Submitted:
04 October 2024
Posted:
07 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
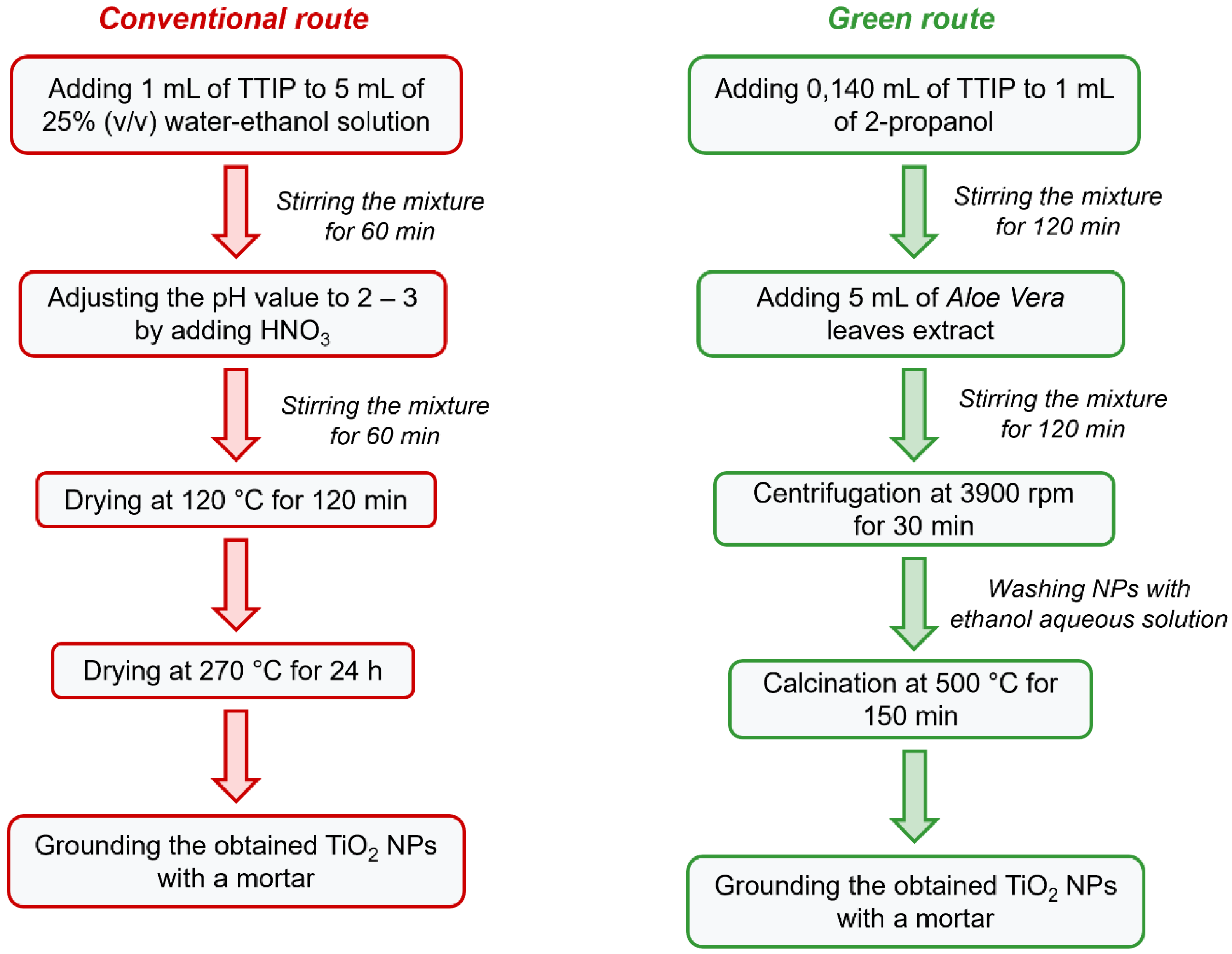
2.2. Synthesis of TiO2 NPs
2.2.1. Conventional route for Synthesis of TiO2 NPs (TiO2-Chem NPs)
2.2.2. Green Synthesis of TiO2 NPs (TiO2-Green NPs)
2.3. Characterization of TiO2 NPs
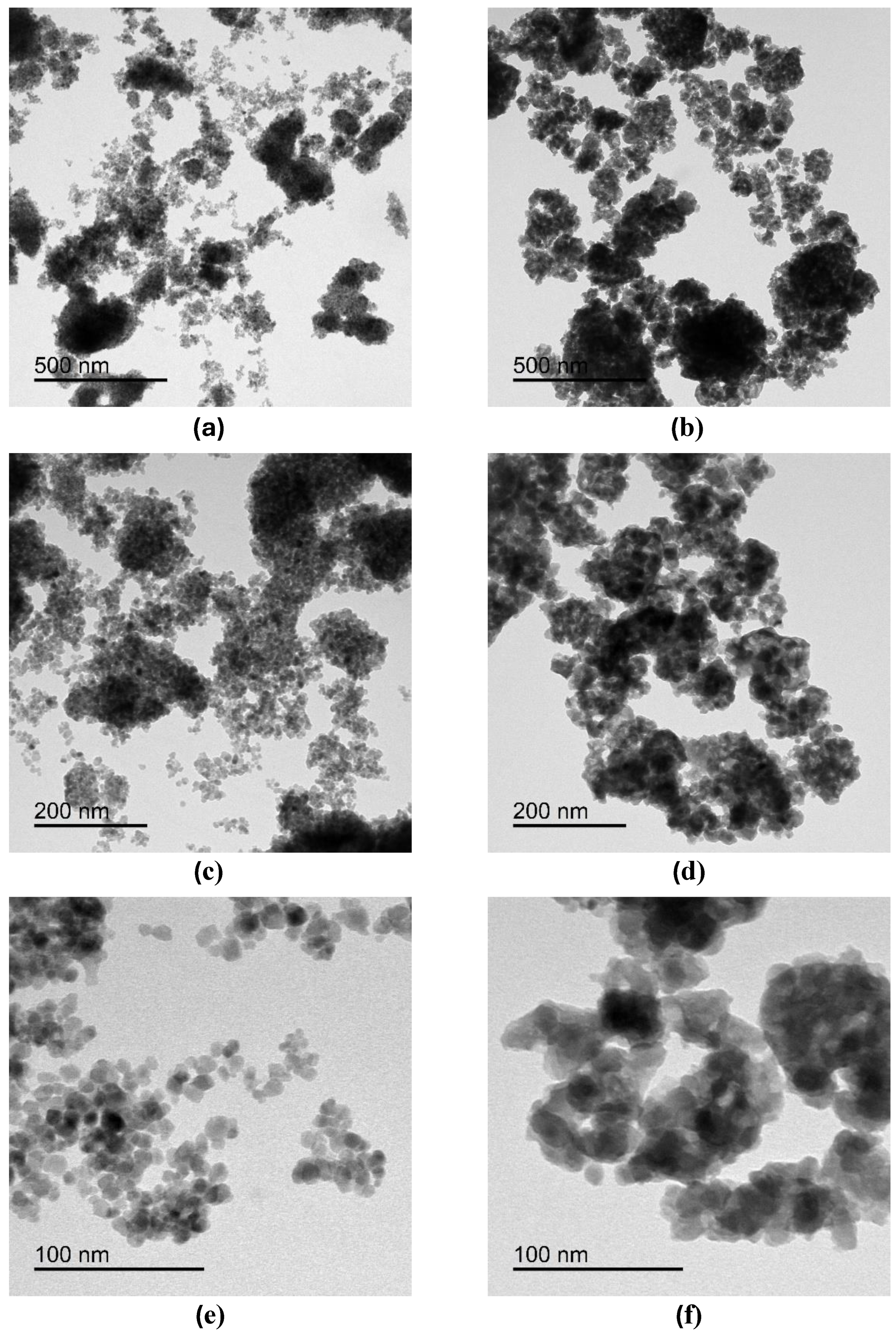
2.3.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
2.3.2. Zeta Potential Analysis
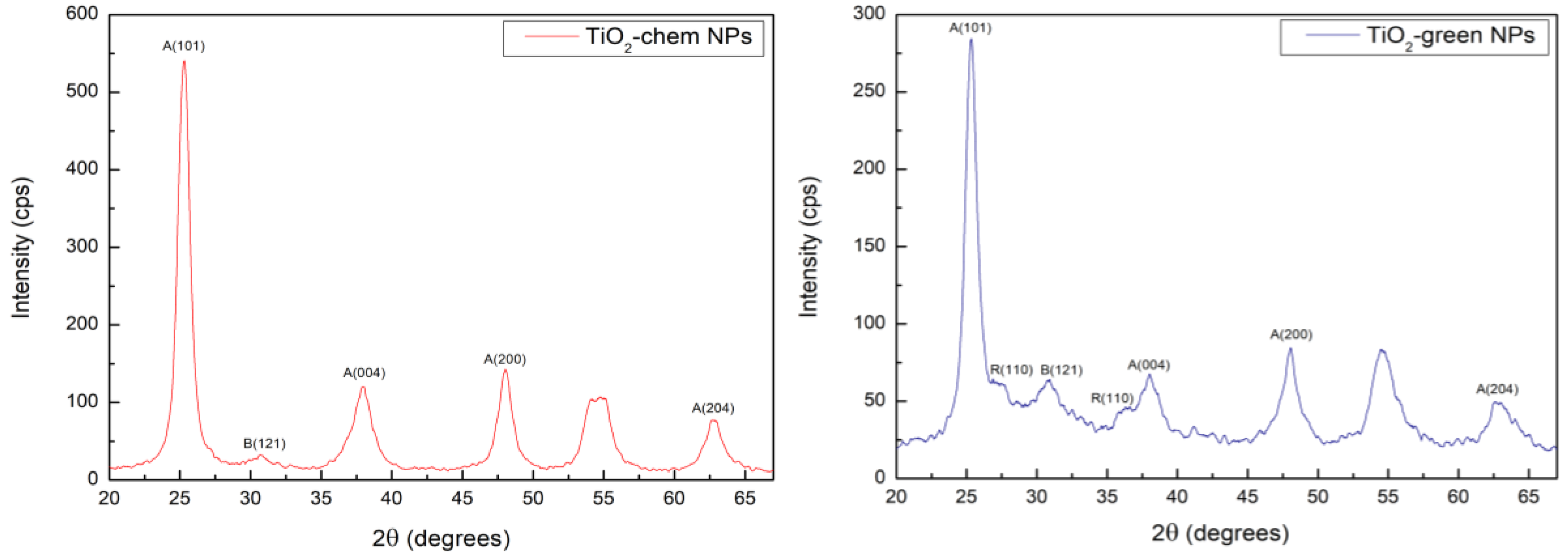
2.3.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
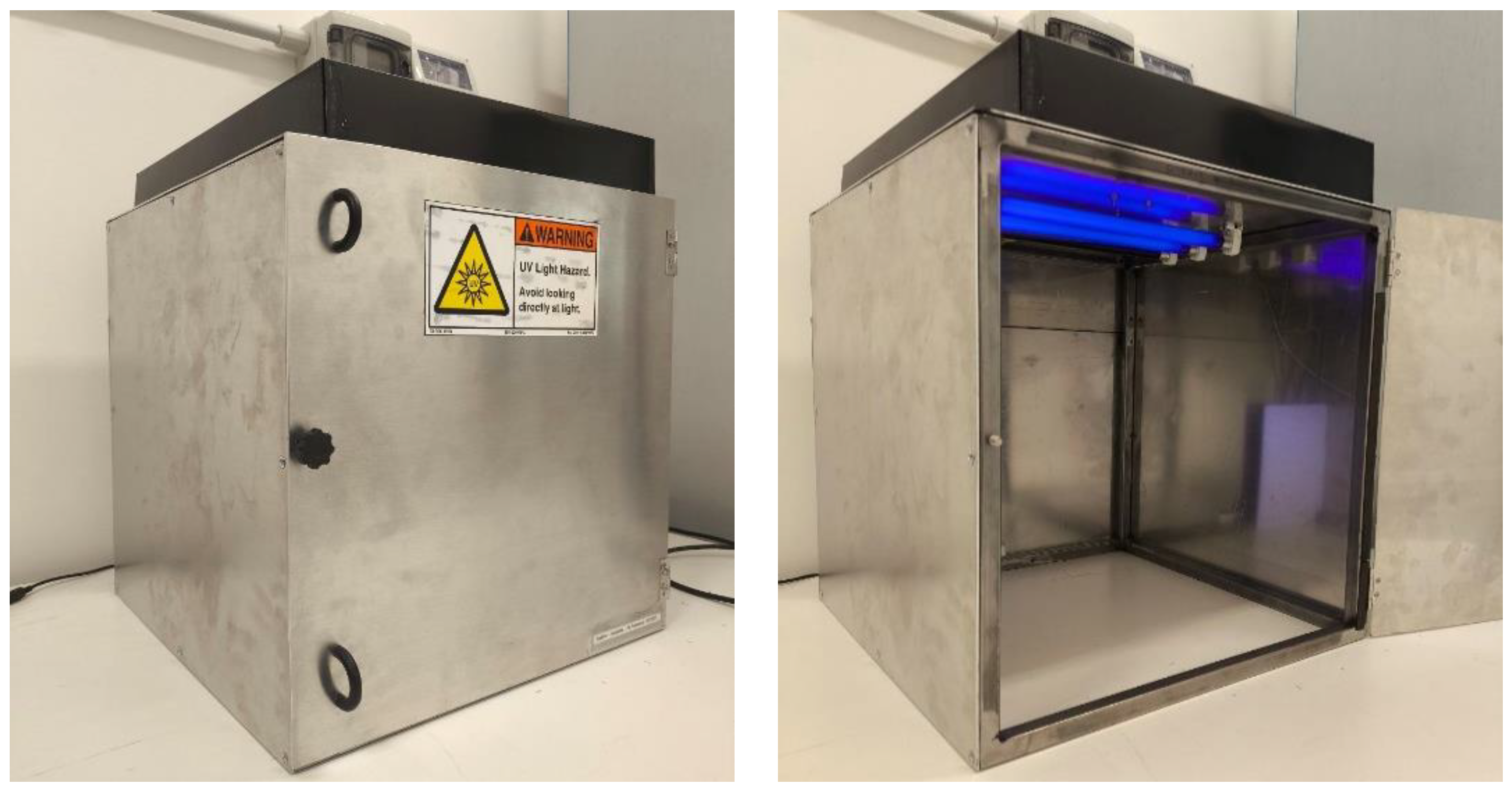
2.4. Assessment of Photocatalytic Activity
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M. Huerta-Fontela, M. T. M. Huerta-Fontela, M. T. Galceran, e F. Ventura, «Fast liquid chromatography–quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometry for the analysis of pharmaceuticals and hormones in water resources», J. Chromatogr. A, vol. 1217, fasc. 25, pp. 4212–4222, giu. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Andreozzi, «Advanced oxidation processes (AOP) for water purification and recovery», Catal. Today, vol. 53, fasc. 1, pp. 51–59, ott. 1999. [CrossRef]
