Submitted:
02 January 2025
Posted:
08 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
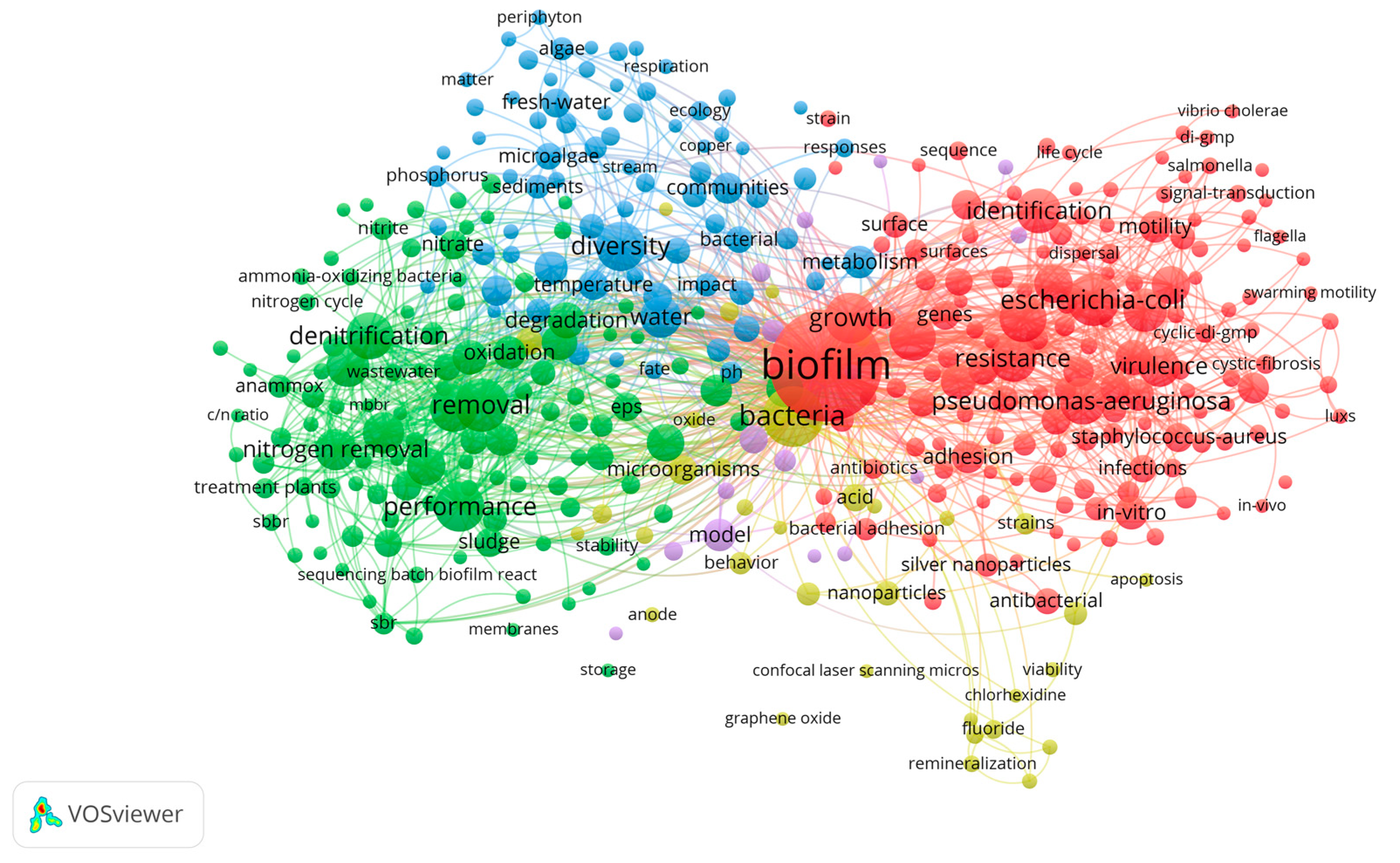
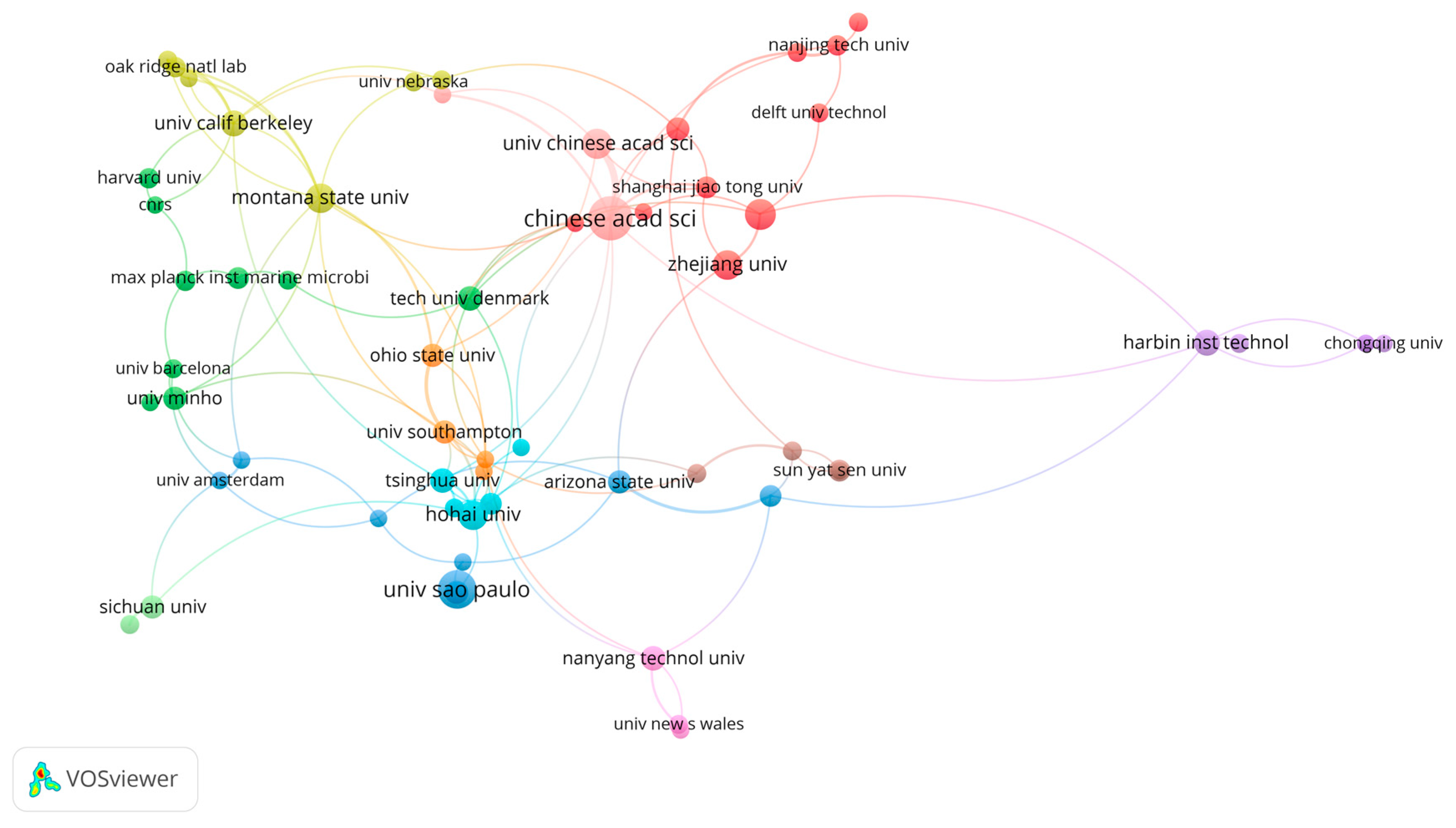
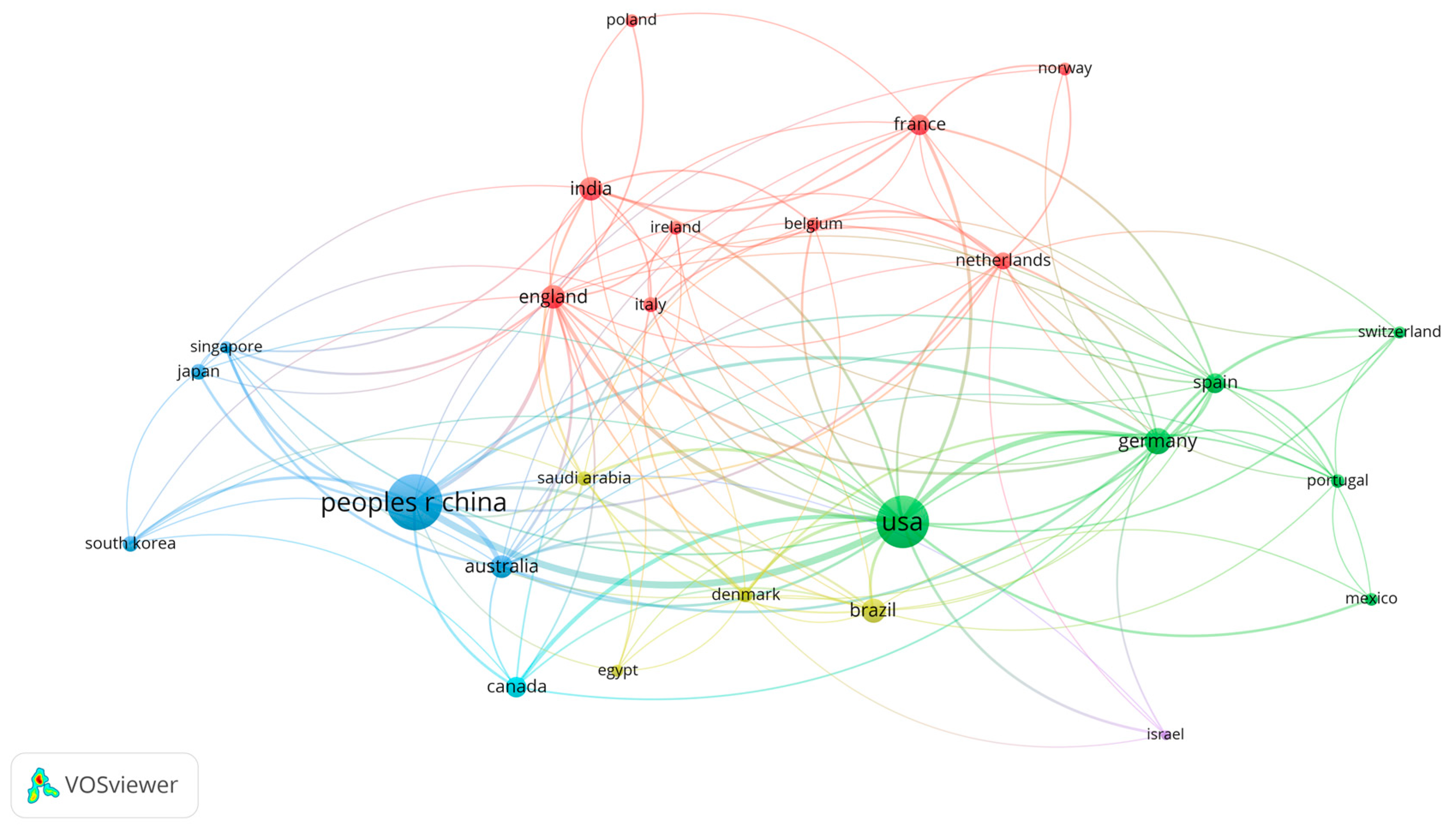
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of the Biofilm Cycle Stages
| Stages | Main Characteristics | References |
|---|---|---|
| 1.Bacteria Land on Surface | - Bacteria touch the surface. - Weak, temporary bonds form (e.g., physical forces). |
[26,27] |
| 2.Irreversible Attachment | - Bacteria stick firmly using structures like pili or slime (EPS). - Hard to remove. |
[28,29] |
| 3.Proliferation | - Bacteria grow and produce slime to form a shield. - They communicate and work together. |
[30,31] |
| 4. Maturation | - Biofilm gets thicker and more complex. - High resistance to antibiotics and harsh conditions. |
[32,33] |
| 5. Dispersal | - Parts of the biofilm break off. - Bacteria spread to new places to start over. |
[34,35] |
4.2. Beneficial Biofilm in Biofilm Reactors and Harmful Biofilm in Infections
4.3. Future Direction: Big Data and Machine Learning on Biofilm Cycle
5. Conclusions
References
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nature reviews microbiology 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Zheng, Y. Overview of microalgal extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and their applications. Biotechnology advances 2016, 34, 1225–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddharth, T.; Sridhar, P.; Vinila, V.; Tyagi, R.D. Environmental applications of microbial extracellular polymeric substance (EPS): a review. Journal of Environmental Management 2021, 287, 112307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Neu, T.R.; Wozniak, D.J. The EPS matrix: the “house of biofilm cells”. Journal of bacteriology 2007, 189, 