1. Introduction
The fall armyworm (
Spodoptera frugiperda, FAW) is an invasive noctuid moth (Lepidoptera) that was first reported in Australia early in 2020 [
1]. FAW is highly polyphagous [
2,
3,
4], causing significant damage to economically important crops through larval feeding on leaves and fruit [
5]. Consequently, the introduction of FAW poses a considerable risk to Australia's agriculture, including sorghum, wheat, cotton, sugarcane, and various vegetables [
6,
7,
8]. To reduce reliance on broad spectrum synthetic insecticides, there is substantial interest in potential biocontrol options as part of an integrated pest management (IPM) strategy to help mitigate damage from FAW.
Entomopathogenic fungi (EPF) represent a group of fungi that infect and kill insect hosts and are valuable resources for natural pest control [
9,
10]. EPF are ubiquitous in nature, and more than 18,000 species have been reported to exhibit entomopathogenesis [
11]. Species in the order Hypocreales, including the genera
Beauveria and
Metarhizium, are particularly well-recognised for their biocontrol potential and applications in sustainable agricultural practices [
12]. This is due to the simplicity of their culture media and growth conditions, as well as their effectiveness [
13]. The general mode of action of EPF in the order Hypocreales starts with infection of insects topically through the cuticle [
14]. Once inside, the fungi proliferate throughout the insect's body, absorbing nutrients required for their growth, which leads to the death of the insect host [
15,
16,
17]. The EPF then emerges from the host's carcass, sporulates, and the cycle repeats [
17]. Incorporating EPF as part of IPM in agriculture could foster sustainability and serve as an alternative to chemical insecticides, addressing the challenges of pesticide resistance, insecticide residues on produce, and environmental contamination.
In addition to the ability to parasitise host species, the production of insecticidal bioactive compounds could also be a crucial factor to the virulence of EPF. A wide range of insecticide compounds is known to be produced by fungi in the genus
Beauveria including beauvericin [
18], bassiacridin [
19], bassianolide [
20], dipicolinic acid [
21], beauveriolide [
22], and more [
18,
23,
24]. Some of these compounds including beauvericin [
18,
23]
, bassiacridin, and bassianolide [
20] have shown efficacy against FAW. For example, beauvericin could reduce the SF-9 (FAW, cell line) cell population by 50% within 48 hours, even when exposed to a low dosage (2.5±0.5 μM) [
23]. In addition, other metabolites, i.e., oosporein, can suppress the immunity of insects [
21,
25,
26,
27], which assists other metabolites or the EPF itself to synergistically take over the insect host’s body.
In our previous study [
28], eleven entomopathogenic fungal isolates were tested against FAW at various life stages. Two
Beauveria isolates, namely B-0571 and B-1311, exhibited high efficacy, causing 73.96 ± 7.85% and 62.08 ± 3.67% mortality in 3
rd instar FAW larvae within 24 hours [
28]. Given the rapidity of larval mortality, it was hypothesised that the mode of action of these isolates might be attributed to the production of insecticidal compounds rather than direct parasitism. Therefore, the objective of this study is to test this hypothesis and to identify and characterise the compounds produced by these two highly virulent
Beauveria isolates, B-0571 and B-1311, that are lethal to FAW.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Isolates
Eleven isolates of entomopathogenic fungi were chosen from CSIRO fungal collection for their efficacy against FAW [
28]. This includes six isolates of
Beauveria species (B-0016, B-0077, B-0079, B-0571, B-0698 and B-1311), and four isolates in the genus
Metarhizium (M-0121-0123 and M-0999) and one isolate of
M. pingshaense (M-1000, JBCAUT000000000). Fungal host species, geographic origins, and collection dates have been previously reported [
28].
Fungal isolates were revived and maintained in Sabouraud dextrose agar media with 1% yeast extract (SDAY; pH 5.6) and incubated at 28 ± 1°C under dark conditions. For further investigation, once fungi have fully sporulated, spores were collected following the protocol as described in [
28].
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction and Whole Genome Sequencing
High molecular weight genomic DNA of fungal isolates was extracted using a protocol from [
29]. The quality of extracted DNA was quantified using a Qubit 2.0 fluorometer (Life Technologies Corporation), gel electrophoresis, and NanoDrop
® (Thermo Scientific
TM). The extracted DNA were submitted to Genomics WA, Western Australia, for library preparation and long read sequencing using PacBio HiFi Sequel
® ll sequencer with SMRTBell technology.
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
PacBio HiFi reads were
de novo assembled using Canu assembler with default parameter [
30] <
https://github.com/marbl/canu>. The quality of assembly was analysed through BUSCO (Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs) [
31] <
https://busco.ezlab.org/> with hypocreales_odb10 (the order of
Beauveria and
Metarhizium genera) dataset and QUAST (QUality ASsessment Tool) [
32] <
https://github.com/ablab/quast>.
2.4. Species Identification and Phylogeny
The genera of the fungal isolates were previously identified through morphology and internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequencing [
28]. However, a sole ITS region has insufficient resolution power to identify species of fungi from the genera
Beauveria and
Metarhizium [
28,
33,
34]. Therefore, a Multi Locus Sequence Typing (MLST) approach was carried out to aid the identification process [
33,
34].
To identify the species of
Beauveria isolates, the sequences of four DNA markers, i.e., B locus nuclear intergenic region (Bloc), the RNA polymerase II largest (RPB1) and second largest (RPB2) subunits, and translation elongation factor (TEF), were used for MLST analysis. For the
Metarhizium isolates, seven DNA markers, i.e., DNA lyase (APN2), beta tubulin (BTUB), RPB1a, RPB1b, RPB2a, RPB2b, and TEF, were used. The marker sequences were acquired from the whole genome sequence. The reference sequences were obtained from [
33] for
Beauveria and [
34] for
Metarhizium and NCBI databases.
Sequences of 20 reference
Beauveria isolates (six species, Table S1) and 22 taxa of ten species within
Metarhizium were used (Table S2). The marker sequences were aligned using MUSCLE with default parameters through Geneious Prime 2023.2.1 (Muscle 5.1 with algorithm: PPP). Maximum likelihood phylogenetic placements of concatenated sequences were constructed through IQ-TREE web server <
http://iqtree.cibiv.univie.ac.at/> with an auto selection for the optimal substitute model, with 1,000 ultrafast bootstrap replications [
35] to estimate node confidence. The phylogenetic trees were modified via iTOL v.6 <
https://itol.embl.de/> [
36].
2.5. Insect Samples and Insect Bioassay
The virulence of the two highly virulent fungal isolates B-0571 and B-1311 was tested on a lab-maintained FAW colony, originally established from 30 field-collected pupae collected from a field station owned by the University of Queensland (Rex Road, Walkamin, Qld, Australia [
37].
The insect bioassay was conducted following the protocol in [
28]. 32 3
rd instar FAW larvae were treated with 0.1% Tween 80
® solutions as control samples and spore suspension of B-0571 or B-1311 at spore concentration ≥ 10
7 conidia/ml as fungal-treated samples. Three caterpillars were collected from day 1 to day 7 (24 hours following treatment = day 1) and preserved in 3:1 ethanol:acetic acid. The samples were stored at room temperature (21±1℃) for further investigation.
2.6. Microscopic Analysis
The two most highly virulent fungal candidates, B-0571 and B-1311 were microscopically assessed. Subsequently, the exterior morphology of the samples was visualised at the CSIRO Black Mountain microImaging Centre
For investigations of external morphology, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used. Samples were critical point dried (Autosamdri®-931, Tousimis) and mounted on aluminium stubs with double-sided adhesive carbon tabs (IA0201, ProSciTech). The samples were then imaged through a SEM (ZEISS EVO LS 15, ZEISS Microscopy) with 10 kV accelerating voltage, 10 Pa vacuum, and backscattered electron detector.
For internal morphology examination, samples were rehydrated through a series of decreasing ethanol solutions (70, 50 and 25%) each for 15 mins. The samples were then cleared using 10% (w/v) potassium hydroxide (KOH) at 85°C for 5-15 mins, with the treatment time varied based on sample size. The treatments ended when samples had optical clarity while also maintaining structural integrity. The samples were then gently washed three times in distilled water, each time for 10 mins. Subsequently, the samples were stained by soaking in 20ug/ml wheat germ agglutinin conjugated with tetramethylrhodamine isothiocyanate-dextran (WGA-TRITC, W849, Thermo Fisher Scientific) at room temperature for 30 minutes with occasional gentle agitation. The samples were washed twice in distilled water and were mounted using glass slides and coverslips. Widefield images were obtained using an optical microscope (ZEISS AxioImager Z1, ZEISS Microscopy) equipped with white and fluorescence light emitting diode illumination (Colibri 7), ZEISS Axiocam 712 colour charge-coupled device camera (ZEISS Microscopy) and a plan-apochromat 10x NA=0.3 and 20x NA=0.5 objectives. ZEISS filter sets 43 HE (DsRed, excitation BP550/25; beam splitter FT 570 HE; emission BP605/70 HE) and 02 (DAPI, excitation 365; beam splitter 395; emission LP 420) filters were used to visualise WGA-TRITC and background tissue autofluorescence respectively. Image capture and post-acquisition image processing were carried out using ZEN blue v3.2 (ZEISS Microscopy).
2.7. Biosynthesis Gene Cluster Prediction
Biosynthesis gene clusters (BGCs) of fungal isolates were predicted from their genome via AntiSMASH – fungal version 7.0.1 (Antibiotics & Secondary Metabolite Analysis Shell, [
38], available at <
https://fungismash.secondarymetabolites.org>. The detective strictness of the prediction was set to ‘relaxed’ and all extra features (e.g., KnownClusterBlast and MIBiG cluster comparison) were activated. Consequently, the results were manually assessed to verify the accuracy of the prediction.
3. Results
3.1. Species Identification
The genomes of ten isolates were assembled, with the average sizes ranging from 37 to 39 Mb for Beauveria isolates and 42 to 45 Mb for Metarhizium isolates, both showing BUSCO completions of 96.9-97% and 96.7-97.5% respectively (Table S3). An exception was M-0999, whose genome was estimated to be larger at 101 Mb and exhibited a high number of duplications, with 88.5% duplicated BUSCOs. Consequently, it is believed that M-0999 possesses a diploid genome with heterozygosity.
