Submitted:
25 September 2024
Posted:
26 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Setting Quantum Fluid Triplets in Their Context
2.1. The Tackling of the Classical and the Quantum Domains
2.2. Hamiltonians and Interparticle Potentials
2.3. Classical Calculations
2.4. Quantum Calculations: Path Integrals
2.5. Quantum Calculations: Closures
2.6. Some Recent Quantum Triplet Facts
3. Equilibrium Classical Fluid Triplets
3.1. r-Space Correlation Functions
3.2. k-Space Structure Factors
- -
- OZ2 equation
- -
- OZ2 pair structure factor
- -
- Baxter’s hierarchy related results
- -
- OZ3 triplet structure factor
3.3. Grand Canonical Triplet Symmetries and Asymptotic Behaviors
3.4. The Interplay between Simulation Techniques and Closures
- -
- Kirkwood superposition (KS3) [37]
3.5. Other Theoretical Features
4. Basic Path Integral Concepts
4.1. PI Partition Functions
4.2. Sum over Histories and Propagators
4.3. The Classical Isomorphism, Bead Roles, and Notational Conventions
4.4. Quantum Exchange Interactions
4.5. The PI-Centroid Variable
5. Theory of Equilibrium Quantum Fluid Triplet Structures under Diffraction Effects
5.1. The PI-Centroid CMn Class
5.1.1. PI-Centroid Linear Response
5.1.2. PI-Centroid Direct Correlation Functions
5.1.3. OZ2 and OZ3 Frameworks
5.1.4. Some Additional Relationships and Further Remarks
5.2. The PI Total Continuous Linear Response TLRn Class
5.3. The PI Instantaneous ETn Class
5.3.1. OZ2 and OZ3 Frameworks
5.3.2. An ETn Functional Digression
5.4. A Joint Consideration of CMn, TLRn, and ETn
- -
- KS3:
- -
- JF3:
- -
- AV3:
6. Systems Studied in This Work, Computational Details and Related Observations
- -
- For helium-3, using Richardson four-point derivative the instantaneous reference is .
- -
7. Final Remarks and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix I: A Formal Analysis of Zero-Spin Bosonic Exchange Structures
Appendix II: List of Main Acronyms and Their Basic References
| AV3 | Intermediate closure for triplet structures [59,60]. |
| BDH | OZ2 Baxter-Dixon-Hutchinson variational procedure [72,125,136]. |
| BHw | OZ2 Baumketner-Hiwatari grand canonical corrections [127]. |
| BHP3 | OZ3 Barrat-Hansen-Pastore variational procedure [41]. |
| BOA | Born-Oppenheimer approximation [119]. |
| CBHSP | Cao-Berne hard-sphere propagator for quantum hard spheres [81]. |
| CMn | Path integral Centroid class of structures at the n-th level [18,19,55,130]. |
| DAS3 | Denton-Ashcroft symmetrized closure for triplet structures [65]. |
| ETn | Path integral Instantaneous class of structures at the n-th level [9,11,35,84]. |
| GFH | Gaussian Feynman-Hibbs picture [4,140,180]. |
| JF3 | Jackson-Feenberg closure for triplet structures [3,40]. |
| kpass | attempted bead moves in a PIMC simulation. |
| KS3 | Kirkwood superposition closure for triplet structures [37]. |
| MC | Monte Carlo simulation method [13,17,66]. |
| MD | Molecular dynamics simulation method [13,17,67]. |
| Mpass | attempted bead moves in a PIMC simulation. |
| OZn | Classical Ornstein-Zernike framework at the n-th level [1,6,41,68,70]. |
| OZ2 | Classical Ornstein-Zernike framework at the pair level. |
| OZ3 | Classical Ornstein-Zernike framework at the triplet level. |
| PA’s | Pair actions for path integral simulations [9,81]. |
| PI | Path integral formalism [4,140]. |
| PIMC | Path integral Monte Carlo computational scheme [7,9,16,35]. |
| PIMD | Path integral molecular dynamics computational scheme [10,89,94]. |
| PP | Primitive propagator [7,9,80]. |
| RISM | OZ2 reference interaction site model [7,71,178,179]. |
| QHS | Quantum hard spheres [62,79,81,136]. |
| SAPT2 | Janzen-Aziz pair potential between two helium atoms [106]. |
| SCVJ | Suzuki-Chin-Voth-Jang-Jang fourth order propagator [82,83,84]. |
| SVP | Saturated vapor pressure conditions. |
| TLRn | Path integral total continuous linear response class of structures at the n-th level [7,11,57,62]. |
| WPIMC | Wigner path integral Monte Carlo [98,99,169]. |
References
- Ornstein, L.S.; Zernike, F. Accidental Deviations of Density and Opalescence at the Critical Point of a Single Substance. Proc. Acad. Sci. Amsterdam 1914, 17, 793–806. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, T.L. Statistical Mechanics; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1987; ISBN 978-0-486-65390-7. [Google Scholar]
- Feenberg, E. Theory of Quantum Fluids; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; ISBN 978-0-122-50850-9. [Google Scholar]
- Feynman, R.P. Statistical Mechanics; Benjamin: Reading, Massachusetts, USA, 1972; ISBN 978-0-805-32509-6. [Google Scholar]
- Balescu, R. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Statistical Mechanics; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1975; ISBN 978-0-471-04600-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.P.; McDonald, I.R. Theory of Simple Liquids; Academic Press: London, UK, 1976; ISBN 978-0-123-23850-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chandler, D.; Wolynes, P.G. Exploiting the Isomorphism Between Quantum Theory and Classical Statistical Mechanics of Polyatomic Fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 1981, 74, 4078–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, D.; Verlet, L. Ground State of Liquid Helium-4 and Helium-3. Phys. Rev. 1967, 160, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceperley, D.M. Path Integrals in the Theory of Condensed Helium. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1995, 67, 279–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.; Tuckerman, M.E. Improving the Convergence of closed and open Path Integral Molecular Dynamics Via Higher-Order Trotter Factorization Schemes. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 064104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. Path Integrals and Effective Potentials in the Study of Monatomic Fluids at Equilibrium. In Advances in Chemical Physics; Rice, S.A., Dinner, A.R., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 160, pp. 49–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, W.W. Computer studies on Fluid Systems of Hard-Core Particles. In Fundamental Problems in Statistical Mechanics; Cohen, E.D.G., Ed.; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; Volume 3, pp. 331–388. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.P.; Tildesley, D.J. Computer Simulation of Liquids; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 1989; ISBN 978-0-198-55645-9. [Google Scholar]
- Alder, B.J. Computer Dynamics. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1973, 24, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, W.G. Nonequilibrium Molecular Dynamics. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1983, 34, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berne, B.J.; Thirumalai, D. On the Simulation of Quantum Systems: Path Integral Methods. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1986, 37, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, D.; Smit, B. Understanding Molecular Simulation; Academic Press: San Diego, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-122-67351-1. [Google Scholar]
- Voth, G.A. Path Integral Centroid Methods in Quantum Statistical Mechanics and Dynamics. In Advances in Chemical Physics; Prigogine, I., Rice, S.S., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 93, pp. 135–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, R.; López-Ciudad, T. The Schrödinger Formulation of the Feynman Path Centroid Density. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 111, 3339–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götze, W. Complex Dynamics of Glass-Forming Liquids; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-0-19-965614-1. [Google Scholar]
