Submitted:
20 November 2024
Posted:
22 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
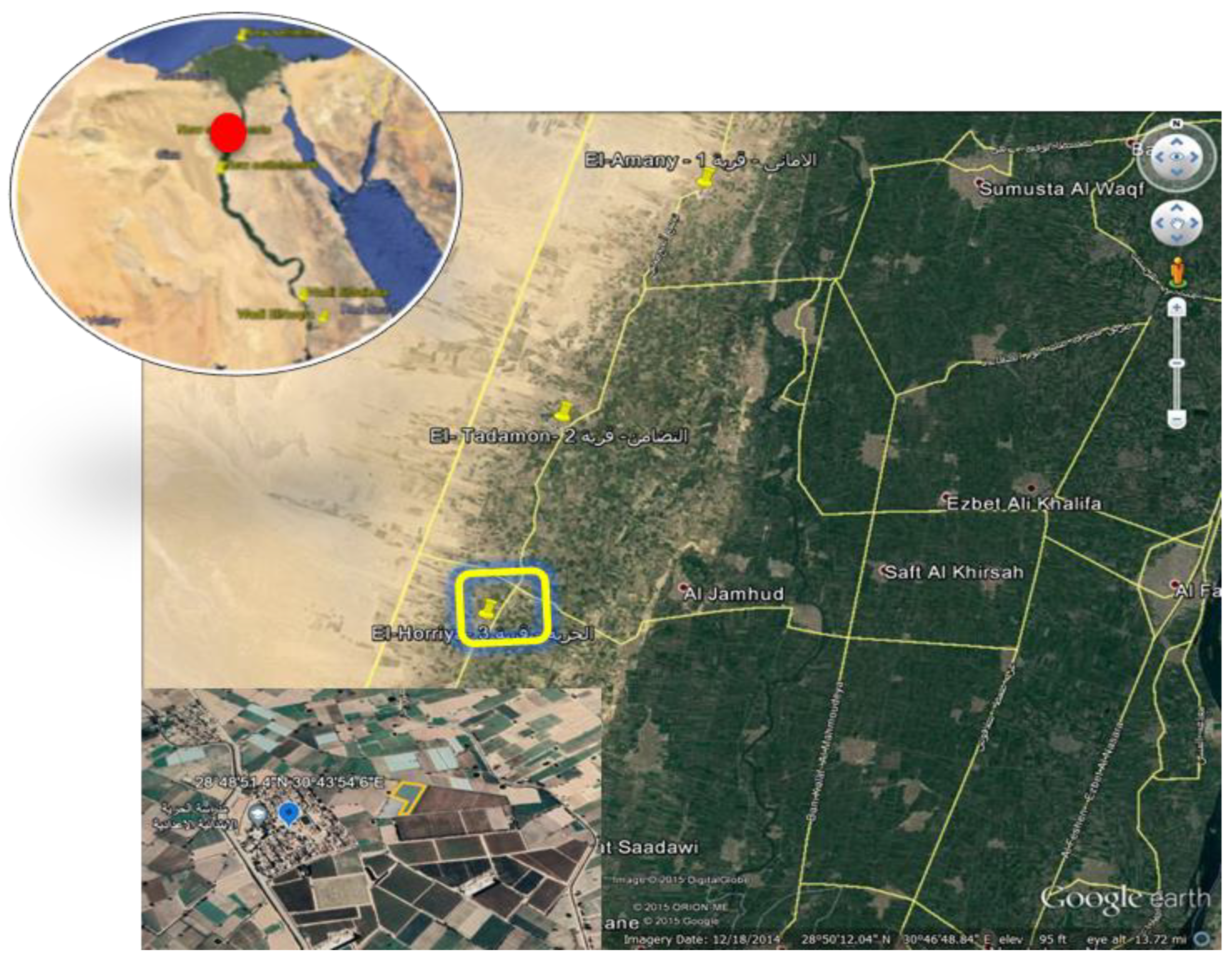
2.1. Site Description and Soil Type
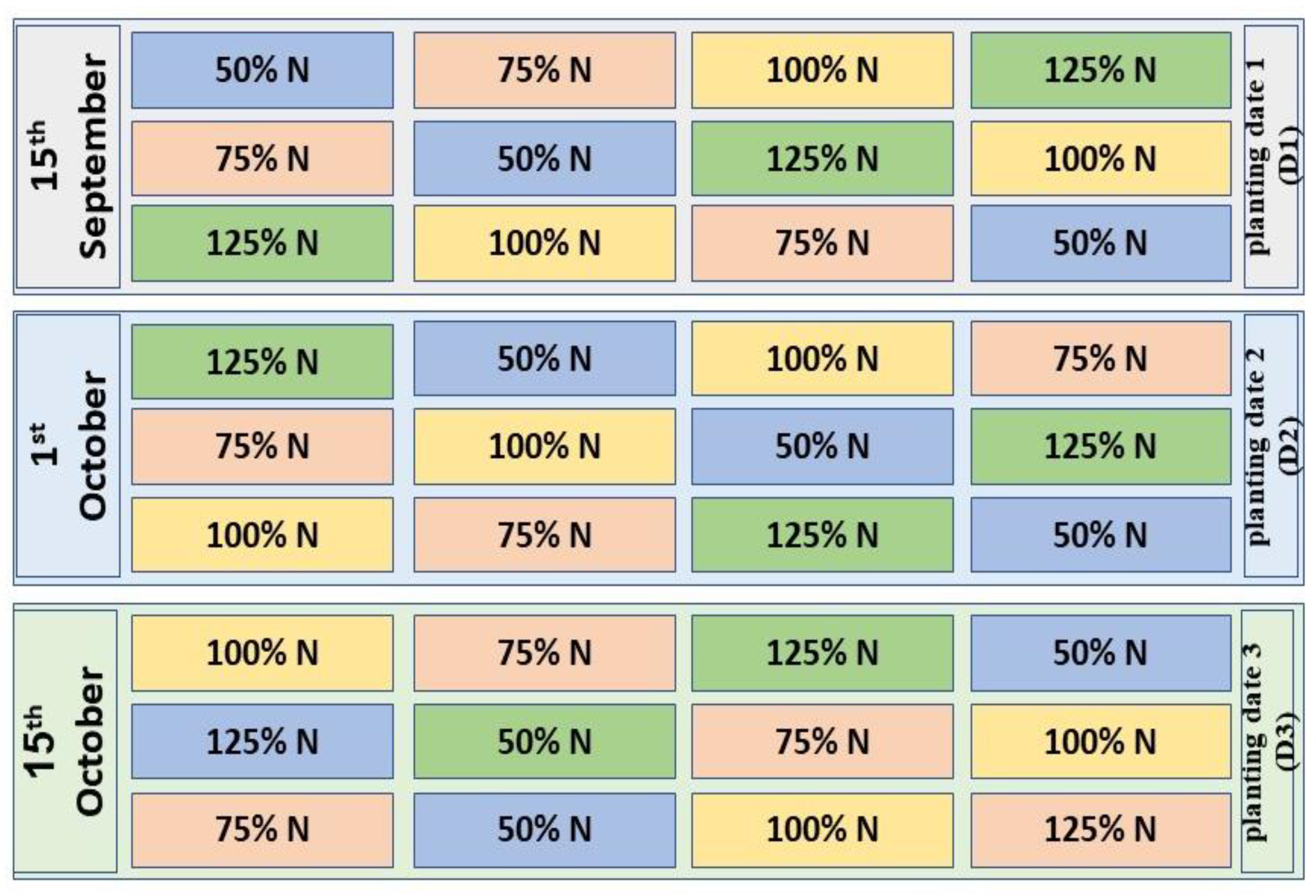
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Planting Technique
2.4. Measurements
2.4.1. Vegetative Growth and Leaves Chemical Composition
2.4.2. Yield Parameters
2.4.3. Biochemical Components in Bulbs
2.4.4. Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
2.4.5. Calculating Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Soil
2.5. Profitability
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Vegetative Growth Parameters
| Planting dates | N levels | Cultivars | Cultivars | Cultivars | Cultivars | ||||||||
| Balady | Sids-40 | Mean | Balady | Sids-40 | Mean | Balady | Sids-40 | Mean | Balady | Sids-40 | Mean | ||
| Plant Height (cm) | Plant Leaves Area (cm2) | Leaves Fresh Weight (g) | Leaves Dry Weight (g) | ||||||||||
| 15th Sep. | 50% | 48.12±0.35 K | 71.24±1.19 E | 59.68±5.2 CDE | 486.44±8.33 L | 535.02±17.76 JK | 510.73±13.96 F | 48.76±0.66 DE | 32.23±0.81 IJ | 40.49±3.73 DE | 7.23±0.06 FG | 5.18±0.03 M | 6.20±0.46 F |
| 75% | 50.96±0.36 IJK | 74.58±1.21 D | 62.77±5.31 A | 524.73±5.95 JKL | 582.69±8.1 HI | 553.71±13.72 A | 47.33±0.38 E | 32.56±0.73 HIJ | 39.95±3.32 A | 7.29±0.1 FG | 6.01±0.17 L | 6.65±0.3 A | |
| 100% | 52.34±0.6 IJ | 77.53±2.1 BCD | 64.94±5.72 B | 524.29±4.52 JKL | 607.43±20.62 FGH | 565.86±20.85 B | 49.35±0.93 CDE | 34.24±1.27 FGHI | 41.8±3.45 B | 6.9±0.49 GHI | 6.32±0.06 KL | 6.61±0.26 B | |
| 125% | 58.43±0.67 G | 75.99±1.11 BCD | 67.21±3.97 C | 584.9±7.52 HI | 630.69±14.06 EFG | 607.79±12.48 D | 51.8±1.36 BC | 35.01±0.82 FGHI | 43.4±3.82 BCD | 8.27±0.05 D | 7.29±0.05 FG | 7.78±0.22 D | |
| Mean | 52.46±1.16 F | 74.83±0.94 C | 63.65±2.44 C | 530.09±11.01 D | 588.96±12.65 C | 559.52±10.24 C | 49.31±0.62 B | 33.51±0.53 D | 41.41±1.7 C | 7.42±0.19 C | 6.20±0.23 E | 6.81±0.19 C | |
| 1st Oct. | 50% | 49.51±0.83 JK | 75.78±0.24 BCD | 62.65±5.89 DE | 501.55±6.26 KL | 555.95±21.45 IJ | 528.75±15.74 EF | 47.15±0.62 E | 31.22±0.28 J | 39.18±3.58 DE | 7.84±0.07 DE | 5.95±0.02 L | 6.89±0.42 E |
| 75% | 53.25±0.91 HI | 74.8±0.92 CD | 64.03±4.85 E | 554.34±1.49 IJ | 600.51±11.38 FGH | 577.43±11.53 FG | 49.73±0.36 CDE | 33.8±1.18 GHIJ | 41.77±3.61 F | 8.11±0.02 D | 6.47±0.05 IJK | 7.29±0.37 F | |
| 100% | 55.78±1 GH | 78.1±1.02 BC | 66.94±5.03 B | 587.41±12.83 GHI | 655.51±16.67 DE | 621.46±17.9 C | 51.57±1.39 BCD | 34.78±0.84 FGHI | 43.18±3.82 BC | 8.73±0.03 C | 7.11±0.05 GH | 7.92±0.36 C | |
| 125% | 63.52±1.33 F | 82.16±0.99 A | 72.84±4.23 C | 681.14±7.12 D | 767.93±10.58 BC | 724.53±20.23 D | 53.03±0.81 B | 36.35±0.86 FG | 44.69±3.77 BCD | 9.81±0.14 B | 8.11±0.03 D | 8.96±0.39 D | |
