Submitted:
01 January 2025
Posted:
02 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
In this research, we have studied the head of the six-banded armadillo, applying advanced imaging techniques such as CT and MRI. Furthermore, by combining the images obtained through these techniques with anatomical cross sections, we present an adequate description of the structures that constitute the head of this species. This anatomical information could provide a valuable diagnostic tool for the clinical evaluation of different desorders in six-banded armadillo including skull malformations, fractures, and neoplasia.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. CT Technique
2.3. MRI Technique
2.4. Anatomical Sections
2.5. Anatomic Evaluation
3. Results
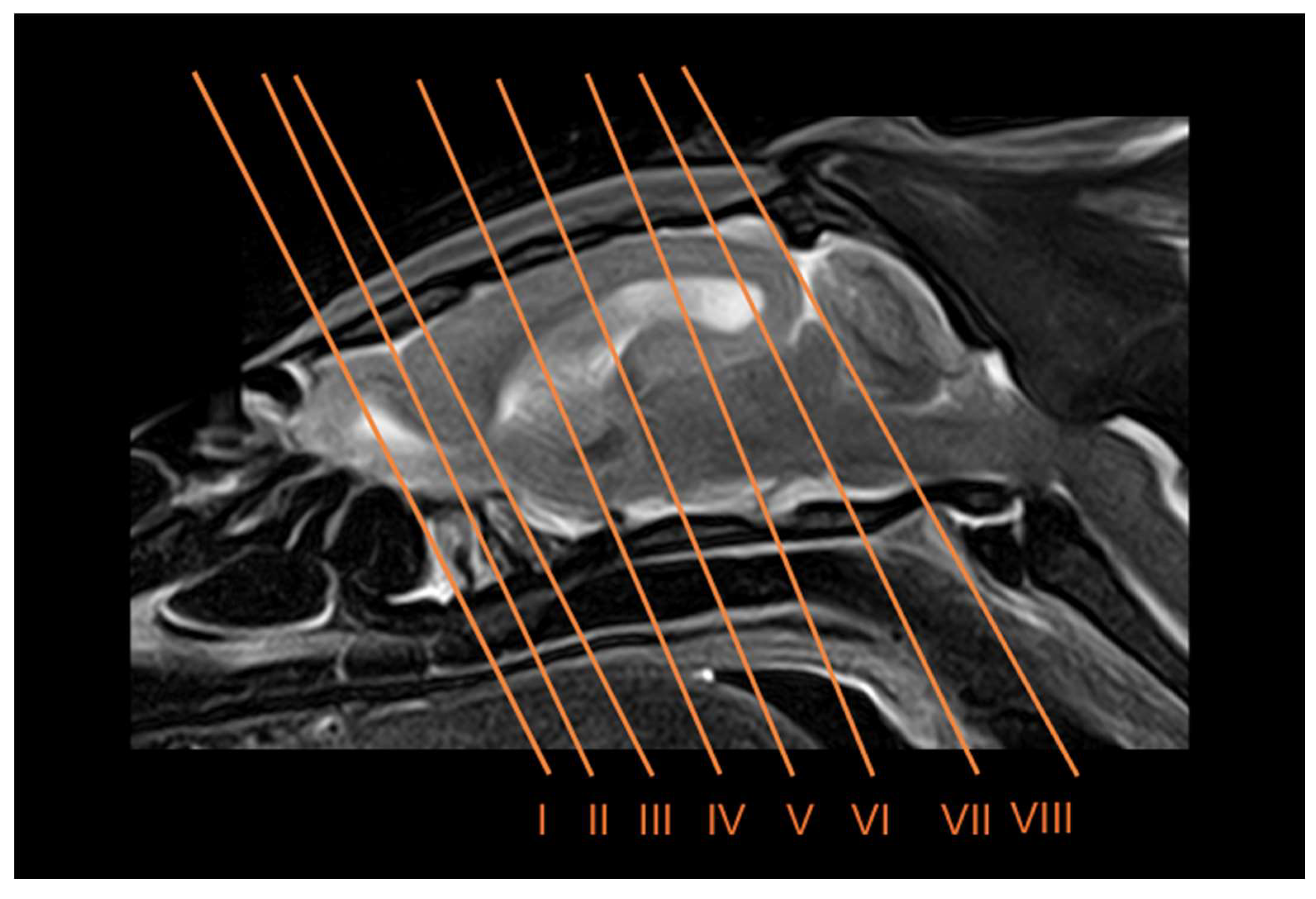
