1. Introduction
Potato (
Solanum tuberosum L.) is the third most important crop for human consumption and the fourth in terms of production worldwide with around 350 million tons produced yearly [
1]. Of the total production, around half is destined for fresh human consumption, while most of the rest is used in the preparation of processed food products, animal feed and seed production [
2].
Enzymatic browning and cold-induced sweetening affect the post-harvest quality of potato tubers. Tuber browning primarily results from the action of Polyphenol Oxidase 2 (PPO2), which is activated when mechanical damage during harvest, transportation, or storage disrupts cellular integrity, releasing PPO2 from vacuoles into the cytoplasm, where it encounters its phenolic substrates later oxidized to quinones. These quinones then react with amino acids or free radicals in proteins, leading to the formation of dark-colored precipitates (Mayer, 2006)[
3]. Cold storage prevents sprouting and minimizes diseases, but also increases vacuolar invertase expression [
4]. Cold-induced sweetening occurs as a response to abiotic stress, where vacuolar invertase hydrolyzes sucrose into reducing sugars fructose and glucose. The accumulation of these sugars is problematic for industrial potato chip and french fries production, as high frying temperatures lead to the formation of dark brown polymeric pigments and harmful compounds, such as acrylamide [
5,
6].
Potato improvement through conventional breeding is a laborious and time-consuming process due to its tetraploid nature, high level of heterozygosity and narrow genetic base. As a clonal crop, incremental breeding on existing successful varieties cannot be achieved through backcrossing, as in autogamous or hybrid crops, unless biotechnological techniques such as genetic transformation or gene editing are applied [
7,
8]. Our group has previously developed a variety derived from cv. Desiree, edited in all four alleles of the PPO2 gene resulting in reductions of up to 69% in PPO enzymatic activiy and 73% in tuber enzymatic browning [
9,
10]. Previous studies have demonstrated that the loss of function of the vacuolar invertase gene through gene editing is sufficient to produce potatoes that maintain chip quality during cold storage [
11,
12]. Additionally, simultaneous editing of the vacuolar invertase and asparagine synthetase genes in cvs. Atlantic and Desiree using stable transformation with the CRISPR/Cas9 system has been reported to reduce in acrilamide concentration up to 80% [
13]. Therefore, applying gene editing techniques to address enzymatic browning and cold-induced sweetening simultaneously result in the development of potato varieties with superior post-harvest quality.
This study aims to develop new potato varieties lacking functional vacuolar invertase through transient CRISPR/Cas9 expression in cvs. Atlantic and Spunta. Furthermore, we report the application of this technology to interrupt the vacuolar invertase and polyphenol oxidase 2 genes simultaneously in the variety Spunta, leading to improved lines with reductions in both cold-induced sweetening and enzymatic browning. Our findings highlight the effectiveness of non-transgenic gene editing in producing potato varieties with enhanced post-harvest traits, including improved cold storage performance and reduced susceptibility to bruising
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. sgRNA Design on Vacuolar Invertase and Polyphenol Oxidase 2 Genes of Solanum tuberosum cv. Atlantic and cv. Spunta
2.1.1. Vacuolar Invertase Gene (InvVac)
The reference sequence PGSC0003DMG400013856 [
14] was used for primer design, for the amplification of the
InvVac gene in
Solanum tubersoum cv. Atlantic and cv. Spunta. Primers InvVac-F1 and InvVac-R5 (
Table 1) were used to amplify a fragment of 2874 bp from de 5´end of the target gene, using 10 ng of genomic DNA as a template in a reaction with Phusion High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (New England Biolabs). Reaction conditions were 95 °C for 2 min, 33 cycles of 95 °C 30 s, 50 °C 15 s, 72 °C 1 min and a final extension of 72 °C for 5 min. PCR products were cloned into the pGem-T Easy vector (Promega) and transformed to One Shot TOP10 Chemically Competent
E. coli (Thermo Fisher Scientific), according to manufacturer instructions. Twelve randomly picked colonies were selected for plasmid purification and Sanger sequencing (Macrogen). The resulting sequences were aligned to avoid allelic variation during sgRNA design and further High Resolution Fragment Analysis (HRFA) primer design. Cas-Designer Tool (CRISRP RGEN Tools,
www.rgenome.net/cas-designer) was used for sgRNA design, using one of the sequences obtained for
InvVac as a query and
Solanum tuberosum (PGSC v4.03) as a target genome [
15]. The secondary structure for each sgRNA was analyzed by RNAFold software (
http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/cgi-bin/RNAWebSuite/RNAfold.cgi).
The sgRNAs were cloned into the pTRANS_100 vector under the
Arabidopsis thaliana U6 promoter, following a Golden Gate-based protocol developed in Daniel Voyta’s lab [
16]. This vector includes the coding sequence of the Cas9 nuclease protein under the control of the constitutive 35S promoter. We obtained two vectors with different combinations of sgRNA (
Table 1) named crG0G4 and crG1G4.
2.1.2. Polyphenol Oxidase 2 Gene (PPO2)
We used the primers reported in González et al., 2020 [
9] (
Table 1) to amplify the
PPO2 gen from cv. Spunta. PCR products were cloned and sequenced as described above, to confirm the suitability of the previously designed sgRNAs (
Table 1) for cv. Spunta
2.2. Protoplasts Transfection and Plant Regeneration
Protoplasts were isolated from 4-week-old plantlets according to González et al., 2020 [
9]. For targeting
InvVac in cv. Spunta, transfections were conducted by incubating 100,000 protoplasts with either crG0G4 or crG1G4 and a solution with 40% Polyethylenglycol (PEG), 0.4 M mannitol and 0.1 M Ca(NO
3)
2 for 30 minutes (experiment 1, E01). For targeting
InvVac in cv. Atlantic, either 25% PEG or 40% PEG were employed in combination with the same vectors as above (experiment 2, E02). For simultaneous targeting of
PPO2 and
InvVac in cv. Spunta, we performed a transfection with ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) following the protocol described in [
9]. We used the sgRNA157 [
9] specific for
PPO2 gene plus sgRNAG0 (experiment 3, E03) and sgRNAG10 specific for
InvVac (experiment 4, E04). Regeneration controls were included for each cultivar, consisting of non-transfected protoplasts.
For plant regeneration, all protoplasts were embedded in sodium alginate and cultured for calli regeneration in Medium E, according to [
9].
Green calli were released from alginate blobs after 21 days of culture, and subcultured in medium F until they reached a size of 2-3 mm. Full-grown calli were transferred to solid medium H, 30 days after transfection for shoot growth induction. To ensure the analysis of independent lines, several shoot were picked per callus and transferred to individual tubes with BM until root development. Samples from leaves of the full regenerated plantlets were picked for genomic DNA extraction and further analysis.
2.3. Identification of Edited Lines and Sequencing Analysis
Genomic DNA of regenerated plants was extracted from leaves following the Haymes´s
et al. (1996) [
16] protocol.
2.3.1. High Resolution Fragment Analysis (HRFA)
The presence of mutations in the
InvVac gene was determined by HRFA, according to [
9]. Primer combinations HRFAG0R-FAM and InvVac-F1, HRFAG1R-VIC and InvVac-F4, and HRFAG4F-NED and InvVac-R5, were used for the analysis of sgRNAG0, sgRNAG1 and sgRNAG4 target sites, respectively (
Table 1) were designed for amplification of the region spanning the three target sites on the
InvVac gene, taking into account the absence of allelic variation in primer annealing sites in the target gene. Primers were used to amplify a fragment of the target gene, using Phusion High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (New England Biolabs). Reaction conditions were 98 °C for 1 min, 30 cycles of 98 °C 30 s, 52 °C 20 s, 72 °C 15 s and a final extension of 72 °C for 5 min.
