1. Introduction
The mosquito
Aedes aegypti transmits arboviruses, including dengue, Zika, and chikungunya, which impact global health. The diseases produced by these viruses cause nearly 400 million infections and 100,000 symptomatic cases, resulting in 40,000 deaths annually [
1]. The Americas witnessed a concerning rise in arboviral prevalence, driven by climate change-induced meteorological phenomena, perpetuating epidemic cycles [
2].
Insecticides used as vector control persist as the primary form of intervention. Chemicals such as organophosphates, carbamates, insect growth regulators (IGR), and pyrethroids control adult and larval forms. Lambda-cyhalothrin, a type-II pyrethroid, is Colombia's most commonly used insecticide[
3]. However, decades of extensive application have exerted high selective pressures on wild populations of
Ae. aegypti significantly hampering vector control efforts by increasing their resistance to insecticides [
4]. Lambda-cyhalothrin resistance is present in at least 76% of
Ae. aegypti populations in Colombia, which is concerning due to their distribution[
3,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9].
Many studies have focused on the classical mechanisms [
10], knockdown resistance (
kdr) mutations, and metabolic enzymes (Also called metabolic resistance) to understand the development of insecticide resistance.
Kdr mutations are modifications in the Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel (VGSC) gene encoding region that impair the insecticide's ability to bind to its molecular target. For example, the mutations F1534C and V1016I have been found in the VGSC gene of resistant field mosquitoes and are correlated with elevation in LC
50 (Lethal Concentration 50) to pyrethroid insecticides [
11]. Other studies also found the contribution of these alleles to lambda-cyhalothrin insecticide resistance [
12], including the mutation V419L [
8,
13]. Likewise, metabolic resistance entails an increase in the activity of detoxifying enzymes such as those that belong to the Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) family, Glutathione S transferases (GST), and carboxylesterases (CE)[
14].
The artificial selection of
Aedes aegypti with insecticides allows the identification of features that could not be found in wild populations. Characterizing the molecular mechanisms is crucial for vector control within this framework, and tracking insecticide-resistance genes is vital for management strategies. Recently, some
Ae. aegypti strains were selected with pyrethroid insecticides over a few generations, and an RNA-seq approach was used to find genes associated with resistant populations[
15]. However, little is known about the response to long-term exposure to the lambda-cyhalothrin insecticide over several generations in
Ae. aegypti.
In this study, we subjected a strain of Ae. aegypti to selective pressure for 13 consecutive generations to understand the development and extent of insecticide resistance. We assessed resistance ratios and the magnitude of resistance in these mosquito populations. Then, kdr mutation typing and enzymatic activity assays were carried out to identify whether the known resistance mechanisms were present in this resistant mosquito population. Lastly, we delved into the transcriptomics of this pressured strain, comparing it to that of the same strain without pressure to gain insights into the molecular changes underlying insecticide resistance in Ae. aegypti.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Mosquito Collections
The
Ae. aegypti population used in this study was collected in 2016 in Acacías, Meta, Colombia (3°59′20″ N 73°45′53″ W)[
16]. The mosquitoes were maintained under controlled conditions with a temperature of 25 ± 5 °C, relative humidity of 72% ± 5%, and a photoperiod of 12 hours light/12 hours dark. Larvae were raised in dechlorinated water and fed Purina® truchina fish food (48% protein). Upon reaching adulthood, they were transferred to cages measuring 50x50x50 cm and provided with 10% sugar solution
ad libitum. The females were exposed to a blood meal from a mouse. After blood feeding, a strip of moist filter paper was placed in each cage as an oviposition substrate. The egg strips were removed and stored in humidity-controlled boxes for future use.
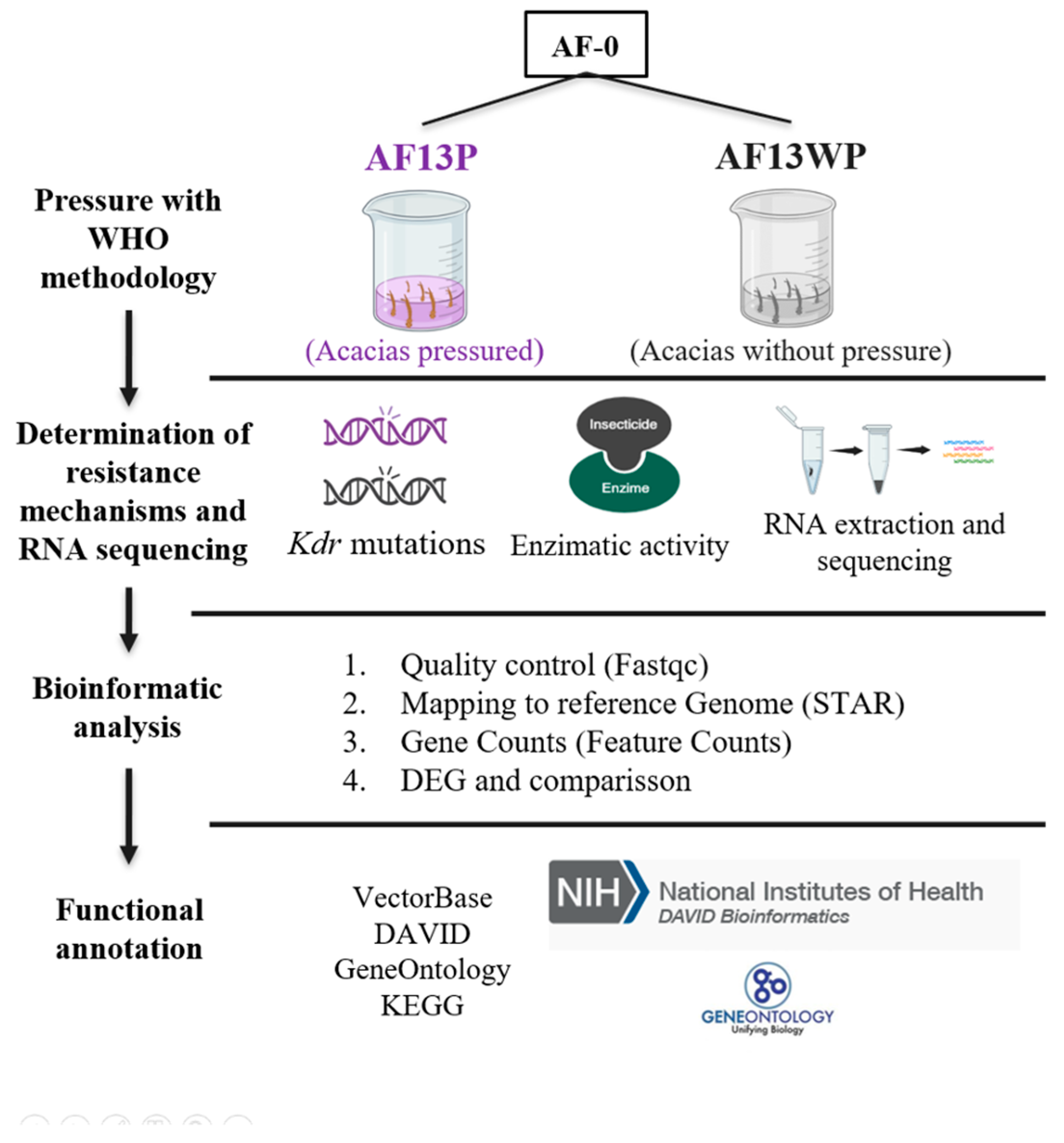
2.2. Experimental Design
To study the effects of long-term exposure to insecticides on
Ae. aegypti population, the parental Acacías population named AF-0, was used. This population was previously reported to have a resistance ratio (RR) of 31.4 to lambda-cyhalothrin[
16]. AF-0 was subsequently separated into two batches. The first batch was pressured with lambda-cyhalothrin at a concentration that generally would kill 90% of the insects (LC
90) for 13 generations and was given the name AFP (Acacías pressured). The second was an independent batch of Acacías AF-0 reared under standard laboratory conditions for 13 generations without insecticide pressure, named AFWP (Acacías without pressure). Bioassays were performed on AFP and AFWP generation 13, also named AF13P and AF13WP, respectively (
Figure 1).
Kdr typing, enzyme metabolic activity, and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) were performed on both populations. Additionally, mosquitoes from generation F7 of Acacías pressured (AF7P) and unpressured (AF7WP), previously reported by Granada et al.[
16], were used to compare RR and allelic frequencies.
2.3. Larval Bioassays and Pressure
Larval bioassays were used to obtain the LC
90 of AF-0. For this, WHO protocol[
17] with technical grade lambda-cyhalothrin (99.8% a.i; CAS number 91465-08-6) from Sigma-Aldrich (USA) was used. Batches of 20 larvae (with three biological replicates) of the third and fourth instar were introduced into 99 mL of distilled water and one mL of insecticide resuspended in ethanol, and mortality was recorded after 24 hours. One percent ethanol was used as a control in the bioassays. Insecticide concentrations were 0.0009 to 0.06 ppm and were based on mortality ranges from 10% to 90%. The results obtained in the bioassays were subjected to probit analysis using the SPSS toolkit (IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 27.0) to determine the LC
50 and LC
90. The LC
90 was used for insecticide pressure in each mosquito generation. Once generation 13
th was reached, the bioassays with AF13P and AF13WP were carried out to obtain the corresponding RR. The susceptible population Rockefeller was used as a reference. The RR was calculated by dividing the LC
50 (or LC
90) values of the population under study by that obtained for the susceptible strain. This calculation yields a 50 (RR
50) or 90 (RR
90) resistance ratio. The statistical significance (p < 0.05) of the comparison of LC
50 and LC
90 between resistant and susceptible strains was assessed using the Lethal Dose Ratios test [
18]. This method involves the overlap of the 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) for each evaluated strain compared with the 95% CI of the Rockefeller strain. After accomplishing this procedure, AF13P and AF13WP were used to determine
kdr mutations and enzymatic activity.
2.4. Determination of kdr Allelic Frequencies
An allele-specific PCR (AS-PCR) within the voltage-gated sodium channel gene encoding region was used to amplify the known
kdr mutations F1534C, V410L, and V1016I circulating in Colombia [
8,
13]. Genomic DNA was extracted using the Grind Buffer protocol [
19]. Each insect was homogenized in 50 µl of buffer and then incubated with 20 µl of proteinase K. After adding potassium acetate [8M], centrifuge steps were performed to precipitate DNA, followed by washing with 70% and 98% ethanol. The resulting DNA pellet was resuspended in 30 µl of water. Subsequently, each PCR reaction was performed in a Rotor-Gene Q thermocycler, following conditions reported by Pareja-Loaiza et al. [
13]. At least 30 adult mosquitoes from the insecticide-pressured and unpressured populations were used. Additionally, wild-type alleles from the Rockefeller population were used as a reference.
