Submitted:
16 October 2024
Posted:
17 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
The effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 1008 (LP1008) on age-related cognitive impairment and skeletal muscle atrophy have been reported previously. However, its role in obesity- and age-related hypogonadism has yet to be explored. This study investigated the therapeutic efficacy of low- and high-dose LP1008 in a high-fat diet-fed male mouse model. Mice were fed a standard diet or 45% high-fat diet for 28 weeks, and the high-fat diet-fed mice were divided into vehicle, low-dose or high-dose LP1008 groups on the basis of the treatment administered for an additional 8 weeks. We found that LP1008 suppressed the increase in total cholesterol levels and liver function parameters and alleviated histological changes in the brain, cecum, gastrocnemius, and testes. In terms of reproductive function, LP1008 attenuated the decreases in sperm quality, sperm maturity, testosterone levels, and levels of enzymes involved in testosterone biosynthesis. Furthermore, LP1008 altered impairments in spatial learning and memory and induced slight alterations in the gut microbiota. Moreover, LP1008 exerted antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects in aged, obese male mice. LP1008 reversed diet-induced obesity, age-related reproductive dysfunction, and pathological damage by increasing testosterone levels and altering the gut microbiome through the regulation of mediators involved in oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Treatment
2.2. Serum Parameters
2.3. Sperm Quality
2.4. Hematoxylin‒Eosin (HE) Staining
2.5. Measurements of Spatial Learning and Memory
2.6. Measurements of Testicular Superoxide Dismutase, Catalase, Glutathione Peroxidase, and Thiobarbituric Acid-Reactive Substances
