Submitted:
06 February 2025
Posted:
06 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
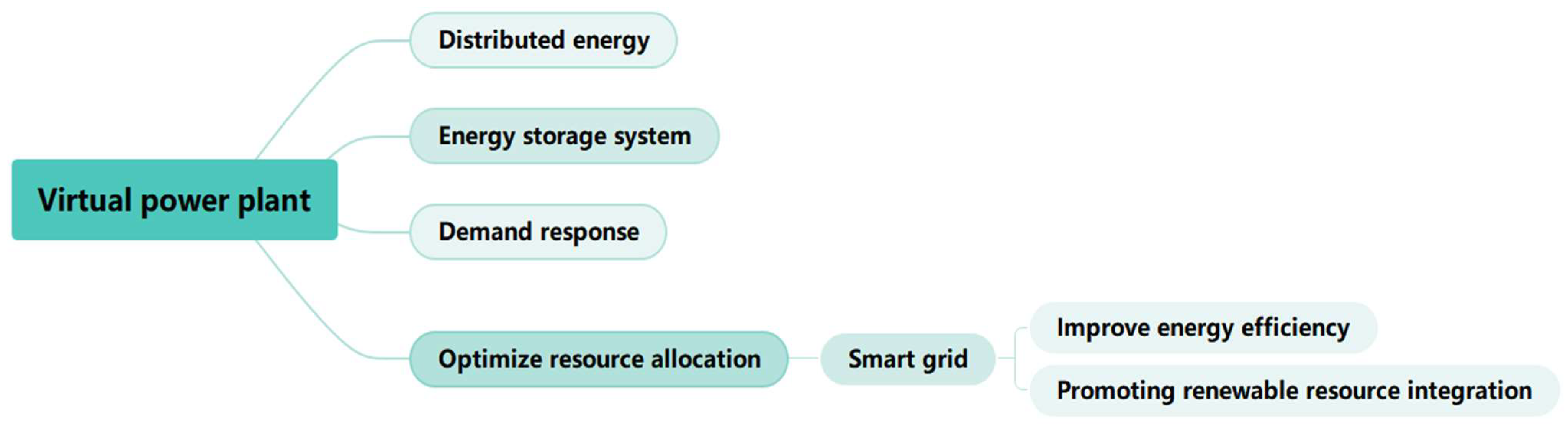
1.1. Characteristics of VPP
1.2. Characteristics of Smart Grid
1.3. The Relationship Between VPP and Smart Grid
2. Literature Review
2.1. Review of Technological Advances and Future Development of Smart Grid
2.2. A Review of Multi-Dimensional Issues and Optimization Strategies of VPP
3. AI Optimization Integrated Optimization Algorithm
3.1. Integrated Optimization Strategy
- (1)
- Minimize power loss
- (2)
- Maximize the utilization rate of renewable energy
- (3)
- Comprehensive optimization objective
- (4)
- Constraint conditions
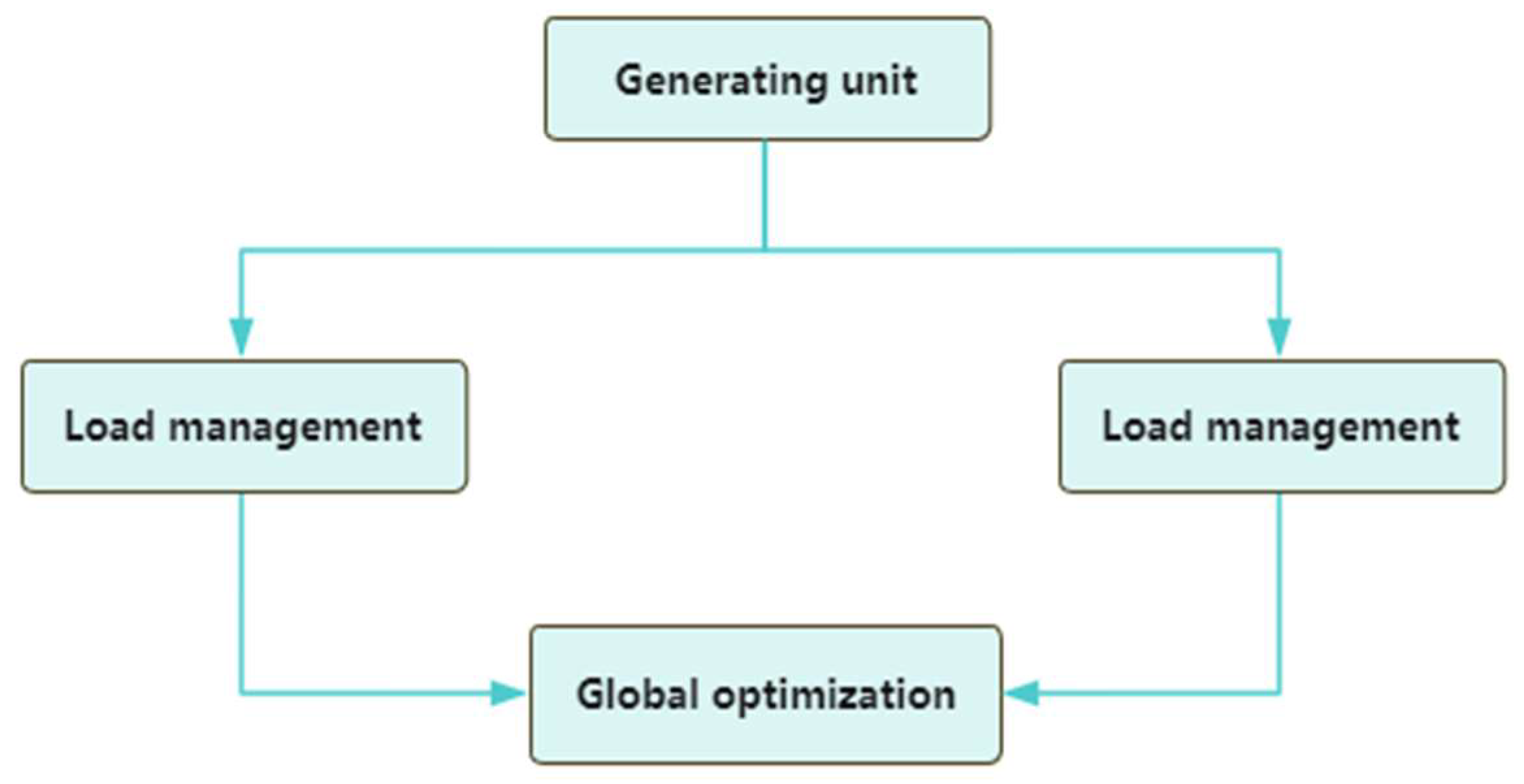
3.2. Power Grid Optimization Research
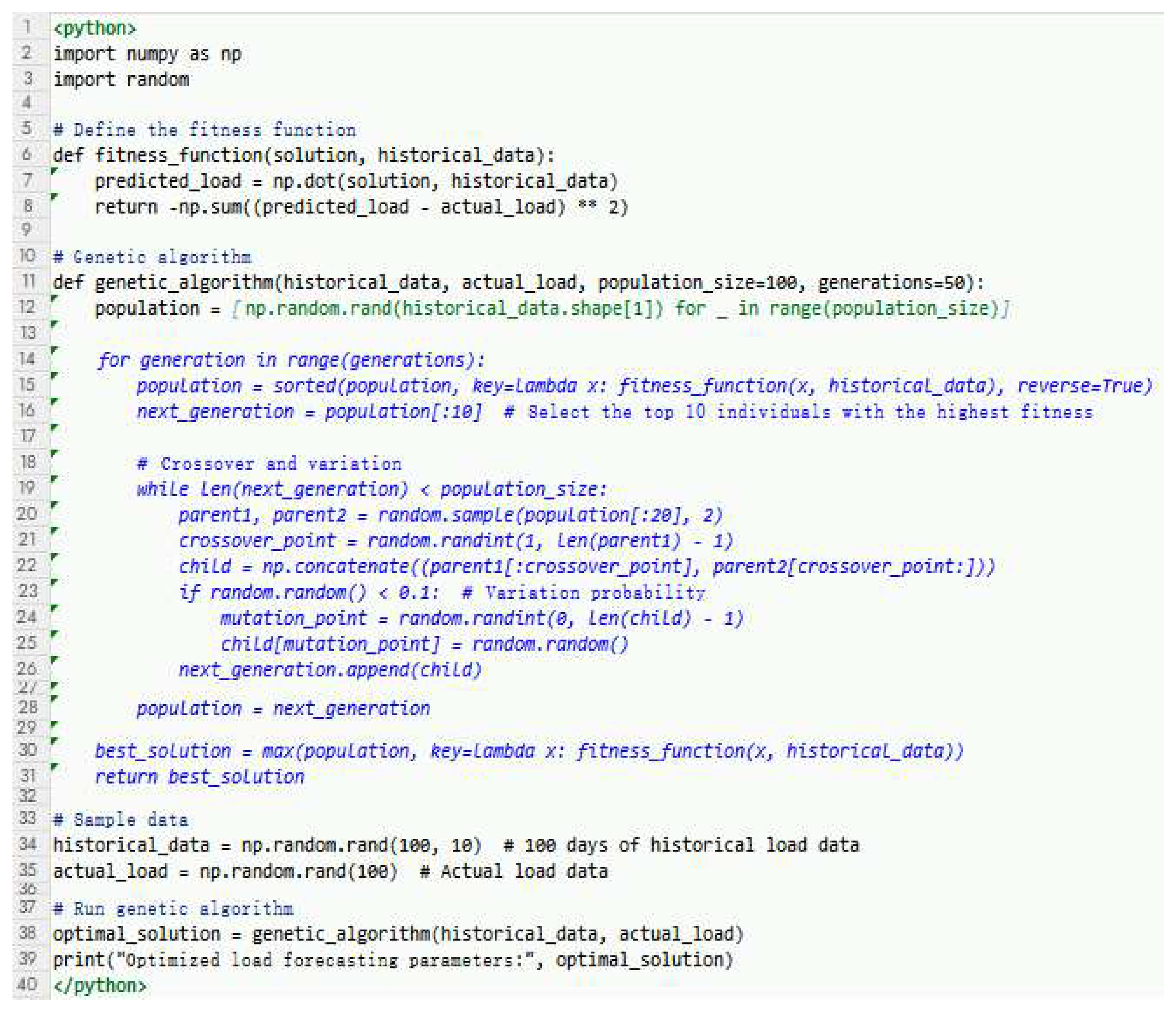
3.3. Optimization Algorithm
- (3)
- Load forecasting
- (4)
- Power dispatch
3.4. Application of AI Technology in Optimization Algorithm
3.5. Comparison of Existing Optimization Algorithm
4. AI-Based Integrated Optimization Algorithm for VPP
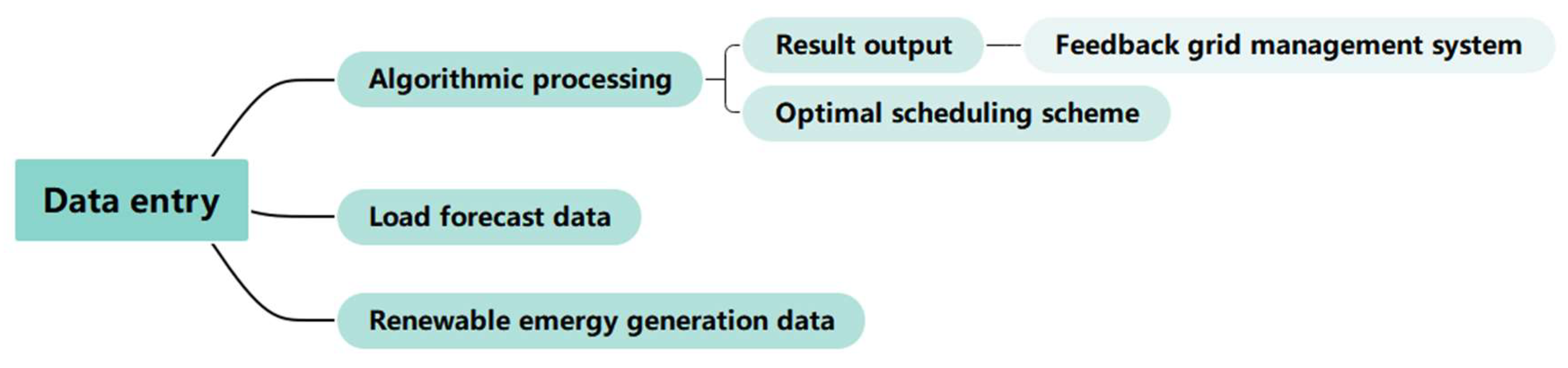
4.1. Algorithm Design Framework
4.2. Data Acquisition and Processing
| Data Acquisition Methods | Pros | Cons | Pretreatment technique | Tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor data | Strong real-time and high precision | High cost and complex maintenance | Data cleansing | Python, R |
| Market data | Large amount of data, wide coverage | There may be noise and inconsistencies | Feature selection | Weka, Scikit-learn |
| Social media data | Reflect user behavior and be dynamic | Data quality is uneven | Data normalization | Pandas, NumPy |