| Mean | 55.51±1.61 E | 77.71±0.93 B | 66.61±2.49 B | 581.11±20 C | 644.97±24.81 B | 613.04±16.95 B | 50.37±0.76 B | 34.04±0.67 D | 42.2±1.77 B | 8.62±0.23 B | 6.91±0.24 D | 7.77±0.24 B | |
| 15th Oct. | 50% | 53.24±0.73 HI | 78.71±0.91 B | 65.97±5.72 CD | 538.07±9.43 JK | 657.01±4.84 DE | 597.54±27.01 DE | 50.35±0.92 BCD | 34.85±1.09 FGHI | 42.6±3.52 CD | 8.17±0.02 D | 6.36±0.03 JKL | 7.26±0.41 E |
| 75% | 56.15±0.69 GH | 77.06±1.06 BCD | 66.6±4.71 E | 589.46±3.64 GHI | 636.72±27.24 EF | 613.09±16.21 GH | 51.53±0.88 BCD | 35.35±0.73 FGH | 43.44±3.65 F | 8.75±0.07 C | 6.78±0.05 HIJ | 7.77±0.44 F | |
| 100% | 57.93±0.79 G | 84.33±1.32 A | 71.13±5.94 F | 630.91±8.78 EFG | 755.5±7.31 C | 693.21±28.32 H | 52.97±0.84 B | 34.86±0.74 FGHI | 43.92±4.08 EF | 9.69±0.03 B | 7.59±0.36 EF | 8.64±0.5 G | |
| 125% | 69.42±1.48 E | 63.65±2.44 C | 76.85±3.44 CD | 797.37±17.68 AB | 559.52±10.24 C | 814.28±13.05 D | 56.65±1.12 A | 41.41±1.7 C | 46.91±4.38 BCD | 10.45±0.11 A | 6.81±0.19 C | 9.67±0.35 D | |
| Mean | 59.18±1.9 D | 71.24±1.19 E | 70.14±2.52 A | 638.95±29.68 B | 535.02±17.76 JK | 679.53±20.67 A | 52.88±0.82 A | 32.23±0.81 IJ | 44.22±1.86 A | 9.27±0.26 A | 5.18±0.03 M | 8.34±0.28 A | |
| N fertilization * Cultivars | N fertilization * Cultivars | N fertilization * Cultivars | N fertilization * Cultivars | ||||||||||
| 50% | 75.24±1.17 B | 75.24±1.17 B | 62.77±3.11 D | 582.66±20.52 D | 582.66±20.52 D | 545.67±14.04 D | 32.76±0.67 F | 32.76±0.67 F | 40.76±1.99 D | 5.83±0.17 G | 5.83±0.17 G | 6.79±0.26 D | |
| 75% | 53.45±0.82 E | 75.48±0.67 B | 64.47±2.72 C | 556.18±9.58 E | 606.64±11.89 C | 581.41±9.61 C | 49.53±0.68 C | 33.9±0.61 EF | 41.72±1.95 C | 8.05±0.21 C | 6.42±0.13 F | 7.24±0.23 C | |
| 100% | 55.35±0.91 D | 79.99±1.34 A | 67.67±3.09 B | 580.87±16.17 D | 672.81±23.21 B | 626.84±17.68 B | 51.3±0.76 B | 34.63±0.5 E | 42.96±2.07 B | 8.44±0.43 B | 7.01±0.21 E | 7.72±0.29 B | |
| 125% | 63.79±1.7 C | 80.81±1.37 A | 72.3±2.32 A | 687.8±31.28 B | 743.27±30.37 A | 715.54±22.19 A | 53.83±0.92 A | 36.18±0.47 D | 45.0±2.2 A | 9.51±0.33 A | 8.1±0.23 C | 8.8±0.26 A | |
| Mean | 55.72±1 B | 77.88±0.71 A | 583.38±14.26 B | 651.35±15.07 A | 50.85±0.49 A | 34.37±0.34 B | 8.44±0.18 A | 6.84±0.17 B | |||||
3.2. Crop Measurements
3.3. Chemical Components of Garlic Leaves and Bulb
3.4. Greenhouse Gas Emission from Nitrogen Fertilization and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
3.5. Profitability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Consent for Publication
References
