Submitted:
13 December 2024
Posted:
13 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
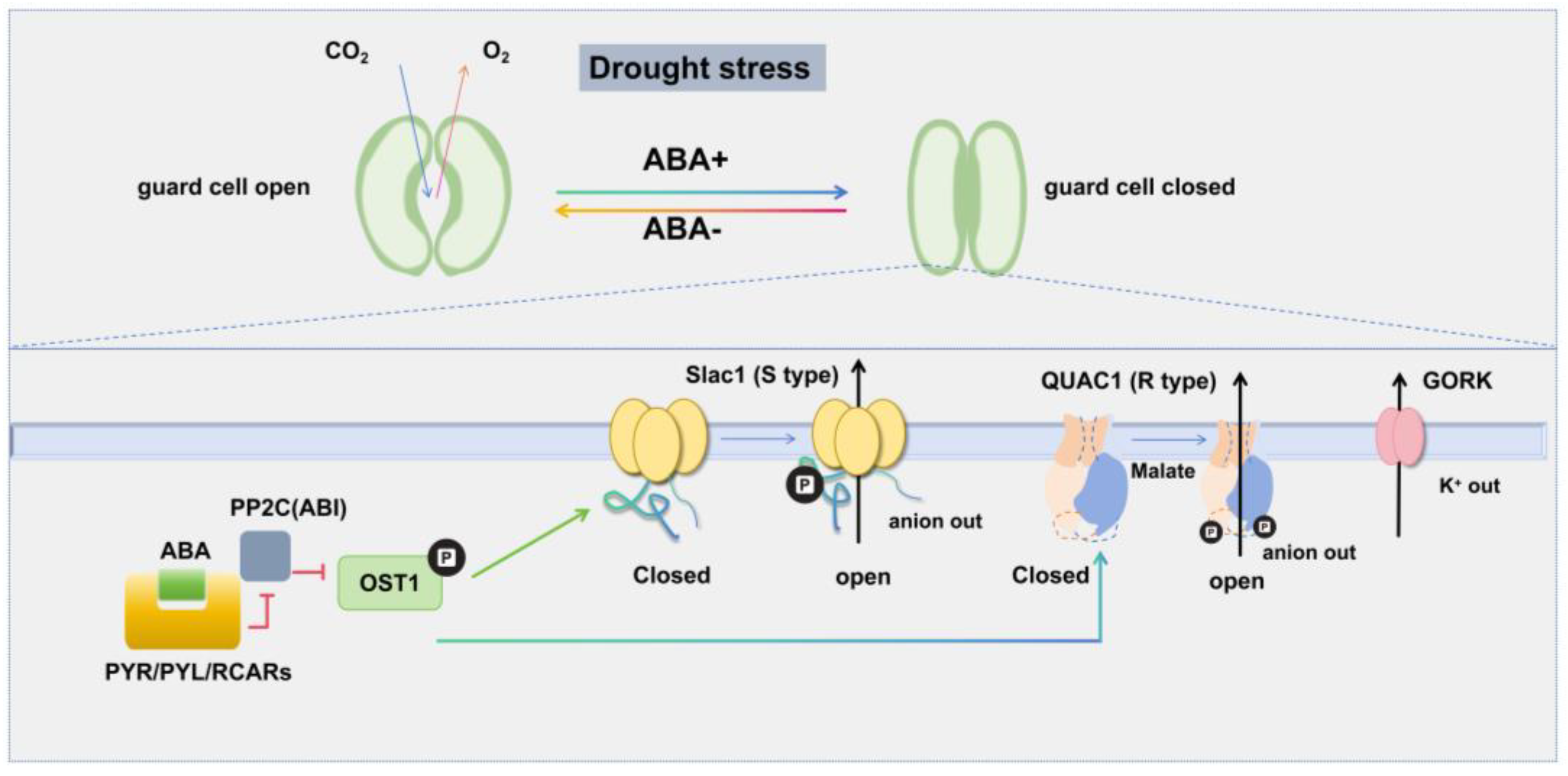
2. Drought Stress
2.1. Ion Channels Mediating Stomatal Closure in Response to Drought Stress
2.2. Drought Stress Receptor - OSCA1
3. Salt Stress
3.1. High-Affinity Potassium Transporters (HKT) in Rice
3.2. Mechanism of Na+ Transport Regulation via the SOS Pathway in Rice
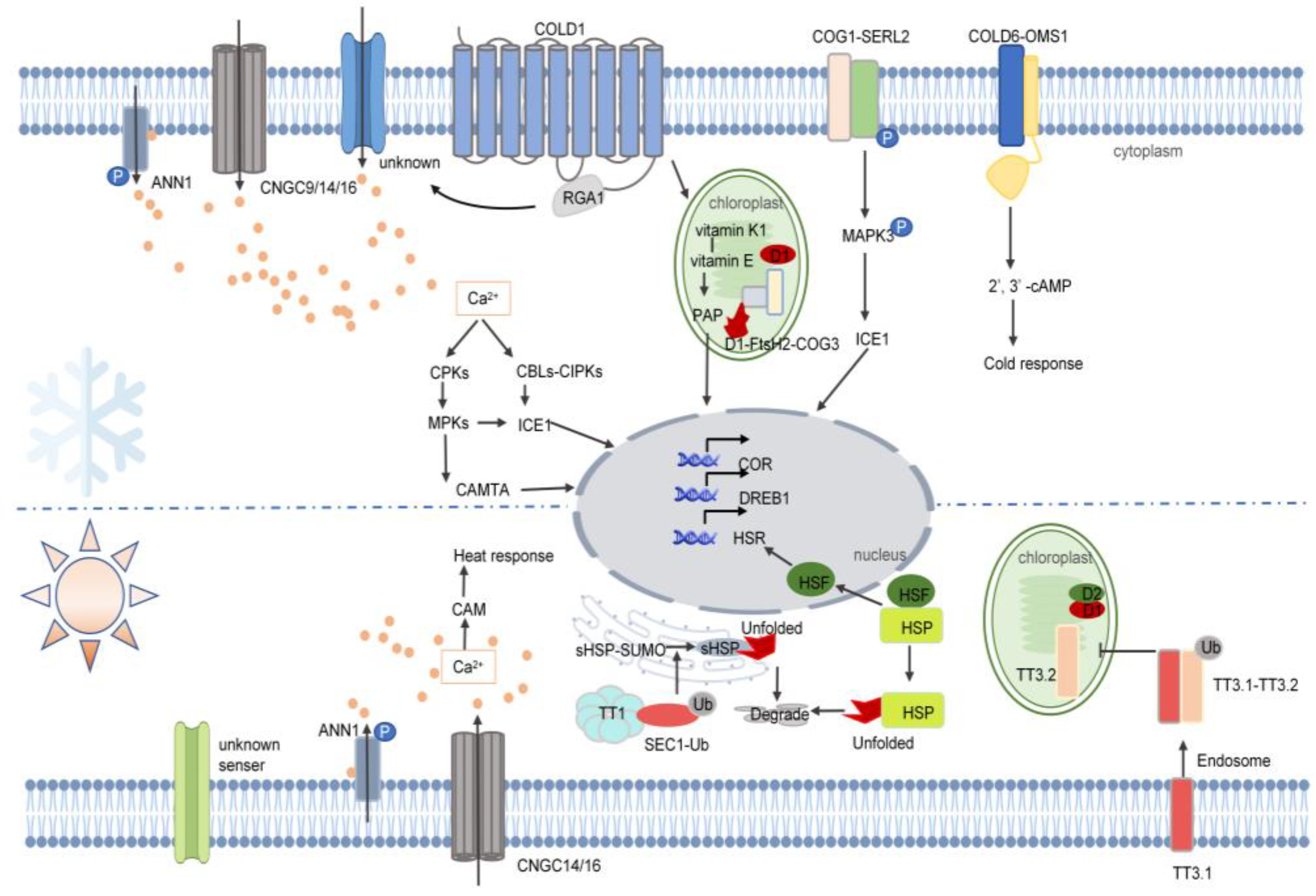
4. Temperature Stress
4.1. Cold Stress
4.2. Heat Stress
5. Heavy Metal Stress
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, R.; Deng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Guo, J.; Qiu, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; et al. Rice functional genomics: decades’ efforts and roads ahead. Sci China Life Sci 2022, 65, 33–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, M.; Turkyilmaz Unal, B.; Garcia-Caparros, P.; Khursheed, A.; Gul, A.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Osmoregulation and its actions during the drought stress in plants. Physiol Plant 2021, 172, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, A.; Lian, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, G. Molecular Mechanisms and Regulatory Pathways Underlying Drought Stress Response in Rice. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhou, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, P. Regulation of Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Mahat, J.; Shrestha, J.; K, C.M.; Paudel, K. Influence of high-temperature stress on rice growth and development. A review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, N.; Ozgur, R.; Turkan, I.; Uzilday, B. Heavy metal toxicity leads to accumulation of insoluble proteins and induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-specific unfolded protein response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2024, 31, 53206–53218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Qi, H.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; et al. The OsFTIP6-OsHB22-OsMYBR57 module regulates drought response in rice. Mol Plant 2022, 15, 1227–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Rico-Medina, A.; Cano-Delgado, A.I. The physiology of plant responses to drought. Science 2020, 368, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinocur, B.; Altman, A. Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to abiotic stress: achievements and limitations. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2005, 16, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, J.; Inze, D.; Nelissen, H.; Saibo, N.J.M. Source-Sink Regulation in Crops under Water Deficit. Trends Plant Sci 2019, 24, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, F.; Li, Z.; Waadt, R.; Schroeder, J.I. SnapShot: Abscisic Acid Signaling. Cell 2017, 171, 1708–1708e1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, J.I.; Allen, G.J.; Hugouvieux, V.; Kwak, J.M.; Waner, D. Guard Cell Signal Transduction. