Submitted:
05 January 2025
Posted:
06 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
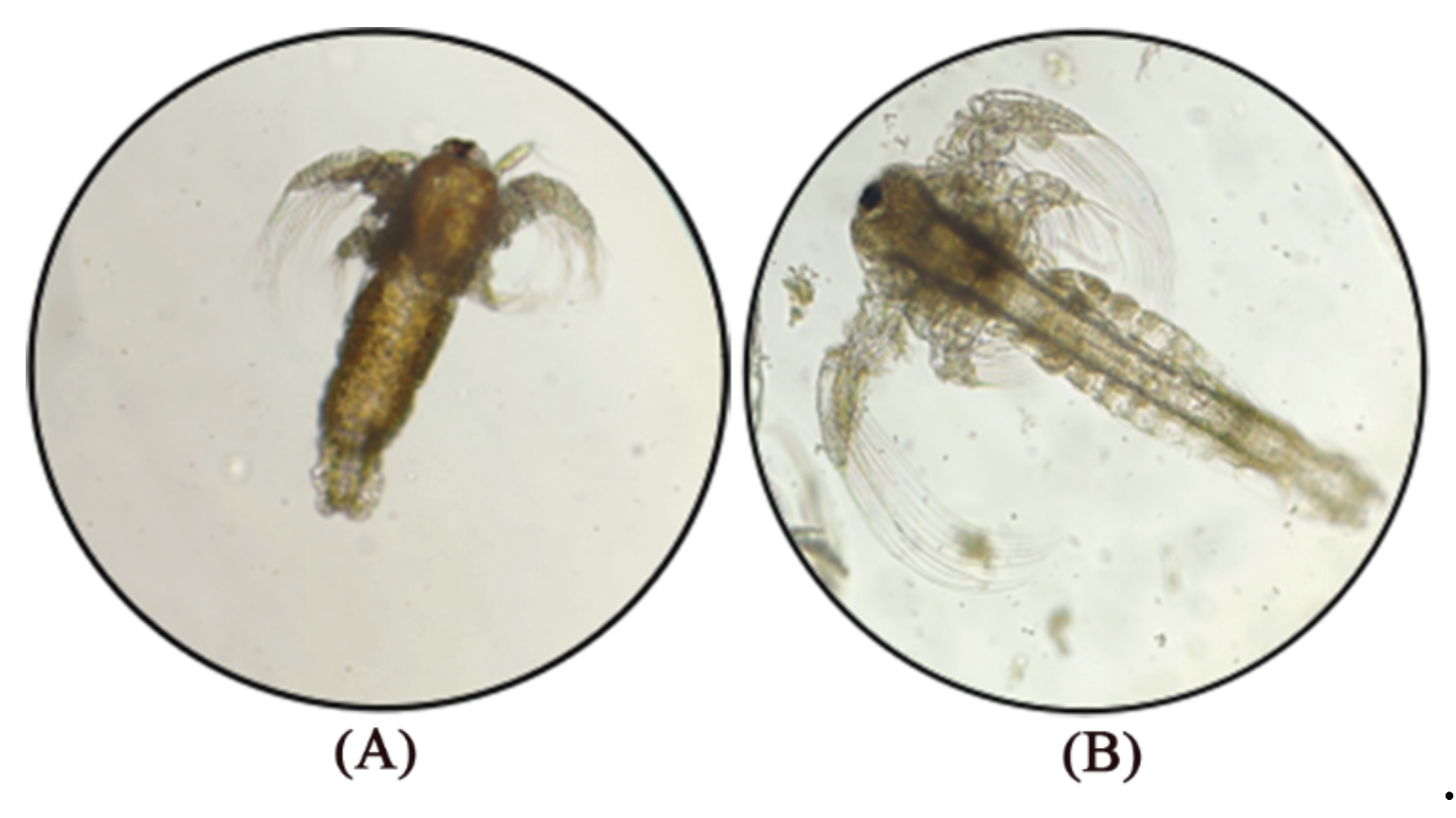
2.1. Artemia Cysts and the Detection of CMNV
2.1.1. Artemia Cysts
2.1.2. RNA Extraction
2.1.3. Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.1.4. Result Determination