2.5. Metabolic Enzyme Activity
Enzyme activity assays were performed to identify metabolic resistance in insecticide-pressured and unpressured populations. The enzymes assessed included acetylcholinesterase (AChE), alfa and beta esterases (α-EST and β-EST, respectively), mixed function oxidases (MFO), and glutathione S-transferase (GST). Forty female mosquitoes that had emerged within the last day were individually macerated in 300 µl of deionized water using a tissue grinder and a MicroPestle system until the sample was homogenized entirely. For the metabolic enzymatic activity assays, we followed standardized protocols [
20]. The enzymatic activity of Acetylcholinesterase (AChE), mixed function oxidase (MFO), α-esterase (α-EST), β-esterase (β-EST), and Glutathione-S-transferase (GST) was determined. All enzyme activity analyses were normalized with the total protein concentration, determined using the Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Scientific, Rock), with 10 – 25 µL of mosquito homogenate or supernatant following the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, for the AChE activity, 25 µl of homogenized mosquito in the presence and absence of inhibitor was determined by adding DTNB substrate. For MFO, 20 µl was used, and the substrate was TMBZ. For α-β-EST, 10 µl of supernatant was pipetted, and α-β naphthyl was used as a substrate. Finally, reduced glutathione as substrate and 15 µl of supernatant were used for GST. All enzymes were measured in an ELISA Multiskan Spectrum from Thermo Fisher Scientific using wavelengths previously reported [
21].
2.6. RNA Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analyses
For the two populations, AF13P and AF13WP, three pools of five female mosquitoes were employed for each RNA extraction using the Spin Tissue RNA Mini Kit. Briefly, mosquito pools were homogenized using Micropestles and lysed using a lysis buffer. RNA was eluted in 30 µl of TE buffer. The samples were sent to the University of Oklahoma (Oklahoma) for sequencing. For library preparation, mRNA was purified using poly-A tails, and the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 kit (Illumina, USA) was used to obtain pair-end reads of 150 base pairs. The average sequencing depth was 20 million reads. Sequence quality was verified using FastQC [
22], and low-quality sequences were cut using Trimmomatic (Phred Score <30, length <36) [
23]. The AaegL5 genome [
24] (Accession: GCA_002204515) was used as a reference for mapping using STAR [
25]. This genome contains 19,804 genes, with 14,718 coding for proteins. Gene counts were obtained through the Rsubread (DEseq2) package, and the Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) were defined based on an absolute log 2-fold change (log
2FC) ≥ 1.0 and a False Discovery Rate (FDR) ≤ 0.05 between the two compared groups (AF13P vs AF13WP). Normalized data were scaled for statistical analysis and subsequent comparisons between the two groups.
2.7. Functional and Enrichment Analysis
The DAVID Gene system was used to elucidate resistance mechanisms by associating overrepresented genes in the RNA-seq data with specific biological processes in the Gene Ontology (GO) database and performing pathway enrichment analysis using KEGG [
26]. The functional analysis and classification were separated into upregulated and downregulated terms using all expressed genes as a background. DAVID uses the EASE Score for functional analysis; it is a modified Fisher exact P-value to test the probability of getting a gene (or a set of genes) from our whole data set, whose associated term is obtained with a particular frequency, over the total gene set of a background genome (in this case,
Aedes aegypti AegL5 genome) and asks if there is more than randomness in selecting that specific term. Gene clustering was made with the option "Functional Annotation Clustering," using a kappa statistic to prevent repeated annotations from being overrepresented in the gene list. Also, the enrichment score is used to classify the grouped genes, and the greater the score, the more significant the classification. An enrichment score ≥ 1.3 equals a p-value of 0.05 (10
-1.3).
In summary, the enrichment score groups terms with similar biological meanings by having similar gene members. It is based on the EASE score, a modified statistical test. The smaller this score is, the more enriched the term (and therefore the gene) is in the list.
The functional classification was performed by grouping genes with a similar function to improve the biological interpretation of gene lists. The GO annotations were filtered based on the classification performed by DAVID. Moreover, a search was conducted using these terms based on the Molecular Function (MF), Cellular Compartment (CC), and Biological Processes (BP) categories. Functional annotation, clustering, and GO analysis were plotted using SRplot (
https://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/en), a free online data analysis and visualization platform.
2.8. Ethics Statement
All animals used in this study were handled strictly according to good animal practice, as defined by the Colombian Code of Practice for the care and use of animals for scientific purposes, established by law 84 of 1989. Ethical approval (Act No. 136, 17/11/2020) was obtained from the Animal Ethics Committee of the University of Antioquia, Medellin, Colombia.
3. Results
3.1. Prolonged Exposure to Lambda-Cyhalothrin Induces a High Degree of Resistance
We explored the effect of insecticide pressure on the RR of AF13P compared to AF13WP using bioassays. The unpressured population exhibited a reduction in RR50 of approximately 1.6 times each generation. While the AF-0 strain showed an RR50 of 31.64, the AF7WP and AF13WP strains had a significantly lower value of 18.99 and 10.54, respectively, indicating greater susceptibility after a long time without insecticide pressure. Conversely, after the insecticide pressure, the AF13P population increased the resistance, reaching an RR50 of 748.94, 23 times higher than the parental AF0 strain and 71 times higher than the AF13WP. The RR50 increased drastically after seven generations under insecticide pressure (AF7P, RR50 662.45) (
Table 1). Nonoverlapping, 95% CIs, was observed between evaluated strains, indicating a significant difference (p < 0.05) between all Acacías strains and Rockefeller.
Our selective pressure experiment yielded a highly resistant strain (AF13P) compared to parental AF-0 and even more resistant than the unpressured AF13WP, showcasing the selection or emergence of resistance mechanisms, which we next explored.
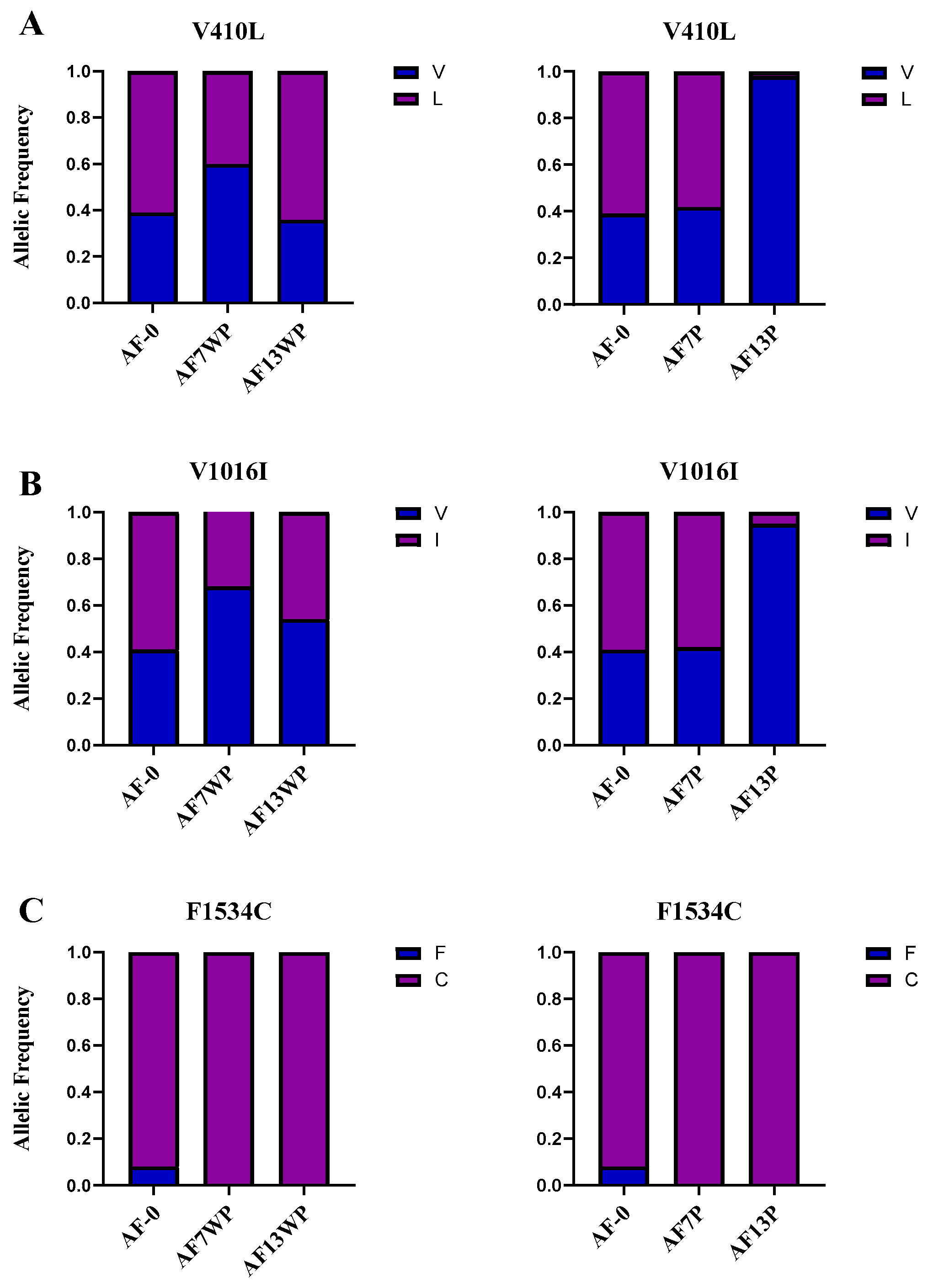
3.2. Low kdr Allelic Frequencies Do Not Rule Out High Lambda-Cyhalothrin Resistance in Aedes aegypti
Since the presence of specific
kdr mutations such as V410L, V1016I, and F1534C are known to be involved in insecticide resistance over successive generations, we sought to identify the frequencies of these mutations in 30 individuals of AF13P and AF13WP and compare them to those of AF-0, AF7P, and AF7WP previously reported. The mutated allele 410L frequency increased from 0.4 to 0.6 in AF7WP and AF13WP, respectively (
Figure 2). A drastic change occurred between pressured strains AF7P and AF13P mutated allele frequency, which dropped from 0.58 to 0.02, respectively. The same tendency was observed in the 1016I mutation for both the unpressured and pressured populations. The 1016I allele in AF7WP and AF13WP mosquitoes experienced an increase in frequency (0.33 to 0.46, respectively). Conversely, AF7P and AF13P individuals diminished their mutated allele frequency (0.58 to 0.05). Nonetheless, the allelic frequency of F1534C remained constant in susceptible and resistant populations, being fixed in tested populations.
