Submitted:
07 March 2025
Posted:
07 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Antibodies
2.3. Development of Hybridomas
2.4. Flow Cytometry
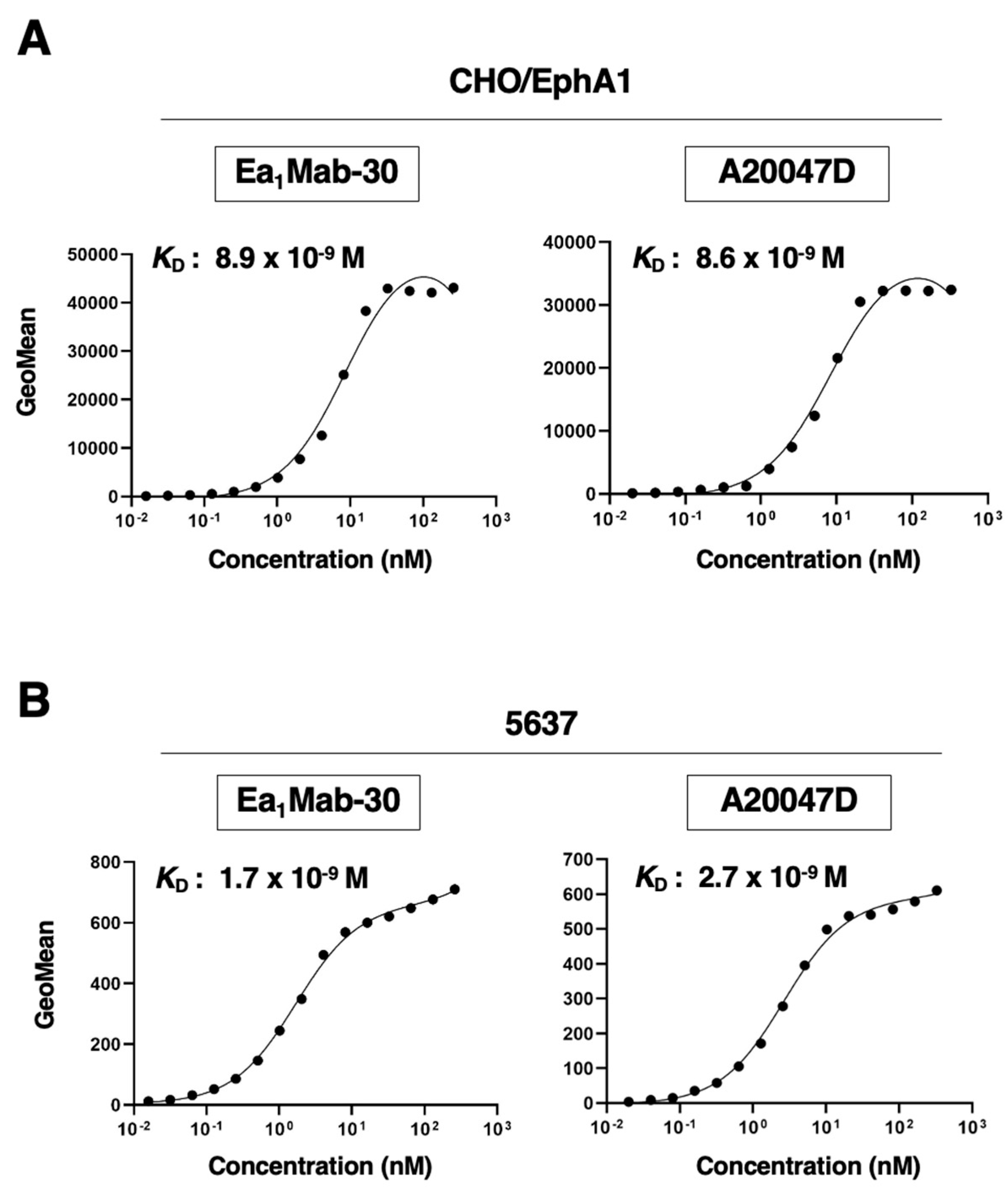
2.5. Determination of the Binding Affinity by Flow Cytometry
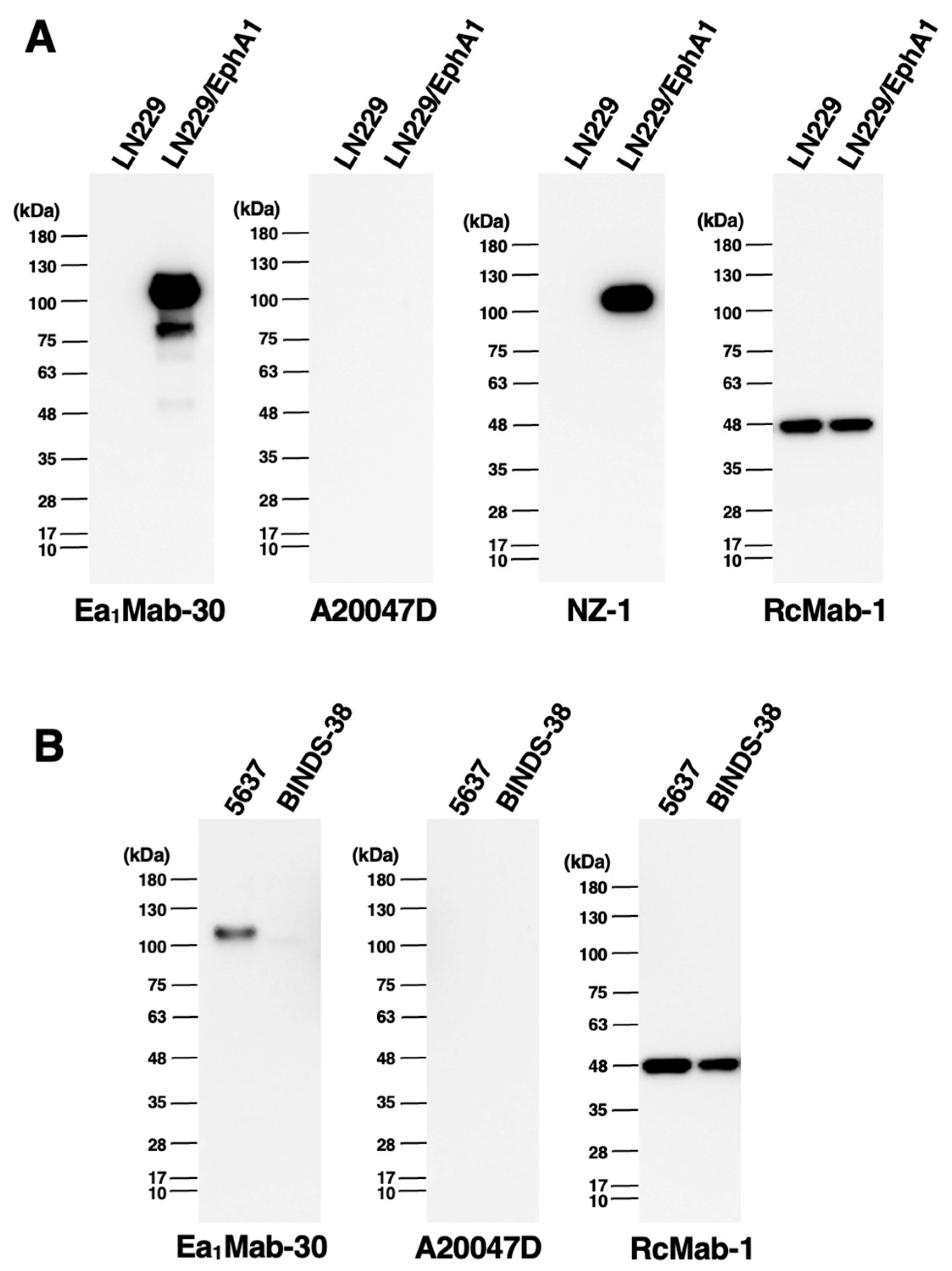
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
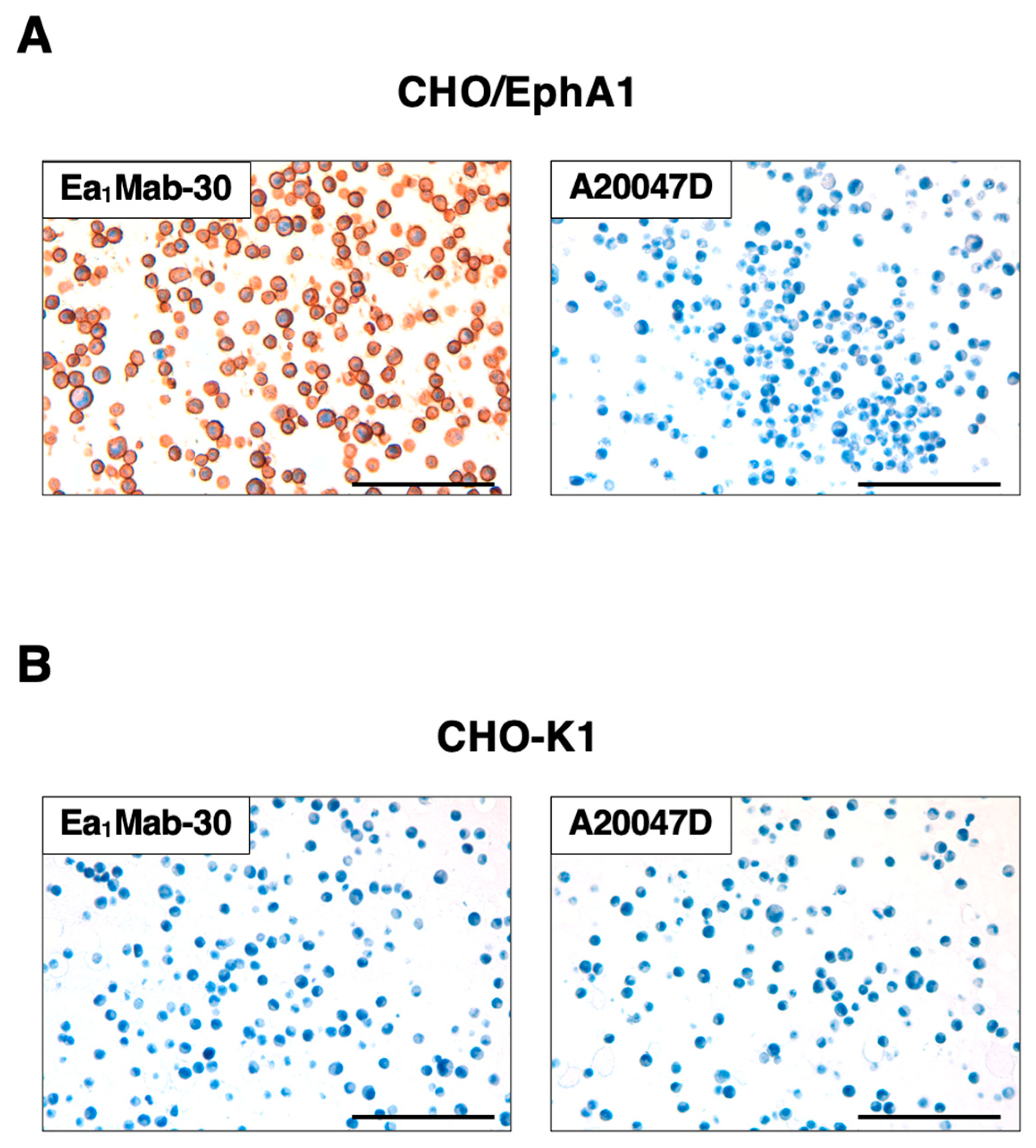
2.7. Immunohistochemistry
3. Results
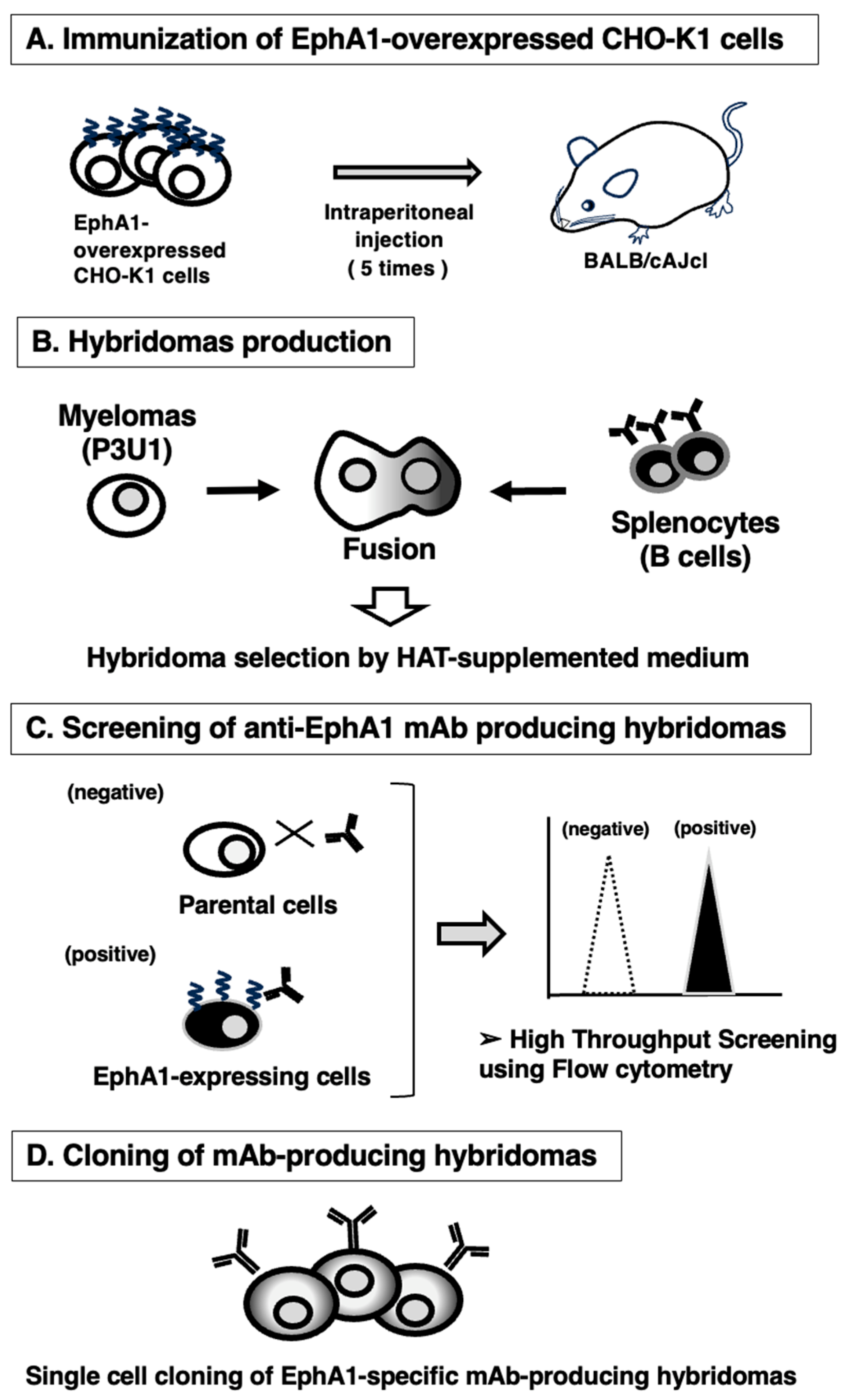
3.1. Development of Anti-EphA1 mAbs Using the CBIS Method
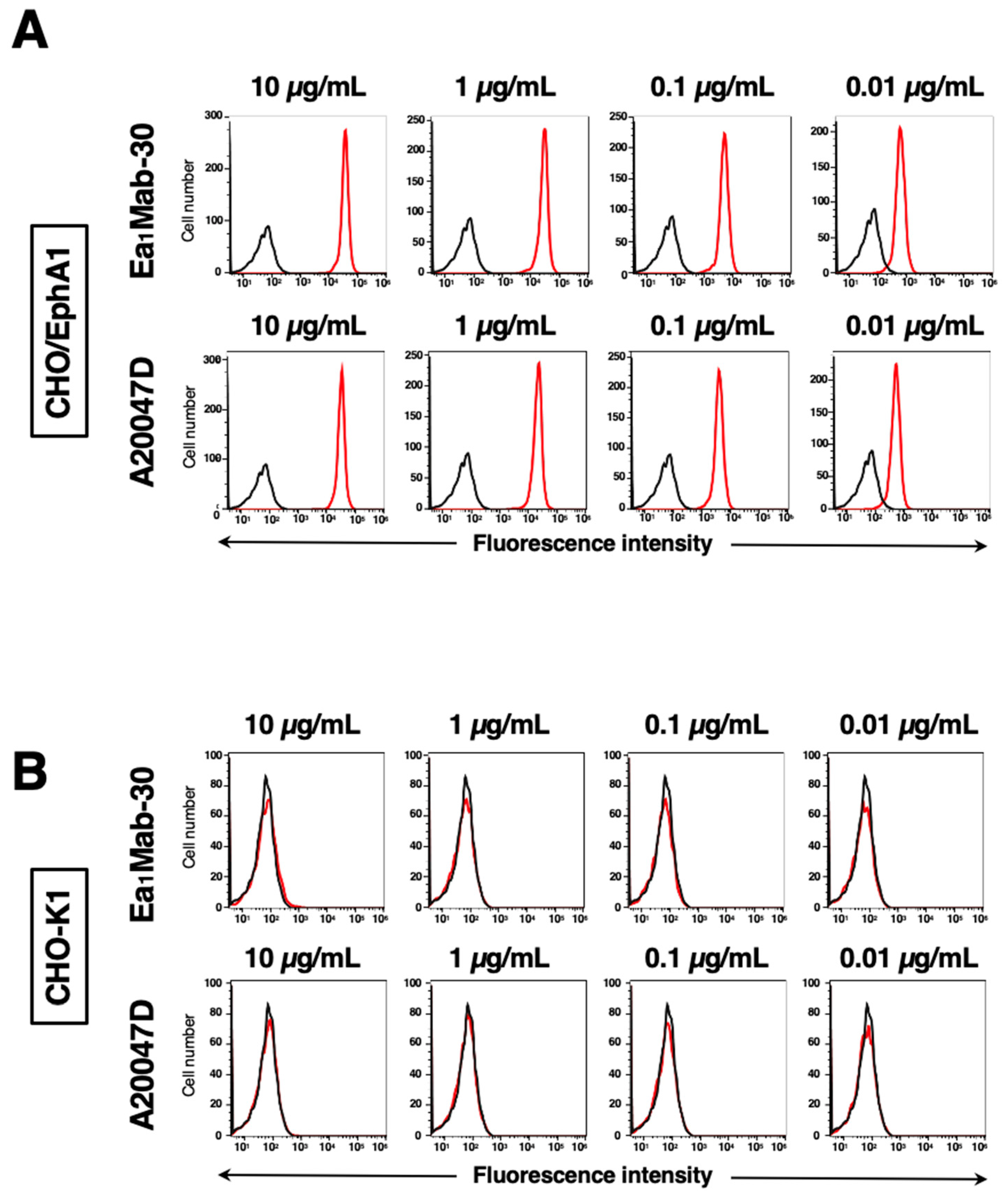
3.2. Investigation of Antibody Reactivities Using Flow Cytometry
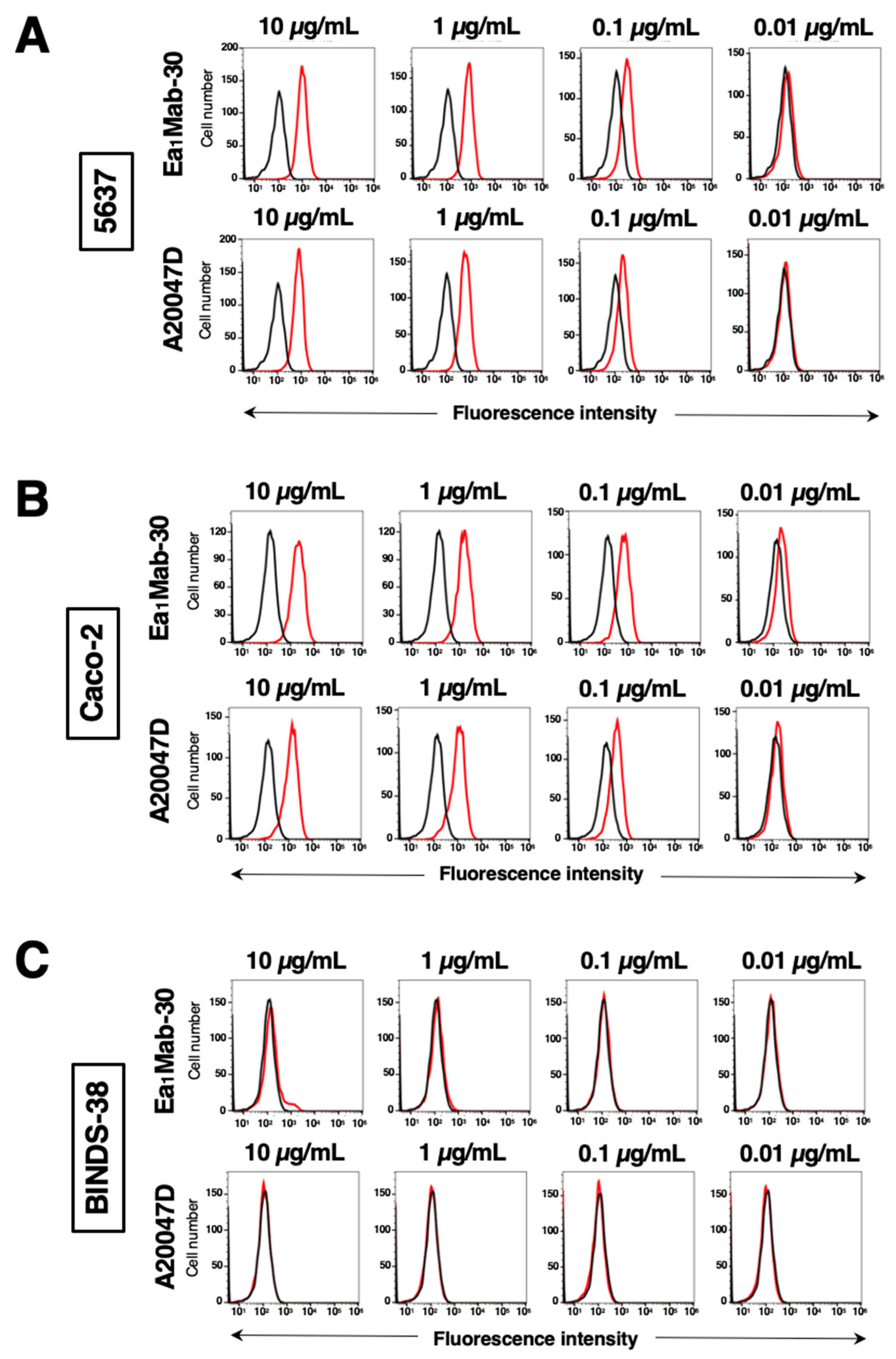
3.3. The Reactivity of Anti-EphA1 mAbs Using Flow Cytometry Against Endogenous EphA1
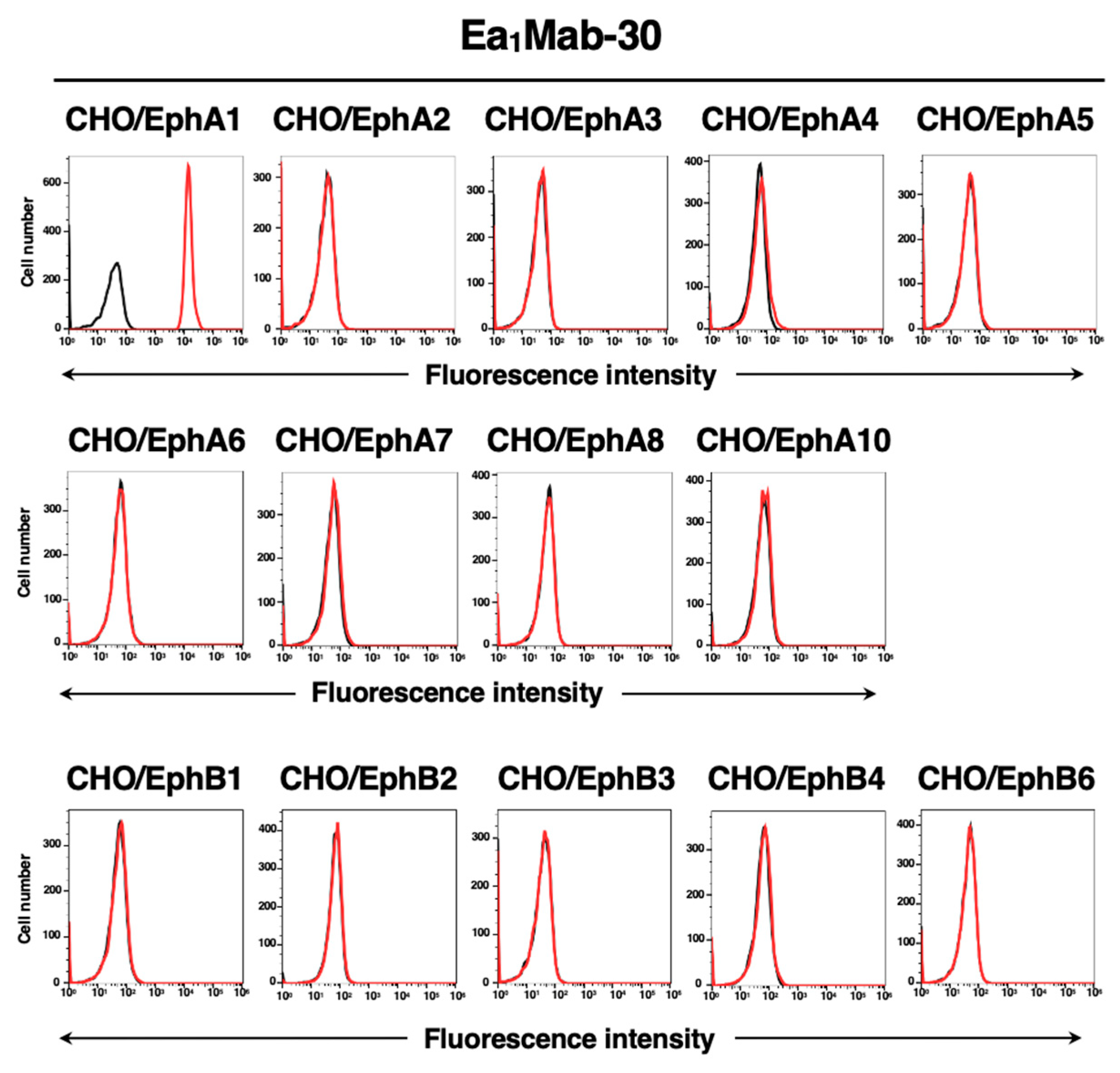
3.4. Specificity of Ea1Mab-30 to Eph Receptor-Overexpressed CHO-K1 Cells
3.5. Calculation of the Binding Affinity of Anti-EphA1 mAbs Using Flow Cytometry
3.6. Western Blot Analysis Using Anti-EphA1 mAbs
3.7. Immunohistochemistry Using Anti-EphA1 mAbs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.U.; Chen, Z.F.; Anderson, D.J. Molecular distinction and angiogenic interaction between embryonic arteries and veins revealed by ephrin-B2 and its receptor Eph-B4. Cell 1998, 93, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawamiphak, S.; Seidel, S.; Essmann, C.L.; Wilkinson, G.A.; Pitulescu, M.E.; Acker, T.; Acker-Palmer, A. Ephrin-B2 regulates VEGFR2 function in developmental and tumour angiogenesis. Nature 2010, 465, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, H.; Maru, Y.; Hagiwara, K.; Nishida, J.; Takaku, F. A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the eph gene. Science 1987, 238, 1717–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulthard, M.G.; Lickliter, J.D.; Subanesan, N.; Chen, K.; Webb, G.C.; Lowry, A.J.; Koblar, S.; Bottema, C.D.; Boyd, A.W. Characterization of the Epha1 receptor tyrosine kinase: expression in epithelial tissues. Growth Factors 2001, 18, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Masuda, J.; Omori, T.; Usui, R.; Akiyama, H.; Maru, Y. EphA1 interacts with integrin-linked kinase and regulates cell morphology and motility. J Cell Sci 2009, 122, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Otal, R.; Sieber, B.A.; Ibáñez, C.; Soriano, E. Disruption of ephrin-A/EphA binding alters synaptogenesis and neural connectivity in the hippocampus. Neuroscience 2005, 135, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.O.; Ip, N.Y. Synapse development and plasticity: roles of ephrin/Eph receptor signaling. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2009, 19, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinski, C.; Li, V.S.; Chan, A.S.; Zhang, J.; Ho, C.; Tsui, W.Y.; Chan, T.L.; Mifflin, R.C.; Powell, D.W.; Yuen, S.T.; et al. Gene expression patterns of human colon tops and basal crypts and BMP antagonists as intestinal stem cell niche factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 15418–15423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, A.; Sugamoto, Y.; Tokunaga, Y.; Yoshimuta, T.; Hayashi, K.; Konno, T.; Kawashiri, M.A.; Takeda, Y.; Yamagishi, M. Expression profiling of the ephrin (EFN) and Eph receptor (EPH) family of genes in atherosclerosis-related human cells. J Int Med Res 2011, 39, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, S.L.; Coulthard, M.G.; Spanevello, M.D.; Herath, N.I.; Yeadon, T.M.; McCarron, J.K.; Carter, J.C.; Tonks, I.D.; Kay, G.F.; Phillips, G.E.; et al. Generation and characterization of EphA1 receptor tyrosine kinase reporter knockout mice. Genesis 2008, 46, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.C.; Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A.; Harold, D.; Naj, A.C.; Sims, R.; Bellenguez, C.; DeStafano, A.L.; Bis, J.C.; Beecham, G.W.; Grenier-Boley, B.; et al. Meta-analysis of 74,046 individuals identifies 11 new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet 2013, 45, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, M.; Delpak, A.; Khalaj-Kondori, M.