Labelled PCR products were analyzed in an Applied Biosystems 3500 Genetic Analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) (UGB sequencing service IABIMO Castelar), using GeneScan 600 LIZ Dye Size Standard (Thermo Fisher Scientific) as internal lane size standard. Fragments length was determined with GeneMarker Software (SoftGenetics,
www.softgenetics.com) and insertions or deletions were identified comparing each line electropherogram versus the control.
2.3.2. Detection of CRISPR-Induced Mutations
InvVac gene PCR amplification of the fragment of the selected edited lines from individual edition were sent for Illumina MiSeq sequencing service (Genomic platform, Malbrán Institute, Argentina). For multiplex-edition
InvVac and
PPO2 gene PCR amplification of the fragments of selected lines from individual edition were sent for NGS sequencing service (Celemics, Korea). Sequencing data were analyzed using Geneious software (
https://www.geneious.com/), and insertions or deletions were identified by comparing each edited line to the wild-type control. Target gene fragments were amplified using primers listed in
Table 1, Q5 DNA Polymerase (New England Biolabs), and the following PCR conditions: initial denaturation at 98 °C for 5 minutes; 34 cycles of 98 °C for 30 seconds, 60 °C for 20 seconds, and 72 °C for 15 seconds; followed by a final extension at 72 °C for 5 minutes.
2.4. Plant Growth Conditions and Tuber Harvesting
Selected in vitro-regenerated plantlets were transferred to 3-L pots with soil and placed in a greenhouse under a 16:8 photoperiod. Fifteen biological replicates were grown for each edited line and for the control lines non-edited of cv. Spunta and cv. Atlantic. Tubers were harvested after 110 days of cultivation, just before plant senescence.
For cold sweetening resistance testing, tubers (both edited and non-edited) were divided into three groups:
Tubers stored at room temperature
Tubers stored at 4°C for 15 days
Tubers stored at 4°C for 60 days
After storage, phenotypic evaluation of fried potato chips was conducted, along with quantification of reducing sugars and sucrose.
For bruising resistance testing, tubers (both edited and non-edited) were used for enzymatic browning assays and PPO activity measurements.
2.5. Fried Product Characterization
Potato slices were fried at 180 °C for 3 minutes or until bubbling ceased, then drained and placed on a white background for visual assessment. Chip color was scored using a nine-point reference chart, ranging from very light yellow (9) to very dark brown (1), developed by the Institute of Storage and Processing of Agricultural Products (Wageningen, Netherlands). Additionally, chip color was quantified with a Minolta CR-300 colorimeter, and luminosity (DW) was calculated based on the instrument's L, a, and b values.
2.6. HPLC-Based Determination of Sucrose and Reducing Sugars
Five grams of frozen slices were weighted and homogenized in an ultraturrax at 11,000 rpm for 1 min with 20 ml of 80% ethanol (v/v). Sugars were extracted from the homogenate by incubation at 80°C for 1 hour. The homogenate was filtered and then centrifuged at 4 °C at 10,000 g for 10 min. The supernatant was eluted in a solid-phase extraction column, previously conditioned with methanol. Glucose and fructose concentration was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC); service provided by Fares Taie Laboratory, Mar del Plata using an Amida-80 column, a mobile phase with 70% acetonitrile/water (v/v) and a flow rate of 1 ml/min and service provided by Analyses of chemical residues laboratory, LARQ-IPADS Balcarce) using an ACQUITY BEH Amide column, mobile phase with 75% acetonitrilo/25%agua 0.2% triethylamine (TEA) and a flow rate of 0.3mL/min. Sugar quantification of the samples was carried out with external standards of glucose and fructose.
2.7. Enzymatic Browning and PPO Activity
Enzymatic Browning and PPO activity for non-edited cv. Spunta and the edited line from transfections with RNPs for
PPO2 gene were measured according to González
et al., (2020) [
10].
2.8. Field Trial of Line 6A
The line 6A edited in the InvVac gene was used for to perform field assays in Río Primero, Córdoba province, Argentina. The trial was conducted with 4 plots of four rows each for the edited line 6A and for the cv. Atlantic (control). The corresponding irrigation and phytosanitary treatments were applied. After 100 days, tubers were harvested, and a group of tubers of each line was stored at 4°C for up to 120 days. Determinations of reducing sugar content by HPLC and fried product characterization were performed at harvest and at 30, 67, 74, 93, and 120 days post-storage at 4°C as described in the previous sections.
2.9. Statistical Analyses
Data were analyzed using a two way ANOVA analysis. Multiple comparison between treatments and lines were evaluated by the Bonferroni´s test (p < 0.05). Regression analyses were performed using software Sigmaplot 12.0 [
17].
4. Discussion
The application of CRISPR/Cas9 technology in potato (
Solanum tuberosum L.) breeding has enabled precise genome modifications to enhance post-harvest quality and storage potential. This study successfully developed gene-edited potato lines with improved resistance to CIS and enzymatic browning, two key factors affecting industrial processing and commercial value. Our findings further demonstrate that targeted gene editing can significantly enhance storage and processing quality in potato, by addressing two quality related traits simultaneously. The results reported here are in line with previous research showing that knockouts of vacuolar invertase (
InvVac) and polyphenol oxidase 2 (
PPO2) genes diminsh quality deterioration in cold-stored and damaged tubers, respectively [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11].
Cold storage is essential for maintaining tuber viability and reducing post-harvest losses; however, it promotes the conversion of sucrose into reducing sugars, negatively affecting fried product color and safety due to acrylamide formation [
12]. In our study, we successfully edited
InvVac gene in 4 lines (5.3% of the total analysed) derived from cv. Spunta and 7 lines (17% of the total analysed) derived from cv. Atlantic. All lines obtained from the cv. Spunta, retained either unedited alleles or alleles containing in-frame mutations, which did not result in the desired CIS phenotype. After 15 days of storage at 4°C, frying quality of all Spunta derived lines deteriorated drastically. In contrast, for cv. Atlantic, we obtained lines with all four
InvVac alleles edited. Among them, only line 6A exhibited a complete knockout and maintained high-quality frying characteristics after cold storage. As observed in the cv. Spunta-derived lines, those lines containing alleles with in-frame mutations did not exhibit resistance to CIS. This is likely because of the presence of one or more alleles encoding for a functional enzyme in these lines. Phenotypic analyses, including chip color assessment and reducing sugar content measurements, confirmed the molecular findings, only lines 6A and 38A exhibited a favorable phenotype after two months at 4°C based on the absence of non-edited alleles for
InvVac in those lines.