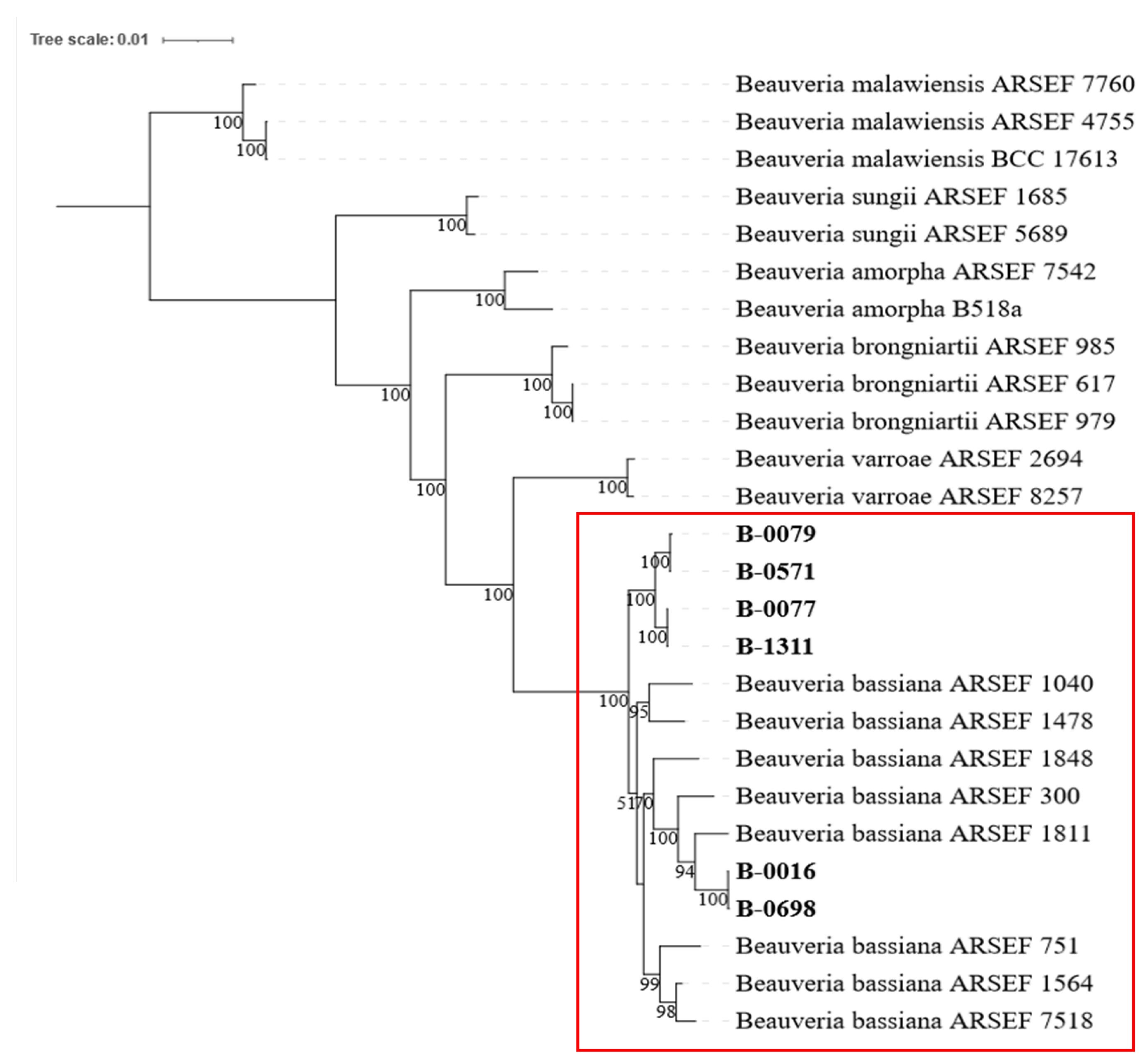
To identify the species of six
Beauveria isolates, a phylogenetic tree was constructed using MLST of four commonly used DNA markers. The analysis showed that these
Beauveria isolates are closely related to eight reference sequences of
B. bassiana, as they were grouped in the same clade. This grouping demonstrated high node confidence levels of 100%, which is highlighted in
Figure 1 with a red box.
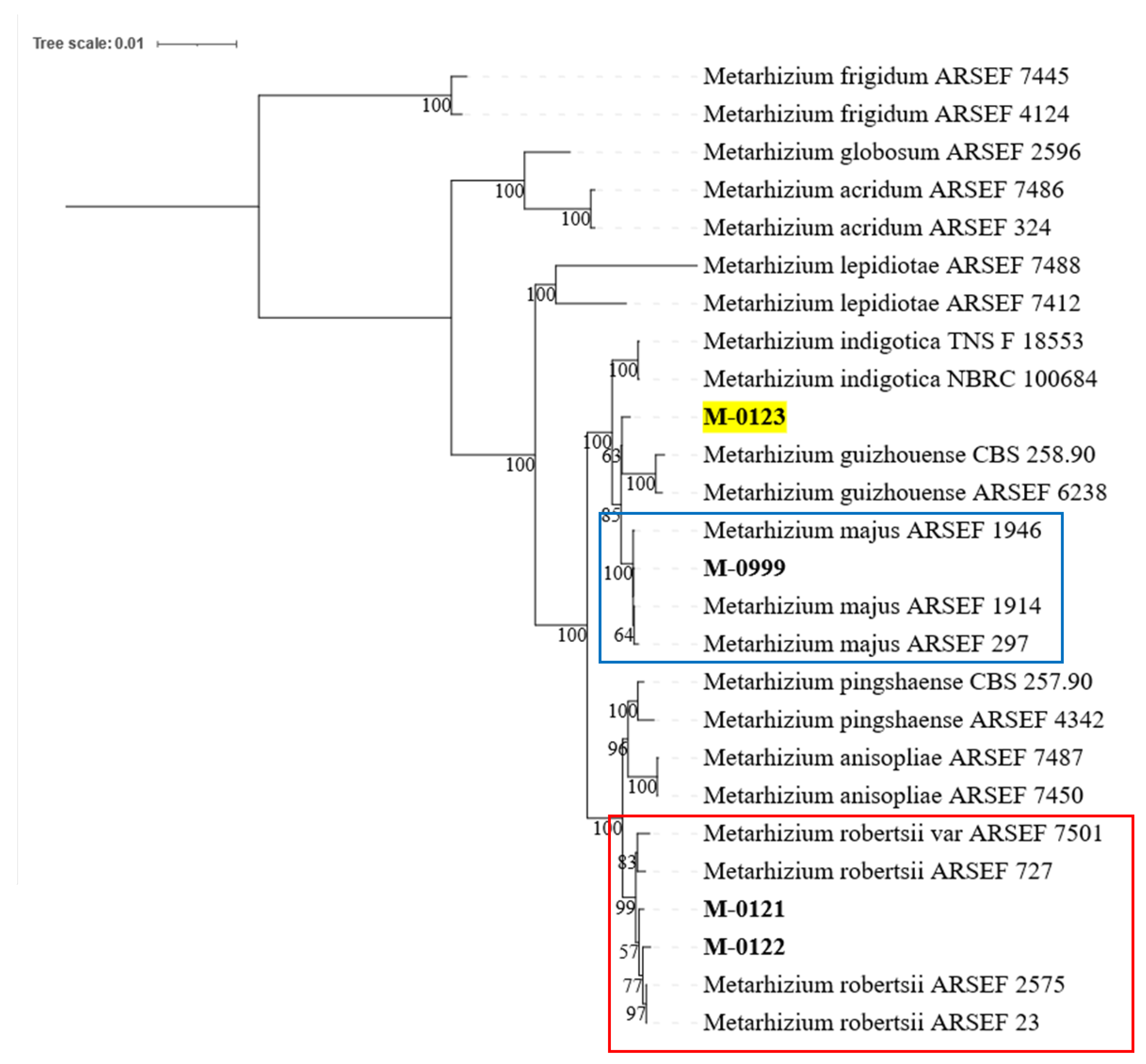
The phylogenetic placement established from seven DNA markers were used to help identify species of four
Metarhizium isolates. The analysis clustered M-0121 and M-0122 with the four
M. robertsii reference sequences with strong bootstrap support (99%,
Figure 2, indicated in red box). The M-0123 isolate was placed as a sister branch to
M. guizhouense but with only 63% node support (
Figure 2, highlighted in yellow). Finally, for M-0999, it was clustered with three isolates of
M. majus with 100 node confidence (
Figure 2, in blue box).