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 2001, 52, 627–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.K.; Takahashi, Y.; Munemasa, S.; Merilo, E.; Laanemets, K.; Waadt, R.; Pater, D.; Kollist, H.; Schroeder, J.I. Abscisic acid-independent stomatal CO(2) signal transduction pathway and convergence of CO(2) and ABA signaling downstream of OST1 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115, E9971–E9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Chinnusamy, V.; Rodrigues, A.; Rubio, S.; Antoni, R.; Park, S.Y.; Cutler, S.R.; Sheen, J.; Rodriguez, P.L.; Zhu, J.K. In vitro reconstitution of an abscisic acid signalling pathway. Nature 2009, 462, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, B.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Gong, Z. Protein kinases in plant responses to drought, salt, and cold stress. J Integr Plant Biol 2021, 63, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, K.E.; de Souza, W.R.; Santiago, T.R.; Sampaio, B.L.; Ribeiro, A.P.; Cotta, M.G.; da Cunha, B.; Marraccini, P.R.R.; Kobayashi, A.K.; Molinari, H.B.C. Identification and characterization of core abscisic acid (ABA) signaling components and their gene expression profile in response to abiotic stresses in Setaria viridis. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, I.; Gomez-Porras, J.L.; Riano-Pachon, D.M.; Hedrich, R.; Geiger, D. Molecular Evolution of Slow and Quick Anion Channels (SLACs and QUACs/ALMTs). Front Plant Sci 2012, 3, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, K.; Rajagopalan, N.; Ching, J.C.H.; Loewen, M.C.; Loewen, M.E. The malate-activated ALMT12 anion channel in the grass Brachypodium distachyon is co-activated by Ca(2+)/calmodulin. J Biol Chem 2019, 294, 6142–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalakas, P.; Nuhkat, M.; Vahisalu, T.; Merilo, E.; Brosche, M.; Kollist, H. Combined action of guard cell plasma membrane rapid- and slow-type anion channels in stomatal regulation. Plant Physiol 2021, 187, 2126–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Kim, J.J.; Shin, S.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Yoon, H.S. ASR Enhances Environmental Stress Tolerance and Improves Grain Yield by Modulating Stomatal Closure in Rice. Front Plant Sci 2019, 10, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, K.; Hashimura, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Negi, J.; Iba, K. Contribution of the S-type Anion Channel SLAC1 to Stomatal Control and Its Dependence on Developmental Stage in Rice. Plant Cell Physiol 2017, 58, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, K.; Hirotsuka, S.; Kumamaru, T.; Iba, K. Increased leaf photosynthesis caused by elevated stomatal conductance in a rice mutant deficient in SLAC1, a guard cell anion channel protein. J Exp Bot 2012, 63, 5635–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.J.; Qi, G.N.; Gao, Q.F.; Wang, H.Q.; Yao, F.Y.; Hussain, J.; Wang, Y.F. Protein kinase OsSAPK8 functions as an essential activator of S-type anion channel OsSLAC1, which is nitrate-selective in rice. Planta 2016, 243, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.N.; Kashtoh, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhen, G.X.; Li, Q.Y.; Tang, L.H.; Gao, H.L.; Zhang, C.R.; Qin, L.; Su, M.; et al. Structure and activity of SLAC1 channels for stomatal signaling in leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ding, Y.; Qu, L.; Li, X.; Lai, Q.; Zhao, P.; Gao, Y.; Xiang, C.; Cang, C.; Liu, X.; et al. Structure of the Arabidopsis guard cell anion channel SLAC1 suggests activation mechanism by phosphorylation. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Delhaize, E.; Ryan, P.R. Altered Expression of a Malate-Permeable Anion Channel, OsALMT4, Disrupts Mineral Nutrition. Plant Physiol 2017, 175, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, Y.; Wu, C.; Long, Y.; Luo, S.; Ma, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Ren, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. OsALMT7 Maintains Panicle Size and Grain Yield in Rice by Mediating Malate Transport. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Tang, L.H.; Xu, J.S.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.R.; Wang, M.H.; Liu, X.L.; Li, F.; Sun, F.; et al. Cryo-EM structure and electrophysiological characterization of ALMT from Glycine max reveal a previously uncharacterized class of anion channels. Sci Adv 2022, 8, eabm3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, F.; Wen, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhu, T.; Zhuo, W.; Jin, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of the OSCA gene family in rice. BMC Plant Biol 2015, 15, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Wen, Z.; Liu, J.; Xi, C.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, S. OsOSCA1.1 Mediates Hyperosmolality and Salt Stress Sensing in Oryza sativa. Biology (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Wen, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhuo, W.; Wang, F.; Xi, C.; Liu, J.; Gao, P.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Heterogeneous expression of plasma-membrane-localised OsOSCA1.4 complements osmotic sensing based on hyperosmolality and salt stress in Arabidopsis osca1 mutant. Cell Calcium 2020, 91, 102261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, K.; Heumann, J.M.; McGrath, A.P.; Kopcho, N.J.; Hsu, P.K.; Lee, C.W.; Mapes, J.H.; Garza, D.; Krishnan, S.; Morgan, G.P.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of OSCA1.2 from Oryza sativa elucidates the mechanical basis of potential membrane hyperosmolality gating. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 14309–14318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Jin, R.; Dai, F.; Ge, Y.; Ju, X.; Ma, X.; He, S.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Mechanical activation opens a lipid-lined pore in OSCA ion channels. Nature 2024, 628, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Kim, W.Y.; Yun, D.J. A New Insight of Salt Stress Signaling in Plant. Mol Cells 2016, 39, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol 2018, 217, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furumoto, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ohshima-Ichie, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Tsuchida-Iwata, Y.; Shimamura, M.; Ohnishi, J.; Hata, S.; Gowik, U.; Westhoff, P.; et al. A plastidial sodium-dependent pyruvate transporter. Nature 2011, 476, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Chen, X.; Xiao, F.; Lin, H.; Guo, Y. Insights into plant salt stress signaling and tolerance. J Genet Genomics 2024, 51, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaq, A.; Ali, A.; Safdar, L.B.; Zafar, M.M.; Rui, Y.; Shakeel, A.; Shaukat, A.; Ashraf, M.; Gong, W.; Yuan, Y. Salt stress induces physiochemical alterations in rice grain composition and quality. J Food Sci 2020, 85, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, C.; Lei, L.; Guo, H.; Zhou, S.; Xu, C.