Submitted:
09 April 2025
Posted:
11 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Model and Analysis
3. Discussion and Conclusions
3.1. Summary of the Model Approach
-
Unified Scaling Law: We identified simple but profound scaling factors S for leptons, light quarks, and heavy quarks, which relate to known geometric volumes:
- -
- Slepton ≈ √5·π²/3
- -
- Slight ≈ √5·π²/4
- -
- Sheavy ≈ π²/√2
-
Geometric-Topological Generation Encoding: Each fermion generation is associated with increasing dimensional spinor representations:
- -
- 1st generation: Quaternion (H)
- -
- 2nd generation: Octonion (O)
- -
- 3rd generation: Sedenion (S)
- 3.
- Cubic Generation Indexing in Quarks: A novel feature discovered in this work is the necessity of using a cubic generation index x = k³ to accurately model the quark mass distribution.
- 4.
- Minimal Parameter, Maximal Fit: With only three parameters per family, the model provides exceptional agreement with experimental data and gives mass ratios across generations and families with striking accuracy.
3.2. Physical Significance and Implications
- -
- Beyond the Standard Model: Our model naturally extends the Standard Model by embedding fermions into a higher-dimensional hypercomplex algebraic structure.
- -
- Triality and Internal Structure: The results support a reinterpretation of elementary particles not as point-like but as composite objects with internal topological and algebraic structure.
- -
- Link to Grand Unified Theories (GUTs): The progression from SU(5) to SO(10) and ultimately to E₈ in our model’s embedding structure suggests a natural pathway for GUT symmetry breaking.
- -
- Foundational Physics and Mass Generation: This mass law may help explain not only the observed mass hierarchy but also resolve longstanding puzzles such as the Koide formula, flavor generation, and possibly even the mass gap in Yang–Mills theory, all from a geometric-topological perspective.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Cottingham, W. N.; Greenwood, D. A. An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics. Cambridge University Press, 2007.
- Hoddeson, L.; Brown, L.; Riordan, M.; Dresden, M. The Rise of the Standard Model: A History of Particle Physics from 1964 to 1979. Cambridge University Press, 1997.
- Vissaami, F. Do experiments support a hierarchy problem? Phys. Rev. D 1998, 50, 7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Cendejas, N.; Herrera-Aguilar, A.; Kanakoglou, K.; et al. Mass hierarchy, mass gap, and corrections to Newton’s law on thick branes with Poincaré symmetry. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2014, 46, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpoot, S. Three-generation models with chiral-color interactions. Phys. Rev. D 1988, 38, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furey, C. Three generations, two unbroken gauge symmetries, and one eight-dimensional algebra. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 785, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Zhang, H. On the Koide-like relations for the running masses of charged leptons, neutrinos, and quarks. Phys. Lett. B 2000, 635, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, R. N.; Smirnov, A. Y. Neutrino mass and new physics. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2006, 56, 569–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H. Standard Model particle physics tested by the fine structure constant. Nature 2020, 588, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athron, P. ; Bimonoid; King, S. F.M. Fine-tuning in the constrained exceptional supersymmetric standard model. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 115023. [Google Scholar]
- alvio, A. Solving the Standard Model problems in softened gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 096007. [Google Scholar]
- Georgi, H.; Glashow, S. Unity of all elementary-particle forces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1974, 32, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgi, H. The state of the art: gauge theories. Proceedings of the 1975 Cargese Summer Institute on the Theories of the Elementary Particle, Ed. by N. Levy, 1976, pp. 575–583.
- Tarazawa, H.; Chikashige, Y.; Akama, K. United model for the Nambu-Jona-Lasinio type for all elementary-particle forces. Phys. Rev. D 1977, 15, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, C. A Clifford algebra-based grand unification program of gravity and the Standard Model: a review study. Canad. J. Phys. 2014, 92, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, O.C. Leptons, quarks, and gauge from the complex Clifford algebra Cl6. Adv. Appl. Clifford Algebra 2018, 28, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, S. Introduction to Octonion and Other Non-Associative Algebras in Physics. Cambridge University Press, 1995.
