Submitted:
16 January 2025
Posted:
16 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
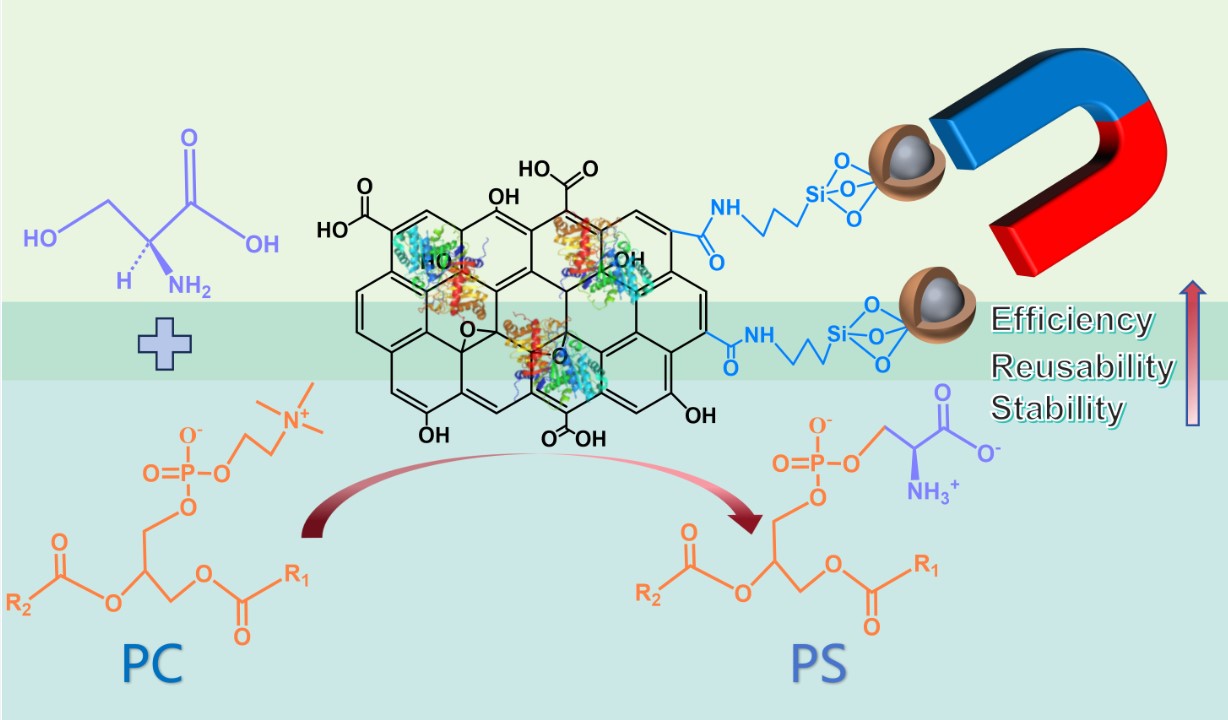
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2-GO Nanoparticles
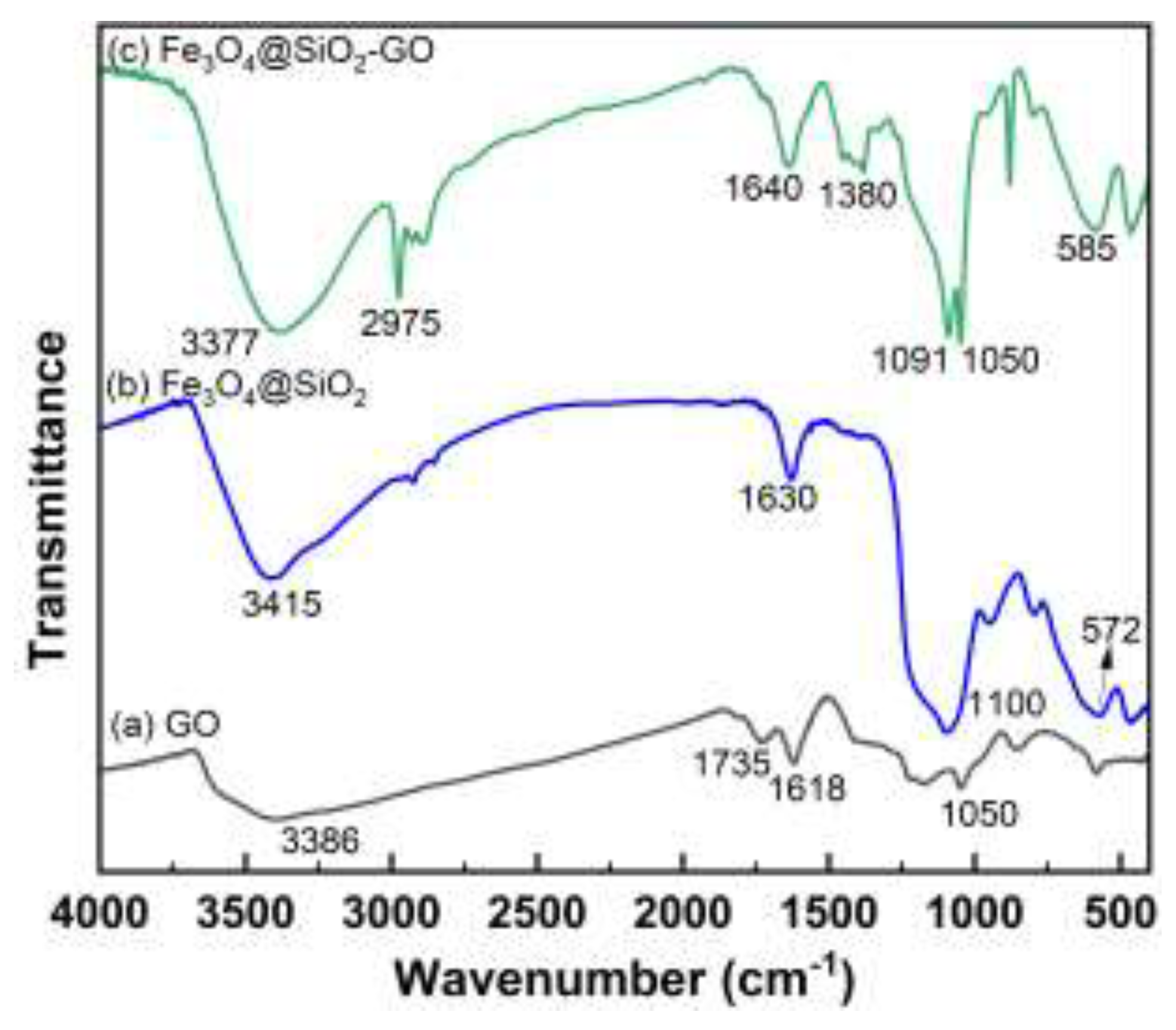
2.1.1. FTIR Analysis
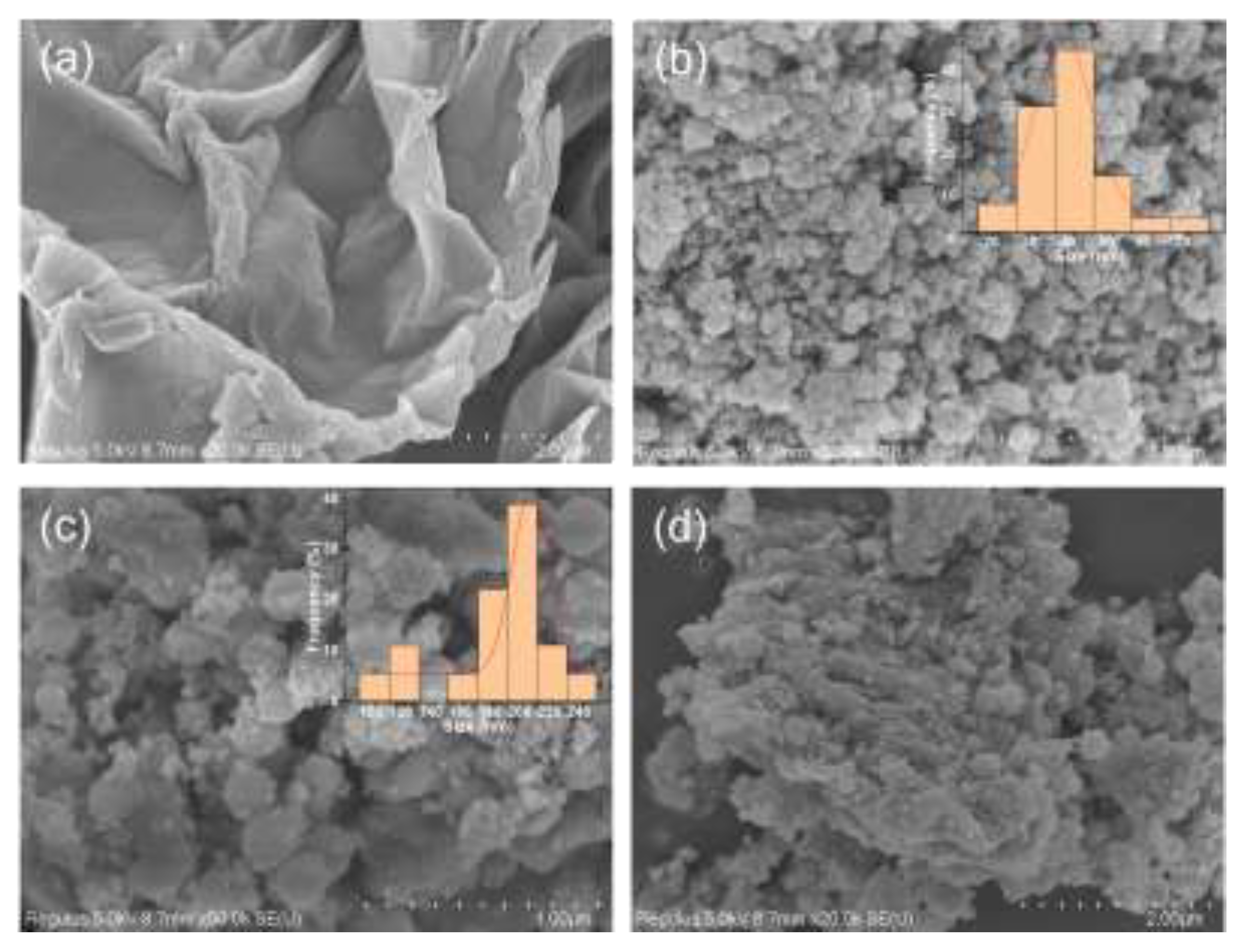
2.1.2. Morphology
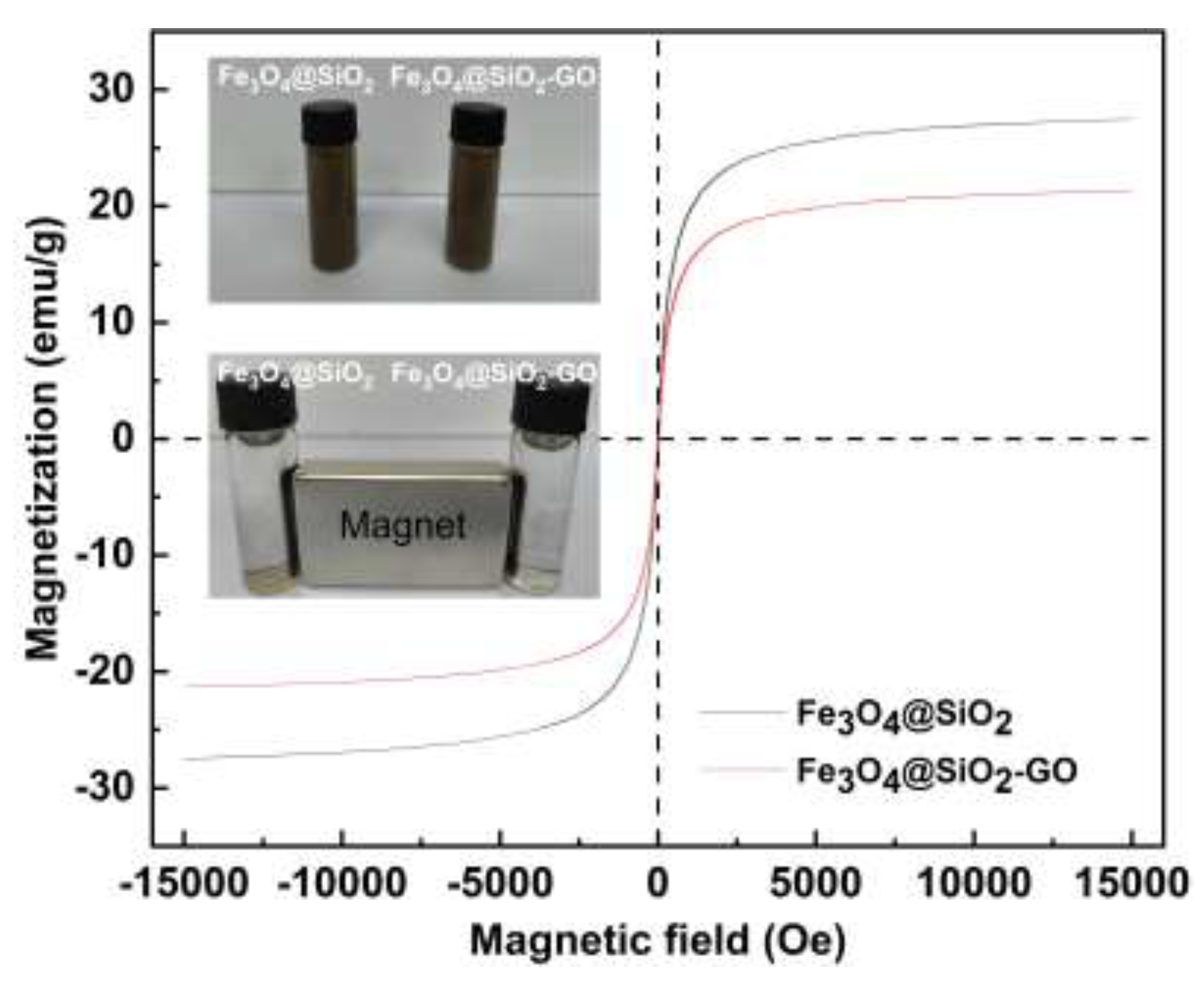
2.1.3. VSM Measurements
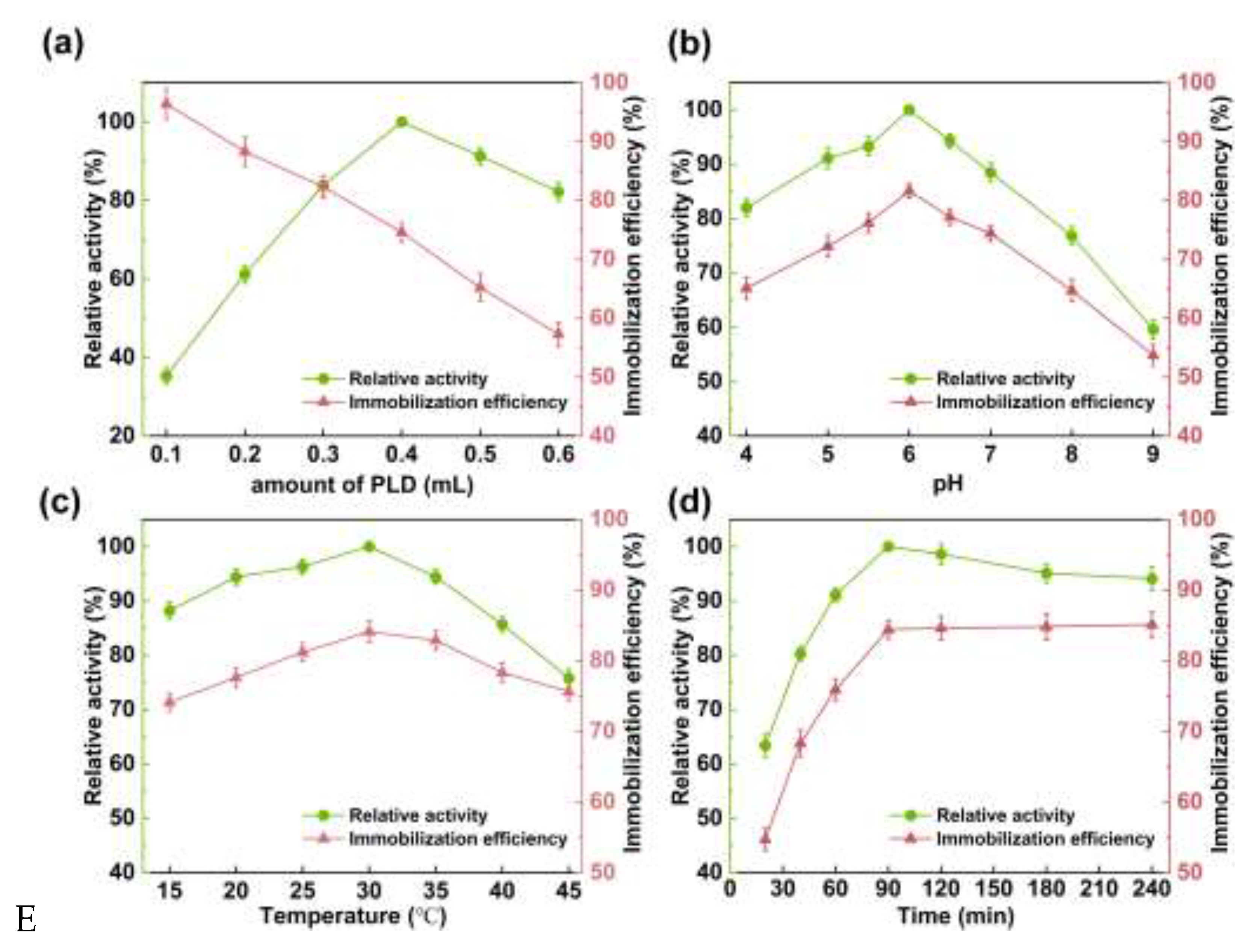
2.2. The PLD Immobilization Parameters
2.2.1. The initial PLD Volume
2.2.2. pH
2.2.3. Temperature
2.2.4. Contact Time
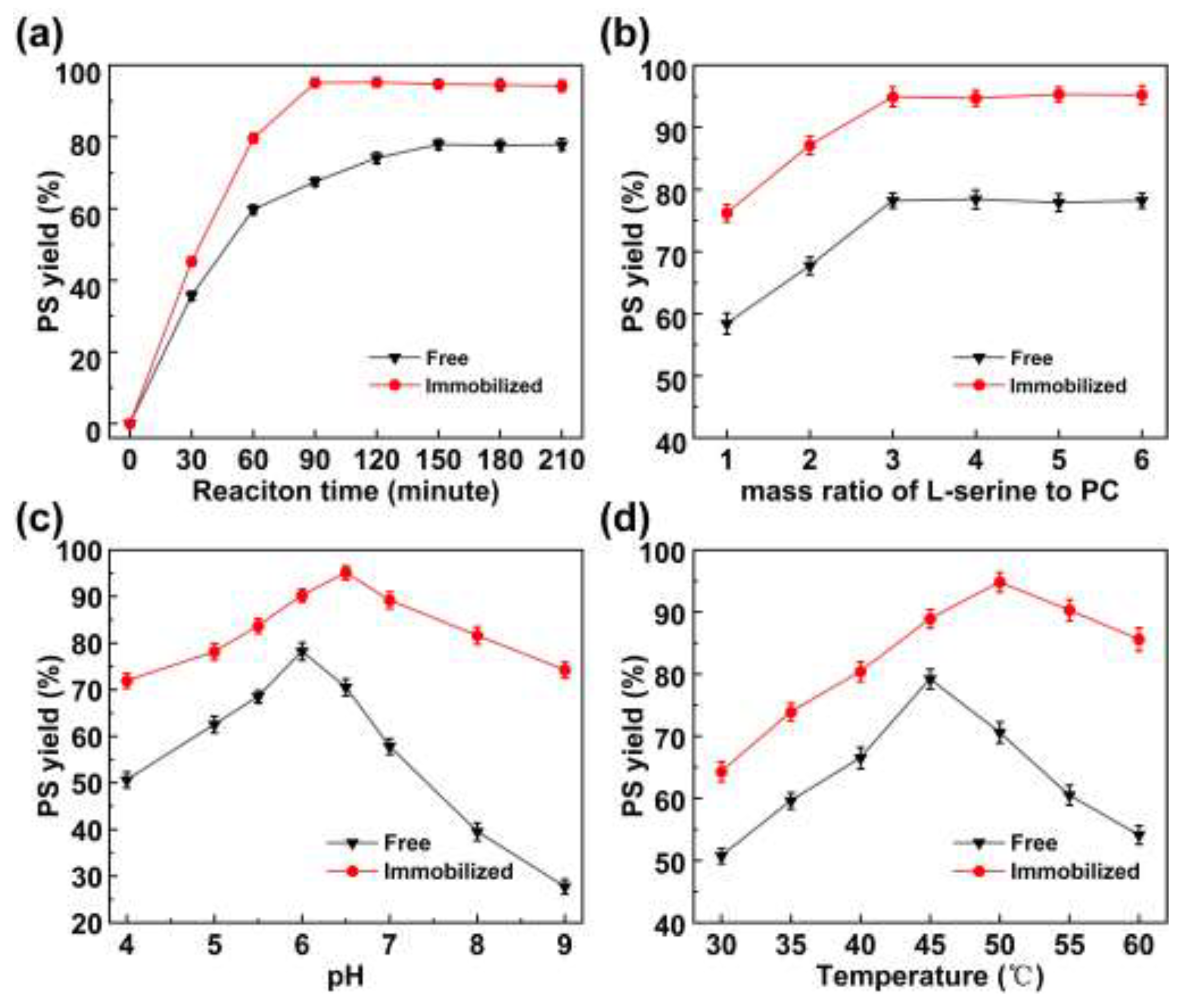
2.3. Optimization of the Transphosphatidylation Reaction
2.3.1. Reaction Time
2.3.2. Effect of Substrate Concentration Ratio
2.3.3. pH
2.3.4. Temperature
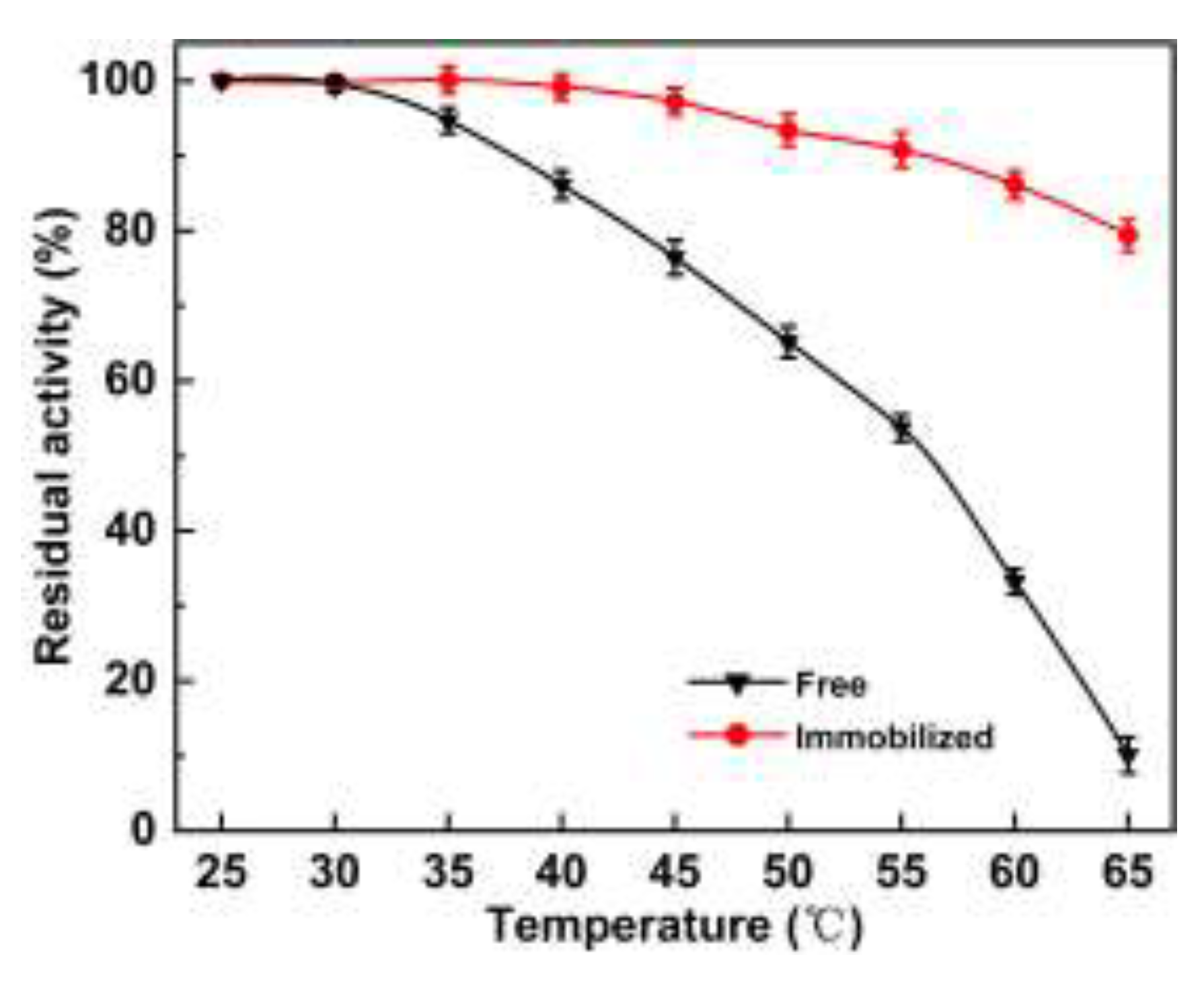
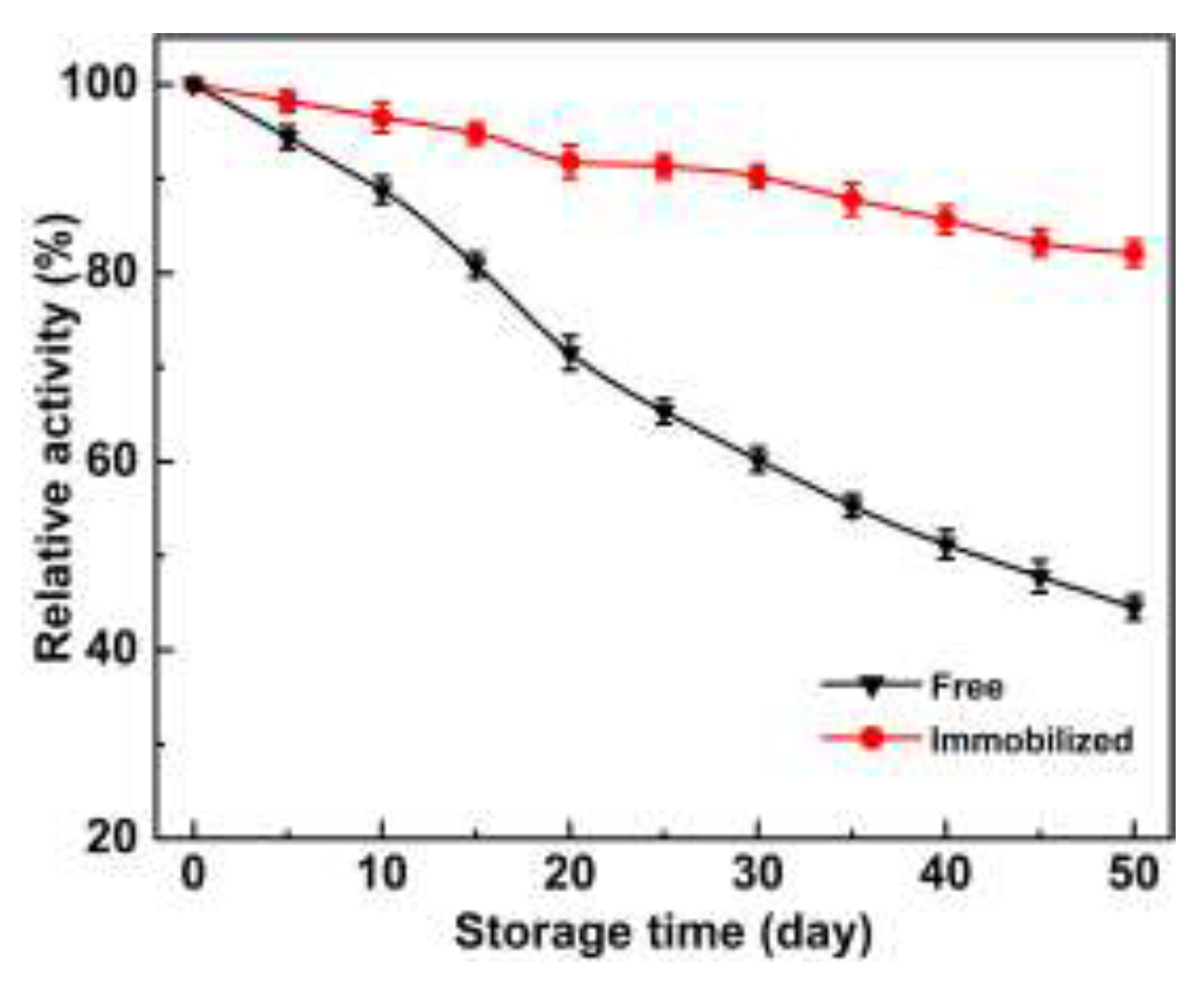
2.4. Stability and Reusability
2.4.1. Thermal Stability
2.4.2. Storage Stability
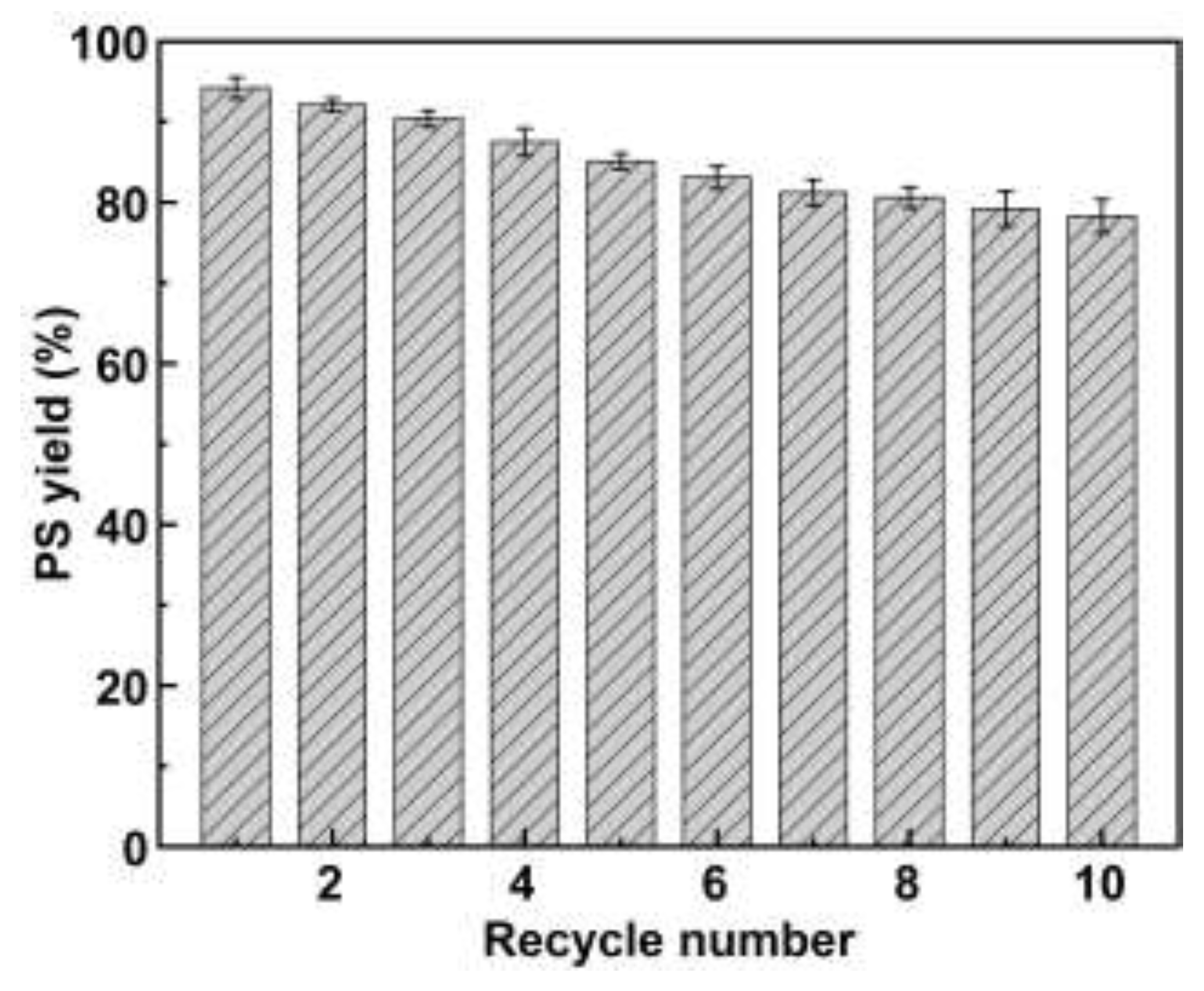
2.4.3. Reusability of Immobilized PLD
2.5. Comparison of PLD Immobilization on Fe3O4@SiO2-GO and Other Supports
Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
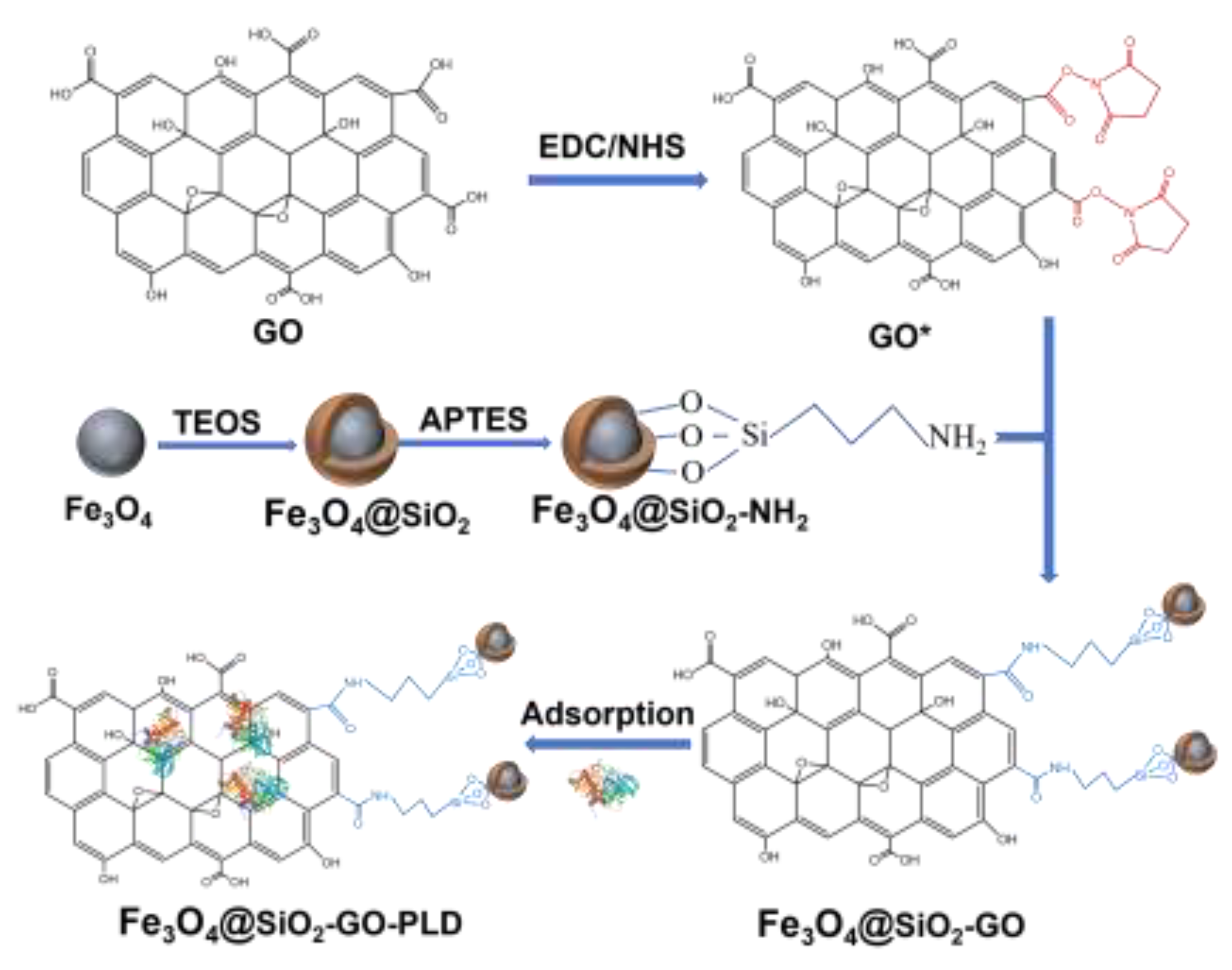
3.2. Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2-GO
3.3. Characterization Methods
3.4. Immobilization of PLD
3.5. Enzyme Activity Assay
3.6. Synthesis of PS
3.7. Thermal Stability
3.8. Storage Stability and Reusability
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glade, M.J.; Smith, K. Phosphatidylserine and the human brain. Nutrition 2015, 31, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Huang, B.X.; Spector, A.A. Phosphatidylserine in the brain: Metabolism and function. Progress in lipid research 2014, 56, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, R.R.; Satzger, W.; Günther, W.; Kathmann, N.; Bove, D.; Gerke, S.; Münch, U.; Hippius, H. Double-blind cross-over study of phosphatidylserine vs. placebo in patients with early dementia of the Alzheimer type. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1992, 2, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato-Kataoka, A.; Sakai, M.; Ebina, R.; Nonaka, C.; Asano, T.; Miyamori, T. Soybean-derived phosphatidylserine improves memory function of the elderly Japanese subjects with memory complaints. Journal of clinical biochemistry and nutrition 2010, 47, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doma, K.M.; Lewis, E.D.; Barracato, J.M.; Brink, L.R.; Gratson, A.A.; Pandey, N.; Crowley, D.C.; Evans, M. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel Study Investigating the Efficacy of a Whole Coffee Cherry Extract and Phosphatidylserine Formulation on Cognitive Performance of Healthy Adults with Self-Perceived Memory Problems. Neurology and Therapy 2023, 12, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruton, A.; Nauman, J.; Hanes, D.; Gard, M.; Senders, A. Phosphatidylserine for the treatment of pediatric attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2021, 27, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, P.; Beinat, L.; Tanzillo, C.; Maj, M.; Kemali, D. Effects of phosphatidylserine on the neuroendocrine response to physical stress in humans. Neuroendocrinology 1990, 52, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.; Greenwood, M. Phosphatidylserine for the Athlete. Strength & Conditioning Journal 2015, 37, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeini, M.B.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Ganjali, S.; Kontush, A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Sahebkar, A. Phosphatidylserine-containing liposomes: Therapeutic potentials against hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. European Journal of Pharmacology 2021, 908, 174308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Loza, I.; Perna-Barrull, D.; Aguilera, E.; Almenara-Fuentes, L.; Gomez-Muñoz, L.; Greco, D.; Vila, M.; Salvado, M.; Mancera-Arteu, M.; Olszowy, M.W. Targeting macrophages with phosphatidylserine-rich liposomes as a potential antigen-specific immunotherapy for type 1 diabetes. Journal of autoimmunity 2024, 145, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, D.; Xu, Y.; Hu, J. Phosphatidylserine-functionalized liposomes-in-microgels for delivering genistein to effectively treat ulcerative colitis. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2023, 11, 10404–10417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damnjanović, J.; Iwasaki, Y. Phospholipase D as a catalyst: Application in phospholipid synthesis, molecular structure and protein engineering. Journal of bioscience and bioengineering 2013, 116, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvy, P.E.; Lavieri, R.R.; Lindsley, C.W.; Brown, H.A. Phospholipase D: Enzymology, functionality, and chemical modulation. Chemical reviews 2011, 111, 6064–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uesugi, Y.; Hatanaka, T. Phospholipase D mechanism using Streptomyces PLD. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 2009, 1791, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Sun, J.; Secundo, F.; Mao, X. Construction of a super-folder fluorescent protein-guided secretory expression system for the production of phospholipase D in Bacillus subtilis. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 2021, 69, 6842–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Fu, Y.; Zheng, D.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lu, F. A novel process for phosphatidylserine production using a Pichia pastoris whole-cell biocatalyst with overexpression of phospholipase D from Streptomyces halstedii in a purely aqueous system. Food chemistry 2019, 274, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wang, F.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L. Whole-Cell Display of Phospholipase D in Escherichia coli for High-Efficiency Extracellular Phosphatidylserine Production. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.-H.; Duan, Z.-Q.; Li, X.-Q.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhao, X.-R. Introducing biobased ionic liquids as the nonaqueous media for enzymatic synthesis of phosphatidylserine. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 2015, 63, 1558–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arrigo, P.; Cerioli, L.; Chiappe, C.; Panzeri, W.; Tessaro, D.; Mele, A. Improvements in the enzymatic synthesis of phosphatidylserine employing ionic liquids. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic 2012, 84, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qi, X.; Yu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, B. Highly efficient biosynthesis of phosphatidylserine by the surface adsorption-catalysis in purely aqueous media and mechanism study by biomolecular simulation. Molecular Catalysis 2021, 502, 111397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Tian, H.; Lu, F.; Liu, Y. Efficient secretion expression of phospholipase D in Bacillus subtilis and its application in synthesis of phosphatidylserine by enzyme immobilization. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2021, 169, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-S.; Li, Y.; Long, N.-B.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, R.-F. Highly active and stable nanobiocatalyst based on in-situ cross-linking of phospholipase D for the synthesis of phosphatidylserine. International journal of biological macromolecules 2018, 117, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yon, J.O.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, B.G.; Kim, S.D.; Nam, D.H. Immobilization of Streptomyces phospholipase D on a Dowex macroporous resin. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering 2008, 13, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-Q.; Xu, X.-M.; Wang, D.-L.; Long, N.-B.; Zhang, R.-F. Immobilization of phospholipase D on macroporous SiO2/cationic polymer nano-composited support for the highly efficient synthesis of phosphatidylserine. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 2020, 142, 109696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, J.-Q.; Long, N.-B.; Zhang, R.-F. Efficient immobilization of phospholipase D on novel polymer supports with hierarchical pore structures. International journal of biological macromolecules 2019, 141, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossato, L.A.M.; Morsali, M.; Ruffini, E.; Bertuzzi, P.; Serra, S.; D'Arrigo, P.; Sipponen, M. Phospholipase D Immobilization on Lignin Nanoparticles for Enzymatic Transformation of Phospholipids. ChemSusChem 2024, 17, e202300803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Jin, Q.; Qi, X.; Zhang, H. Design of amino-functionalized hollow mesoporous silica cube for enzyme immobilization and its application in synthesis of phosphatidylserine. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2021, 202, 111668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, M.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Li, B.; Wang, J. Immobilization of Bio-imprinted Phospholipase D and Its Catalytic Behavior for Transphosphatidylation in the Biphasic System. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2023, 195, 7808–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, H.; Huang, Z.; Han, Z.; Hou, J.; Lu, F.; Liu, Y. Immobilization of Phospholipase D for Production of Phosphatidylserine via Enzyme-Inorganic Hybrid Nanoflower Strategy. Fermentation 2023, 9, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Fan, C.; Jin, Z.; Yu, F. One-pot synthesis and biochemical characterization of the novel magnetic phospholipase D nanoflowers modified with polyphenols. Molecular Catalysis 2024, 559, 114056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhang, H.; Mao, X. Cellulose nanofibril-stabilized Pickering emulsion as a high-performance interfacial biocatalysis system for the synthesis of phosphatidylserine. Food Chemistry 2023, 399, 133865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chu, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, W.-c.; Xue, C.; Mao, X. A novel autolysis system for extracellular production and direct immobilization of a phospholipase D fused with cellulose binding domain. BMC biotechnology 2019, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Yang, K.; Yao, K.; Zhang, S.; Tao, H.; Lee, S.-T.; Liu, Z.; Peng, R. Functionalized graphene oxide in enzyme engineering: A selective modulator for enzyme activity and thermostability. ACS nano 2012, 6, 4864–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badoei-Dalfard, A.; Karami, Z.; Malekabadi, S. Construction of CLEAs-lipase on magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite: An efficient nanobiocatalyst for biodiesel production. Bioresource technology 2019, 278, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirbandeh, M.; Taheri-Kafrani, A. Immobilization of glucoamylase on triazine-functionalized Fe3O4/graphene oxide nanocomposite: Improved stability and reusability. International journal of biological macromolecules 2016, 93, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Huang, M. Immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase onto graphene oxide Fe3O4 nanocomposite: Characterization and application for biodiesel production. Energy Conversion and Management 2018, 159, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Miao, S.; Yu, S.; Ma, L.P.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Fabrication of Fe3O4/SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles attached to graphene oxide and its use as an adsorbent. Journal of colloid and interface science 2012, 379, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y. One-pot synthesis of magnetic graphene oxide composites as an efficient and recoverable adsorbent for Cd (II) and Pb (II) removal from aqueous solution. Journal of hazardous materials 2020, 381, 120914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Jang, J. Thiol containing polymer encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles as reusable and efficiently separable adsorbent for heavy metal ions. Chemical communications 2007, 4230–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royvaran, M.; Taheri-Kafrani, A.; Isfahani, A.L.; Mohammadi, S. Functionalized superparamagnetic graphene oxide nanosheet in enzyme engineering: A highly dispersive, stable and robust biocatalyst. Chemical Engineering Journal 2016, 288, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Guo, B.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, H. Immobilization of Phospholipase D on Magnetic Graphene Oxide for Efficient Phosphatidylserine Production. Catalysts 2024, 14, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xia, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Ding, M. Facile and tunable fabrication of Fe3O4/graphene oxide nanocomposites and their application in the magnetic solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental water samples. Talanta 2012, 101, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjeri, V.; Sheppard, C.; Prinsloo, A.; Ngila, J.; Ndungu, P. Isotherm and kinetic investigations on the adsorption of organophosphorus pesticides on graphene oxide based silica coated magnetic nanoparticles functionalized with 2-phenylethylamine. Journal of environmental chemical engineering 2018, 6, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donga, C.; Mishra, S.B.; Abd-El-Aziz, A.S.; Ndlovu, L.N.; Mishra, A.K.; Kuvarega, A.T. (3-Aminopropyl) Triethoxysilane (APTES) functionalized magnetic nanosilica graphene oxide (MGO) nanocomposite for the comparative adsorption of the heavy metal [Pb (II), Cd (II) and Ni (II)] ions from aqueous solution. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials 2022, 32, 2235–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.W.; Fan, X.; Guo, L.A.; Wei, W.T. Graphene Oxide/Fe3O4 Composites Prepared via In Situ Precipitation. Advanced Materials Research 2014, 904, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Jin, Q.; Qi, X.; Zhang, H. A novel immobilized enzyme enhances the conversion of phosphatidylserine in two-phase system. Biochemical Engineering Journal 2021, 172, 108035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-P.; Ren, C.-L.; Qu, J.-C.; Chen, X.-G. Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4/graphene nanocomposite and investigation of its adsorption performance for aniline and p-chloroaniline. Applied Surface Science 2012, 261, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh Al-Makhathi, A.A.; Khan, H.; Malik, S.; Taube, P.S.; Ara, B.; Gul, K.; Khan, A. Ternary magnetic silica–graphene oxide composite for remediation of textile dyes from aqueous environment and real samples. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie 2024, 238, 883–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishiri, M.; Abdollahi, S.A.; Neysari, A.N.; Ranjbar, S.F.; Abdoli, N.; Afsharjahanshahi, M. Removal of ciprofloxacin and cephalexin antibiotics in water environment by magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposites; optimization