Submitted:
04 November 2024
Posted:
05 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Cell Culture Conditions
2.3. Label-Free Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
2.4. MS Data Processing and Analysis
2.5. Bioinformatic Analyses
2.6. Cells Transfection
2.7. mRNA and miRNA Expression Analyses
2.8. Protein Quantification by Immunoblotting
3. Results
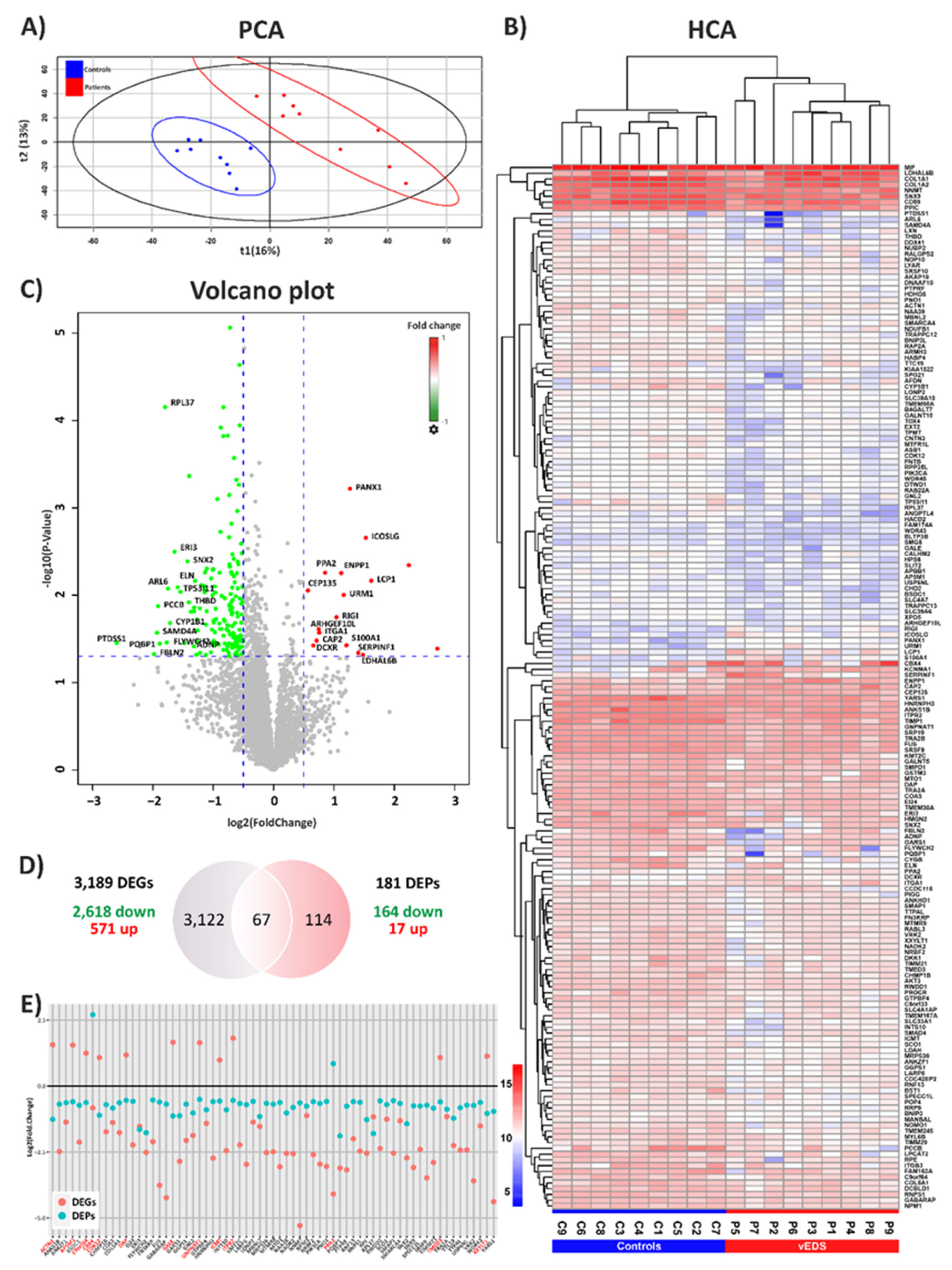
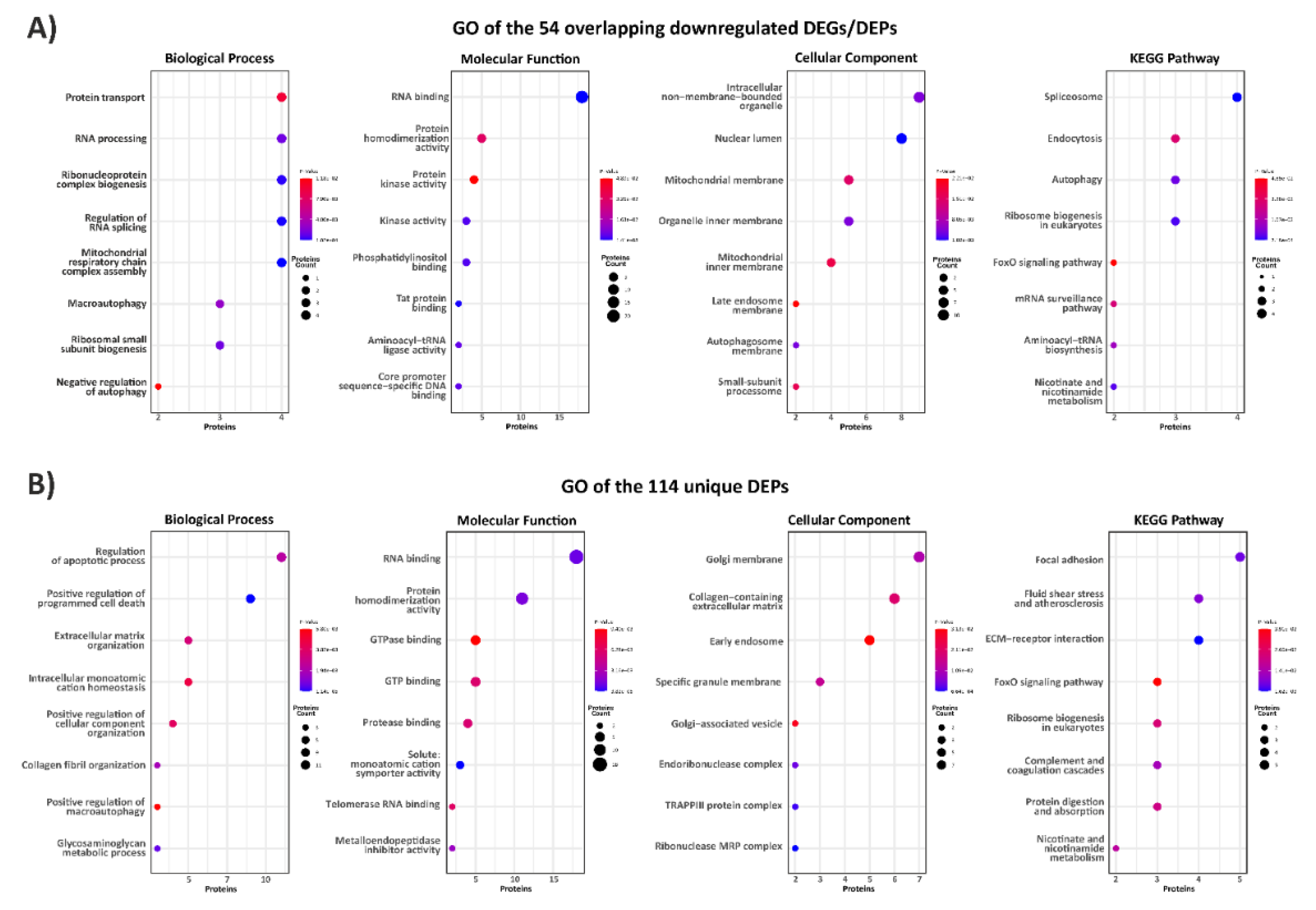
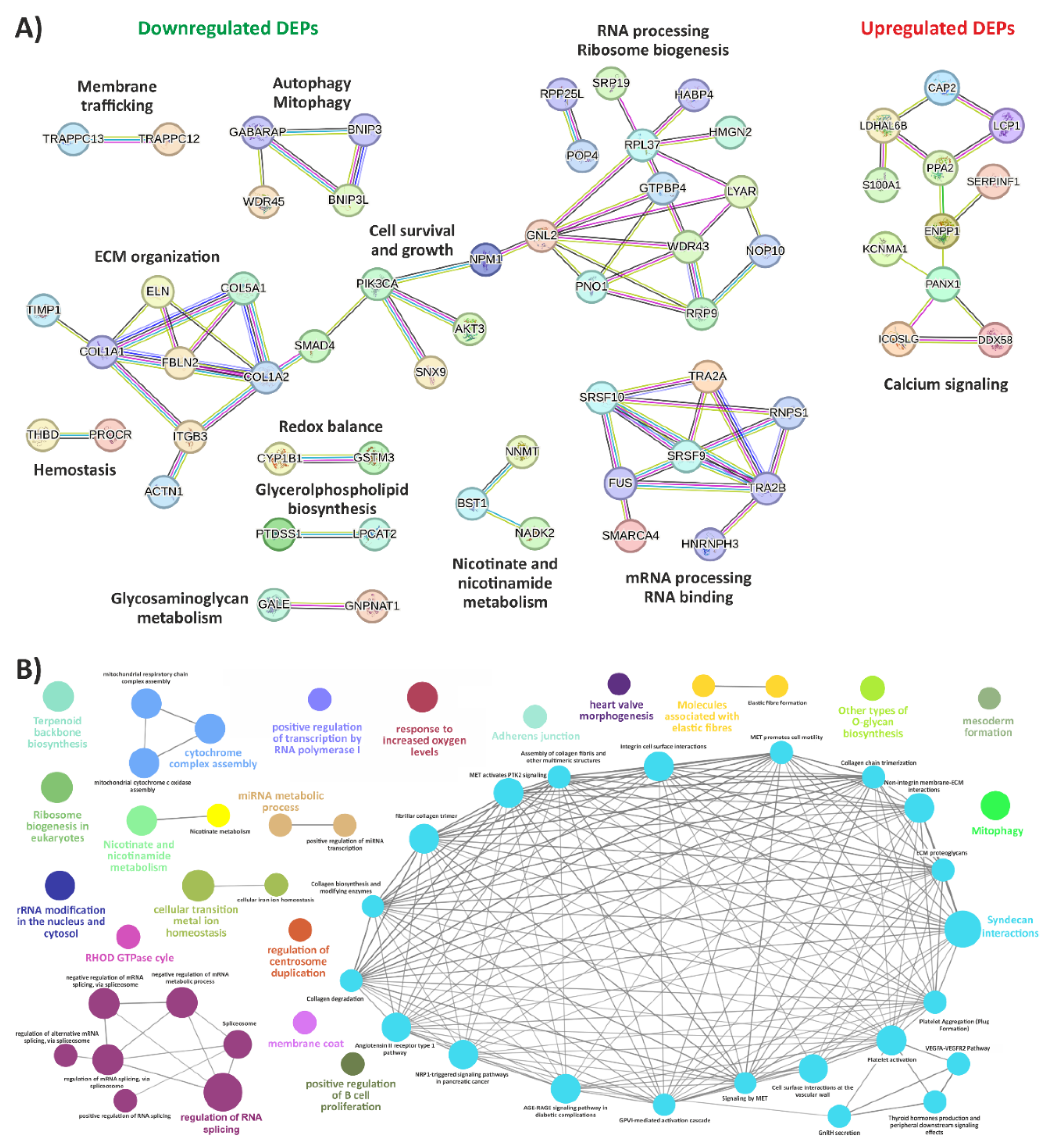
3.1. Exploring the Proteomic Landscape of vEDS Patient Fibroblasts and Its Integration with Transcriptomic Insights
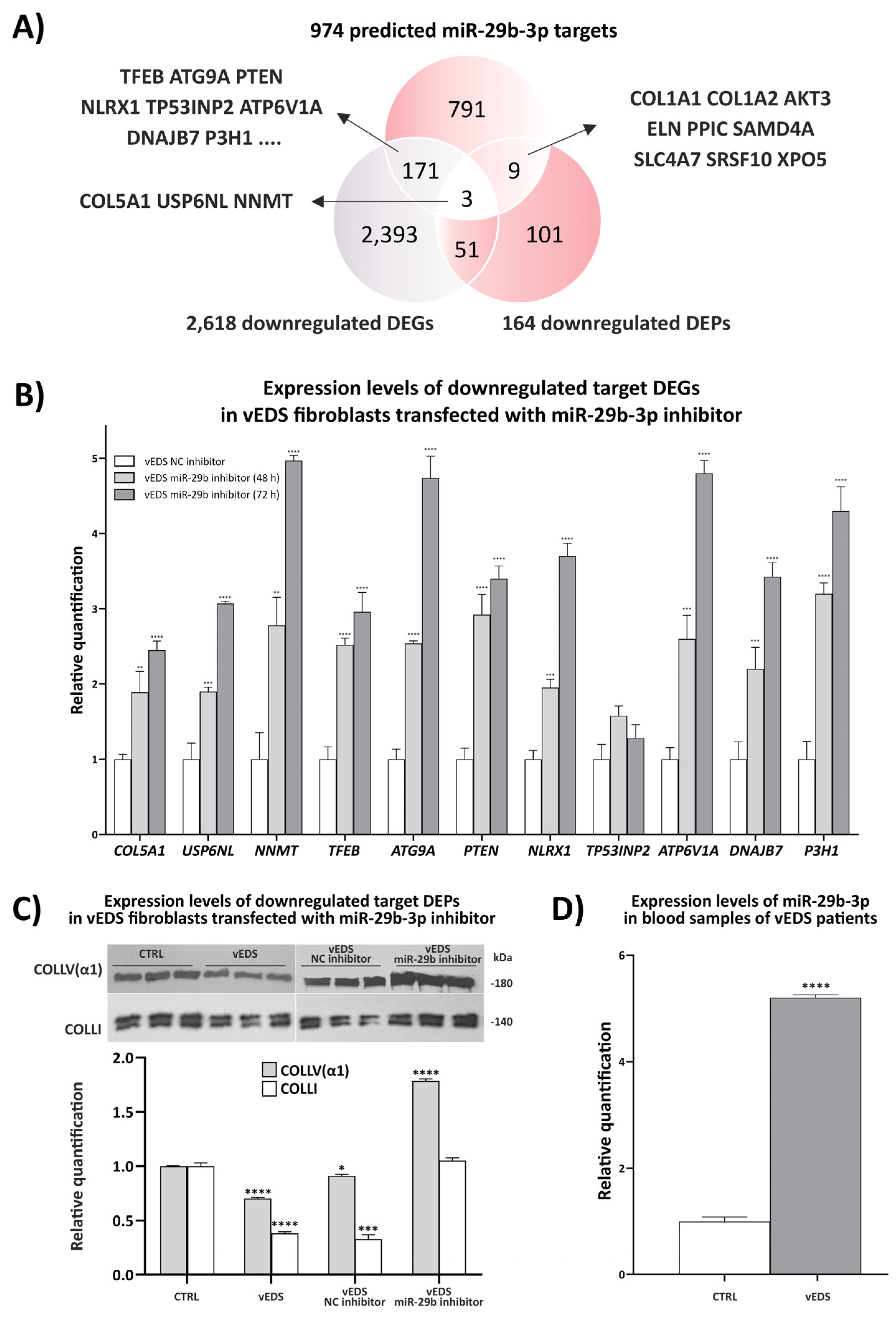
3.2. Exploring the Role of miR-29b-3p in Disease Mechanisms and Its Therapeutic Potential
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Byers, P.H.; Belmont, J.; Black, J.; De Backer, J.; Frank, M.; Jeunemaitre, X.; Johnson, D.; Pepin, M.; Robert, L.; Sanders, L.; et al. Diagnosis, Natural History, and Management in Vascular Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 40–47. [CrossRef]
- Ritelli, M.; Rovati, C.; Venturini, M.; Chiarelli, N.; Cinquina, V.; Castori, M.; Colombi, M. Application of the 2017 Criteria for Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome in 50 Patients Ascertained According to the Villefranche Nosology. Clin. Genet. 2020, 97, 287–295. [CrossRef]
- Bowen, J.M.; Hernandez, M.; Johnson, D.S.; Green, C.; Kammin, T.; Baker, D.; Keigwin, S.; Makino, S.; Taylor, N.; Watson, O.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: Experience of the UK National Diagnostic Service, Sheffield. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 31, 749–760. [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.; Adham, S.; Seigle, S.; Legrand, A.; Mirault, T.; Henneton, P.; Albuisson, J.; Denarié, N.; Mazzella, J.M.; Mousseaux, E.; et al. Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: Long-Term Observational Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1948–1957. [CrossRef]