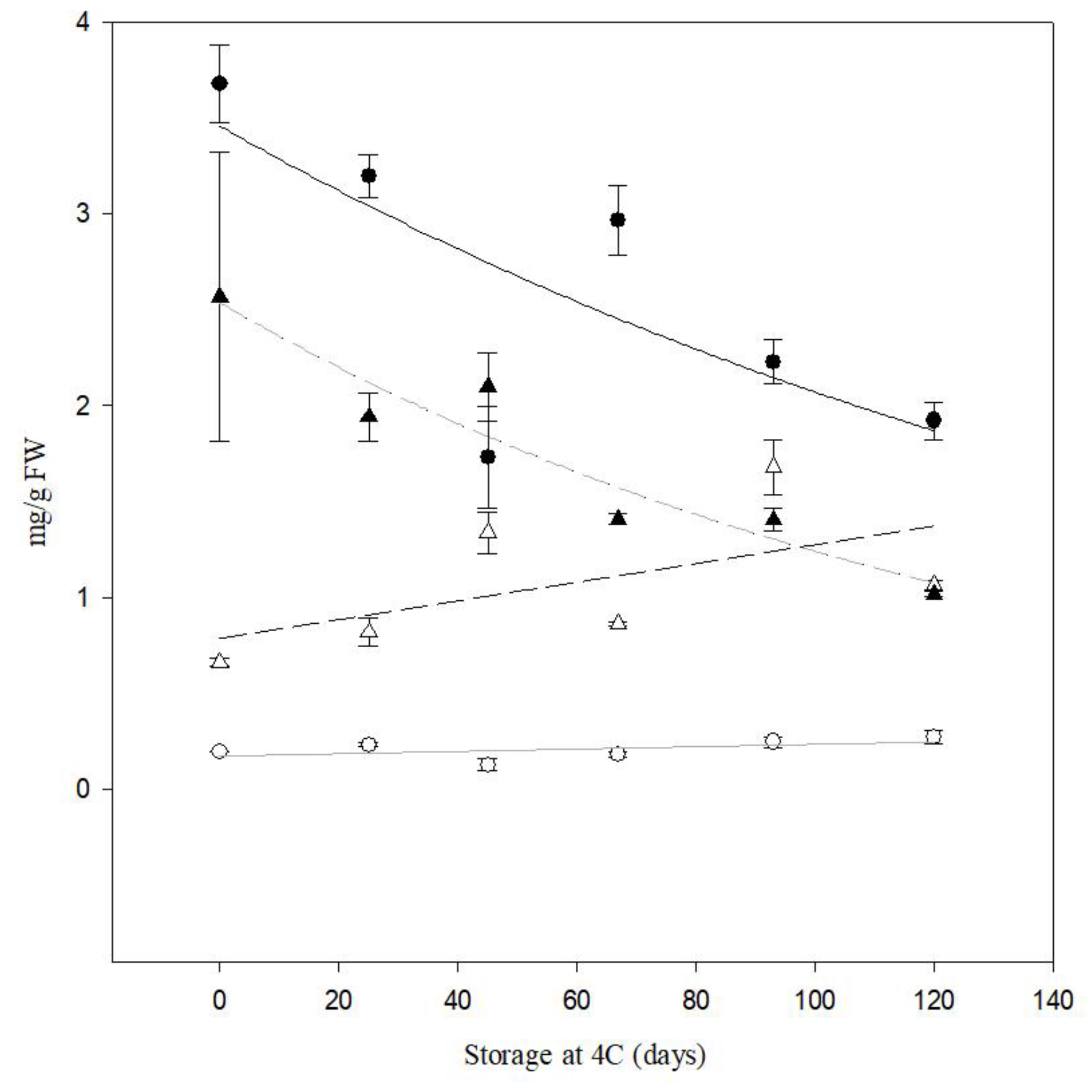
Additionally, we observed a direct correlation between optimal chip color (evaluated using a color card or colorimeter) and lower reducing sugar content (
Figure 8). This aligns with the findings of [
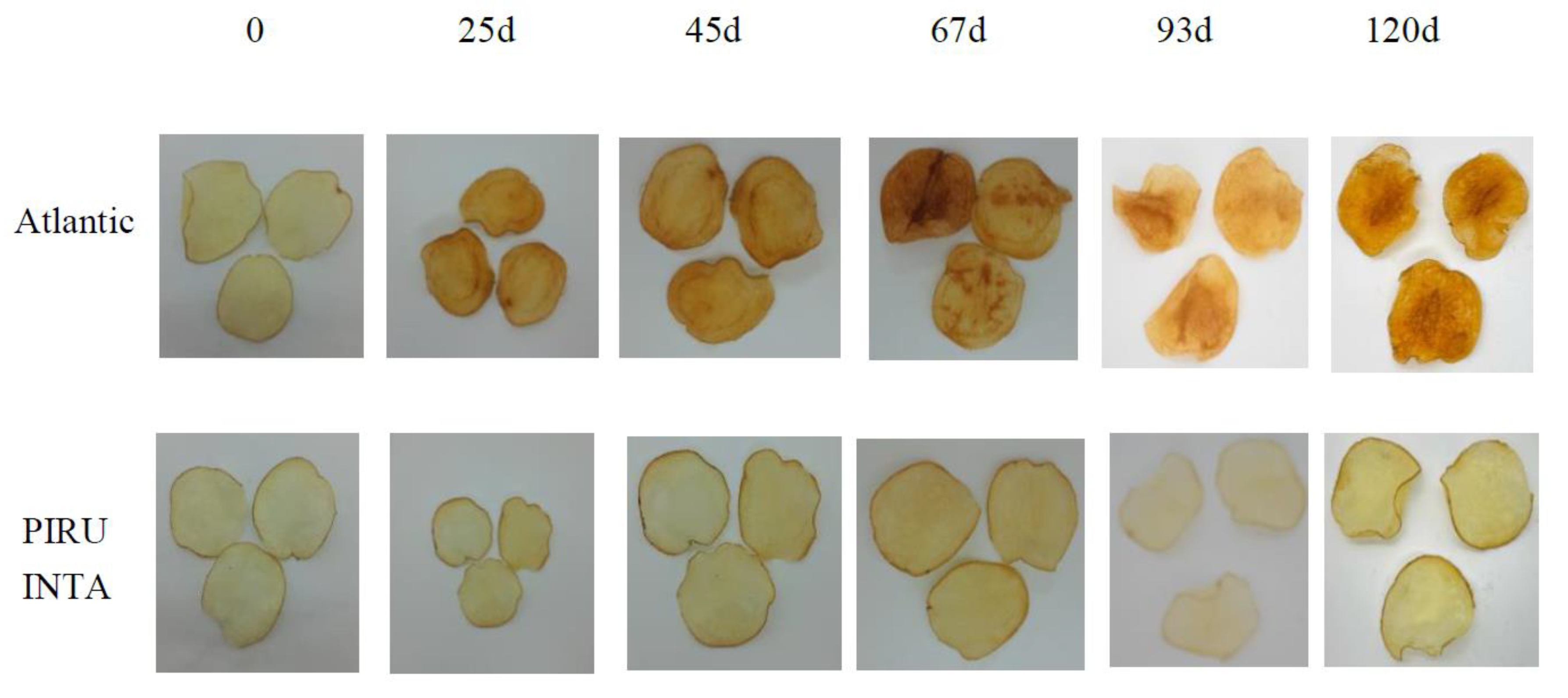
19], where reducing sugar levels were directly correlated with chip color. Line 6A, which exhibited full knock-out of all alleles and the best CIS phenotype, was renamed PIRU INTA and subjected to field trials for registration purposes. Our results demonstrated that PIRU INTA accumulated significantly fewer reducing sugars compared to its wild-type counterpart, cv. Atlantic. After 120 days at 4°C, PIRU INTA retained an optimal color card score of 8.5, whereas cv. Atlantic showed a significant quality decline with a score of 4 as early as 40 days of storage. These findings are consistent with prior research showing that
InvVac knockout lines maintain lower reducing sugar levels, improving frying quality and reducing acrylamide formation [
11,
12,
13]. Furthermore, the sustained low reducing sugar content for up to 120 days post-harvest highlights the potential for extended storage without compromising industrial processing standards.