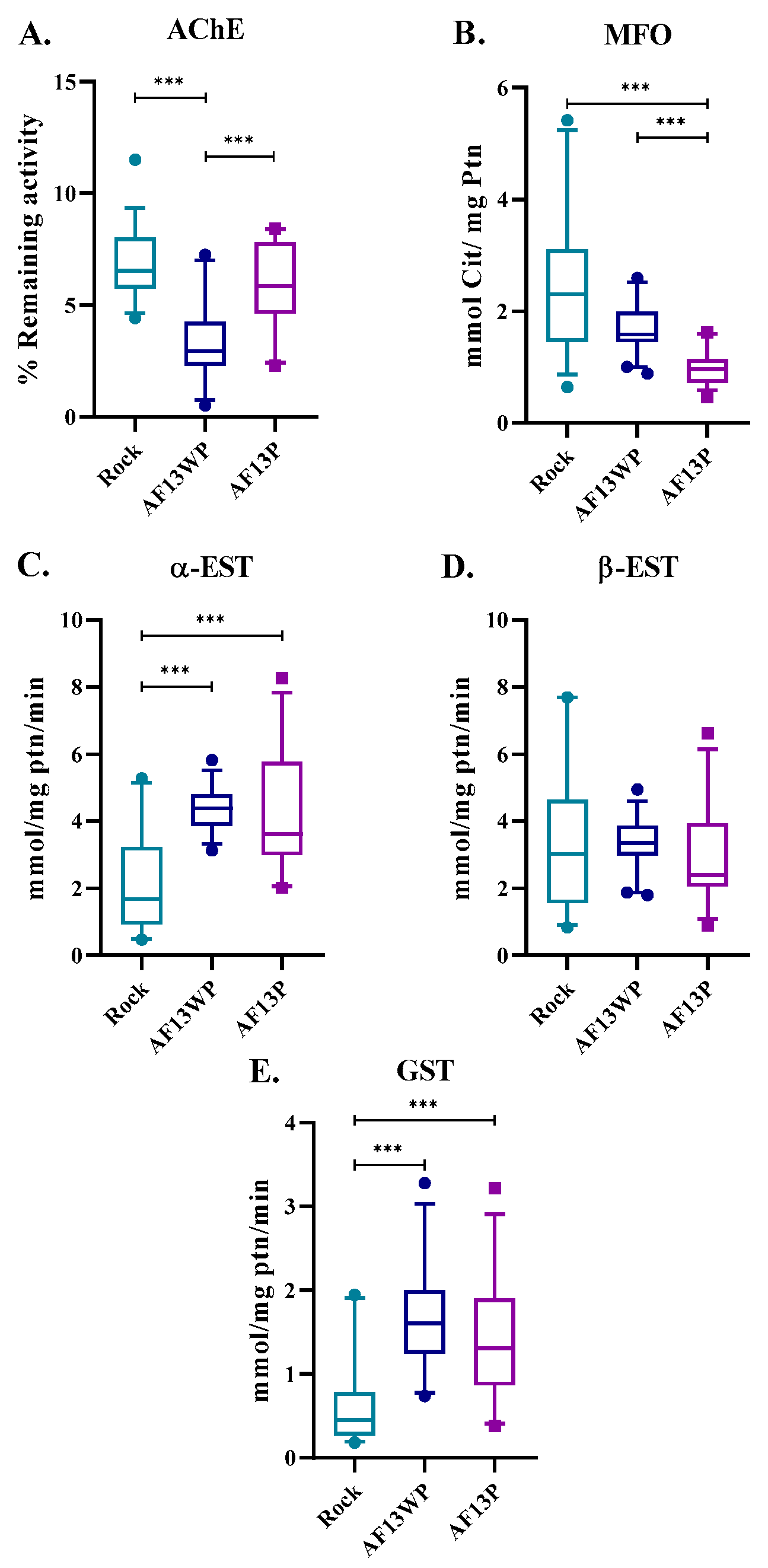
3.3. Metabolic Enzyme Activity Is Not Showing Significant Changes in Acacias Populations
Given the unexpected findings in the analysis of
kdr mutations, we looked for alternative mechanisms involved in resistance, such as metabolic resistance. Thus, enzymatic activities were determined in AF13WP and AF13P (
Figure 3). It was apparent that even after prolonged exposure to lambda-cyhalothrin over 13 generations, the AF13P exhibited no substantial increases in enzymatic activity across most enzymes compared to AF13WP, specifically α-EST, β-EST, and GST. Interestingly, AF13P exhibited a slight increase in ACHE activity compared to AF13WP, while MFO levels were increased in AF13WP. However, it is to be noted that both Acacías strains had low ACHE and MFO and high α-EST and GST when compared with the susceptible reference strain Rockefeller. These results suggest that some enzymes presented altered levels, potentially indicating adaptative mechanisms or resistance maintenance in these populations when compared with Rockefeller. Nonetheless, the AF13P-resistant population did not portray representative changes in enzymatic activity compared to its susceptible counterpart, from which we could not account for the high RR previously obtained (
Table 1).
3.4. Identifying New Insecticide Resistance Mechanisms Through RNA-seq
Our data showed that mosquitoes highly resistant to lambda-cyhalothrin do not have a high frequency of mutated alleles or altered activity of selected metabolic enzymes, so additional resistant mechanisms should be involved. Therefore, we employed RNA sequencing to identify genes differentially expressed in the insecticide-resistant strains that might contribute to understanding the insecticide resistance phenotype.
We obtained 790,369,834 total trimmed reads, with approximately 93% mapping coverage to the reference AegL5 genome (Supplementary
Table 1). Trimmed reads were used for mapping using STAR with the latest
Ae. aegypti genome version (LVP_AGWG AaegL5.3). After filtering low-expressed genes (<32 gene counts), 12,893 (65.1%) genes remained, of which 78.79% were uniquely mapped genes and 13.64% were mapped to multiple loci.
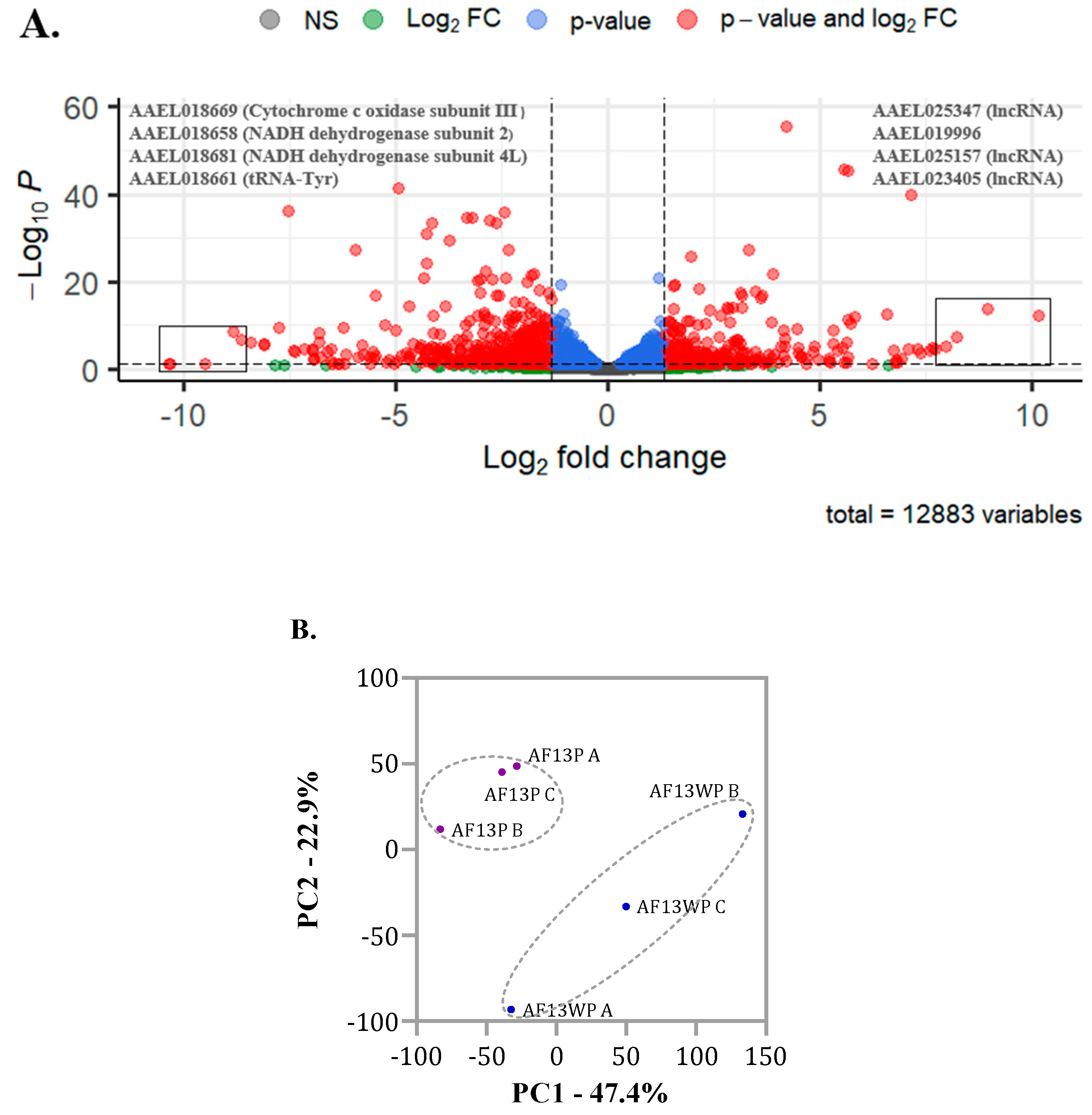
DEseq2 was used to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between AF13P and AF13WP populations. Of the initial 12,893 genes, 320 were upregulated, and 602 were down-regulated in the AF13P-resistant population compared to AF13WP-susceptible (
Figure 4A). Normalized counts of DEGs were used to construct a PCA, revealing a distinct separation in expression data between AF13P and AF13WP populations for the Principal Component 1 (PC1) and 2 (PC2), contributing to a cumulative explained variance of 70.3% (
Figure 4B). Among the 320 up-regulated genes, 231 were protein-coding genes: 150 corresponded to unspecified products (hypothetical genes), and 81 were annotated (Supplementary
Table 1). Of the 602 down-regulated genes, 475 were protein-coding genes. Among them, 230 were successfully annotated, while 245 were reported as hypothetical genes (
Supplementary Table S1).