2.2. Treatments of CMNV+ Artemia Cysts
2.3. CMNV Detection and Viral Load Quantification
3. Results
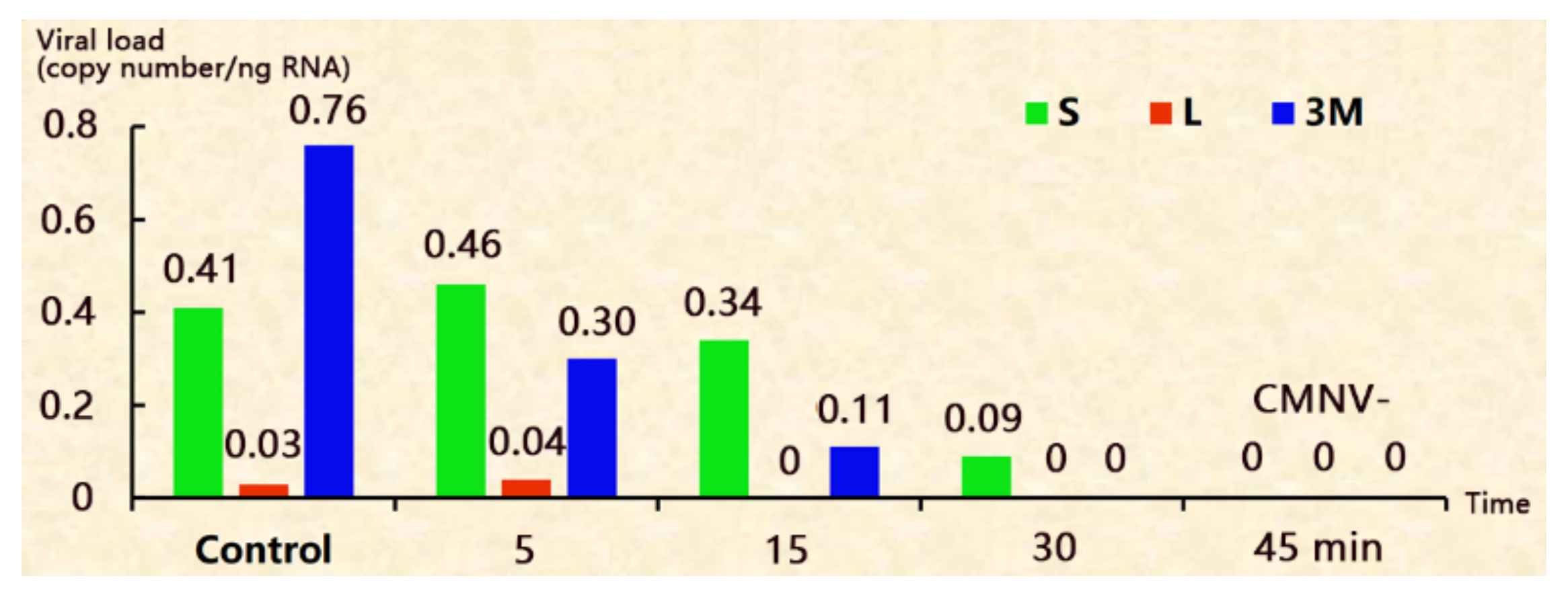
3.1. No Treatment (the Control Group)
3.2. Decapsulation with Na2CO3-NaClO
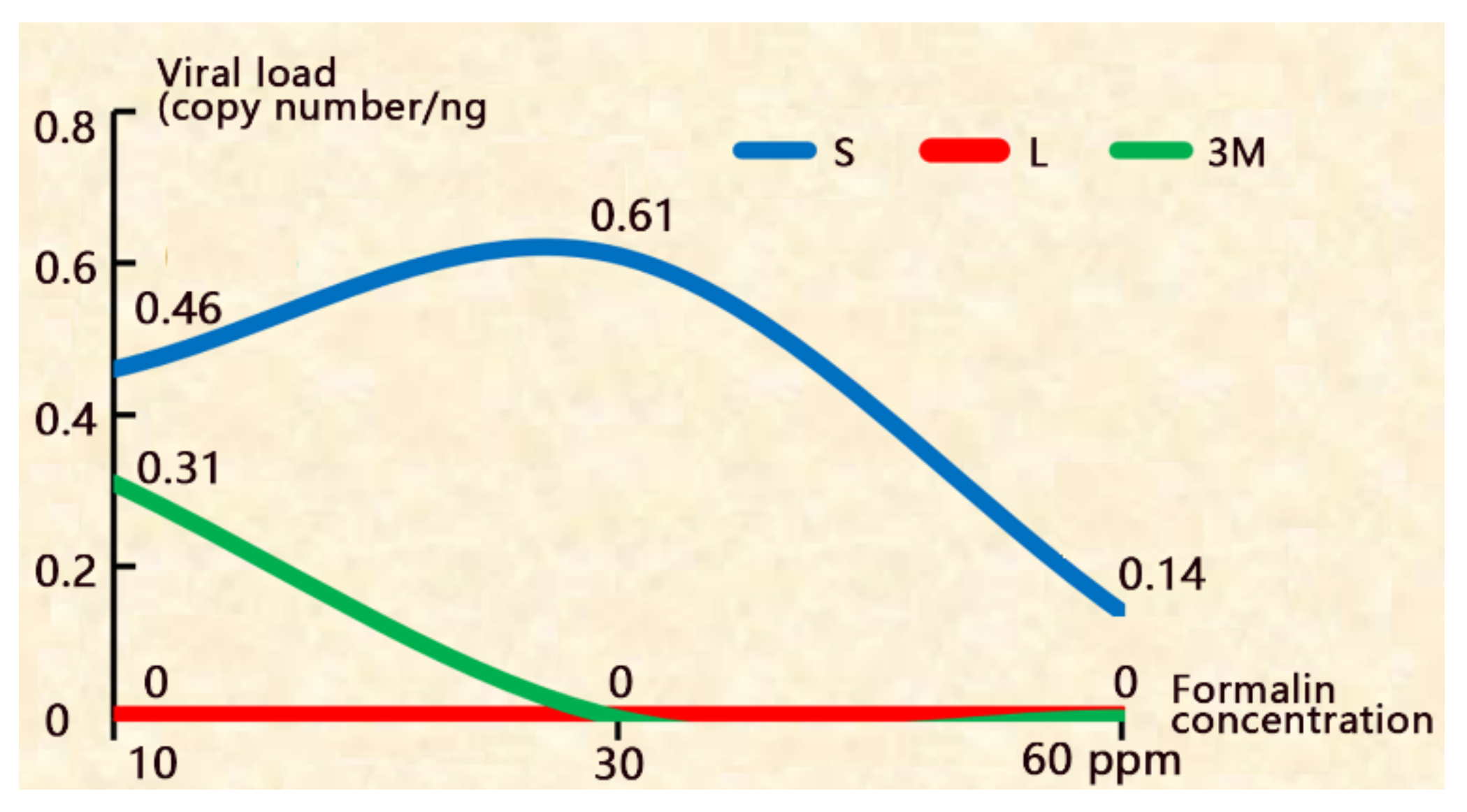