Unlike the findings reported by Bhaskar et al. (2010) and Yasmeen et al. (2022) [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20], PIRU INTA exhibited a 56% reduction in yield. This outcome may be related to the central role of vacuolar invertase in carbohydrate metabolism [
21], as it influences sugar accumulation, regulates carbohydrate composition in tubers, and affects the distribution of sucrose and hexoses. Despite this potential yield penalty, PIRU INTA offers a significant advantage in terms of post-harvest quality, maintaining chip color for extended periods of cold storage, an essential trait for industrial processing. This improved storage performance could translate into tangible economic and logistic benefits. In Argentina, for example, local potato stocks are often exhausted by April-May, forcing processing industries to source tubers from distant provinces such as Córdoba and Tucumán (located approximately 800 km and 1,100 km, respectively, from the South-East Buenos Aires region) thereby increasing transportation costs. The availability of a locally grown variety like PIRU INTA with enhanced storage and processing qualities could reduce dependence on long-distance sourcing and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
PPO2 plays a critical role in enzymatic browning by catalyzing the oxidation of polyphenols to quinones, which subsequently polymerize into dark pigments [
3]. A multiplex-editing approach targeting both
InvVac and
PPO2 provides an effective strategy for developing potato varieties with improvements in these two crucial post-harvest traits. Our research group previously obtained full
PPO2 knockout lines in cv. Desirée, which showed a 73% reduction in enzymatic activity and a 63% decrease in enzymatic browning. In the present study, we aimed to generate cv. Spunta lines with edits in both
InvVac and
PPO2. We obtained two edited lines E03-3 and E04-5B with two and three edited alleles, respectively, resulting in reduced enzymatic browning. This was qualitatively confirmed by lower discoloration scores. Furthermore, a quantitative measurement of enzymatic browning in tubers, showed reductions in lines E03-3 and E04-5B of 40% and 80% related to the control, respectively. Lower levels of browning in tubers of these lines coincide with the observed reductions in PPO activity levels. Thus, reductions of 70% and 74% of that in the control was determined for PPO activity in lines E03-3 and E04-5B, respectively. Despite the presence of remaining non-edited allele/s in both lines, the induced edits in
PPO2 caused significant reductions in the total enzymatic activity in the tubers. This observation is in line with previous studies in potato, which have reported that induction of mutations in multiple alleles can significantly alter gene function, despite the presence of one or more predictively active alleles [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22]. Wszelaczyńska et al., 2007 [
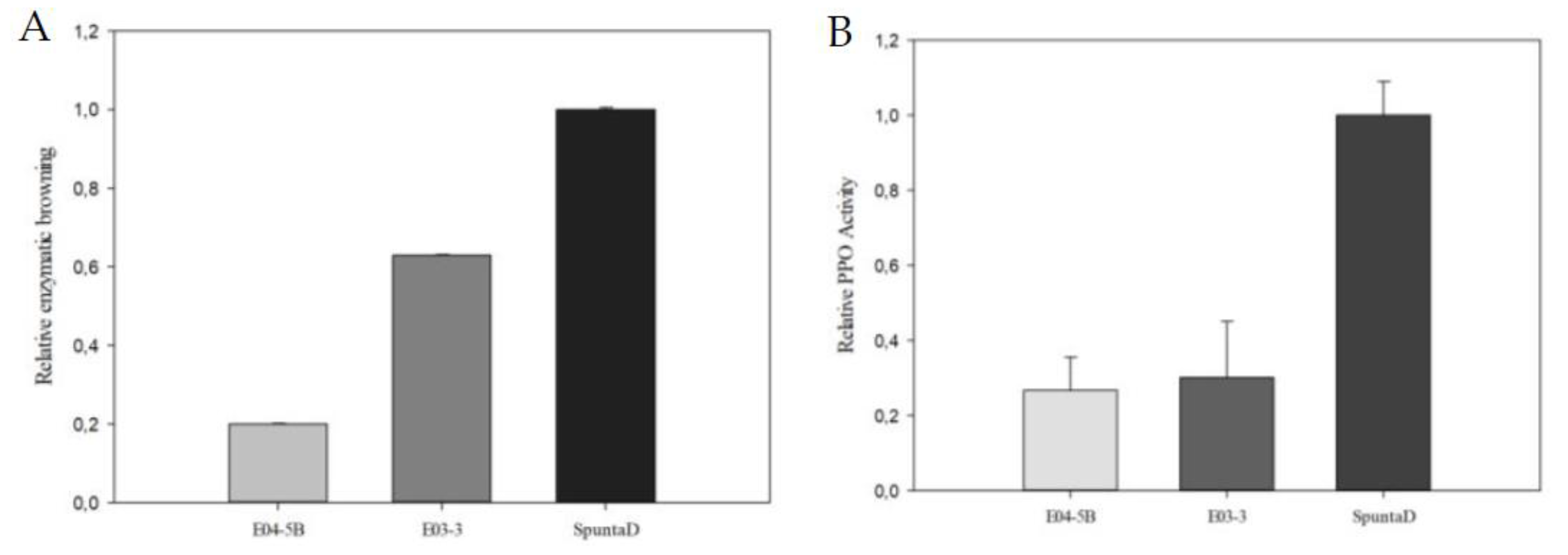
23] reported a strong correlation between visual and absorbance-based methods. Conversely, in our study, visual tuber discoloration did not fully reflect the quantified reductions in enzymatic activity and browning. In addition to the reduced enzymatic browning, line E03-3 demonstrated resistance to CIS, evidenced by a lower reducing sugars content after 60 days storage at 4°C, confirming the stacking of both quality traits in a single line. We did not obtain any lines with all four alleles edited for both genes, likely due to the slightly lower efficiency of multiplex editing compared to single-gene editing. This suggests that further optimization of multiplex editing strategies could enhance both traits simultaneously. Moreover, subsequent editing experiments on lines E03-3 and E04-5B could render full alleles knock-out on both genes.
Traditional potato breeding for improved storage and processing traits is a slow and complex process due to the crop’s tetraploid genome and high heterozygosity [
8]. In contrast, CRISPR/Cas9 technology allows precise, targeted modifications with high specificity, reducing the need for extensive backcrossing and selection cycles. Our approach significantly accelerated the development of storage-resistant potato lines compared to conventional breeding methods, demonstrating the efficiency of genome editing in addressing post-harvest challenges [
11]. Moreover, the gene editing techniques allows the improvement of existing successful varieties in key traits, maintaining the advantage of previous allelic combination of the rest of the genome [
7]. Additionally, the non-transgenic nature of our edited lines aligns with regulatory frameworks that favor genome-edited crops without foreign DNA insertion, enhancing their commercial acceptability [
24,
25].
The improved resistance to CIS and enzymatic browning in our edited potato lines offers substantial benefits to the food industry. Reduced sugar accumulation translates into lower acrylamide levels, mitigating health risks associated with fried potato consumption [
26]. Additionally, the enhanced cold storage stability of PIRU INTA, without significant quality deterioration, reduces storage losses, contributing to a more efficient supply chain and lower environmental impact. A genome-editing strategy that does not compromise yield in CIS-resistant potatoes would be desirable. For example, CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing of the
InvVac intron 2 enhancer significantly reduced
InvVac expression under cold storage conditions, confirming its cold-responsive function in cv. Katahdin [
27]. Other strategies targeting genetic factors involved in the expression on
InvVac triggered by cold may also provide an alternative approach.
From an economic standpoint, reducing post-harvest losses significantly enhances profitability for potato processors by minimizing waste and decreasing dependence on costly anti-sprouting agents such as chlorpropham (CIPC), which has been restricted in some markets due to environmental and health concerns [
28]. The ability to store potatoes at low temperatures without compromising chip quality also contributes to lower refrigeration costs while preserving tuber viability.
Moreover, environmental conditions, particularly extreme temperatures driven by climate change, may expose potato crops to chilling conditions before harvest [
29]. CIS-resistant varieties could help minimize reducing sugar accumulation in unharvested tubers.