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Miao, Y.; Han, Y.; et al. Disease resistance conferred by components of essential chrysanthemum oil and the epigenetic regulation of OsTPS1. Sci China Life Sci 2023, 66, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabia, S.; Shah, M.N.A.; Sami, A.A.; Ghosh, A.; Islam, T. Identification and expression profiling of proline metabolizing genes in Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa to reveal their stress-specific transcript alteration. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 2021, 27, 1469–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Niu, X.; Yu, J.; Yan, J.; Gou, X.; Lu, B.R.; Liu, Y. Rice choline monooxygenase (OsCMO) protein functions in enhancing glycine betaine biosynthesis in transgenic tobacco but does not accumulate in rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Plant Cell Rep 2012, 31, 1625–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Jing, W.; Xiao, L.; Jin, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhang, W. The Rice High-Affinity Potassium Transporter1;1 Is Involved in Salt Tolerance and Regulated by an MYB-Type Transcription Factor. Plant Physiol 2015, 168, 1076–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, S.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Tran, S.T.H.; Katsuhara, M. Identification and Characterization of Rice OsHKT1;3 Variants. Plants (Basel) 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Mohamed, S.; Regnault, T.; Mieulet, D.; Guiderdoni, E.; Sentenac, H.; Very, A.A. Constitutive Contribution by the Rice OsHKT1;4 Na(+) Transporter to Xylem Sap Desalinization and Low Na(+) Accumulation in Young Leaves Under Low as High External Na(+) Conditions. Front Plant Sci 2020, 11, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.I.; Yamaji, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Okubo, K.; Ueno, H.; Costa, A.; Tanoi, K.; Matsumura, H.; Fujii-Kashino, M.; Horiuchi, T.; et al. OsHKT1;5 mediates Na(+) exclusion in the vasculature to protect leaf blades and reproductive tissues from salt toxicity in rice. Plant J 2017, 91, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, T.N.; Thomas, A.S.; Maathuis, F.J.M. A role for the OsHKT 2;1 sodium transporter in potassium use efficiency in rice. J Exp Bot 2020, 71, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oomen, R.J.; Benito, B.; Sentenac, H.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A.; Talon, M.; Very, A.A.; Domingo, C. HKT2;2/1, a K(+)-permeable transporter identified in a salt-tolerant rice cultivar through surveys of natural genetic polymorphism. Plant J 2012, 71, 750–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Costa, A.; Nakayama, H.; Katsuhara, M.; Shinmyo, A.; Horie, T. OsHKT2;2/1-mediated Na(+) influx over K(+) uptake in roots potentially increases toxic Na(+) accumulation in a salt-tolerant landrace of rice Nona Bokra upon salinity stress. J Plant Res 2016, 129, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, W.; Lin, H.; Luan, S.; Gao, J.; Lan, W. The Rice High-Affinity K(+) Transporter OsHKT2;4 Mediates Mg(2+) Homeostasis under High-Mg(2+) Conditions in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 2017, 8, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, X.