To identify genes associated with insecticide resistance, we explored the genes with the highest and lowest FC (Fold Change). The most up-regulated genes were AAEL019996, AAEL025347, AAEL025157, and AAEL023405, which are not annotated in the genome.
Gene AAEL019996 is 8.9 times up-regulated and belongs to a probable 34 kDa protein reported as a salivary-secreted peptide in Uniprot [
27]. The up-regulated genes AAEL025347 (FC = 10.1, FDR = 7.08E-13), AAEL025157 (FC = 8.20380676, FDR = 6.06E-08), and AAEL023405 (FC = 7.969957451, FDR = 6.96E-06) correspond to ncRNAs (non-coding RNA) (
Supplementary Table S1, DEGs).
The top 3 down-regulated genes AAEL018681, AAEL018658, and AAEL018671 code for subunits of NADH dehydrogenase (FC= -13.4736225, -13.1435047, -11.2037335, respectively). Additionally, gene AAEL018661 ranks the least expressed in all datasets, with a log2FC of -14.1, corresponding to tRNA-Tyr (Transfer RNA-Tyrosine).
3.5. Prolonged Exposure to Lambda-Cyhalothrin Reveals Clusters of Genes from the Cuticle and Respiratory Chain
After identifying DEGs in the resistant strain, we studied the biological role of up-and-down-regulated genes and analyzed their relationship with insecticide resistance. For this purpose, we used DAVID for functional annotation, clustering (
Supplementary Table S2 and
Table S3), and Gene Ontology (GO) to analyze gene functions (
Figure 5).
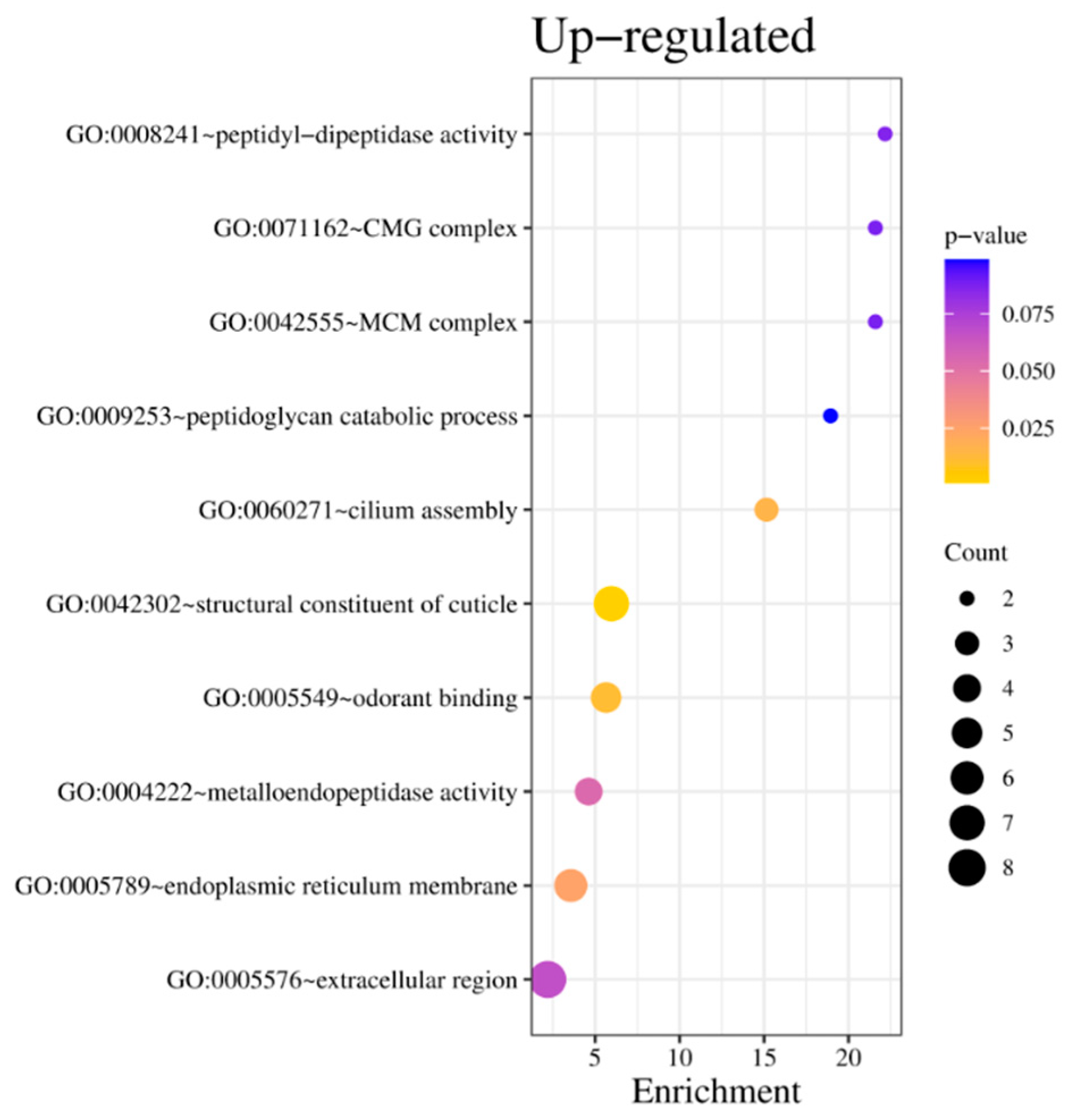
Using DAVID on the list of 320 up-regulated DEGs within the broader context of the entire dataset, nine distinct clusters were revealed (
Supplementary Table S2). Only two were significant, displaying an enrichment score above 1%. The first gene cluster, characterized by an enrichment score of 4.3%, includes a conserved protein domain SCP (Sperm-Coating Glycoprotein) and pathogenesis-stress-related protein, P14a type (
Supplementary Table S2). The second cluster (enrichment score of 2.5%) comprises terms directed toward cuticle structure. Finally, Cytochrome P450, although having an enrichment score <1, emerged from the data as a third cluster (
Supplementary Table S2).
According to GO term separation, the overexpressed genes with the most significant p-value are those of structural constituents of the cuticle (GO:0042302) and odorant binding (GO:0005549) (
Figure 5A), portraying a similar picture between DAVID clustering and GO.
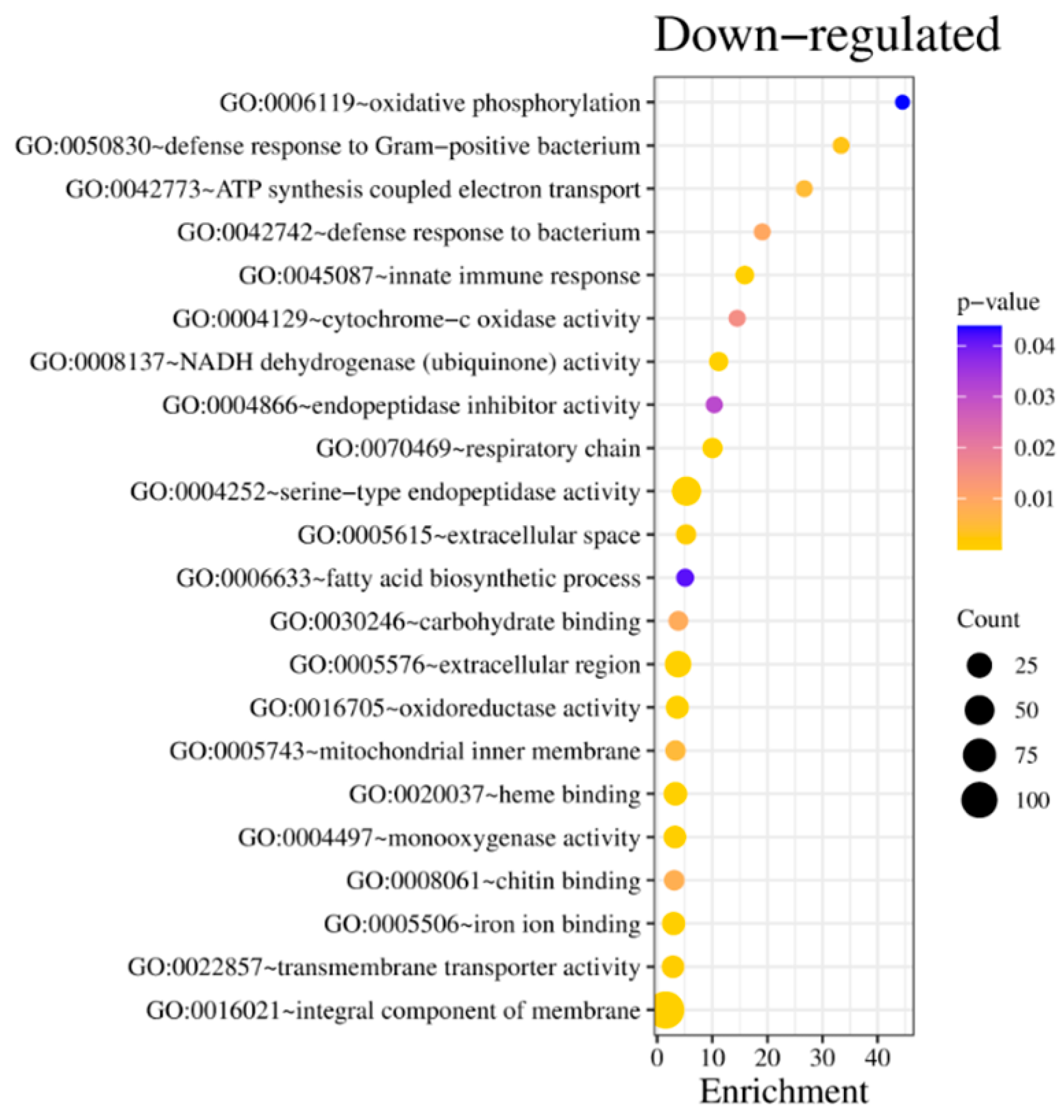
The 602 down-regulated genes included six statistically significant clusters (enrichment score above 1). Cluster one and two were dominated by enzymes, mainly trypsin, peptidases, proteases, collagenases, and transmembrane proteins. The third cluster comprised genes related to cytochrome P450, iron, heme binding, and enzymes of the electron chain transporter (
Supplementary Table S3); the terms GO:0005506 ion binding and GO:0004129 cytochrome-c oxidase activity were also significant. The fourth and fifth clusters included terms related to transmembrane components and transmembrane activity, such as GO:002857 transmembrane transporter activity (
Figure 5B). The last cluster, showing an enrichment score above 1, incorporated leucine-rich repeats, but GO terms did not represent it.
