 | Vesical miRNAs modulating synaptic vesicle pathways and transcriptional activator activity | MYH9 | |
| Vesical miRNAs modulating endocytosis, transcription, protein kinase activity, and ubiquitination | miR-412-5p, leading to deregulation of the cell cycle | CYP1A | |
| NOS3 | miR-4729, leading to overexpression of TIE1 and angiogenesis via METTL14 regulation | PON1 | |
| NOS and NO | miR-424-5p, caused by estrogens, leading to increased expression of VEGF | ANO1 | |
| vWF, CD31, CD34, endoglin | Fibulin-3 and fibulin-5 | SPRX* | |
| VEGF, VEGFR2 | Collagen levels, collagen I/III ratio | SRTT* | |
| MMPs | ·· | GSDMC* | |
| NOX1 | ·· | COL5A2 | |
| CALM3 | ·· | ·· | |
| ACHE | ·· | ·· | |
| MYH11 | ·· | ·· | |
| ELN | ·· | ·· | |
| PRDM | ·· | ·· | |
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FOXC2 | Forkhead Box C2 |
| NOX | NADPH Oxidase |
| NOS | Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| CALM3 | Calmodulin 3 |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| mRNA | messenger RNA |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| COX2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| RYBP | Ring1 and YY1-binding protein |
| PRC1 | Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa-light-chain-enhancer of Activated B Cells |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| ncRNA | non-coding RNA |
| lncRNA | long non-coding RNA |
| rRNA | ribosomal RNA |
| tRNA | transfer RNA |
| snRNA | small nuclear RNA |
| UTR | Untranslated Region |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
| RANTES | Regulated on Activation, Normal T-cell Expressed and Secreted |
| CCL-5 | Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand 5 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IFN-γ | Interferon Gamma |
| CGRP | Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide |
| SP | Substance P |
| TRPV1 | Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| AMPK | AMP-Activated Protein Kinase |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| UBQLN1 | Ubiquilin-1 |
| HERC3 | HECT and RLD Domain Containing E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase 3 |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| vWF | von Willebrand Factor |
| CD | Cluster of Differentiation |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| Xpo1 | Exportin 1 |
| PI3K/AKT | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B |
| AP-1 | Activator Protein 1 |
| SHC | Src Homology 2 Domain Containing |
| m6A | N6-methyladenosine |
| METTL14 | Methyltransferase Like 14 |
| METTL3 | Methyltransferase Like 3 |
| WTAP | Wilms Tumor 1 Associated Protein |
| VIRMA | Vir-Like m6A Methyltransferase Associated |
| RBM15/15B | RNA Binding Motif Protein 15/15B |
| ZC3H13 | Zinc Finger CCCH-Type Containing 13 |
| TIE1 | Tyrosine Kinase with Immunoglobulin Like and EGF Like Domains 1 |
| VEGFA | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A |
| ESR1 | Estrogen Receptor 1 |
| ERα | Estrogen Receptor Alpha |
| IBS | Irritable Bowel Syndrome |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 |
| TSP-1 | Thrombospondin-1 |
| NGAL | Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin |
| SANRA | Scale for the Assessment of Narrative Review Articles |
References
- Margetis, N. Pathophysiology of Internal Hemorrhoids. Ann Gastroenterol 2019, 32, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, W.H.F. The Nature of Haemorrhoids. Br J Surg 1975, 62, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loder, P.B.; Kamm, M.A.; Nicholls, R.J.; Phillips, R.K.S. Haemorrhoids: Pathology, Pathophysiology and Aetiology. Br J Surg 1994, 81, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pata, F.; Sgró, A.; Ferrara, F.; Vigorita, V.; Gallo, G.; Pellino, G. Anatomy, Physiology and Pathophysiology of Haemorrhoids. Rev Recent Clin Trials 2021, 16, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, A.; Tietze, P.H.; Ramakrishnan, K. Anorectal Conditions: Hemorrhoids. FP Essent 2014, 419, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burkitt, D.P.; Graham-Stewart, C.W. Haemorrhoids--Postulated Pathogenesis and Proposed Prevention. Postgrad Med J 1975, 51, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohsiriwat, V. Hemorrhoids: From Basic Pathophysiology to Clinical Management. World Journal of Gastroenterology : WJG 2012, 18, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugerman, D.T. olmach Hemorrhoids. JAMA 2014, 312, 2698–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Rivero, S. Article Commentary: Hemorrhoids: Diagnosis and Current Management. https://doi.org/10.1177/000313480907500801 2009, 75, 635–642. [CrossRef]
- Picciariello, A.; Rinaldi, M.; Grossi, U.; Verre, L.; De Fazio, M.; Dezi, A.; Tomasicchio, G.; Altomare, D.F.; Gallo, G. Management and Treatment of External Hemorrhoidal Thrombosis. Front Surg 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgado, P.J.; Suárez, J.A.; Gómez, L.G.; Morgado, P.J. Histoclinical Basis for a New Classification of Hemorrhoidal Disease. Dis Colon Rectum 1988, 31, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, D. Clinical Practice. Hemorrhoids. N Engl J Med 2014, 371, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, W.A. Office Management of Hemorrhoids. Am J Gastroenterol 2018, 113, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohsiriwat, V. Treatment of Hemorrhoids: A Coloproctologist’s View. World J Gastroenterol 2015, 21, 9245–9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakinic, J.; Poola, V.P. Hemorrhoids and Fistulas: New Solutions to Old Problems. Curr Probl Surg 2014, 51, 98–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelzner, F. Die Hämorrhoiden Und Andere Krankheiten Des Corpus Cavernosum Recti Und Des Analkanals. DMW - Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 1963, 88, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, R.A. The Evaluation and Treatment of Hemorrhoids: A Guide for the Gastroenterologist. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013, 11, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parish Budiono, B.; Adi Presetyo, S.; Riwanto, I.; Sulistyaningsih, S.; Nugroho, E.A. Graptophyllum Pictum Extract in the Treatment of Experimental Hemorrhoids: Effects on Vascular Leakage and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Levels. Open Access Maced J Med Sci 2021, 9, 1785–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peery, A.F.; Crockett, S.D.; Barritt, A.S.; Dellon, E.S.; Eluri, S.; Gangarosa, L.M.; Jensen, E.T.; Lund, J.L.; Pasricha, S.; Runge, T.; et al. Burden of Gastrointestinal, Liver, and Pancreatic Diseases in the United States. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1731–1741.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzioni, D.A.; Beart, R.W.; Madoff, R.D.; Ault, G.T. Impact of the Aging Population on the Demand for Colorectal Procedures. Dis Colon Rectum 2009, 52, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Műzes, G.; Bohusné Barta, B.; Szabó, O.; Horgas, V.; Sipos, F. Cell-Free DNA in the Pathogenesis and Therapy of Non-Infectious Inflammations and Tumors. Biomedicines 2022, Vol. 10, Page 2853 2022, 10, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrard, J.; Ratajczak, F.; Elsens, J.; Leroy, C.; Kong, R.; Geoffroy, L.; Comte, A.; Fournet, G.; Joseph, B.; Li, X.; et al. Identifying Potent Nonsense-Mediated MRNA Decay Inhibitors with a Novel Screening System. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Mailliot, J.; Schaffitzel, C. Nonsense-Mediated MRNA Decay Factor Functions in Human Health and Disease. Biomedicines 2023, Vol. 11, Page 722 2023, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vebr, M.; Pomahačová, R.; Sýkora, J.; Schwarz, J. A Narrative Review of Cytokine Networks: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Implications for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathogenesis. Biomedicines 2023, Vol. 11, Page 3229 2023, 11, 3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, P.S.; Bartolo, D.C.C. Hemorrhoids and Fissure in Ano. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2008, 37, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, R.; Gallelli, L.; Grande, R.; Amato, B.; De Caridi, G.; Sammarco, G.; Ferrari, F.; Butrico, L.; Gallo, G.; Rizzuto, A.; et al. Hemorrhoids and Matrix Metalloproteinases: A Multicenter Study on the Predictive Role of Biomarkers. Surgery 2016, 159, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Ge, X.; Deng, Y. Identification of the MicroRNA Alterations in Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Haemorrhoids. Exp Physiol 2023, 108, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASHWIN PORWAL, G.C.K.G.B. and R.B. Herbal Medicine AnoSpray Suppresses Proinflammatory Cytokines COX-2 and RANTES in the Management of Hemorrhoids, Acute Anal Fissures and Perineal Wounds. Available online: https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/etm.2021.11009 (accessed on 16 February 2024).