- Taha, N.M.; Abd-Elrahman, S.H.; Hashem, F.A. Improving yield and quality of garlic (Allium sativum L.) under water stress conditions. Middle East J. Agric. Res. 2019, 8, 330–346. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, K.; Kaur, A.; Singh, M. Effect of planting time and planting methods on the performance of garlic (Allium sativum L.) under Punjab conditions. Pharma Innov. J. 2022, 11, 2431–2435. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. World Food and Agriculture Statistical Yearbook 2022; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, K.; Hoq, O.; Uddin, S. Medicinal plant Allium sativum. A review. J. Med. Plant Stud. 2016, 4, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Alsup-Egbers, C.; Byers, P.; McGowan, K.; Trewatha, P.B.; McClain, W.E. Effect of three planting dates on three types of garlic in southwest Missouri. Hort Technol. 2020, 30, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; El-Damarany, A.; Marey, R. Effect of planting dates and fertilization on yield and yield components of onion (Allium cepa L.) grown from Sets. J. Plant Prod. 2018, 9, 1031–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, A.; Debsharma, S.K.; Mondal, S.; Maniruzzaman, S.; Islam, M.; Rahim, M.A.; Haque, M.A. Effect of planting time on growth and yield of garlic (Allium sativum L.) genotypes. Asian J. Res. Crop Sci. 2022, 7, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murmu, D.; Hembram, T.; Das, A.; Das, B. Influence of planting time and spacing for growth and yield of garlic (Allium sativum L.). J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Gashaw, B. Evaluation of different rates of NPS on growth and yield performances of garlic (Allium sativum L.) in Cheha District, Gurage Zone, Ethiopia. Int. J. Agron. 2021, 2021, 7742386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevlani, L.; Leghari, Z.; Wahocho, N.A.; Talpur, K.H.; Ahmed, W.; Jamali, M.F.; Kubar, A.A.; Wahocho, S.A. Nitrogen nutrition affect the growth and bulb yield of garlic (Allium Sativum L.). J. Appl. Res. Plant Sci. 2023, 4, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, G.; Mamo, T. Effects of nitrogen and NPS fertilizer rates on fresh yield of garlic (Allium sativum L.) at Debre Berhan, Ethiopia. J. Agric. Crops 2020, 6, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, W.; Du, E.; Pan, Y.; Goulding, K. Reduced nitrogen dominated nitrogen deposition in the United States, but its contribution to nitrogen deposition in China decreased. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3590–E3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulatu, A.; Tesfaye, B.; Getachew, E. Growth and bulb yield garlic varieties affected by nitrogen and phosphorus application at Mesqan Woreda, South Central Ethiopia. Sky J. Agric. Res. 2014, 3, 249–255. [Google Scholar]