| Remote sensing data | Wide space coverage and easy access | The analysis is complicated and the processing time is long | Data interpolation | ArcGIS, QGIS |
4.3. Algorithm Implementation and Testing
5. Conclusions
References
- Bo, Q.; et al. Robust Optimal Dispatching of Power Grid with the Participation of Virtual Power Plants. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2024, 2788, 012023. [CrossRef]
- Xinfa, T.; et al. The Optimization of Supply–Demand Balance Dispatching and Economic Benefit Improvement in a Multi-Energy Virtual Power Plant within the Jiangxi Power Market. Energies 2024, 17, 4691. [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; et al. Adaptive Partitioning Approach to Self-Sustained Smart Grid. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution 2017, 11, 485-494. [CrossRef]
- Kiasari, M.M.; Aly, H.H. A Proposed Controller for Real-Time Management of Electrical Vehicle Battery Fleet with MATLAB/SIMULINK. Journal of Energy Storage 2024, 99, 113235. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, D. Optimizing Domestic Energy Management with a Wild Mice Colony-Inspired Algorithm: Enhancing Efficiency and Coordination in Smart Grids through Dynamic Distributed Energy Storage. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35462. [CrossRef]
- Khemakhem, S.; et al. Home Energy Management Based on Plug-in Electric Vehicle Power Control in a Residential Smart Grid. International Journal of Digital Signals and Smart Systems 2019, 3, 173-186. [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, S.; et al. Virtual Power Plants: An In-Depth Analysis of Their Advancements and Importance as Crucial Players in Modern Power Systems. Energy, Sustainability and Society 2024, 14, 52. [CrossRef]