- Yoon, S.O.; Park, S.J.; Yun, C.H.; Chung, A.S. Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Tumor Metastasis and Angiogenesis. J Biochem Mol Biol 2003, 36, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Zhou, H.; Lu, H.; Luo, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Xin, Y.; Liu, T.; Yang, W. Aberrant Expression for MicroRNA Is Potential Crucial Factors of Haemorrhoid. Hereditas 2020, 157, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, H.; Lu, H.; Luo, C.; Wang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Yang, W.; Xin, Y. MiR-4729 Regulates TIE1 MRNA M6A Modification and Angiogenesis in Hemorrhoids by Targeting METTL14. Ann Transl Med 2021, 9, 232–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Luo, C.; Song, C.; Wang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Xin, Y.; Liu, T.; Yang, W. MiR-412-5p Targets Xpo1 to Regulate Angiogenesis in Hemorrhoid Tissue. Gene 2019, 705, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wei, W.; Wang, H.; Dong, J. N6-Methyladenosine-Sculpted Regulatory Landscape of Noncoding RNA. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 743990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, W.; Chen, Q.; Chen, M. Non-Coding RNAs and Their Integrated Networks. J Integr Bioinform 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rooij, E. The Art of MicroRNA Research. Circ Res 2011, 108, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.K.L.; Sharp, P.A. MicroRNA Functions in Stress Responses. Mol Cell 2010, 40, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA Expression Profiles Classify Human Cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghini, A.; Andreassi, M.G. Genetic Polymorphisms Offer Insight into the Causal Role of MicroRNA in Coronary Artery Disease. Atherosclerosis 2018, 269, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.; Singh, D.; Ganju, L.; Kumar, B. MicroRNA in Gastrointestinal Cell Signalling. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creugny, A.; Fender, A.; Pfeffer, S. Regulation of Primary MicroRNA Processing. FEBS Lett 2018, 592, 1980–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendell, J.T.; Olson, E.N. MicroRNAs in Stress Signaling and Human Disease. Cell 2012, 148, 1172–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, Y.P.; Hsieh, W.F.; Tsai, Y.Y.; Lu, Y.L.; Liau, E.S.; Hsu, H.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Liu, T.C.; Chang, M.; Li, J.; et al. Dlk1-Dio3 Locus-Derived LncRNAs Perpetuate Postmitotic Motor Neuron Cell Fate and Subtype Identity. Elife 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Lin, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, Z.; Chen, C.; Liu, T. MiR-758 Mediates OxLDL-Dependent Vascular Endothelial Cell Damage by Suppressing the Succinate Receptor SUCNR1. Gene 2018, 663, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Shen, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, T.; Xi, H.; Chen, C. Curcumin Suppresses In Vitro Proliferation and Invasion of Human Prostate Cancer Stem Cells by Modulating DLK1-DIO3 Imprinted Gene Cluster MicroRNAs. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 2018, 22, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, T.; Huang, Y. MicroRNA-134 Suppresses Endometrial Cancer Stem Cells by Targeting POGLUT1 and Notch Pathway Proteins. FEBS Lett 2015, 589, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Liu, T.; Huang, Y.; Qin, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, J. MicroRNA-134-3p Is a Novel Potential Inhibitor of Human Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells by Targeting RAB27A. Gene 2017, 605, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, P.; Sun, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Hu, L.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, D.; Pan, Y.; et al. Physiological Oxygen Prevents Frequent Silencing of the DLK1-DIO3 Cluster during Human Embryonic Stem Cells Culture. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwin Porwal Gopal, C. Kundu Gajanan Bhagwat Ramesh Butti Polyherbal Formulation Anoac-H Suppresses the Expression of RANTES and VEGF for the Management of Bleeding Hemorrhoids and Fistula. Available online: https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/mmr.2021.12376# (accessed on 12 February 2024).