The use of high-quality tubers with fewer processing defects reduces the need for surplus raw materials, thereby lowering the overall water footprint associated with potato production. This is particularly relevant given the water-intensive nature of potato processing, which includes multiple stages such as washing, peeling, and frying [
30]. By enhancing processing efficiency and reducing tuber rejection due to poor quality, our gene-edited lines contribute to more sustainable and resource-efficient agricultural practices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.F. and G.A.M.; methodology, G.A.M., C.D.O., M.N.G., A.P.H., A.A., S.S., S.D.; software, G.A.M and A.P.H.; validation, G.A.M., C.D.O. and S.F..; formal analysis, G.A.M.; investigation, G.A.M. and C.D.O.; resources, G.A.M. and S.F.; data curation, G.A.M. and M.G.; writing—original draft preparation, G.A.M.; writing—review and editing, G.A.M., C.D.O., S.S., M.G., S.F.; visualization, G.A.M. and S.S.; supervision, S.F.; project administration, G.A.M. and S.F.; funding acquisition, G.A.M. and S.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
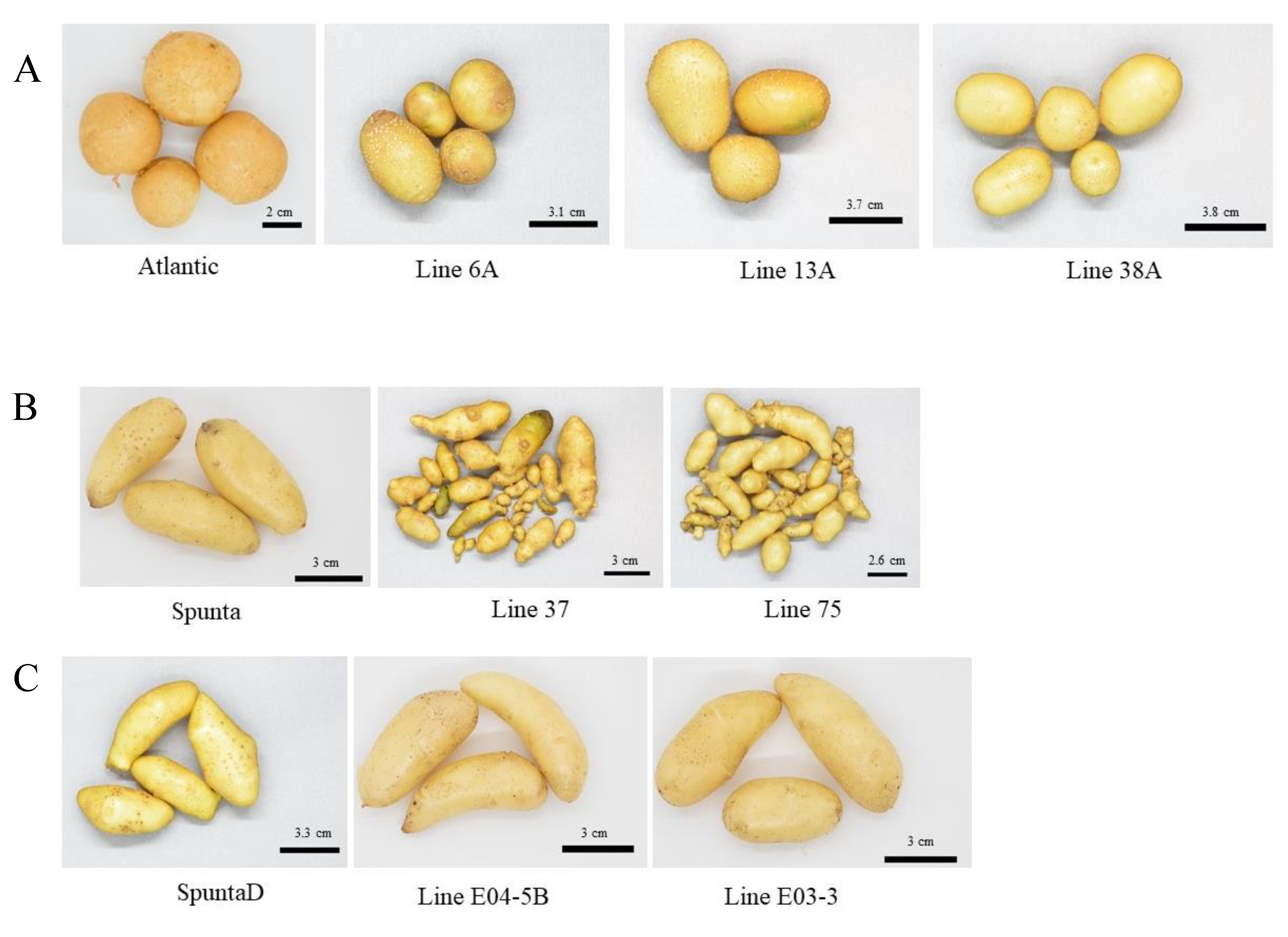
Figure 1.
Tubers harvested from greenhouse multiplication of each edited line and their respective control (a) tubers from cv. Atlantic and edited lines (6A, 13A and 38A), (b) tubers from cv. Spunta and edited line (37 and 75) and (c) tubers from double edited plants of cv. Spunta (SpuntaD) and edited lines (E04-5B and E03-3).
Figure 1.
Tubers harvested from greenhouse multiplication of each edited line and their respective control (a) tubers from cv. Atlantic and edited lines (6A, 13A and 38A), (b) tubers from cv. Spunta and edited line (37 and 75) and (c) tubers from double edited plants of cv. Spunta (SpuntaD) and edited lines (E04-5B and E03-3).
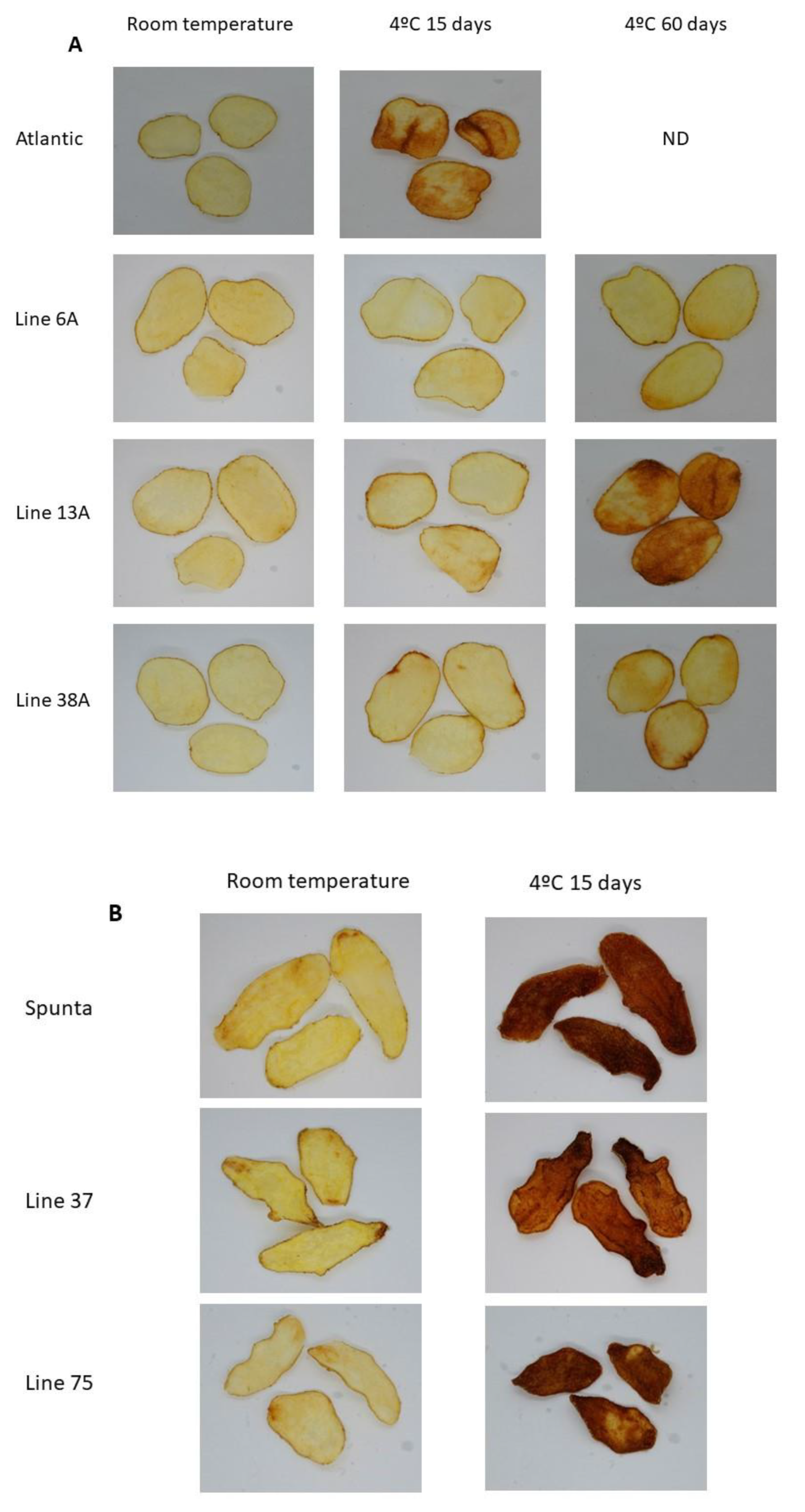
Figure 2.