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Talebi, M.; Mehdizadeh, E.; Majdi, A. ABCA7 and EphA1 Genes Polymorphisms in Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease. J Mol Neurosci 2020, 70, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naj, A.C.; Jun, G.; Beecham, G.W.; Wang, L.S.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Buros, J.; Gallins, P.J.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Jarvik, G.P.; Crane, P.K.; et al. Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1 are associated with late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet 2011, 43, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karch, C.M.; Goate, A.M. Alzheimer's disease risk genes and mechanisms of disease pathogenesis. Biol Psychiatry 2015, 77, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Sabermarouf, B.; Majdi, A.; Talebi, M.; Farhoudi, M.; Mahmoudi, J. Amyloid-beta: a crucial factor in Alzheimer's disease. Med Princ Pract 2015, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Gomez-Soler, M.; Lombardi, S.; Lechtenberg, B.C.; Pasquale, E.B. Missense mutations of the ephrin receptor EPHA1 associated with Alzheimer's disease disrupt receptor signaling functions. J Biol Chem 2024, 301, 108099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingworth, P.; Harold, D.; Sims, R.; Gerrish, A.; Lambert, J.C.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Abraham, R.; Hamshere, M.L.; Pahwa, J.S.; Moskvina, V.; et al. Common variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP are associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet 2011, 43, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Chen, X.; Bao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Jin, S.; Tian, R.; Bai, W.; et al. Alzheimer's Disease rs11767557 Variant Regulates EPHA1 Gene Expression Specifically in Human Whole Blood. J Alzheimers Dis 2018, 61, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karch, C.M.; Jeng, A.T.; Nowotny, P.; Cady, J.; Cruchaga, C.; Goate, A.M. Expression of novel Alzheimer's disease