- Shrivastava, L.; Silva Borges, G. da; Shrivastava, R. Clinical Efficacy of a Dual Action, Topical Anti-Edematous and Antiinflammatory Device for the Treatment of External Hemorrhoids. Clin Exp Pharmacol 2018, 08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A. Cytokines and Their Role in Health and Disease: A Brief Overview. MOJ Immunol 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yachha, S.K.; Thomas, M.A.; Saraswat, V.A.; Gupta, R.K. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Are Raised in Extrahepatic Portal Venous Obstruction, with Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011, 26, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojdasiewicz, P.; Poniatowski, Ł.A.; Szukiewicz, D. The Role of Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Jin, W.; Li, P.; Wang, R.; Guo, X. Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Hemorrhoids—a Review of Preparations Used and Their Mechanism of Action. Front Pharmacol 2023, 14, 1270339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porwal, A.; Kundu, G.; Bhagwat, G.; Nimma, R.; Chowdhury, J. Turmocin Plus Suppresses Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Macrophage Infiltration in the Management of Perineal Wounds, Anal Fistula, Acute Anal Fissures and Haemorrhoids. Journal of Natural Remedies 2024, 24, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, M.C.; Quintero, L.; Pons, H.; Suarez-Roca, H. Substance P and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Increase IL-1β, IL-6 and TNFα Secretion from Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Neurochem Int 2002, 40, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.; Alliger, K.; Weidinger, C.; Yerinde, C.; Wirtz, S.; Becker, C.; Engel, M.A. Functional Role of Transient Receptor Potential Channels in Immune Cells and Epithelia. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torii, H.; Hosoi, J.; Beissert, S.; Xu, S.; Fox, F.E.; Asahina, A.; Takashima, A.; Rook, A.H.; Granstein, R.D. Regulation of Cytokine Expression in Macrophages and the Langerhans Cell-like Line XS52 by Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide. J Leukoc Biol 1997, 61, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Piao, S.; Li, G.; Yan, M. The Beneficial Effect of Sanhuang Ointment and Its Active Constituents on Experimental Hemorrhoids in Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2024, 319, 117173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klink, C.; Binnebösel, M.; Kämmer, D.; Willis, S.; Prescher, A.; Klinge, U.; Schumpelick, V. Haemorrhoids Are Related to Changes of Cell Function in Mucosa and Submucosa. Int J Colorectal Dis 2009, 24, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, L.S. Role and Regulation of Cyclooxygenase-2 during Inflammation. Am J Med 1999, 106, 37S–42S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, T.; Zhong, S.; Yang, W. MicroRNA-770 Promotes Polarization of Macrophages and Hemorrhoids by Suppressing RYBP Expression and Monoubiquitination of Histone H2A on Lys119 Modification. Mol Immunol 2025, 182, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwland, R.; Falcon-Perez, J.M.; Soekmadji, C.; Boilard, E.; Carter, D.; Buzas, E.I. Essentials of Extracellular Vesicles: Posters on Basic and Clinical Aspects of Extracellular Vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 2016, 164, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, J.; Ryan, A.E.; Griffin, M.D.; Ritter, T. Extracellular Vesicles as Modulators of Wound Healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2018, 129, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorova, D.; Simoncini, S.; Lacroix, R.; Sabatier, F.; Dignat-George, F. Extracellular Vesicles in Angiogenesis. Circ Res 2017, 120, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, S.L.N.; Breakefield, X.O.; Weaver, A.M. Extracellular Vesicles: Unique Intercellular Delivery Vehicles. Trends Cell Biol 2017, 27, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, Secretion, and Intercellular Interactions of Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crewe, C.; Joffin, N.; Rutkowski, J.M.; Kim, M.; Zhang, F.; Towler, D.A.; Gordillo, R.; Scherer, P.E. An Endothelial-to-Adipocyte Extracellular Vesicle Axis Governed by Metabolic State. Cell 2018, 175, 695–708.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abels, E.R.; Breakefield, X.O. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene UBQLN1 ubiquilin 1 [ Homo sapiens (human) ]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), N.C. for B.I. 2004 – cited 11/03/2024 UBQLN1 Ubiquilin 1 [ Homo Sapiens (Human) ]. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=29979 (accessed on 11 March 2024).
- Hochrainer, K.; Pejanovic, N.; Olaseun, V.A.; Zhang, S.; Iadecola, C.; Anrather, J. The Ubiquitin Ligase HERC3 Attenuates NF-ΚB-Dependent Transcription Independently of Its Enzymatic Activity by Delivering the RelA Subunit for Degradation. Nucleic Acids Res 2015, 43, 9889–9904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Meng, Q.; Wei, L.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Liang, X.; Lin, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Myocardial Ischemia-reperfusion Induced Cardiac Extracellular Vesicles Harbour Proinflammatory Features and Aggravate Heart Injury. J Extracell Vesicles 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braicu, C.; Buse, M.; Busuioc, C.; Drula, R.; Gulei, D.; Raduly, L.; Rusu, A.; Irimie, A.; Atanasov, A.G.; Slaby, O.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on MAPK: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahún-Español, Á.; Clemente, C.; Jiménez-Loygorri, J.I.; Sierra-Filardi, E.; Herrera-Melle, L.; Gómez-Durán, A.; Sabio, G.; Monsalve, M.; Boya, P.; Arroyo, A.G. P38 MAPK Priming Boosts VSMC Proliferation and Arteriogenesis by Promoting PGC1α-Dependent Mitochondrial Dynamics. Scientific Reports 2022 12:1 2022, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Cheng, H.; Xu, L.; Pei, G.; Wang, Y.; Fu, C.; Jiang, Y.; He, C.; et al. Signaling Pathways and Targeted Therapy for Myocardial Infarction. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, H.Y.; Koh, M.S.; Moon, A. The P38 MAPK Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2009, 18, 1893–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haviarová, Z.; Janegová, A.; Janega, P.; Durdík, S.; Kováč, P.; Stvrtinová, V.; Mráz, P. Expression of Constitutive Nitric Oxide Synthase Isoforms in Varicose Vein Wall; Preliminary Results. Int J Vasc Med 2011, 2011, 204723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokce, A.H.; Gokce, F.S.; Durmus, S.; Hajiyeva, R.; Ersoz, F.; Gelisgen, R.; Uzun, H. The Effect of Nitric Oxide, Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthetase, and Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Hemorrhoidal Disease. Rev Assoc Med Bras 2020, 66, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohsiriwat, V.; Wilson, V.G.; Scholefield, J.H.; Dashwood, M.R. Regional Distribution of Nitric Oxide Synthase in Human Anorectal Tissue: A Pilot Study on the Potential Role for Nitric Oxide in Haemorrhoids. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2018, 18, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.C.; Hou, Y.C.; Pan, A.C.H. Endoglin (CD105) Expression in the Development of Haemorrhoids. Eur J Clin Invest 2004, 34, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, T.; Xie, M. Fulvestrant, an Estrogen Receptor Inhibitor, Relieves Postoperative Hemorrhoid Edema via up-Regulation of MiR- 424-5p. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2022, 21, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parés, D.; Iglesias, M.; Pera, M.; Pascual, M.; Torner, A.; Baró, T.; Alonso, S.; Grande, L. Expression of Estrogen and Progesterone Receptors in the Anal Canal of Women According to Age and Menopause. Dis Colon Rectum 2010, 53, 1687–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorga, A.; Cunningham, C.M.; Moazeni, S.; Ruffenach, G.; Umar, S.; Eghbali, M. The Protective Role of Estrogen and Estrogen Receptors in Cardiovascular Disease and the Controversial Use of Estrogen Therapy. Biol Sex Differ 2017, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), N.C. for B.I. 2004 – cited 12/03/2024ESR1 estrogen receptor 1 [ H. sapiens (human) ] ESR1 Estrogen Receptor 1 [ Homo Sapiens (Human) ].