Fried product characterization. (A) Fried potato chips from non-edited (cv. Atlantic) and edited lines 6A, 3A, and 38A. (B) Fried potato chips from non-edited (cv. Spunta) and edited lines 37S and 75S.
Figure 2.
Fried product characterization. (A) Fried potato chips from non-edited (cv. Atlantic) and edited lines 6A, 3A, and 38A. (B) Fried potato chips from non-edited (cv. Spunta) and edited lines 37S and 75S.
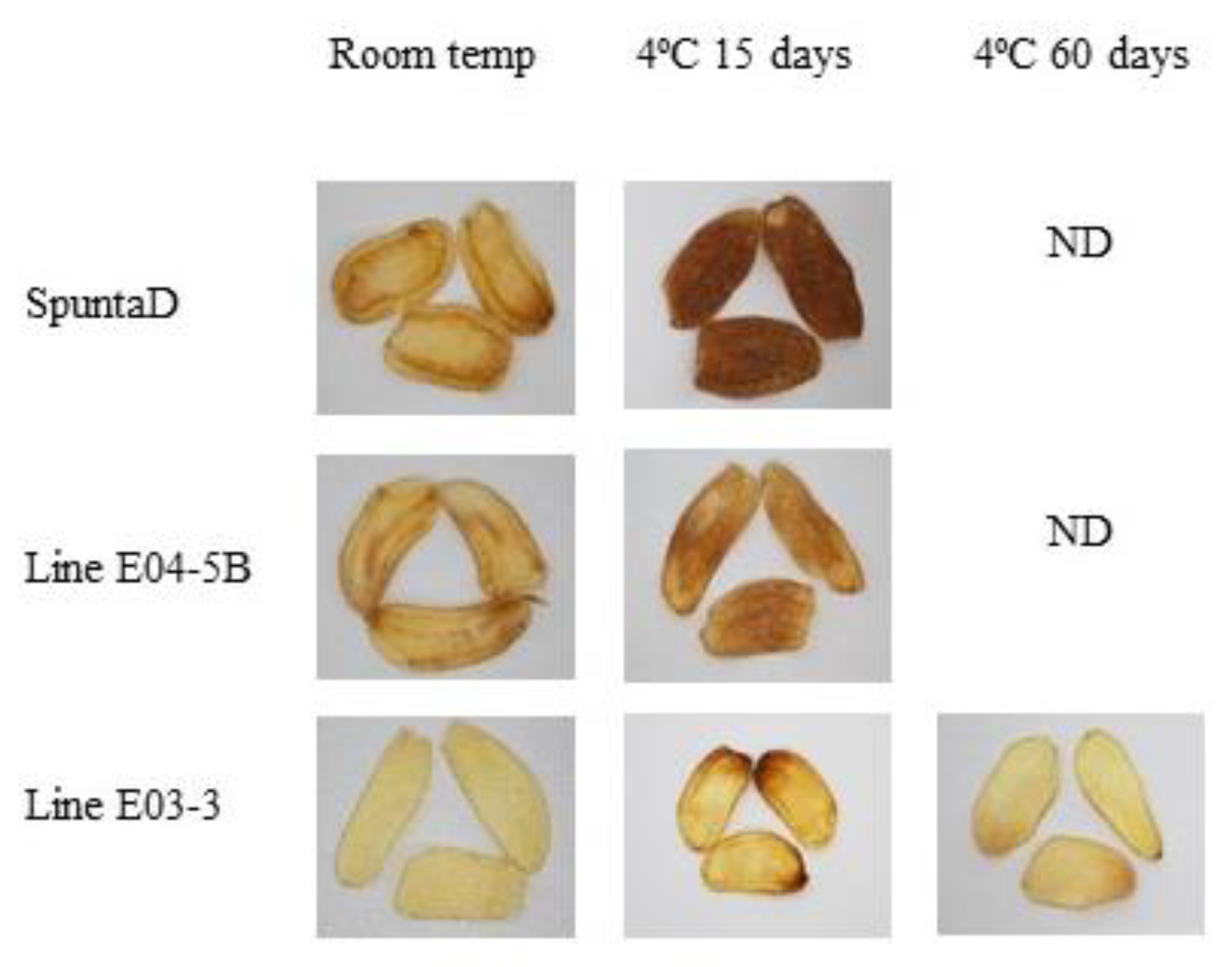
Figure 3.
Fried product characterization from double edited lines (E04-5B and E03-3) and their respective non-edited controls (cv. SpuntaD). ND: not determined.
Figure 3.
Fried product characterization from double edited lines (E04-5B and E03-3) and their respective non-edited controls (cv. SpuntaD). ND: not determined.
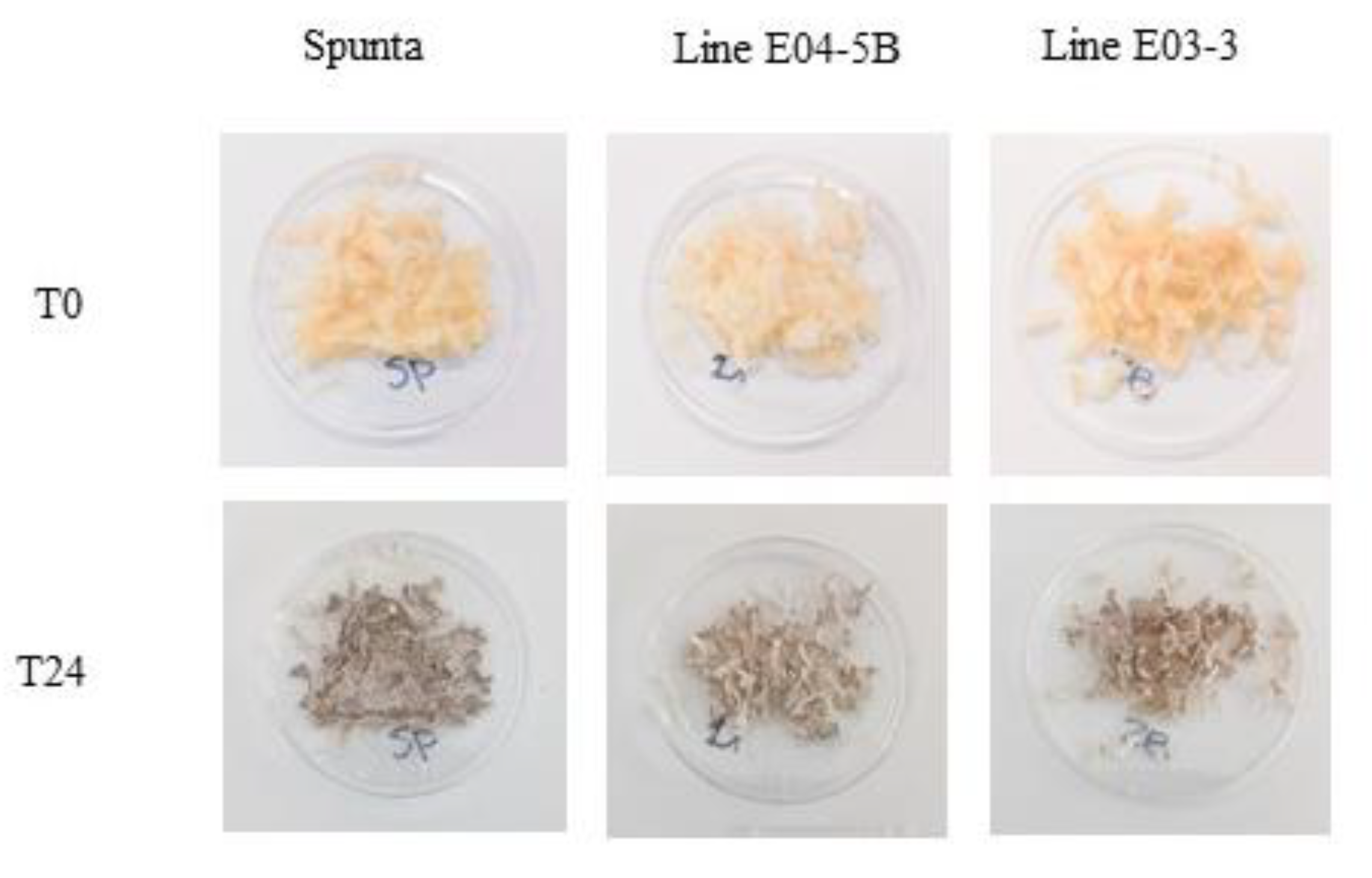
Figure 4.