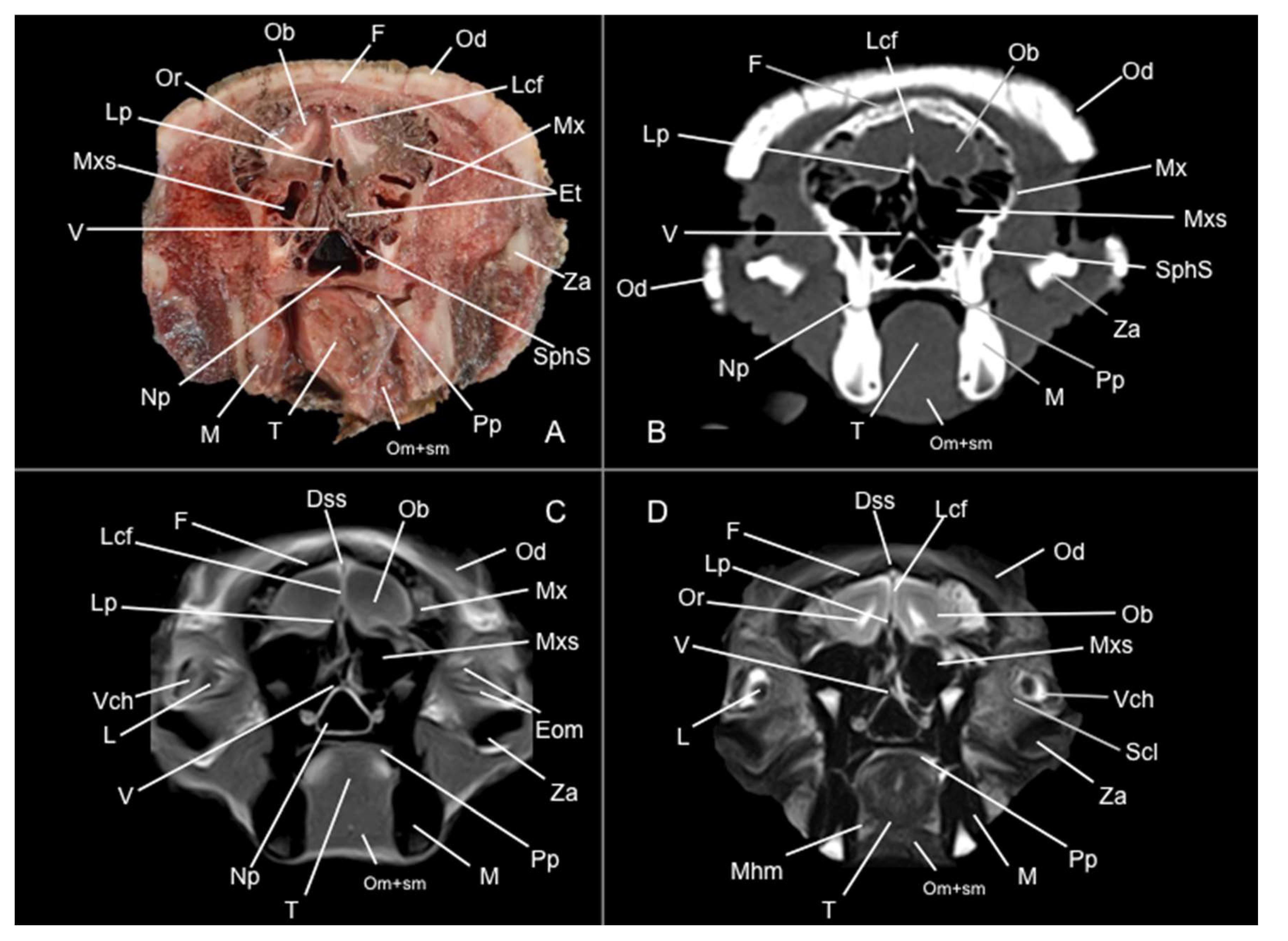
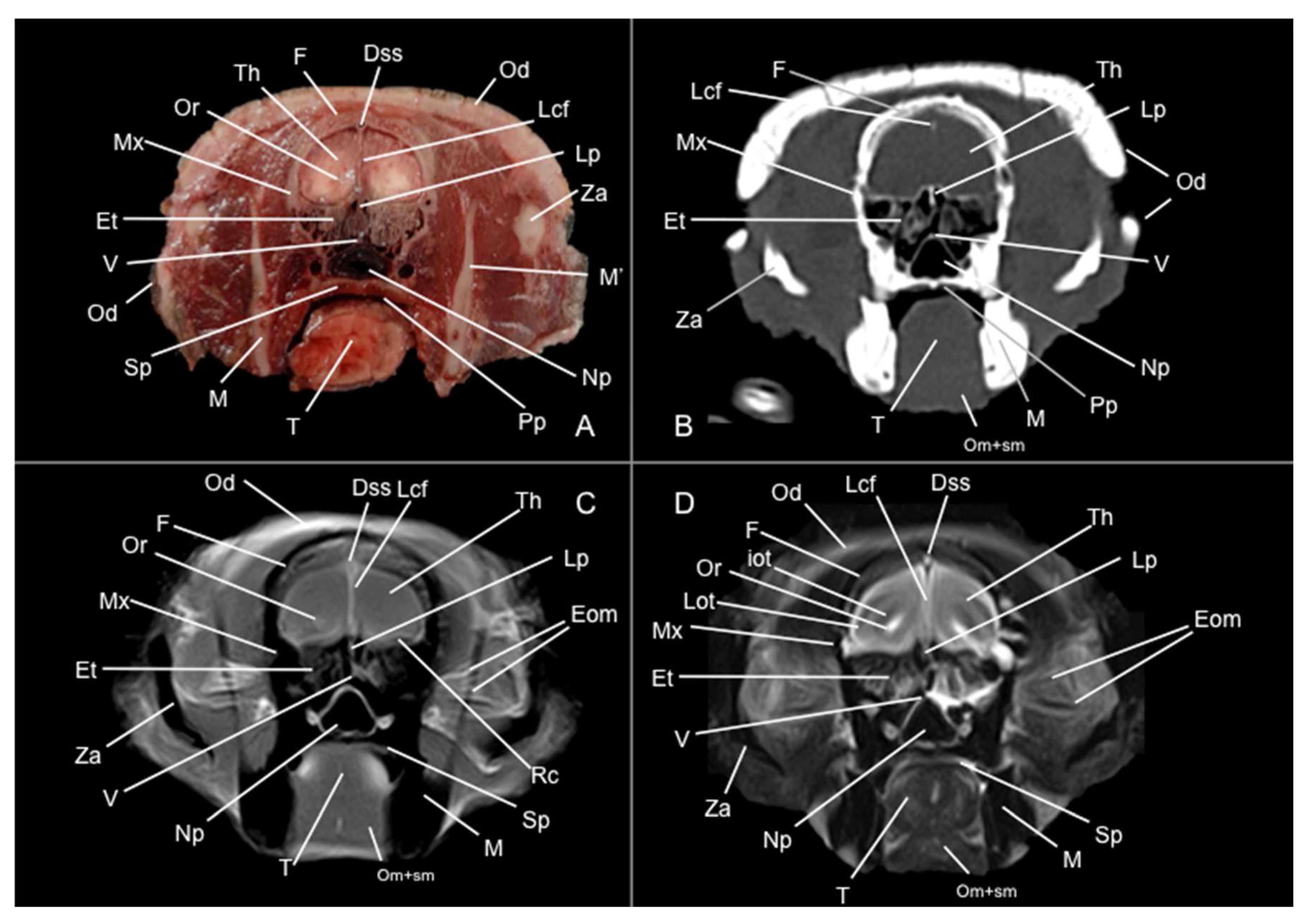
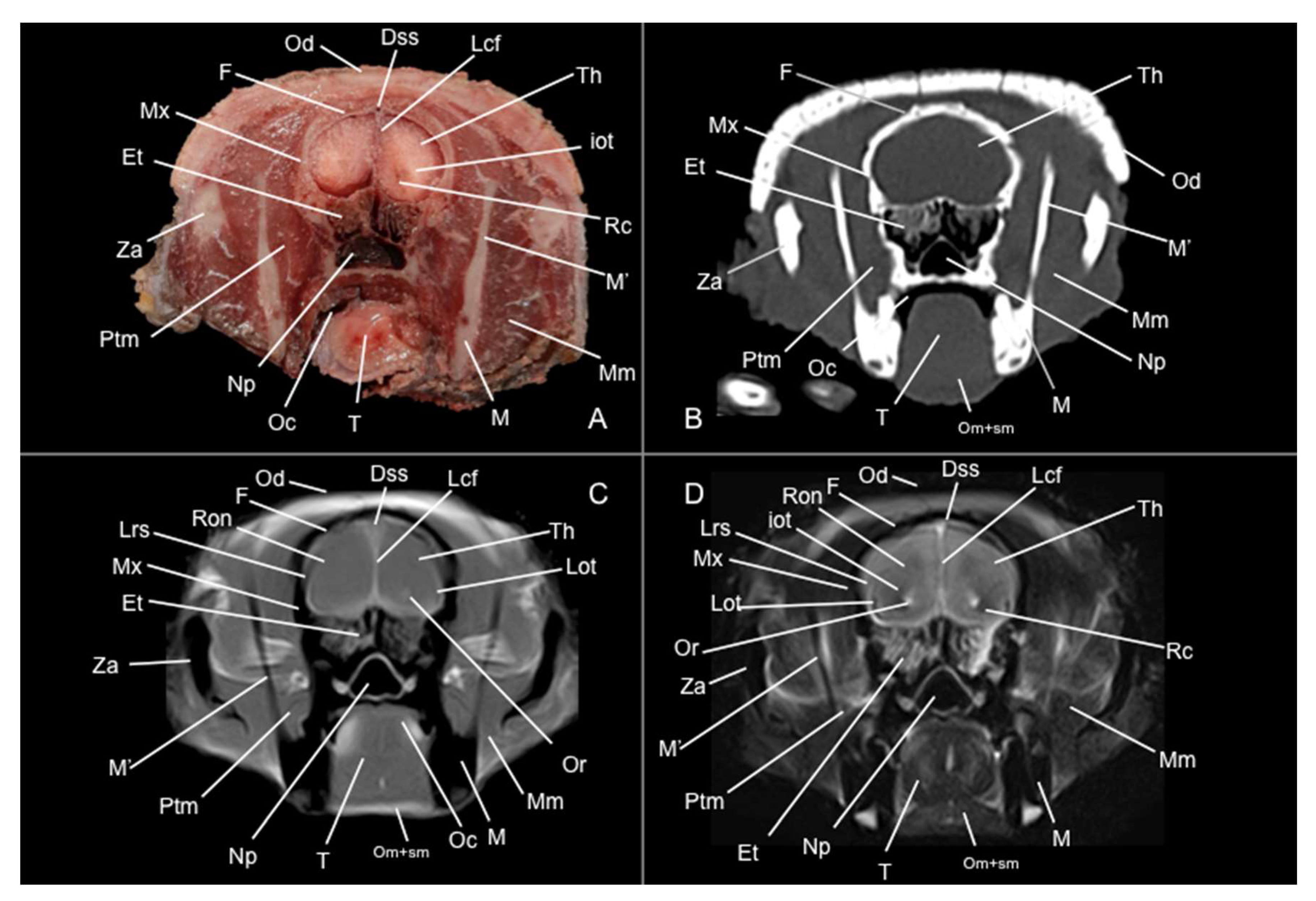
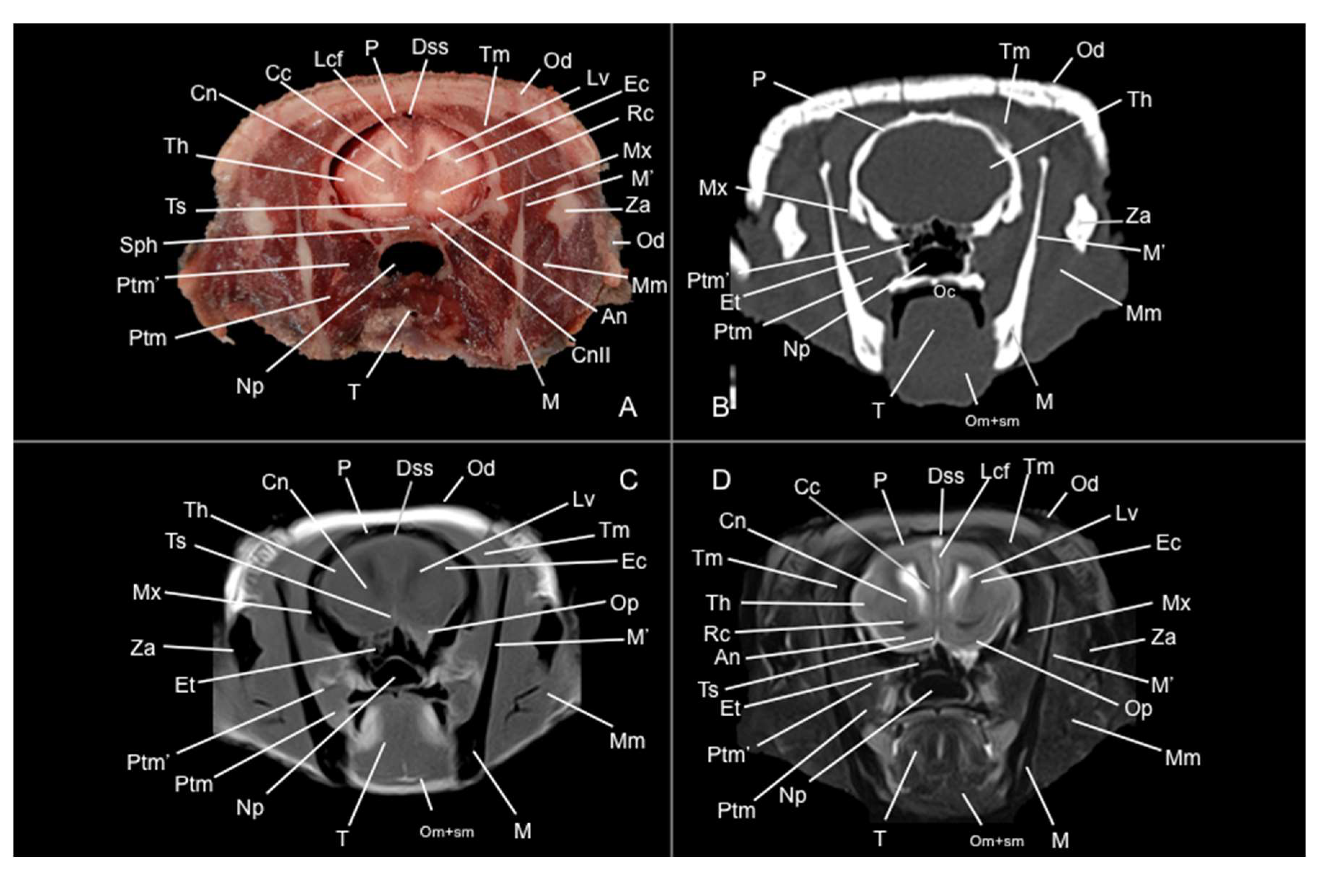
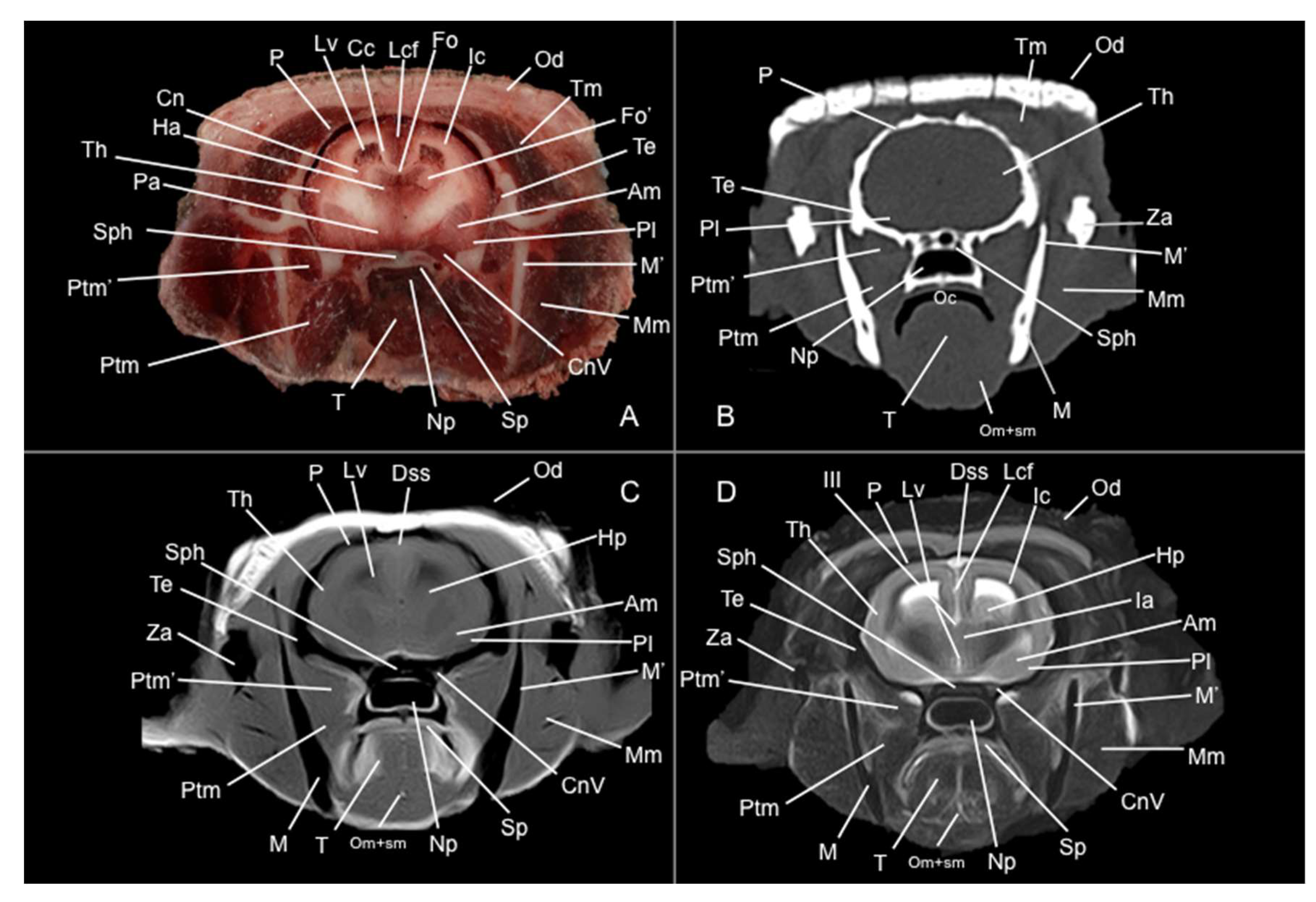
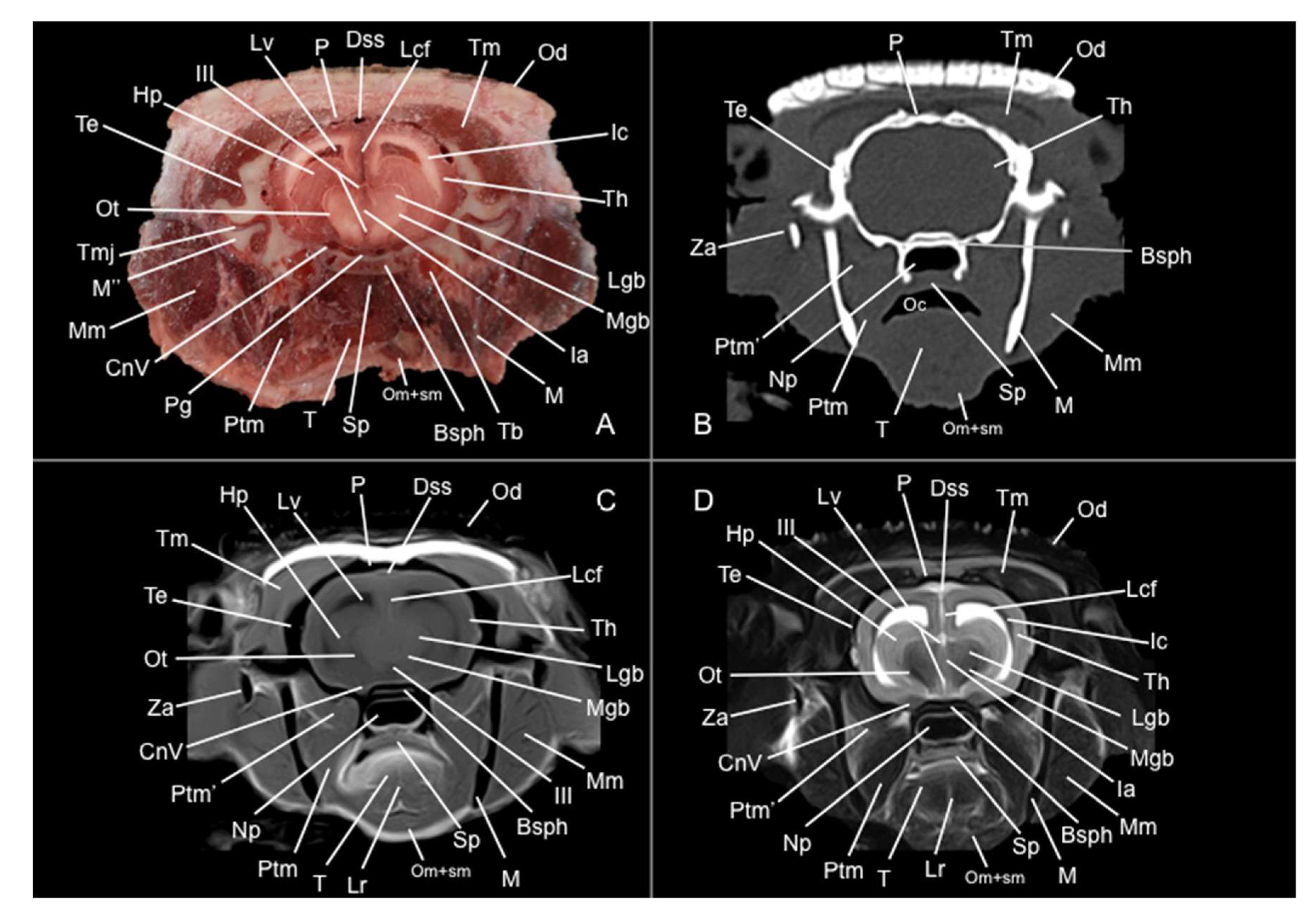