using response surface methodology. Results in Engineering 2023, 20, 101507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Shang, H.; Du, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Zhu, H. Efficient Biosynthesis of Phosphatidylserine in a Biphasic System through Parameter Optimization. Processes 2023, 11, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Hao, N.; Yan, M. Bioconversion of phosphatidylserine by phospholipase D from Streptomyces racemochromogenes in a microaqueous water-immiscible organic solvent. Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry 2013, 77, 1939–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanová, S.; Zarevúcká, M.; Bouša, D.; Pumera, M.; Sofer, Z. Graphene oxide immobilized enzymes show high thermal and solvent stability. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 5852–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S., Jr.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. Journal of the american chemical society 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, S.; Horiuti, Y. Enzymatic determination of phospholipase D activity with choline oxidase. The Journal of Biochemistry 1978, 83, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Support/Method | Immobilization efficiency(%) | Enzyme loading (mg/gsupport) |
PS yield (%) |
Time | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@SiO2-GO/adsorption | 84.4 | 111.4 | 95.1 | 90 min | This tudy |
| magnetic GO/covalent linkage | 30.1 | 90.3 | 92.8 | 6 h | [41] |
| non-porous SiO2/cross-linking | / | / | 97 | 6 h | [28] |
| macroporous SiO2-cationic polymer/adsorption | / | 61.5 | 96.2 | 40 min | [24] |
| epoxy resin hierarchical porous polymer/adsorption | / | 223 | 95.5 | 40 min | [25] |
| cellulose nanofibrils/cellulose-binding domain | 56.3 | / | 95.4 | 2 h | [31] |
| ZnO nanowires-macroporous SiO2/in-situ cross-linking | / | 68.1 | 94.8 | 40 min | [22] |
| ordered mesoporous silica cube/adsorption | 76.27 | / | 91.2 | 2 h | [46] |
| amino hollow mesoporous silica cube/cross-linking | 87.15 | 1.859 | 90.4 | 10 h | [27] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