Discoloration of selected edited lines at times 0 and 24h after cutting. Tubers were randomly selected for each edited line and the control non-edited, fresh grate and exposed to the air for 24 h at room temperature (24°C). Photos were taken immediately after grating (0hs) and 24 h later.
Figure 4.
Discoloration of selected edited lines at times 0 and 24h after cutting. Tubers were randomly selected for each edited line and the control non-edited, fresh grate and exposed to the air for 24 h at room temperature (24°C). Photos were taken immediately after grating (0hs) and 24 h later.
Figure 5.
(A) Analysis of Relative Enzymatic Browning and (B) Relative PPO Activity in tubers of the edited lines E03-3 and E04-5B. Each bar represents data from three technical replicates, each consisting of a sample with three biological replicates. Data are presented relative to the control line SpuntaD.
Figure 5.
(A) Analysis of Relative Enzymatic Browning and (B) Relative PPO Activity in tubers of the edited lines E03-3 and E04-5B. Each bar represents data from three technical replicates, each consisting of a sample with three biological replicates. Data are presented relative to the control line SpuntaD.
Figure 6.
Fried product characterization for PIRU INTA and the control cv. Atlantic at different storage periods at 4ºC.
Figure 6.
Fried product characterization for PIRU INTA and the control cv. Atlantic at different storage periods at 4ºC.
Figure 7.
Phenotypic analyses of color potato chips from cv. Atlantic and PIRU INTA. (a) Color card developed by Institute of Storage and Processing of Agricultural Products in Wageningen, Netherlands and a Minolta colorimeter. The color card has nine points, ranging from very light yellow (9) to very dark brown (1). Black circles represent PIRU INTA and black triangles represent cv. Atlantic. The solid line represents the fit of PIRU INTA with R2 = 0.7424 and p = 0.013. The dashed line represents the fit of cv. Atlantic with R2 = 0.6190 and p = 0.035. (b) Colorimeter Minolta. The values a, b, and L obtained from the colorimeter were used to calculate the DW parameter, which is an indicator of the whitening of the sample. Black circles represent PIRU INTA and black triangles represent cv. Atlantic. The solid line represents the fit of PIRU INTA with R2 = 0.1505 and p = 0.3898. The dashed line represents the fit of cv. Atlantic with R2 = 0.6805 and p = 0.022.
Figure 7.
Phenotypic analyses of color potato chips from cv. Atlantic and PIRU INTA. (a) Color card developed by Institute of Storage and Processing of Agricultural Products in Wageningen, Netherlands and a Minolta colorimeter. The color card has nine points, ranging from very light yellow (9) to very dark brown (1). Black circles represent PIRU INTA and black triangles represent cv. Atlantic. The solid line represents the fit of PIRU INTA with R2 = 0.7424 and p = 0.013. The dashed line represents the fit of cv. Atlantic with R2 = 0.6190 and p = 0.035. (b) Colorimeter Minolta. The values a, b, and L obtained from the colorimeter were used to calculate the DW parameter, which is an indicator of the whitening of the sample. Black circles represent PIRU INTA and black triangles represent cv. Atlantic. The solid line represents the fit of PIRU INTA with R2 = 0.1505 and p = 0.3898. The dashed line represents the fit of cv. Atlantic with R2 = 0.6805 and p = 0.022.
Figure 8.
Quantification of reducing sugars (RS) and sucrose content by HPLC of tubers from cv. Atlantic and PIRU INTA from field trial . Black circle represents sucrose PIRU INTA and black triangle represents sucrose cv. Atlantic. White circle represents RS PIRU INTA and white triangle represents RS cv. Atlantic.
Figure 8.
Quantification of reducing sugars (RS) and sucrose content by HPLC of tubers from cv. Atlantic and PIRU INTA from field trial . Black circle represents sucrose PIRU INTA and black triangle represents sucrose cv. Atlantic. White circle represents RS PIRU INTA and white triangle represents RS cv. Atlantic.
Table 1.
Primers and sgRNA guides used in this study.
Table 1.
Primers and sgRNA guides used in this study.
| Primer name |
Sequence (5´ - 3´) |
Purpose |
| InvVac-F1 |
CAATTCAGTTGCCCCCTGTC |
Sequence analysis of InvVac gene of Solanum tubersoum cv. Spunta and cv. Atlantic |
| InvVac-R5 |
CGCACGATTATTGTGTATGGTGCA |
| sgRNAG0 |
CCTCCCATTACACATTCCTC |
sgRNA guide for InvVac
|
| sgRNAG1 |
CTATTTGGGGAAATATCACA |
sgRNA guide for InvVac
|
| sgRNAG4 |
GAAGAAACAACGAAGAGTAC |
sgRNA guide for InvVac
|
| sgRNAG10 |
GGTCAAGTACAAAGGCAACC |
sgRNA guide for InvVac
|
| sgRNA157 |
TTTTCGATGTAACACGTGAC |
sgRNA guide for PPO2 from González et al., 2020 [9] |
| HRFAG0R-FAM |
TCGGAAAGAAGGCTACAGAAAG |
Amplification of InvVac gene fragment spanning the sgRNAG0 target site for HRFA and NGS. This primer was combined with InvVac-F1 |
| HRFAG4F-NED |
TGGGTTGAAGCTGGATTATGG |
Amplification of InvVac gene fragment spanning the sgRNAG4 target site for HRFA. This primer was combined with InvVac-R5 |
| HRFAG1R-VIC |
ATCGTACCATTGATCAGGAACC |
Amplification of InvVac gene fragment spanning the sgRNAG1 target site for HRFA. |
| InvVac-F4 |
TTGGTCAACAGGTCCATTGT |
| PPO2_2Bf |
GCTCCATTTCGGTGACTTT |
Amplification of PPO2 gene fragment spanning the sgRNA157 target site for NGS from González et al., 2020 [9] |
| PPO2_2Br |
TGGTGGCAAAGAGTTACAAG |
| G2-R |
TGGTTCCTGATCAATGGTAC |
Amplification of InvVac gene fragment spanning the sgRNAG10 target site for NGS. |
| G3-R |
GTCCAAGCAGTGGTGGGGTC |
Table 2.
Edited lines detected by HRFA and NGS. G0 and G4 are the sgRNA guides specific for InvVac gene. (+) indicates nucleotide insertions and (-) indicates nucleotide deletions. ND: no determinated.
Table 2.