- P. O. Oladoye, T. O. P. O. Oladoye, T. O. Ajiboye, E. O. Omotola, e O. J. Oyewola, «Methylene blue dye: Toxicity and potential elimination technology from wastewater», Results Eng., vol. 16, p. 100678, dic. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y. Deng e R. Zhao, «Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Wastewater Treatment», Curr. Pollut. Rep., vol. 1, fasc. 3, pp. 167–176, set. 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. R. Bolton, K. G. J. R. Bolton, K. G. Bircher, W. Tumas, e C. A. Tolman, «Figures-of-merit for the technical development and application of advanced oxidation technologies for both electric- and solar-driven systems (IUPAC Technical Report)», Pure Appl. Chem., vol. 73, fasc. 4, pp. 627–637, gen. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. B. Miklos, C. D. B. Miklos, C. Remy, M. Jekel, K. G. Linden, J. E. Drewes, e U. Hübner, «Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment – A critical review», Water Res., vol. 139, pp. 118–131, ago. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhang, B. Y. Zhang, B. Zhou, H. Chen, e R. Yuan, «Heterogeneous photocatalytic oxidation for the removal of organophosphorus pollutants from aqueous solutions: A review», Sci. Total Environ., vol. 856, p. 159048, gen. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. Wang et al., «A review on heterogeneous photocatalysis for environmental remediation: From semiconductors to modification strategies», Chin. J. Catal., vol. 43, fasc. 2, pp. 178–214, feb. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. San Martín, M. J. S. San Martín, M. J. Rivero, e I. Ortiz, «Unravelling the Mechanisms that Drive the Performance of Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production», Catalysts, vol. 10, fasc. 8, p. 901, ago. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Pelaez et al., «A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications», Appl. Catal. B Environ., vol. 125, pp. 331–349, ago. 2012. [CrossRef]
- M. V. Shinnur, M. Pedeferri, e M. V. Diamanti, «Properties and photocatalytic applications of black TiO2 produced by thermal or plasma hydrogenation», Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem., vol. 8, p. 10 0415, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Y. Ma, X. Y. Ma, X. Wang, Y. Jia, X. Chen, H. Han, e C. Li, «Titanium Dioxide-Based Nanomaterials for Photocatalytic Fuel Generations», Chem. Rev., vol. 114, fasc. 19, pp. 9987–10043, ott. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. R. Eddy et al., «Heterophase Polymorph of TiO2 (Anatase, Rutile, Brookite, TiO2 (B)) for Efficient Photocatalyst: Fabrication and Activity», Nanomaterials, vol. 13, fasc. 4, p. 704, feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Yu et al., «Effects of acidic and basic hydrolysis catalysts on the photocatalytic activity and microstructures of bimodal mesoporous titania», J. Catal., vol. 217, fasc. 1, pp. 69–78, lug. 2003. [CrossRef]
- L. Linsebigler, G. L. Linsebigler, G. Lu, e J. T. Yates, «Photocatalysis on TiO2 Surfaces: Principles, Mechanisms, and Selected Results», Chem. Rev., vol. 95, fasc. 3, pp. 735–758, mag. 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. Mironyuk, L. M. F. Mironyuk, L. M. Soltys, T. R. Tatarchuk, e Kh. O. Savka, «Methods of Titanium Dioxide Synthesis (Review)», Phys. Chem. Solid State, vol. 21, fasc. 3, pp. 462–477, set. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. C. Collazzo, S. L. G. C. Collazzo, S. L. Jahn, N. L. V. Carreño, e E. L. Foletto, «Temperature and reaction time effects on the structural properties of titanium dioxide nanopowders obtained via the hydrothermal method», Braz. J. Chem. Eng., vol. 28, fasc. 2, pp. 265–272, giu. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. Li, X. B. Li, X. Wang, M. Yan, e L. Li, «Preparation and characterization of nano-TiO2 powder», Mater. Chem. Phys., 2002.