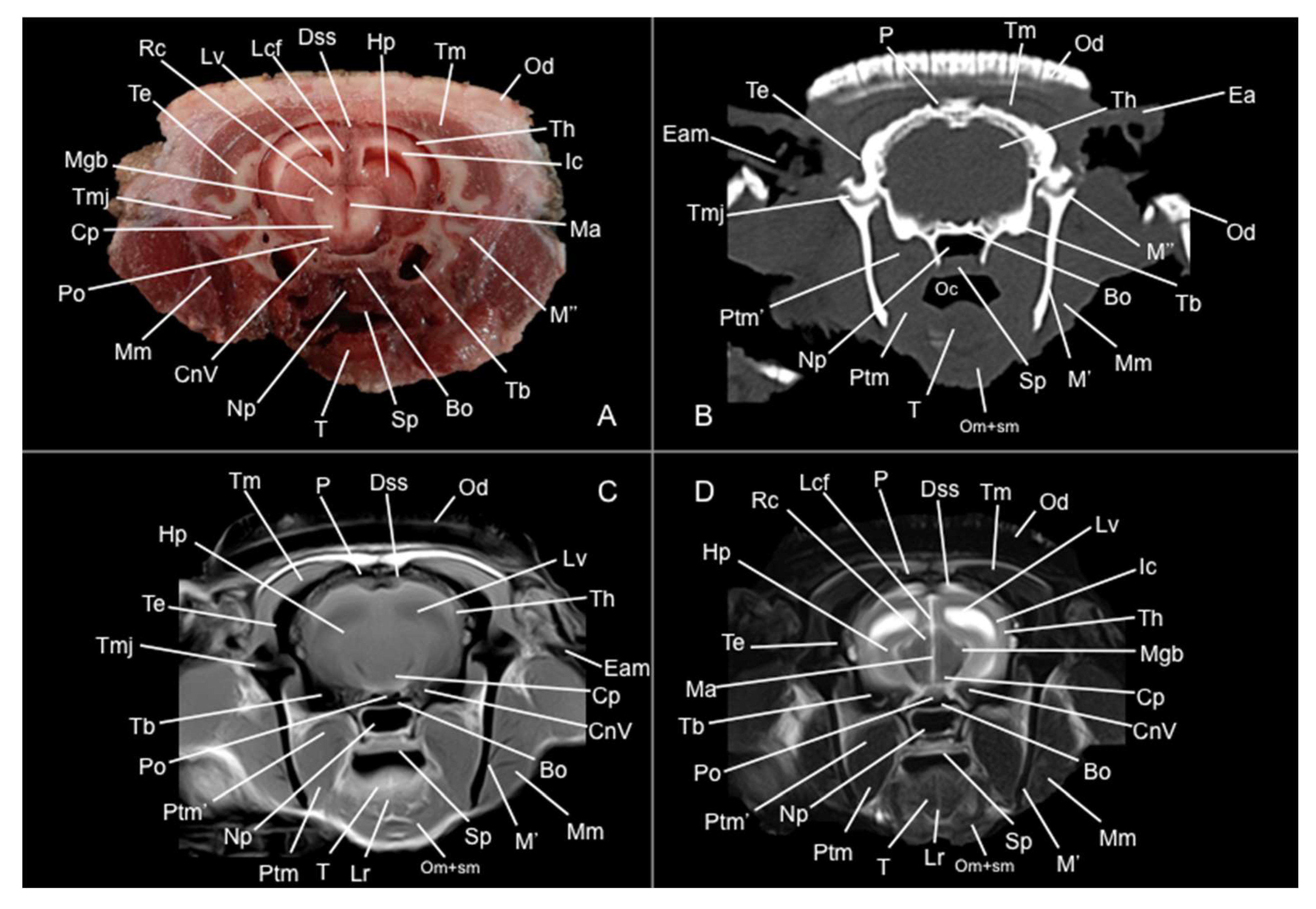
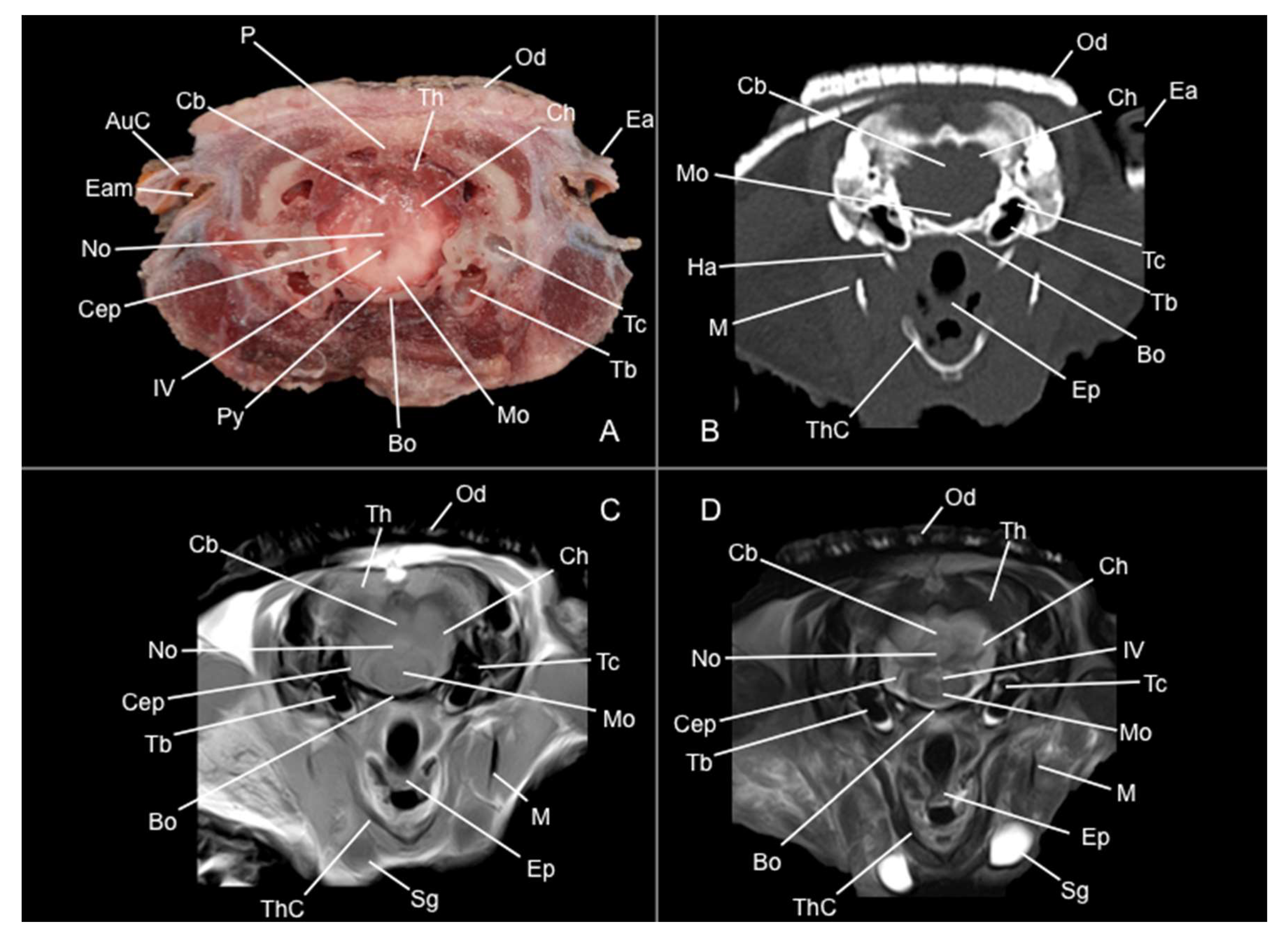
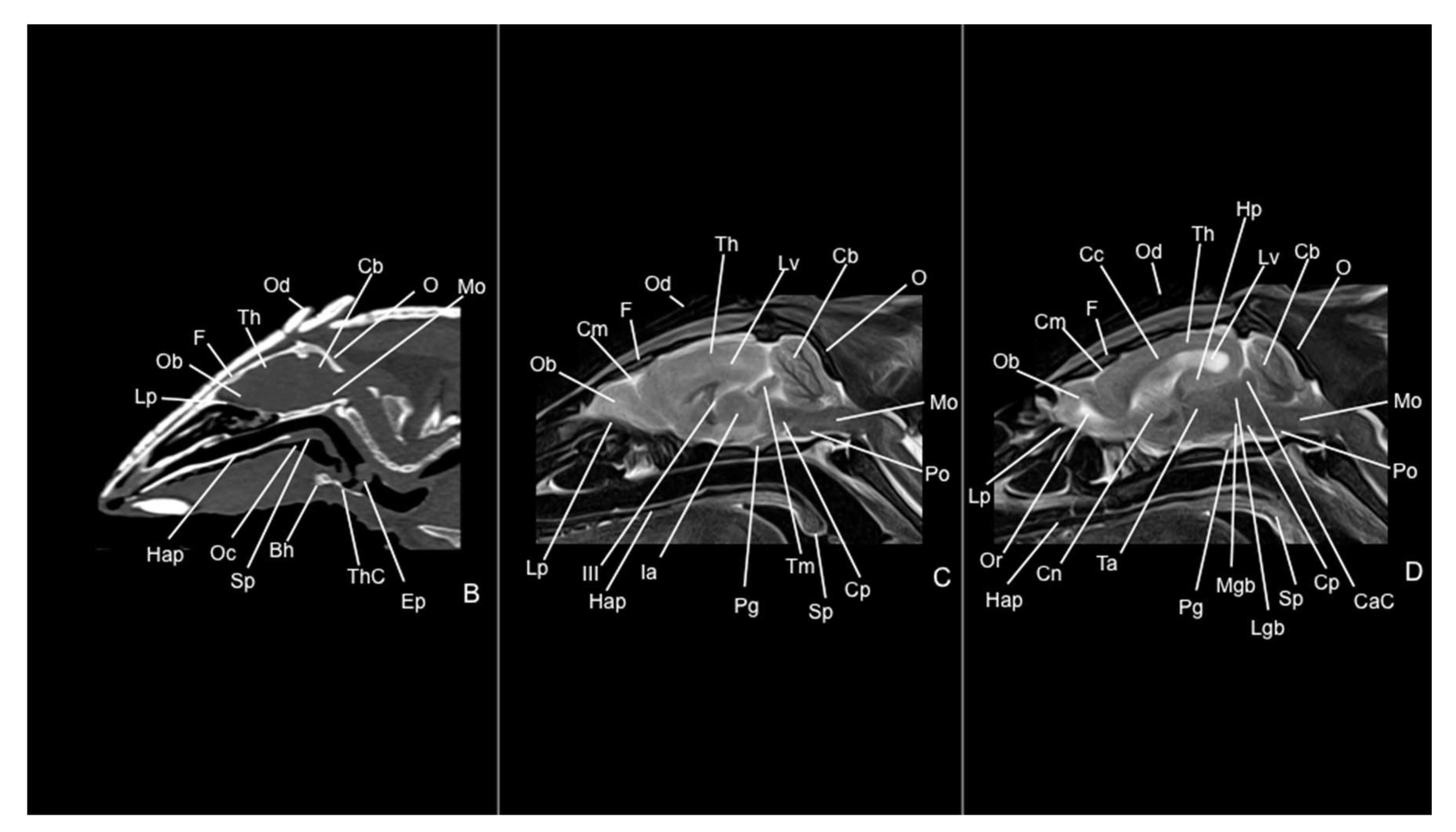
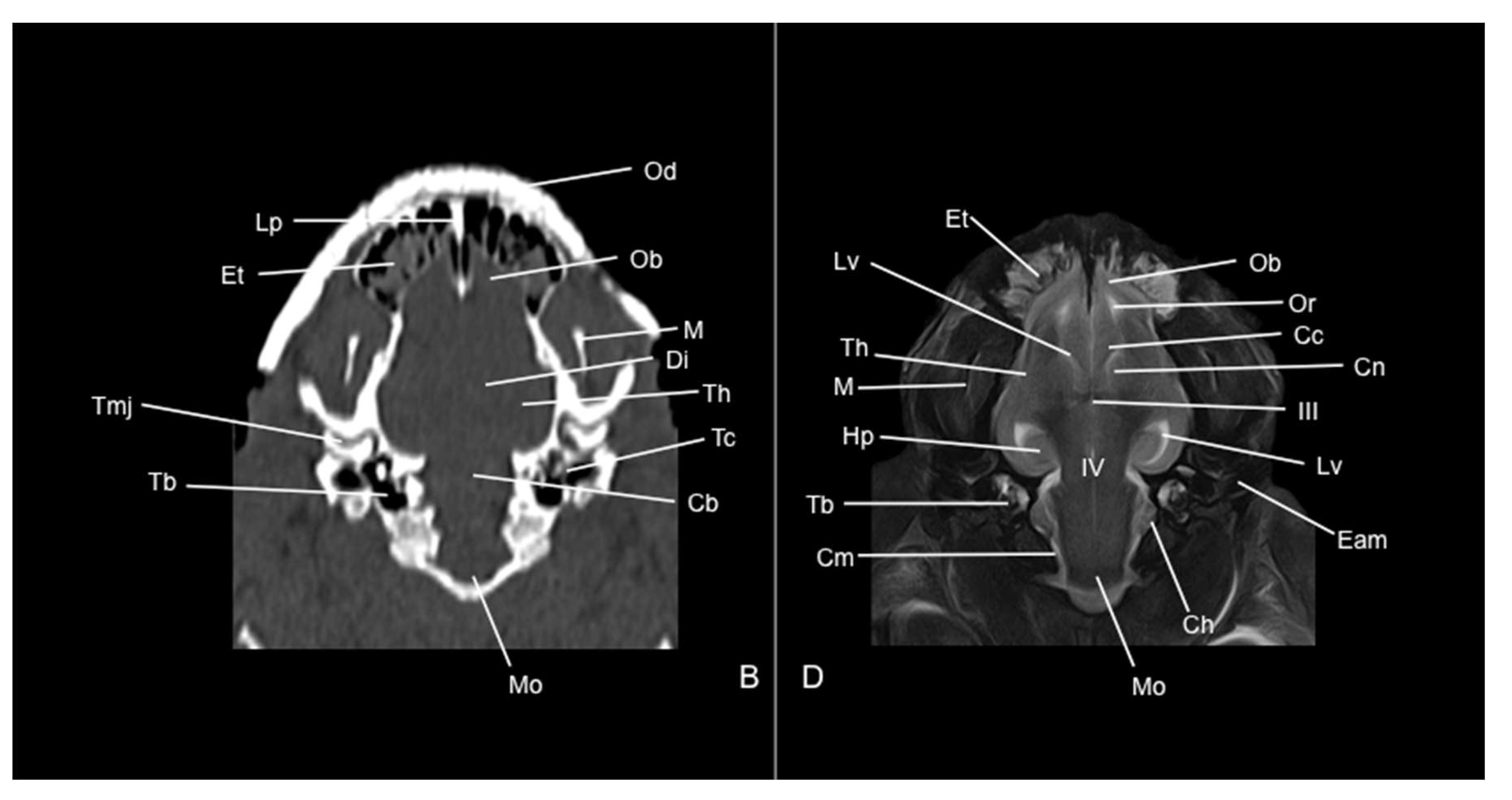
3.1. Anatomical Sections
3.2. Computed Tomography Study
3.3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gardner, A.L. Order Cingulata. In Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, 3rd ed.; Wilson, D.E., Reeder, D.M., Eds.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005; p. 97. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0.