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Fecal Microbial Profiling
2.9. Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acids
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
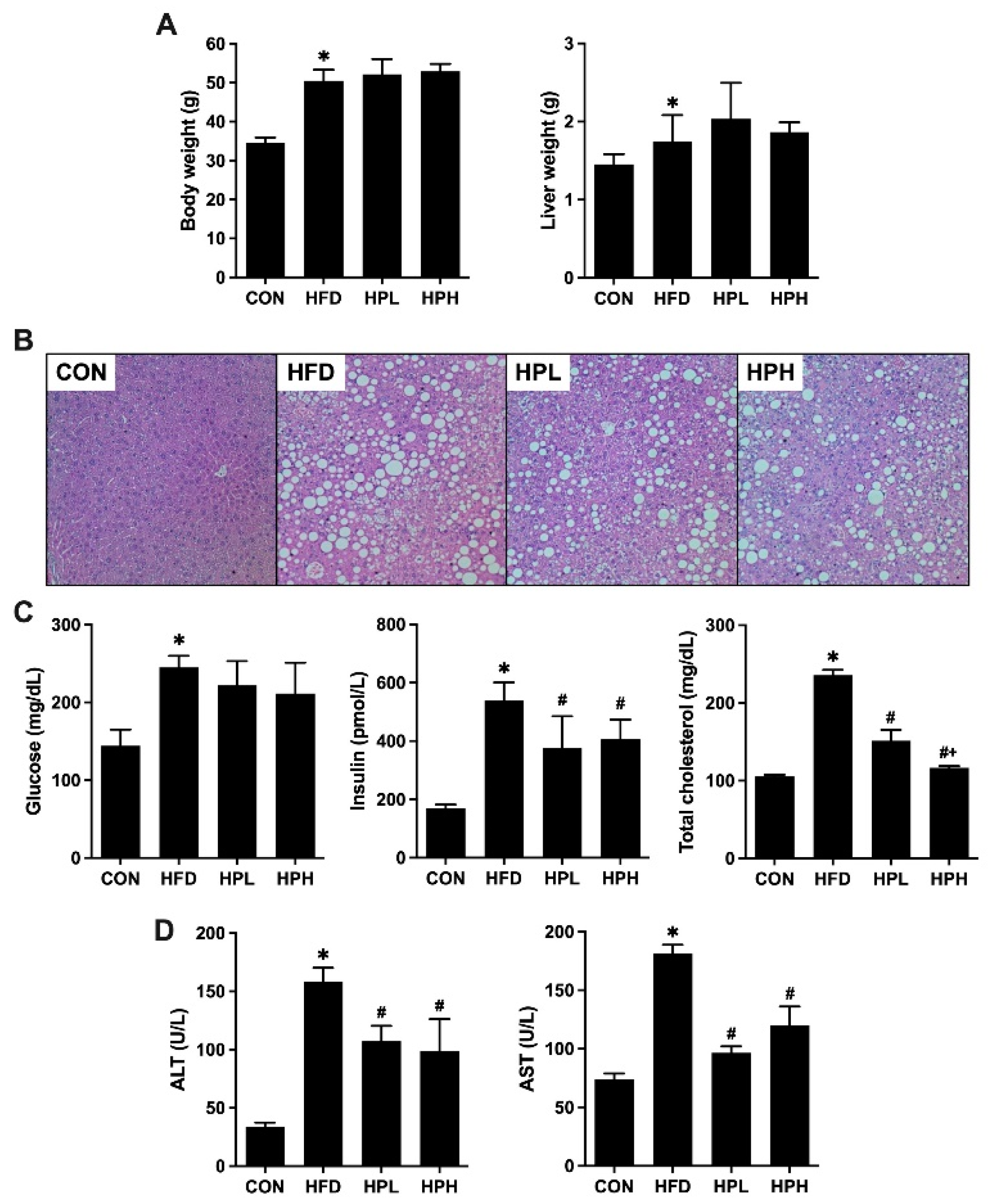
3.1. Effects of LP1008 on Body Weight, Liver Weight, Liver Histology, and Biochemical Parameters in Aged and Obese Mice
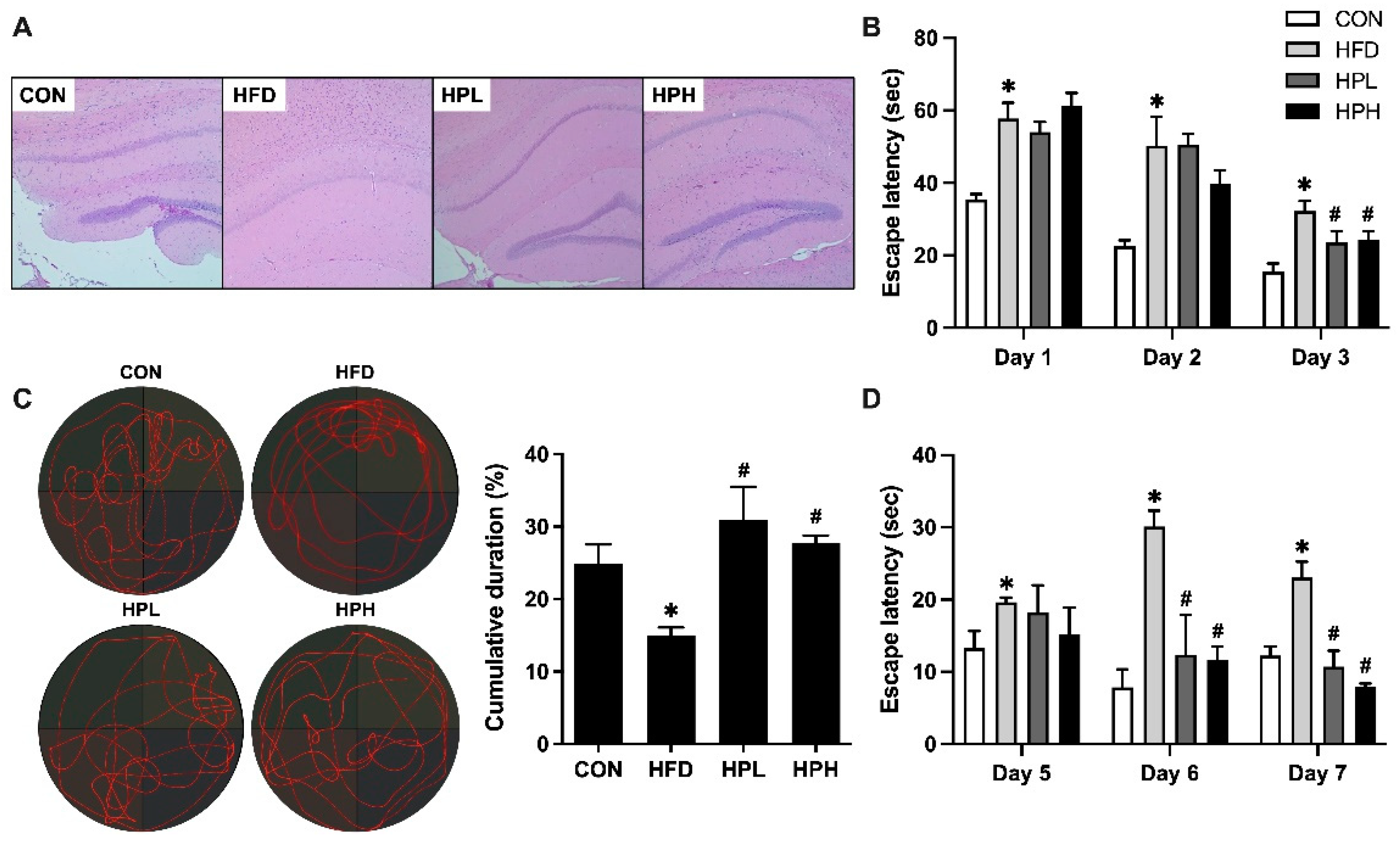
3.2. Effects of LP1008 on Brain Histology, Spatial Learning, and Memory in Aged and Obese Mice
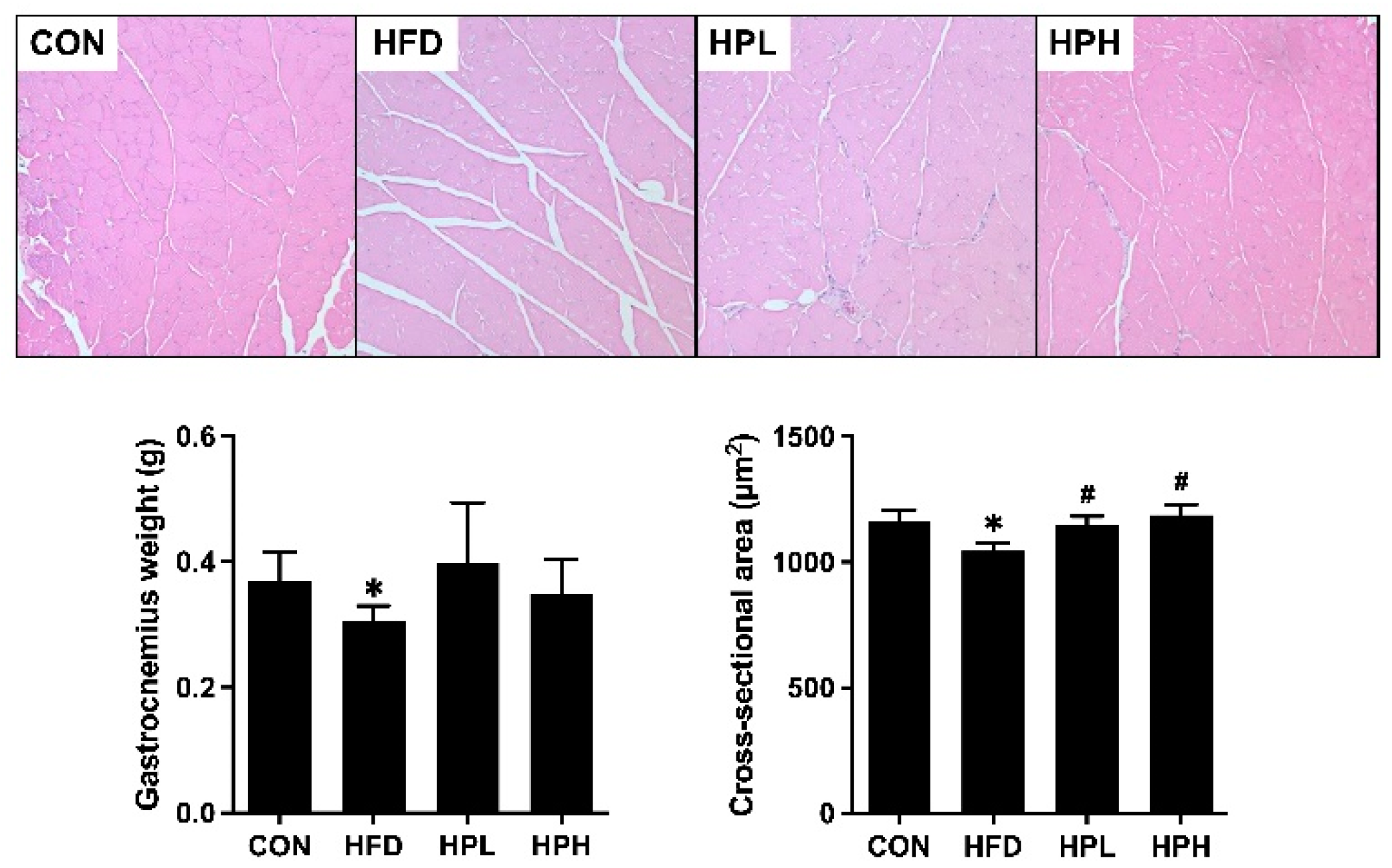
