Submitted:
29 October 2024
Posted:
04 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Traditional Optimization Techniques
2.2. AI-Based Optimization Techniques
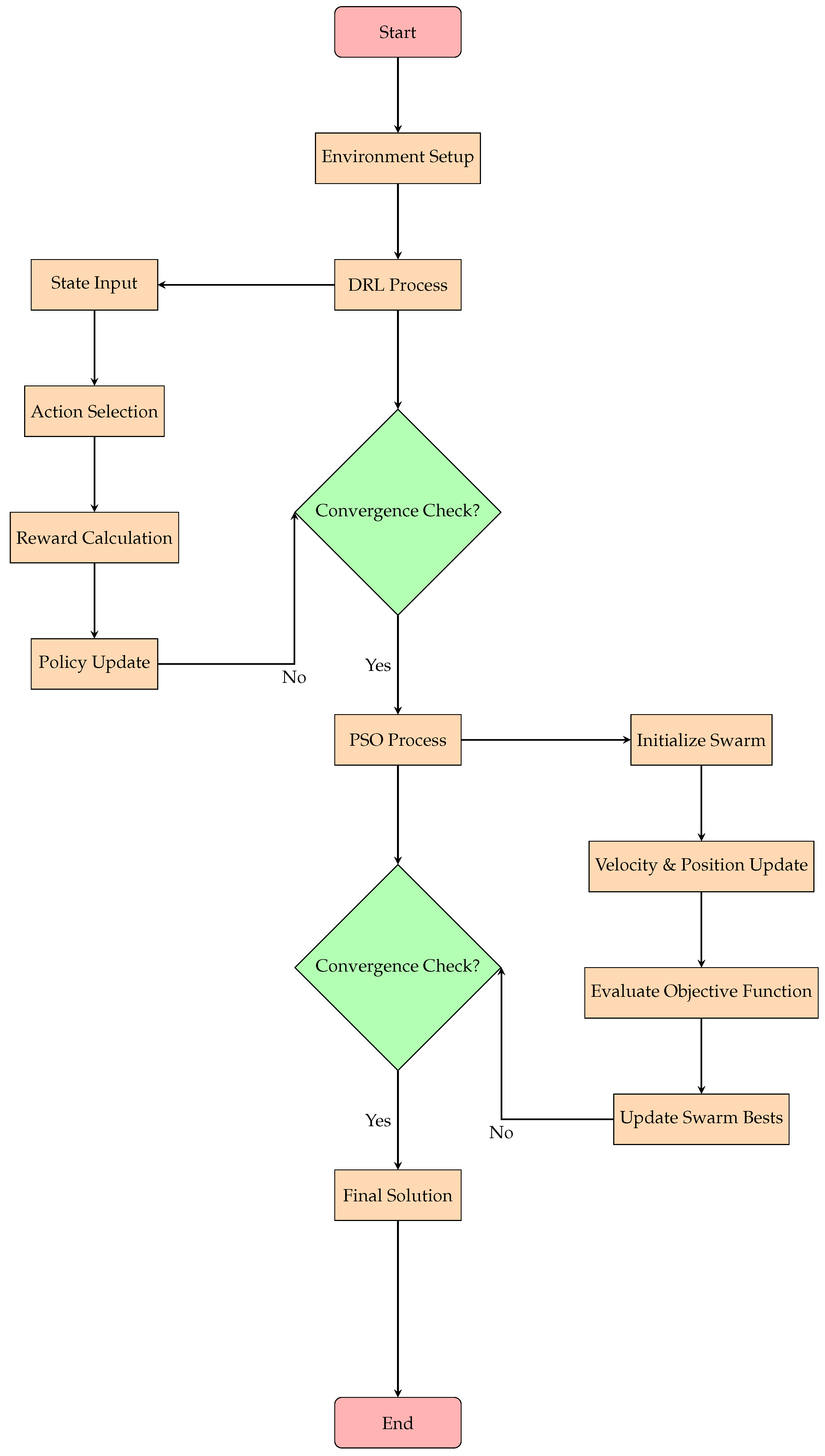
3. Proposed DRL-PSO Optimization Framework
