Submitted:
23 December 2024
Posted:
24 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- This paper meticulously constructs a high-quality risk assessment (RA) dataset based on the gas alarm data collected by sensors at the coal mine production site, including historical alarm data from various measurement points such as CO, laser methane, smoke, etc., for fine-tuning a general-purpose large language model (LLM).
- Based on real-time data collection from wireless sensor networks and coal mine gas judgment standards, a specialized knowledge base is constructed. Through the integration of RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) technology, efficient indexing, semantic matching, and intelligent inference analysis of the knowledge base are achieved, forming an efficient workflow covering alarm judgment to emergency measure suggestions, and ultimately enabling the automatic generation of safety reports for mine production.
- The framework adopts a hierarchical graph structure from LangGraph to optimize the collaborative interaction between LLM multi-agent systems. Through fine-tuning the parameters of agent models and task scheduling configuration, it ensures the efficient execution of report generation tasks within the predefined workflow. A Human-in-the-loop feedback mechanism is introduced to strengthen the model's decision-making through real-time user feedback.
2. Related Work
2.1. Current Research on Intelligent Assessment Systems
2.2. Current Research on LLMs and Multi-Agent Structures
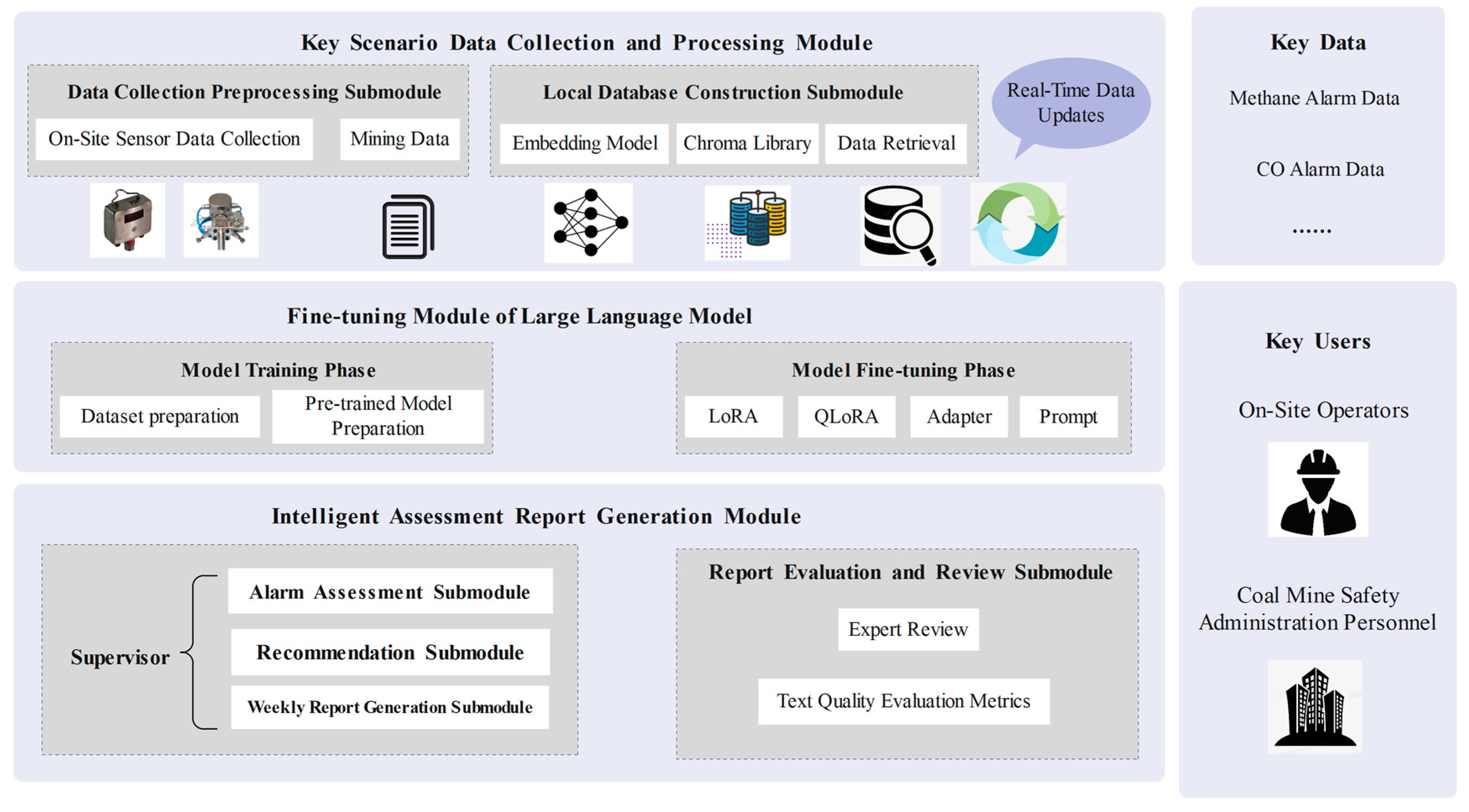
3. Overall Framework of IGRARG
4. Key Modules
4.1. Data Collection and Processing Module in Coal Mine Scenarios
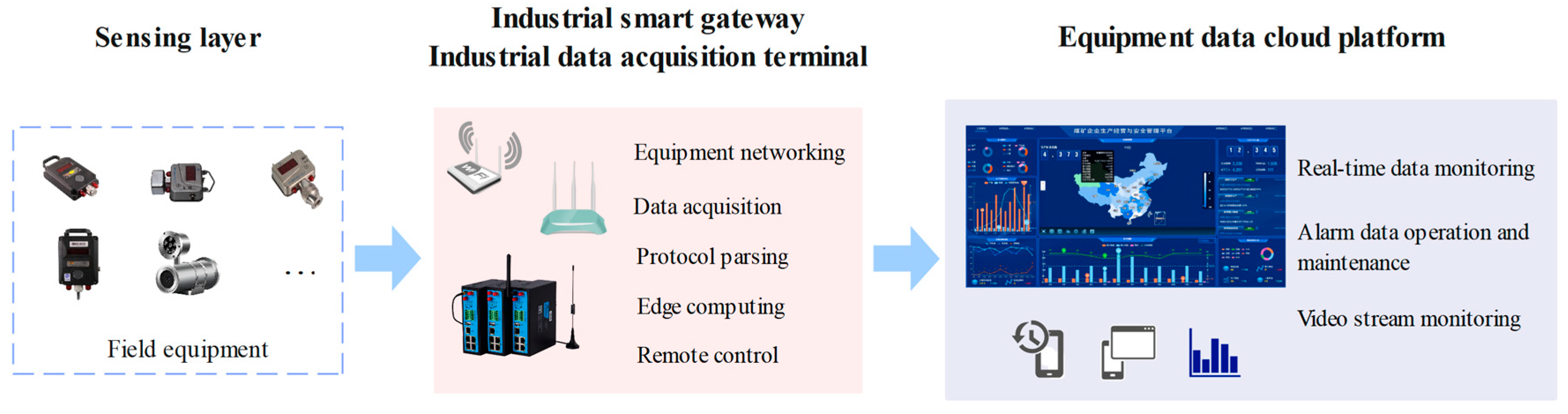
4.1.1. Data Collection
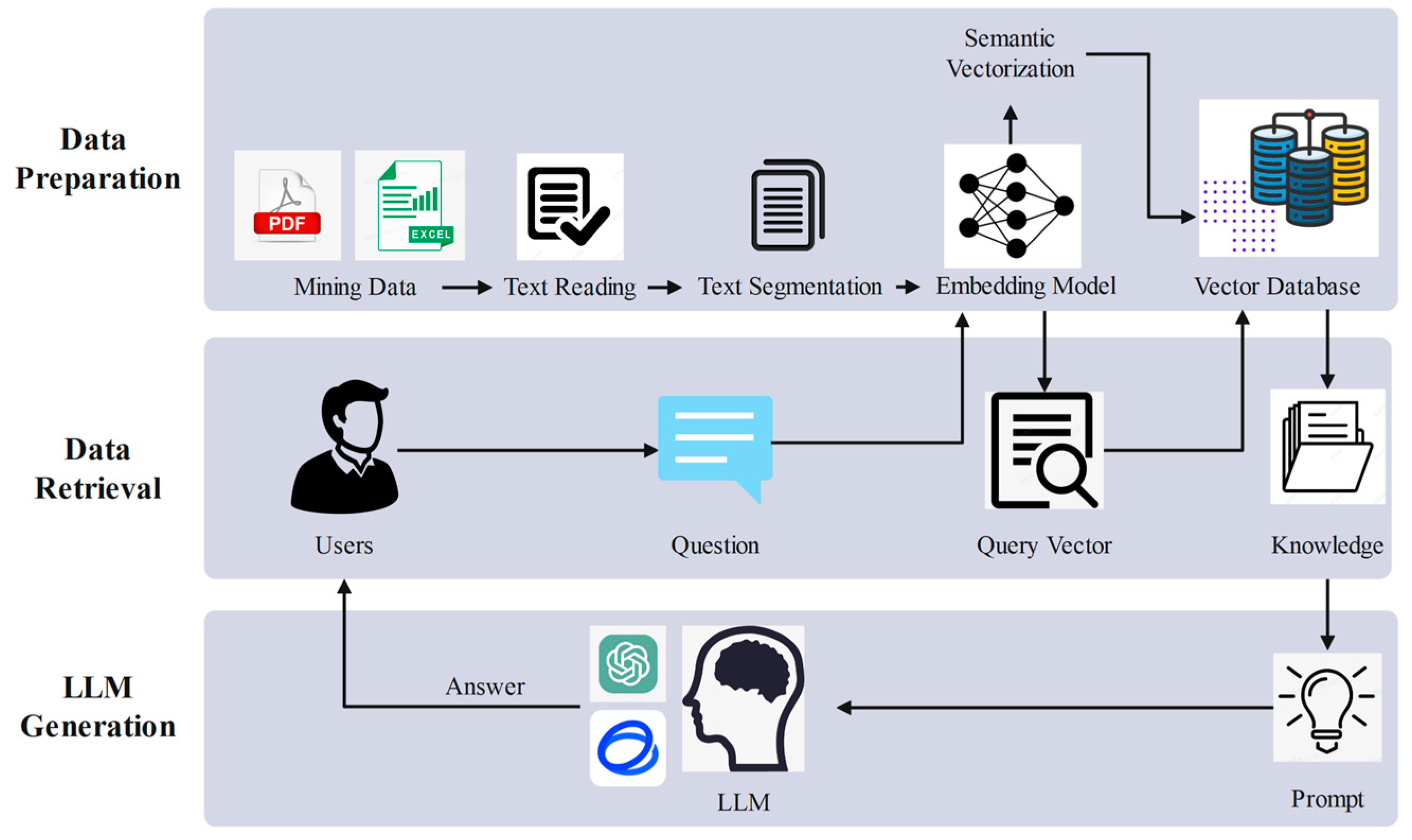
4.1.2. Data Processing and Knowledge Base Construction
- Retrieval Phase;
- Generation Phase;
4.2. Fine-Tuning of the Large Language Model Phase
4.2.1. Selection of the Base Large Language Model
4.2.2. Dataset Construction
4.2.3. Fine-Tuning
4.2.4. Testing and Optimization
4.3. Intelligent Judgment Report Generation Module
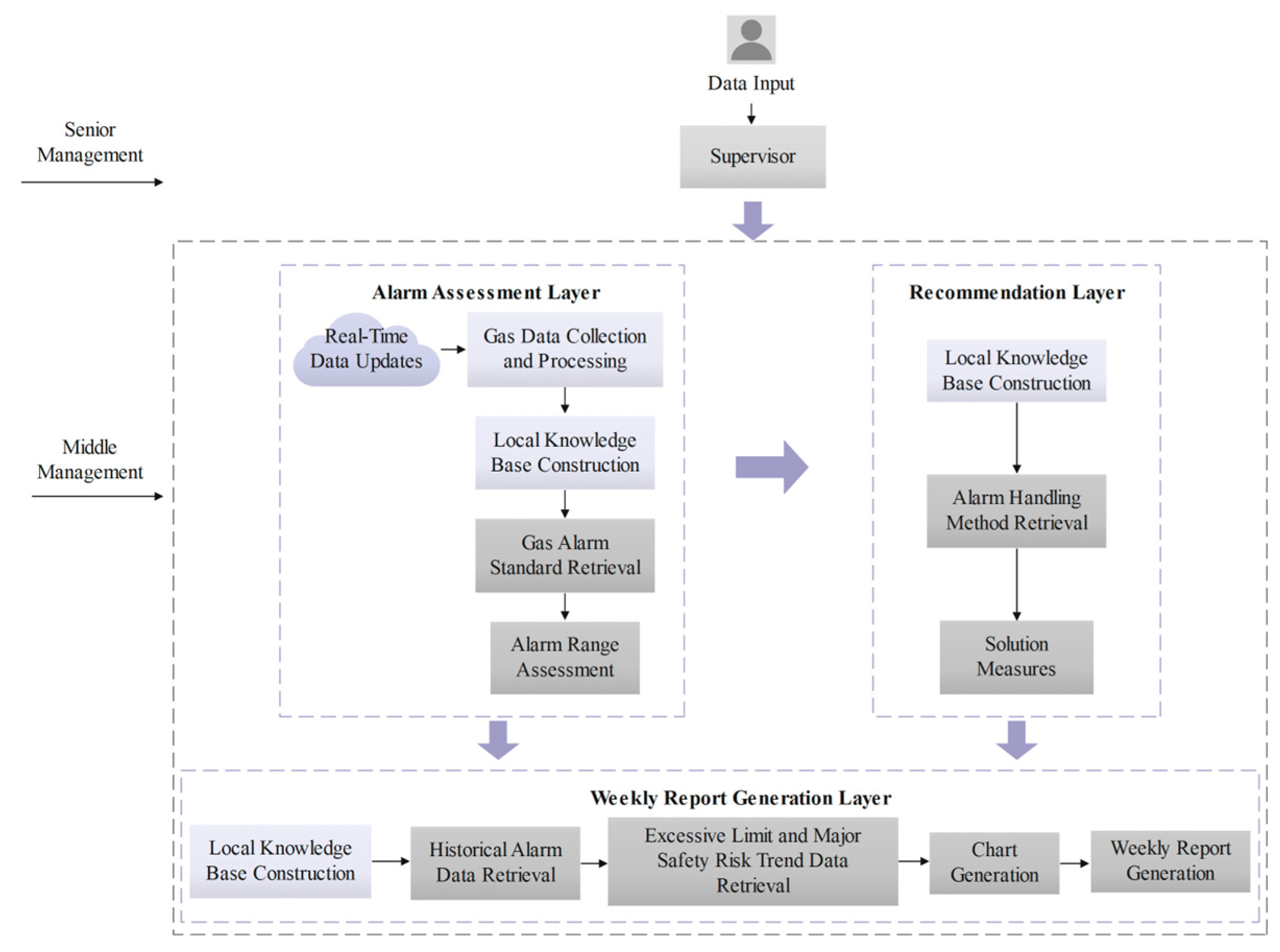
4.3.1. Report Automatic Generation Process
- Alarm Judgment Layer;
- Gas Standard Retrieval Agent.