4. Microscope Analysis
4.1. External Morphology Analysis
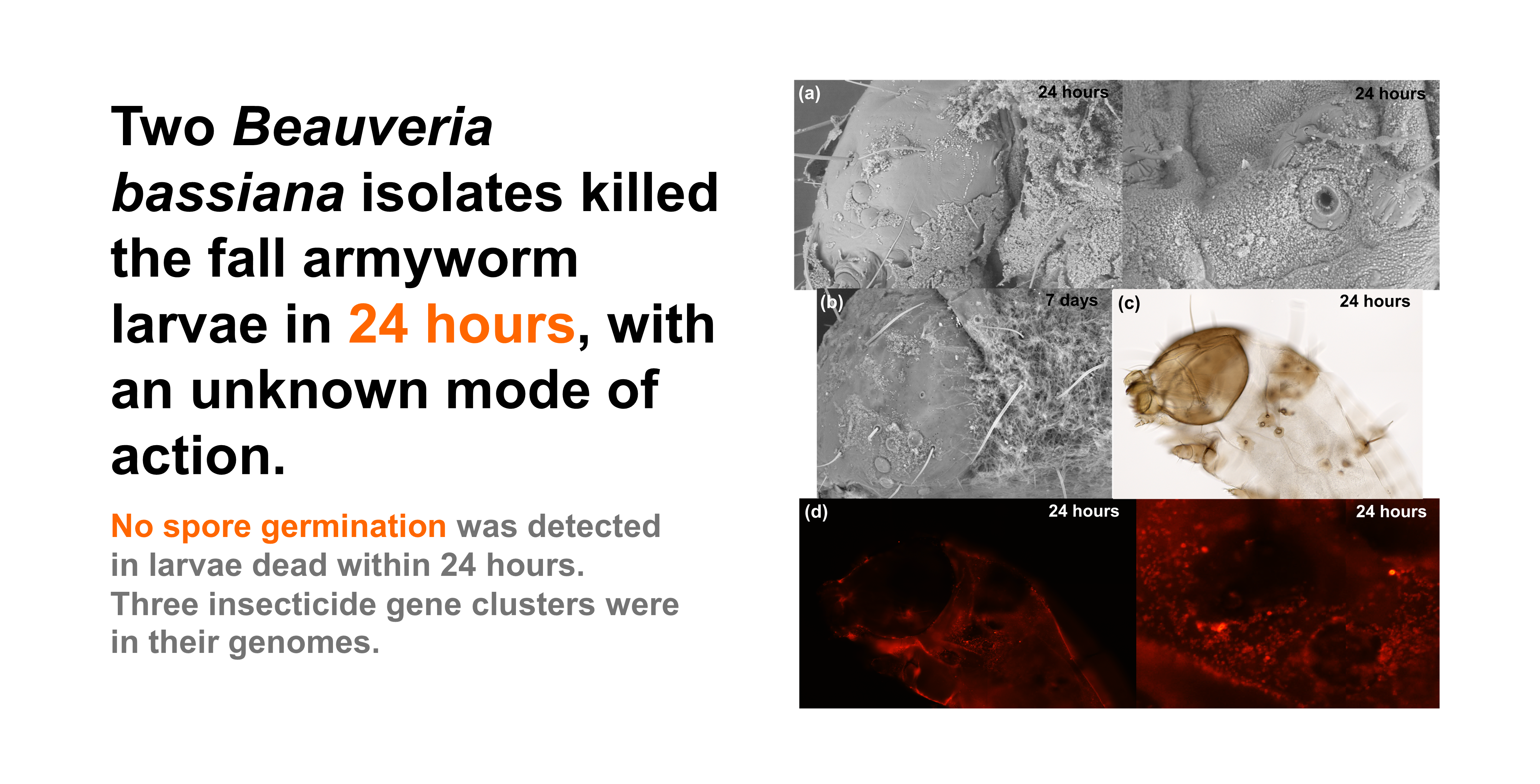
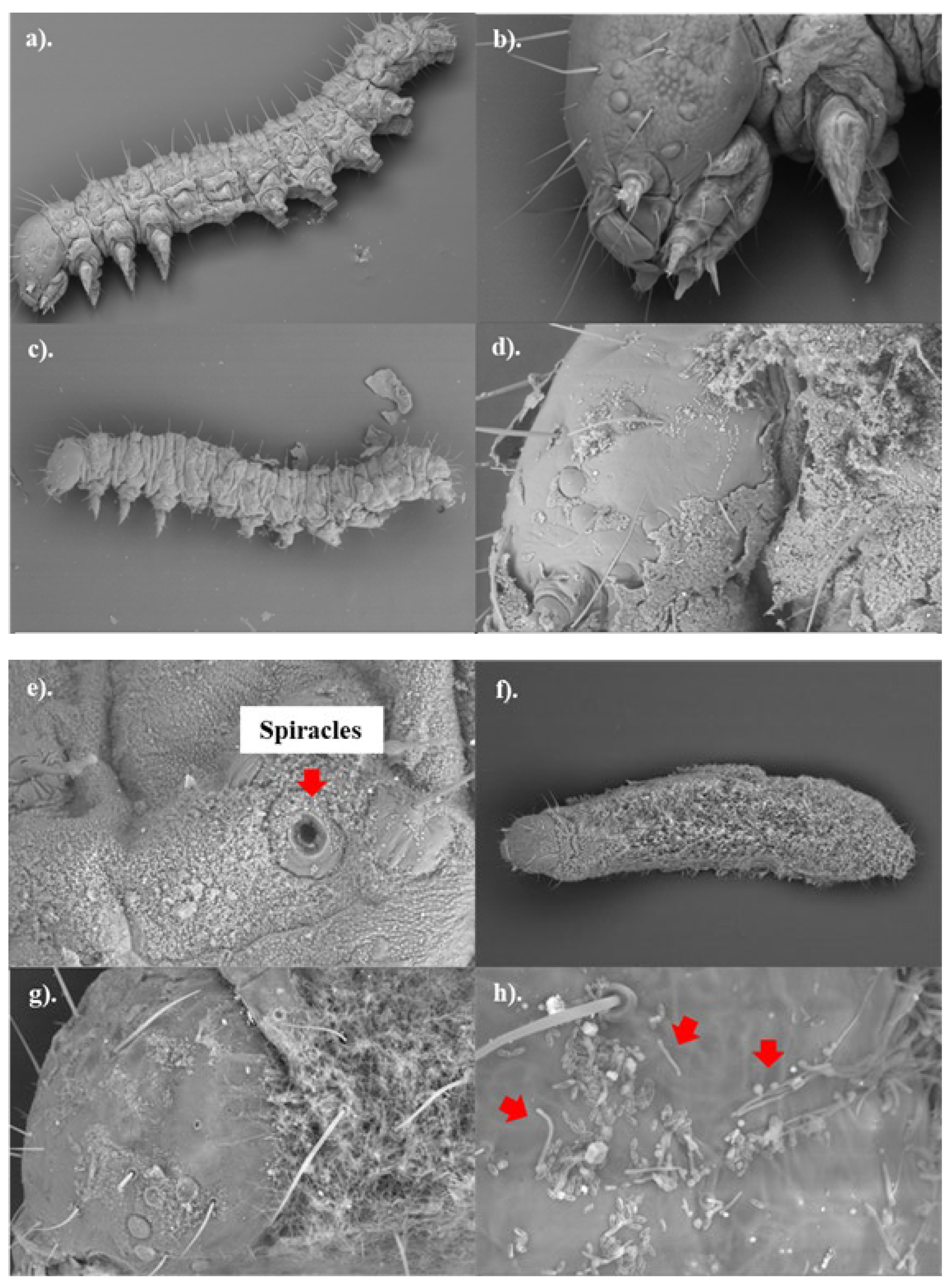
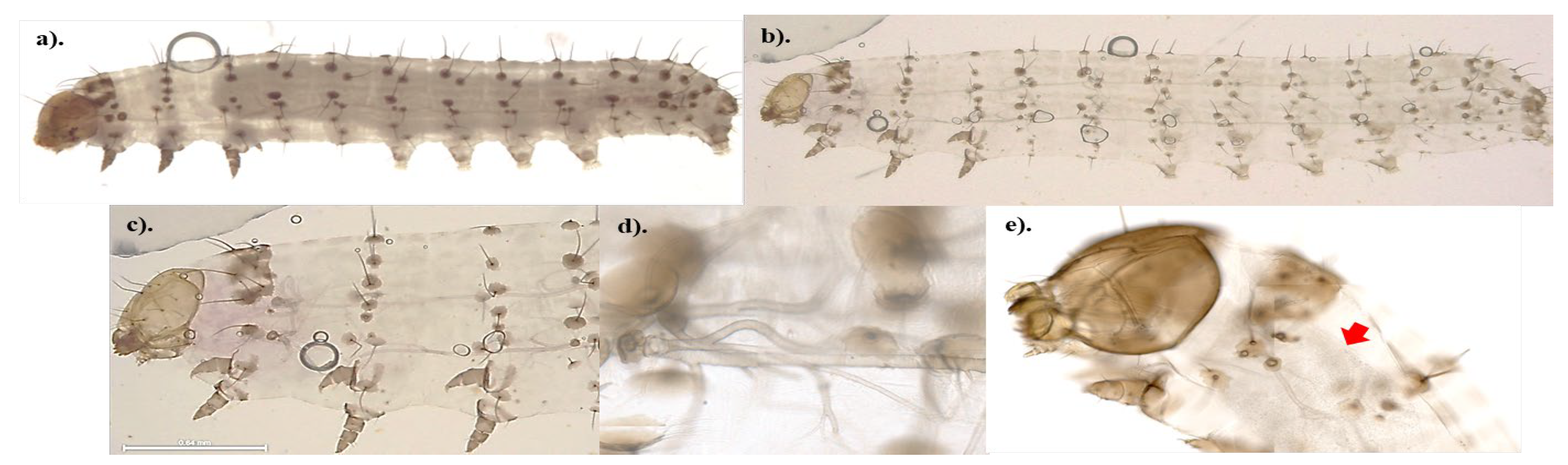
To better understand the pathogenicity of highly virulent
B. bassiana isolates towards FAW, the external morphology of control and fungus-treated samples was observed. The results suggest that no spore germination occurred within 24 hours post-treatment. A substantial number of fungal spores were visible on the surface of the fungus-treated samples (
Figure 3, c-e), while no fungal spores were detected in the control samples (
Figure 3, a-b). The spores were mostly found on the bodies of insects (thorax and abdomen), with fewer on the heads. The fungal spores were located around the spiracles (external respiratory pores of the caterpillars,
Figure 3f); however, they did not appear to obstruct the spiracles. In addition, the fungal spores appear to be much smaller than insect spiracles.
Seven days following the fungal treatments, the bodies of the insects were covered in the hyphae which could be seen easily with naked eyes. The germination of spores and signs of parasitism were evident throughout the whole insect (
Figure 3, f-h). On day 7 following the treatment, control samples developed into 5
th-6
th instar caterpillars, displaying a noticeable size difference when compared to the treated samples. Therefore, the control for the 7-day fungus-treated samples was collected from the first 24 hours post treatment (
Figure 3, a-b). For the fungus-treated samples (
Figure 3, f-h), signs of fungal germination and parasitism were detected throughout the bodies of insects including the head. However, the hyphae appeared to be located mostly on the bodies.
4.2. Internal Morphology Analysis
To locate signs of fungal germination and parasitisation, the internal morphology of treated third instar caterpillars was examined. Light microscope images showed spots in the digestive tract of 24-hour fungal treated samples (
Figure 4, e) that did not appear in the control samples (
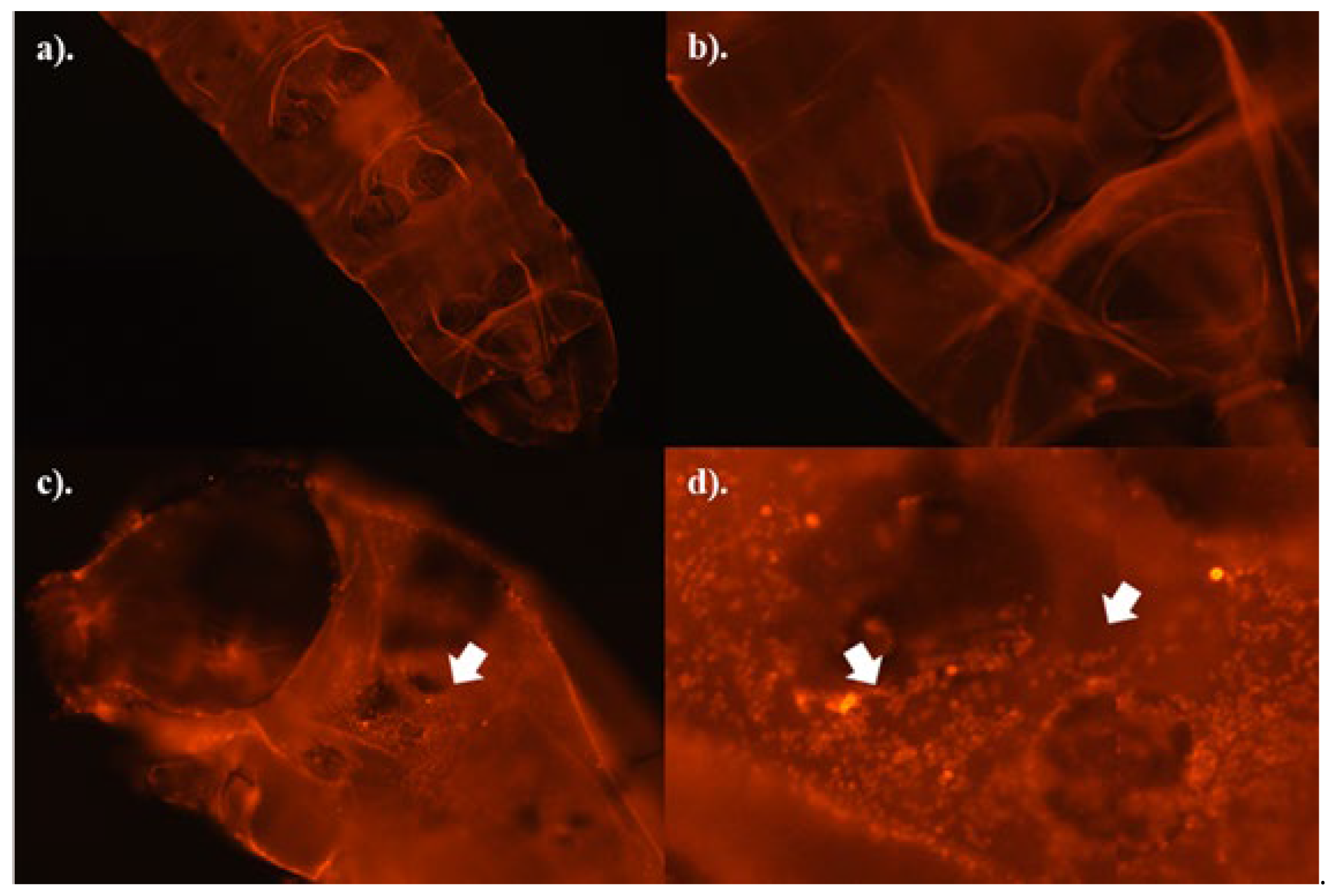
Figure 4, b-d). These spots were suspected to be fungal spores, although the image resolution was not sufficiently high enough to enable better confirmation or to determine if early spore germination processes had commenced. Hence, control and fungus-treated samples were stained with WGS-TRITC to assist with confirmation.