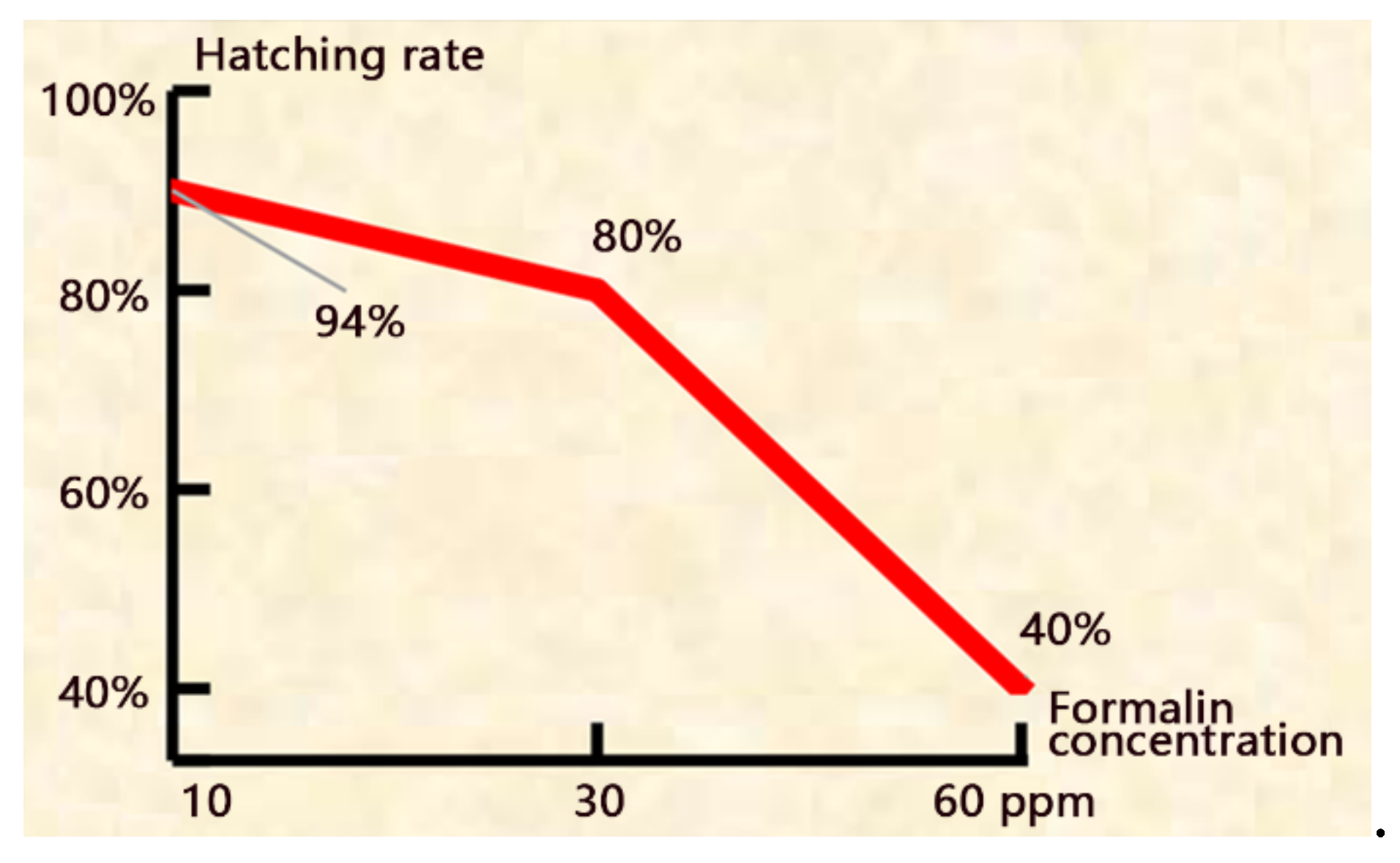
3.3. Adding Formalin in the Hatching Water
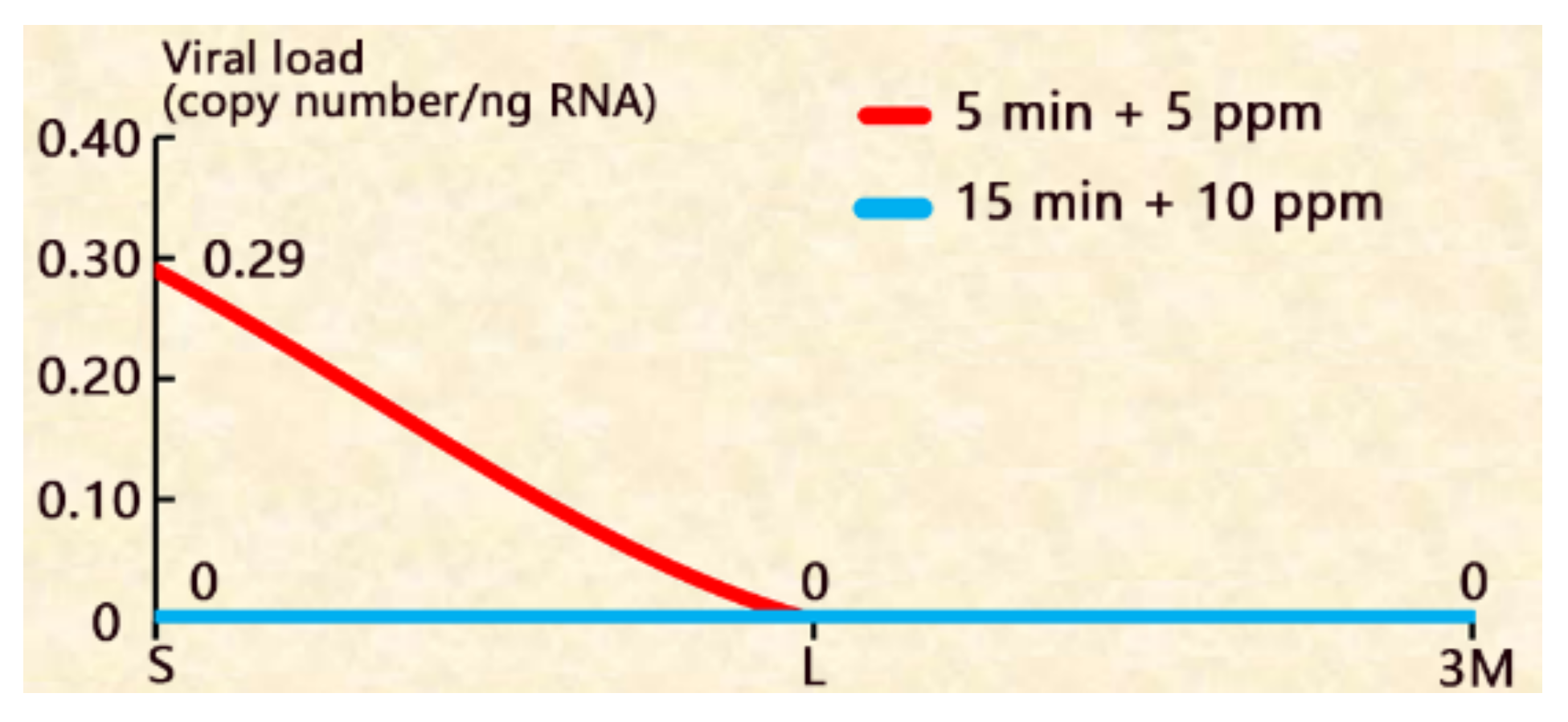
3.4. Combination of Decapsulation and Adding Formalin in the Hatching Water
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
References
- Xu, Z.; Ji, F. Comprehensive control of the covert mortality disease of Pacific white shrimp. Fish Guide to be Rich 2009, 1, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, S.; Zhu, L.; Yang, B.; Jin, J.; Ding, L.; Wang, X. A new nodavirus is associated with covert mortality disease of shrimp. Journal of General Virology 2014, 95, 2700–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S. Chapter 38 - Nodaviruses of crustaceans. In Aquaculture Virology (Second Edition), Kibenge, F.S.B., Godoy, M.G., Eds.; Academic Press: 2024; pp. 621–641.