In summary, DAVID allowed the identification of genes into organized categories. GO corroborated this analysis by portraying overlapping GO categories and enrichment gene terms. In terms of insecticide resistance-related genes, the most exciting categories for the reported DEGs were cuticle protein genes for up-regulated genes and chain transporter and stress-related proteins (proteases, peptidases, and leucine-rich repeat genes) for the down-regulated genes. We included four additional categories of metabolic resistance genes to expand our analysis further and provide context for the high Resistance Ratio (RR) observed in
Table 1 and the varying degrees of enzymatic activity in our strains (
Figure 3). These categories comprised GST, esterase, dehydrogenase, and CYP450. We examined the FC distribution of these genes to gain a more comprehensive understanding of their potential role in insecticide resistance mechanisms.
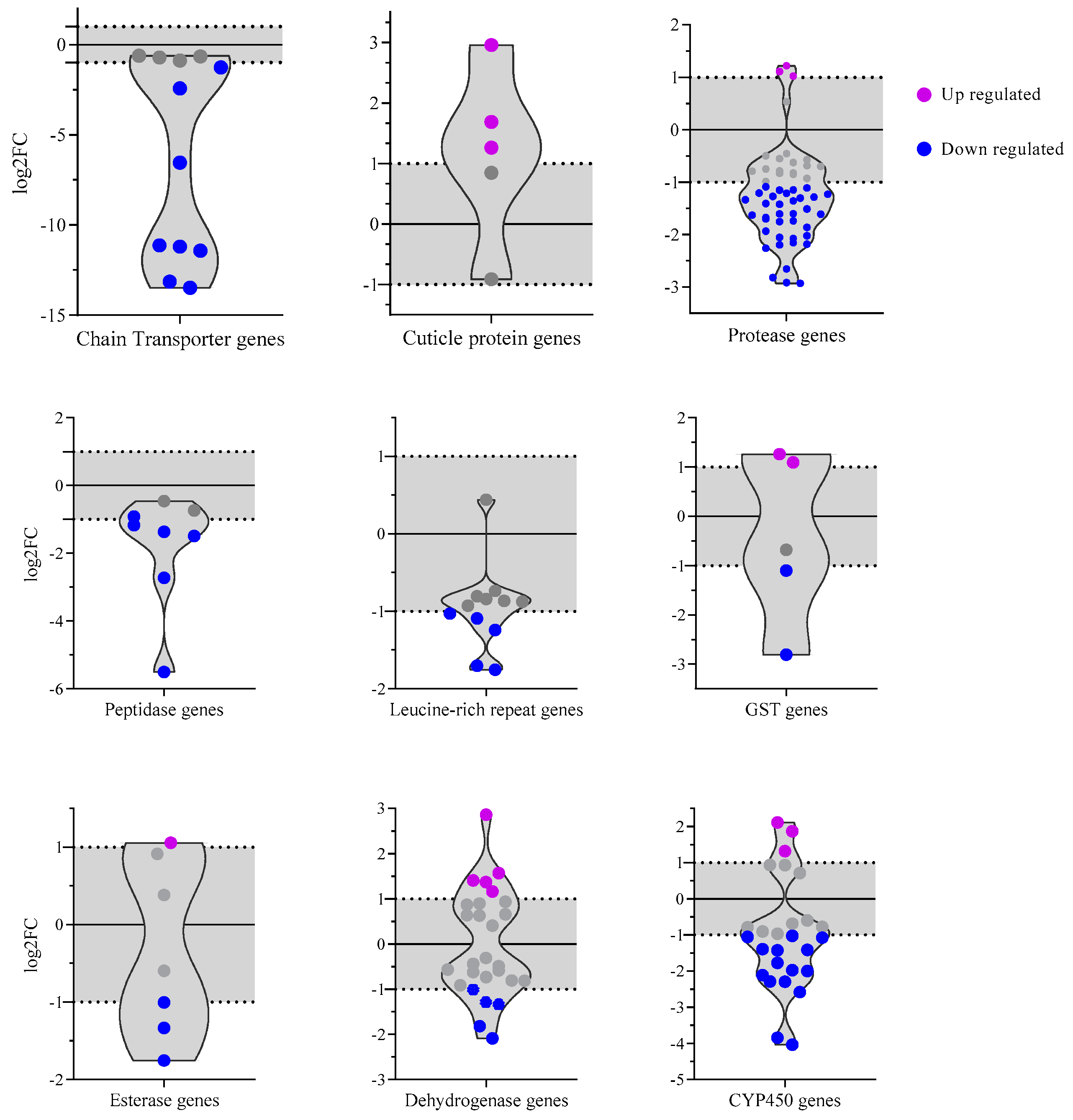
3.6. Prolonged Exposure to Lambda-Cyhalothrin Reveals Broad Distribution of DEGs Among Gene Categories
According to DAVID's classification, we displayed the log
2FC of each gene category that was significant (p-value < 0.05) in
Figure 6. This organization compares the FC of genes with the same biological function and explains their potential role in insecticide resistance based on the relationship between up and down-regulated genes. Additional information on each of the displayed genes, log2FC, and VectorBase annotation is shown in
Supplementary Table S4.
Accounting for all the genes in the categories, we showed that only 17 genes of the 116 total genes were upregulated (
Figure 6), exhibiting a similar tendency of low quantity of up-regulated vs down-regulated DEGs (320 vs. 602 genes). Of the total 17 genes, eleven up-regulated genes belonged to metabolic enzyme categories. Of these, only the cuticle category showed a significant up-regulation (AAEL007739- pupal cuticle protein, AAEL011504- pupal cuticle protein, AAEL013380- Adult cuticle protein). However, enzymatic-related categories, CYP450, dehydrogenase, GST, and esterase, showed a bimodal distribution of log
2FC.
The CYP450 category depicts three upregulated genes. The genes encoding for CYP9J29, CYP6AG4, and the CYP450- AAEL009018 of an unknown family (
Supplementary Table S5). Of the 15 downregulated genes, the majority of them correspond to the family of CYP6 (8 genes), followed by the family CYP4 (3 genes) and CYP9 (2 genes), with only one gene of the CYP12 family. The most downregulated gene of this category is CYP6F3, which has an FC of -4.03.
In the dehydrogenase category, ten genes are significant, and of those, AAEL013603 (log
2FC = 2.8) is one of the most upregulated genes that encodes a short-chain dehydrogenase (
Figure 6). In contrast, the down-regulated gene AAEL011130 is identified as alcohol dehydrogenase, exhibiting a log
2FC of -2.1.
These bimodal distributions exhibit genes with distinct responses to lambda-cyhalothrin pressure according to its log
2FC, suggesting varied sensitivities among these enzymes. We showed that Glutathione transferase genes GSTX2 and GSTX1 were upregulated, whereas the snRNA phosphodiesterase AAEL009090 was the only gene of the esterase category with elevated transcription. Interestingly, two GSTs and microsomal glutathione s-transferase were downregulated, while the only down-regulated gene of CCE is CCEAE1A (
Supplementary Table S5 and
Figure 6).
Surprisingly, electron chain transporter genes had downregulated genes with the lowest value compared to other categories. They corresponded to NADH dehydrogenases and cytochrome c oxidases with a log
2FC ranging from -1.2 to -13.4 (
Figure 6 and
Supplementary Table S5).
On the other hand, the protease group had the most downregulated genes, with 56 genes involved in protein production, of which only three were significantly up-regulated (AAEL007420—Serine Protease, AAEL012219—Ubiquitin-specific protease, AAEL014946—Protease U48). Another group separated by DAVID was the peptidases and LRR, with six and five significant down-regulated genes each. Serine Type endopeptidase and LRIM1 are the least downregulated exponent of peptidases and LRR categories. It is to be noted that the most downregulated gene in our data set (AAEL018661), which encodes a tRNA-Tyr, does not correspond to any of these classifications and displays a substantial log
2FC of -14.1 (
Figure 5).
4. Discussion
This study measured the differential expression profile in an Ae. aegypti strain that exhibits a significant increase in resistance to lambda-cyhalothrin, independent of kdr mutations and metabolic resistance mechanisms. We found several genes that could be responsible for heightened resistance.
4.1. Classical Mechanisms of Insecticide Resistance Are Underrepresented in AF13P
Mosquitoes typically exhibit primary resistance mechanisms through VGSC gene alterations and metabolic enzymes [
28,
29,
30]. The frequencies of the mutated alleles 410L and 1016I in the highly insecticide-resistant AF13P strain were drastically diminished to 0.02 and 0.05, respectively. Similarly, other studies have found that the
kdr frequencies may decline among resistant populations due to fitness costs[
31,
32,
33]. However, these findings differ from previous studies that examined the sequential evolution of the 1534C and 1016I mutations[
34], where co-occurrence of these alleles was associated with the pyrethroids’ increased resistance. Additionally, it was suggested that the combination of 410L+1016I+1534C alleles results in high fitness costs without insecticides[
33], but in the presence of deltamethrin, this combination enhances resistance compared to having only the 1534C allele[
35]. Our findings indicate that prolonged exposure to lambda-cyhalothrin across multiple generations maintained the 1534C allele fixed in the population, which could play a key role in insecticide resistance. Since this mutation was fixed in the F7 generation, but the resistance ratio continued increasing, other mechanisms should be involved in expressing insecticide resistance.
Detoxifying enzymes like CYP450 initiate detoxification as a defense mechanism against insecticides[
36]. Surprisingly, we did not observe elevated levels of CYP450 in the resistant AF13P strain compared with the susceptible strain, despite the actual differences between AF13P/AF13WP strains with Rockefeller. This is coherent with findings from studies in Colombia[
4,
16,
37,
38] and elsewhere[
39,
40], which have suggested a link between this enzyme and resistance to all pyrethroids. Heightened GST enzyme activity has been implicated in varying degrees of resistance to all main classes of insecticides[
41]. We didn´t find significant differences in GST enzyme activity between AF13WP and AF13P mosquito populations (
Figure 3). This indicates that this enzyme is unlikely to be a factor responsible for the differences between the resistant AF13P and susceptible phenotype AF13WP (
Table 1).