- Alarm Judgment Agent.
- 2.
- Measures Suggestion Layer;
- Alarm Response Method Retrieval Agent.
- Solution Measures Agent.
- 3.
- Weekly Report Generation Layer.
- Historical Alarm Data Retrieval Agent.
- Exceedance and Major Safety Risk Trend Data Retrieval Agent.
- Chart Generation Agent.
- Weekly Report Generation Agent.
4.3.2. Report Evaluation and Review
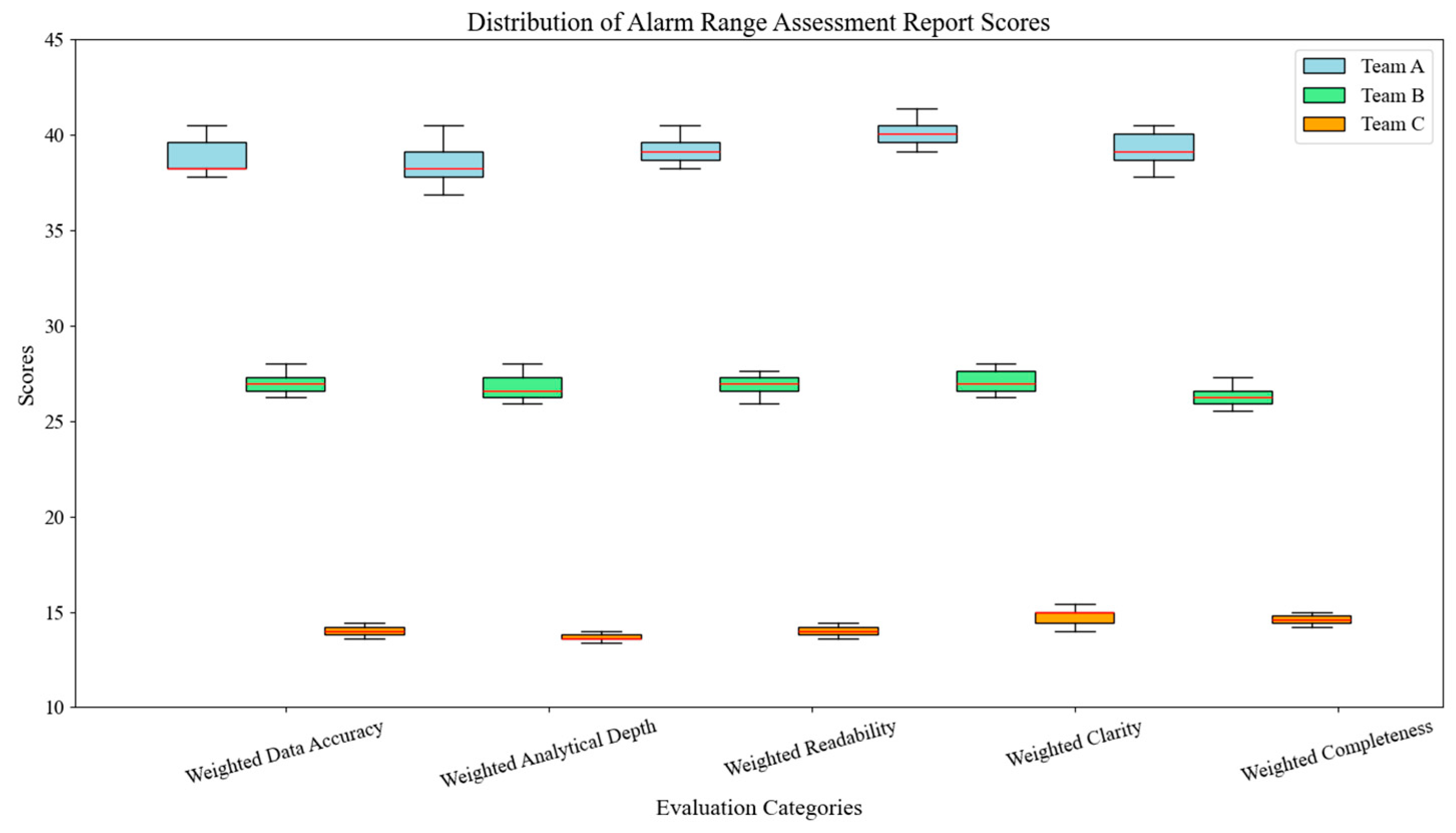
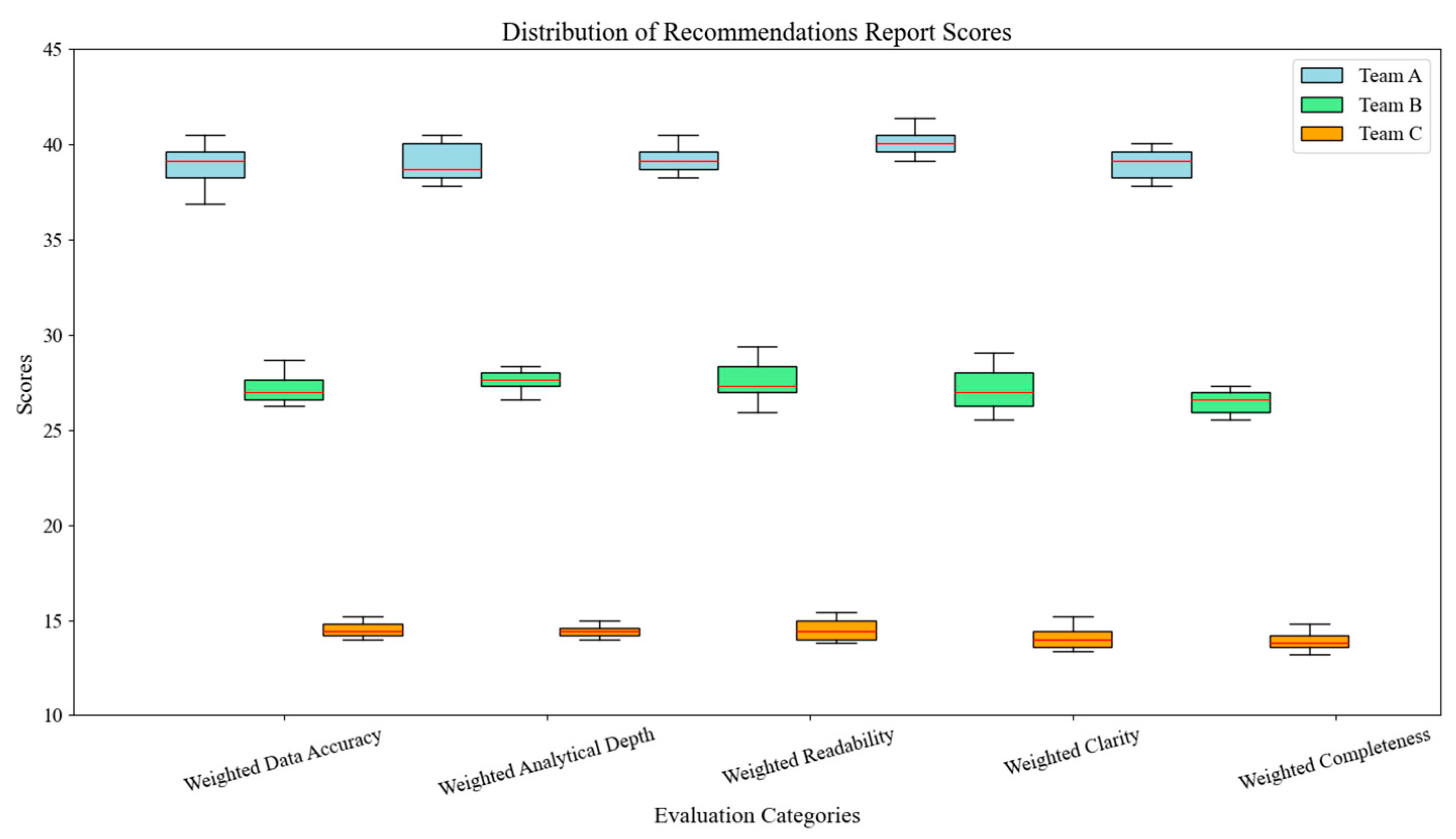
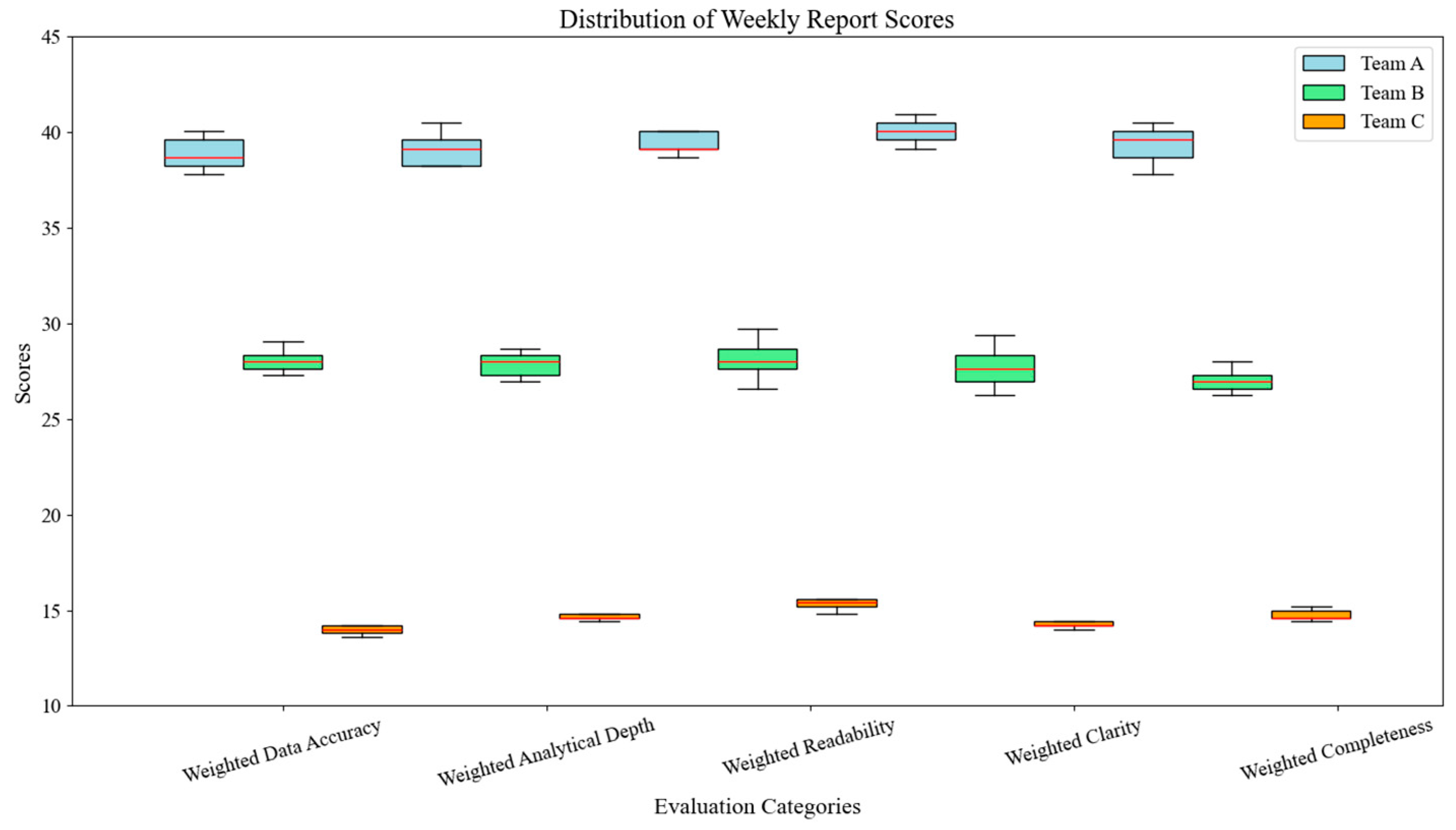
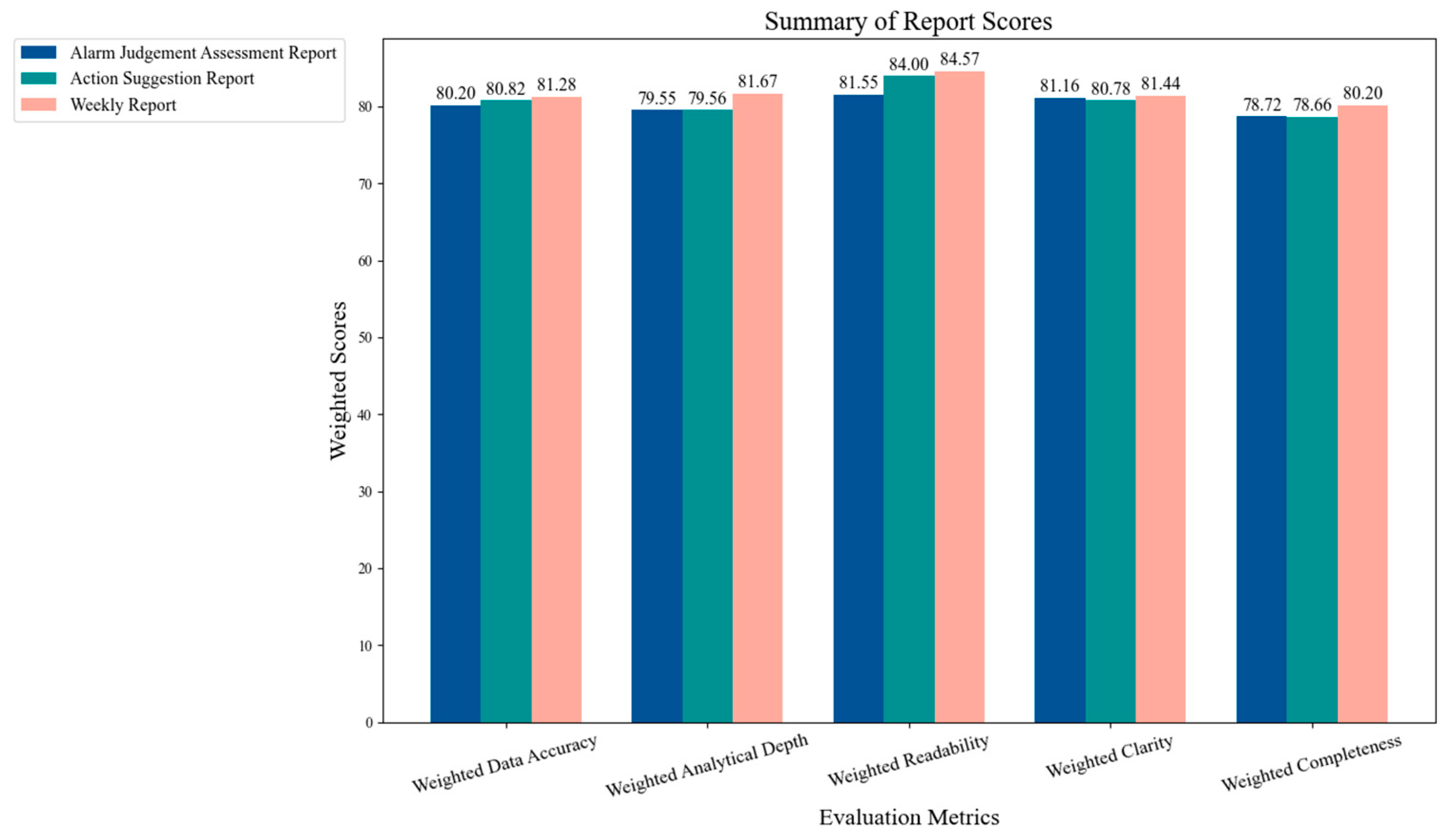
5. Experiment Results and Analysis
5.1. Experimental Platform and Model Configuration
5.2. Experimental Results Analysis
5.3. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhai, W.; Li, J.; Ouyang, S.; Gao, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G. Research on Coal Mine Safety Management Based on Digital Twin. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Qin, B.; Xu, J.; Li, N.; Liu, X. Big data monitoring and early warning cloud platform for coal mine gas disaster risk and potential danger and its application. Coal Sci. Technol. 2022, 50, 142–150. [Google Scholar]
- You, M.; Li, S.; Li, D.; Xu, S. Applications of Artificial Intelligence for Coal Mine Gas Risk Assessment. Safety Science 2021, 143, 105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, E.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, D. A Comprehensive Risk Assessment Method for Coal and Gas Outburst in Underground Coal Mines Based on Variable Weight Theory and Uncertainty Analysis. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 167, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, T.; Ning, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Recent Advances in Laser Gas Sensors for Applications to Safety Monitoring in Intelligent Coal Mines. Front. Phys. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Fu, G.; Xie, X.; Hu, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, J. LPG Leakage and Explosion Accident Analysis Based on a New SAA Method. J. Loss Prevent. Process Ind. 2021, 71, 104467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Wang, Y.; Jia, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, S.; Geng, Y. A Content-Aware Corpus-Based Model for Analysis of Marine Accidents. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2023, 184, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, H.; Agarwal, S. Automated Analysis through Natural Language Processing of DGMS Fatality Reports on Indian Non-Coal Mines. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks (ISCON), Mathura, India, 22–23 October 2021; IEEE; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Luo, X. Summarization of Coal Mine Accident Reports: A Natural-Language-Processing-Based Approach. In Proceedings of the International 2020 Cyberspace Congress on Cyberspace Data and Intelligence, and Cyber-Living, Syndrome, and Health (CyberDI/CyberLife 2020), Beijing, China, 10–12 December 2020; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.; Fu, G.; Xie, X.; Xue, Y.; Hu, S. Enhancing Accident Cause Analysis through Text Classification and Accident Causation Theory: A Case Study of Coal Mine Gas Explosion Accidents. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 185, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.; Vinkovic, K.; de Vries, M.; Kers, B.; Necki, J.; Swolkien, J.; Roiger, A.; Peters, W.; Chen, H. Quantifying Methane Emissions from Coal Mining Ventilation Shafts Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-Based Active AirCore System. Atmospheric Environment: X 2021, 12, 100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Kong, W.; Hu, H. A Review of Monitoring, Calculation, and Simulation Methods for Ground Subsidence Induced by Coal Mining. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, B.; Karimi, M.; Saydam, S.; Hassan, M. Recent Advancements in IoT Implementation for Environmental, Safety, and Production Monitoring in Underground Mines. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 14507–14526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y. U. A. N. Research Progress on Risk Identification, Assessment, Monitoring and Early Warning Technologies of Typical Dynamic Hazards in Coal Mines. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Xuecai, X.; Shifei, S.; Gui, F.; Xueming, S.; Jun, H.; Qingsong, J.; Zhao, S. Accident Case Data–Accident Cause Model Hybrid-Driven Coal and Gas Outburst Accident Analysis: Evidence from 84 Accidents in China during 2008–2018. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 164, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Zhu, N.; Chen, J.; An, S.; Zhang, H. Theoretical Method and Technology of Precision Identification for Coal and Gas Outburst Hazard. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Matloob, S.; Li, Y.; Khan, K. Z. Safety Measurements and Risk Assessment of Coal Mining Industry Using Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. Open J. Bus. Manag. 2021, 9, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anani, A.; Adewuyi, S. O.; Risso, N.; Nyaaba, W. Advancements in Machine Learning Techniques for Coal and Gas Outburst Prediction in Underground Mines. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2024, 104471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Maity, T. Review on Machine Learning-Based Underground Coal Mines Gas Hazard Identification and Estimation Techniques. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2024, 31, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xu, W.; Zhao, J.; Duan, Y.; Yang, X. Research on Large Language Model for Coal Mine Equipment Maintenance Based on Multi-Source Text. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Tian, G.; Zhao, T. AdaBoost-Driven Multi-Parameter Real-Time Warning of Rock Burst Risk in Coal Mines. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 125, 106591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuecai, X.; Xueming, S.; Gui, F.; Shifei, S.; Qingsong, J.; Jun, H.; Zhirong, W. Accident Causes Data-Driven Coal and Gas Outburst Accidents Prevention: Application of Data Mining and Machine Learning in Accident Path Mining and Accident Case-Based Deduction. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 162, 891–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ren, H.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, D.; Wen, Z.; Meng, L.; Gong, S. Research and Practice of Intelligent Coal Mine Technology Systems in China. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2022, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onifade, M.; Adebisi, J.A.; Shivute, A.P.; Genc, B. Challenges and Applications of Digital Technology in the Mineral Industry. Resources Policy 2023, 85, 103978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ranjith, P. G.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, P. New Insights on Ground Control in Intelligent Mining with Internet of Things. Comput. Commun. 2020, 150, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Yan, J.; Tang, Z.; Ren, S. Research Progress and Prospect of Mine Fire Intelligent Monitoring and Early Warning Technology in Recent 20 Years. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 52, 154–177. [Google Scholar]