- Eagleton, M.J. Arterial Complications of Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 1869–1880. [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.T.; Perdu, J.; De Backer, J.; Bozec, E.; Collignon, P.; Emmerich, J.; Fauret, A.L.; Fiessinger, J.N.; Germain, D.P.; Georgesco, G.; et al. Effect of Celiprolol on Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: A Prospective Randomised, Open, Blinded-Endpoints Trial. Lancet (London, England) 2010, 376, 1476–1484. [CrossRef]
- Buso, G.; Paini, A.; Agabiti-Rosei, C.; De Ciuceis, C.; Bertacchini, F.; Stassaldi, D.; Salvetti, M.; Ritelli, M.; Venturini, M.; Colombi, M.; et al. Despite Celiprolol Therapy, Patients with Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Remain at Risk of Vascular Events: A 12-Year Experience in an Italian Referral Center. Vasc. Med. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Baderkhan, H.; Wanhainen, A.; Stenborg, A.; Stattin, E.L.; Björck, M. Celiprolol Treatment in Patients with Vascular Ehlers‐Danlos Syndrome. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2021, 61, 326–331. [CrossRef]
- Legrand Id, A.; Guery, C.; Faugeroux, J.; Fontaine Id, E.; Beugnon, C.; Lie Gianfermi, A.; Loisel-Ferreiraid, I.; Verpont, M.-C.; Adhamid, S.; Miraultid, T.; et al. Comparative Therapeutic Strategies for Preventing Aortic Rupture in a Mouse Model of Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. PLoS Genet. 2022 Mar 4;18(3):e1010059. [CrossRef]