While we do not have sufficient information that explains the differences in resistance between AF13P and AF13WP, our evidence suggests that the discrepancy between these strains and Rockefeller is answered by
kdr frequencies and enzymatic activity, showcased by RR50 and RR90 in
Table 1. Our data suggest that additional mechanisms beyond classical ones influence AF13P mosquito resistance.
4.2. Diverse Regulation of CYP and GST Genes After Lambda-Cyhalothrin Exposure
Our comprehensive RNAseq analysis provided significant insights into the additional mechanisms related to insecticide resistance in AF13P mosquitoes. Our findings have underscored the crucial role of specific genes in insecticide resistance. Firstly, we detected the overregulation of the CYP6CB1 gene (AAEL009018). This gene was also detected in a modified
Ae.
aegypti strain[
42], and it is relevant in deltamethrin-resistant field and laboratory
Ae.
aegypti populations[
43] and within Asian strains[
44]. Second, the CYP9J29 gene (AAEL014610), the most over-regulated gene of the CYP450 family in our data set, is a significant locus linked to pyrethroid resistance in
Ae.
aegypti [
45]. Third, the upregulated CYP6AG4 (AAEL007010) gene was also found with a higher frequency in resistant mosquitoes[
46], which probably contributes to insecticide resistance.
In addition, the GST genes GSTX1 (AAEL000092) and GSTX2 (AAEL010500) were also up-regulated in resistant mosquitoes (
Supplementary Table S4). These genes also presented overregulation in Mexican
Ae. aegypti strains after insecticide selection, aligning with findings from prior studies[
47]. Interestingly, these genes do not exhibit upregulation in response to a single pressure generation and are found after four to five generations.
Transcriptomic studies on lambda-cyhalothrin resistance have only been performed on field-collected mosquitoes that have survived insecticide applications for a few generations[
48]. Our insecticide-pressure procedure entails some aspects that should be highlighted. As stated[
47], some genes do not exhibit upregulation in response to a single pressure generation but are found after four to five generations.
Additionally, a comparative transcriptomic analysis of
Ae. aegypti, explored gene regulation across various time points following exposure to permethrin and revealed that after 24 hours of insecticide exposure, there was a notable shift in the number of upregulated (371) and downregulated genes (476)[
49]. This suggests a temporal dynamic in the molecular response to insecticide exposure that has to be encompassed, with potential implications for understanding the insecticide's impact on gene regulation over time. In this sense, it is plausible that the genes identified in our study are associated with long-term exposure responses to insecticide, aligning with previous research findings[
47,
49]. The transcriptional response to insecticides in resistant mosquitoes involves a complex pattern of upregulation and downregulation of detoxification genes (
Figure 6). This suggests that the net production of transcripts, and therefore the overall enzymatic activity detected by biochemical assays, remains relatively stable despite these opposing changes. For example, a study of multiple resistant strains of
Ae. aegypti reported that CYPs are involved in insecticide resistance; however, their MFO activity was not different between contrasting phenotypes[
39]. This emphasizes that solely assessing enzymatic activity may not consistently identify enzymes as responsible for insecticide resistance, challenging the conventional belief associating heightened enzyme activity with resistance mechanisms. Therefore, these studies should be conducted with functional genomics approaches to demonstrate the natural role of new genes in resistance.
We hypothesize that the AF13WP strain may represent an early-stage mechanism of resistance that hasn´t lost its enzymatic activity. Furthermore, with long-term exposure, these enzymes and mutations become less relevant and more costly, opting for a more energy-efficient state, as shown by the AF13P strain. It retains specific genes that could contribute to resistance. These transcripts are further enhanced and preserved in the AF13P strain.
4.3. Highly Enriched Constituents of the Cuticle in Response to Prolonged Exposure to Lambda-Cyhalothrin
It is known that the cuticle is the primary barrier that insecticides must overcome to anchor to their molecular targets physically. The enlargement or modification of structural components of this barrier significantly increases the time required to act upon VGSC protein, making it difficult to achieve its intended effect[
50,
51]. Our findings suggest this mechanism may play a role in the lambda-cyhalothrin highly resistant AF13P strain. Thus, it is not surprising that we found upregulation of cuticle genes (
Figure 6) and enrichment of terms related to "structural constituent of the cuticle” GO:0042302 (
Figure 5). Genes AAEL007739 and AAEL011504 code for pupal structural constituents, while AAEL013380 codes for adult structural constituents (
Figure 6 and
Supplementary Table S1). According to the literature, these genes have mixed responses and implications. AAEL011504 was significantly upregulated in mosquitoes infected with Zika virus and Wolbachia[
52]. AAEL013380 putative adult cuticle protein has an ortholog in
Anopheles albimanus (AALB005312) from the family of cuticular proteins RR-1[
53]. It has also been identified as down-regulated in laboratory-selected strains to
Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis toxins[
54]. This role of cuticle genes and their mixed cocktail of responses have to be elucidated in more detail as modifications in these proteins could modify the interconnection between hard, intersegmental, and soft cuticles, providing a complicated environment for insecticide passage[
55].
Cuticle modifications are not thought to be a primary mechanism of insecticide resistance, as they are insufficient to elevate the resistance[
55]. However, experiments are needed to confirm the relative contribution of this resistance mechanism to overall insecticide resistance[
51]. One approach could be to overregulate cuticle protein genes within the background of a susceptible strain such as Rockefeller and test whether RR rises.
4.4. Resistant Mosquitos Exhibit Down-Regulation of Proteases and Transport Electron Chain Subunits
Proteases are a group of enzymes with multiple functions across insects, including development and digestion. They act by hydrolyzing peptide bonds to separate amino acids and facilitate digestion[
56]. Some insecticides act by inhibiting midgut proteases that are fundamental for feeding processes[
57]. The insecticide lambda-cyhalothrin has shown different effects on proteases. In
Periplaneta americana, all cytoplasmic proteases were increased after treatment with this insecticide, but levels of lysosomal proteases in the head and thorax[
58]were reduced. In a more related dipteran,
Culex pipiens protease levels fall after lambda-cyhalothrin treatment[
59]. Our study mainly showed down-regulation among protease genes (
Figure 6), which may contribute to developing a resistant phenotype that offers some degree of protection against insecticides and the oxidative damage resulting from their effects.
On the other side, oxidative stress is caused by an imbalance between producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and a system's capacity to detoxify these species. Many insecticides, including lambda-cyhalothrin, induce oxidative stress by increasing the accumulation of ROS. Studies on
Myzus persicae have indicated that exposure to lambda-cyhalothrin results in oxidative damage[
60]. In Chinese honeybees, a serine protease is involved in defending against oxidative stress; notably, a study found that lambda-cyhalothrin treatment dramatically reduced the expression of this protease[
61]. Future studies must be conducted to answer this question.
We also observed a marked decline in the regulation of Cytochrome c oxidase subunits I, III, and NADH dehydrogenase subunits 2, 3, and 4L (
Supplementary Table S4 and
Figure 6). Accordingly, enrichment scores of GO analysis explored the cytochrome c oxidase activity, NADH dehydrogenase activity, ATP synthesis coupled electron transport, and respiratory chain terms (
Figure 5B). ROS are produced in reactions in which the electron transport chain plays a primary role[
62]. This downregulation of genes indicates shifts in enzymatic activities and metabolic processes that reduce energy production[
49], resulting in less oxidative stress.
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit-3 levels were detected as elevated in
Ae. aegypti following permethrin exposure[
63]. In the pupation of
Bactrocera dorsalis, down-regulation of NADH dehydrogenase and cytochrome c oxidase genes has also been identified[
64].
Exploring the implications of electron chain transporter genes could account for the reduction in fitness observed in many resistant strains. Drops in respiration rate after exposure to pyrethroid insecticides, similar to those observed in the Malaria vector
Anopheles coluzzi[
65], could explain this.
Overall, our data presents a novel perspective on the response of Aedes aegypti to lambda-cyhalothrin insecticide. We have observed that the response varies depending on the exposure time. Initially, when mosquitoes are exposed to insecticides, they modulate the expression of metabolic enzymes and gain some point mutations in the sodium channel genes. After long-term exposure, the mosquitoes respond to insecticides by expressing different proteins involved in the cuticle, energetic metabolism, and protease synthesis.
In previous work[
7], our group has delved into the microbiota as a resistance mechanism in this Acacías strain and showed that removing its bacteriome produces a significant drop in resistance. We cannot rule out the possible involvement of microbiota in this strain's resistance, especially its involvement in the high RR of AF13P. This novel understanding of the response mechanisms, including the role of enzymatic activity, opens up new avenues for further research and exploration.