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F. L.; McGrew, B. GPT-4 Technical Report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.; Mishkin, P.; Lowe, R. Training Language Models to Follow Instructions with Human Feedback. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 27730–27744. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Mao, H.; Li, H.; Jin, W.; Wen, H.; Wei, X.; Tang, J. Exploring the Potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Learning on Graphs. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2024, 25, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Liu, P. J. Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Hu, X.; Liu, Z.; Tu, C.; Sun, M. LawFormer: A Pre-trained Language Model for Chinese Legal Long Documents. AI Open 2021, 2, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavukarasu, A. J.; Ting, D. S. J.; Elangovan, K.; Gutierrez, L.; Tan, T. F.; Ting, D. S. W. Large Language Models in Medicine. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1930–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A. H.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y. FinBERT: A Large Language Model for Extracting Information from Financial Text. Contemp. Account. Res. 2023, 40, 806–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Chang, R.; Pei, S.; Chawla, N. V.; Zhang, X. Large Language Model Based Multi-Agents: A Survey of Progress and Challenges. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.01680. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, X.; Hong, S.; Li, W.; He, X. Exploring Large Language Model Based Intelligent Agents: Definitions, Methods, and Prospects. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.03428. [Google Scholar]
- Barua, S. Exploring Autonomous Agents through the Lens of Large Language Models: A Review. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.04442. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, H.; Mu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, C.; Luo, P.; Li, S.E.; Tomizuka, M.; Zhan, W.; Ding, M. LanguageMPC: Large Language Models as Decision Makers for Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.03026. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Park, C.; Jeong, H.; Chan, Y.S.; Xu, X.; McDuff, D.; Breazeal, C.; Park, H.W. Adaptive Collaboration Strategy for LLMs in Medical Decision Making. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.15155. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; et al. LoRA: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.09685. [Google Scholar]