The WGS-TRITC fluorescent dye, used to stain both the insect cuticle and the cell walls of fungal spores, showed distinct spots in the digestive tracts of fungus-treated caterpillars (
Figure 5c-d), which were absent in the control samples (
Figure 5a-b). As such, these spots are believed to be fungal spores. However, no signs of germination were detected in the 24-hour fungus-treated samples (
Figure 5d).
4.3. Biosynthesis Gene Clusters Prediction
There are 43-51 biosynthesis gene clusters (BGCs) recognised in six
B. bassiana isolates and 56-111 in five
Metarhizium isolates. Although many remain unknown, 13-16 of the BGCs from
B. bassiana and 24-42 from
Metarhizium spp. share similarities with reference clusters from the Minimum Information about a Biosynthesis Gene cluster (MIBiG) database. The clusters that share more than 50% similarity with the reference clusters from the MIBiG database are listed in
Table 4S.
4.4. Beauveria bassiana
Among the known BGCs found in tested
B. bassiana isolates; there is evidence suggesting that some possess insecticide properties. This includes bassianolide, beauvericin, and beauveriolide. Although oosporein does not exhibit insecticidal properties, it has been shown to suppress the immune response in insects [
25], which is also discussed further below.
A bassianolide gene cluster was found in all tested
B. bassiana isolates, with their entire cluster sharing a similarity of 53-66% to a reference gene cluster (BGC0000312 from
B. bassiana,
Table 1). All these clusters contained a core biosynthesis gene for bassianolide production (
bsls), with the
B. bassiana isolates exhibiting 85-97% similarity to the reference
bsls.
All tested
B. bassiana isolates also possess one beauvericin gene cluster, with the clusters exhibiting 70-90% similarity to the MIBiG-reported cluster (BGC0000313 from
B. bassiana,
Table 1). The core biosynthesis gene, beauvericin nonribosomal cyclodepsipeptide synthetase (Beas), is found in all
B. bassiana isolates, showing 88-97% similarity.
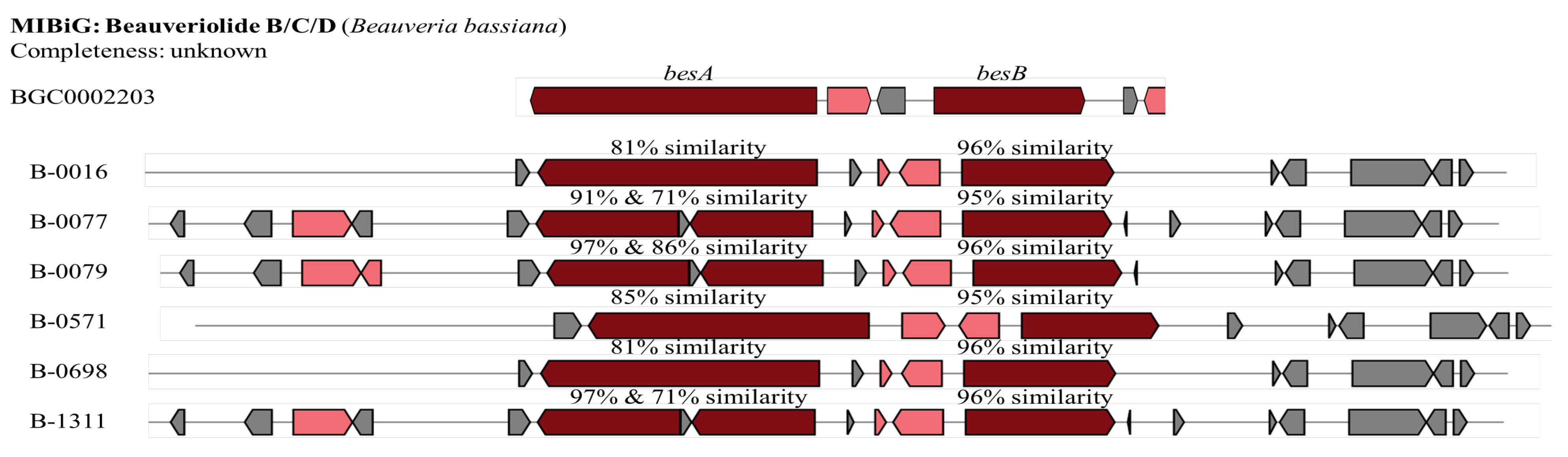
The gene cluster for beauveriolide B/C/D was recognised in all tested
B. bassiana isolates, the whole cluster exhibiting similarities ranging from 66% to 83% compared to a reference cluster (BGC0002203 from
B. bassiana, Table 1). Beauveriolide B/C/D gene cluster contained two core biosynthesis genes including
BesA and
BesB. These two genes were detected in all
B. bassiana isolates. The
BesA of three isolates including B-0077, B-0079, and B-1311, however, appears to be inserted by an unknown sequence (132 nucleotides (nt),
Figure 6). The similarities of the
nrps in
B. bassiana isolates to the reported gene ranges from 81% to 97% while it is 95-96% for
BesB gene.
All tested
B. bassiana isolates possessed an oosporein gene cluster. While not identical, they all shared 85% similarity across the entire cluster compared to the reference cluster (BGC0001720 from B. bassiana,
Table 1). For the core biosynthesis gene, they shared 89-92% similarity compared to the reference gene. However, B-0077 and B-1311 had an incomplete transport gene, and it remains to be investigated whether this would impact oosporein production.
4.5. Metarhizium Species
Among the fungal isolates, four distinct species of
Metarhizium were identified (Figure. 2; see also [
28]), with each exhibiting considerable variance in their BGCs. In this study, our focus was on one specific isolate, M-0121 (
M. robertsii), because of the highest efficacy demonstrated against the FAW when compared to other tested
Metarhizium isolates [
28]. Two insecticide compound gene clusters, i.e., destruxin and enniatin, were identified in M-0121 and will be further discussed below.
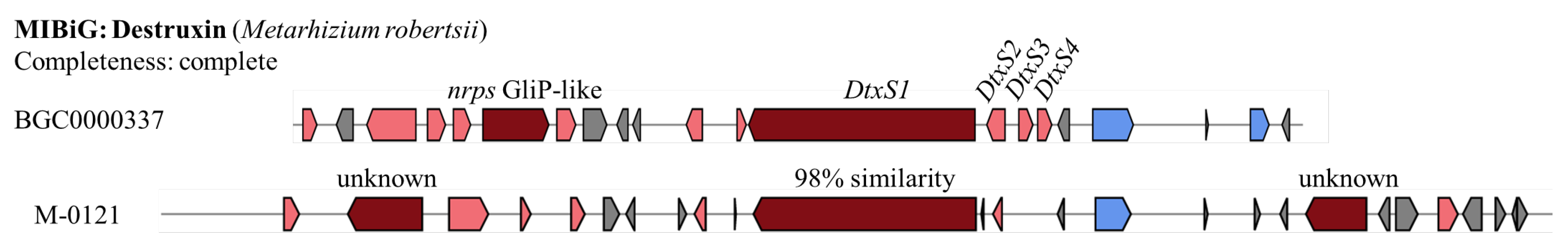
A destruxin (Dtx) gene cluster is found only in the M-0121 genome, with the whole cluster sharing 76% similarity to the reported cluster (BGC0000337 from
M. robertsii). BGC0000337 has two core biosynthesis genes, i.e.,
nrps GliP-like and
DtxS1. However, only
DtxS1 is found in M-0121 with 98% similarity (
Figure 7). In addition, the core biosynthesis genes
DtxS2, DtxS3, and
DtxS4 are also missing in the M-0121 isolate.
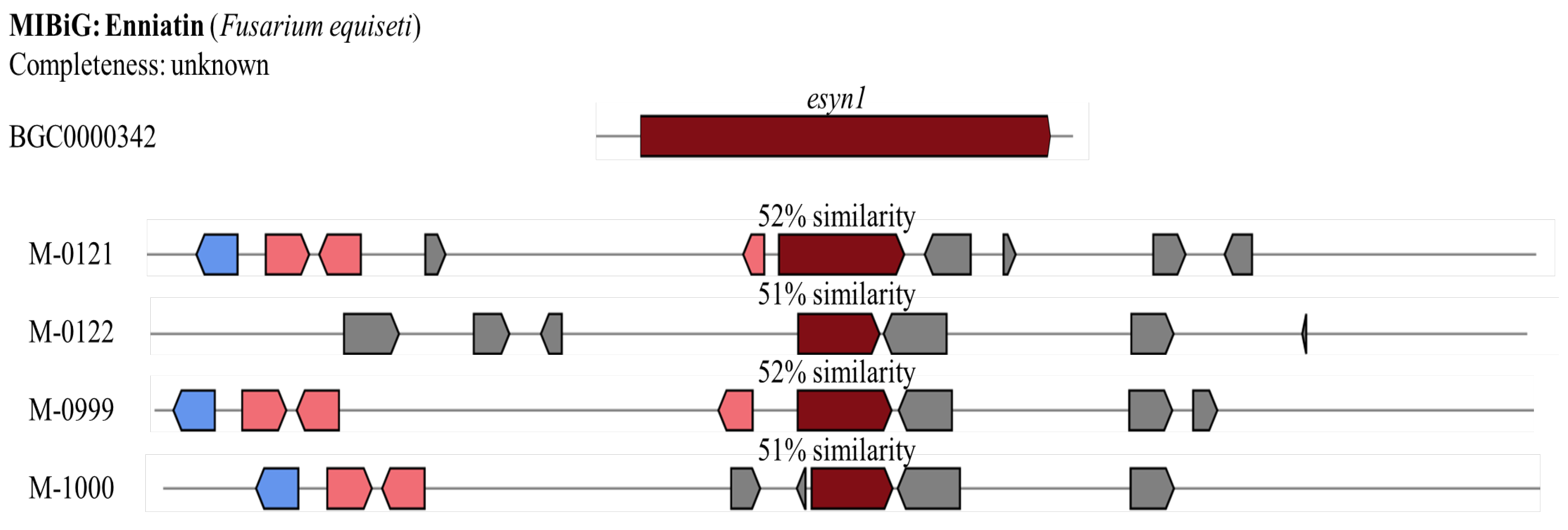
A reported enniatin gene cluster (BGC0000342 from
Fusarium equiseti) contains only one gene:
esyn1. Although
esyn1 is found in four isolates of
Metarhizium including M-0121, M-0122, M-0999, and M-1000,
esyn1 in these isolates contain less than half the length of the reported
esyn1 (
Figure 8). Moreover, the percentage of similarity on their core biosynthesis gene is only 51-52%. Therefore, enniatin gene clusters in
Metarhizium isolates are incomplete and hypothesised to not be able to produce enniatin.