- H. Xu, M. H. Xu, M. Li, e Z. Jun, «Preparation, characterization, and photocatalytic studies on anatase nano-TiO2 at internal air lift circulating photocatalytic reactor», Mater. Res. Bull., vol. 48, fasc. 9, pp. 3144–3148, set. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, O.; et al. , «Synthesis by sol-gel method and characterization of nano-TiO2 powders», Mater. Today Proc., vol. 66, pp. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V. Verma, M. V. Verma, M. Al-Dossari, J. Singh, M. Rawat, M. G. M. Kordy, e M. Shaban, «A Review on Green Synthesis of TiO2 NPs: Photocatalysis and Antimicrobial Applications», Polymers, vol. 14, fasc. 7, p. 1444, apr. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. T. Anastas, «Green Chemistry and the Role of Analytical Methodology Development», Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem., vol. 29, fasc. 3, pp. 167–175, set. 1999. [CrossRef]
- P. Singh, Y.-J. P. Singh, Y.-J. Kim, D. Zhang, e D.-C. Yang, «Biological Synthesis of Nanoparticles from Plants and Microorganisms», Trends Biotechnol., vol. 34, fasc. 7, pp. 588–599, lug. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. Santhoshkumar et al., «Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Psidium guajava extract and its antibacterial and antioxidant properties», Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med., vol. 7, fasc. 12, pp. 968–976, dic. 2014. [CrossRef]
- W. Ahmad, K. K. W. Ahmad, K. K. Jaiswal, e S. Soni, «Green synthesis of titanium dioxide (TiO 2 ) nanoparticles by using Mentha arvensis leaves extract and its antimicrobial properties», Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem., vol. 50, fasc. 10, pp. 1032–1038, ott. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Saini e P. Kumar, «Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using Tinospora cordifolia plant extract & its potential application for photocatalysis and antibacterial activity», Inorg. Chem. Commun., vol. 156, p. 111221, ott. 2023. [CrossRef]
- G. Rao, C. G. Rao, C. Ashok, K. V. Rao, e C. S. Chakra, «Green Synthesis of TiO2 Nanoparticles Using Aloe Vera Extract».