- Dettmers, T.; Pagnoni, A.; Holtzman, A.; et al. QLoRA: Efficient finetuning of quantized LLMs. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Kishore, V.; Wu, F.; Weinberger, K.Q.; Artzi, Y. BERTScore: Evaluating Text Generation with BERT. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.09675. [Google Scholar]




| Mine Name | Installation Location | Measurement Type | Maximum Value | Unit | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mine A | Main Return Airway | Methane Gas (CH4) | 0 | %CH4 | December 13, 2024, 10:43:47 |
| Mine B | Longwall Face Spontaneous Combustion Monitoring Point | Carbon Monoxide (CO) | 29 | ppm | December 14, 2024, 12:23:03 |
| Mine C | Upper Corner of Coal Face | Oxygen (O2) | 18 | % | December 14, 2024, 11:34:03 |
| Mine D | Return Air Roadway | carbon dioxide (CO2) | 2.06 | % | December 7, 2024, 22:56:17 |
| Instruction | You are an expert in coal mine gas risk assessment. Please conduct a risk evaluation of the input laser methane data based on coal mine safety regulations. |
| Input | The coal mine is named xxx, and the specific installation location is at the upper mouth of the No. 2 coal bin underground; the measurement type at this point is laser methane, with a maximum concentration reading of 2.01% CH4; please output the corresponding alarm status for the current gas concentration and provide the appropriate response measures. |
| Output | The current alarm type is calibration; the potential cause of the alarm is gas electrical interlock testing; the response measure for this alarm type is to follow standard operating procedures. |
| Model | Frequency | BERTScore Precision | BERTScore Recall | BERTScore F1 | Grammar Errors | Diversity Score | Generation Time (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine-tuned GLM | 300 | 0.9431 | 0.9427 | 0.9429 | 0.025 | 0.82 | 4.6 |
| Base GLM | 300 | 0.9274 | 0.9289 | 0.9281 | 0.032 | 0.84 | 3.2 |
| Model | Frequency | BERTScore Precision | BERTScore Recall | BERTScore F1 | Grammar Errors | Diversity Score | Generation Time (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine-tuned GLM | 300 | 0.9149 | 0.9153 | 0.9151 | 0.038 | 0.79 | 3.7 |
| Base GLM | 300 | 0.8984 | 0.8902 | 0.8942 | 0.029 | 0.81 | 2.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