Table 1.
Insecticide compound gene clusters predicted in the fungal isolates.
Table 1.
Insecticide compound gene clusters predicted in the fungal isolates.
| Biosynthesis gene clusters |
CSIRO isolates |
Overall similarity (%) |
Core biosynthesis gene similarity (%) |
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
| Beauveria bassiana |
|
|
|
|
|
| Bassianolide |
B-0016 |
53 |
85 |
|
|
| |
B-0077 |
60 |
97 |
|
|
| |
B-0079 |
53 |
97 |
|
|
| |
B-0571 |
66 |
97 |
|
|
| |
B-0698 |
60 |
88 |
|
|
| |
B-1311 |
53 |
97 |
|
|
| Beauvericin |
B-0016 |
70 |
97 |
|
|
| |
B-0077 |
80 |
93 |
|
|
| |
B-0079 |
70 |
93 |
|
|
| |
B-0571 |
70 |
88 |
|
|
| |
B-0698 |
70 |
97 |
|
|
| |
B-1311 |
80 |
93 |
|
|
| Beauveriolide B/C/D |
B-0016 |
66 |
81 |
|
96 |
| |
B-0077 |
83 |
91 |
71 |
95 |
| |
B-0079 |
66 |
97 |
86 |
96 |
| |
B-0571 |
83 |
85 |
|
95 |
| |
B-0698 |
66 |
81 |
|
96 |
| |
B-1311 |
83 |
97 |
71 |
96 |
| Oosporein |
B-0016 |
85 |
89 |
|
|
| |
B-0077 |
85 |
91 |
|
|
| |
B-0079 |
85 |
89 |
|
|
| |
B-0571 |
85 |
92 |
|
|
| |
B-0698 |
85 |
89 |
|
|
| |
B-1311 |
85 |
91 |
|
|
| Metarhizium species |
|
|
|
|
|
| Destruxin |
M-0121 |
76 |
- |
98 |
- |
| Enniatin |
M-0121 |
100 |
52 |
|
|
| |
M-0122 |
100 |
52 |
|
|
| |
M-0999 |
100 |
51 |
|
|
| |
M-1000 |
100 |
52 |
|
|
5. Discussion
5.1. Species Identification
We inferred the six Beauveria isolates (i.e., B-0016, B-0077, B-0079, B-0571, B-0698, and B-1311) to likely represent different isolates of B. bassiana based on MLST analysis.
The phylogenetic results suggest that there are four species within tested Metarhizium isolates. M-0121 and M-0122 are grouped with various isolates of M. robertsii which suggests that these two isolates are also likely to be M. robertsii. The species of M-0123, however, remained uncertain since M-0123 is the only sample currently found to be basal to M. guizhouense but divergent from M. indigotica. More sequences (which currently are not available) from other closely related species will be required to better define the species status of M-0123 isolate. Finally, the isolate M-0999 is likely to be M. majus, as it grouped with three other isolates of M. majus.
5.2. Microscope Analysis
The external and internal morphology of dead B-0571 or B-1311-treated samples indicate that no fungal germination occurred within 24 hours post fungal treatment. While many fungal spores were detected on the surface of caterpillars; they did not appear to obstruct insect spiracles. Hence, the cause of insect death is unlikely to be due to fungal parasitisation or hypoxia. We hypothesise that these fungal candidates produce bioactive compounds with insecticidal properties harmful to FAW larvae. In addition, optical white and fluorescence light microscopy was used to observe the internal morphology of caterpillars. Spores from B-0571 and B-1311 were observed in the digestive tracts of caterpillars, suggesting that these insecticidal bioactive compounds may require oral ingestion to be effective. This hypothesis is supported by the lack of effectiveness of B-0571 and B-1311 against pupae and adults in the first 24 hours [
28]; as these later instar stages have lower to no consumption of food.
5.3. Biosynthesis Gene Cluster Prediction
To better understand the genomic basis of high virulence observed in the previously tested fungal isolates, including production of compounds harmful toward FAW, their BGCs were annotated and characterised. Our findings indicated that four insecticidal BGCs were recognised in all tested
B. bassiana isolates. This includes bassianolide, beauvericin, beauveriolide B/C/D, and oosporein. At least one of these compounds are speculated to be expressed in high virulence isolates (i.e., B-0571 and B-1311). In the case of B-0077, B-0079, and B-1311, the
besA gene within the beauveriolide B/C/D gene cluster was shown to be disrupted. This cluster contained two main biosynthetic core genes, namely
besA and
besB. The research by Yin et al. [
39] indicated that these genes were likely responsible for producing different analogues of beauveriolide. In addition, there are no studies comparing the virulence of Δ
besA mutants to the wild type. Therefore, the effects of
besA disruption on B-0077, B-0078, and B-1311, such as whether these isolates still express functional BesA, and how the absence of BesA might affect the virulence of these isolates, remained to be investigated. Furthermore, the function of more than half of BGCs predicted in
B. bassiana remained unidentified. The remained possibilities that some of these could encode compounds with insecticide properties.
For M-0121, the isolate with the highest virulence among tested
Metarhizium isolates, two insecticide compound gene clusters were detected: Dtx and enniatin. However, the enniatin gene clusters appeared to be incomplete and they were therefore hypothesised to either not produce enniatin or possibly produced unknown compounds instead. The Dtx gene cluster appeared to be different from the reference gene cluster, missing one of the core genes and many additional biosynthesis genes. The work of Wang and colleagues [
40] suggests that the absence of
DtxS2,
DtxS3, and
DtxS4, which encode cytochrome P450, aldo/keto reductase, and decarboxylase enzymes, respectively, affects Dtx production by reducing the ability to convert Dtx B to Dtx A, C, D, and E, and significantly reduced its virulence against insects. However, the effect of the missing
nrps GliP-like gene is still unknown. Therefore, the production of Dtx B in M-0121 remains unknown. In addition, as with the
B. bassiana isolates
, there may be unidentified insecticide compounds produced by M-0121. Alternatively, the virulence of M-0121 might not be contingent on insecticidal compounds but rather on another factor yet to be determined.
Herein, six Beauveria species and four Metarhizium species were identified. All Beauveria isolates were identified as B. bassiana. Among the Metarhizium isolates, two were identified as M. robertsii, one as M. majus, and one as an unknown species. We analysed the entomopathogenicity of two highly effective B. bassiana isolates (i.e., B-0571 and B-1311) using microscopy, with results showing no germination of fungi in the dead, fungus-treated FAW caterpillars after 24 hours. The absence of fungal germination indicated that the virulence of the fungal candidates likely depended on factors other than parasitisation. These factors may include the production of compounds with insecticidal properties. Annotation and characterisation of the predicted secondary metabolite gene clusters in these fungal isolates identified four insecticidal compound gene clusters in all B. bassiana isolates. At least one of these compounds was hypothesised to contribute to the virulence of B-0571 and B-1311. Further research, such as transcriptomic, metabolomic, or proteomic studies, will be necessary to confirm this hypothesis and to better understand the virulence mechanisms of these fungal isolates.
Apart from isolates M-0121 and M-0122, the other Metarhizium isolates were different species and may exhibit varying levels of virulence toward FAW. Additionally, an insecticide gene cluster (i.e., Dtx) was found only in M-0121, which exhibited the highest efficacy among the Metarhizium isolates. The expression of the Dtx gene cluster is therefore hypothesised to underpin the superior efficacy of M-0121 compared to the other Metarhizium isolates.
6. Conclusions
The discovery and characterisation of two highly virulent EPFs targeting FAW open promising new avenues for the development of sustainable pest management tools. A better understanding of their entomopathogenic properties allows these isolates to be applied directly, or their derived toxins can be utilised as biocontrol agents. These can be employed as standalone treatments or integrated with existing pest management approaches. This advancement holds the potential to provide more effective and sustainable solutions to mitigate the impact of FAW on crops, ultimately leading to improved crop productivity and quality.
7. Supplementary Materials
Table 1S.
Information on Beauveria species, including their origin, host, and accession numbers, used in this study.
Table 1S.
Information on Beauveria species, including their origin, host, and accession numbers, used in this study.
| Strain |
Species |
Geography |
Host |
GenBank accession numbers |
| Bloc |
TEF |
RPB1 |
RPB2 |
| ARSEF 7542 |
B. amorpha
|
USA |
Hymenoptera |
HQ880736 |
HQ881007 |
HQ880877 |
HQ880949 |
| B518a |
Chile |
Soil |
HQ880806 |
HQ881008 |
HQ880878 |
HQ880950 |
| ARSEF 300 |
B. bassiana
|
Australia |
Hemiptera |
HQ880690 |
AY531924 |
HQ880831 |
HQ880903 |
| ARSEF 751 |
Vietnam |
Coleoptera |
HQ880694 |
AY531954 |
HQ880835 |
HQ880907 |
| ARSEF 1040 |
Japan |
Lepidoptera |
HQ880689 |
AY531881 |
HQ880830 |
HQ880902 |
| ARSEF 1478 |
Brazil |
Hemiptera |
HQ880695 |
AY531890 |
HQ880836 |
HQ880908 |
| ARSEF 1564 |
Italy |
Lepidoptera |
HQ880692 |
HQ880974 |
HQ880833 |
HQ880905 |
| ARSEF 1811 |
Morocco |
Coleoptera |
HQ880696 |
AY531901 |
HQ880837 |
HQ880909 |
| ARSEF 1848 |
Belgium |
Coleoptera |
HQ880696 |
AY531904 |
HQ880832 |
HQ880904 |
| ARSEF 7518 |
Japan |
Hymenoptera |
HQ880693 |
HQ880975 |
HQ880834 |
HQ880906 |
| ARSEF 617 |
B. brongniartii
|
France |
Coleoptera |
HQ880713 |
HQ880991 |
HQ880854 |
HQ880926 |
| ARSEF 979 |
France |
Coleoptera |
HQ880714 |
HQ880992 |
HQ880855 |
HQ880927 |
| ARSEF 985 |
Japan |
Coleoptera |
HQ880699 |
HQ880978 |
HQ880840 |
HQ880912 |
| ARSEF 4755 |
B. malawiensis
|
Australia |
Soil |
HQ880754 |
HQ881015 |
HQ880895 |
HQ880967 |
| ARSEF 7760 |
Malawi |
Coleoptera |
HQ880756 |
DQ376246 |
HQ880897 |
HQ880969 |
| BCC17613 |
Australia |
NA |
HQ880755 |
HQ881016 |
HQ880896 |
HQ880968 |
| ARSEF 1685 |
B. sungii
|
Japan |
Coleoptera |
HQ880740 |
AY531899 |
HQ880881 |
HQ880953 |
| ARSEF 5689 |
South Korea |
Coleoptera |
HQ880741 |
AY531939 |
HQ880882 |
HQ880954 |
| ARSEF 2694 |
B. varroae
|
Switzerland |
Coleoptera |
HQ880733 |
HQ881004 |
HQ880874 |
HQ880946 |
| ARSEF 8257 |
France |
Acari |
HQ880731 |
HQ881002 |
HQ880872 |
HQ880944 |
Table 2S.