- Bowen, C.J.; Giadrosic, J.F.C.; Burger, Z.; Rykiel, G.; Davis, E.C.; Helmers, M.R.; Benke, K.; MacFarlane, E.G.; Dietz, H.C. Targetable Cellular Signaling Events Mediate Vascular Pathology in Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 2020, 130, 686–698. [CrossRef]
- Buso, G.; Corvini, F.; Fusco, E.M.; Messina, M.; Cherubini, F.; Laera, N.; Paini, A.; Salvetti, M.; Ciuceis, C. De; Ritelli, M.; et al. Current Evidence and Future Perspectives in the Medical Management of Vascular Ehlers—Danlos Syndrome : Focus on Vascular Prevention. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(14), 4255; [CrossRef]
- Omar, R.; Lee, M.; Gonzalez-Trueba, L.; Lianos, S.; Hazarika, S.; Ammar, M.A.; Cassels, J.; Michie, A.M.; Bulleid, N.J.; Malfait, F.; et al. The Chemical Chaperone 4-Phenylbutyric Acid Rescues Molecular Cell Defects of COL3A1 Mutations That Cause Vascular Ehlers Danlos Syndrome. bioRxiv 2024, 2024.06.20.599980. [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, N.; Cinquina, V.; Martini, P.; Bertini, V.; Zoppi, N.; Venturini, M.; Ritelli, M.; Colombi, M. Deciphering Disease Signatures and Molecular Targets in Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome through Transcriptome and MiRNome Sequencing of Dermal Fibroblasts. Biochim. Biophys. acta. Mol. basis Dis. 2024, 1870. [CrossRef]
- Terriaca, S.; Monastero, R.; Orlandi, A.; Balistreri, C.R. The Key Role of MiRNA in Syndromic and Sporadic Forms of Ascending Aortic Aneurysms as Biomarkers and Targets of Novel Therapeutic Strategies. Front Genet. 2024 Feb 21:15:1365711. [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, N.; Carini, G.; Zoppi, N.; Ritelli, M.; Colombi, M. Transcriptome Analysis of Skin Fibroblasts with Dominant Negative COL3A1 Mutations Provides Molecular Insights into the Etiopathology of Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. PLoS One 2018, 13. [CrossRef]