- Markland, T.E.; Morrone, J.A.; Miyazaki, K.; Berne, B.J.; Reichman, D.R.; Rabani, E. Theory and Simulations of Quantum Glass-Forming Liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 074511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendagorta, J.R.; Bacic, Z.; Tuckerman, M. An Open-Chain Imaginary-Time Path- Integral Sampling Approach to the Calculation of Approximate Symmetrized Quantum Time Correlation Functions. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 102340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovesey, S.W. Theory of Neutron Scattering from Condensed Matter; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 1987; Volume 1, ISBN 978-0-198-52028-3. [Google Scholar]
- Egelstaff, P.A. The Structure of Simple Liquids. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1973, 24, 159–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferziger, J.H.; Leonard, A. Multiple Scattering of Neutrons in the Static Approximation. Phys. Rev. 1962, 128, 2188–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egelstaff, P.A.; Page, D.I; Heard, C.R.T. Experimental Study of the Triplet Correlation Function for Simple Liquids. J. Phys. C: Solid St. Phys. 1971, 4, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winfield, D.J.; Egelstaff, P.A. Short Range Triplet Correlations in Krypton Near the Critical Point. Can. J. Phys. 1973, 51, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallock, R.B. X-Ray Scattering from Gaseous 3He and 4He at Small Momentum Transfer. Phys. Rev. A 1973, 8, 2143–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, A.D.B.; Svensson, E.C.; Martel, P. Neutron Scattering from Nonsuperfluid 4He. Can. J. Phys. 1978, 56, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, A.D.B.; Svensson, E.C.; Martel, P. The Dynamic Structure Factor of 4He at 4.2 K. In Low Temperature Physics-LT14, Krusius, M., Vuorio, M, Eds.; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; Volume 1, pp. 187–190. ISBN 978-0-720-49301-6. [Google Scholar]
- Montfrooij, W.; de Graaf, L.A.; van den Bosch, P.J.; Soper, A.K.; Howells, W.S. Density and Temperature Dependence of the Structure Factor of Dense Fluid Helium. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 1991, 3, 4089–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveché, H.J.; Mountain, R.D. Structure Studies in Liquid 4He. Phys. Rev. A 1974, 9, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, R.; López-Ciudad, T.; Noya, J.C. Feynman Effective Classical Potential in the Schrödinger Formulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 3303–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Okazaki, S.; Kinugawa, K. A Path Integral Centroid Molecular Dynamics Study of Nonsuperfluid Liquid Helium-4. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 4523–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boninsegni, M. Permutations Sampling in Path Integral Monte Carlo. J. Low Temp. Phys. 2005, 141, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boninsegni, M.; Prokof’ev, N.V.; Svistunov, B.V. Worm Algorithm and Diagrammatic Monte Carlo: A New Approach to Continuous-Space Path Integral Monte Carlo Simulations. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 036701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkwood, J.G. Statistical Mechanics of Fluid Mixtures. J. Chem. Phys. 1935, 3, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, R. On the Kirkwood Superposition Approximation. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1959, 21, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, H.W.; Feenberg, E. Perturbation Methods for Low States of a Many-Particle Boson System. Ann. Phys. 1961, 15, 266–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, H.W.; Feenberg, E. Energy Spectrum of Elementary Excitations in Helium II. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1962, 34, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrat, J.L.; Hansen, J.P.; Pastore, G. On the Equilibrium Structure of Dense Fluids. Triplet Correlations, Integral Equations and Freezing. Mol. Phys. 1988, 63, 747–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Fukui, Y. Simulation of the Three-Particle Distribution Function in a Long-Range Oscillatory Potential Liquid. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1975, 53, 1547–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, A.; Evans, D.J. Direct Entropy Calculation from Computer Simulation of Liquids. Phys. Rev A 1989, 40, 3817–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, A.; Evans, D.J. Three-Particle Contribution to the Configurational Entropy of Simple Fluids. Phys. Rev. A 1990, 42, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge, S.; Kahl, G.; Lomba, E.; Abascal, J.L.F. On the Triplet Structure of Binary Liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 3302–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. Path-Integral and Ornstein-Zernike Computations of Quantum Fluid Structures under Strong Fluctuations. AIP Advances 2017, 7, 025204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A.; Podolsky, B.; Rosen, N. Can Quantum Mechanical Description of Physical Reality Be Considered Complete. Phys. Rev. 1935, 47, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.S. On the Problem of Hidden-Variables in Quantum Mechanics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1966, 38, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, S.J.; Clauser, J.F. Experimental Test of Local Hidden-Variable Theories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1972, 28, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspect, A.; Dalibard, J.; Roger, G. Experimental Test of Bell’s Inequalities Using Time-Varying Analyzers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 49, 1804–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.-W.; Bouwmeester, D.; Wienfurter, H. Experimental Entanglement Swapping: Entangling Photos that Never Interacted. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 3891–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werlang, T.; Ribeiro, G.A.P.; Rigolin, G. Interplay Between Quantum Phase Transitions and the Behavior of Quantum Correlations at Finite Temperatures. Int. J. Modern Phys. B 2013, 27, 1345032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duplij, S.; Vogl, R. Innovative Quantum Computing. IOP Publishing, 2023, Chps. 5-6. [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. Triplet Correlations in the Quantum Hard-Sphere Fluid. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123, 104507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. Computational Study of the Structures of Gaseous Helium-3 at Low Temperatures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 10241–10254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesé, L.M. A Study of the Pair and Triplet Structures of the Quantum Hard-Sphere Yukawa Fluid. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 074504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesé, L.M. On Static Triplet Structures in Fluids with Quantum Behavior. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 102312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesé, L.M. Computation of Static Quantum Triplet Structure Factors of Liquid Para-Hydrogen. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 124507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. Real Space Triplets in Quantum Condensed Matter: Numerical Experiments Using Path Integrals, Closures, and Hard Spheres. Entropy 2020, 22, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. A Glimpse into Quantum Triplet Structures in supercritical 3He. Entropy 2023, 25, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melrose, J.R.; Singer, K. An Investigation of Supercooled Lennard-Jones Argon by Quantum Mechanical and Classical Monte Carlo Simulations. Mol. Phys. 1989, 66, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L. M. Path-Integral and Ornstein-Zernike Study of Quantum Fluid Structures on the Crystallization Line. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.M.; Lin, B.; Rice, S.A. Three-Particle Correlation Functions of Quasi-Two-Dimensional One-Component and Binary Colloid Suspensions. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 184715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-T.; Monchiet, V.; Bonnet, G.; To, Q.-D. Conductivity Estimates of Spherical-Particle Suspensions Based on Triplet Structure Factors. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 022105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, A.R.; Ashcroft, N.W. High-Order Direct Correlation Functions of Uniform Classical Liquids. Phys. Rev. A 1989, 39, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metropolis, N.; Rosenbluth, A.W.; Rosenbluth, M.N.; Teller, A.H; Teller, E. Equation of State Calculations by Fast Computing Machines. J. Chem. Phys. 1953, 21, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, B.J.; Wainwright, T.E. Phase transition for a hard sphere system. J. Chem. Phys. 1957, 27, 1208–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, R.J. Direct Correlation Functions and Their Derivatives with Respect to Particle Density. J. Chem. Phys. 1964, 41, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihara, J. Integral Equations for Neutral and Charged Quantum Fluids Including Extension of the Percus-Yevick Equation. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1973, 50, 1156–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.L. Correlation Functions of Classical Fluids III. The method of Partition Function Variation Applied to the Chemical Potential: Cases of PY and HNC2. J. Chem. Phys. 1974, 60, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, C.G.; Gubbins, K.E. Theory of Molecular Fluids; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 2011; Volume 1, ISBN 978-0-19-855602-2. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, R.J. Ornstein-Zernike Relation for a Disordered Fluid. Aust. J. Phys. 1968, 21, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.A. A Quantum-Statistical Monte Carlo Method; Path Integrals with Boundary Conditions. J. Chem. Phys. 1979, 70, 2914–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, M.F.; Bruskin, E.J.; Berne, B.J. On Path Integral Monte Carlo Simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 76, 5150–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Imada, M. Monte Carlo Calculation of Quantum System. II Higher-Order Correction. J. Phys. Soc. Japan 1984, 53, 3765–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-P.; Broughton, J.Q. High-Order Correction to the Trotter Expansion for Use in Computer Simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 1987, 86, 5094–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, E.L.; Ceperley, D.M. Simulation of Quantum Many-Body Systems by Path-Integral Methods. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 30, 2555–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceperley, D.M.; Pollock, E.L. Path-Integral Computation of the Low-Temperature Properties of Liquid 4He. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runge, K.J.; Chester, G.V. Solid-Fluid Phase Transition of Quantum Hard Spheres at Finite Temperatures. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 38, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, K.; Smith, W. Path-Integral Simulations of Condensed Phase Lennard-Jones Systems. Mol. Phys. 1988, 64, 1215–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Berne, B.J. A New Quantum Propagator for Hard Sphere and Cavity Systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2382–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M. New Scheme of Hybrid Exponential Product Formulas with Applications to Quantum Monte Carlo Simulations. In Computer Simulation Studies in Condensed Matter Physics VIII, Springer Proceedings in Physics, Volume 80; Landau, D.P., Mon, K.K., Schüttler, H.-B., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1995; pp. 169–174. ISBN 978-3-642-79993-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, S.A. Symplectic Integrators from Composite Operator Factorizations. Phys. Letters A 1997, 226, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Jang, S.; Voth, G.A. Applications of Higher-Order Composite Factorization Schemes in Imaginary Time Path Integral Simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 7832–7842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müser, M.H.; Berne, B.J. Path Integral Monte Carlo Scheme for Rigid Tops: Application to the Quantum Rotator Phase Transition in Solid Methane, Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 2638–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, D.; Müser, M.H. Path Integral Simulations of Rotors: Theory and Applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1999, 11, R117–R155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noya, E.G.; Sesé, L.M.; Ramírez, R.; McBride, C.; Conde, M.M.; Vega, C. Path Integral Monte Carlo Simulations for Rigid Rotors and their Application to Water. Mol. Phys. 2011, 109, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, C.P.; Ramírez, R. Path-Integral Simulation of Solids. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 233201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharf, D.; Martyna, G.J.; Klein, M. Path-Integral Monte Carlo Study of a Lithium Impurity in Para-Hydrogen: Clusters and the Bulk Liquid. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 99, 8997–9012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Johnson, J.K.; Broughton, J.Q. Path Integral Grand Canonical Monte Carlo. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 5108–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüter, P.; Ceperley, D.M.; Laloë, F. Critical Temperature of Bose-Einstein Condensation of Hard-Sphere Gases. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 3549–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, M.; Moroni, S.; Boninsegni, M. Quasi-2D Liquid 3He. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 045303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinitskiy, A.V.; Voth, G.A. A Reductionist Perspective on Quantum Statistical Mechanics: Coarse-Graining of Path Integrals. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 094104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyna, G.J.; Hughes, A.; Tuckerman, M.E. Molecular Dynamics Algorithms for Path Integrals at Constant Pressure. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 3275–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, R.; Herrero, C.P.; Antonelli, A.; Hernández, E.R. Path Integral Calculation of Free Energies: Quantum Effects on the Melting Temperature of Neon. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 064110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Okazaki, S. Path Integral Molecular Dynamics Method Based on a Pair Density Matrix Approximation: An Algorithm for Distinguishable and Identical Particle Systems. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 5353–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Tanaka, J. Path-Integral Hybrid Monte Carlo Algorithm for Correlated Bose Fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filinov, V.; Levashov, P.; Larkin, A. Density of States of a 2D System of Soft-Sphere Fermions by Path Integral Monte Carlo Simulations. J. Phys. A: Math. and Theor. 2023, 56, 345201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filinov, V.S.; Syrovatka, R.A.; Levashov, P.R. Exchange-Correlation Bound States of the Triplet Soft-Sphere Fermions by Path Integral Monte Carlo Simulations. Phys. Rev E 2023, 108, 024136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceperley, D.M. Path Integral Calculations of Normal Liquid 3He. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 69, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzmann, M.; Bernu, B.; Ceperley, D.M. Many-Body Wavefunctions for Normal Liquid 3He. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 104510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axilrod, B.M.; Teller, E. Interaction of the Van der Waals Type Between Three Atoms. J. Chem. Phys. 1943, 11, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruch, L.W.; McGee, I.J. Calculations and Estimates of the Ground State Energy of Helium Trimers. J. Chem. Phys. 1973, 59, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistenmacher, H.; Popkie, H.; Clementi, E.; Watts, R.O. Study of the Structure of Molecular Complexes VII. Effect of Correlation Energy Corrections to the Hartree-Fock Water-Water Potential on Monte Carlo Simulations of Liquid Water. J. Chem. Phys. 1974, 60, 4455–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.A; Slaman, M.J. An Analysis of the ITS-90 Relations for the Non-Ideality of 3He and 4He: Recommended Relations Based on a New Interatomic Potential for Helium. Metrologia 1990, 27, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzen, A.R.; Aziz, R.A. An Accurate Potential Energy Curve for Helium Based on Ab-Initio Calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cencek, W.; Przybytek, M.; Komasa, J.; Mehl, J.B.; Jeziorski, B.; Szalewicz, K. Effects of Adiabatic, Relativistic, and Quantum Electrodynamics Interactions on the Pair Potential and Thermophysical Properties of Helium. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 224303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cencek, W.; Patkowski, K.; Szalewicz, K. Full Configuration-Interaction Calculation of Three-Body Nonadditive Contribution to Helium Interaction Potential. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131, 064105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M.; Gómez, P.C.; Sueiro, F. An Application of Quantum Chemical Methodology to Liquid Phase Studies: Monte Carlo Simulation of Nonrigid Acetone Dissolved in Carbon Disulfide. J. Mol. Liq. 1986, 32, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. Molecular Electronic States in Liquid Phase: Configuration Interaction States. J. Mol. Liq. 1988, 37, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Tortajada, J.; Sesé, L.M. A Theoretical Analysis of the Ultraviolet Spectrum (180-260 nm) of Pure Liquid Benzene. Z. Phys. D: Atoms, Molecules and Clusters 1988, 9, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. Environmental Effects on Molecules Immersed in Liquids. Z. Phys. D: Atoms, Molecules and Clusters 1990, 17, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, H.F.; Fosdick, L.D. Three-Particle Effects in the Pair Distribution Function for 4He Gas. Phys. Rev. 1968, 171, 128–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistenmacher, H.; Lie, G.C.; Popkie, H.; Clementi, E. Study of the Structure of Molecular Complexes VI. Dimers and Small Clusters of Water Molecules in the Hartree-Fock Approximation. J. Chem. Phys. 1974, 61, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boninsegni, M.; Pierleoni, C.; Ceperley, D.M. Isotopic Shift of Helium Melting Pressure: Path Integral Monte Carlo Study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 72, 1854–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, S.; Pederiva, F.; Fantoni, S.; Boninsegni, M. Equation of State of Solid 3He. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 2650–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, A.L.; Hinde, R.J. Three-Body Interactions and the Elastic Constants of HCP Solid 4He. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 114504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, P.T.; Ricaud, J.; Triay, A. Dilute Bose Gas with Three-Body Interaction: Recent Results and Open Questions. J. Math. Phys. 2022, 63, 061103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, B.T. Fundamentals of Computational Quantum Chemistry. In Computational Techniques in Quantum Chemistry and Molecular Physics, Diercksen, G.H.F., Sutcliffe, B.T, Veillard, A., Eds.; NATO Advanced Study Institutes Series; Springer: Dordrecht, Holland, 1975; Volume 15, pp. 1–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildstein, B.; Kahl, G. Triplet Correlation Functions for Hard Spheres: Computer Simulation Results. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 100, 5882–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildstein, B.; Kahl, G. Triplet Correlation Functions for Hard Spheres: Comparison of Different Approaches. Phys. Rev. E 1993, 47, 1712–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciortino, F.; Kob, W. Debye-Waller Factor of Liquid Silica: Theory and Simulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, S.; Lomba, E.; Abascal, J.L.F. Theory and Simulation of the Triplet Structure Factor and Triplet Direct Correlation Functions in Binary Mixtures. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 116, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coslovich, D. Static Triplet Correlations in Glass-Forming Liquids: A Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 12A539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.; Hutchinson, P. A Method for the Extrapolation of Pair Distribution Functions. Mol. Phys. 1977, 33, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salacuse, J.J.; Denton, A.R.; Egelstaff, P.A. Finite-Size Effects in Molecular Dynamics Simulations: Static Structure Factor and Compressibility I. Theoretical Method. Phys. Rev. E 1996, 53, 2382–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumketner, A.; Hiwatari, Y. Finite-Size Dependence of the Bridge Function Extracted from Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 63, 061201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, W.A.; Ashcroft, N.W. Weighted-Density-Functional Theory of Inhomogeneous Liquids and the Freezing Transition. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 32, 2909–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.L. Constructing a New Closure Theory Based on the Third-Order Ornstein-Zernike Equation and a Study of the Adsorption of Simple Fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 204706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesé, L.M. The Compressibility Theorem for Quantum Simple Fluids at Equilibrium. Mol. Phys. 2003, 101, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. Determination of the Quantum Static Structure Factor of Liquid Neon within the Feynman-Hibbs Picture. Mol. Phys. 1996, 89, 1783–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.-N.; Jang, S.; Voth, G.A. Feynman Path Centroid Dynamics for Fermi-Dirac Statistics. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 111, 5303–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinov, N.V.; Roy, P.-N.; Voth, G.A. Path Integral Formulation of Centroid Dynamics for Systems Obeying Bose-Einstein Statistics. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 4484–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinov, N.; Roy, P.-N. Operator Formulation of Centroid Dynamics for Bose-Einstein and Fermi-Dirac Statistics. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 7822–7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinov, N.; Roy, P.-N. Connection Between the Observable and Centroid Structural Properties of a Quantum Fluid: Application to Liquid Para-Hydrogen. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 3759–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. On the Accurate Direct Computation of the Isothermal Compressibility for Normal Quantum Simple Fluids: Application to Quantum Hard Spheres. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 244504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. Path Integral Monte Carlo Study of Quantum-Hard Sphere Solids. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 044502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotter, H.F. Approximation of Semi-Groups of Operators. Pacific J. Math. 1958, 8, 887–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, J.D.; Freeman, D.L.; Beck, T.L. Equilibrium and Dynamical Fourier Path Integral Methods. Adv. Chem. Phys. 1990, 78, 61–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feynman, R.P.; Hibbs, A.R. Quantum Mechanics and Path Integrals; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1965; ISBN 978-0-070-20650-2. [Google Scholar]