3.1. Overview of the Proposed DRL-PSO
3.2. Mathematical Formulation
3.3. Constraints
3.4. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
3.5. Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)
3.6. Hybrid DRL-PSO Algorithm Integration
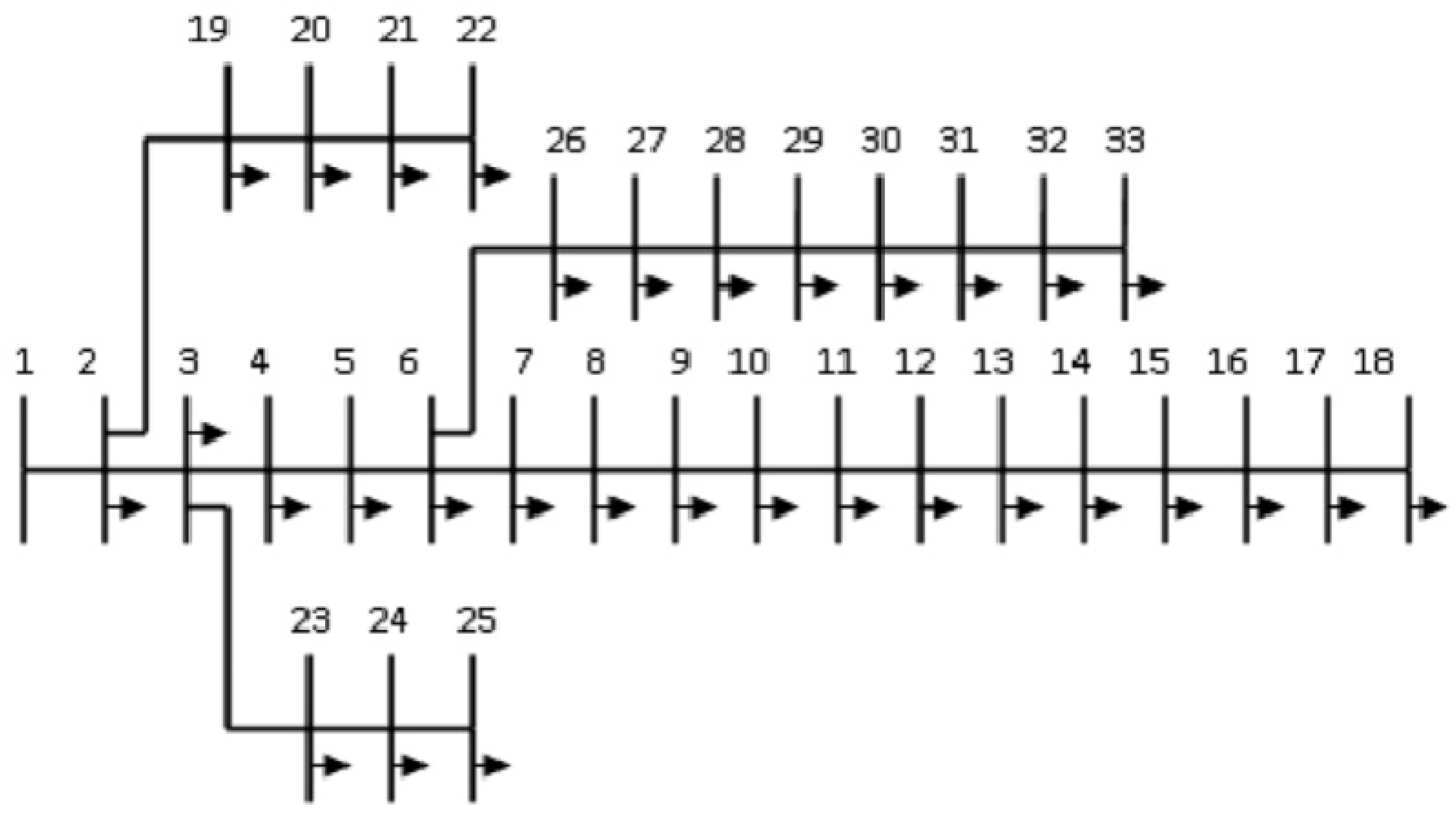
4. Test System: IEEE 33-Bus System
4.1. Simulation Setup
4.2. Comparative Analysis
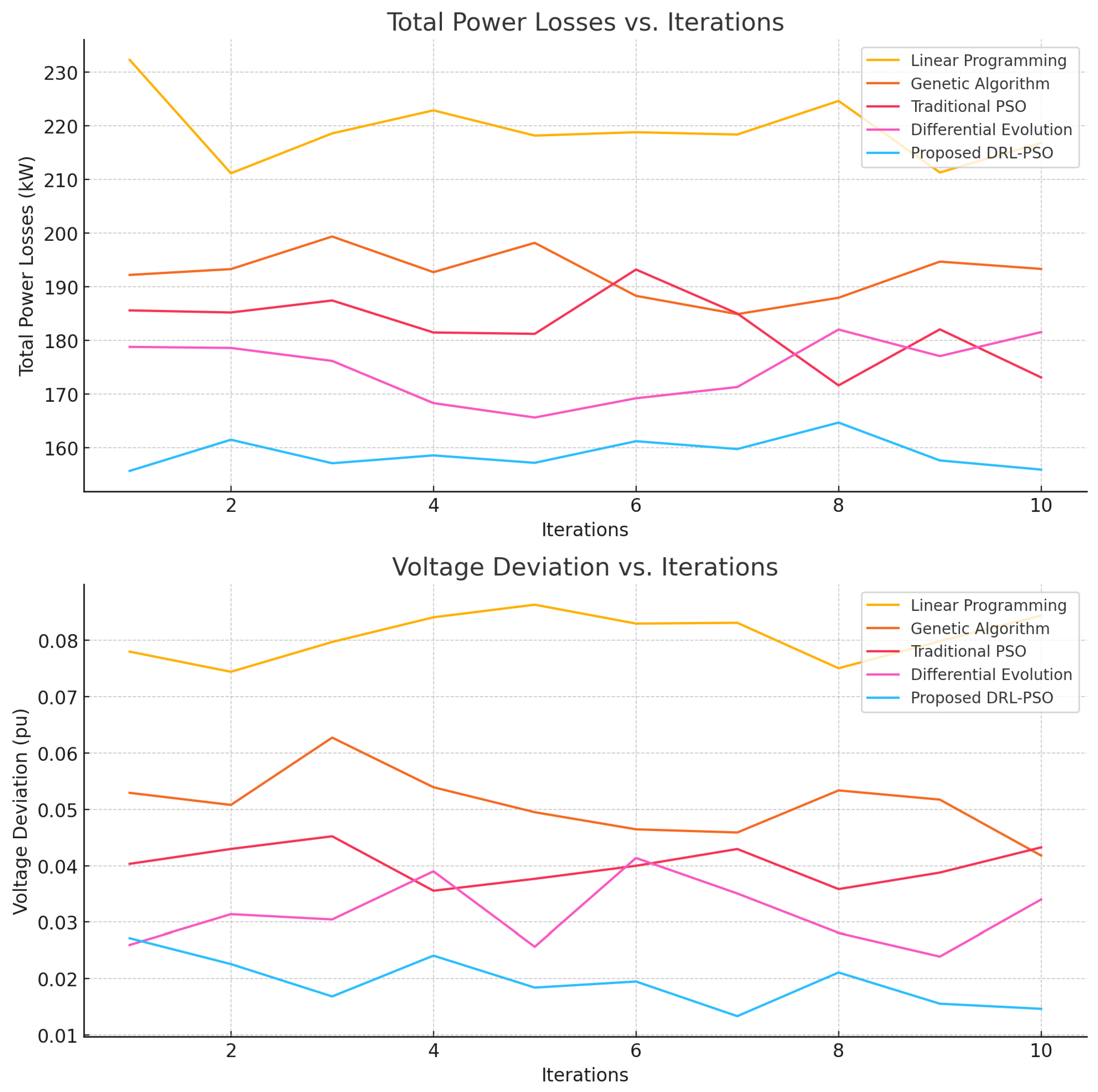
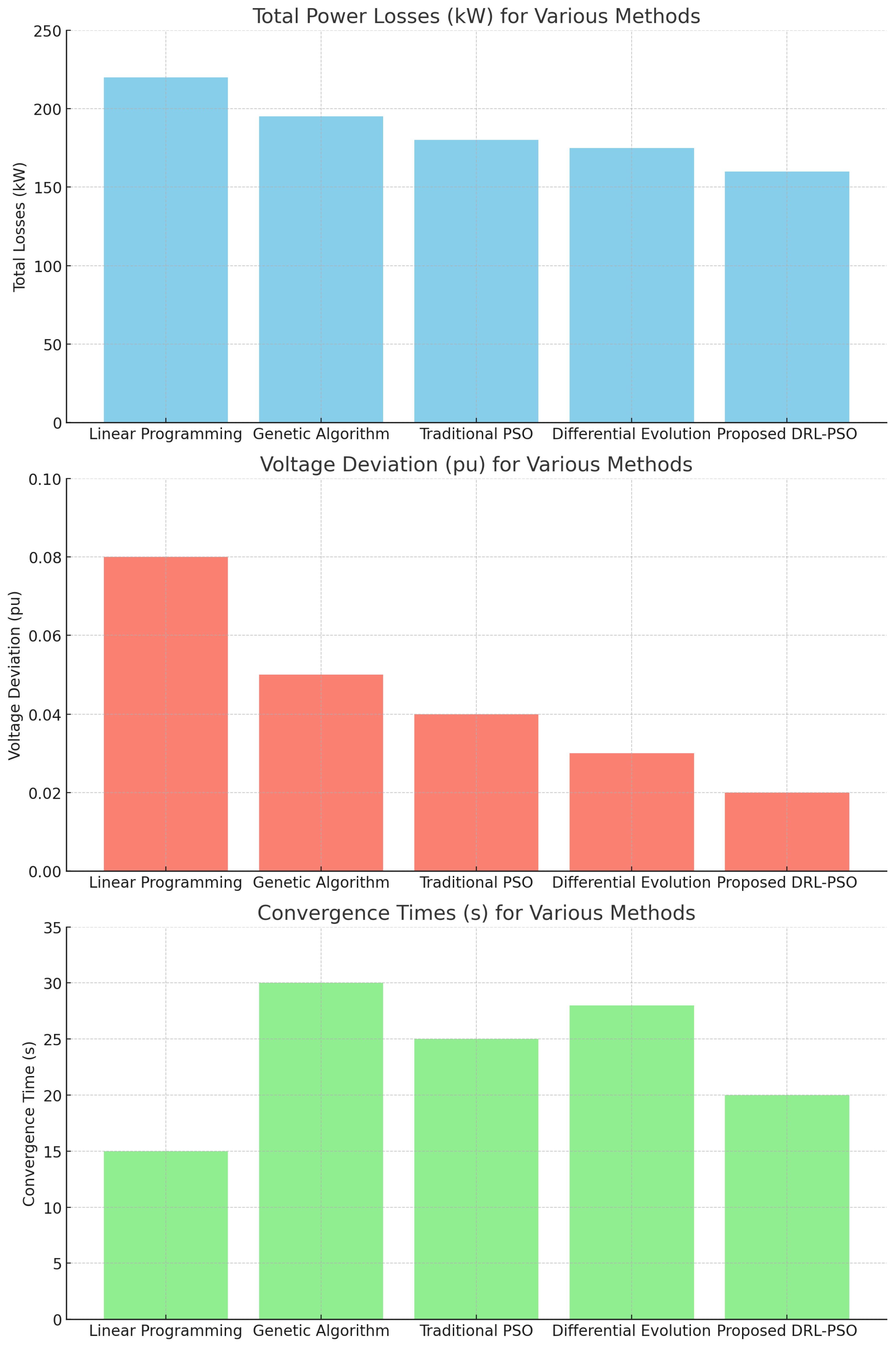
5. Conclusion
References
- A. H. Etemadi, “Smart grids: Opportunities and challenges,” IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, vol. 31, no. 1, 2016.
- D. W. Gao and S. Mohagheghi, "Challenges in smart grid implementation," IEEE PES General Meeting, 2015.