3.3. Effects of LP1008 on Gastrocnemius Muscle Histology and Related Parameters in Aged and Obese Mice
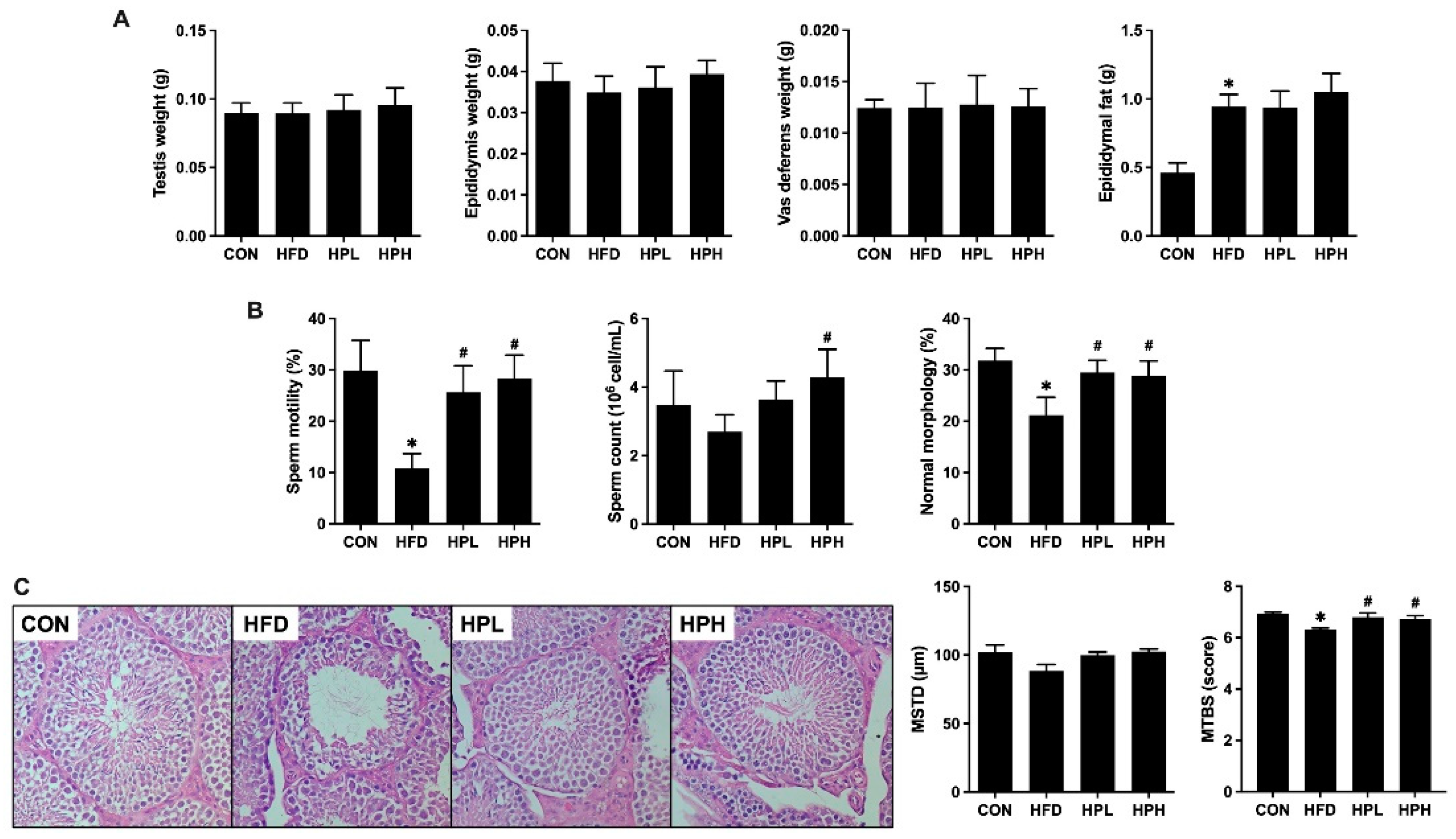
3.4. Effects of LP1008 on Reproductive Organ Weight, Sperm Quality, Testicular Histology, and Related Parameters in Aged and Obese Mice
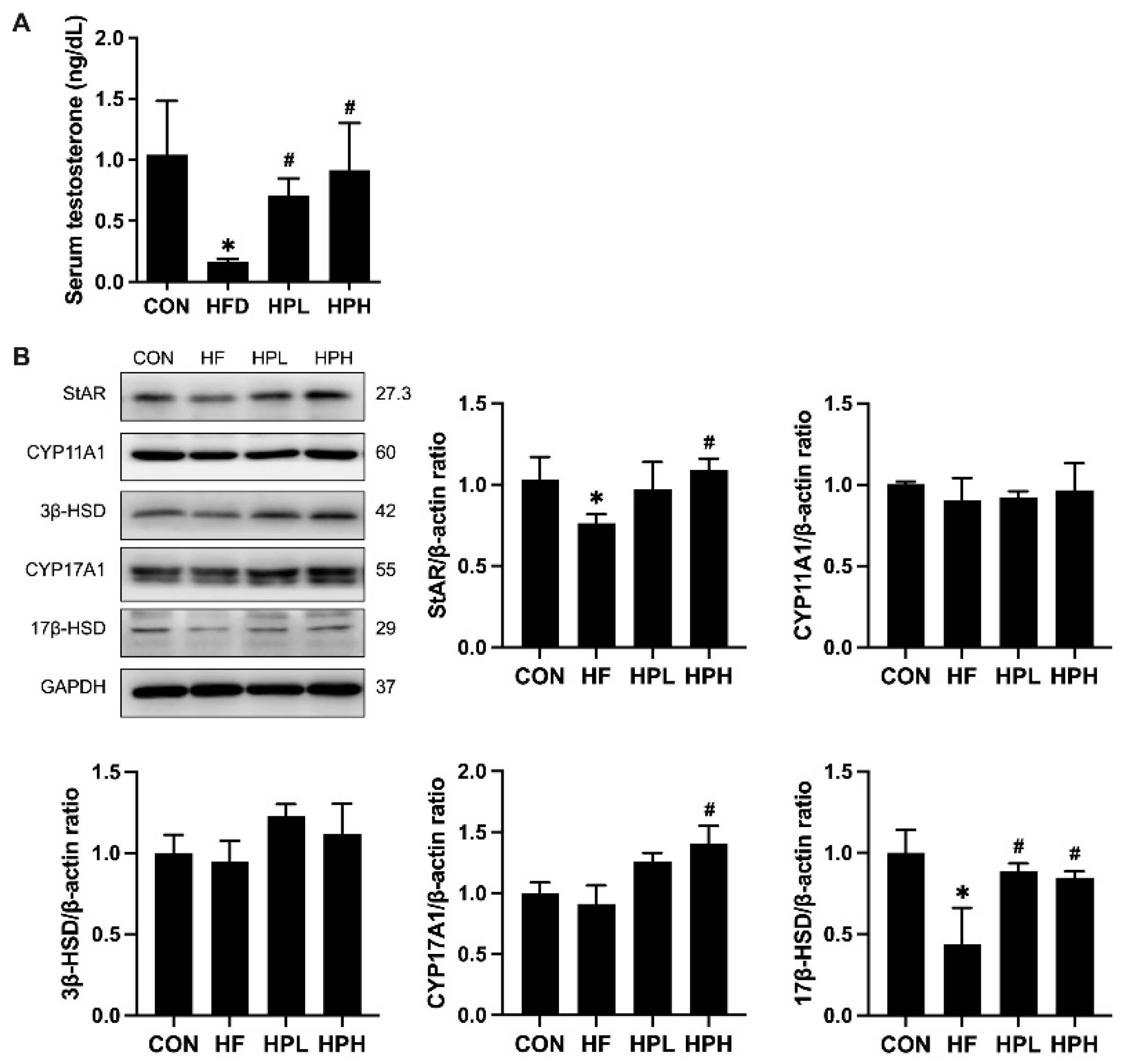
3.5. Effects of LP1008 on the Levels of Serum Testosterone and Testosterone Biosynthesis-Related Proteins in Aged and Obese Mice
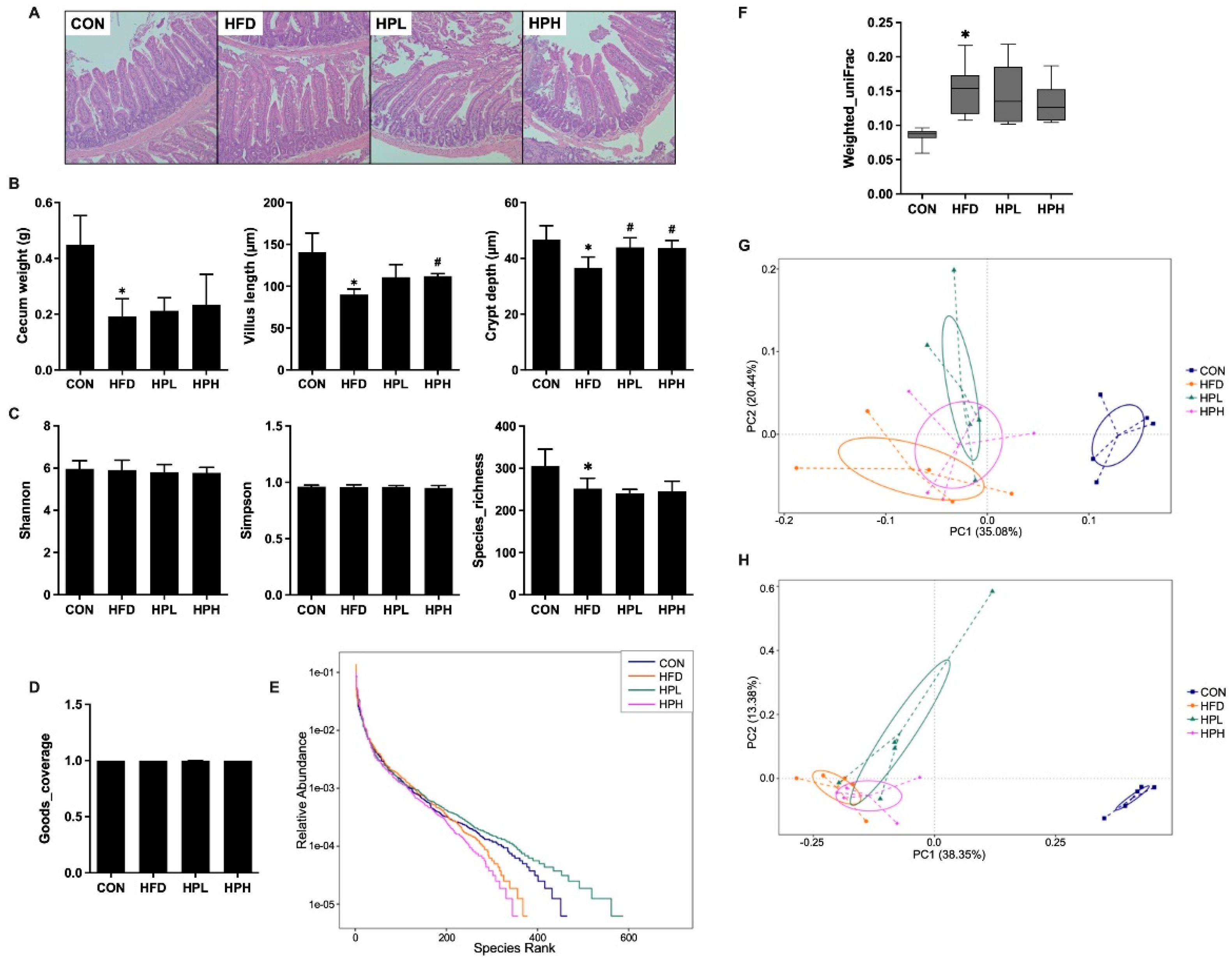
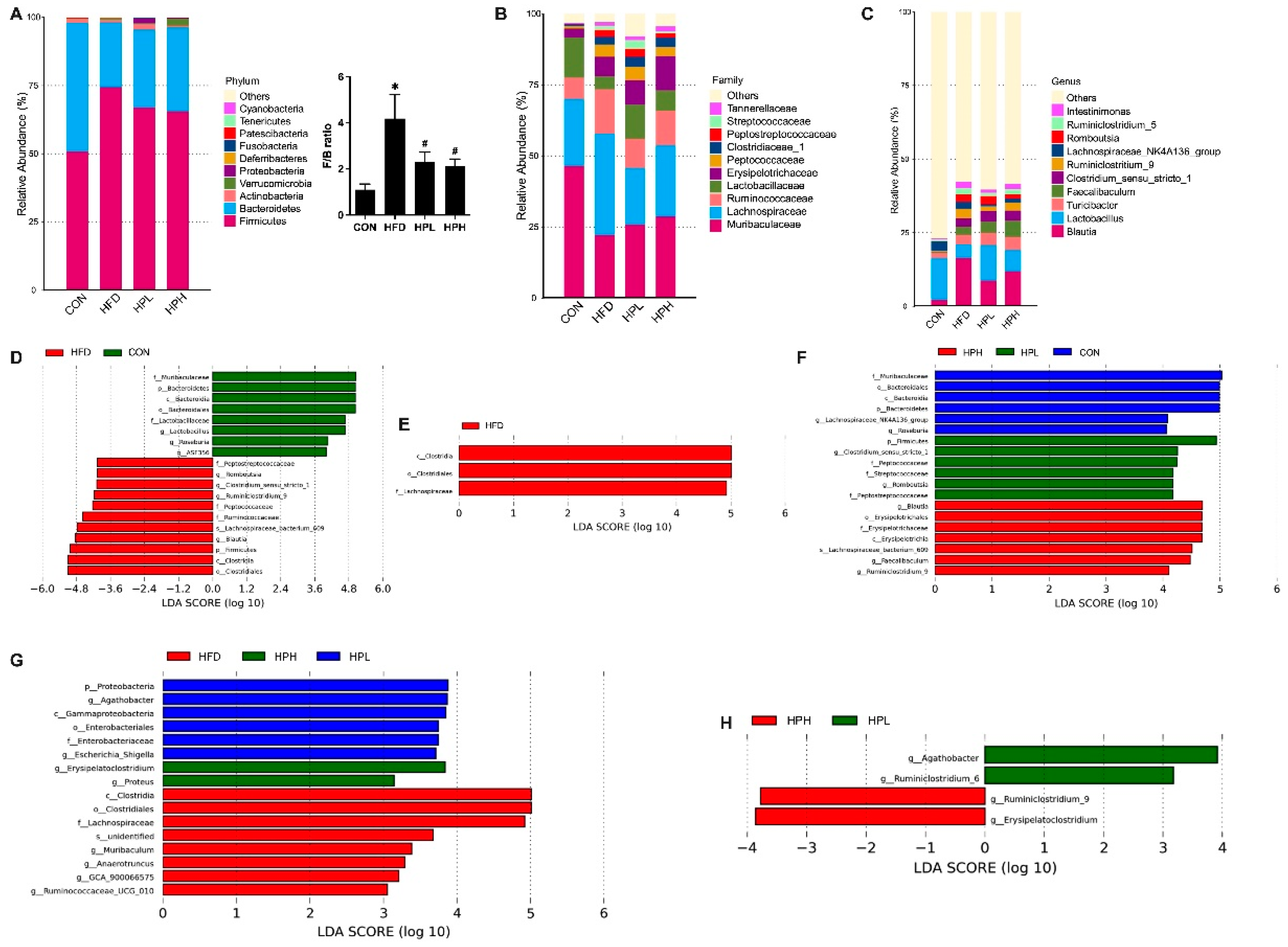