- Zoppi, N.; Chiarelli, N.; Ritelli, M.; Colombi, M. Multifaced Roles of the αvβ3 Integrin in Ehlers-Danlos and Arterial Tortuosity Syndromes’ Dermal Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [CrossRef]
- Reggio, A.; Buonomo, V.; Berkane, R.; Bhaskara, R.M.; Tellechea, M.; Peluso, I.; Polishchuk, E.; Lorenzo, G. Di; Cirillo, C.; Esposito, M.; et al. Role of FAM134 Paralogues in Endoplasmic Reticulum Remodeling, ER-phagy, and Collagen Quality Control. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Michalski, A.; Damoc, E.; Hauschild, J.P.; Lange, O.; Wieghaus, A.; Makarov, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Cox, J.; Mann, M.; Horning, S. Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics Using Q Exactive, a High-Performance Benchtop Quadrupole Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2011, 10. [CrossRef]
- Welten, S.M.J.; Goossens, E.A.C.; Quax, P.H.A.; Nossent, A.Y. The Multifactorial Nature of MicroRNAs in Vascular Remodelling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 110, 6–22. [CrossRef]
- Rega, S.; Farina, F.; Bouhuis, S.; de Donato, S.; Chiesa, M.; Poggio, P.; Cavallotti, L.; Bonalumi, G.; Giambuzzi, I.; Pompilio, G.; et al. Multi-Omics in Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm: The Complex Road to the Simplification. Cell Biosci. 2023, 13, 1–27. [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, J.M.A.; Burger, J.; Bekkers, J.A.; Den Dekker, A.T.; von der Thüsen, J.H.; Zajec, M.; Brüggenwirth, H.T.; van der Sterre, M.L.T.; van den Born, M.; Luider, T.M.; et al. Multi-Omics Profiling in Marfan Syndrome: Further Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Aortic Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 438. [CrossRef]