- Cheng, J.; et al. , «Highly Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from an Aqueous Solution Using Cellulose Acetate Nanofibrous Membranes Modified by Polydopamine», ACS Omega, vol. 5, fasc. 10, pp. 5389–5400, mar. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leena e, S. Srinivasan, «Synthesis and ultrasonic investigations of titanium oxide nanofluids», J. Mol. Liq., vol. 206, pp. 103–109, giu. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Li, Y. S. Li, Y. Cui, M. Wen, e G. Ji, «Toxic Effects of Methylene Blue on the Growth, Reproduction and Physiology of Daphnia magna», Toxics, vol. 11, fasc. 7, p. 594, lug. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Modi et al., «Recent and Emerging Trends in Remediation of Methylene Blue Dye from Wastewater by Using Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles», Water, vol. 14, fasc. 11, p. 1749, mag. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Krishna Moorthy, B. Govindarajan Rathi, S. P. Shukla, K. Kumar, e V. Shree Bharti, «Acute toxicity of textile dye Methylene blue on growth and metabolism of selected freshwater microalgae», Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., vol. 82, p. 103552, feb. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; et al. , «Review on Methylene Blue: Its Properties, Uses, Toxicity and Photodegradation», Water, vol. 14, fasc. 2, p. 242, gen. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, I. Ali, K. Modu, e S. Adamu, «Adsorption Study of Methylene Blue onto Power Activated Carbon Prepared from Ananas Comosus Peels», Nanochemistry Res., vol. 8, fasc. 4, ott. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. A. Yasin, J. A. S. A. Yasin, J. A. Abbas, M. M. Ali, I. A. Saeed, e I. H. Ahmed, «Methylene blue photocatalytic degradation by TiO2 nanoparticles supported on PET nanofibres», Mater. Today Proc., vol. 20, pp. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. Niu et al., «Difference in performance and mechanism for methylene blue when TiO2 nanoparticles are converted to nanotubes», J. Clean. Prod., vol. 297, p. 126498, mag. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan e, T. White, «Degradation of Methylene Blue by Three-Dimensionally Ordered Macroporous Titania», Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 41, fasc. 12, pp. 4405–4409, giu. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. H. Abdellah, S. A. M. H. Abdellah, S. A. Nosier, A. H. El-Shazly, e A. A. Mubarak, «Photocatalytic decolorization of methylene blue using TiO2/UV system enhanced by air sparging», Alex. Eng. J., vol. 57, fasc. 4, pp. 3727–3735, dic. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. Sethy, Z. K. Sethy, Z. Arif, P. K. Mishra, e P. Kumar, «Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles from Syzygium cumini extract for photo-catalytic removal of lead (Pb) in explosive industrial wastewater», Green Process. Synth., vol. 9, fasc. 1, pp. 171–181, feb. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V. De Matteis, M. V. De Matteis, M. Cascione, e R. Rinaldi, «Titanium dioxide: antimicrobial surfaces and toxicity assessment», in Titanium Dioxide (Tio₂) and Its Applications, Elsevier, 2021, pp. 373–393. [CrossRef]
- S. Venkatesh et al., «Facile one step synthesis of novel TiO2 nanocoral by sol–gel method using Aloe vera plant extract», Indian J. Phys., vol. 89, fasc. 5, pp. 445–452, mag. 2015. [CrossRef]
- F. Pellegrino, E. F. Pellegrino, E. Ortel, J. Mielke, R. Schmidt, V. Maurino, e V.-D. Hodoroaba, «Customizing New Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles with Controlled Particle Size and Shape Distribution: A Feasibility Study Toward Reference Materials for Quality Assurance of Nonspherical Nanoparticle Characterization», Adv. Eng. Mater., vol. 24, fasc. 6, p. 2101347, giu. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almomen, A.; et al. , «In Vitro Safety Assessment of In-House Synthesized Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Impact of Washing and Temperature Conditions», Int. J. Mol. Sci., vol. 24, fasc. 12, p. 9966, giu. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Syamsol Bahri et al., «Review on recent advance biosynthesis of TiO 2 nanoparticles from plant-mediated materials: characterization, mechanism and application», IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., vol. 1142, fasc. 1, p. 012005, apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Guillard, H. C. Guillard, H. Lachheb, A. Houas, M. Ksibi, E. Elaloui, e J.-M. Herrmann, «Influence of chemical structure of dyes, of pH and of inorganic salts on their photocatalytic degradation by TiO2 comparison of the efficiency of powder and supported TiO2», J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem., vol. 158, fasc. 1, pp. 27–36, mag. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Zhang, L. M. Zhang, L. Shi, S. Yuan, Y. Zhao, e J. Fang, «Synthesis and photocatalytic properties of highly stable and neutral TiO2/SiO2 hydrosol», J. Colloid Interface Sci., vol. 330, fasc. 1, pp. 113–118, feb. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V. De Matteis, M. V. De Matteis, M. Cascione, C. C. Toma, P. Pellegrino, L. Rizzello, e R. Rinaldi, «Tailoring Cell Morphomechanical Perturbations Through Metal Oxide Nanoparticles», Nanoscale Res. Lett., vol. 14, fasc. 1, p. 109, dic. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. John, S. K. John, S. Palaty, e S. S. Sharma, «Greener approach towards the synthesis of titanium dioxide nanostructures with exposed {001} facets for enhanced visible light photodegradation of organic pollutants», J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., vol. 31, fasc. 23, pp. 20868–20882, dic. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, M. Bellardita, e L. Palmisano, «Brookite, the Least Known TiO2 Photocatalyst», Catalysts, vol. 3, fasc. 1, pp. 36–73, gen. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. A. H. Hanaor e C. C. Sorrell, «Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation», J. Mater. Sci., vol. 46, fasc. 4, pp. 855–874, feb. 2011. [CrossRef]
- D. L. Liao, G. S. D. L. Liao, G. S. Wu, e B. Q. Liao, «Zeta potential of shape-controlled TiO2 nanoparticles with surfactants», Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp., vol. 348, fasc. 1–3, pp. 270–275, set. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y. Wei, M. V. Y. Wei, M. V. Tokina, A. V. Benderskii, Z. Zhou, R. Long, e O. V. Prezhdo, «Quantum dynamics origin of high photocatalytic activity of mixed-phase anatase/rutile TiO2», J. Chem. Phys., vol. 153, fasc. 4, p. 044706, lug. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Shen, X. S. Shen, X. Wang, T. Chen, Z. Feng, e C. Li, «Transfer of Photoinduced Electrons in Anatase–Rutile TiO 2 Determined by Time-Resolved Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy», J. Phys. Chem. C, vol. 118, fasc. 24, pp. 12661–12668, giu. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. Vasei, Y. Sang, H. Liu, e J. P. Claverie, «TiO 2 @Carbon Photocatalysts: The Effect of Carbon Thickness on Catalysis», ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 8, fasc. 3, pp. 1903–1912, gen. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

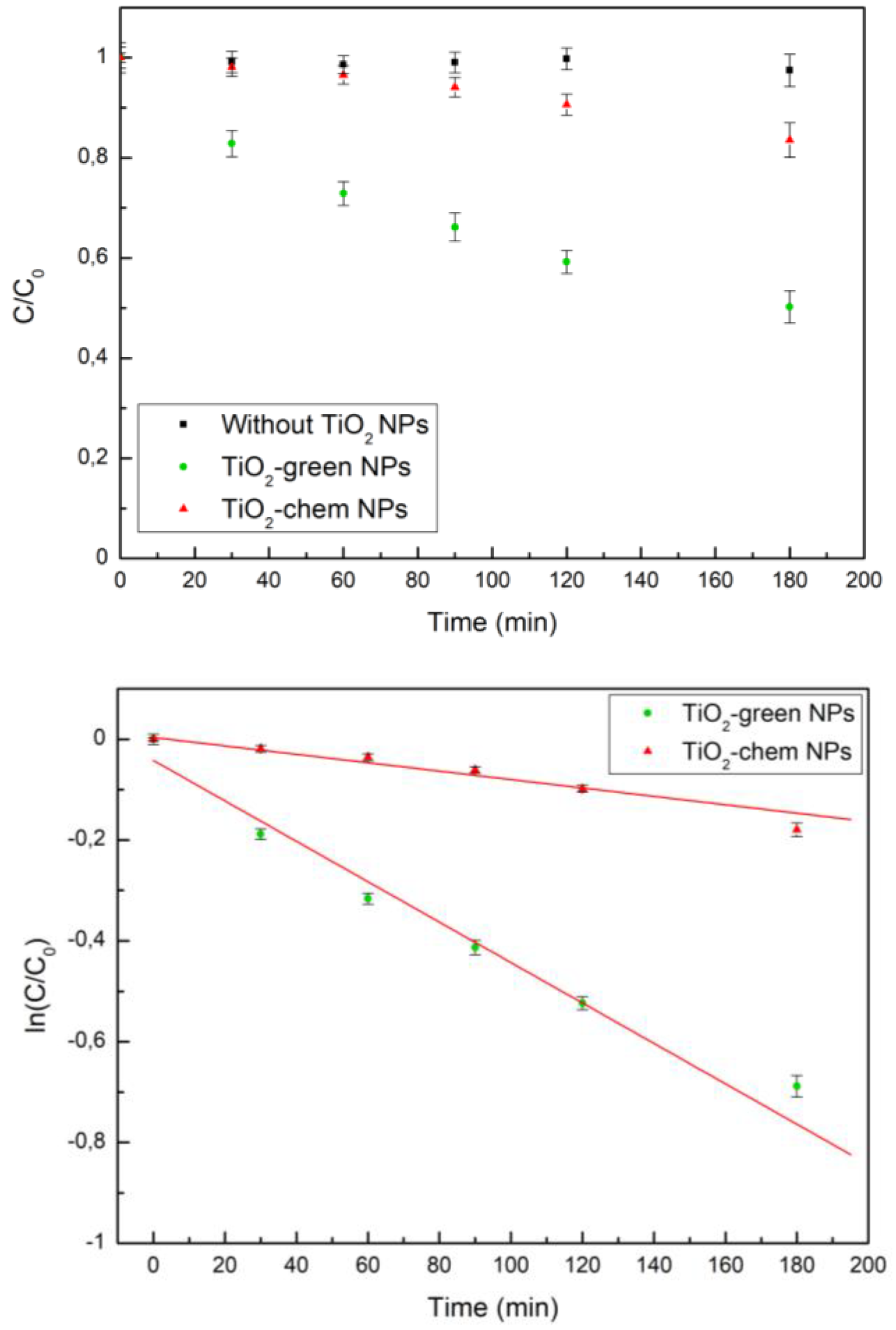
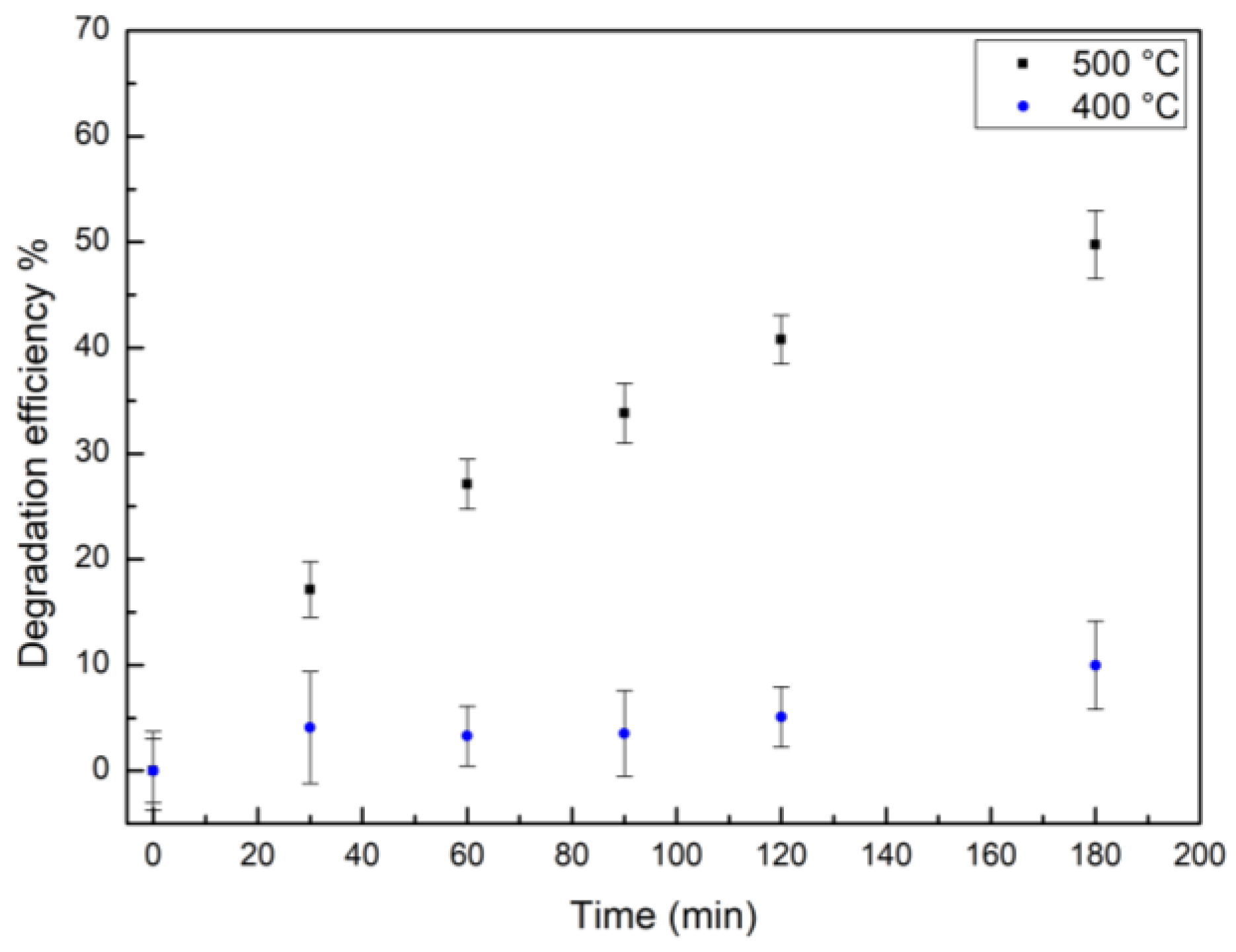
| Catalyst | Degradation after 180 min | K |
|---|---|---|
| TiO2-green NPs | (50 ± 3) % | 0.004 min-1 |
| TiO2-chem NPs | (16 ± 3) % | 0.0008 min-1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