- Zhang, J.; Song, H.; Lu, Y.; Chen, H.; Jiang, S.; Li, L. Effects of Estradiol on VEGF and BFGF by Akt in Endometrial Cancer Cells Are Mediated through the NF-ΚB Pathway. Oncol Rep 2016, 36, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losordo, D.W.; Isner, J.M. Estrogen and Angiogenesis: A Review. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2001, 21, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karas, R.H.; Gauer, E.A.; Bieber, H.E.; Baur, W.E.; Mendelsohn, M.E. Growth Factor Activation of the Estrogen Receptor in Vascular Cells Occurs via a Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Independent Pathway. J Clin Invest 1998, 101, 2851–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shifren, J.L.; Tseng, J.F.; Zaloudek, C.J.; Ryan, I.P.; Meng, Y.G.; Ferrara, N.; Jaffe, R.B.; Taylor, R.N. Ovarian Steroid Regulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in the Human Endometrium: Implications for Angiogenesis during the Menstrual Cycle and in the Pathogenesis of Endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996, 81, 3112–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, M. Neovascularization in Experimental Retinal Venous Obstruction in Rabbits. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2001, 45, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.G.; Chung, H.; Hyon, J.Y. Experimental Preretinal Neovascularization by Laser-Induced Thrombosis in Albino Rats. Korean J Ophthalmol 1999, 13, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravina, G.L.; Senapedis, W.; McCauley, D.; Baloglu, E.; Shacham, S.; Festuccia, C. Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Transport as a Therapeutic Target of Cancer. J Hematol Oncol 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Camacho, S.C.; Silvers, T.R.; Razak, A.R.A.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Gerecitano, J.F.; Kalir, E.; Pereira, E.; Evans, B.R.; Ramus, S.J.; et al. Inhibition of the Nuclear Export Receptor XPO1 as a Therapeutic Target for Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer. Clinical Cancer Research 2017, 23, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikström, P.; Lissbrant, I.F.; Stattin, P.; Egevad, L.; Bergh, A. Endoglin (CD105) Is Expressed on Immature Blood Vessels and Is a Marker for Survival in Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2002, 51, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupinski, J.; Kaluza, J.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, S.; Wang, J.M. Role of Angiogenesis in Patients with Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 1994, 25, 1794–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcovich, A.L.; Morad, Y.; Sandbank, J.; Huszar, M.; Rosner, M.; Pollack, A.; Herbert, M.; Bar-Dayan, Y. Angiogenesis in Pterygium: Morphometric and Immunohistochemical Study. Curr Eye Res 2002, 25, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomonte, M.; Montagner, R.; Fonsatti, E.; Colizzi, F.; Cattarossi, I.; Brasoveanu, L.I.; Nicotra, M.R.; Cattelan, A.; Natali, P.G.; Maio, M. Expression and Structural Features of Endoglin (CD105), a Transforming Growth Factor Beta1 and Beta3 Binding Protein, in Human Melanoma. Br J Cancer 1996, 74, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LIANG, W.; CAO, J.; YANG, P.; LI, W.; SUN, Z.; CHEN, X.; WANG, Q.; LIU, F. Clinical Significance and Distribution Characteristics of Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 in Hemorrhoid Mucosa. The Journal of Practical Medicine 2015, 2830–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Han, W.; Wang, L.; Shang, W.; Cao, X. Role of MiR-143-3p in the Development of Hemorrhoids and Postoperative Wound Healing. Journal of Investigative Surgery 2025, 38, 2480799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, M.; Ishizawa, J.; Ruvolo, V.; Dilip, A.; Quintás-Cardama, A.; Mcdonnell, T.J.; Neelapu, S.S.; Kwak, L.W.; Shacham, S.; Kauffman, M.; et al. Induction of P53-Mediated Transcription and Apoptosis by Exportin-1 (XPO1) Inhibition in Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Sci 2014, 105, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camus, V.; Miloudi, H.; Taly, A.; Sola, B.; Jardin, F. XPO1 in B Cell Hematological Malignancies: From Recurrent Somatic Mutations to Targeted Therapy. J Hematol Oncol 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrocini, G.; Kisslinger, A.; Iannelli, P.; Vitale, N.; Procaccini, C.; Sparaneo, G.; Chieffi, P.; Ayala, F.; Mancini, F.P.; Tramontano, D. Resveratrol Regulates P66Shc Activation in HaCaT Cells. Exp Dermatol 2010, 19, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliaccio, E.; Giogio, M.; Mele, S.; Pelicci, G.; Reboldi, P.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Lanfrancone, L.; Pelicci, P.G. The P66shc Adaptor Protein Controls Oxidative Stress Response and Life Span in Mammals. Nature 1999, 402, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Hu, Y.; Tang, H.; Hu, H.; Pang, L.; Xing, J.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, B.; Liu, T.; et al. RNA Methyltransferase NSUN2 Promotes Stress-Induced HUVEC Senescence. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, R.F.; Terada, L.S. P66Shc Restrains Ras Hyperactivation and Suppresses Metastatic Behavior. Oncogene 2010, 29, 5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.S.; Anand, D.; Khanday, F.A. P66Shc as a Switch in Bringing about Contrasting Responses in Cell Growth: Implications on Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis. Mol Cancer 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camici, G.G.; Schiavoni, M.; Francia, P.; Bachschmid, M.; Martin-Padura, I.; Hersberger, M.; Tanner, F.C.; Pelicci, P.G.; Volpe, M.; Anversa, P.; et al. Genetic Deletion of P66Shc Adaptor Protein Prevents Hyperglycemia-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoli, C.; Martin-Padura, I.; De Nigris, F.; Giorgio, M.; Mansueto, G.; Somma, P.; Condorelli, M.; Sica, G.; De Rosa, G.; Pelicci, P.G. Deletion of the P66Shc Longevity Gene Reduces Systemic and Tissue Oxidative Stress, Vascular Cell Apoptosis, and Early Atherogenesis in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100, 2112–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francia, P.; Delli Gatti, C.; Bachschmid, M.; Martin-Padura, I.; Savoia, C.; Migliaccio, E.; Pelicci, P.G.; Schiavoni, M.; Lüscher, T.F.; Volpe, M.; et al. Deletion of P66shc Gene Protects against Age-Related Endothelial Dysfunction. Circulation 2004, 110, 2889–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamori, T.; White, A.R.; Mattagajasingh, I.; Khanday, F.A.; Haile, A.; Qi, B.; Byeong, H.J.; Bugayenko, A.; Kasuno, K.; Berkowitz, D.E.; et al. P66shc Regulates Endothelial NO Production and Endothelium-Dependent Vasorelaxation: Implications for Age-Associated Vascular Dysfunction. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2005, 39, 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinei, M.; Giorgio, M.; Cicalese, A.; Barozzi, S.; Ventura, A.; Migliaccio, E.; Milia, E.; Padura, I.M.; Raker, V.A.; Maccarana, M.; et al. A P53-P66Shc Signalling Pathway Controls Intracellular Redox Status, Levels of Oxidation-Damaged DNA and Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis. Oncogene 2002, 21, 3872–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jia, G.; Yu, M.; Lu, Z.; Deng, X.; et al. A METTL3-METTL14 Complex Mediates Mammalian Nuclear RNA N6-Adenosine Methylation. Nat Chem Biol 2014, 10, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wei, L.; Law, C.T.; Tsang, F.H.C.; Shen, J.; Cheng, C.L.H.; Tsang, L.H.; Ho, D.W.H.; Chiu, D.K.C.; Lee, J.M.F.; et al. RNA N6-Methyladenosine Methyltransferase-like 3 Promotes Liver Cancer Progression through YTHDF2-Dependent Posttranscriptional Silencing of SOCS2. Hepatology 2018, 67, 2254–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Yi, C.; Lindahl, T.; Pan, T.; Yang, Y.G.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine in Nuclear RNA Is a Major Substrate of the Obesity-Associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol 2011, 7, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Klukovich, R.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Klungland, A.; Yan, W. ALKBH5-Dependent M6A Demethylation Controls Splicing and Stability of Long 3’-UTR MRNAs in Male Germ Cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115, E325–E333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Gomez, A.; Hon, G.C.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Fu, Y.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Jia, G.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine-Dependent Regulation of Messenger RNA Stability. Nature 2014, 505, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, I.; Tzelepis, K.; Pandolfini, L.; Shi, J.; Millán-Zambrano, G.; Robson, S.C.; Aspris, D.; Migliori, V.; Bannister, A.J.; Han, N.; et al. Promoter-Bound METTL3 Maintains Myeloid Leukaemia by M6A-Dependent Translation Control. Nature 2017, 552, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Hao, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.M.; Wang, M.; Han, W.; Wu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Hao, J.; Wang, L.; et al. M(6)A RNA Methylation Is Regulated by MicroRNAs and Promotes Reprogramming to Pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savant, S.; La Porta, S.; Budnik, A.; Busch, K.; Hu, J.; Tisch, N.; Korn, C.; Valls, A.F.; Benest, A. V.; Terhardt, D.; et al. The Orphan Receptor Tie1 Controls Angiogenesis and Vascular Remodeling by Differentially Regulating Tie2 in Tip and Stalk Cells. Cell Rep 2015, 12, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.; Sandi, M.J.; Cordelier, P.; Binétruy, B.; Pouysségur, J.; Iovanna, J.L.; Tournaire, R. Tie1 Deficiency Induces Endothelial–Mesenchymal Transition. EMBO Rep 2012, 13, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torigata, M.; Yamakawa, D.; Takakura, N. Elevated Expression of Tie1 Is Accompanied by Acquisition of Cancer Stemness Properties in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Med 2017, 6, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Porta, S.L.; Roth, L.; Singhal, M.; Mogler, C.; Spegg, C.; Schieb, B.; Qu, X.; Adams, R.H.; Scott Baldwin, H.; Savant, S.; et al. Endothelial Tie1-Mediated Angiogenesis and Vascular Abnormalization Promote Tumor Progression and Metastasis. J Clin Invest 2018, 128, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiainen, L.; Korhonen, E.A.; Leppänen, V.M.; Luukkaala, T.; Hämäläinen, M.; Tanner, M.; Lahdenperä, O.; Vihinen, P.; Jukkola, A.; Karihtala, P.; et al. High Baseline Tie1 Level Predicts Poor Survival in Metastatic Breast Cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), N.C. for B.I. 2004 – cited 12/03/2024Gene [Internet]. B. (MD): N.L. of M. (US), N.C. for B.I. 2004 – [cited Y.M.D. TIE1 Tyrosine Kinase with Immunoglobulin like and EGF like Domains 1 [ Homo Sapiens (Human) ].
- Haas, P.A.; Fox, T.A.; Haas, G.P. The Pathogenesis of Hemorrhoids. Dis Colon Rectum 1984, 27, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardiñas, C.; Arreaza, D.D.; Osorio, H. Changes in the Proportions of Types I and III Collagen in Hemorrhoids: The Sliding Anal Lining Theory. Journal of Coloproctology 2016, 36, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, S.; Junge, K.; Ebrahimi, R.; Prescher, A.; Schumpelick, V. Haemorrhoids - a Collagen Disease? Colorectal Dis 2010, 12, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasseri, Y.Y.; Krott, E.; Van Groningen, K.M.; Berho, M.; Osborne, M.C.; Wollman, S.; Weiss, E.G.; Wexner, S.D. Abnormalities in Collagen Composition May Contribute to the Pathogenesis of Hemorrhoids: Morphometric Analysis. Tech Coloproctol 2015, 19, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F. The Effect of Tonifying Qi Method on the Expression of Anti-Aging FIbulin Proteins Family of Internal Prolapsed Hemorrhoids. 2014.
- Sun, F., X.T., C.H., and L.Y. Study on Effect of Buzhong Yiqi Tang on Expression of FIbulin-5 in Grade-Iii Prolapsed Hemorrhoid Tissues. 2018.
- Jin, X., W.X., H.D., L.Y., and S.F. Therapeutic Efficacy of Buzhong Yiqi Decoction Containing Different Doses of Radix Astragali for Stage i Internal Hemorrhoids Patients with Spleen Deficiency and Sinking of Qi and Its Effect on FIbulin-3 Expression in Hemorrhoid Tissues. 2017.
- Zhong, P. Study on Clinical Efficiency and FIbulin-3’ Expression of Buzhong-Yiqi-Decoction Containing Different Dose Astragalus in Hemorrhoids’ Patient Belongs to Spleen-Type Gas Trap. 2016.
- Xiao, T. The Study of the Effect of Buzhong Yiqi Decoction on Expression of FIbulin-5 in Iii Degree of Prolapsed Internal Hemorrhoids Tissues. 2016.
- Albig, A.R.; Schiemann, W.P. Fibulin-5 Antagonizes Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Signaling and Angiogenic Sprouting by Endothelial Cells. DNA Cell Biol 2004, 23, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vega, S.; Iwamoto, T.; Yamada, Y. Fibulins: Multiple Roles in Matrix Structures and Tissue Functions. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009, 66, 1890–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Rosa, C.C.D. La; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Human Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisli, E.; Kemik, A.; Sümer, A.; Kemik, Ö. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Pathogenesis of Hemorrhoidal Disease. https://doi.org/10.1177/000313481307901122 2013, 79, 1181–1184. [CrossRef]
- Xie, D. Effects of Mmp-7 and Mmp-9 on the Pathogenesis of Hemorrhoids. 2008.
- Qin, L., and Q.X. Expression and Significance of Mmp-9 and Vegfr2 in Patients with Internal Hemorrhoids. . 2020.
- Wei Han, Z.W.B.Z.X.Y.D.W.J.W.X.T.F.Z.Y.H. Pathologic Change of Elastic Fibers with Difference of Microvessel Density and Expression of Angiogenesis-Related Proteins in Internal Hemorrhoid Tissues. 2005.
- Di, Y.; Nie, Q.Z.; Chen, X.L. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression Change in Experimental Retinal Neovascularization. Int J Ophthalmol 2016, 9, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollborn, M.; Stathopoulos, C.; Steffen, A.; Wiedemann, P.; Kohen, L.; Bringmann, A. Positive Feedback Regulation between MMP-9 and VEGF in Human RPE Cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007, 48, 4360–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenghao Zheng, D.E.S.J. Genome-Wide Analysis of 944 133 Individuals Provides Insights into the Etiology of Haemorrhoidal Disease - Record Details - Embase. Available online: https://www-1embase-1com-1qtgcbczf0003.han.bg.umw.edu.pl/records?subaction=viewrecord&id=L634938305 (accessed on 15 February 2024).