- Udugampolage, N.S.; Frolova, S.; Taurino, J.; Pini, A.; Martelli, F.; Voellenkle, C. Coding and Non-Coding Transcriptomic Landscape of Aortic Complications in Marfan Syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2024, Jul 5;25(13):7367. [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Qiu, P.; Wu, Z.; Ding, A.; Hu, J.; Hou, J.; Jiang, Y.; Pu, H.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, X.; et al. Integrative Multi-Omics Analyses Reveal Vesicle Transport as a Potential Target for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 170, 108071. [CrossRef]
- Stratton, M.S.; Farina, F.M.; Elia, L. Epigenetics and Vascular Diseases. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2019, 133, 148. [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Shkurat, T.P.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Grechko, A. V.; Orekhov, A.N. The Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Disease: A Brief Review. Ann. Med. 2018, 50, 121–127. [CrossRef]
- Van Der Pluijm, I.; Burger, J.; Van Heijningen, P.M.; IJpma, A.; Van Vliet, N.; Milanese, C.; Schoonderwoerd, K.; Sluiter, W.; Ringuette, L.J.; Dekkers, D.H.W.; et al. Decreased Mitochondrial Respiration in Aneurysmal Aortas of Fibulin-4 Mutant Mice Is Linked to PGC1A Regulation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1776–1793. [CrossRef]
- Németh, C.E.; Marcolongo, P.; Gamberucci, A.; Fulceri, R.; Benedetti, A.; Zoppi, N.; Ritelli, M.; Chiarelli, N.; Colombi, M.; Willaert, A.; et al. Glucose Transporter Type 10-Lacking in Arterial Tortuosity Syndrome-Facilitates Dehydroascorbic Acid Transport. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 1630–1640. [CrossRef]