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Shen, H. Structural insights into ion selectivity and transport mechanisms of Oryza sativa HKT2;1 and HKT2;2/1 transporters. Nat Plants 2024, 10, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Jia, Y.; Xu, X.; Fu, P.; Zhou, J.; Yang, G. Structural insights into the Oryza sativa cation transporters HKTs in salt tolerance. J Integr Plant Biol 2024, 66, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.S.; Guo, Y.; Dietrich, M.A.; Schumaker, K.S.; Zhu, J.K. Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99, 8436–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mahi, H.; Perez-Hormaeche, J.; De Luca, A.; Villalta, I.; Espartero, J.; Gamez-Arjona, F.; Fernandez, J.L.; Bundo, M.; Mendoza, I.; Mieulet, D.; et al. A Critical Role of Sodium Flux via the Plasma Membrane Na(+)/H(+) Exchanger SOS1 in the Salt Tolerance of Rice. Plant Physiol 2019, 180, 1046–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Tang, L.H.; Nie, J.W.; Zhang, C.R.; Han, X.; Li, Q.Y.; Qin, L.; Wang, M.H.; Huang, X.; Yu, F.; et al. Structure and activation mechanism of the rice Salt Overly Sensitive 1 (SOS1) Na(+)/H(+) antiporter. Nat Plants 2023, 9, 1924–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Dai, X.; Xu, Y.; Luo, W.; Zheng, X.; Zeng, D.; Pan, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; et al. COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice. Cell 2015, 160, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Huan, Q.; Xu, Y.; Qian, W.; Chong, K.; Zhang, J. Integrated global analysis reveals a vitamin E-vitamin K1 sub-network, downstream of COLD1, underlying rice chilling tolerance divergence. Cell Reports 2021, 36, 109397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Lu, S.; Li, Z.; Cheng, J.; Hu, P.; Zhu, T.; Wang, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; et al. CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE-GATED ION CHANNELs 14 and 16 Promote Tolerance to Heat and Chilling in Rice. Plant Physiol 2020, 183, 1794–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, N.; Los, D.A. Membrane Fluidity and Temperature Perception. Plant Physiol 1997, 115, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidokoro, S.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Transcriptional regulatory network of plant cold-stress responses. Trends in Plant Science 2022, 27, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wan, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Transcriptional activation and phosphorylation of OsCNGC9 confer enhanced chilling tolerance in rice. Mol Plant 2021, 14, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, J.; Lu, H.-P.; Liu, J.