risk genes in control and Alzheimer's disease brains. PLoS One 2012, 7, e50976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Dong, Y.; Shen, Z.; Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Shi, S.; Wu, J.; Lu, G.; Peng, L.; et al. High expression of EphA1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with lymph node metastasis and advanced disease. Apmis 2013, 121, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Sheng, Z.; Li, G.; Lu, G.; Sugimura, H.; Zhou, X. Expression of EphA1 in gastric carcinomas is associated with metastasis and survival. Oncol Rep 2010, 24, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Dai, Y.; Xu, G.L.; Yu, W.; Quan, R.L.; Zhao, Y.J. Association Between EphA1 and Tumor Microenvironment in Gastric Carcinoma and its Clinical Significance. Med Sci Monit 2020, 26, e923409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; He, F.; Pretlow, T.; Kung, H.J. A tyrosine kinase profile of prostate carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996, 93, 5958–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Wang, H.; Dong, Y.; Ma, J.; Wen, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J. Increased expression of EphA1 protein in prostate cancers correlates with high Gleason score. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013, 6, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, H.M.; Jang, B.G.; Lee, D.H.; Hyun, C.L.; Kim, D.C. The association between ephrin receptor-A1 expression and survival in patients with cancer: a meta-analysis. Transl Cancer Res 2022, 11, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagare, R.P.; Sneha, S.; Krishnapriya, S.; Ramachandran, B.; Murhekar, K.; Vasudevan, S.; Shabna, A.; Ganesan, T.S. ALDH1A1+ ovarian cancer stem cells co-expressing surface markers CD24, EPHA1 and CD9 form tumours in vivo. Exp Cell Res 2020, 392, 112009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieguchi, K.; Tomita, T.; Omori, T.; Komatsu, A.; Deguchi, A.; Masuda, J.; Duffy, S.L.; Coulthard, M.G.; Boyd, A.; Maru, Y. ADAM12-cleaved