Strains used in the Metarhizium phylogenetic analysis, including geography, host, and GenBank numbers.
Table 2S.
Strains used in the Metarhizium phylogenetic analysis, including geography, host, and GenBank numbers.
| Strain |
Species |
Geography |
Host |
GenBank accession numbers |
| APN2 |
BTUB |
RPB1a |
RPB1b |
RPB2a |
RPB2b |
TEF |
| ARSEF 324 |
M. acridum
|
Australia |
Orthoptera |
KJ398492 |
EU248812 |
EU248896 |
EU248896 |
EU248924 |
EU248924 |
EU248844 |
| ARSEF 7486 |
Niger |
Orthoptera |
KJ398534 |
EU248813 |
EU248897 |
EU248897 |
EU248925 |
EU248925 |
EU248845 |
| ARSEF 7450 |
M. anisopliae
|
Australia |
Coleoptera |
KJ398533 |
EU248823 |
EU248904 |
EU248904 |
EU248932 |
EU248932 |
EU248852 |
| ARSEF 7487 |
Ethiopia |
Orthoptera |
KJ398535 |
EU248822 |
DQ468355 |
KJ398685 |
DQ468370 |
KJ398778 |
DQ463996 |
| ARSEF 4124 |
M. frigidum
|
Australia |
Coleoptera |
KJ398523 |
EU248828 |
DQ468361 |
KJ398676 |
DQ468376 |
KJ398769 |
DQ463978 |
| ARSEF 7445 |
Australia |
Isoptera |
KJ398532 |
KJ398590 |
KJ398628 |
KJ398684 |
KJ398727 |
KJ398777 |
KJ398818 |
| ARSEF 2596 |
M. globosum |
India |
Lepidoptera |
KJ398520 |
EU248814 |
EU248898 |
EU248898 |
EU248926 |
EU248926 |
EU248846 |
| CBS 258.90 |
M. guizhouense
|
China |
Lepidoptera |
KJ398481 |
EU248834 |
EU248914 |
EU248914 |
EU248942 |
EU248942 |
EU248862 |
| ARSEF 6238 |
China |
Lepidoptera |
KJ398527 |
EU248830 |
EU248909 |
EU248909 |
EU248937 |
EU248937 |
EU248857 |
| NBRC 100684 |
M. indigotica
|
Japan |
Lepidoptera |
KJ398482 |
KJ398544 |
KJ398595 |
KJ398635 |
KJ398692 |
KJ398732 |
KJ398784 |
| TNS-F 18553 |
Japan |
Lepidoptera |
KJ398508 |
KJ398569 |
JN049886 |
KJ398661 |
JF415992 |
KJ398756 |
JF416010 |
| ARSEF 7412 |
M. lepidiotae
|
Australia |
Coleoptera |
KJ398531 |
EU248836 |
EU248916 |
EU248916 |
EU248944 |
EU248944 |
EU248864 |
| ARSEF 7488 |
Australia |
Coleoptera |
KJ398536 |
EU248837 |
EU248917 |
EU248917 |
EU248945 |
EU248945 |
EU248865 |
| ARSEF 297* |
M. majus
|
Samoa |
Coleoptera |
GCA_000814945.1 |
| ARSEF 1914 |
Philippines |
Coleoptera |
KJ398510 |
KJ398571 |
KJ398610 |
KJ398663 |
KJ398708 |
KJ398758 |
KJ398801 |
| ARSEF 1946 |
Philippines |
Coleoptera |
KJ398512 |
EU248839 |
EU248919 |
EU248919 |
EU248947 |
EU248947 |
EU248867 |
| CBS 257.90 |
M. pingshaense
|
China |
Coleoptera |
KJ398480 |
EU248820 |
EU248902 |
EU248902 |
EU248930 |
EU248930 |
EU248850 |
| ARSEF 4342 |
Solomon Islands |
Coleoptera |
KJ398524 |
EU248821 |
EU248903 |
EU248903 |
EU248931 |
EU248931 |
EU248851 |
| ARSEF 23 |
M. robertsii
|
USA |
Coleoptera |
GCA_000187425.2 |
| ARSEF 2575* |
NA |
NA |
GCA_000591435.1 |
| ARSEF 727* |
Brazil |
Orthoptera |
KJ398502 |
EU248816 |
DQ468353 |
KJ398655 |
DQ468368 |
KJ398750 |
DQ463994 |
| ARSEF 7501 |
M. robertsii var. |
Australia |
Orthoptera |
KJ398502 |
EU248816 |
DQ468353 |
KJ398655 |
DQ468368 |
KJ398750 |
DQ463994 |
Table 3S.
Summary of genome assembly of the fungal isolates.
Table 3S.
Summary of genome assembly of the fungal isolates.
| Samples |
Total length (bp) |
N50 |
N90 |
L50 |
L90 |
GC (%) |
Complete BUSCOs (%) |
Complete single copy BUSCOs (%) |
Complete duplicated BUSCOs (%) |
Fragmented BUSCOs (%) |
Missing BUSCOs (%) |
| B-0016 |
39278729 |
4998638 |
622445 |
4 |
9 |
49.3 |
96.9 (4355) |
92.7(4165) |
4.2(190) |
1.0(44) |
2.1(95) |
| B-0077 |
36567361 |
4612569 |
892064 |
4 |
8 |
50.69 |
96.7 (4346) |
93.3(4195) |
3.4(151) |
1.2(53) |
2.0(95) |
| B-0079 |
38641929 |
3866667 |
257946 |
4 |
12 |
50.71 |
96.9 (4356) |
92.2(4143) |
4.7(213) |
1.2(44) |
1.8(94) |
| B-0571 |
38165003 |
4757165 |
241903 |
4 |
14 |
50.71 |
96.8 (4353) |
90.3(4060) |
6.5(293) |
1.2(53) |
2.1(88) |
| B-0698 |
37641885 |
4920772 |
879087 |
4 |
8 |
49.18 |
97 (4358) |
92(4135) |
5(223) |
1.0(52) |
2.1(84) |
| B-1311 |
37934090 |
4613704 |
2244516 |
4 |
12 |
50.84 |
96.9 (4354) |
90.9(4085) |
6(269) |
1.2(53) |
1.9(87) |
| M-0121 |
42652463 |
4431075 |
3164479 |
4 |
8 |
50.35 |
97 (4359) |
95.4(4286) |
1.6(73) |
0.7(31) |
2.3(104) |
| M-0122 |
41590696 |
4597068 |
3242667 |
4 |
8 |
50.18 |
97.1 (4364) |
95.1(4273) |
2(91) |
0.6(27) |
2.3(103) |
| M-0123 |
44906997 |
5064791 |
1335515 |
4 |
10 |
49.71 |
97.1 (4364) |
95.2(4279) |
1.9(86) |
0.7(32) |
2.2(98) |
| M-0999 |
101495676 |
356791 |
729308 |
10 |
31 |
42.15 |
97.5 (4382) |
9(406) |
88.5(3976) |
0.6(26) |
1.9(86) |
Table 4S.
The biosynthesis gene clusters of the fungal candidates and their similarity to MIBiG reference clusters.
Table 4S.
The biosynthesis gene clusters of the fungal candidates and their similarity to MIBiG reference clusters.