-X. The hot science in rice research: How rice plants cope with heat stress. Plant, Cell & Environment 2023, 46, 1087–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, S. Surviving and thriving: How plants perceive and respond to temperature stress. Developmental Cell 2022, 57, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Huan, Q.; Xu, Y.; Qian, W.; Chong, K.; Zhang, J. Integrated global analysis reveals a vitamin E-vitamin K1 sub-network, downstream of COLD1, underlying rice chilling tolerance divergence. Cell Rep 2021, 36, 109397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.J.; Min, M.K.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, D.Y.; Yoon, I.S.; Kwon, T.R.; Byun, M.O.; Kim, B.G. Ectopic Expression of OsDREB1G, a Member of the OsDREB1 Subfamily, Confers Cold Stress Tolerance in Rice. Front Plant Sci 2019, 10, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, P.; Si, T.; Hsu, C.C.; Wang, L.; Zayed, O.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, J.; Tao, W.A.; et al. MAP Kinase Cascades Regulate the Cold Response by Modulating ICE1 Protein Stability. Dev Cell 2017, 43, 618–629.e615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Ding, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Gong, Z.; Yang, S. Plasma Membrane CRPK1-Mediated Phosphorylation of 14-3-3 Proteins Induces Their Nuclear Import to Fine-Tune CBF Signaling during Cold Response. Molecular Cell 2017, 66, 117–128.e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutbrod, K.; Romer, J.; Dörmann, P. Phytol metabolism in plants. Progress in Lipid Research 2019, 74, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Gu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Qi, Y. Chloroplast-to-Nucleus Signaling Regulates MicroRNA Biogenesis in Arabidopsis. Developmental Cell 2019, 48, 371–382.e374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Xu, Y.; Cao, J.; Guo, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Liang, G.; et al. COLD6-OSM1 module senses chilling for cold tolerance via 2′,3′-cAMP signaling in rice. Molecular Cell 2024, 84, 4224–4238.e4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Liang, G.; Chong, K.; Xu, Y. The COG1-OsSERL2 complex senses cold to trigger signaling network for chilling tolerance in japonica rice. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Luo, S.; Li, Z.; Liang, G.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chong, K. COG3 confers the chilling tolerance to mediate OsFtsH2-D1 module in rice. New Phytologist 2024, 241, 2143–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Pan, G.; Zaidi, S.H.; Cheng, F. Involvement of Abscisic Acid in PSII Photodamage and D1 Protein Turnover for Light-Induced Premature Senescence of Rice Flag Leaves. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0161203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Han, T.; Yang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, D.; Ruan, X. The essential roles of OsFtsH2 in developing the chloroplast of rice. BMC Plant Biology 2021, 21, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Y.; Mu, X.R.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Shan, J.X.; Ye, W.W.; Lin, H.X. TT2 controls rice thermotolerance through SCT1-dependent alteration of wax biosynthesis. Nat Plants 2022, 8, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.F.; Kan, Y.; Shan, J.X.; Ye, W.W.; Dong, N.Q.; Guo, T.; Xiang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.B.; Li, Y.C.; et al. A genetic module at one locus in rice protects chloroplasts to enhance thermotolerance. Science 2022, 376, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-X.; Cao, Y.