- Sebnie, W.; Mengesha, M.; Girmay, G.; Feyisa, T. Response of garlic (Allium sativum L.) to nitrogen and phosphorus under irrigation in Lasta district of Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 2018, 4, 1532862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.; DeBusk, W.; DeLaune, R.; Koch, M. Long-term nutrient accumulation rates in the Everglades. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, A.; Rahim, M.; Anwar, H. Effects of planting time and different levels of nitrogen on the growth and yield of garlic. Bangladesh J. Train. Dev. 2000, 13, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, M.; Hashem, M.; Jahiruddin, M.; Rahim, M. Effect of nitrogen for yield maximization of garlic in old brahmaputra flood plain soil. Bangladesh J. Agric. Res. 2011, 36, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Hemada, A.; Toney, H. Response of garlic plants to the application of two bio-fertilizers and four mineral nitrogen levels. Minia J. Agric. Res. Develop. 2012, 32, 593–611. [Google Scholar]
- Diriba-Shiferaw, G.; Nigussie-Dechassa, R.; Kebede, W.; Getachew, T.; Sharma, J. Bulb quality of garlic (Allium sativum L.) as influenced by the application of inorganic fertilizers. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2014, 9, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.G.; Fagam, A.; Dayi, R.U.; Isah, Z. Phenotypic response of two garlic varieties to different nitrogen fertilization grown under irrigation in Sudan Savannah ecological zone of Nigeria. Int. J. Agron. 2016, 2016, 2495828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Dong, H.; Ma, C.; Mo, Q.; Liu, B.; Irshad, A.; Li, H.; Yang, B.; Ding, R.; Shayakhmetoya, A. Inhibiting N2O emissions and improving environmental benefits by integrating garlic growing in grain production systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 347, 108371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Change, I.C. The physical science basis, 2013. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1/ (last accessed: 04/07/2024).
- Water, W.C. WMO greenhouse gas bulletin, 2019. https://library.wmo.int/records/item/58687-no-15-25-november-2019?offset=5 (last accessed: 04/07/2024).
- Shukla, P.R.; Skea, J.; Calvo Buendia, E.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Pörtner, H.O.; Roberts, D.; Zhai, P.; Slade, R.; Connors, S.; Van Diemen, R. Climate Change and Land: An IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems, 2019. https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2019/11/SRCCL-Full-Report-Compiled-191128.pdf.