- Ng, M.Y.M.; Andrew, T.; Spector, T.D.; Jeffery, S. Linkage to the FOXC2 Region of Chromosome 16 for Varicose Veins in Otherwise Healthy, Unselected Siblings Pairs. J Med Genet 2005, 42, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendran, S.; Girijamma, A.; Nair, R.; Ramegowda, K.S.; Nair, D.H.; Thulaseedharan, J. V.; Lakkappa, R.B.; Kamalapurkar, G.; Kartha, C.C. Forkhead Box C2promoter Variant C<512C.T Is Associated with Increased Susceptibility to Chronic Venous Diseases. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brice, G.; Mansour, S.; Bell, R.; Collin, J.R.O.; Child, A.H.; Brady, A.F.; Sarfarazi, M.; Burnand, K.G.; Jeffery, S.; Mortimer, P.; et al. Analysis of the Phenotypic Abnormalities in Lymphoedema-Distichiasis Syndrome in 74 Patients with FOXC2 Mutations or Linkage to 16q24. J Med Genet 2002, 39, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kume, T. The Cooperative Roles of Foxcl and Foxc2 in Cardiovascular Development. Adv Exp Med Biol 2009, 665, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.; Andreucci, M.; Ielapi, N.; Serraino, G.F.; Mastroroberto, P.; Bracale, U.M.; Serra, R. Molecular Determinants of Chronic Venous Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murk, W.; de Wan, A.T. Exhaustive Genome-Wide Search for SNP-SNP Interactions across 10 Human Diseases. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics 2016, 6, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qar, J.; Al Zoubi, M.S.; Baydoun, I.M.A.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Al-Trad, B.; Rabi, F.; Al Batayneh, K.M. Truncating Mutation in FOXC2 Gene in Familial Hemorrhoids and Varicose Veins. International Journal of Biology and Biomedical Engineering 2020, 14, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, T. V.; Karpanen, T.; Norrmén, C.; Mellor, R.; Tamakoshi, T.; Finegold, D.; Ferrell, R.; Kerjaschki, D.; Mortimer, P.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; et al. Defective Valves and Abnormal Mural Cell Recruitment Underlie Lymphatic Vascular Failure in Lymphedema Distichiasis. Nat Med 2004, 10, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharath, V.; Kahn, S.R.; Lazo-Langner, A. Genetic Polymorphisms of Vein Wall Remodeling in Chronic Venous Disease: A Narrative and Systematic Review. Blood 2014, 124, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adikusuma, W.; Firdayani, F.; Irham, L.M.; Darmawi, D.; Hamidy, M.Y.; Nopitasari, B.L.; Soraya, S.; Azizah, N. Integrated Genomic Network Analysis Revealed Potential of a Druggable Target for Hemorrhoid Treatment. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal 2023, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwerd, T.; Bryant, R. V.; Pandey, S.; Capitani, M.; Meran, L.; Cazier, J.B.; Jung, J.; Mondal, K.; Parkes, M.; Mathew, C.G.; et al. NOX1 Loss-of-Function Genetic Variants in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mucosal Immunology 2018 11:2 2017, 11, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, E.A.; Cohen, A.F. Sapropterin: New Drug Mechanisms. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2010, 69, 576–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanhewicz, A.E.; Alexander, L.M.; Kenney, W.L. Oral Sapropterin Acutely Augments Reflex Vasodilation in Aged Human Skin through Nitric Oxide-Dependent Mechanisms. J Appl Physiol 2013, 115, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free Radicals and Antioxidants in Normal Physiological Functions and Human Disease. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Xue, M.; Kang, C.; Gao, L.; Zhang, M.; Ma, C.; Jia, W.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, L.; Chen, P.; et al. Increased NOX1 and DUOX2 Expression in the Colonic Mucosa of Patients with Chronic Functional Constipation. Medicine (United States) 2022, 101, E30028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.W.; Mason, J.B. Folate Status: Effects on Pathways of Colorectal Carcinogenesis. Journal of Nutrition 2002, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, I.; Tran, P.; Christensen, B.; Sibani, S.; Rozen, R. A Second Genetic Polymorphism in Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) Associated with Decreased Enzyme Activity. Mol Genet Metab 1998, 64, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Promthet, S.; Pientong, C.; Ekalaksananan, T.; Songserm, N.; Poomphakwaen, K.; Chopjitt, P.; Wiangnon, S.; Tokudome, S. Risk Factors for Rectal Cancer and Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Polymorphisms in a Population in Northeast Thailand. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention 2012, 13, 4017–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, R.; Ssempijja, L.; Provenzano, M.; Andreucci, M. Genetic Biomarkers in Chronic Venous Disease. Biomark Med 2020, 14, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuoğlu, H.H.; Gunay, E.; Uzunoğlu, H. Effect of Genetic Factors on the Etiopathogenesis of Thrombosed Hemorrhoidal Disease. Chirurgia (Romania) 2019, 114, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, H.; Song, X.; Yuan, S.; Luo, Y. The Angiogenic Function of Nucleolin Is Mediated by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Nonmuscle Myosin. Blood 2006, 107, 3564–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salnikova, L.E.; Khadzhieva, M.B.; Kolobkov, D.S. Biological Findings from the PheWAS Catalog: Focus on Connective Tissue-Related Disorders (Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Abdominal Hernia, Varicose Veins and Hemorrhoids). Hum Genet 2016, 135, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecci, A.; Klersy, C.; Gresele, P.; Lee, K.J.D.; De Rocco, D.; Bozzi, V.; Russo, G.; Heller, P.G.; Loffredo, G.; Ballmaier, M.; et al. MYH9-Related Disease: A Novel Prognostic Model to Predict the Clinical Evolution of the Disease Based on Genotype-Phenotype Correlations. Hum Mutat 2014, 35, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillarp, A.; Dahlbäck, B.; Zöller, B. Actuated Protein C Resistance: From Phenotype to Genotype and Clinical Practice. Blood Rev 1995, 9, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, I.M.; Montgomery, G.W.; Mortlock, S. Genomic Characterisation of the Overlap of Endometriosis with 76 Comorbidities Identifies Pleiotropic and Causal