- Redford, K.H.; Wetzel, R.M. Euphractus sexcinctus. Mamm. Species 1985, 252, 1–4.
- Brittany, B. Euphractus sexcinctus. Available online: https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Euphractus_sexcinctus/ (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Farrow, C.S. Veterinary Diagnostic Imaging: Birds, Exotic Pets and Wildlife; Mosby Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2009.
- Lauridsen, H.; Hansen, K.; Wang, T.; Agger, P.; Andersen, J.L.; Knudsen, P.S.; Rasmussen, A.S.; Uhrenholt, L.; Pedersen, M. Inside out: Modern Imaging Techniques to Reveal Animal Anatomy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17879.
- Behroozi, M.; Billings, B.K.; Helluy, X.; Manger, P.R.; Güntürkün, O.; Ströckens, F. Functional MRI in the Nile Crocodile: A New Avenue for Evolutionary Neurobiology. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20180178.
- Knipe, M.F. Principles of Neurological Imaging of Exotic Animal Species. Vet. Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2007, 10, 893–907.
- Banzato, T.; Hellebuyck, T.; Van Caelenberg, A.; Saunders, J.H.; Zotti, A. A Review of Diagnostic Imaging of Snakes and Lizards. Vet. Rec. 2013, 173, 43–49.
- Morales Bordon, D.; Suárez-Cabrera, F.; Ramírez, G.; Paz-Oliva, P.; Morales-Espino, A.; Arencibia, A.; Encinoso, M.; Ventura, M.R.; Jaber, J.R. Study of the Normal Crested Porcupine (Hystrix Cristata) Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses by Cross-Sectional Anatomy and Computed Tomography. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 611.
- Morales-Bordon, D.; Encinoso, M.; Arencibia, A.; Jaber, J.R. Cranial Investigations of Crested Porcupine (Hystrix cristata) by Anatomical Cross-Sections and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Animals 2023, 13, 2551.
- Fumero-Hernández, M.; Encinoso, M.; Melian, A.; Nuez, H.A.; Salman, D.; Jaber, J.R. Cross Sectional Anatomy and Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Juvenile Atlantic Puffin Head (Aves, Alcidae, Fratercula arctica). Animals 2023, 13, 3434.
- Gaudin, T.J.; Biewener, A.A. The functional morphology of xenarthrous vertebrae in the armadillo Dasypus novemcinctus (Mammalia, Xenarthra). J. Morphol. 1992, 214, 63–81.
- Oliver, J.D.; Jones, K.E.; Pierce, S.E.; Hautier, L. Size and shape regional differentiation during the development of the spine in the nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus). Evol. Dev. 2021, 23, 496–512.
- Alves, L.S.; Babicsak, V.R.; Charlier, M.G.S.; Vulcano, L.C. Radiography, computed tomography and 3D reconstruction of the pelvis in the nine-banded armadillo, Dasypus novemcinctus. In Proceedings of the 40th World Small Animal Veterinary Association Congress, Bangkok, Thailand, 15–18 May 2015; Volume 40, pp. 66–67.
- Vizcaıno, S.F.; Milne, N. 2002: Structure and function in armadillo limbs (Mammalia: Xenarthra: Dasypodidae). J. Zool. 2002, 257, 117–127.
- Wible, J.R. Petrosal anatomy of the nine-banded armadillo, Dasypus novemcintus Linnaeus, 1758 (Mammalia, Xenarthra, Dasypodidae). Ann. Carnegie Mus. 2010, 79, 1–28.
- Alves, L.S.; Midon, M.; Filadelpho, A.L.; Vulcano, L.C.; Knotek, Z. Gross Osteology, Radiographic and Computed Tomographic Morphology of the Axial Skeleton of the Nine-Banded Armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2017, 46, 162–177.
- Silva, A.B.; Sousa, M.M.; Silva, J.V.; Oliveira, I.M.; Barbosa, C.M.; Santos, M.; Conde, A.M. Anatomy of the nasal cavity of nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus, Linnaeus, 1758). J. Interdiscip. Biocienc. 2016, 1, 1–4.
- Billet, G.; Hautier, L.; de Thoisy, B.; Delsuc, F. The hidden anatomy of paranasal sinuses reveals biogeographically distinct morphotypes in the nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus). PeerJ 2017, 5, e3593.
- Fonseca, C.M.B.; da Silva, A.B.S.; Cavalcante, M.M.A.S.; de Oliveira, I.M.; Moura, S.M.S.; Cunha, B.M.; Leite, C.M.C.; de Carvalho, M.A.M.; Moura, W.R.A.; Rizzo, M.D.S.; et al. Morphology of laryngeal cartilage of the nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus) Linnaeus, 1758. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2017, 80, 1089–1095.
- Vizcaíno, S.F.; Fariña, R.A.; Bargo, M.S.; De Iuliis, G. Functional and phylogenetic assessment of the masticatory adaptations in Cingulata (Mammalia, Xenarthra). Rev. Asos. Paleontol. Argent. 2004, 41, 651–664.
- Alves, L.S.; Oliva, L.R.; Charlier, M.G.S.; Bonatelli, S.P.; Inamassu, L.R.; Vulcano, L.C.; Teixeira, C.R. Fratura em seguimento lombar da coluna vertebral em um tatugalinha (Dasypus novemcinctus). An. Simp. Intern. Diag. Imag. SINDIV 2013, 3, 57–58.
- Boyde, A.; Mills, D.; Abba, A.M.; Ezquiaga, M.C. Fleas and lesions in armadillo osteoderms. J. Anat. 2023, 242, 1029–1036.
- Jaber, J.R.; Morales Bordon, D.; Arencibia, A.; Corbera, J.A.; Conde-Felipe, M.; Ayala, M.D.; Encinoso, M. Correlation between Cross-Sectional Anatomy and Computed Tomography of the Normal Six-Banded Armadillo (Euphractus Sexcintus) Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses. Animals (Basel) 2024, 14, 1135.