- Feynman, R.P.; Kleinert, H. Effective Classical Partition Function. Phys. Rev. A 1986, 34, 5080–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giachetti, R.; Tognetti, V. Variational Approach to Quantum Statistical Mechanics of Nonlinear Systems with Applications to Sine-Gordon Chains. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1985, 55, 912–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesé, L.M. Feynman-Hibbs Quantum Effective Potentials for Monte Carlo Simulations of Liquid Neon. Mol. Phys. 1993, 78, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. Quantum Effects on the Static Structure Factor of Lennard-Jones Fluids. Mol. Phys. 1997, 92, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. An Application of the Self-Consistent Variational Effective Potential Against the Path-Integral to Compute Equilibrium Properties of Quantum Simple Fluids. Mol. Phys. 1999, 97, 881–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percus, J.K. Approximation Methods in Classical Statistical Mechanics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1962, 8, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebowitz, J.L.; Percus, J.K. Statistical Thermodynamics of Nonuniform Fluids. J. Math. Phys. 1963, 4, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvon, J. Note sur un Calcul de Perturbation en Mécanique Statistique. Suppl. Nuovo Cimento 1958, 9, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, R.D.; van der Eerden, J.P.; Faber, N.M. The Direct Correlation Function in Hard Sphere Fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 1987, 87, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveché, H.J.; Mountain, R.D. Three-Body Correlations in Simple Dense Fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 53, 3101–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveché, H.J.; Mountain, R.D. Three Atom Correlations in Liquid Neon. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 57, 3987–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stell, G. The Percus-Yevick Equation for the Radial Distribution Function of a Fluid. Physica 1963, 29, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.E.; Widom, B. Decay of Correlations in Linear Systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 50, 3756–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tago, Y.; Smith, W.R. Decay of Pair Correlation Functions. Can. J. Phys. 1997, 55, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.; Henderson, J.R.; Hoyle, D.C.; Parry, A.D.; Sabeur, Z.A. Asymptotic Decay of Liquid Structure: Oscillatory Liquid-Vapour Density Profiles and the Fisher-Widom line. Mol. Phys. 1993, 80, 755–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haymet, A.D.J; Rice, S.A.; Madden, W.G. An Accurate Integral Equation for the Pair and Triplet Distribution Functions of a Simple Liquid. J. Chem. Phys. 1981, 74, 3033–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbins, K.E.; Gray, C.G.; Egelstaff, P.A. Thermodynamic Derivatives of Correlation Functions. Mol. Phys. 1978, 35, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacuzzi, G.; Omerti, E. Monte Carlo Calculation of the Radial Distribution Function of Quantum Hard Spheres at Finite Temperatures Using Path Integrals with Boundary Conditions. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 3051–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M.; Ledesma, R. Path-Integral Monte Carlo Energy and Structure of the Quantum Hard-Sphere System Using Efficient Propagators. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 102, 3776–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierz, M. Connection Between Pair Density and Pressure for a Bose Gas Consisting of Rigid Spherical Atoms. Phys. Rev. 1957, 106, 412–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filinov, V.; Levashov, P.; Larkin, A. Monte Carlo Simulation of the Electron Short-Range Quantum Ordering in Coulomb Systems and the ‘Fermionic Sign Problem’. J. Phys. A: Mathematical and Theoretical 2022, 55, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.J. Chemical Potential of Hard Sphere fluids by Monte Carlo Methods, Mol. Phys. 1974, 28, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinert, H. Path Integrals in Quantum Mechanics, Statistical Physics, and Polymer Physics; Chp. 7; World Scientific: Singapore, 1995; ISBN 981-0-21472-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kalos, M.H.; Levesque, D.; Verlet, L. Helium at Zero Temperature with Hard-Sphere and other Forces. Phys. Rev. A 1974, 9, 2178–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceperley, D.; Chester, G.V.; Kalos, M.H. Monte Carlo Simulation of a Many-Fermion Study. Phys. Rev. B 1977, 16, 3081–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirling, W.G.; Scherm, R.; Hilton, P.A.; Cowley, R.A. Neutron inelastic scattering from Liquid Helium Three. J. Phys. C.: Solid State Phys. 1976, 9, 1643–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sköld, K.; Pelizzari, C.A. Neutron inelastic scattering from Liquid 3He at 40mK and at 1.2 K. J. Phys. C. Solid State Phys. 1978, 11, L589–L592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, P.A.; Cowley, R.A.; Scherm, R.; Stirling, W.G. Lifetime of zero sound in Liquid Helium Three. J. Phys. C.: Solid State Phys. 1980, 13, L295–L299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filinov, V.S.; Levashov, P.R.; Larkin, A.S. The Quantum Density of States and Distribution Functions of the Helium-3: Wigner Approach in Path Integral Monte Carlo simulations. Mol. Phys. 2024, e2323645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. Structural and Response Functions at Equilibrium in Path-Integral Quantum Simple Fluids. Mol. Phys. 2002, 100, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R. The Nature of the Liquid-Vapour Interface and other topics in the Statistical Mechanics of Non-Uniform Classical Fluids. Adv. Phys. 1979, 28, 143–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R. Density Functionals in the Theory of Nonuniform Fluids. In Fundamentals of Inhomogeneous Fluids; Henderson, D., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1992; ISBN 0-8247-8711-0. [Google Scholar]
- Haymet, A.D.J. Freezing. In Fundamentals of Inhomogeneous Fluids; Henderson, D., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1992; ISBN 0-8247-8711-0. [Google Scholar]
- McCoy, J.D.; Rick, S.W.; Haymet, A.D.J. Density Functional Theory of Freezing for Quantum Systems. I. Path Integral Formulation of General Theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1990, 92, 3034–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rick, S.W.; McCoy, J.D.; Haymet, AD.J. Density Functional Theory of Freezing for Quantum Systems. II. Application to Helium. J. Chem. Phys. 1990, 92, 3040–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous Electron Gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864–B871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermin, N.D. Thermal Properties of the Inhomogeneous Electron Gas. Phys. Rev. 1965, 137, A1441–A1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, K.; Miura, S.; Okazaki, S. A Molecular Approach to Quantum Fluids Based on a Generalized Ornstein-Zernike Equation. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 114, 7497–7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, K.; Miura, S.; Okazaki, S. A Generalized Ornstein-Zernike Integral Equation Study of Atomic Impurities in Quantum Fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 4161–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.M. Properties of the Path-Integral Quantum Hard-Sphere Fluid in k-Space. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 116, 8492–8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogoyavlenski, I.V.; Karnatsevich, I.V.; Konareva, V.G. Experimental Investigation of the Equation of State of Helium Isotopes (He4 and He3) in the Temperature Range from 3.3 K to 14 K. Sov. J. Low Temp. Phys. 1978, 4, 265-277.