- Adu-Poku, D.; Ackerson, N.O.B.; Devine, R.N.O.A.; Addo, A.G. Climate mitigation efficiency of nitrification and urease inhibitors: Impact on N2O emission–A review. Sci. Afr. 2022, 16, e01170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, Q. Identification of current research intensity and influence factors of agricultural nitrogen loss from cropping systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klute, A. Water retention: Laboratory methods. Methods of soil analysis: Part 1. Phys. Mineral. Methods 1986, 5, 635–662. [Google Scholar]
- Troll, W.; Lindsley, J. A photometric method for the determination of proline. J. Biol. Chem. 1955, 215, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, W.; Beck, E.; Piepenbrock, M.; Lenz, B.; Schmitt, J.M. Cytokinin as a negative effector of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase induction in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. J. Plant Physiol. 1997, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, H.D.; Pratt, P.F. Methods of analysis for soils, plants and waters. Soil Sci. 1962, 93, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M. Soil Chemical Analysis Prentice; Hall. Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1958; Volume Voulne 498, pp. 183–204. [Google Scholar]
- Kalra, Y.P. Soil pH: First soil analysis methods validated by the AOAC International. J. For. Res. 1996, 1, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers Pt Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhindsa, R.; Plumb-Dhindsa, P.; Thorpe, T. Leaf senescence correlated permeability, lipid peroxidation and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J. Exp. Bot. 1981, 32, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, E. Antioxidative and antigenotoxic effects of garlic (Allium sativum L.) prepared by different processing methods. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2009, 64, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Harnly, J.M. Free amino acid and cysteine sulfoxide composition of 11 garlic (Allium sativum L.) cultivars by gas chromatography with flame ionization and mass selective detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9100–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RB, C. Plant response to mineral element toxicity and deficiency. Breed. Plants Less Favourable Environ. 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Neville, M. Nitrogen fertilizer management for nitrous oxide (N2O) mitigation in intensive corn (Maize) production: An emissions reduction protocol for US Midwest agriculture. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2010, 15, 185–204. [Google Scholar]
- El-Beltagi, H.S.; Hashem, F.A.; Maze, M.; Shalaby, T.A.; Shehata, W.F.; Taha, N.M. Control of gas emissions (N2O and CO2) associated with applied different rates of nitrogen and their influences on growth, productivity, and physio-biochemical attributes of green bean plants grown under different irrigation methods. Agronomy 2022, 12, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Change, I.C. Mitigation of climate change. Contrib. Work. Group III Fifth Assess. Rep. Intergov. Panel Clim. Chang. 2014, 1454, 147. [Google Scholar]
- CIMMYT. From Agronomic Data to Farmer Recommendation, An Economic Workbook; CIMMYT: México-Veracruz, Mexico, 1988; pp. 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Waller, R.A.; Duncan, D.B. A Bayes rule for the symmetric multiple comparisons problem. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1969, 64, 1484–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Awadelkareem, W.; Haroun, M.; Wang, J.; Qian, X. Nitrogen interactions cause soil degradation in greenhouses: Their relationship to soil preservation in China. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, M.; Feizienė, D.; Tilvikienė, V.; Feiza, V.; Baltrėnaitė-Gedienė, E.; Ullah, S. Biochar with inorganic nitrogen fertilizer reduces direct greenhouse gas emission flux from soil. Plants 2023, 12, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayel, M.; El-Dardiry, E.I.; Shaaban, S.; Sabreen, K.P. Effect of injector types and irrigation and nitrogen levels on: III-cost analysis of garlic production. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2010, 6, 822–829. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, B. Effect of planting time on the performance of onion cultivars. Veg. Sci. 2001, 28, 140–142. [Google Scholar]
- Jamroz, M.; Ishtiaq, M.; Nisar, N.; Niaz, M.; Jamiher, B.; Iqbal, J. Effect of different planting dates and spacing on growth and yield of garlic cv. Bianco. J. Biol. Sci. 2001, 1, 206–208. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, I.A.; Gad, A.; Bardisi, A.; Mohsen, A. Effect of planting dates and nitrogen sources on dry weight, yield and nitrogen use efficiency of garlic plants grown under South Sinai governorate conditions. Zagazig J. Agric. Res. 2018, 45, 1855–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.; Chowdhury, M.; Anwar, H.; Alam, M. Effect of planting dates on the growth and yield of garlic germplasm. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2003, 2, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya, G.; Padma, M.; Rajkumar, M. Effect of planting time and plant densities on yield, quality and cost of production in garlic (Allium sativum L.) cv. Jamnagar. Asian J. Hortic. 2013, 8, 552–555. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, N.; Tony, H. Influence of different planting date on the performance of new garlic genotypes grown under El-Minia Governorate conditions. Nat. Sci. 2014, 12, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, K. Effect of Sowing Time and Sulphur Levels on Growth Yield and Quality of Garlic (Allium sativum L.). Master’s Thesis, Sri Karan Narendra Agriculture University, Jobner, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby, G.; El-Muraba, A.; Kandeel, N.; Gamie, A. Effect of some cultural practices on onion bulbs production grown by sets. 3.-planting date direction of ridges and cultivars. Assiut J. Agric. Sci. 1991. [Google Scholar]
- El-Zohiri, S.; Farag, A. Relation planting date, cultivars and growing degree-days on growth, yield and quality of garlic. Middle East J. Agric. Res. 2014, 3, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, A.V.; Pilbeam, D.J. Handbook of Plant Nutrition; Blume, H.P., Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; Methods of soil analysis; 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, 2. Aufl. 1184 S., American Soc. of Agronomy (Publ.), Madison, Wisconsin, USA, gebunden 36 Dollar. Wiley Online Library.