7945–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-e.; Chen, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, V.B.; Bao, B.; Kjelleberg, S.; Cao, B.; Loo, S.C.J.; Wang, L.; Huang, W. Chemically functionalized conjugated oligoelectrolyte nanoparticles for enhancement of current generation in microbial fuel cells. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2015, 7, 14501–14505. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Peng, N.; Du, Y.; Ji, L.; Cao, B. Disruption of putrescine biosynthesis in Shewanella oneidensis enhances biofilm cohesiveness and performance in Cr (VI) immobilization. Applied and environmental microbiology 2014, 80, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S. Battling biofilms. Scientific American 2001, 285, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, M.A.; Gupta, K.; Bardhan, P.; Borah, M.; Sarkar, A.; Eldiehy, K.S.H.; Bhuyan, S.; Mandal, M. Microbial biofilm: A matter of grave concern for human health and food industry. Journal of Basic Microbiology 2021, 61, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, N.M.; Bedi, B.; Sadikot, R.T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: host response and clinical implications in lung infections. American journal of respiratory cell and molecular biology 2018, 58, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trautner, B.W.; Darouiche, R.O. Role of biofilm in catheter-associated urinary tract infection. American journal of infection control 2004, 32, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, K.; Stoodley, P.; Goeres, D.M.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Burmølle, M.; Stewart, P.S.; Bjarnsholt, T. The biofilm life cycle: expanding the conceptual model of biofilm formation. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2022, 20, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teughels, W.; Van Assche, N.; Sliepen, I.; Quirynen, M. Effect of material characteristics and/or surface topography on biofilm development. Clinical oral implants research 2006, 17, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappin-Scott, H.M.; Bass, C. Biofilm formation: attachment, growth, and detachment of microbes from surfaces. American journal of infection control 2001, 29, 250–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. From bibliography to understanding: water microbiology and human health. Journal of Water and Health 2024, 22, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. A bibliography study of Shewanella oneidensis biofilm. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 2023, 99, fiad124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, J.; Su, Z.; Zhu, C. Strategies to prevent, curb and eliminate biofilm formation based on the characteristics of various periods in one biofilm life cycle. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2022, 12, 1003033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.A.; Tan, C.H.; Mikkelsen, P.J.; Kung, V.; Woo, J.; Tay, M.; Hauser, A.; McDougald, D.; Webb, J.S.; Kjelleberg, S. The biofilm life cycle and virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa are dependent on a filamentous prophage. The ISME journal 2009, 3, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. Tackling heavy metal pollution: evaluating governance models and frameworks. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. Bibliographic Insights into Biofilm Engineering. Acta Microbiologica Hellenica 2024, 69, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W. A tale of two databases: the use of Web of Science and Scopus in academic papers. Scientometrics 2020, 123, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongeon, P.; Paul-Hus, A. The journal coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: a comparative analysis. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Citation-based clustering of publications using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukar, U.A.; Sayeed, M.S.; Razak, S.F.A.; Yogarayan, S.; Amodu, O.A.; Mahmood, R.A.R. A method for analyzing text using VOSviewer. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Stoodley, P. Biofilm formation and dispersal and the transmission of human pathogens. Trends in microbiology 2005, 13, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyofuku, M.; Roschitzki, B.; Riedel, K.; Eberl, L. Identification of proteins associated with the Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm extracellular matrix. Journal of proteome research 2012, 11, 4906–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.; Flint, S.; Brooks, J. Bacterial cell attachment, the beginning of a biofilm. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology 2007, 34, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.-Y.; Borca-Tasciuc, D.A.; Worobo, R.W.; Moraru, C.I. Bacterial attachment and biofilm formation on surfaces are reduced by small-diameter nanoscale pores: how small is small enough? npj Biofilms and Microbiomes 2015, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsa, S.M.; Espinosa-Urgel, M.; Ramos, J.L.; O'Toole, G.A. Transition from reversible to irreversible attachment during biofilm formation by Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 requires an ABC transporter and a large secreted protein. Molecular microbiology 2003, 49, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazza, N.C.; O'Toole, G.A. SadB is required for the transition from reversible to irreversible attachment during biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14. 2004.