3.6. Effects of LP1008 on Cecal Weight, Cecal Histology, the Gut Microbiota, and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production in Aged and Obese Mice
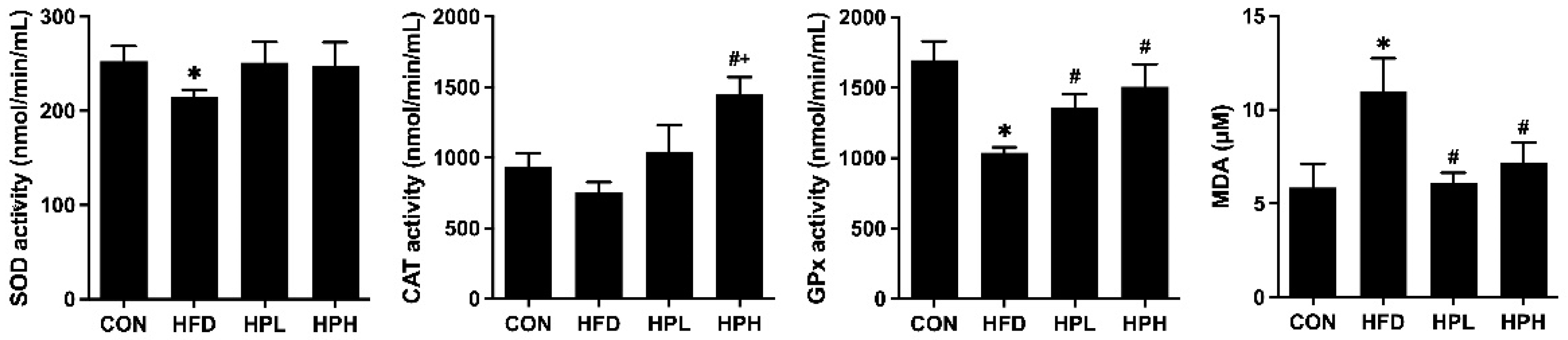
3.7. Effects of LP1008 on Testicular Redox Status in Aged and Obese Mice
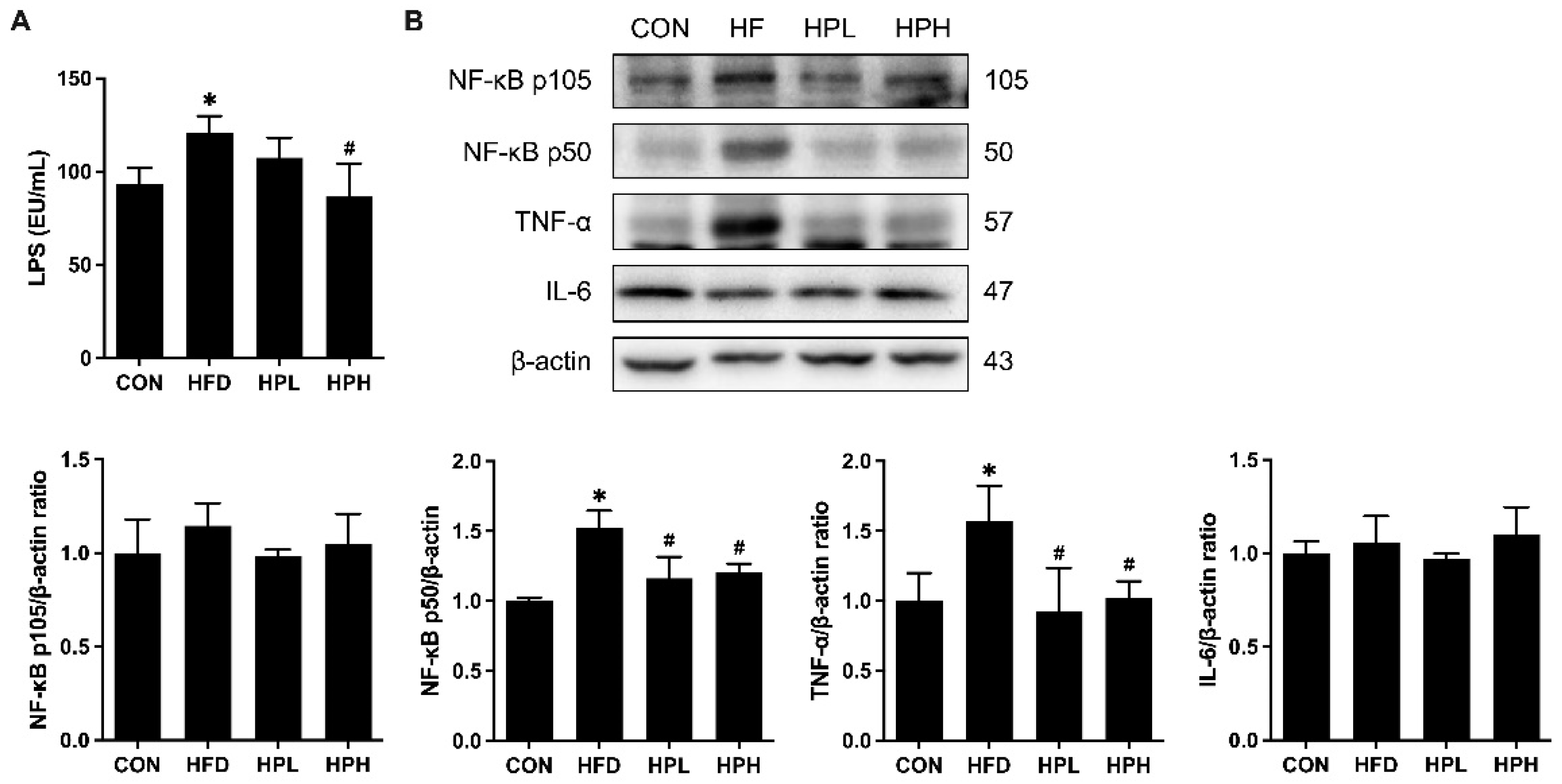
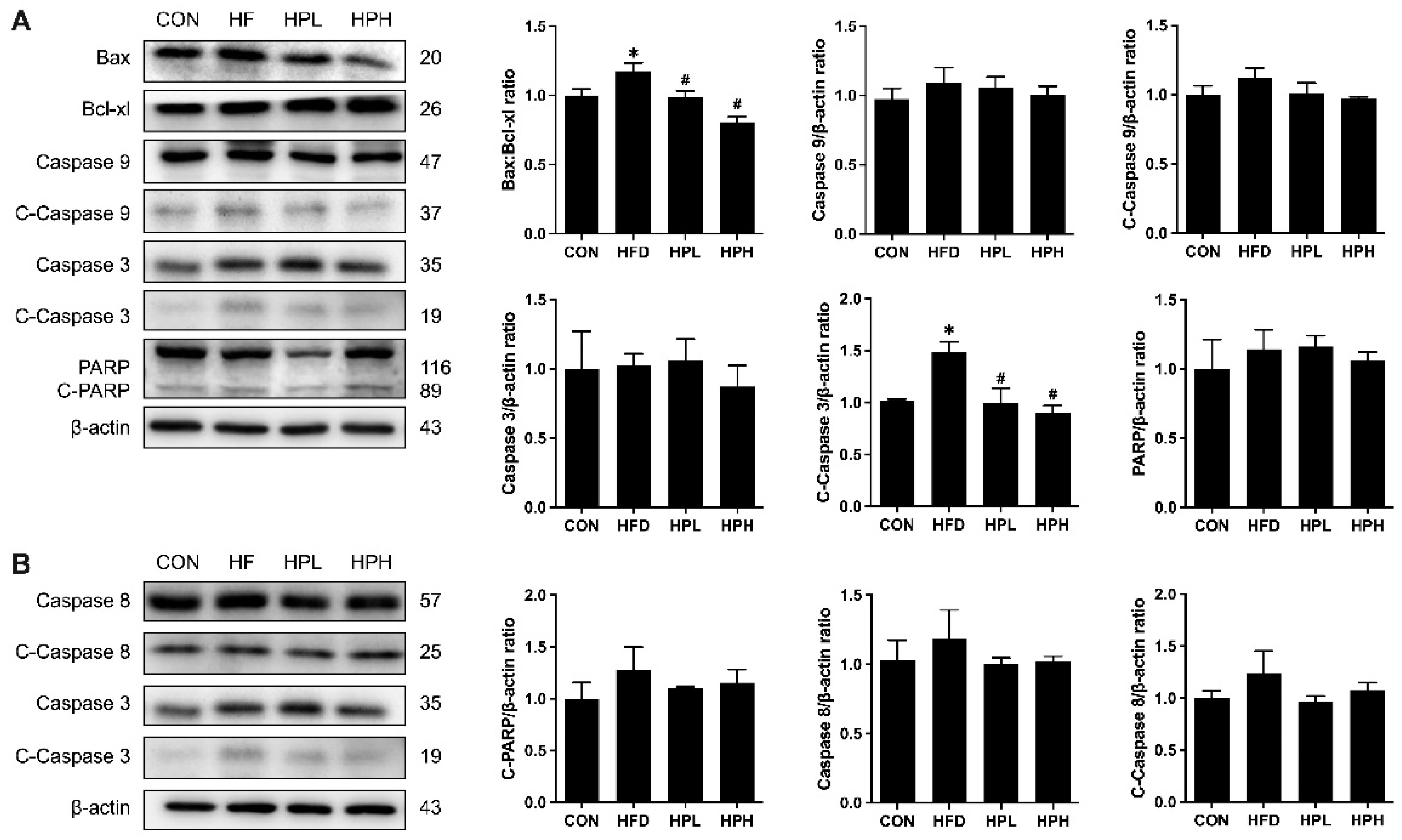
3.8. Effects of LP1008 on Serum LPS Levels, Testicular Inflammation, and Apoptosis-Related Proteins in aged and OBESE Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2016 [OP]: Monitoring Health for the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs); World Health Organization: 2016.