- Ralston, A.; Rabinowitz, P. A First Course in Numerical Analysis; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 0-486-41454-X. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, L.E.; Sesé, L.M. The Asymptotic Decay of Pair Correlations in the Path-Integral Quantum Hard-Sphere Fluid. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 6557–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, L.E.; Sesé, L.M. The Decay of Pair Correlations in Quantum Hard-Sphere Fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 10076–10087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Flannery, B.P.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T. Numerical Recipes; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988; ISBN 0-521-30811-9. [Google Scholar]
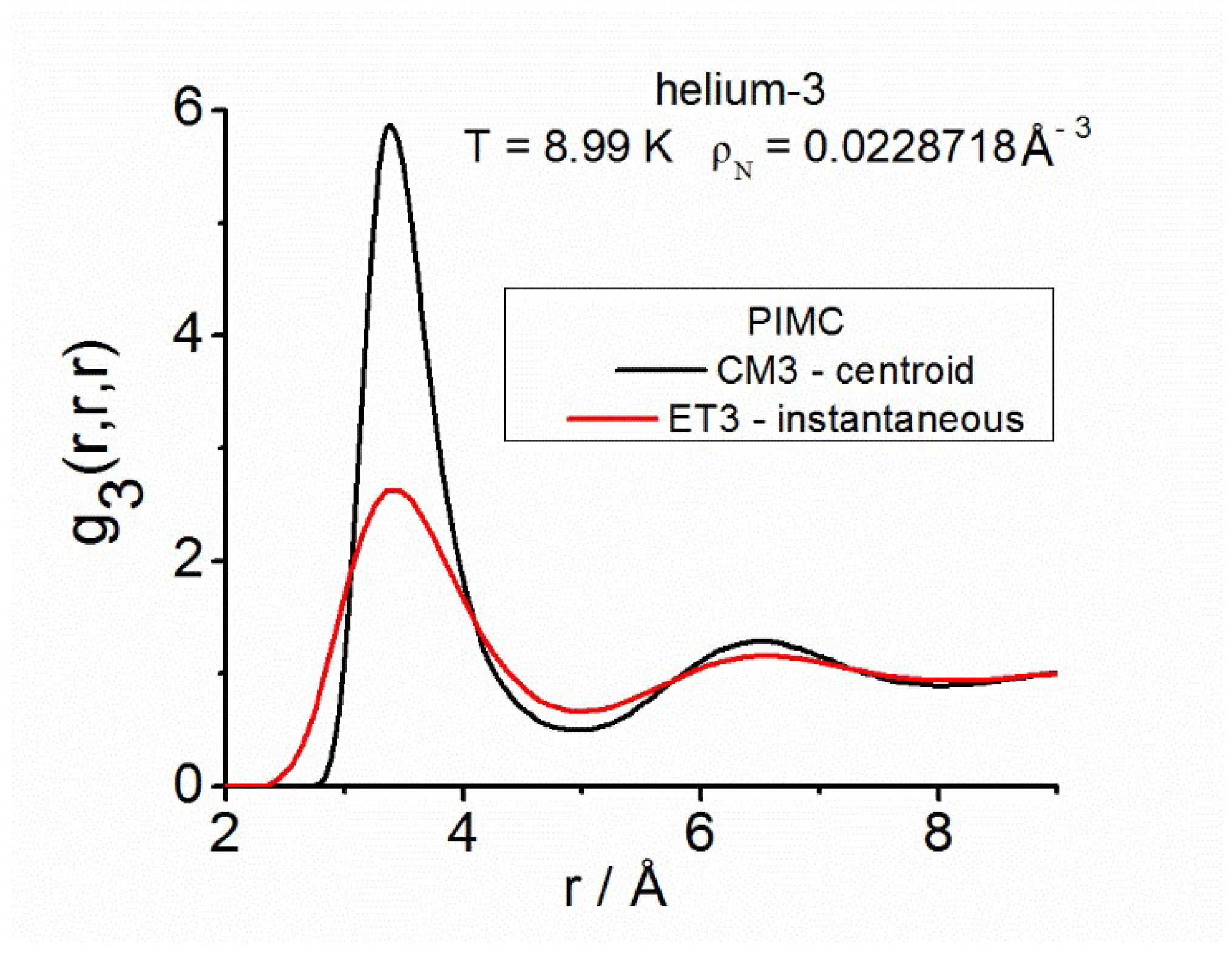
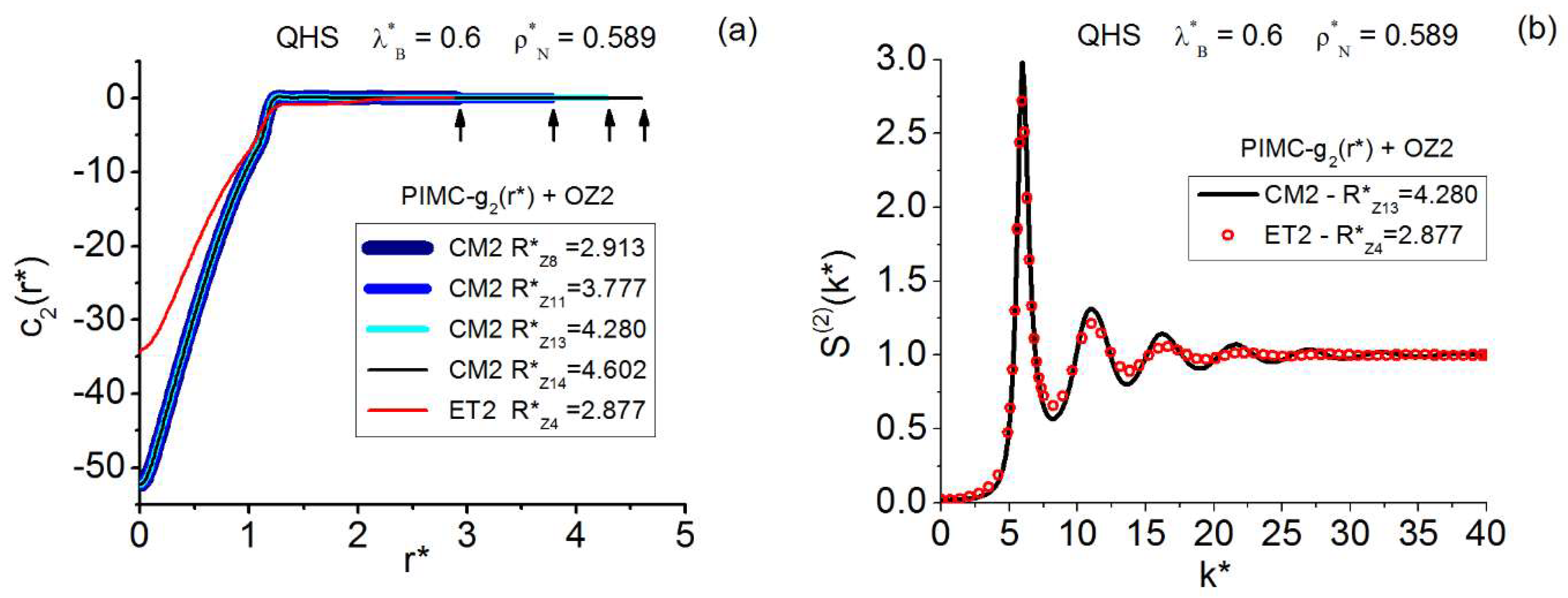