-J.; Yang, Y.-B.; Shan, J.-X.; Ye, W.-W.; Dong, N.-Q.; Kan, Y.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Lu, Z.-Q.; Guo, S.-Q.; et al. A TT1–SCE1 module integrates ubiquitination and SUMOylation to regulate heat tolerance in rice. Molecular Plant 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, K.D.; Berberich, T.; Ebersberger, I.; Nover, L. The plant heat stress transcription factor (Hsf) family: structure, function and evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012, 1819, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Chao, D.Y.; Wu, Y.; Huang, X.; Chen, K.; Cui, L.G.; Su, L.; Ye, W.W.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.C.; et al. Natural alleles of a proteasome α2 subunit gene contribute to thermotolerance and adaptation of African rice. Nat Genet 2015, 47, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meharg, A.A.; Rahman, M.M. Arsenic contamination of Bangladesh paddy field soils: implications for rice contribution to arsenic consumption. Environ Sci Technol 2003, 37, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uraguchi, S.; Tanaka, N.; Hofmann, C.; Abiko, K.; Ohkama-Ohtsu, N.; Weber, M.; Kamiya, T.; Sone, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Takanezawa, Y.; et al. Phytochelatin Synthase has Contrasting Effects on Cadmium and Arsenic Accumulation in Rice Grains. Plant Cell Physiol 2017, 58, 1730–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Li, B.; Li, Q.; Chen, G.; Chen, W.; Wang, F. Cadmium adsorption, chelation and compartmentalization limit root-to-shoot translocation of cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2017, 24, 11319–11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrnstorfer, I.A.; Manatschal, C.; Arnold, F.M.; Laederach, J.; Dutzler, R. Structural and mechanistic basis of proton-coupled metal ion transport in the SLC11/NRAMP family. Nature Communications 2017, 8, 14033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanadane, K.; Liziczai, M.; Markovic, D.; Straub, M.S.; Rosalen, G.T.; Udovcic, A.; Dutzler, R.; Manatschal, C. Structural and functional properties of a plant NRAMP-related aluminum transporter. Elife 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.; Wang, W.; Yamaji, N.; Fukuoka, S.; Che, J.; Ueno, D.; Ando, T.; Deng, F.; Hori, K.; Yano, M.; et al. Duplication of a manganese/cadmium transporter gene reduces cadmium accumulation in rice grain. Nature Food 2022, 3, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, D.; Sasaki, A.; Yamaji, N.; Miyaji, T.; Fujii, Y.; Takemoto, Y.; Moriyama, S.; Che, J.; Moriyama, Y.; Iwasaki, K.; et al. A polarly localized transporter for efficient manganese uptake in rice. Nature Plants 2015, 1, 15170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-D.; Huang, S.; Yamaji, N.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J.F.; Zhao, F.