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, T.; Wan, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Dong, X.; Yang, B.; Huang, J. Prevalence and distribution of covert mortality nodavirus (CMNV) in cultured crustacean. Virus Research 2017, 233, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wang, C.; Yao, L.; Wang, W.; Zhao, W.; Jia, T.; Yu, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Q. Investigation on natural infection of covert mortality nodavirus in farmed giant freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii). Animals 2022, 12, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.X.; Wan, X.Y.; Xia, J.T.; Yao, L.; Xu, R.D.; Wang, W.; Yu, X.T.; Zhang, Q.L. Investigation of the prevalence of covert mortality nodavirus (CMNV) in shrimp from 2021 to 2022. Progress in Fishery Sciences 2024, 45, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, T.; Li, X.; Du, L.; Zhang, Q. Vectors and reservoir hosts of covert mortality nodavirus (CMNV) in shrimp ponds. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 2018, 154, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavens, P.; Sorgeloos, P. The history, present status and prospects of the availability of Artemia cysts for aquaculture. Aquaculture 2000, 181, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgeloos, P.; Bossuyt, E.; Laviña, E.; Baeza-Mesa, M.; Persoone, G. Decapsulation of Artemia cysts: a simple technique for the improvement of the use of brine shrimp in aquaculture. Aquaculture 1977, 12, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Genomic characterization of covert mortality nodavirus from farming shrimp: Evidence for a new species within the family Nodaviridae. Virus research 2020, 286, 198092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Zhu, L.; Wan, X.; Li, X.; Huang, J. Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid and quantitative assay of covert mortality nodavirus in shrimp. Journal of invertebrate pathology 2017, 150, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zeng, C.; Xia, J.; Liu, Q.; Fang, J.; Zhang, Q. Disinfection of Perinereis aibuhitensis eggs with peroxymonosulfate to eliminate covert mortality nodavirus (CMNV). Aquaculture 2023, 572, 739539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millamena, O.M.; Bombeo, R.F.; Jumalon, N.A.; Simpson, K. Effects of various diets on the nutritional value of Artemia sp. as food for the prawn Penaeus monodon. Marine Biology 1988, 98, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, C.; Sui, L.; Ye, S.; Dong, X.; Huang, J. Research progress on the risk of Artemia acting as a kind of live feed to spread shrimp pathogens. China Anim Health Inspect 2020, 37, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Defoirdt, T.; Crab, R.; Wood, T.K.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W.; Bossier, P. Quorum sensing-disrupting brominated furanones protect the gnotobiotic brine shrimp Artemia franciscana from pathogenic Vibrio harveyi, Vibrio campbellii, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates. Applied and environmental microbiology 2006, 72, 6419–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Sudhakaran, R. Exploring the potentiality of Artemia salina to act as a reservoir for microsporidian Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei of penaeid shrimp. Biocatalysis and agricultural biotechnology 2020, 25, 101607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-S.; Dong, S.-L.; Dong, Y.-W.; Tian, X.-L.; Cao, Y.-C.; Li, Z.-J.; Yan, D.-C. Assessment of the role of brine shrimp Artemia in white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) transmission. Veterinary research communications 2010, 34, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhakaran, R.; Yoganandhan, K.; Ahmed, V.I.; Hameed, A.S. Artemia as a possible vector for Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus (MrNV) and extra small virus transmission (XSV) to Macrobrachium rosenbergii post-larvae. Diseases of aquatic organisms 2006, 70, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Liang, Y.; Huang, J. Global Biosecurity Strategy and Enlightenments from Worldwide Practice. Engineering Science in China 2016, 18, 110–114. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