- Smith, D. A.; Conway, J. H. On Quaternions and Octonions: Their Geometry, Arithmetic, and Symmetry. AK Peters, 2003.
- Baez, J.C. Review of On Quaternions and Octonions: Their Geometry, Arithmetic, and Symmetry by Conway and Smith. Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 2005, 42, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresnigt, N. A sedenion algebraic representation of three colored fermion generations. XII International Symposium on Quantum Theory and Symmetries (QTS12), Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2023, 2667.
- Gillard, A. B.; Gresnigt, N. G. Three fermion generations with two unbroken gauge symmetries from the complex sedenions. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79. 1-11.
- Tang, Q.; Tang, J. Sedenion algebra model as an extension of the Standard Model and its link to SU(5). Symmetry 2024, 16, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia. n-Sphere. Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/N-sphere.
- Ibanez, L. E. , & Uranga, A. M. String Theory and Particle Physics: An Introduction to String Phenomenology. Cambridge University Press: 2012.
- Bailin, D.; Love, A. "Kaluza-Klein Theories. " Reports on Progress in Physics 1987, 50, 1087–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, Y. A new view of quark and lepton mass hierarchy. Physics Letters B, 1983, 120, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia. Cayley–Dickson Construction. Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cayley–Dickson_construction.
- Georgi, H.; Glashow, S.L. Unity of All Elementary-Particle Forces. Physical Review Letters 1974, 32, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsch, H.; Minkowski, P. (). Unified interactions of leptons and hadrons. Annals of Physics 1975, 93, 193–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, D. J. , Harvey, J. A., Martinec, E. J., & Rohm, R. Heterotic String Theory. I. The Free Heterotic String. Nuclear Physics B 1985, 256, 253–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terazawa, H. and Yasue M. , J., Composite Higgs Boson in the Unified Subquark Model of All Fundamental Particles and Forces. Modern Phys. 2014, 5, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Terazawa, H. , Qurak Matter: From Subquarks to the Universe, (Nova Science Publishing, New York, 2018).
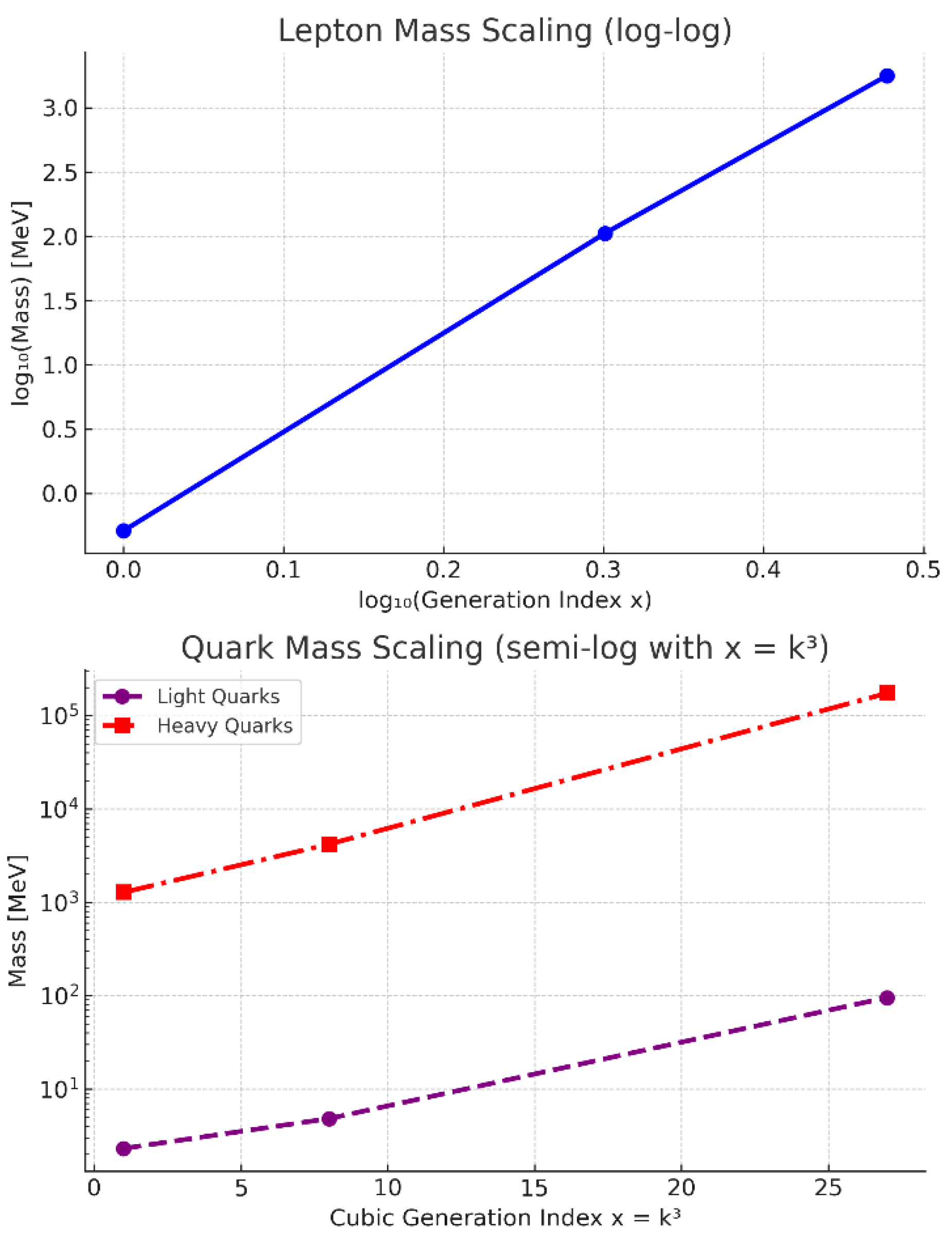
| Classification | Generation | Particle | Experimental Mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leptons | 1st generation | Electron (e) | 0.51099895000 (15) MeV |
| 2nd generation | Muon (μ) | 105.6583755 (23) MeV | |
| 3rd generation | Tau (τ) | 1776.86 (12) MeV | |
| Light quarks | 1st generation | Up (u) | 2.16 (0.19) MeV |