- Jaschke, N.; Wang, A.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Rauner, M.; Rachner, T.D. Late-onset hypogonadism: Clinical evidence, biological aspects and evolutionary considerations. Ageing research reviews 2021, 67, 101301. [CrossRef]
- Nieschlag, E.; Swerdloff, R.; Behre, H.M.; Gooren, L.J.; Kaufman, J.M.; Legros, J.J.; Lunenfeld, B.; Morley, J.E.; Schulman, C.; Wang, C.; et al. Investigation, treatment, and monitoring of late-onset hypogonadism in males: ISA, ISSAM, and EAU recommendations. J Androl 2006, 27, 135-137. [CrossRef]
- Dudek, P.; Kozakowski, J.; Zgliczyński, W. Late-onset hypogonadism. Prz Menopauzalny 2017, 16, 66-69. [CrossRef]
- Tajar, A.; Huhtaniemi, I.T.; O’Neill, T.W.; Finn, J.D.; Pye, S.R.; Lee, D.M.; Bartfai, G.; Boonen, S.; Casanueva, F.F.F.; Forti, G.; et al. Characteristics of Androgen Deficiency in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Results from the European Male Aging Study (EMAS). The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2012, 97, 1508-1516. [CrossRef]
- Pye, S.R.; Huhtaniemi, I.T.; Finn, J.D.; Lee, D.M.; O’Neill, T.W.; Tajar, A.; Bartfai, G.; Boonen, S.; Casanueva, F.F.; Forti, G.; et al. Late-Onset Hypogonadism and Mortality in Aging Men. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2014, 99, 1357-1366. [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.B.; O’Donnell, A.B.; Brambilla, D.J.; Simpson, W.B.; Longcope, C.; Matsumoto, A.M.; McKinlay, J.B. Prevalence and incidence of androgen deficiency in middle-aged and older men: estimates from the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004, 89, 5920-5926. [CrossRef]
- Trinick, T.R.; Feneley, M.R.; Welford, H.; Carruthers, M. International web survey shows high prevalence of symptomatic testosterone deficiency in men. Aging Male 2011, 14, 10-15. [CrossRef]
- Bettocchi, C. Late-Onset Hypogonadism (LOH): Incidence, Diagnosis, and Short-Term Effects. European Urology Supplements 2005, 4, 4-9. [CrossRef]
- Požarskis, A.; Lejnieks, A. Detection of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Men with Chronic Internal Diseases. Proceedings of the Latvian Academy of Sciences. Section B. Natural, Exact, and Applied Sciences. 2019, 73, 24-33. [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, M.; Ng Tang Fui, M.; Cheung, A.S. Late-onset hypogonadism: metabolic impact. Andrology 2020, 8, 1519-1529. [CrossRef]
- Tremellen, K. Gut Endotoxin Leading to a Decline IN Gonadal function (GELDING) - a novel theory for the development of late onset hypogonadism in obese men. Basic and clinical andrology 2016, 26, 7. [CrossRef]
- Seddik, H.A.; Bendali, F.; Gancel, F.; Fliss, I.; Spano, G.; Drider, D. Lactobacillus plantarum and Its Probiotic and Food Potentialities. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins 2017, 9, 111-122. [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhao, R.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, X.; Luo, D.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Kushmaro, A.; Marks, R.S.; et al. Modulatory effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on chronic metabolic diseases. Food Science and Human Wellness 2023, 12, 959-974. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Liao, Y.C.; Lee, M.C.; Lin, K.J.; Hsu, H.Y.; Chiou, S.Y.; Young, S.L.; Lin, J.S.; Huang, C.C.; Watanabe, K. Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 Attenuates Aging-Associated Muscle Weakness, Bone Loss, and Cognitive Impairment by Modulating the Gut Microbiome in Mice. Frontiers in nutrition 2021, 8, 708096. [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C.; Tu, Y.T.; Lee, C.C.; Tsai, S.C.; Hsu, H.Y.; Tsai, T.Y.; Liu, T.H.; Young, S.L.; Lin, J.S.; Huang, C.C. Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 Improves Muscle Mass and Functional Performance in Frail Older Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1466. [CrossRef]
- Morrison, C.D.; Pistell, P.J.; Ingram, D.K.; Johnson, W.D.; Liu, Y.; Fernandez-Kim, S.O.; White, C.L.; Purpera, M.N.; Uranga, R.M.; Bruce-Keller, A.J.; et al. High fat diet increases hippocampal oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in aged mice: implications for decreased Nrf2 signaling. Journal of neurochemistry 2010, 114, 1581-1589. [CrossRef]
- Valcarcel-Ares, M.N.; Tucsek, Z.; Kiss, T.; Giles, C.B.; Tarantini, S.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Balasubramanian, P.; Gautam, T.; Galvan, V.; Ballabh, P.; et al. Obesity in Aging Exacerbates Neuroinflammation, Dysregulating Synaptic Function-Related Genes and Altering Eicosanoid Synthesis in the Mouse Hippocampus: Potential Role in Impaired Synaptic Plasticity and Cognitive Decline. The journals of gerontology. Series A, Biological sciences and medical sciences 2019, 74, 290-298. [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wen, Z.; Li, X.; Meng, K.; Yang, P. Lactobacillus plantarum FRT10 alleviated high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice through regulating the PPARα signal pathway and gut microbiota. Applied microbiology and biotechnology 2020, 104, 5959-5972. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Song, L.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, S.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Ren, Z. Lactobacillus plantarum prevents obesity via modulation of gut microbiota and metabolites in high-fat feeding mice. Journal of Functional Foods 2020, 73, 104103. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Fei, Y.; Han, X.; Liu, G.; Fang, J. Lactobacillus plantarum Alleviates Obesity by Altering the Composition of the Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Frontiers in nutrition 2022, 9, 947367. [CrossRef]
- Salaj, R.; Stofilová, J.; Soltesová, A.; Hertelyová, Z.; Hijová, E.; Bertková, I.; Strojný, L.; Kružliak, P.; Bomba, A. The effects of two Lactobacillus plantarum strains on rat lipid metabolism receiving a high fat diet. TheScientificWorldJournal 2013, 2013, 135142. [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.N.; Yu, Q.F.; Fu, N.; Liu, X.W.; Lu, F.G. Effects of four Bifidobacteria on obesity in high-fat diet induced rats. World journal of gastroenterology 2010, 16, 3394-3401. [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wen, Z.; Zhao, L.; Yu, D.; Meng, K.; Yang, P. Lactobacillus plantarum FRT4 alleviated obesity by modulating gut microbiota and liver metabolome in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Food & nutrition research 2022, 66, 7974. [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Tang, M.W.; Tan, F.; Zhou, X.R.; Fan, L.; Xie, Y.X.; Zhao, X. Anti-obesity effect of Lactobacillus plantarum CQPC01 by modulating lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced C57BL/6 mice. Journal of food biochemistry 2020, 44, e13491. [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Mao, Y.; Wei, L.; Zhao, A.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F.; Cui, X.; Pan, M.-H.; Wang, B. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum JS19-adjunctly fermented goat milk alleviates D-galactose-induced aging by modulating oxidative stress and intestinal microbiota in mice. Journal of Dairy Science 2024, 107, 7564-7577. [CrossRef]
- Joseph, M. Reference memory, working memory and adaptive forgetting : a comparative study in rats. UNIVERSITY OF LYON, Lyon, 2014.