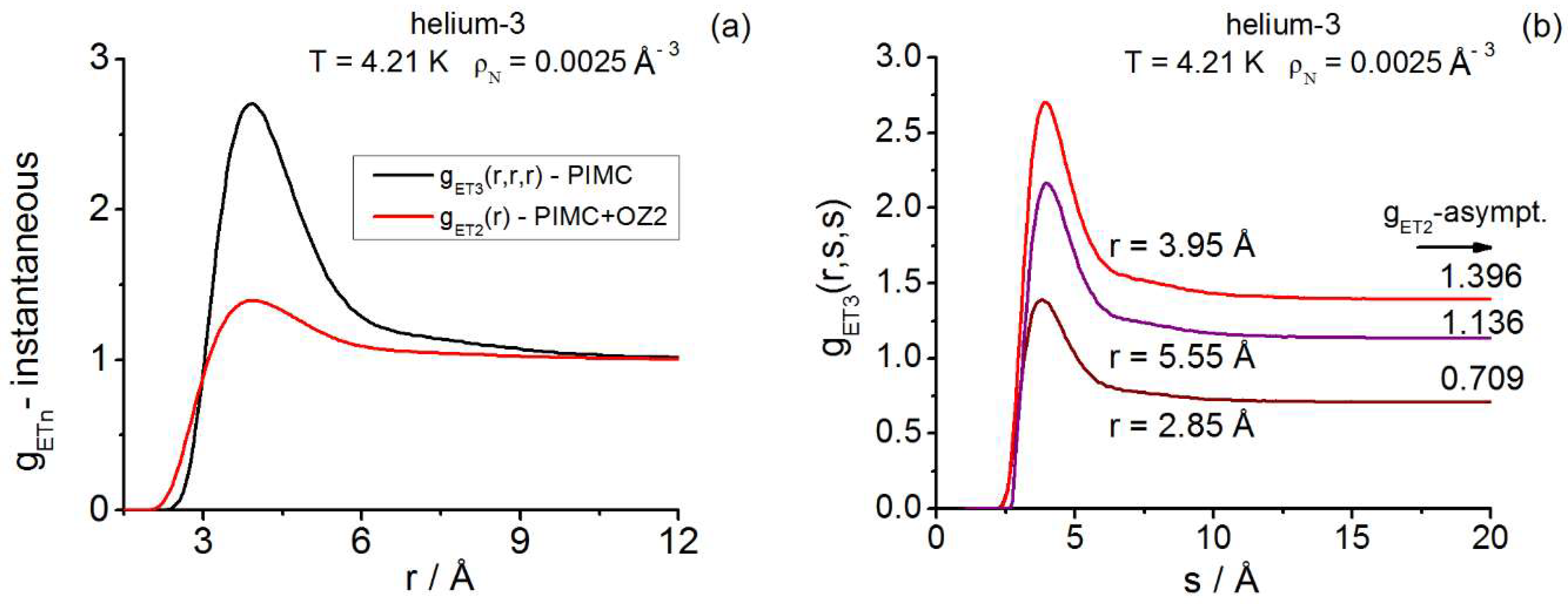
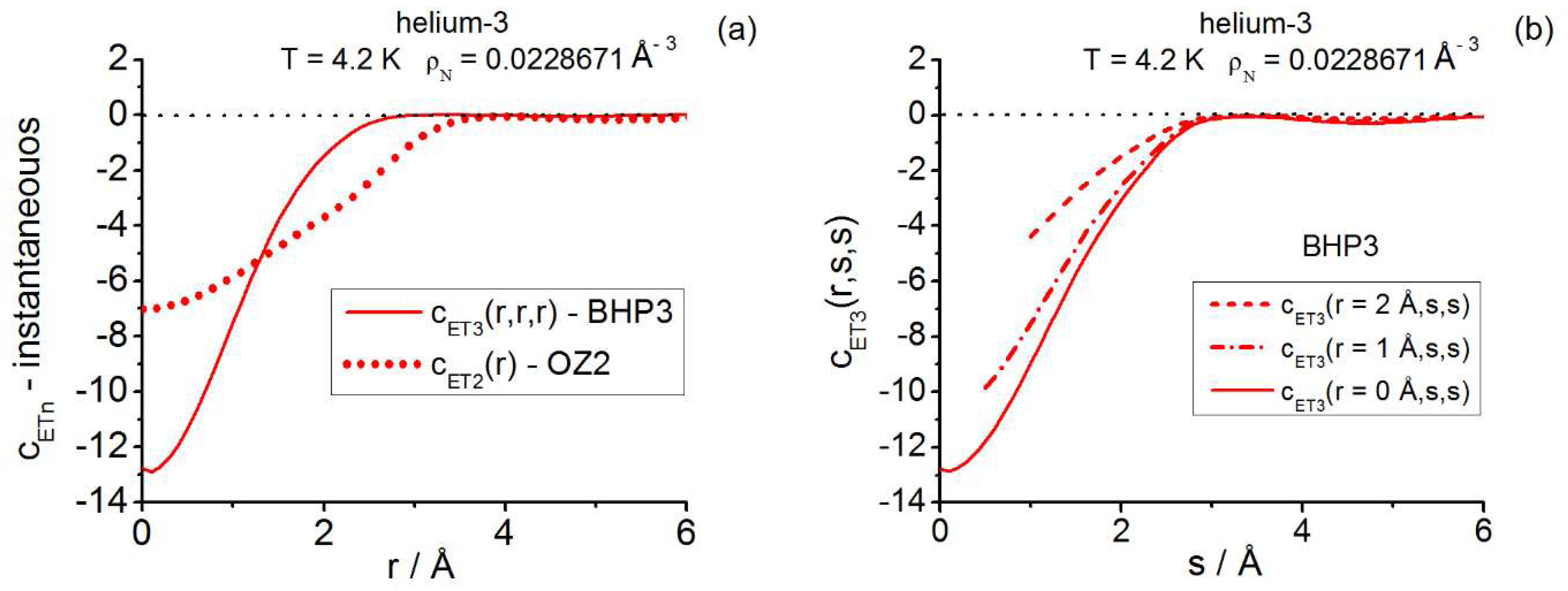
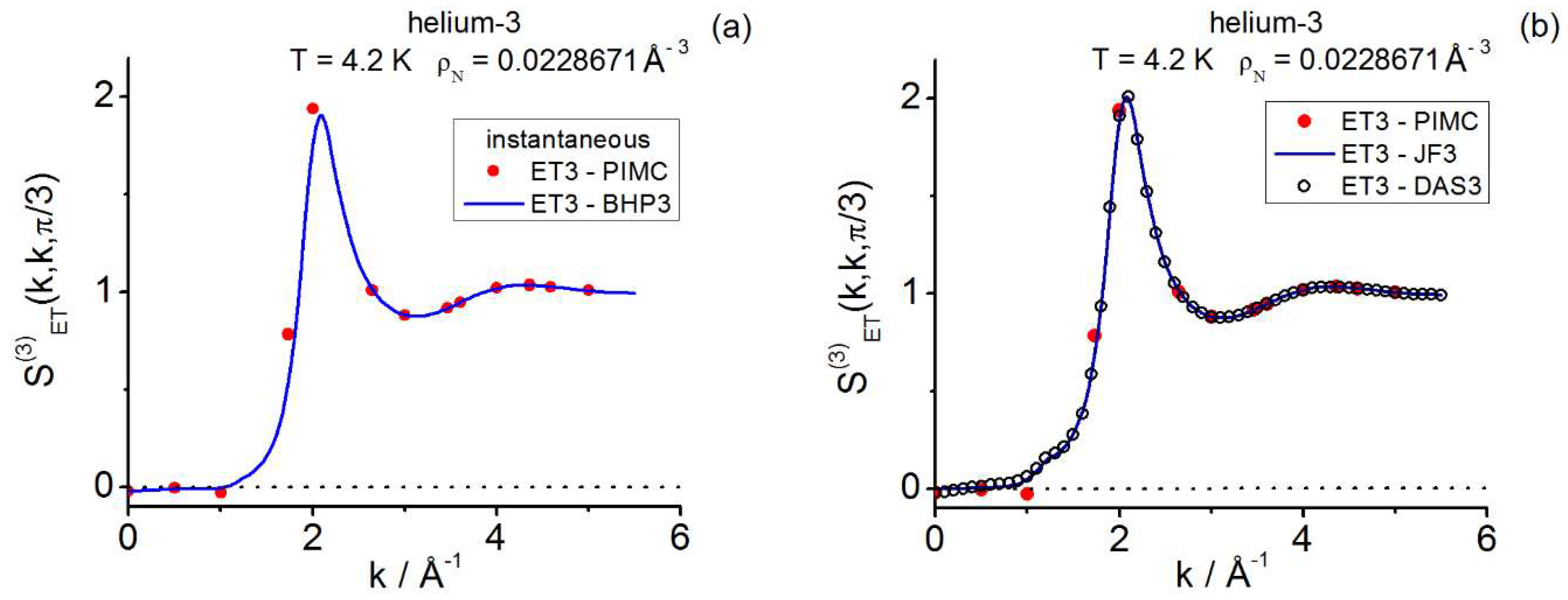
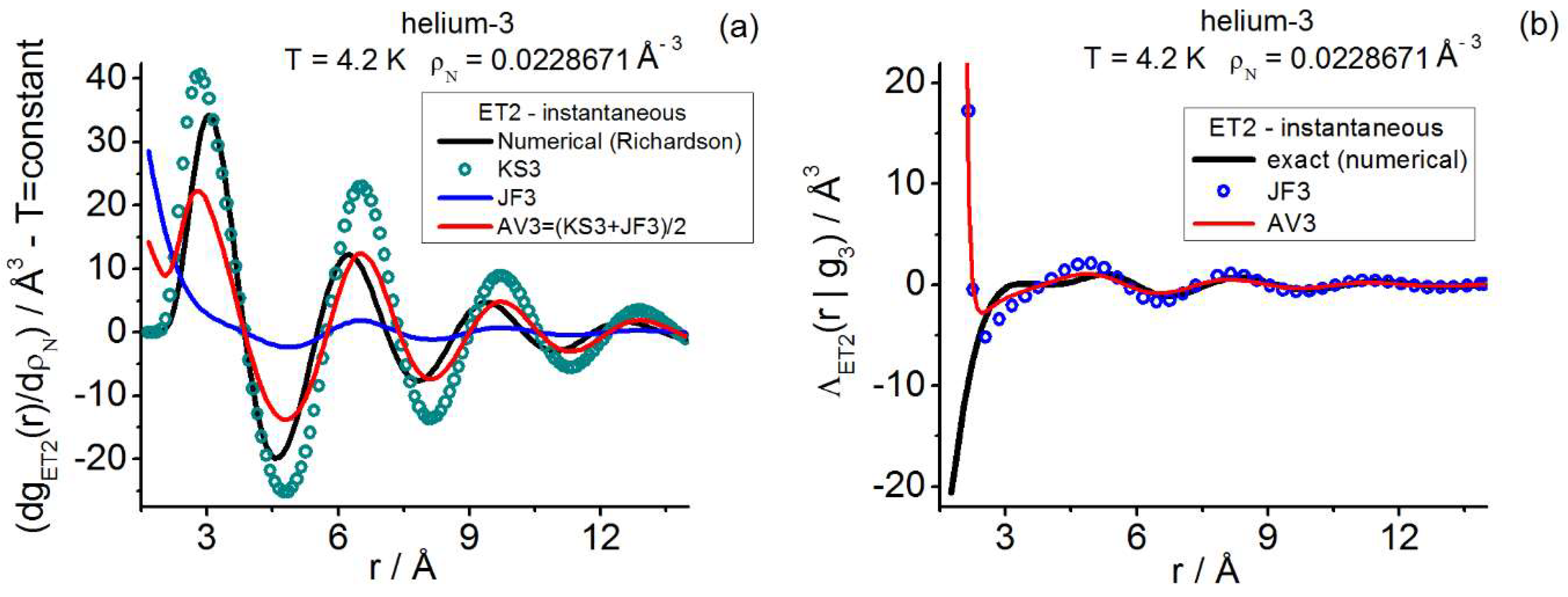
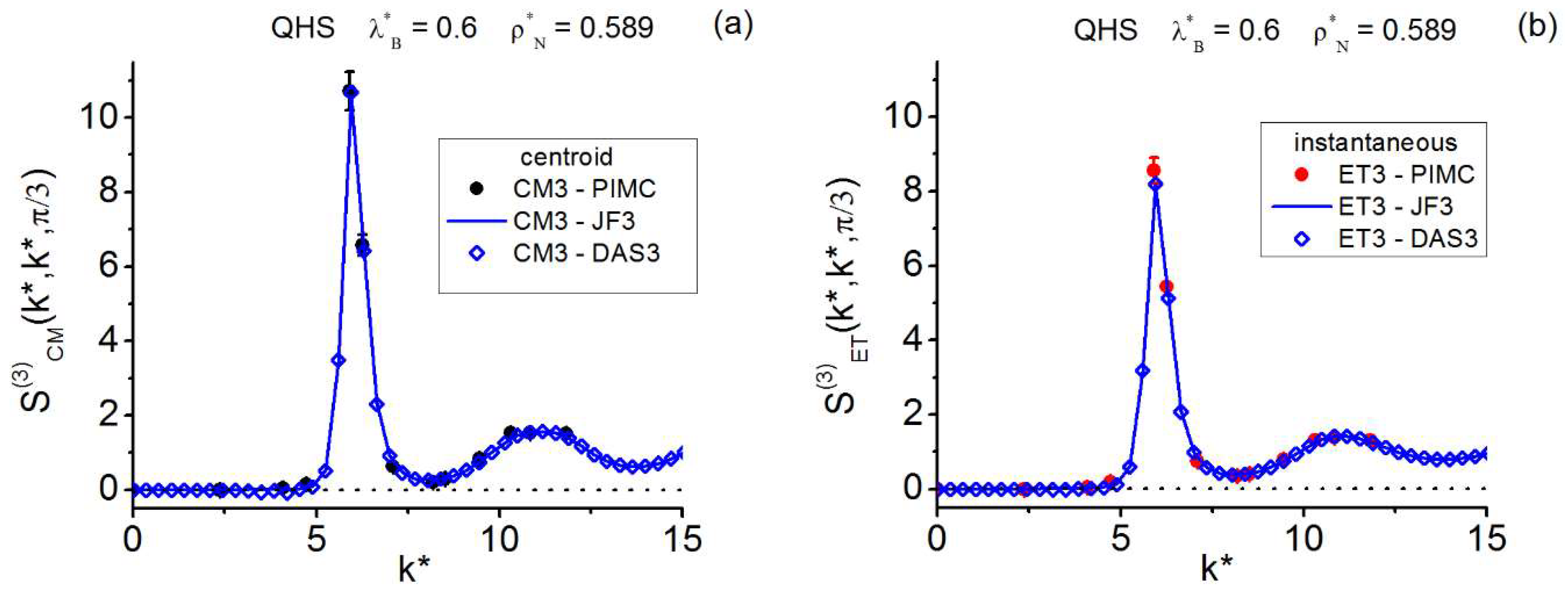
| Instantaneous— | |||||
| PIMC | JF3 | AV3 | BHP3 | DAS3 | |
| 0 | ------ | ||||
| 0.5 | |||||
| 1 | |||||
| 2 | |||||
| 2.1 | ------ | ||||
| 5 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