| 2nd generation | Down (d) | 4.67 (0.48) MeV | |
| 3rd generation | Strange (s) | 93.40 (0.86) MeV | |
| Heavy quarks | 1st generation | Charm (c) | 1270 (20) MeV |
| 2nd generation | Bottom (b) | 4180 (0.03) MeV | |
| 3rd generation | Top (t) | 17269 (500) MeV |
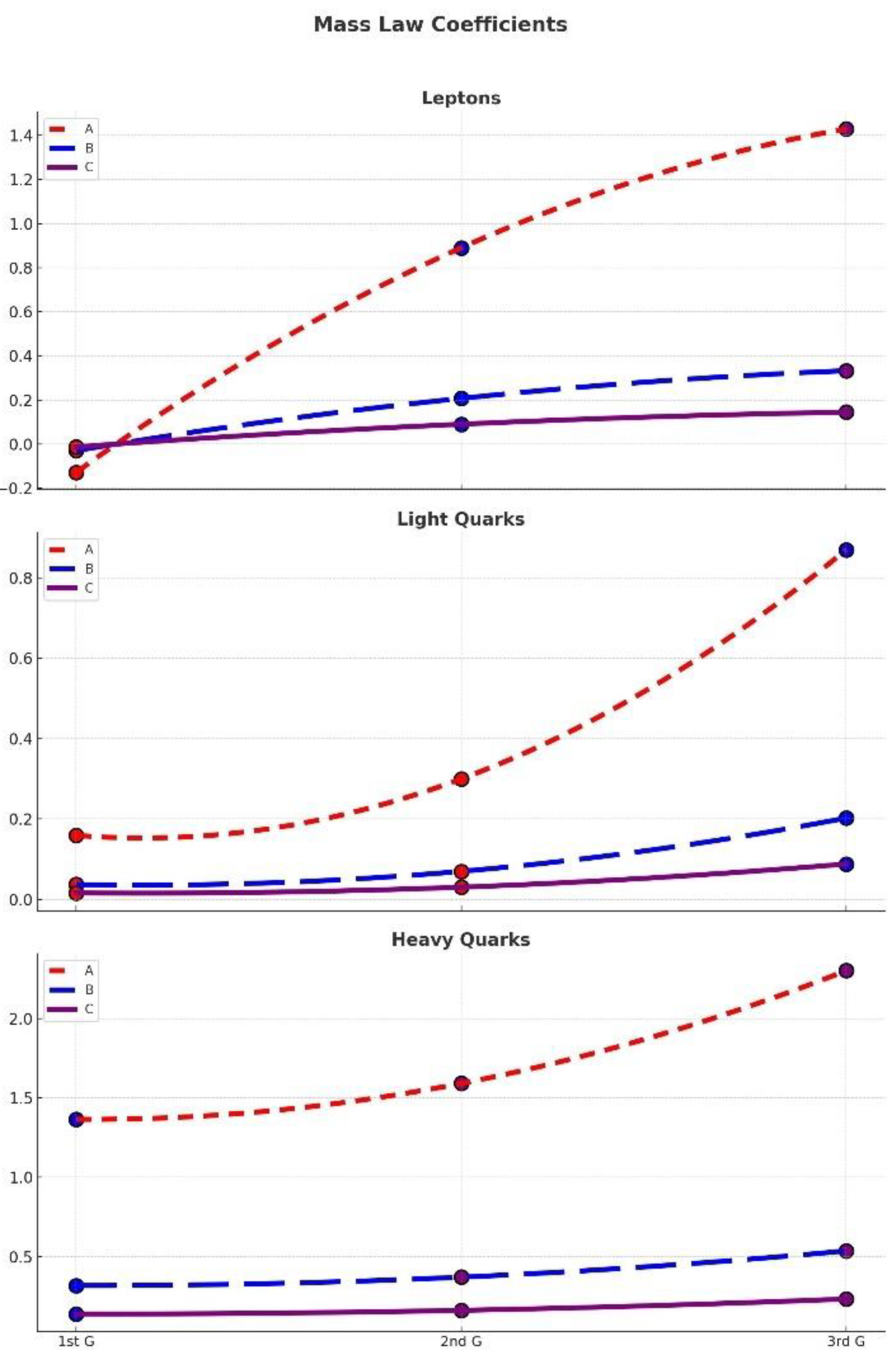
| Category | Fitting Formula | A | B | C | Scaling factor S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lepton (e, m, t) x = 1, 2, 3 |
|
8.7222 | 0.01856 | -0.3101 |
|
| Light Quark (u, d, s) x = k3 k = 1, 2, 3 |
m = |
0.0741 | 0.2603 | -0.2039 | 5.531 |
| Heavy Quark (c, b, t) x = k3 k = 1, 2, 3 |
m = = |
0.0881 | 3.0157 | -0.1101 | 6.973 |
| Particle | Generation | Clifford Algebra | Cayley–Dickson Algebra | Spinor Dimension | Suggested GUT Embedding |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| electron | 1st | Cl(1,7) | Complex (C) | 2 | SU(5)/SO(10) |
| muon | 2nd | Cl(1,7) | Quaternion (H) | 4 | SO(10) |
| tau | 3rd | Cl(1,7) | Octonion (O) | 8 | E₆ or E₈ |
| u quark | 1st | Cl(1,7) | Quaternion (H) | 4 | SU(5) |
| d quark | 1st | Cl(1,7) | Quaternion (H) | 4 | SU(5) |
| s quark | 2nd | Cl(1,7) | Octonion (O) | 8 | SO(10) |
| c quark | 2nd | Cl(1,15) | Octonion (O) | 8 | SO(10) |
| b quark | 3rd | Cl(1,15) | Sedenion (S) | 16 | E₆ or E₈ |
| t quark | 3rd | Cl(1,15) | Sedenion (S) | 16 | E₈ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