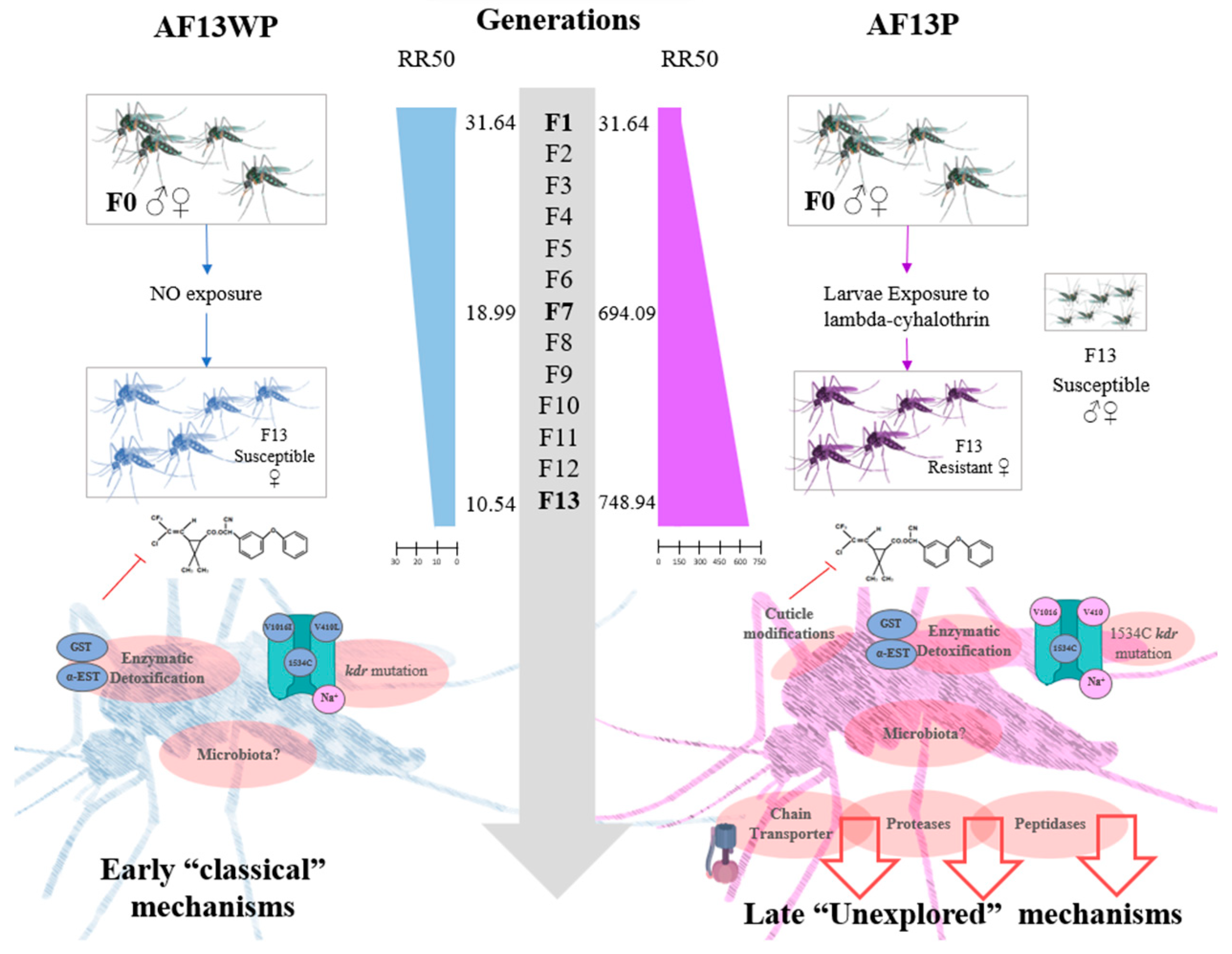
Finally, we propose a modified model that incorporates novel mechanisms that complement the established insecticide resistance models based on
kdr and metabolic resistance[
10]. These mechanisms differ in their time of expression and the appearance of resistance factors in the insect, affirming the vast divergence of insecticide resistance mechanisms yet to be explored (
Figure 7).
5. Conclusions
This study presents a novel perspective on the response of Aedes aegypti to lambda-cyhalothrin insecticide. Long-term exposure leads mosquitoes to express different proteins related to the cuticle, energetic metabolism, and protease synthesis. We propose a new model that incorporates these novels, yet complementary, mechanisms into the established insecticide resistance literature based largely on kdr and metabolic resistance. These data now provide the basis for expanding our understanding of complex mechanisms used by insects to resist insecticide treatments.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Table S1: Differential gene expression between AF13P vs AF13WP Aedes aegypti mosquitoes; Table S2: Functional clustering using DAVID of upregulated genes; Table S3: Functional clustering using DAVID of downregulated genes; Table S4: Genes regulated associated with insecticide resistance; Table S5: Annotation of regulated genes and its association with DAVID categories.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M., A.M.M.J., and O.T.C.; Methodology, A.M., Y.G., A.M.M.J, G.F., and O.T.C.; Investigation, A.M., Y.G., A.M.M.J., G.F., and O.T.C., Writing – original draft, A.M; Writing, review and editing, A.M., A.M.M.J., C.L., G.F., O.T.C.; data curation, A.M., A.M.M.J and G.F.; Project administration, O.T.C.; Supervision, O.T.C.; Funding acquisition, O.T.C. and C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the University of Antioquia, UdeA, Grant CPT-2005, and an NSERC Discovery grant to CL.
Data Availability Statement
All data presented in this article are available in five Excel files (see Supplementary Table Files 1 to 5). Moreover, analyses of transcriptome data are provided. The RNAseq datasets generated for this study are in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) DataSets (
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gds) under the accession number GSE254270.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Vector-Borne Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/vector-borne-diseases (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Dengue – the Region of the Americas. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2023-DON475 (accessed on 18 September 2023).
- Maestre-Serrano, R.; Flórez-Rivadeneira, Z.; Castro-Camacho, J.M.; Soto-Arenilla, E.; Gómez-Camargo, D.; Pareja-Loaiza, P.; Ponce-Garcia, G.; Juache-Villagrana, A.E.; Flores, A.E. Spatial Distribution of Pyrethroid Resistance and Kdr Mutations in Aedes Aegypti from La Guajira, Colombia. Insects 2022, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyes, C.L.; Vontas, J.; Martins, A.J.; Ng, L.C.; Koou, S.Y.; Dusfour, I.; Raghavendra, K.; Pinto, J.; Corbel, V.; David, J.-P.; et al. Contemporary Status of Insecticide Resistance in the Major Aedes Vectors of Arboviruses Infecting Humans. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases 2017, 11, e0005625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrato, I.M.; Moreno-Aguilera, D.; Caicedo, P.A.; Orobio, Y.; Ocampo, C.B.; Maestre-Serrano, R.; Peláez-Carvajal, D.; Ahumada, M.L. Vector Competence of Lambda-Cyhalothrin Resistant Aedes Aegypti Strains for Dengue-2, Zika and Chikungunya Viruses in Colombia. PLOS ONE 2022, 17, e0276493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, A.; Penilla, R.P.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Ocampo, C.B. Mechanisms of Pyrethroid Resistance in Aedes (Stegomyia) Aegypti from Colombia. Acta Tropica 2019, 191, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo-Cortés, A.; Mejia-Jaramillo, A.M.; Granada, Y.; Coatsworth, H.; Lowenberger, C.; Triana-Chavez, O. The Midgut Microbiota of Colombian Aedes Aegypti Populations with Different Levels of Resistance to the Insecticide Lambda-Cyhalothrin. Insects 2020, 11, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granada, Y.; Mejía-Jaramillo, A.M.; Strode, C.; Triana-Chavez, O. A Point Mutation V419L in the Sodium Channel Gene from Natural Populations of Aedes Aegypti Is Involved in Resistance to λ-Cyhalothrin in Colombia. Insects 2018, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Obando, O.A.; Bona, A.C.D.; Duque L., J. E.; Navarro-Silva, M.A. Insecticide Resistance and Genetic Variability in Natural Populations of Aedes (Stegomyia) Aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) from Colombia. Zoologia (Curitiba) 2015, 32, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amichot, M.; Brun-Barale, A.; Haddi, K.; Nauen, R.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Tarès, S. Current Knowledge on the Origin of Insecticide Resistance Mechanisms: The Tip of the Iceberg? entomologia 2023, 43, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre-Serrano, R.; Pareja-Loaiza, P.; Gomez Camargo, D.; Ponce-García, G.; Flores, A.E. Co-Occurrence of V1016I and F1534C Mutations in the Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel and Resistance to Pyrethroids in Aedes Aegypti (L.) from the Colombian Caribbean Region. Pest Management Science 2019, 75, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ommer Dahala, 2019 Knockdown Resistance Mutations Contributing to Pyrethroid Resistance in Aedes Aegypti Population, Saudi Arabia.Pdf. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Kfg3GhOpJRXaa-wL4U_FUfZpn8VPAwHS/view?usp=drive_open&usp=embed_facebook (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Pareja-Loaiza, P.X.; Varon, L.S.; Vega, G.R.; Gómez-Camargo, D.; Maestre-Serrano, R.; Lenhart, A. Mechanisms Associated with Pyrethroid Resistance in Populations of Aedes Aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) from the Caribbean Coast of Colombia. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0228695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, J.A.; Fan, R.; Naz, H.; Bamisile, B.S.; Hafeez, M.; Ghani, M.I.; Wei, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X. Insights into Insecticide-Resistance Mechanisms in Invasive Species: Challenges and Control Strategies. Front Physiol 2023, 13, 1112278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.-P.; Faucon, F.; Chandor-Proust, A.; Poupardin, R.; Riaz, M.A.; Bonin, A.; Navratil, V.; Reynaud, S. Comparative Analysis of Response to Selection with Three Insecticides in the Dengue Mosquito Aedes Aegypti Using mRNA Sequencing. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granada, Y.; Mejía-Jaramillo, A.M.; Zuluaga, S.; Triana-Chávez, O. Molecular Surveillance of Resistance to Pyrethroids Insecticides in Colombian Aedes Aegypti Populations. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2021, 15, e0010001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, N. Mosquito Larval Bioassays. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2023, 2023, pdb.prot108040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.L.; Jones, M.M.; Olguin, E.; Alberts, B. Bioassays with Arthropods; 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Third edition. | Boca Raton : CRC Press, 2017., 2017; ISBN 978-1-315-37377-5.