Mechanisms Underlying Disease Risk. Hum Genet 2023, 142, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsatsakis, A.M.; Zafiropoulos, A.; Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Tzanakakis, G.N.; Kafatos, A. Relation of PON1 and CYP1A1 Genetic Polymorphisms to Clinical Findings in a Cross-Sectional Study of a Greek Rural Population Professionally Exposed to Pesticides. Toxicol Lett 2009, 186, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, R.; Adler, D.A.; Disteche, C.M.; Hassett, C.; Omiecinski, C.J.; Furlong, C.E. The Molecular Basis of the Human Serum Paraoxonase Activity Polymorphism. Nat Genet 1993, 3, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassett, C.; Omiecinski, C.J.; Richter, R.J.; Humbert, R.; Humbert, R.; Furlong, C.E.; Furlong, C.E.; Omiecinski, C.J.; Richter, R.J.; Humbert, R.; et al. Characterization of CDNA Clones Encoding Rabbit and Human Serum Paraoxonase: The Mature Protein Retains Its Signal Sequence. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 10141–10149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatter Garin, M.C.; James, R.W.; Dussoix, P.; Blanché, H.; Passa, P.; Froguel, P.; Ruiz, J. Paraoxonase Polymorphism Met-Leu54 Is Associated with Modified Serum Concentrations of the Enzyme. A Possible Link between the Paraoxonase Gene and Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1997, 99, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Isbell, H.M.; Fressart, V.; Denjoy, I.; Debbiche, A.; Itoh, H.; Poinsot, J.; George, A.L.; Coulombe, A.; Shea, M.A.; et al. Novel CALM3 Variant Causing Calmodulinopathy With Variable Expressivity in a 4-Generation Family. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2022, 15, E010572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Ni, Z.; Li, Z. CALM3 Affects the Prognosis of Leukemia and Hemorrhoids. Medicine 2023, 102, e36027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naba, A.; Clauser, K.R.; Whittaker, C.A.; Carr, S.A.; Tanabe, K.K.; Hynes, R.O. Extracellular Matrix Signatures of Human Primary Metastatic Colon Cancers and Their Metastases to Liver. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.W.; Johnson, G. Acetylcholinesterase in Hirschsprung’s Disease. Pediatr Surg Int 2005, 21, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwartler, C.S.; Chen, J.; Thakur, D.; Li, S.; Baskin, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. V.; Walker, L.; Hill, J.A.; Epstein, H.F.; et al. Overexpression of Smooth Muscle Myosin Heavy Chain Leads to Activation of the Unfolded Protein Response and Autophagic Turnover of Thick Filament-Associated Proteins in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2014, 289, 14075–14088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plackett, T.P.; Kwon, E.; Ronald A Gagliano, J.; Oh, R.C. Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome—Hypermobility Type and Hemorrhoids. Case Rep Surg 2014, 2014, 171803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, W.; Alkhouri, R.; Baker, R.D.; Bard, J.E.; Quigley, E.M.; Baker, S.S. Structural Changes in the Gut Microbiome of Constipated Patients. Physiol Genomics 2014, 46, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisinda, G. How to Treat Haemorrhoids. Prevention Is Best; Haemorrhoidectomy Needs Skilled Operators. BMJ 2000, 321, 582–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hullar, M.A.J.; Fu, B.C. Diet, the Gut Microbiome, and Epigenetics. Cancer Journal (United States) 2014, 20, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, M.M.; van der Giezen, M.; Søreide, K. Gut Microbiome Influence on Human Epigenetics, Health, and Disease. Handbook of Epigenetics: The New Molecular and Medical Genetics, Third Edition 2023, 669–686. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Li, Y.; Stoll, M.L.; Tollefsbol, T.O. The Epigenetic Connection Between the Gut Microbiome in Obesity and Diabetes. Front Genet 2020, 10, 453795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, V.D.; Tutino, R.; Messina, M.; Santarelli, M.; Nigro, C.; Lo Secco, G.; Piceni, C.; Montanari, E.; Barletta, G.; Venturelli, P.; et al. Altered Gut Microbic Flora and Haemorrhoids: Could They Have a Possible Relationship? J Clin Med 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibret, A.A.; Oumer, M.; Moges, A.M. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Hemorrhoids among Adult Patients Visiting the Surgical Outpatient Department in the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. PLoS One 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peery, A.F.; Sandler, R.S.; Galanko, J.A.; Bresalier, R.S.; Figueiredo, J.C.; Ahnen, D.J.; Barry, E.L.; Baron, J.A. Risk Factors for Hemorrhoids on Screening Colonoscopy. PLoS One 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riss, S.; Weiser, F.A.; Schwameis, K.; Riss, T.; Mittlböck, M.; Steiner, G.; Stift, A. The Prevalence of Hemorrhoids in Adults. Int J Colorectal Dis 2012, 27, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.E.; Kang, J.H.; Shin, J.Y.; Song, Y.M. Factors Associated with Hemorrhoids in Korean Adults: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Korean J Fam Med 2014, 35, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frezza, E.E.; Shebani, K.O.; Robertson, J.; Wachtel, M.S. Morbid Obesity Causes Chronic Increase of Intraabdominal Pressure. Dig Dis Sci 2007, 52, 1038–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.S.; Holmes, M. V.; Zheng, J.; Sanderson, E.; Carter, A.R. The Impact of Education Inequality on Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk Is Mediated by Smoking and Body Mass Index: Mendelian Randomization Study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2022, 61, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Gui, Y.; Qin, H.; Xie, Y. Causal Association between Adiposity and Hemorrhoids: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front Med (Lausanne) 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalán, V.