- Zoppi, N.; Chiarelli, N.; Cinquina, V.; Ritelli, M.; Colombi, M. GLUT10 Deficiency Leads to Oxidative Stress and Non-Canonical Avβ3 Integrin-Mediated TGFβ Signalling Associated with Extracellular Matrix Disarray in Arterial Tortuosity Syndrome Skin Fibroblasts. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 6769–6787. [CrossRef]
- Oller, J.; Gabandé-Rodríguez, E.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, M.J.; Desdín-Micó, G.; Aranda, J.F.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.; Ballesteros-Martínez, C.; Blanco, E.M.; Roldan-Montero, R.; Acuña, P.; et al. Extracellular Tuning of Mitochondrial Respiration Leads to Aortic Aneurysm. Circulation 2021, 143, 2091–2109. [CrossRef]
- De Leonibus, C.; Maddaluno, M.; Ferriero, R.; Besio, R.; Cinque, L.; Lim, P.J.; Palma, A.; De Cegli, R.; Gagliotta, S.; Montefusco, S.; et al. Sestrin2 Drives ER-Phagy in Response to Protein Misfolding. Dev. Cell 2024, 59, 2035-2052.e10. [CrossRef]
- De Cavanagh, E.M.; Ferder, M.; Inserra, F.; Ferder, L. Angiotensin II, Mitochondria, Cytoskeletal, and Extracellular Matrix Connections: An Integrating Viewpoint. Am. J. Physiol.—Hear. Circ. Physiol. 2009, Mar;296(3):H550-8. [CrossRef]
- Zoppi, N.; Barlati, S.; Colombi, M. FAK-Independent Alphavbeta3 Integrin-EGFR Complexes Rescue from Anoikis Matrix-Defective Fibroblasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1783, 1177–1188. [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, N.; Ritelli, M.; Zoppi, N.; Colombi, M. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms in the Pathogenesis of Classical, Vascular, and Hypermobile Ehlers‒Danlos Syndromes. Genes (Basel). 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F. Non-Coding RNA-Targeted Therapy: A State-of-the-Art Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25. [CrossRef]