| Samples |
No. clusters detected |
No. known clusters |
Known clusters |
Similarity to reference cluster (%) |
B. bassiana
B-0016 |
51 |
15 |
Bassianolide |
53 |
| |
|
|
Beauvericin |
70 |
| |
|
|
Beauveriolide B/C/D |
66 |
| |
|
|
Choline |
100 |
| |
|
|
Clavaric acid |
100 |
|
| |
|
|
Metachelin C/A/A-CE/B/dimerumic acid |
62 |
| |
|
|
Oosporein |
85 |
| |
|
|
Phomasetin |
71 |
| |
|
|
Tenellin |
100 |
| |
|
|
ε-Poly-L-lysine |
100 |
| B-0077 |
46 |
13 |
Bassianolide |
60 |
| |
|
|
Beauvericin |
90 |
| |
|
|
Beauveriolide B/C/D |
83 |
| |
|
|
Choline |
100 |
| |
|
|
Clavaric acid |
100 |
| |
|
|
Oosporein |
85 |
| |
|
|
Tenellin |
100 |
| |
|
|
ε-Poly-L-lysine |
100 |
| B-0079 |
47 |
13 |
Bassianolide |
53 |
| |
|
|
Beauvericin |
70 |
| |
|
|
Beauveriolide B/C/D |
66 |
| |
|
|
Choline |
100 |
| |
|
|
Clavaric acid |
100 |
| |
|
|
Ilicicolin H/J/8-epi-ilicicolin H |
60 |
| |
|
|
Metachelin C/A/A-CE/B/dimerumic acid |
62 |
| |
|
|
Oosporein |
85 |
| |
|
|
ε-Poly-L-lysine |
100 |
| B-0571 |
43 |
13 |
Bassianolide |
66 |
| |
|
|
Beauvericin |
70 |
| |
|
|
Beauveriolide B/C/D |
83 |
| |
|
|
Choline |
100 |
| |
|
|
Clavaric acid |
100 |
| |
|
|
Metachelin C/A/A-CE/B/dimerumic acid |
62 |
| |
|
|
Oosporein |
85 |
| |
|
|
Tenellin |
100 |
| |
|
|
ε-Poly-L-lysine |
100 |
| B-0698 |
49 |
16 |
AbT1 |
100 |
| |
|
|
Bassianolide |
60 |
| |
|
|
Beauvericin |
70 |
| |
|
|
Beauveriolide B/C/D |
66 |
| |
|
|
Choline |
100 |
| |
|
|
Clavaric acid |
100 |
| |
|
|
Metachelin C/A/A-CE/B/dimerumic acid |
75 |
| |
|
|
Oosporein |
85 |
| |
|
|
Phomasetin |
71 |
| |
|
|
Tenellin |
100 |
| |
|
|
ε-Poly-L-lysine |
100 |
| B-1311 |
46 |
14 |
Bassianolide |
53 |
| |
|
|
Beauvericin |
90 |
| |
|
|
Beauveriolide B/C/D |
83 |
| |
|
|
Choline |
100 |
| |
|
|
Clavaric acid |
100 |
| |
|
|
Oosporein |
85 |
| |
|
|
Tenellin |
100 |
| |
|
|
ε-Poly-L-lysine |
100 |
M. robertsii
M-0121 |
76 |
26 |
AKML A/B/C/D |
100 |
| |
|
|
BAB/BAA |
100 |
| |
|
|
Choline |
100 |
| |
|
|
Claveric acid |
100 |
| |
|
|
Destruxin A |
76 |
| |
|
|
Enniatin |
100 |
| |
|
|
Metachelin C/A/A-CE/B/dimerumic acid |
75 |
| |
|
|
Pseurotin/azaspirene |
80 |
| |
|
|
Swainsonine |
64 |
| |
|
|
Terpendole E |
85 |
| |
|
|
UNII-YC2Q1O94PT |
100 |
| |
|
|
YWA1 |
100 |
| |
|
|
ε-Poly-L-lysine |
100 |
| M-0122 |
66 |
32 |
AKML A/B/C/D |
100 |
| |
|
|
Aspulvinone H |
100 |
| |
|
|
Choline |
100 |
| |
|
|
Clapurines |
54 |
| |
|
|
Enniatin |
100 |
| |
|
|
HC-toxin |
100 |
| |
|
|
Metachelin C/A/A-CE/B/dimerumic acid |
75 |
| |
|
|
Pseurotin/azaspirene |
80 |
| |
|
|
Swainsonine |
64 |
| |
|
|
Terpendole E |
57 |
| |
|
|
UNII-YC2Q1O94PT |
100 |
| |
|
|
YWA1 |
100 |
| |
|
|
ε-Poly-L-lysine |
100 |
Unknown
M-0123 |
58 |
26 |
AbT1 |
100 |
| |
|
|
AKML A/B/C/D |
100 |
| |
|
|
BAB/BAA |
100 |
| |
|
|
Choline |
100 |
| |
|
|
Helvolic acid |
100 |
| |
|
|
Metachelin C/A/A-CE/B/dimerumic acid |
75 |
| |
|
|
Shearinine D |
83 |
| |
|
|
Swainsonine |
57 |
| |
|
|
YWA1 |
100 |
| |
|
|
ε-Poly-L-lysine |
100 |
M. majus
M-0999 |
111 |
42 |
Aspulvinone H/B1 |
100 |
| *Diploid |
|
|
Chaetolivacine A/B/C |
100 |
| |
|
|
Choline |
100 |
| |
|
|
Clapurines |
54 |
| |
|
|
Clavaric acid |
100 |
| |
|
|
Enniatin |
100 |
| |
|
|
Metachelin C/A/A-CE/B/dimerumic acid |
75 |
| |
|
|
Peramine/intermediate 1/2 |
100 |
| |
|
|
Terpendole E |
71 |
| |
|
|
ε-Poly-L-lysine |
100 |
M. pingshaense
M-1000 |
66 |
27 |
AKML A/B/C/D |
100 |
| |
|
|
Aspulvinone H/B1 |
100 |
| |
|
|
BAB/BAA |
100 |
| |
|
|
Choline |
100 |
| |
|
|
Enniatin |
100 |
| |
|
|
Lucilactaene |
53 |
| |
|
|
Metachelin C/A/A-CE/B/dimerumic acid |
62 |
| |
|
|
Peramine |
100 |
| |
|
|
Pseurotin/azaspirene |
80 |
| |
|
|
Serinocyclin A/B |
100 |
| |
|
|
Shearinine D |
83 |
| |
|
|
Swainsonine |
71 |
| |
|
|
YWA1 |
100 |
| |
|
|
ε-Poly-L-lysine |
100 |
Original images
The original, unmodified microscopy images are provided in the additional file.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, NBA, WTT, TKW, BW, PT; Methodology NBA, WTT and TKW; Software, NBA; Validation, WTT; Formal analysis, NBA; Investigation, NBA; Resources, TKW and WTT; Data Curation, NBA and TKW; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, NBA; Writing – Review & Editing, WTT, BW, PT, and TKW; Visualisation, NBA; Supervision, WTT, BM, PT, and TKW; Project Administration, NBA and WTT; Funding Acquisition, TKW.
Funding
The fungal genomes were sequenced with support from CSIRO – Applied Genomics Initiative (awarded to TKW). This project was part of an NBA’s PhD funded by MQ through the International Macquarie University Research Excellence Scholarship (iMQRES). The project was completed with support from CSIRO – Health & Biosecurity and Environment.
Acknowledgments
Leon Court (CSIRO) helped with sample submissions for sequencing. Dr. Cecile Gueidan (CSIRO) provided guidance on phylogenetic analysis. Timothy Hogarty (CSIRO) and Ray Yang (Murdoch University/CSIRO) helped take care of the insects. Dr. Phil Hands and Dr. Vivien Rolland (BMIC & CSIRO) provided discussions on experiment design and assisted with microscopy analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tay, W.T.; Rane, R.; James, B. Characterisation of Spodoptera Frugiperda (Fall Armyworm) Populations in South-East Asia and Northern Australia (Co-Funded with GRDC); Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research and Grains Research and Development Corporation: ACIAR GPO Box 1571 Canberra ACT 2601 Australia, 2023; pp. 1–102.
- Luginbill, P. The Fall ArmyWorm; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, D.C., United States, 1928; pp. 1-91.
- Sparks, A.N. A Review of the Biology of the Fall Armyworm. The Florida Entomologist 1979, 62, 82. [CrossRef]
- Sisay, B.; Sevgan, S.; Weldon, C.W.; Krüger, K.; Torto, B.; Tamiru, A. Responses of the Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera Frugiperda) to Different Host Plants: Implications for Its Management Strategy. Pest Management Science 2023, 79, 845–856. [CrossRef]
- Day, R.; Abrahams, P.; Bateman, M.; Beale, T.; Clottey, V.; Cock, M.; Colmenarez, Y.; Corniani, N.; Early, R.; Godwin, J.; et al. Fall Armyworm: Impacts and Implications for Africa. Outlooks on Pest Management 2017, 28, 196–201. [CrossRef]
- Agriculture and Fisheries Fall Armyworm. Available online: https://www.business.qld.gov.au/industries/farms-fishing-forestry/agriculture/biosecurity/plants/insects/field-crop/fall-armyworm (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action, Agriculture Victoria Fall Armyworm - Agriculture Available online: https://agriculture.vic.gov.au/biosecurity/pest-insects-and-mites/priority-pest-insects-and-mites/fall-armyworm (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development, Government of Western Australia Fall Armyworm in Western Australia. Available online: https://www.agric.wa.gov.au/fall-armyworm-western-australia?nopaging=1 (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Shah, P.A.; Pell, J.K. Entomopathogenic Fungi as Biological Control Agents. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2003, 61, 413–423. [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.P.M.; Hughes, D.P. Diversity of Entomopathogenic Fungi: Which Groups Conquered the Insect Body? Adv Genet 2016, 94, 1–39. [CrossRef]
- Marin-Felix, Y.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Cai, L.; Chen, Q.; Marincowitz, S.; Barnes, I.; Bensch, K.; Braun, U.; Camporesi, E.; Damm, U.; et al. Genera of Phytopathogenic Fungi: GOPHY 1. Stud Mycol 2017, 86, 99–216. [CrossRef]
- Litwin, A.; Nowak, M.; Różalska, S. Entomopathogenic Fungi: Unconventional Applications. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 2020, 19, 23–42. [CrossRef]
- Chandler, D. Chapter 5 - Basic and Applied Research on Entomopathogenic Fungi. In Microbial Control of Insect and Mite Pests; Lacey, L.A., Ed.; Academic Press, United States, 2017; pp. 69–89 ISBN 978-0-12-803527-6.
- Altinok, H.H.; Altinok, M.A.; Koca, A.S. MODES OF ACTION OF ENTOMOPATHOGENIC FUNGI. 2019, 8.
- Dar, S.A.; Rather, B.A.; Kandoo, A.A. Insect Pest Management by Entomopathogenic Fungi. Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies 2017.
- Trakimas, G.; Krams, R.; Krama, T.; Kortet, R.; Haque, S.; Luoto, S.; Eichler Inwood, S.; Butler, D.M.; Jõers, P.; Hawlena, D.; et al. Ecological Stoichiometry: A Link Between Developmental Speed and Physiological Stress in an Omnivorous Insect. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13. [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Baksi, S.; Koris, A.; Vatai, G. Journey of Enzymes in Entomopathogenic Fungi. Pacific Science Review A: Natural Science and Engineering 2016, 18, 85–99. [CrossRef]
- Caloni, F.; Fossati, P.; Anadón, A.; Bertero, A. Beauvericin: The Beauty and the Beast. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 2020, 75, 103349. [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Moraga, E.; Vey, A. Bassiacridin, a Protein Toxic for Locusts Secreted by the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria Bassiana. Mycol Res 2004, 108, 441–452. [CrossRef]
- Rosas-García, N.M.R.; Martínez, M.M.; Villegas-Mendoza, J.M. Detección de bassianolida y beauvericina en cepas de Beauveria bassiana y su participación en la actividad patogénica hacia Spodoptera sp. Biotecnia 2020, 22, 93–99. [CrossRef]
- Cheong, P. Bioactive Metabolites of an Isolate of the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria Bassiana, Doctoral (PhD) Thesis, Lincoln University, New Zealand, 2015.
- Kim, J.-C.; Hwang, I.M.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, S.; Shin, T.S.; Woo, S.-D.; Park, H.W. Rapid Analysis of Insecticidal Metabolites from the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria Bassiana 331R Using UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS. Mycotoxin Res 2024, 40, 123–132. [CrossRef]
- Fornelli, F.; Minervini, F.; Logrieco, A. Cytotoxicity of Fungal Metabolites to Lepidopteran (Spodoptera frugiperda) Cell Line (SF-9). Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 2004, 85, 74–79. [CrossRef]
- Kanaoka, M.; Isogai, A.; Murakoshi, S.; Ichinoe, M.; Suzuki, A.; Tamura, S. Bassianolide, a New Insecticidal Cyclodepsipeptide from Beauveria Bassiana and Verticillium Lecanii. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 1978, 42, 629–635. [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Shang, Y.; Cen, K.; Wang, C. Fungal Biosynthesis of the Bibenzoquinone Oosporein to Evade Insect Immunity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2015, 112, 11365–11370. [CrossRef]
- Altimira, F.; Arias-Aravena, M.; Jian, L.; Real, N.; Correa, P.; González, C.; Godoy, S.; Castro, J.F.; Zamora, O.; Vergara, C.; et al. Genomic and Experimental Analysis of the Insecticidal Factors Secreted by the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria Pseudobassiana RGM 2184. Journal of Fungi 2022, 8, 253. [CrossRef]
- Abendstein, D.; Schweigkofler, W.; Strasser, H. Study on Insecticidal, Antifeedant and Growth Inhibitory Properties of Oosporein on Selected Pest Organisms. Insect Pathogens and Insect Parasitic Nematodes 2003, 26, 103–106.