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Frühbeck, G. Role of Extracellular Matrix Remodelling in Adipose Tissue Pathophysiology: Relevance in the Development of Obesity. Histol Histopathol 2012, 27, 1515–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaskova, E.; Velganova-veghova, M.; Geryk, M.; Foltenova, H.; Kucerova, V.; Karasek, D. Role of Adipose Tissue in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, C. Pathophysiology of Obesity. Nurs Clin North Am 2021, 56, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidell, J.C.; de Groot, L.C.P.G.M.; van Sonsbeek, J.L.A.; Deurenberg, P.; Hautvast, J.G. Associations of Moderate and Severe Overweight with Self-Reported Illness and Medical Care in Dutch Adults. Am J Public Health 1986, 76, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, E.; Pagano, R.; Decarli, A.; La Vecchia, C. Body Weight and the Prevalence of Chronic Diseases. J Epidemiol Community Health (1978) 1988, 42, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.S.; Jung, K.U.; Rampal, S.; Zhao, D.; Guallar, E.; Ryu, S.; Chang, Y.; Kim, H.O.; Kim, H.; Chun, H.K.; et al. Risk Factors for Hemorrhoidal Disease among Healthy Young and Middle-Aged Korean Adults. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, S.J.; Molloy, P.L.; Varinli, H.; Morrison, J.L.; Muhlhausler, B.S.; Buckley, M.; Clark, S.J.; McMillen, I.C.; Noakes, M.; Samaras, K.; et al. Epigenetics and Human Obesity. International Journal of Obesity 2015 39:1 2014, 39, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, B.M.; Keildson, S.; Lindgren, C.M. Genetics and Epigenetics of Obesity. Maturitas 2011, 69, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, K.; Keller, M.; la Cour Poulsen, L.; Blüher, M.; Kovacs, P.; Böttcher, Y. Genetics and Epigenetics in Obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigot, F.; Siproudhis, L.; Allaert, F.A. Risk Factors Associated with Hemorrhoidal Symptoms in Specialized Consultation. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 2005, 29, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcò, F.; Sonnenberg, A. Associations between Hemorrhoids and Other Diagnoses. Dis Colon Rectum 1998, 41, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, D.; Davis, K.L.; Baran, R.W. Healthcare Costs and Clinical Sequelae Associated with Constipation in a Managed Care Population. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2007, 102, S432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsson, H.Ö.; Graf, W.; Påhlman, L. Bowel Habits in Hemorrhoid Patients and Normal Subjects. Am J Gastroenterol 2005, 100, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helvaci, M.R.; Algin, M.C.; Kaya, H. Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Chronic Gastritis, Hemorrhoid, Urolithiasis. Eurasian J Med 2009, 41, 158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rusu, F.; Dumitraşcu, D.L. Four Years Follow-up of Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Rom J Intern Med 2015, 53, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dothel, G.; Barbaro, M.R.; Di Vito, A.; Ravegnini, G.; Gorini, F.; Monesmith, S.; Coschina, E.; Benuzzi, E.; Fuschi, D.; Palombo, M.; et al. New Insights into Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pathophysiological Mechanisms: Contribution of Epigenetics. Journal of Gastroenterology 2023 58:7 2023, 58, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
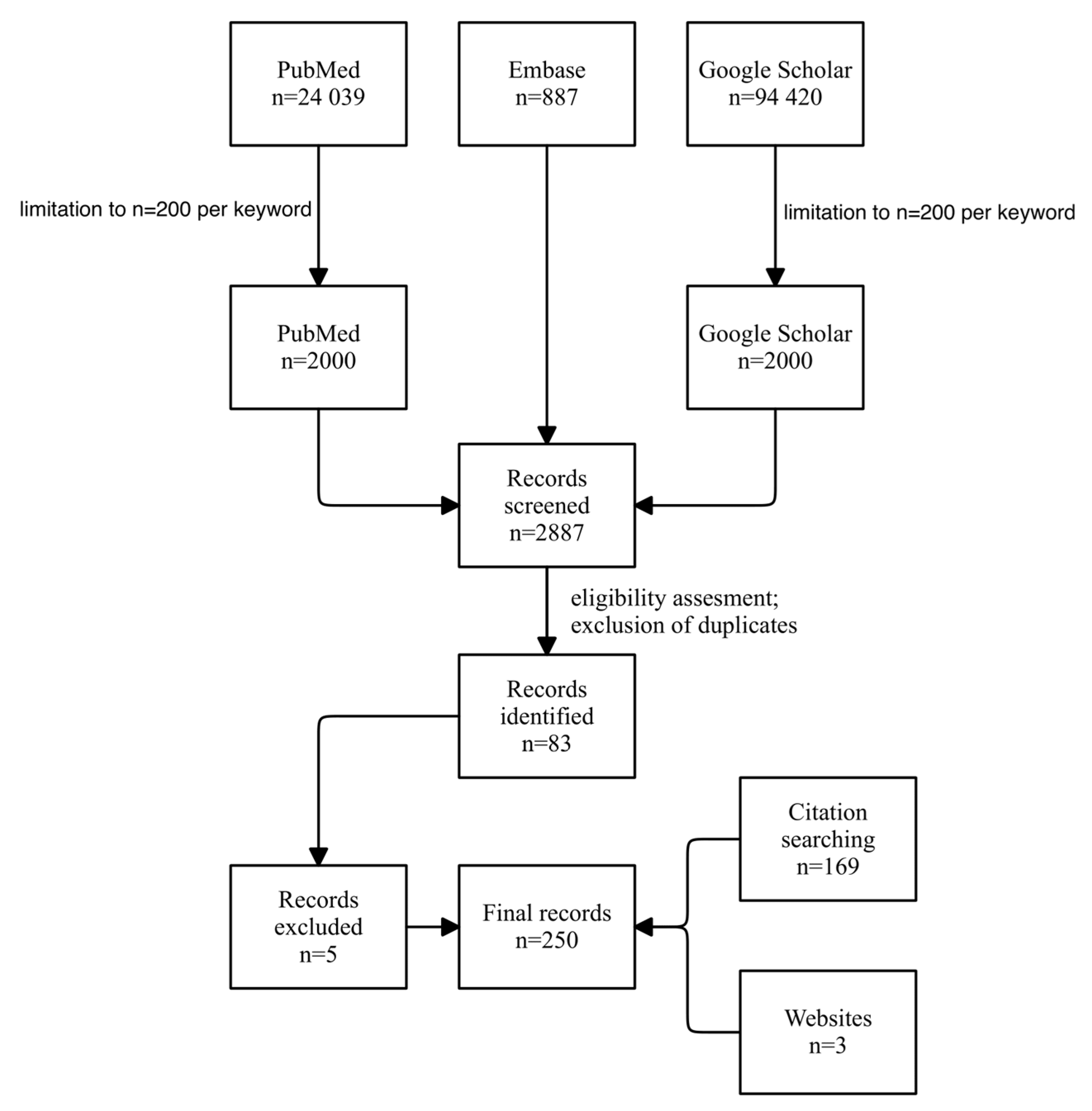
- Baethge, C.; Goldbeck-Wood, S.; Mertens, S. SANRA—a Scale for the Quality Assessment of Narrative Review Articles. Res Integr Peer Rev 2019, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramer, W.M.; Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kleijnen, J.; Franco, O.H. Optimal Database Combinations for Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews: A Prospective Exploratory Study. Syst Rev 2017, 6, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins JPT; Thomas J; Chandler J; Cumpston M; Li T; Page MJ; Welch VA (editors) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.4; version 6.4.; Cochrane, 2023.
| Cytokines Expressed in Hemorrhoids | |
|---|---|
| Pro-inflammatory Cytokines | Anti-inflammatory Cytokines |
| RANTES | IL-10 |
| TNF-α | ·· |
| VEGF | ·· |
| IL-1β | ·· |
| IL-6 | ·· |
| IL-8 | ·· |
| IL-17 | ·· |
| IFN-γ | ·· |
| MiRNAs in vesical pathways in hemorrhoids | MiRNAs in extracellular vesical pathways in hemorrhoids | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probable targeted processes * | Endocytosis | Synaptic vesicle pathways | Transcription, protein kinase activity, and ubiquitination | Transcriptional activator activity |
| Status | Upregulated | Downregulated | Upregulated | Downregulated |
| Type of miRNA | miR-375 | miR-376b-3p | miR-6741-3p | miR-548t-5p |
| miR-215-5p | miR-34a-5p | miR-6834-3 | miR-323b-5p | |
| miR-192-5p | miR-152-3p | miR-425 | miR-1322 | |
| miR-143-3p | let-7c-5p | miR-6804-3 | miR-3928-5p | |
| miR-187-3p | miR-107 | miR-744-3 | miR-346 | |
| miR-194-5p | miR-517a-3p | miR-848 | miR-4704-5p | |
| miR-145-5p | miR-517b-3p | miR-299-5 | miR-1913 | |
| miR-490-3p | miR-1307-5p | miR-463 | miR-876-3p | |
| miR-145-3p | miR-190a-5p | miR-317 | miR-4460 | |
| ·· | miR-378a-5p | miR-465 | miR-892a | |
| ·· | miR-708-3p | ·· | ·· | |
| ·· | miR-450a-5p | ·· | ·· | |
| ·· | miR-30e-5p | ·· | ·· | |
| ·· | miR-532-5p | ·· | ·· | |
| Genes Significant to the Development of Hemorrhoids | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Product | Function | Mechanism of Action | Mutations | Reported Associated Conditions | |
| FOXC2 | FOXC2 (forkhead box protein) [143,144] |
|
— | |||
| NOX1 and NOS3 | NOX1 (NADPH oxidase) NOS3 (nitric oxide synthase) |
|
— | |||
| MTHFR | methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase |
|
— |
|
||
| MYH9 | heavy chain of non-muscle myosin IIA |
|
— |
|
||
| F5 | coagulation factor V |
|
— |
|
||
| CYP1A | aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase in hepatic and extrahepatic cytochrome P450 | — | — |
|
|
|
| PON1 | serum paraoxonase 1 | — | — |
|
||
| CALM3 | calmodulin 3 |
|
— | — |
|
|
| ANO1 | anoctamin-1 (voltage-gated calcium-activated anion channel) |
|
|
|
— | |
| SPRX | — |
|
|
|
— | |
| ACHE | acetylcholinesterase |
|
— |
|
||
| SRTT | capped-RNA binding protein | — | — | — |
|
|
| GSDMC | gasdermin C |
|
— |
|
|
|
| MYH11 | muscle myosin heavy chain 11 |
|
|
|
|
|
| ELN | elastin |
|
— | — |
|
|
| COL5A2 | type V collagen (regulatory) | — | — | — | ||
| PRDM | histone methyltransferase |
|
— | — |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