- Collins, F.H.; Mendez, M.A.; Rasmussen, M.O.; Mehaffey, P.C.; Besansky, N.J.; Finnerty, V. A Ribosomal RNA Gene Probe Differentiates Member Species of the Anopheles Gambiae Complex. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1987, 37, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metodologia Para Quantificação de Atividade de Enzimas Relacionadas Com a Resistência a Inseticidas Em Aedes Aegypti - Brasília DF — Ministério Da Saúde Available online:. Available online: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/svsa/dengue/manual_novo_protocolo_dengue.pdf/view (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Pinto, J.; Palomino, M.; Mendoza-Uribe, L.; Sinti, C.; Liebman, K.A.; Lenhart, A. Susceptibility to Insecticides and Resistance Mechanisms in Three Populations of Aedes Aegypti from Peru. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babraham Bioinformatics - FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 29 October 2022).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, B.J.; Dudchenko, O.; Kingan, S.B.; Koren, S.; Antoshechkin, I.; Crawford, J.E.; Glassford, W.J.; Herre, M.; Redmond, S.N.; Rose, N.H.; et al. Improved Reference Genome of Aedes Aegypti Informs Arbovirus Vector Control. Nature 2018, 563, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A Web Server for Functional Enrichment Analysis and Functional Annotation of Gene Lists (2021 Update). Nucleic Acids Research 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salivary Secreted Peptide - Aedes Aegypti (Yellowfever Mosquito) | UniProtKB | UniProt. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/Q1HRS2/entry (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Uemura, N.; Itokawa, K.; Komagata, O.; Kasai, S. Recent Advances in the Study of Knockdown Resistance Mutations in Aedes Mosquitoes with a Focus on Several Remarkable Mutations. Current Opinion in Insect Science 2024, 63, 101178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Nayak, B.; Xiong, L.; Xie, C.; Dong, Y.; You, M.; Yuchi, Z.; You, S. The Role of Insect Cytochrome P450s in Mediating Insecticide Resistance. Agriculture 2022, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, R.; Bass, C.; Feyereisen, R.; Vontas, J. The Role of Cytochrome P450s in Insect Toxicology and Resistance. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2022, 67, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.B.; Silva, J.J.; Chen, C.; Harrington, L.C.; Scott, J.G. Fitness Costs of Individual and Combined Pyrethroid Resistance Mechanisms, Kdr and CYP-Mediated Detoxification, in Aedes Aegypti. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2021, 15, e0009271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.R.; Dressel, A.E.; Silva, J.J.; Scott, J.G. A Globally Distributed Insecticide Resistance Allele Confers a Fitness Cost in the Absence of Insecticide in Aedes Aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae), the Yellow Fever Mosquito. Journal of Medical Entomology 2023, 60, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.J.; Fisher, C.R.; Dressel, A.E.; Scott, J.G. Fitness Costs in the Presence and Absence of Insecticide Use Explains Abundance of Two Common Aedes Aegypti Kdr Resistance Alleles Found in the Americas. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2023, 17, e0011741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Maloof, F.Z.; Saavedra-Rodriguez, K.; Elizondo-Quiroga, A.E.; Lozano-Fuentes, S.; Iv, W.C.B. Coevolution of the Ile1,016 and Cys1,534 Mutations in the Voltage Gated Sodium Channel Gene of Aedes Aegypti in Mexico. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases 2015, 9, e0004263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, L.P.; Linss, J.G.B.; Lima-Camara, T.N.; Belinato, T.A.; Peixoto, A.A.; Lima, J.B.P.; Valle, D.; Martins, A.J. Assessing the Effects of Aedes Aegypti Kdr Mutations on Pyrethroid Resistance and Its Fitness Cost. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, W.C.; Snell, T.K.; Saavedra-Rodriguez, K.; Kading, R.C.; Campbell, C.L. From Global to Local-New Insights into Features of Pyrethroid Detoxification in Vector Mosquitoes. Insects 2021, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestre S, R.; Rey V, G.; De Las Salas A, J.; Vergara S, C.; Santacoloma V, L.; Goenaga O, S.; Carrasquilla F, M.C. Susceptibility Status of Aedes Aegypti to Insecticides in Atlántico (Colombia). Revista Colombiana de Entomología 2010, 36, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo, C.B.; Salazar-Terreros, M.J.; Mina, N.J.; McAllister, J.; Brogdon, W. Insecticide Resistance Status of Aedes Aegypti in 10 Localities in Colombia. Acta Tropica 2011, 118, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelboin, Y.; Wang, L.; Giai Gianetto, Q.; Choumet, V.; Gaborit, P.; Issaly, J.; Guidez, A.; Douché, T.; Chaze, T.; Matondo, M.; et al. CYP450 Core Involvement in Multiple Resistance Strains of Aedes Aegypti from French Guiana Highlighted by Proteomics, Molecular and Biochemical Studies. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0243992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, J.-P.; Ismail, H.M.; Chandor-Proust, A.; Paine, M.J.I. Role of Cytochrome P450s in Insecticide Resistance: Impact on the Control of Mosquito-Borne Diseases and Use of Insecticides on Earth. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2013, 368, 20120429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlidi, N.; Vontas, J.; Van Leeuwen, T. The Role of Glutathione S-Transferases (GSTs) in Insecticide Resistance in Crop Pests and Disease Vectors. Current Opinion in Insect Science 2018, 27, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Mertz, R.W.; Smith, L.B.; Scott, J.G. Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analysis of Pyrethroid Resistance in the CKR Strain of Aedes Aegypti. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2021, 15, e0009871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucon, F.; Gaude, T.; Dusfour, I.; Navratil, V.; Corbel, V.; Juntarajumnong, W.; Girod, R.; Poupardin, R.; Boyer, F.; Reynaud, S.; et al. In the Hunt for Genomic Markers of Metabolic Resistance to Pyrethroids in the Mosquito Aedes Aegypti: An Integrated next-Generation Sequencing Approach. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2017, 11, e0005526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, I.H.; Kamgang, B.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Riveron, J.M.; Irving, H.; Wondji, C.S. Pyrethroid Resistance in Malaysian Populations of Dengue Vector Aedes Aegypti Is Mediated by CYP9 Family of Cytochrome P450 Genes. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2017, 11, e0005302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra-Rodriguez, K.; Beaty, M.; Lozano-Fuentes, S.; Denham, S.; Garcia-Rejon, J.; Reyes-Solis, G.; Machain-Williams, C.; Loroño-Pino, M.A.; Flores-Suarez, A.; Ponce-Garcia, G.; et al. Local Evolution of Pyrethroid Resistance Offsets Gene Flow Among Aedes Aegypti Collections in Yucatan State, Mexico. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2015, 92, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra-Rodriguez, K.; Campbell, C.L.; Lozano, S.; Penilla-Navarro, P.; Lopez-Solis, A.; Solis-Santoyo, F.; Rodriguez, A.D.; Perera, R.; Black IV, W.C. Permethrin Resistance in Aedes Aegypti: Genomic Variants That Confer Knockdown Resistance, Recovery, and Death. PLoS Genet 2021, 17, e1009606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra-Rodriguez, K.; Strode, C.; Flores, A.E.; Garcia-Luna, S.; Reyes-Solis, G.; Ranson, H.; Hemingway, J.; Black, W.C. Differential Transcription Profiles in Aedes Aegypti Detoxification Genes Following Temephos Selection. Insect Mol Biol 2014, 23, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derilus, D.; Impoinvil, L.M.; Muturi, E.J.; McAllister, J.; Kenney, J.; Massey, S.E.; Hemme, R.; Kothera, L.; Lenhart, A. Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Insecticide-Resistant Aedes Aegypti from Puerto Rico Reveals Insecticide-Specific Patterns of Gene Expression. Genes 2023, 14, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, L.K.; Attardo, G.M. Time-Series Analysis of Transcriptomic Changes Due to Permethrin Exposure Reveals That Aedes Aegypti Undergoes Detoxification Metabolism over 24 h. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 16564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, R.R.; Kumar, S. Cuticular Thickening Associated with Insecticide Resistance in Dengue Vector, Aedes Aegypti L. Int J Trop Insect Sci 2021, 41, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balabanidou, V.; Grigoraki, L.; Vontas, J. Insect Cuticle: A Critical Determinant of Insecticide Resistance. Current Opinion in Insect Science 2018, 27, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, M.; Ramos, L.F.C.; Murillo, J.R.; Torres, A.; de Carvalho, S.S.; Domont, G.B.; de Oliveira, D.M.P.; Mesquita, R.D.; Nogueira, F.C.S.; Maciel-de-Freitas, R.; et al. Comprehensive Quantitative Proteome Analysis of Aedes Aegypti Identifies Proteins and Pathways Involved in Wolbachia Pipientis and Zika Virus Interference Phenomenon. Frontiers in Physiology 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannini, L.; Willis, J.H. Localization of RR-1 and RR-2 Cuticular Proteins within the Cuticle of Anopheles Gambiae. Arthropod Struct Dev 2017, 46, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Després, L.; Stalinski, R.; Tetreau, G.; Paris, M.; Bonin, A.; Navratil, V.; Reynaud, S.; David, J.-P. Gene Expression Patterns and Sequence Polymorphisms Associated with Mosquito Resistance to Bacillus Thuringiensis Israelensis Toxins. BMC Genomics 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, E.; Chrissian, C.; Rankin-Turner, S.; Wear, M.; Camacho, E.; Broderick, N.A.; McMeniman, C.J.; Stark, R.E.; Casadevall, A. Cuticular Profiling of Insecticide Resistant Aedes Aegypti. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, A.; Ghadamyari, M.; Sajedi, R.H.; Sharifi, M.; Kouchaki, B. Identification and Partial Characterization of Midgut Proteases in the Lesser Mulberry Pyralid, Glyphodes Pyloalis. J Insect Sci 2013, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharat Nareshkumar, S.M.A.; Hari Chand Sharma, K.S. Evaluation of Flubendiamide-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Metabolic Changes in Helicoverpa Armigera (Hubner).
- (12) (PDF) In Vivo Effects of Lambda-Cyhalothrin on Proteases of Various Body Compartments of Periplaneta Americana Adults. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258022867_In_vivo_Effects_of_Lambda-cyhalothrin_on_Proteases_of_Various_Body_Compartments_of_Periplaneta_americana_Adults (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Shaurub, E.; El-Aziz, N.A. Biochemical Effects of Lambda-Cyhalothrin and Lufenuron on Culex Pipiens L. (Diptera: Culicidae). International Journal of Mosquito Research 2015.
- Dong, B.; Liu, X.-Y.; Li, B.; Li, M.-Y.; Li, S.-G.; Liu, S. A Heat Shock Protein Protects against Oxidative Stress Induced by Lambda-Cyhalothrin in the Green Peach Aphid Myzus Persicae. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology 2022, 181, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, B.; Guo, X. Role of a Serine Protease Gene (AccSp1) from Apis Cerana Cerana in Abiotic Stress Responses and Innate Immunity. Cell Stress and Chaperones 2019, 24, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sule, R.O.; Condon, L.; Gomes, A.V. A Common Feature of Pesticides: Oxidative Stress—The Role of Oxidative Stress in Pesticide-Induced Toxicity. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2022, 2022, e5563759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridgeon, J.W.; Becnel, J.J.; Clark, G.G.; Linthicum, K.J. Permethrin Induces Overexpression of Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit 3 in <I>Aedes Aegypti</I>. me 2009, 46, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.-H.; Hou, Q.-L.; Dou, W.; Wei, D.-D.; Yue, Y.; Yang, R.-L.; Yu, S.-F.; De Schutter, K.; Smagghe, G.; Wang, J.-J. RNA-Seq Analysis of Gene Expression Changes during Pupariation in Bactrocera Dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae). BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingham, V.A.; Tennessen, J.A.; Lucas, E.R.; Elg, S.; Yates, H.C.; Carson, J.; Guelbeogo, W.M.; Sagnon, N.; Hughes, G.L.; Heinz, E.; et al. Integration of Whole Genome Sequencing and Transcriptomics Reveals a Complex Picture of the Reestablishment of Insecticide Resistance in the Major Malaria Vector Anopheles Coluzzii. PLOS Genetics 2021, 17, e1009970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).