- Hibender, S.; Franken, R.; Van Roomen, C.; Ter Braake, A.; Van Der Made, I.; Schermer, E.E.; Gunst, Q.; Van Den Hoff, M.J.; Lutgens, E.; Pinto, Y.M.; et al. Resveratrol Inhibits Aortic Root Dilatation in the Fbn1C1039G/+ Marfan Mouse Model. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1618–1626. [CrossRef]
- Boon, R.A.; Dimmeler, S. MicroRNAs and Aneurysm Formation. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2011, 21, 172–177. [CrossRef]
- Maegdefessel, L.; Azuma, J.; Toh, R.; Merk, D.R.; Deng, A.; Chin, J.T.; Raaz, U.; Schoelmerich, A.M.; Raiesdana, A.; Leeper, N.J.; et al. Inhibition of MicroRNA-29b Reduces Murine Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Development. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 497–506. [CrossRef]
- Merk, D.R.; Chin, J.T.; Dake, B.A.; Maegdefessel, L.; Miller, M.O.; Kimura, N.; Tsao, P.S.; Iosef, C.; Berry, G.J.; Mohr, F.W.; et al. MiR-29b Participates in Early Aneurysm Development in Marfan Syndrome. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 312–324. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.S. Therapeutic Advances of MiRNAs: A Preclinical and Clinical Update. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 28, 127–138. [CrossRef]
- Moraes, F.C.; Pichon, C.; Letourneur, D.; Chaubet, F. MiRNA Delivery by Nanosystems: State of the Art and Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.C.; Langer, R.; Wood, M.J.A. Advances in Oligonucleotide Drug Delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 673–694. [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.; Hossain, G.S.; Kocerha, J. The Potential for MicroRNA Therapeutics and Clinical Research. Front. Genet. 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