- Yadav, R.; Sen, N.; Fageria, M.; Dhaka, R. Effect of nitrogen and potassium fertilization on quality bulb production of onion. Haryana J. Hortic. Sci. 2002, 31, 297–297. [Google Scholar]
- Boyhan, G.E.; Torrance, R.L.; Hill, C.R. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium rates and fertilizer sources on yield and leaf nutrient status of short-day onions. HortScience 2007, 42, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.; Marey, R.; Karam, S.; Abo-Dahab, A. Productivity and storability of onion as influenced by the different levels of NPK fertilization. J. Agric. Res. Kafr El-Sheikh Univ. 2012, 38, 171–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kandil, A.A.; Sharief, A.E.; Fathalla, F.H. Effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on vegetative growth, bulb yield and quality of onion cultivars. Crop Prod. 2013, 2, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, E.; El-Gizawy, E.; Geries, L. Effect of compost extract, N2-fixing bacteria and nitrogen levels applications on soil properties and onion crop. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2015, 61, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, A.; Farnia, A.; Maleki, A. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorous biofertilizers on yield and yield components of corn AS71 in Dareh-shahr, Iran. J. Crop Ecophysiol. 2013, 7, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, A. Role of nitrogen (N) in plant growth, photosynthesis pigments, and N use efficiency: A review. Agrisost 2022, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, A.; Zeidali, E. Conservation tillage and nitrogen fertilizer: A review of corn growth and yield and weed management. Cent. Asian J. Plant Sci. Innov. 2021, 1, 121–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.S.; Ali, A.A.; Farag, F.M. Interaction effects of planting date or/and clove weight on growth, yield, storability and severity of downy mildew disease on two garlic cultivars. Egypt. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 98, 214–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dissoky, R.; Gahwash, M. Effect of mineral nitrogen fertilization and some organic materials on garlic yield and soil fertility under different irrigation intervals. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2018, 9, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasim, W.; Ahmad, A.; Hammad, H.M.; Chaudhary, H.J.; Munis, M.F.H. Effect of nitrogen on growth and yield of sunflower under semi-arid conditions of Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 639–648. [Google Scholar]
- Ghobadi, R.; Ghobadi, M.; Honarmand, S.; Farhadi, B.; Mondani, F. Study the responses of some leaf physiologic characteristics to different water and nitrogen levels in grainy maize (Zea mays L.). Iran. J. Field Crops Res. 2018, 16, Fa583–Fa597. [Google Scholar]
- Drury, C.; Yang, X.; Reynolds, W.; McLaughlin, N. Nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide emissions from monoculture and rotational cropping of corn, soybean and winter wheat. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 88, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusenbury, M.; Engel, R.; Miller, P.; Lemke, R.; Wallander, R. Nitrous oxide emissions from a northern great plains soil as influenced by nitrogen management and cropping systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorson, A.D.; Del Grosso, S.J.; Reule, C.A. Nitrogen, tillage, and crop rotation effects on nitrous oxide emissions from irrigated cropping systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.K.; Bali, S.K. A review of methods to improve nitrogen use efficiency in agriculture. Sustainability 2017, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Tan, D.K.Y.; Afridi, M.Z.; Luo, H.; Tung, S.A.; Ajab, M.; Fahad, S. Nitrogen fertility and abiotic stresses management in cotton crop: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14551–14566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudin, A.C.; Janovicek, K.; Deen, B.; Hooker, D.C. Wheat improves nitrogen use efficiency of maize and soybean-based cropping systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 210, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lela, K.M.; El-Sebaay, A.S.; Abd-Elrahman, S.H.; Elbordiny, M.M. Nitrogen management in a sandy loam soil grown with cucumber plants and fertilized by vermicompost. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2024, 2023137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, M.A.; El-Gabry, Y.A.; Sayed, A.N.; Shahin, M.G.; Darwish, H.A.; Aboukota, M.E.; Hashem, F.A.; Abd-Elrahman, S.H. Evaluation of physio-biochemical criteria in maize inbred lines and their F1 hybrids grown under water-deficit conditions. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2022, 67, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elrahman, S.H.; Hashem, F.A.; Farag, A.A. Mitigation of heat stress effects on snake cucumber plants by silicon additions and rice straw soil cover. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2022, 53, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Air Temperature (°C) | Solar Radiation (W m−2) | Relative Humidity (%) | Wind Speed (m s−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Avg | Max | Min | Avg | Avg | Max | Min | Avg | Max |
| 2020/2021 | |||||||||
| September 2019 | 28.5 | 39.9 | 20.8 | 149 | 51.8 | 90.7 | 12.7 | 2.7 | 5.3 |
| October 2019 | 24.4 | 36.2 | 13.5 | 124 | 53.4 | 89.2 | 18.3 | 2.0 | 5.5 |
| November 2019 | 19.2 | 30.5 | 10.3 | 86 | 59.1 | 92.2 | 18.3 | 1.0 | 4.8 |
| December 2019 | 14.5 | 22.7 | 9.84 | 128 | 63.4 | 93.8 | 30.6 | 0.9 | 4.1 |
| January 2020 | 11.6 | 24.9 | 7.91 | 152 | 54.0 | 95.0 | 13.3 | 0.8 | 3.6 |
| February 2020 | 13.7 | 29.5 | 8.48 | 178 | 55.6 | 92.8 | 14.1 | 0.9 | 4.3 |
| 2021/2022 | |||||||||
| September 2020 | 28.7 | 39.5 | 20.9 | 218 | 51.1 | 85.9 | 20.4 | 1.3 | 4.3 |
| October 2020 | 23.2 | 35.5 | 14.5 | 147 | 59.5 | 95.2 | 19.7 | 1.1 | 3.9 |
| November 2020 | 20.4 | 35.8 | 10.0 | 124 | 54.3 | 97.5 | 12.2 | 1.0 | 3.8 |
| December 2020 | 14.6 | 24.4 | 8.39 | 111 | 63.7 | 96.0 | 25.9 | 1.1 | 3.7 |
| January 2021 | 11.7 | 20.1 | 7.25 | 130 | 54.9 | 88.1 | 26.6 | 0.8 | 3.0 |
| February 2021 | 14.2 | 29.0 | 9.39 | 158 | 64.2 | 99.5 | 13.9 | 0.9 | 4.3 |
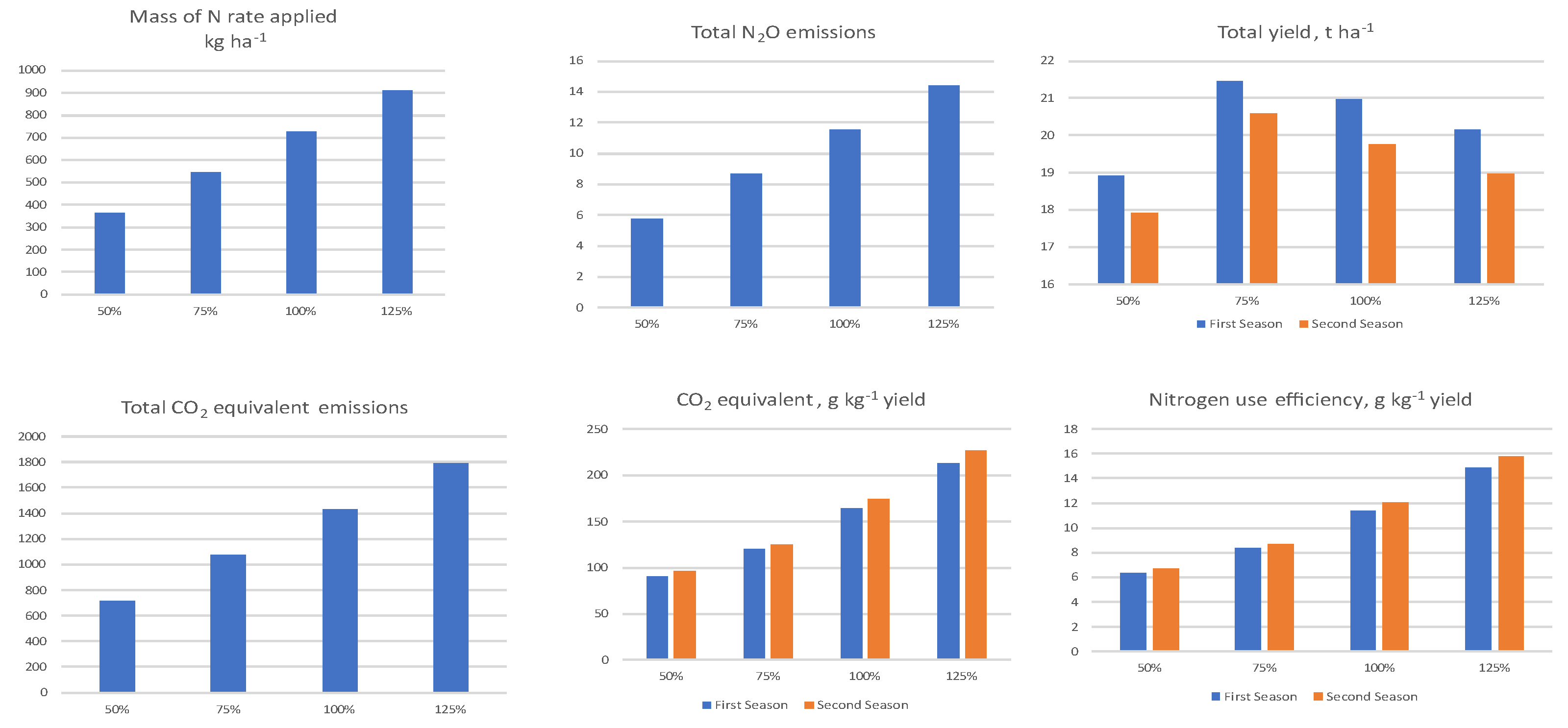
| Nitrogen level (%) |
Mass of N rate applied | Total yield | Total N2O | Total CO2 Equivalent | CO2 equivalent | Nitrogen use efficiency | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg ha−1 | emissions | emissions | g kg−1 yield | g kg−1 yield | |||||
| kg ha−1 | First season | Second season | kg ha−1 | kg ha−1 | First season | Second season | First season | Second season | |
| 50% | 364 | 18.9 | 17.9 | 5.8 | 1720 | 91 | 96 | 6.35 | 6.69 |
| 75% | 545 | 21.5 | 20.6 | 8.7 | 2580 | 120 | 125 | 8.39 | 8.74 |