Edited lines detected by HRFA and NGS. G0 and G4 are the sgRNA guides specific for InvVac gene. (+) indicates nucleotide insertions and (-) indicates nucleotide deletions. ND: no determinated.
| Cultivar |
Line |
Allelic variants in target site sgRNAG0 by HRFA |
Allelic variants in target site sgRNAG4 by HRFA |
Allelic variants in target site sgRNAG0 by NGS |
Allelic variants in target site sgRNAG4 by NGS |
| Spunta |
37S |
-2;-5;-6;-12 |
0 |
-2;-5;-6;-12 |
0 |
| 38S |
-3 |
-2;-3;-5 |
-2; 0 |
-2;-3;-5 |
| 44S |
-2;0 |
0 |
ND |
ND |
| 75S |
-1;-3;-7 |
0 |
-1;-3;-7 |
0 |
| Atlantic |
6A |
+2;-2;-4 |
0 |
+1;-2 |
0 |
| 13A |
-3;-4 |
-6;-12;-28;0 |
ND |
ND |
| 16A |
0;-3;-6 |
0 |
ND |
ND |
| 30A |
0;-3 |
0 |
ND |
ND |
| 38A |
+1;-1 |
0 |
+1;-1; 0 |
0 |
Table 3.
Edited lines per experiment (E03 and E04) detected by NGS. G0 and G10 are the sgRNA guides specific for InvVac gene and G157 is the sg RNA guide specific for PPO2 gene. (+) indicates nucleotide insertions and (-) indicates nucleotide deletions. NR: no results obtained.
Table 3.
Edited lines per experiment (E03 and E04) detected by NGS. G0 and G10 are the sgRNA guides specific for InvVac gene and G157 is the sg RNA guide specific for PPO2 gene. (+) indicates nucleotide insertions and (-) indicates nucleotide deletions. NR: no results obtained.
| Line |
Allelic variants
G0 |
Allelic variants
G157 |
Line |
Allelic variants
G10 |
Allelic variants
G157 |
| E03-2A |
-1;0 |
-2; 0 |
E04-2A |
- 1;-1;0 |
-2; 0 |
| E03-3 |
+3; -5; -4; -2 |
-2; - 1; 0 |
E04-2B |
0 |
-1; -1; 0 |
| E03-4 |
0 |
2; 0 |
E04-3 |
-1; 0 |
NR |
| E03-5A |
0 |
-2; 0 |
E04-4A |
-1; -1; 0 |
-2; 0 |
| E03-5B |
0 |
-2; 0 |
E04-4B |
-1; -1; 0 |
-2; 0 |
| E03-6A |
-2; -1; 0 |
-2; 0 |
E04-4C |
-1; 0 |
NR |
| E03-7A |
0 |
-2; 0 |
E04-4D |
0 |
-2; -1; 0 |
| E03-7B |
-1; 0 |
-2; 0 |
E04-5A |
+1; -1;0 |
+1; -1; -2; 0 |
| E03-8A |
NR |
-2; 0 |
E04-5B |
+1; -1;0 |
+1; -1; -2; 0 |
| E03-8D |
0 |
-2; 0 |
E04-5C |
+1; -1;0 |
+1; -1; -2; 0 |
| E03-10B |
NR |
-2; 0 |
E04-5D |
+1; -1;0 |
NR |
| E03-11C |
0 |
-2; -47; -49; 0 |
E04-6A |
0 |
-2; 0 |
| E03-14B |
0 |
-2; -49; -47; 0 |
E04-6B |
-2; 0 |
-2; 0 |
| E03-15C |
-1; 0 |
-2; -35; -49; 0 |
E04-6C |
0 |
-2; 0 |
| E03-17B |
0 |
-2; - 14; 0 |
E04-6D |
-1; 0 |
-2; -1;0 |
| E03-17D |
0 |
-2; 0 |
E04-6E |
0 |
-2; 0 |
| E03-20B |
-1; -2; 0 |
-2; 0 |
E04-6F |
-1;0 |
-2; 0 |
| E03-20C |
0 |
-2; -1; 0 |
E04-7A |
0 |
-2; 0 |
| E03-21B |
0 |
-2; -5; 0 |
E04-7B |
-1; 0 |
-2; - 1; 0 |
| E03-28 |
0 |
-2; 0 |
E04-8A |
0 |
-2; -1; 0 |
| E03-29 |
0 |
-2; 0 |
E04-8B |
0 |
-1;0 |
| E03-33B |
0 |
NR |
E04-8C |
-1; 0 |
-2; -1; 0 |
| E03-34 |
0 |
-2; 0 |
|
|
|
Table 4.
Phenotypic characterization of edited lines and their respective controls. The control non-edited for multiplex editing was designated as “SpuntaD” to differentiate it from the control Spunta used for lines targeted solely in VacInv gene.
Table 4.
Phenotypic characterization of edited lines and their respective controls. The control non-edited for multiplex editing was designated as “SpuntaD” to differentiate it from the control Spunta used for lines targeted solely in VacInv gene.
| Line |
Storage at 4ºC (days) |
Average scale values of color card |
Average DW |
Average Reducing sugar (mg/gr. FW) |
Average Sucrose (mg/gr. FW) |
Atlantic
|
0 |
8.8 + 0.45 A |
36.6 + 3.4 A |
0.6 + 0.02 A |
2.6 + 0.75 A |
| 15 |
4 + 0 B |
52.1 + 3.5 B |
7.2 + 0.69 B |
6.1 + 0.46 B |
6A
|
0 |
8.3 + 0.5 A |
44.6 + 1.7 A |
0.4 + 0.01 A |
7.7 + 1.75 A |
| 15 |
8.3 + 0.96 A |
41.9 + 3.5 A |
0.7 + 0.18 A |
3.5 + 0.27 B |
| 60 |
8 + 0.71 A |
42.1 + 4.9 A |
0.9 + 0.03 A |
7.8 + 1.39 A |
13A
|
0 |
8.3 + 0.96 A |
41.7 + 2.7 A |
0.2 + 0.07 A |
1.8 + 1.13 A |
| 15 |
6.3 + 0.5 B |
47.3 + 4.3 A |
1.8 + 0.61 B |
4.7 + 1.45 A |
| 60 |
3 + 0 C |
54.7 + 4.7 B |
6.3 + 1.33 C |
3.0 + 0.59 A |
38A
|
0 |
8.8 + 0.5 A |
36.2 + 1.7 A |
0.1 + 0.02 A |
1.1 + 0.10 A |
| 15 |
8 + 0.82 A |
45.2 + 4.3 B |
0.8 + 0.27 A |
5.5 + 2.14 B |
| 60 |
6.4 + 0.55 B |
47.3 + 1.3 B |
2.4 + 0.52 B |
5.5 + 2.20 B |
Spunta
|
0 |
7.8 + 1.5 A |
45.1 + 4.0 A |
0.7 + 0.04 A |
2.9 + 0.87 A |
| 15 |
1.3 + 0.5 B |
59.9 + 2.2 B |
7.9 + 0.58 B |
2.2 + 0.31 A |
37S
|
0 |
7.3 + 1.5 A |
47.9 + 0.8 A |
2.7 + 0.64 A |
2.7 + 1.32 A |
| 15 |
2 + 1.41 B |
63.5 + 1.8 B |
6.8 + 1.61 A |
7.7 + 1.76 B |
75S
|
0 |
7.3 + 1.5 A |
42.7 + 6.4 A |
0.9 + 0.05 A |
2.2 + 0.42 A |
| 15 |
1.5 + 1 B |
64.9 + 0.2 B |
8.6 + 0.55 A |
6.8 + 0.20 B |
SpuntaD
|
0 |
4.8 + 0.4 A |
53.5 + 1.84 A |
2.3 + 0.26 A |
1.5 + 0.55 A |
| 15 |
1.4 + 0.5 B |
61.1 + 0.96 B |
10 + 2.61 A |
1.7 + 0.15 A |
E04-5B
|
0 |
6 + 0 A |
45.9 + 1.56 A |
ND |
ND |
| 15 |
4 + 0.7 B |
57.6 + 2.14 B |
ND |
ND |
| E03-3 |
0 |
9 + 0 A |
41.6 + 3.97 A |
0.4 + 0.03 A |
1.7 + 0.36 A |
| 15 |
7 + 0 B |
44.7 + 2.32 A |
1.5 + 0.89 A |
7.1 + 0.03 B |
| 60 |
5.3 + 0.6 C |
58.1 + 0.68 B |
2.9 + 0.13 B |
9.1 + 0.21 B |