- Apirajkamol, N.; Hogarty, T.M.; Mainali, B.; Taylor, P.W.; Walsh, T.K.; Tay, W.T. Virulence of Beauveria Sp. and Metarhizium Sp. Fungi towards Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera Frugiperda). Arch Microbiol 2023, 205, 328. [CrossRef]
- Apirajkamol, N.; Tay, W.T.; Mainali, B.; Taylor, P.; Walsh, T.K. High Molecular Weight DNA Extraction from Fungal Spores for Long Read Sequencing. Protocol.io 2024. [CrossRef]
- Nurk, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Rhie, A.; Vollger, M.R.; Logsdon, G.A.; Grothe, R.; Miga, K.H.; Eichler, E.E.; Phillippy, A.M.; Koren, S. HiCanu: Accurate Assembly of Segmental Duplications, Satellites, and Allelic Variants from High-Fidelity Long Reads. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 1291–1305. [CrossRef]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing Genome Assembly and Annotation Completeness with Single-Copy Orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality Assessment Tool for Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [CrossRef]
- Rehner, S.A.; Minnis, A.M.; Sung, G.-H.; Luangsa-ard, J.J.; Devotto, L.; Humber, R.A. Phylogeny and Systematics of the Anamorphic, Entomopathogenic Genus Beauveria. Mycologia 2011, 103, 1055–1073. [CrossRef]
- Kepler, R.M.; Humber, R.A.; Bischoff, J.F.; Rehner, S.A. Clarification of Generic and Species Boundaries for Metarhizium and Related Fungi through Multigene Phylogenetics. Mycologia 2014, 106, 811–829. [CrossRef]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.-T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A Fast Online Phylogenetic Tool for Maximum Likelihood Analysis. Nucleic Acids Research 2016, 44, W232–W235. [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Research 2021, 49, W293–W296. [CrossRef]
- Tay, W.T.; Rane, R.V.; James, W.; Gordon, K.H.J.; Downes, S.; Kim, J.; Kuniata, L.; Walsh, T.K. Resistance Bioassays and Allele Characterization Inform Analysis of Spodoptera Frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) Introduction Pathways in Asia and Australia. Journal of Economic Entomology 2022, 115, 1790–1805. [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Augustijn, H.E.; Reitz, Z.L.; Biermann, F.; Alanjary, M.; Fetter, A.; Terlouw, B.R.; Metcalf, W.W.; Helfrich, E.J.N.; et al. antiSMASH 7.0: New and Improved Predictions for Detection, Regulation, Chemical Structures and Visualisation. Nucleic Acids Research 2023, 51, W46–W50. [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Chen, B.; Song, S.; Li, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, C. Production of Diverse Beauveriolide Analogs in Closely Related Fungi: A Rare Case of Fungal Chemodiversity. mSphere 2020, 5, 10.1128/msphere.00667-20. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Kang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Bai, L.; Wang, C. Unveiling the Biosynthetic Puzzle of Destruxins in Metarhizium Species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2012, 109, 1287–1292. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis of six Beauveria isolates including B-0016, B-0077, B-0079, B-0571, B-0698, and B-1311 (in bold). All six Beauveria isolates were clustered with eight B. bassiana reference sequences with high node confidence (100%).
Figure 1.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis of six Beauveria isolates including B-0016, B-0077, B-0079, B-0571, B-0698, and B-1311 (in bold). All six Beauveria isolates were clustered with eight B. bassiana reference sequences with high node confidence (100%).
Figure 2.
Maximum Phylogeny placements of four Metarhizium isolates (M-0121, M-0122, M-0123, and M-0999). Both M-0121 and M-0122 isolates were clustered with four M. robertsii reference sequences (indicated in red box, 99% bootstrap value). The M-0123 isolate was placed as a solitary branch (highlighted in yellow) sharing 63% node confidence to the M. guizhouense sister clade. The M-0999 isolate was shown to group with three reference sequences of M. majus with 100% node support (shown in blue box).
Figure 2.
Maximum Phylogeny placements of four Metarhizium isolates (M-0121, M-0122, M-0123, and M-0999). Both M-0121 and M-0122 isolates were clustered with four M. robertsii reference sequences (indicated in red box, 99% bootstrap value). The M-0123 isolate was placed as a solitary branch (highlighted in yellow) sharing 63% node confidence to the M. guizhouense sister clade. The M-0999 isolate was shown to group with three reference sequences of M. majus with 100% node support (shown in blue box).
Figure 3.
External morphology of control (a-b) and fungus-treated (c-h) third instar FAW. The living control samples (0.1%(v/v) Tween 80® solution) and the dead fungus-treated samples (B-0571 or B-1311 at spore concentration ≥ 107 conidia/ml) were collected from day 1 (24 hours post treatment, a-e) to day 7 (g-h). The samples were preserved in 3:1 ethanol: acetic acid and the surface morphology was visualised using a SEM with 96-1.65Kx magnification. The red arrows indicate the hyphae/germination of B. bassiana spores. .
Figure 3.
External morphology of control (a-b) and fungus-treated (c-h) third instar FAW. The living control samples (0.1%(v/v) Tween 80® solution) and the dead fungus-treated samples (B-0571 or B-1311 at spore concentration ≥ 107 conidia/ml) were collected from day 1 (24 hours post treatment, a-e) to day 7 (g-h). The samples were preserved in 3:1 ethanol: acetic acid and the surface morphology was visualised using a SEM with 96-1.65Kx magnification. The red arrows indicate the hyphae/germination of B. bassiana spores. .
Figure 4.
The internal morphology of control (a-d) and fungus-treated (e) third instar FAW larvae. The larvae were treated with 0.1%(v/v) Tween 80® solution for the control samples, or in a spore suspension of B-0571 or B-1311 isolates (spore concentration ≥ 107 conidia/ml) as fungal-treated samples. The samples were clarified with 10% KOH at 85℃ for 10-15 mins. The internal morphology of the samples was captured before (a) and after (b-e) the clearing process with an optical microscope. The photos were captured with an optical microscope using white lights. The suspect fungal spores in treated samples were indicated by a red arrow (e).
Figure 4.
The internal morphology of control (a-d) and fungus-treated (e) third instar FAW larvae. The larvae were treated with 0.1%(v/v) Tween 80® solution for the control samples, or in a spore suspension of B-0571 or B-1311 isolates (spore concentration ≥ 107 conidia/ml) as fungal-treated samples. The samples were clarified with 10% KOH at 85℃ for 10-15 mins. The internal morphology of the samples was captured before (a) and after (b-e) the clearing process with an optical microscope. The photos were captured with an optical microscope using white lights. The suspect fungal spores in treated samples were indicated by a red arrow (e).
Figure 5.
Fluorescent images of WGA-TRITC staining of the control (a-b) and fungal treated (c-d) third instar FAW larvae. Living third instar FAW treated with 0.1%(v/v) Tween 80® solution (control samples) and dead caterpillars treated with spore suspension of B-0571 or B-1311 isolates (≥ 107 conidia/ml) were collected 24 hours following the treatment (N=3). The samples were clarified with 10% KOH and stained with WGA-TRITC. The fluorescence signal was captured with an optical microscope using ZEISS DsRed and DAPI filter sets. The stained spots of the fungal cell wall were indicated by white arrows in (c) and (d).
Figure 5.
Fluorescent images of WGA-TRITC staining of the control (a-b) and fungal treated (c-d) third instar FAW larvae. Living third instar FAW treated with 0.1%(v/v) Tween 80® solution (control samples) and dead caterpillars treated with spore suspension of B-0571 or B-1311 isolates (≥ 107 conidia/ml) were collected 24 hours following the treatment (N=3). The samples were clarified with 10% KOH and stained with WGA-TRITC. The fluorescence signal was captured with an optical microscope using ZEISS DsRed and DAPI filter sets. The stained spots of the fungal cell wall were indicated by white arrows in (c) and (d).
Figure 6.
Comparison of the Beauveriolide B/C/D gene clusters identified in the B. bassiana isolates (B-0016, B-0077, B-0079, B-0571, B-0698, and B-1311) against the reference Beauveriolide gene cluster from MIBiG (BGC0002203 from B. bassiana). The Beauveriolide B/C/D gene clusters are predicted from the genomes of B. bassiana isolates. The core biosynthesis genes are in red; additional biosynthesis genes are coloured in pink, and non-specific genes are shaded in grey. Source: modified from figure generated by antiSMASH 7.0.1.
Figure 6.
Comparison of the Beauveriolide B/C/D gene clusters identified in the B. bassiana isolates (B-0016, B-0077, B-0079, B-0571, B-0698, and B-1311) against the reference Beauveriolide gene cluster from MIBiG (BGC0002203 from B. bassiana). The Beauveriolide B/C/D gene clusters are predicted from the genomes of B. bassiana isolates. The core biosynthesis genes are in red; additional biosynthesis genes are coloured in pink, and non-specific genes are shaded in grey. Source: modified from figure generated by antiSMASH 7.0.1.
Figure 7.
The gene clusters for Destruxin predicted from the genome of M-0121 and the MIBiG reference cluster BGC0000337 from M. robertsii are compared. The reference cluster was identified to have all the components required to produce destruxin (complete cluster). Additional synthesis genes are indicated in pink, core biosynthesis genes in red, and genes related to transportation in blue. Source: modified from figure generated by antiSMASH 7.0.1.
Figure 7.
The gene clusters for Destruxin predicted from the genome of M-0121 and the MIBiG reference cluster BGC0000337 from M. robertsii are compared. The reference cluster was identified to have all the components required to produce destruxin (complete cluster). Additional synthesis genes are indicated in pink, core biosynthesis genes in red, and genes related to transportation in blue. Source: modified from figure generated by antiSMASH 7.0.1.
Figure 8.
Comparison of the Enniatin gene clusters predicted from genomes of four Metarhizium spp. (i.e., M-0121, M-0122, M-0999, and M-1000) with the Fusarium equiseti reference cluster BGC0000342 from MIBiG. Blue indicates genes related to transportation, pink denotes additional biosynthesis genes, and red represents core biosynthesis genes. Source: modified from figure generated by antiSMASH 7.0.1.
Figure 8.
Comparison of the Enniatin gene clusters predicted from genomes of four Metarhizium spp. (i.e., M-0121, M-0122, M-0999, and M-1000) with the Fusarium equiseti reference cluster BGC0000342 from MIBiG. Blue indicates genes related to transportation, pink denotes additional biosynthesis genes, and red represents core biosynthesis genes. Source: modified from figure generated by antiSMASH 7.0.1.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).