- Xiu, J.; et al. Energy Management Optimization Strategy of Virtual Power Plant Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2022, 2384, 012041. [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; et al. A Review on the Study of Management and Interaction Mechanism for Distributed Energy in Virtual Power Plants. Power System Technology 2020, 44, 2097-2108. [CrossRef]
- Hongying, L. Research on the Application of Artificial Intelligence Technology in Power System Intelligent Dispatching Automation. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2021, 2083, 042047. [CrossRef]
- He, F.; et al. Application and Development of Internet of Things in Smart Grid. Power System Protection and Control 2020, 48, 58-69. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y. A Brief Description of the Basics of the Smart Grid. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology) 2020, 53, 551-556. [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; et al. Study of NIST’s Interoperable Smart Grid Technology Architecture. Power System Protection and Control 2020, 48, 9-21. [CrossRef]
- Asl, S.A.F.; et al. A New Two-Layer Model for Energy Management in the Smart Distribution Network Containing Flexi-Renewable Virtual Power Plant. Electric Power Systems Research 2021, 194, 107085. [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasulu, G.; Balakrishna, P. Optimal Dispatch of Renewable and Virtual Power Plants in Smart Grid Environment through Bilateral Transactions. Electric Power Components and Systems 2021, 49, 488-503. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, H. Paillier-Based Data Aggregation and Stimulation Scheme in the Smart Grid. Computer Engineering 2021, 47, 166-174. [CrossRef]
- Li, K. Research on Data Aggregation and User Query Privacy Protection in Smart Grid. Ph.D. Thesis, North China Electric Power University (Beijing), 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wiezorek, C.; et al. Validating Algorithms for Flexible Load Control in a Smart Grid Laboratory Environment. In Proceedings of the 11th IEEE-PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (IEEE-PES ISGT Europe), 2021; pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y. Smart Grid Based on Bi-Level Programming False Data Injection Attacks Research. Ph.D. Thesis, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on Residential Demand Side Management Strategies in Smart Grid Environment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7170. [CrossRef]
- Akbari, E.; et al. Multi-Objective Economic Operation of Smart Distribution Network with Renewable-Flexible Virtual Power Plants Considering Voltage Security Index. Scientific Reports 2024, 14, 70095. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. Overview of Smart Grid Development in China. Power System Protection and Control 2021, 49, 180-187. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; et al. Application of Data-Driven Technology in Virtual Power Plant. Power System Technology 2020, 44, 2411-2419.