- Bischof, G.N.; Park, D.C. Obesity and Aging: Consequences for Cognition, Brain Structure, and Brain Function. Psychosomatic medicine 2015, 77, 697-709. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chan, J.S.; Ren, L.; Yan, J.H. Obesity Reduces Cognitive and Motor Functions across the Lifespan. Neural plasticity 2016, 2016, 2473081. [CrossRef]
- Dye, L.; Boyle, N.B.; Champ, C.; Lawton, C. The relationship between obesity and cognitive health and decline. The Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 2017, 76, 443-454. [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yao, M.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Ge, S. High-fat diet aggravates postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged mice. BMC anesthesiology 2018, 18, 20. [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Wang, X.; Luo, Y.; Kong, F.; Mu, G.; Wu, X. Mechanism Explanation on Improved Cognitive Ability of D-Gal Inducing Aged Mice Model by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum MWFLp-182 via the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2024, 72, 9795-9806. [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.H.; Chavan, S.S.; Pavlov, V.A. Cholinergic Control of Inflammation, Metabolic Dysfunction, and Cognitive Impairment in Obesity-Associated Disorders: Mechanisms and Novel Therapeutic Opportunities. 2019, 13, 263. [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Kiss, T.; Tarantini, S.; Nyúl-Tóth, Á.; Ahire, C.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Csipo, T.; Lipecz, A.; Tabak, A.; Institoris, A.; et al. Obesity-induced cognitive impairment in older adults: a microvascular perspective. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology 2021, 320, H740-h761. [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.A.; McGee, H.; Bhatta, S.; Palm, R.; Casadesus, G. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis involvement in learning and memory and Alzheimer’s disease: more than "just" estrogen. Frontiers in endocrinology 2015, 6, 45. [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Li, Y.; Ma, L. Sarcopenic Obesity: An Emerging Public Health Problem. Aging and disease 2022, 13, 379-388. [CrossRef]
- Kovacheva, E.L.; Sinha Hikim, A.P.; Shen, R.; Sinha, I.; Sinha-Hikim, I. Testosterone Supplementation Reverses Sarcopenia in Aging through Regulation of Myostatin, c-Jun NH2-Terminal Kinase, Notch, and Akt Signaling Pathways. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 628-638. [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Qi, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, L.; Yu, C.; Guan, Q. Involvement of p38 MAPK in Leydig cell aging and age-related decline in testosterone. Frontiers in endocrinology 2023, 14, 1088249. [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, O.; Howlett, S. Testosterone modulates cardiac contraction and calcium homeostasis: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Biology of sex differences 2015, 6, 9. [CrossRef]
- Rahimiyan-Heravan, M.; Roshangar, L.; Karimi, P.; Sefidgari-Abrasi, S.; Morshedi, M.; Saghafi-Asl, M.; Bavafa-Valenlia, K. The potential therapeutic effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and inulin on serum and testicular reproductive markers in diabetic male rats. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2020, 12, 53. [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Yu, Z.; Feng, P.; Ye, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Kakade, A.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Lactobacillus plantarum TW1-1 Alleviates Diethylhexylphthalate-Induced Testicular Damage in Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Decreasing Inflammation. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2019, 9, 221. [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.B.; Walker, W.H. The regulation of spermatogenesis by androgens. Seminars in cell & developmental biology 2014, 30, 2-13. [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Sengupta, P.; Slama, P.; Roychoudhury, S. Oxidative Stress, Testicular Inflammatory Pathways, and Male Reproduction. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22, 10043. [CrossRef]
- Matzkin, M.E.; Calandra, R.S.; Rossi, S.P.; Bartke, A.; Frungieri, M.B. Hallmarks of Testicular Aging: The Challenge of Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Therapies Using Natural and/or Pharmacological Compounds to Improve the Physiopathological Status of the Aged Male Gonad. Cells 2021, 10, 3114. [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio: A Relevant Marker of Gut Dysbiosis in Obese Patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.D.; Parikh, I.; Green, S.J.; Chlipala, G.; Mohney, R.P.; Keaton, M.; Bauer, B.; Hartz, A.M.S.; Lin, A.L. Age Drives Distortion of Brain Metabolic, Vascular and Cognitive Functions, and the Gut Microbiome. Frontiers in aging neuroscience 2017, 9, 298. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Akbar, M.T.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhi, L.; Shen, Q. Exploration of the Muribaculaceae Family in the Gut Microbiota: Diversity, Metabolism, and Function. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2660.
- Nie, K.; Ma, K.; Luo, W.; Shen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, M.; Tong, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Roseburia intestinalis: A Beneficial Gut Organism From the Discoveries in Genus and Species. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021, 11, 757718. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Shanahan, F.; O’Toole, P.W. The gut microbiome as a modulator of healthy ageing. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022, 19, 565-584. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Li, D.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Feng, X.; et al. Discrepant gut microbiota markers for the classification of obesity-related metabolic abnormalities. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 13424. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Huang, W.; Lin, Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; Ng, S.C. Gut microbiota in patients with obesity and metabolic disorders — a systematic review. Genes & Nutrition 2022, 17, 2. [CrossRef]
- Verdam, F.J.; Fuentes, S.; de Jonge, C.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Erbil, R.; Greve, J.W.; Buurman, W.A.; de Vos, W.M.; Rensen, S.S. Human intestinal microbiota composition is associated with local and systemic inflammation in obesity. Obesity 2013, 21, E607-E615. [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Fernández, M.; Porras, D.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Román-Sagüillo, S.; González-Gallego, J.; Nistal, E.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Aging, Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Diseases: Management through Physical Exercise and Nutritional Interventions. Nutrients 2021, 13, 16. [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Yang, Y.; Kong, Y.; Guo, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xing, P.; Sun, Y.; Qian, J.; Xu, R.; Xie, L.; et al. Gut Bacteria Erysipelatoclostridium and Its Related Metabolite Ptilosteroid A Could Predict Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury. Front Public Health 2022, 10, 862598. [CrossRef]
- Fei, N.; Zhao, L. An opportunistic pathogen isolated from the gut of an obese human causes obesity in germfree mice. The ISME Journal 2012, 7, 880-884. [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Huang, J.; Luo, Y.; Wen, Y.; Chen, B.; Qiu, H.; Chen, H.; Yue, T.; He, L.; Feng, B.; et al. Gut microbiota is involved in male reproductive function: a review. Front Microbiol 2024, 15, 1371667. [CrossRef]
- Fusco, W.; Lorenzo, M.B.; Cintoni, M.; Porcari, S.; Rinninella, E.; Kaitsas, F.; Lener, E.; Mele, M.C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Collado, M.C.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty-Acid-Producing Bacteria: Key Components of the Human Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2211. [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.H. Nutrition and Health Survey in Taiwan, 2017–2020. Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=3999&pid=15562 (accessed on Sep 1, 2024).

| Nutrients | 5001 | D12451 |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrate (%) | 48.1 | 40.3 |
| Protein (%) | 24.1 | 23.7 |
| Fat (%) | 5.1 | 23.4 |
| Fiber (%) | 5.3 | 5.8 |
| Energy from carbohydrate (% of kcal) | 57 | 35 |
| Energy from protein (% of kcal) | 14 | 20 |
| Energy from fat (% of kcal) | 29 | 45 |
| Metabolizing energy (kcal/g) | 2.86 | 4.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