- Krsmanovic, M.; Biswas, D.; Ali, H.; Kumar, A.; Ghosh, R.; Dickerson, A.K. Hydrodynamics and surface properties influence biofilm proliferation. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2021, 288, 102336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Tay, F.R.; Shen, Y. The dynamics of bacterial proliferation, viability, and extracellular polymeric substances in oral biofilm development. Journal of Dentistry 2024, 143, 104882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcal infections: mechanisms of biofilm maturation and detachment as critical determinants of pathogenicity. Annual review of medicine 2013, 64, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisner, A.; Haagensen, J.A.J.; Schembri, M.A.; Zechner, E.L.; Molin, S. Development and maturation of Escherichia coli K-12 biofilms. Molecular microbiology 2003, 48, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, J.á. Biofilm dispersal: mechanisms, clinical implications, and potential therapeutic uses. Journal of dental research 2010, 89, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbaugh, K.P.; Sauer, K. Biofilm dispersion. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2020, 18, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierek-Pearson, K.; Karatan, E. Biofilm development in bacteria. Advances in applied microbiology 2005, 57, 79–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.e.; Wu, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, V.B.; Zhang, Y.; Kjelleberg, S.; Loo, J.S.C.; Cao, B.; Zhang, Q. Hybrid conducting biofilm with built-in bacteria for high-performance microbial fuel cells. ChemElectroChem 2015, 2, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Hu, Y.; Cao, B.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S.; Song, H. Enhancing bidirectional electron transfer of Shewanella oneidensis by a synthetic flavin pathway. ACS synthetic biology 2015, 4, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Influence of bacterial incorporation on mechanical properties of engineered cementitious composites (ECC). Construction and Building Materials 2019, 196, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Weng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Use of genetically modified bacteria to repair cracks in concrete. Materials 2019, 12, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S. Mechanical performance of strain-hardening cementitious composites (SHCC) with bacterial addition. Journal of Infrastructure Preservation and Resilience 2022, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D.; Kollef, M. The epidemiology and pathogenesis and treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: an update. Drugs 2021, 81, 2117–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, K.; Baishya, J.; Wakeman, C.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa polymicrobial interactions during lung infection. Current opinion in microbiology 2020, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenkham-Huntsinger, P.; Hyre, A.N.; Hanson, B.S.; Donati, G.L.; Adams, L.G.; Ryan, C.; Londoño, A.; Moustafa, A.M.; Planet, P.J.; Subashchandrabose, S. Copper resistance promotes fitness of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus during urinary tract infection. Mbio 2021, 12, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selim, S.; Faried, O.A.; Almuhayawi, M.S.; Saleh, F.M.; Sharaf, M.; El Nahhas, N.; Warrad, M. Incidence of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains among patients with urinary tract infections. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins-Browne, R.M.; Hartland, E.L. Escherichia coli as a cause of diarrhea. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology 2002, 17, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Sosa, L.; Ochoa, T.J. Escherichia coli diarrhea. In Hunter's Tropical Medicine and Emerging Infectious Diseases; Elsevier: 2020; pp. 481–485.
- Hamdany, A.H.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Graphene-Based TiO2 Cement Composites to Enhance the Antibacterial Effect of Self-Disinfecting Surfaces. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdany, A.H.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Visible light antibacterial potential of graphene-TiO2 cementitious composites for self-sterilization surface. Journal of Sustainable Cement-Based Materials 2023, 12, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdany, A.H.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Cementitious Composite Materials for Self-Sterilization Surfaces. ACI Materials Journal 2022, 119, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdany, A.H.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Mechanical and antibacterial behavior of photocatalytic lightweight engineered cementitious composites. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 2021, 33, 04021262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Pan, S.; Wang, J.; Vasilakos, A.V. Machine learning on big data: Opportunities and challenges. Neurocomputing 2017, 237, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’heureux, A.; Grolinger, K.; Elyamany, H.F.; Capretz, M.A.M. Machine learning with big data: Challenges and approaches. Ieee Access 2017, 5, 7776–7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.; Shmarko, K.; Lomas, E. The ethics of facial recognition technologies, surveillance, and accountability in an age of artificial intelligence: a comparative analysis of US, EU, and UK regulatory frameworks. AI and Ethics 2022, 2, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Krishan, K.; Sharma, S.K.; Kanchan, T. Facial-recognition algorithms: A literature review. Medicine, Science and the Law 2020, 60, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atakishiyev, S.; Salameh, M.; Yao, H.; Goebel, R. Explainable artificial intelligence for autonomous driving: A comprehensive overview and field guide for future research directions. IEEE Access 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.; Yin, R.; Ullah, A.; Shi, F. A survey on hybrid human-artificial intelligence for autonomous driving. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2021, 23, 6011–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. Machine learning and its applications in studying the geographical distribution of ants. Diversity 2022, 14, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. A machine learning approach to predicting academic performance in Pennsylvania’s schools. Social Sciences 2023, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-T.; Kristiani, E.; Leong, Y.K.; Chang, J.-S. Big data and machine learning driven bioprocessing–recent trends and critical analysis. Bioresource technology 2023, 372, 128625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, A. Applications of artificial neural networks and machine learning in civil engineering. Studies in computational intelligence 2024, 1168, 472. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Ye, J.; Wang, X. Factorizing knowledge in neural networks. 2022; pp. 73–91.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