- Summeren, L.F.M.v.; et al. 2020. Community energy meets smart grids: Reviewing goals, structure, and roles in Virtual Power Plants in Ireland, Belgium and the Netherlands. Energy Research & Social Science 63, 101415. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; et al. Economic dispatch model of virtual power plant considering electricity consumption under a carbon trading mechanism. Power System Protection and Control 2020. 48, 154-163. [CrossRef]
- Mei, G.; et al. Scheduling Strategy for Multi-energy Complementary Virtual Power Plant Considering the Correlation Between Wind and Solar Output and Carbon Emission Quota. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA 2021. 33, 62-69. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; et al. Optimal Dispatching of Virtual Power Plant Containing Electric Vehicles in Multi-Cooperative Market. Southern Power System Technology 2021. 15, 45-55. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, Y. Optimal Scheduling Strategy for Virtual Power Plant Considering 5G Base Station Technology, Energy-storage, and Energy-saving Measures. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA 2022. 34, 8-15. [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; et al. Real-time Electricity Management Optimization Algorithm for the Household Prosumer in Smart Grid. Southern Power System Technology 2022. 16, 20-28. [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; et al. Flexible Block Order Trading Clearing Model for New Power Systems. Power System Technology 2022. 46, 4150-4159. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; et al. Multi-Time Scale of New Energy Scheduling Optimization for Virtual Power Plant Considering Uncertainty of Wind Power and Photovoltaic Power. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica 2022. 43, 529-537. [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; et al. Dynamic aggregation method of virtual power plants considering reliability of renewable energy. Electric Power Automation Equipment 2022. 42, 102-110. [CrossRef]
- Goia, B.; et al. 2022. Virtual Power Plant Optimization in Smart Grids: A Narrative Review. Future Internet 14. [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.Y.; et al. Robust stochastic optimal dispatching method of multi-energy virtual power plant considering multiple uncertainties. Applied Energy 2020. 279. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; et al. Review of Key Technologies for Mega-City Virtual Power Plants upon Regional Unified Power Market. Southern Power System Technology 2023. 17, 90. [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; et al. Coalition Game Optimization Method for Multiple Virtual Power Plants Considering Carbon Trading. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA 2023. 35, 77-85. [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.S.; et al. Optimal dispatching of electric-thermal interconnected virtual power plant considering market trading mechanism. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021. 279. [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; et al. A Two-Stage Dispatch Mechanism for Virtual Power Plant Utilizing the CVaR Theory in the Electricity Spot Market. Energies 2019. 12. [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; et al. Evolutionary Game Decision and Mechanism Analysis of Dynamical Aggregation of Distributed Energy Resources Into Virtual Power Plant. Power System Technology 2023. 47, 4958-4977. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Tang, C. Research on optimization of virtual power plants dispatch by considering the consumption of new energy under time-of-use electricity price environment. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology 2023. 38, 24-34. [CrossRef]
- Hui, W.; et al. A novel approach to hybrid dynamic environmental-economic dispatch of multi-energy complementary virtual power plant considering renewable energy generation uncertainty and demand response. Renewable Energy 2023. 219. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.O. Research on optimal dispatch method of virtual power plant considering various energy complementary and energy low carbonization. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2022. 136. [CrossRef]
| Features | Smart grid | Traditional power grid |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time monitoring | Support real-time data acquisition and analysis | It relies on regular inspections and human monitoring |
| Two-way communication | Two-way information flow between users and the power grid | Only one-way information flow is supported |
| Automated control | With self-regulation and fault self-healing ability | The control system is relatively simple, slow response |
| Energy Management | Support the integration and optimization of renewable energy sources | It is difficult to integrate renewable energy effectively |
| Application Scenarios | Smart home, distributed power generation, demand response | Traditional industry, centralized power generation |
| Indicators | Current level | Expected increase | Specific impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peak load | 1000 MW | 10% lower | Reduce stress on the grid and reduce the cost of supplying electricity |
| Load balancing capability | 75% | 15% boost | Improve grid stability and reduce the risk of power outages |
| Utilization rate of wind energy | 30% | 20% improvement | Increase the share of renewable energy and reduce dependence on fossil fuels |
| Solar integration capacity | 25% | 25% boost | Improve the efficiency of solar power generation and optimize resource allocation |
| Name of algorithm | Features | Applicable scenarios | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic algorithms | Based on the principles of natural selection and genetics, it is good at dealing with multi-objective nonlinear problems | Multi-constraint optimization problems in power scheduling | Able to search the solution space globally and find good quality solutions | The convergence rate is relatively slow, which may increase the calculation time |
| Particle swarm optimization algorithm | Simulate the foraging behavior of birds and realize fast convergence through information sharing | Real-time power dispatching requires fast response | Fast convergence, suitable for dynamic environment | It is easy to fall into local optimal solutions, affecting global optimality |
| Ant colony algorithm | Based on the principle of swarm intelligence, strong path optimization ability | Power load scheduling, need to consider a variety of path selection | Strong adaptability, able to flexibly respond to changes | High computational complexity when dealing with large-scale problems |
| Simulated annealing algorithm | Simulate the physical annealing process to avoid falling into local optimality | Combinatorial optimization problems, such as resource allocation in electricity markets | Strong global search ability, can effectively avoid local optimization | The parameter Settings are complex and need to be fine-tuned to obtain the best performance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