ephrin-A1 contributes to lung metastasis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, J.; Sheng, Z.; Li, G.; Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Lu, G.; Hu, Q.; Sugimura, H.; et al. Downregulation of EphA1 in colorectal carcinomas correlates with invasion and metastasis. Mod Pathol 2009, 22, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, N.I.; Doecke, J.; Spanevello, M.D.; Leggett, B.A.; Boyd, A.W. Epigenetic silencing of EphA1 expression in colorectal cancer is correlated with poor survival. Br J Cancer 2009, 100, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, C.; Becker, B.; Landthaler, M.; Vogt, T. Expression profile of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands in human skin and downregulation of EphA1 in nonmelanoma skin cancer. Mod Pathol 2006, 19, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wan, L.; Lu, M.; Liu, Y.; Huang, G.; Wang, J.; Xi, Q. Decreased Eph receptor-A1 expression is related to grade in ovarian serous carcinoma. Mol Med Rep 2018, 17, 5409–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajdzis, M.; Theocharis, S.; Gajdzis, P.; Cassoux, N.; Gardrat, S.; Donizy, P.; Klijanienko, J.; Kaczmarek, R. Ephrin Receptors (Eph): EphA1, EphA5, and EphA7 Expression in Uveal Melanoma-Associations with Clinical Parameters and Patient Survival. Life (Basel) 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satofuka H, S.H., Tanaka T, Li G, Kaneko MK, Kato Y. An Anti-Human EphA2 Monoclonal Antibody Ea2Mab-7 Shows High Sensitivity for Flow Cytometry, Western Blot, and Immunohistochemical Analyses. Preprint 2024. [CrossRef]
- Ubukata, R.; Suzuki, H.; Hirose, M.; Satofuka, H.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Establishment of a highly sensitive and specific anti-EphB2 monoclonal antibody (Eb2Mab-12) for flow cytometry. MI 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanamiya, R.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of an Anti-EphB4 Monoclonal Antibody for Multiple Applications Against Breast Cancers. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2023, 42, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Li, G.; Fujisawa, S.; Satofuka, H.; Shinoda, K.; Nakamura, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Development of a novel anti-erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular receptor B6 monoclonal antibody Eb6Mab-3 for flow cytometry. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports 2025, 41, 101960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. MAP Tag: A Novel Tagging System for Protein Purification and Detection. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2016, 35, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Kaneko, M.; Neyazaki, M.; Nogi, T.; Kato, Y.; Takagi, J. PA tag: a versatile protein tagging system using a super high affinity antibody against a dodecapeptide derived from human podoplanin. Protein Expr Purif 2014, 95, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikota, H.; Nobusawa, S.; Arai, H.; Kato, Y.; Ishizawa, K.; Hirose, T.; Yokoo, H. Evaluation of IDH1 status in diffusely infiltrating gliomas by immunohistochemistry using anti-mutant and wild type IDH1 antibodies. Brain Tumor Pathol 2015, 32, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Zhang, C. Inhibition of angiogenesis by leflunomide via targeting the soluble ephrin-A1/EphA2 system in bladder cancer. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, N.I.; Boyd, A.W. The role of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 2010, 126, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, G.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, J. Expression of the EphA1 protein is associated with Fuhrman nuclear grade in clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015, 8, 6821–6827. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arimori, T.; Mihara, E.; Suzuki, H.; Ohishi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Takagi, J.; Kato, Y. Locally misfolded HER2 expressed on cancer cells is a promising target for development of cancer-specific antibodies. Structure 2024, 32, 536–549.e535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, H.; Ohishi, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. A Cancer-Specific Anti-Podoplanin Monoclonal Antibody, PMab-117-mG(2a) Exerts Antitumor Activities in Human Tumor Xenograft Models. Cells 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Wang, X.; Dong, K.; Li, X.; Qin, C.; Zhou, H. Expression Pattern and Prognostic Value of EPHA/EFNA in Breast Cancer by Bioinformatics Analysis: Revealing Its Importance in Chemotherapy. Biomed Res Int 2021, 2021, 5575704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.N.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.Y.; Hsu, H.P.; Lai, M.D.; Li, C.Y.; Chen, C.F.; Chiao, C.C.; Yen, M.C.; Sun, Z.; et al. Overexpressed gene signature of EPH receptor A/B family in cancer patients-comprehensive analyses from the public high-throughput database. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2020, 13, 1220–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquale, E.B. Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2024, 24, 5–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarron, J.K.; Stringer, B.W.; Day, B.W.; Boyd, A.W. Ephrin expression and function in cancer. Future Oncol 2010, 6, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, P.W.; Vail, M.E.; Gan, H.K.; Scott, A.M. Antibody Targeting of Eph Receptors in Cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, C.L.; Bateman, R.; Blennow, K.; Rowe, C.C.; Sperling, R.A.; Cummings, J.L. Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015, 1, 15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenguez, C.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Lambert, J.C. Genetics of Alzheimer's disease: where we are, and where we are going. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2020, 61, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Laws, S.M.; Miles, L.A.; Wiley, J.S.; Huang, X.; Masters, C.L.; Gu, B.J. Genomics of Alzheimer's disease implicates the innate and adaptive immune systems. Cell Mol Life Sci 2021, 78, 7397–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.C.; Heath, S.; Even, G.; Campion, D.; Sleegers, K.; Hiltunen, M.; Combarros, O.; Zelenika, D.; Bullido, M.J.; Tavernier, B.