- Scholl B Rylee, J.; Luci, J.J.; Priebe, N.J.; Padberg, J. Orientation selectivity in the visual cortex of the nine-banded armadillo. J. Neurophysiol 2017, 117, 1395–1406.
- Jacqmot, O.; Van Thielen, B.; Hespel, A.-M.; Luijten, P.R.; de Mey, J.; Van Binst, A.; Provyn, S.; Tresignie, J. T2-Weighted Turbo Spin-Echo Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Canine Brain Anatomy at 1.5T, 3T, and 7T Field Strengths. Anat. Rec. (Hoboken) 2022, 305, 222–233.
- Araújo, J.V.S.; Cavalcante, M.M.A. de S.; Gonçalves, P.C. de J.; Guerra, S.P.L.; Da Silva, A.B.S.; Conde Júnior, A.M. Descriptive macroscopic anatomy of the central nervous system six-banded armadillo (Euphractus sexcintus, Linnaeus, 1758) and nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus, Linnaeus, 1758). J. Interdiscip. Biociênc. 2015, 1, 13.
- González Rodríguez, E.; Encinoso Quintana, M.; Morales Bordon, D.; Garcés, J.G.; Artiles Nuez, H.; Jaber, J.R. Anatomical Description of Rhinoceros Iguana (Cyclura cornuta cornuta) Head by Computed Tomography, Magnetic Resonance Ima-ging and Gross-Sections. Animals 2023, 13.
- Arencibia, A.; Vazquez, J.M.; Rivero, M.; Latorre, R.; Sandoval, J.A.; Vilar, J.M.; Ramirez, J.A. Computed tomography of normal cranioencephalic structures in two horses. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2000, 29, 295–299.
- Mahdy, M. Correlation between computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and cross-sectional anatomy of the head of the guinea pig (Cavia porcellus, Linnaeus 1758). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2022, 51, 51–61.
- De Rycke, L.M.; Saunders, J.H.; Gielen, I.M.; van Bree, H.J.; Simoens, P.J. Magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, and cross-sectional views of the anatomy of normal nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses in mesaticephalic dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2003, 64, 1093–1098.
- Van Caelenberg, A.I.; De Rycke, L.M.; Hermans, K.; Verhaert, L.; Van Bree, H.J.; Gielen, I.M. Low-field magnetic resonance imaging and cross-sectional anatomy of the rabbit head. Vet. J. 2011, 188, 83–91.
- Ferrari, C.C.; Carmanchahi, P.D.; Aldana Marcos, H.J.; Affanni, J.M. Ultrastructural Characterisation of the Olfactory Mucosa of the Armadillo Dasypus Hybridus (Dasypodidae, Xenarthra). J. Anat. 2000, 196, 269–278.
- Carmanchahi, P.D.; Aldana Marcos, H.J.; Ferrari, C.C.; Affanni, J.M. The Vomeronasal Organ of the South American Armadillo Chaetophractus Villosus (Xenarthra, Mammalia): Anatomy, Histology and Ultrastructure. J. Anat. 1999, 195, 587–604.
- Basso, A.P.; Sidorkewicj, N.S.; Casanave, E.B.; Mason, M.J. The Middle Ear of the Pink Fairy Armadillo Chlamyphorus Truncatus (Xenarthra, Cingulata, Chlamyphoridae): Comparison with Armadillo Relatives Using Computed Tomography. J. Anat. 2020, 236, 809–826.
- Ruby, J.R.; Allen, E.R. Ultrastructure of the Salivary Bladder of the Nine-Banded Armadillo. Cell Tissue Res. 1976, 169, 383–394.
- Le Verger, K.; González Ruiz, L.R.; Billet, G. Comparative Anatomy and Phylogenetic Contribution of Intracranial Osseous Canals and Cavities in Armadillos and Glyptodonts (Xenarthra, Cingulata). J. Anat. 2021, 239, 1473–1502.
- Phillips, J.A.; Harlow, H.J.; McArthur, N.H.; Ralph, C.L. Epithalamus of the Nine-Banded Armadillo, Dasypus Novemcinctus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Comp. Physiol. 1986, 85, 477–481.
- Squarcia, S.M.; Sidorkewicj, N.S.; Camina, R.; Casanave, E.B. Sexual dimorphism in the mandible of the armadillo Chaetophractus villosus (Desmarest, 1804) (Dasypodidae) from northern Patagonia, Argentina. Braz. J. Biol. 2009, 69, 347–352.
- Sigurdsson, B.; Hauglund, N.L.; Lilius, T.O.; Mogensen, F.L.-H.; Mortensen, K.N.; Beschorner, N.; Klinger, L.; Bærentzen, S.L.; Rosenholm, M.P.; Shalgunov, V.; et al. A SPECT-Based Method for Dynamic Imaging of the Glymphatic System in Rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2023, 43, 1153–1165.
- Mrzílková, J.; Patzelt, M.; Gallina, P.; Wurst, Z.; Šeremeta, M.; Dudák, J.; Krejčí, F.; Žemlička, J.; Musil, V.; Karch, J.; et al. Imaging of Mouse Brain Fixated in Ethanol in Micro-CT. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2054262.
- Boscaini, A.; Iurino, D.A.; Billet, G.; Hautier, L.; Sardella, R.; Tirao, G.; Gaudin, T.J.; Pujos, F. Phylogenetic and Functional Implications of the Ear Region Anatomy of Glossotherium Robustum (Xenarthra, Mylodontidae) from the Late Pleistocene of Argentina. Sci. Nat. 2018, 105, 28.
- Hautier, L.; Billet, G.; de Thoisy, B.; Delsuc, F. Beyond the Carapace: Skull Shape Variation and Morphological Systematics of Long-Nosed Armadillos (Genus Dasypus). PeerJ 2017, 5.
- Feijó, A.; Patterson, B.D.; Cordeiro-Estrela, P. Taxonomic Revision of the Long-Nosed Armadillos, Genus Dasypus Linnaeus, 1758 (Mammalia, Cingulata). PLoS One 2018, 13.
- Craven, B.A.; Paterson, E.G.: Settles, G.S. The fluid dynamics of canine olfaction: unique nasal airflow patterns as an explanation of macrosmia. J. Roy. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 933-943.
- Eiting, T.P.; Smith, T.D.; Perot, J.B.; Dumont, E.R. The role of the olfactory recess in olfactory airflow. J Exp Biol 2014, 217, 1799-1803.
- Ferrari, C.; Aldana, H.; Carmanchahi, P.D.; Benítez, I.; Affanni, J.M. The brain of the armadillo Dasypus hybridus. A general view of its most salient features. Biocell 1998, 22, 123-140.
- Sisson, S.; Grossman, J.D. Anatomía de los animales domésticos. 1972, Salvat Editores, S.A, Madrid.
- Köning, J.F.; Klippel, R.A. The rat brain. An stereotaxic atlas. 1967, R. Krieger Publishing Co. Inc, New York.
- Ariëns Kappers, C.U.; Huber, G.C.; Crosby, E.C. The comparative anatomy of the nervous system of vertebrates including the man Vol II. 1960. Hafner Publishing Company, New York.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