-J. OsNRAMP1 transporter contributes to cadmium and manganese uptake in rice. Plant, Cell & Environment 2020, 43, 2476–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyadate, H.; Adachi, S.; Hiraizumi, A.; Tezuka, K.; Nakazawa, N.; Kawamoto, T.; Katou, K.; Kodama, I.; Sakurai, K.; Takahashi, H.; et al. OsHMA3, a P1B-type of ATPase affects root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in rice by mediating efflux into vacuoles. New Phytologist 2011, 189, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Sun, Z. OsCD1 encodes a putative member of the cellulose synthase-like D sub-family and is essential for rice plant architecture and growth. Plant Biotechnology Journal 2011, 9, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Qu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, C.; Wang, J.; Gao, D.; Chen, C. ZINC TRANSPORTER5 and ZINC TRANSPORTER9 Function Synergistically in Zinc/Cadmium Uptake. Plant Physiol 2020, 183, 1235–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerinot, M.L. The ZIP family of metal transporters. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2000, 1465, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiuf, A.; Steffen, J.H.; Becares, E.R.; Grønberg, C.; Mahato, D.R.; Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Andersson, M.; Croll, T.; Gotfryd, K.; Gourdon, P. The two-domain elevator-type mechanism of zinc-transporting ZIP proteins. Sci Adv 2022, 8, eabn4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.S.; Feng, S.J.; Zhang, B.Q.; Wang, M.Q.; Cao, H.W.; Rono, J.K.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.M. OsZIP1 functions as a metal efflux transporter limiting excess zinc, copper and cadmium accumulation in rice. BMC Plant Biol 2019, 19, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rono, J.K.; Le Wang, L.; Wu, X.C.; Cao, H.W.; Zhao, Y.N.; Khan, I.U.; Yang, Z.M. Identification of a new function of metallothionein-like gene OsMT1e for cadmium detoxification and potential phytoremediation. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essig, Y.J.; Leszczyszyn, O.I.; Almutairi, N.; Harrison-Smith, A.; Blease, A.; Zeitoun-Ghandour, S.; Webb, S.M.; Blindauer, C.A.; Stürzenbaum, S.R. Juggling cadmium detoxification and zinc homeostasis: A division of labour between the two C. elegans metallothioneins. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 141021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beil, A.; Jurt, S.; Walser, R.; Schönhut, T.; Güntert, P.; Palacios, Ò.; Atrian, S.; Capdevila, M.; Dallinger, R.; Zerbe, O. The Solution Structure and Dynamics of Cd-Metallothionein from Helix pomatia Reveal Optimization for Binding Cd over Zn. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 4570–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.Y.; Park, J.; Mendoza-Cózatl, D.G.; Suter-Grotemeyer, M.; Shim, D.; Hörtensteiner, S.; Geisler, M.; Weder, B.; Rea, P.A.; Rentsch, D.; et al. Arsenic tolerance in Arabidopsis is mediated by two ABCC-type phytochelatin transporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 21187–21192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, B.; Sunitha, N.C.; Sah, R.P.; T, P.M.; Krishna, G.K.; Umesh, D.K.; Thomas, S.; Anilkumar, C.; Upadhyay, S.; Kumar, A.; et al. Physiological and molecular implications of multiple abiotic stresses on yield and quality of rice. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13, 996514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