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet 2009, 41, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, H.A.; Thorburn, L.E.; Walsby, E.; Moon, O.R.; Rizkallah, P.; Sherwani, S.; Tinsley, C.L.; Rogers, L.; Cerutti, C.; Ridley, A.J.; et al. Alzheimer's disease-associated P460L variant of EphA1 dysregulates receptor activity and blood-brain barrier function. Alzheimers Dement 2024, 20, 2016–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl, E.; Kim, Y.A.; Parsons, T.; Zhu, B.; Santa-Maria, I.; Lefort, R.; Hodge, J.J.L. Effects of Eph/ephrin signalling and human Alzheimer's disease-associated EphA1 on Drosophila behaviour and neurophysiology. Neurobiol Dis 2022, 170, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.R.; Buck, M. Structural and Functional Insights into the Transmembrane Domain Association of Eph Receptors. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, A.K.; Ip, N.Y. Bidirectional signaling of ErbB and Eph receptors at synapses. Neuron Glia Biol 2008, 4, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Sun, W.; Gu, Q.; Li, D.; Zheng, J.; Yang, H.; Li, X. EphA1 Activation Induces Neuropathological Changes in a Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease Through the CXCL12/CXCR4 Signaling Pathway. Mol Neurobiol 2021, 58, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Miller, G.W.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Z. Deciphering proteins in Alzheimer's disease: A new Mendelian randomization method integrated with AlphaFold3 for 3D structure prediction. Cell Genom 2024, 4, 100700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Kaneko, M.K. A cancer-specific monoclonal antibody recognizes the aberrantly glycosylated podoplanin. Sci Rep 2014, 4, 5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