- A. T. Dimeas et al., "Smart grid technologies for real-time control of distributed energy resources," IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 62, no. 4, 2015.
- M. Pipattanasomporn et al., “Load profiles of selected major household appliances and their demand response opportunities,” IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 5, no. 2, 2014.
- M. H. Bhuiyan et al., “Loss minimization in distribution networks using linear programming,” Energy Conversion and Management, vol. 134, 2017.
- J. S. Jeromino et al., “A review of optimization techniques for smart grids,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 76, 2017.
- R. E. Brown, “Impact of smart grid on distribution system design,” IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, 2008.
- P. Taylor et al., “Technological drivers for the smart grid,” IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, vol. 2, no. 3, 2011.
- K. Deb, “An introduction to optimization in smart grids,” IEEE Smart Grid Symposium, 2016.
- J. Chao et al., “AI and machine learning for smart grid optimization,” Renewable Energy Reports, vol. 25, 2020.
- S. E. Papadopoulou et al., "Deep reinforcement learning for energy management in microgrids," IEEE Access, vol. 7, 2019.
- Y. Q. Zhang et al., “Deep learning-based optimization for power distribution networks,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, vol. 31, 2020.
- X. Wang et al., “An efficient hybrid PSO and reinforcement learning approach for grid optimization,” Journal of Power Sources, vol. 342, 2020.
- E. L. Xydis, "LP-based optimization in distribution systems," Energy Procedia, vol. 101, 2016.
- N. Hatziargyriou et al., “Distributed energy management using mixed-integer programming,” IEEE PES Transactions, vol. 104, 2017.
- A. B. Carlson, "Loss minimization using genetic algorithms," IEEE Trans. Power Systems, vol. 17, no. 3, 2008.
- M. Clerc et al., “Particle swarm optimization applied to the energy loss minimization,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 49, 2012.
- R. Storn and K. Price, "Differential evolution - a simple and efficient heuristic," Journal of Global Optimization, vol. 11, 1997.
- B. Hammer et al., “Machine learning for smart grids: A comprehensive review,” IEEE Access, vol. 5, 2019.
- J. S. He and P. Jirutitijaroen, "Forecasting methods for load prediction in smart grids," Energy Reports, vol. 7, 2021.
- Z. Zhao et al., "Deep learning for power grid applications," Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, vol. 4, 2017.
- H. Liu et al., “Reinforcement learning for dynamic power system management,” IEEE Control Systems Magazine, vol. 40, 2020.
- P. Yang et al., "Metaheuristic optimization techniques for smart grids," IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, vol. 7, no. 4, 2016.
- S. Tan et al., “Hybrid ACO and PSO for power distribution optimization,” Electric Power Systems Research, vol. 120, 2019.
- P. Sharma et al., “Linear programming approaches to power flow optimization,” IEEE PES Transactions, vol. 110, 2018.
- A. M. Khaleghian et al., "Genetic algorithms in smart grid optimization," IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., vol. 49, no. 4, 2013.
- K. K. Gosavi et al., "A survey on PSO in power system optimization," Electric Power Systems Research, vol. 111, 2020.
- C. Ling et al., "Differential evolution for power grid optimization: A survey," Renewable Energy Reports, vol. 22, 2019.
| Method | Total Losses | Voltage Deviation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| (kW) | (pu) | ||
| Linear Programming | 220 | 0.08 | [25] |
| Genetic Algorithm | 195 | 0.05 | [16,26] |
| Traditional PSO | 180 | 0.04 | [17,27] |
| Differential Evolution | 175 | 0.03 | [18,28] |
| Proposed DRL-PSO | 160 | 0.02 | This work |
| Method | Convergence | Algorithm | Real-time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (s) | Complexity | Adaptability | ||
| Linear Programming | 15 | Low | Low | [25] |
| Genetic Algorithm | 30 | Medium | Medium | [16,26] |
| Traditional PSO | 25 | Medium | Medium | [17,27] |
| Differential Evolution | 28 | Medium | Medium | [18,28] |
| Proposed DRL-PSO | 20 | High | High | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