| 100% | 727 | 21.0 | 19.8 | 11.5 | 3440 | 164 | 174 | 11.44 | 12.14 |
| 125% | 909 | 20.2 | 19.0 | 14.4 | 4300 | 213 | 227 | 14.88 | 15.82 |
| Planting Dates | Nitrogen Levels | Cultivars | Yield | Grass Income | Total Cost | Net Income | Incremental Income | Yield | Grass Income | Total Cost | Net Income | Incremental Income |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ton ha−1 | hectare | Cost EGP | EGP ha−1 | EGP ha−1 | ton ha−1 | hectare | Cost EGP | EGP ha−1 | EGP ha−1 | |||
| First Season | Second Season | |||||||||||
| 15 September | 50% N | Balady | 21.60 | 118800 | 26400 | 92400 | -9996 | 20.21 | 111144 | 26400 | 84744 | -6696 |
| Sids-40 | 14.88 | 148800 | 29760 | 119040 | 16644 | 14.33 | 143280 | 29760 | 113520 | 22080 | ||
| 75% N | Balady | 26.21 | 144144 | 28200 | 115944 | 13548 | 22.90 | 125928 | 28200 | 97728 | 6288 | |
| Sids-40 | 17.28 | 172800 | 31560 | 141240 | 38844 | 16.10 | 161040 | 31560 | 129480 | 38040 | ||
| 100% N | Balady | 24.07 | 132396 | 30000 | 102396 | 0 | 22.08 | 121440 | 30000 | 91440 | 0 | |
| Sids-40 | 16.49 | 164880 | 33360 | 131520 | 29124 | 14.93 | 149280 | 33360 | 115920 | 24480 | ||
| 125% N | Balady | 22.90 | 125928 | 31800 | 94128 | -8268 | 20.66 | 113652 | 31800 | 81852 | -9588 | |
| Sids-40 | 15.79 | 157920 | 35160 | 122760 | 20364 | 14.40 | 144000 | 35160 | 108840 | 17400 | ||
| 1 October | 50% N | Balady | 22.44 | 123420 | 26400 | 97020 | -5376 | 20.83 | 114576 | 26400 | 88176 | -3264 |
| Sids-40 | 16.18 | 161760 | 29760 | 132000 | 29604 | 15.14 | 151440 | 29760 | 121680 | 30240 | ||
| 75% N | Balady | 21.70 | 119328 | 28200 | 91128 | -11268 | 24.10 | 132528 | 28200 | 104328 | 12888 | |
| Sids-40 | 18.96 | 189600 | 31560 | 158040 | 55644 | 17.09 | 170880 | 31560 | 139320 | 47880 | ||
| 100% N | Balady | 24.65 | 135564 | 30000 | 105564 | 3168 | 23.21 | 127644 | 30000 | 97644 | 6204 | |
| Sids-40 | 18.10 | 180960 | 33360 | 147600 | 45204 | 16.44 | 164400 | 33360 | 131040 | 39600 | ||
| 125% N | Balady | 23.66 | 130152 | 31800 | 98352 | -4044 | 22.92 | 126060 | 31800 | 94260 | 2820 | |
| Sids-40 | 17.33 | 173280 | 35160 | 138120 | 35724 | 15.72 | 157200 | 35160 | 122040 | 30600 | ||
| 15 October | 50% N | Balady | 22.85 | 125664 | 26400 | 99264 | -3132 | 21.82 | 119988 | 26400 | 93588 | 2148 |
| Sids-40 | 15.50 | 155040 | 29760 | 125280 | 22884 | 15.22 | 152160 | 29760 | 122400 | 30960 | ||
| 75% N | Balady | 26.93 | 148104 | 28200 | 119904 | 17508 | 25.25 | 138864 | 28200 | 110664 | 19224 | |
| Sids-40 | 17.71 | 177120 | 31560 | 145560 | 43164 | 18.10 | 180960 | 31560 | 149400 | 57960 | ||
| 100% N | Balady | 24.77 | 136224 | 30000 | 106224 | 3828 | 24.43 | 134376 | 30000 | 104376 | 12936 | |
| Sids-40 | 17.76 | 177600 | 33360 | 144240 | 41844 | 17.62 | 176160 | 33360 | 142800 | 51360 | ||
| 125% N | Balady | 24.62 | 135432 | 31800 | 103632 | 1236 | 23.04 | 126720 | 31800 | 94920 | 3480 | |
| Sids-40 | 19.90 | 198960 | 35160 | 163800 | 61404 | 18.19 | 181920 | 35160 | 146760 | 55320 | ||
| Average price EGP 5500 ton−1 Balady, EGP 10,000 ton−1 Sids-40 | The average cost for Farmyard manure is EGP 3840 ha−1 | The average cost for mineral fertilizer is EGP 7200 ha−1 | ||||||||||
| The average cost for seeds is EGP 5760 ha−1 Balady, EGP 9120 ha−1 Sids-40 | The average cost for pest control is EGP 7200 ha−1 | The average cost for agricultural labor is EGP 3600 ha−1 | ||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





