Submitted:
25 September 2024
Posted:
26 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analytical equipment
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Botanical Extracts
2.4. Cell viability – MTT assay
2.5. ROS/RNS Assay
2.6. Gene expression analysis by qRT-PCR
2.7. Quantification of BDNF protein levels by ELISA
2.8. Quantification of AChE protein levels by ELISA
2.9. Clinical trial information
2.10. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. MTT analysis of individual extracts
3.2. ROS/RNS and Cell Death Markers in Individual Extracts
3.3. Trophic Factor Release in Individual Extracts
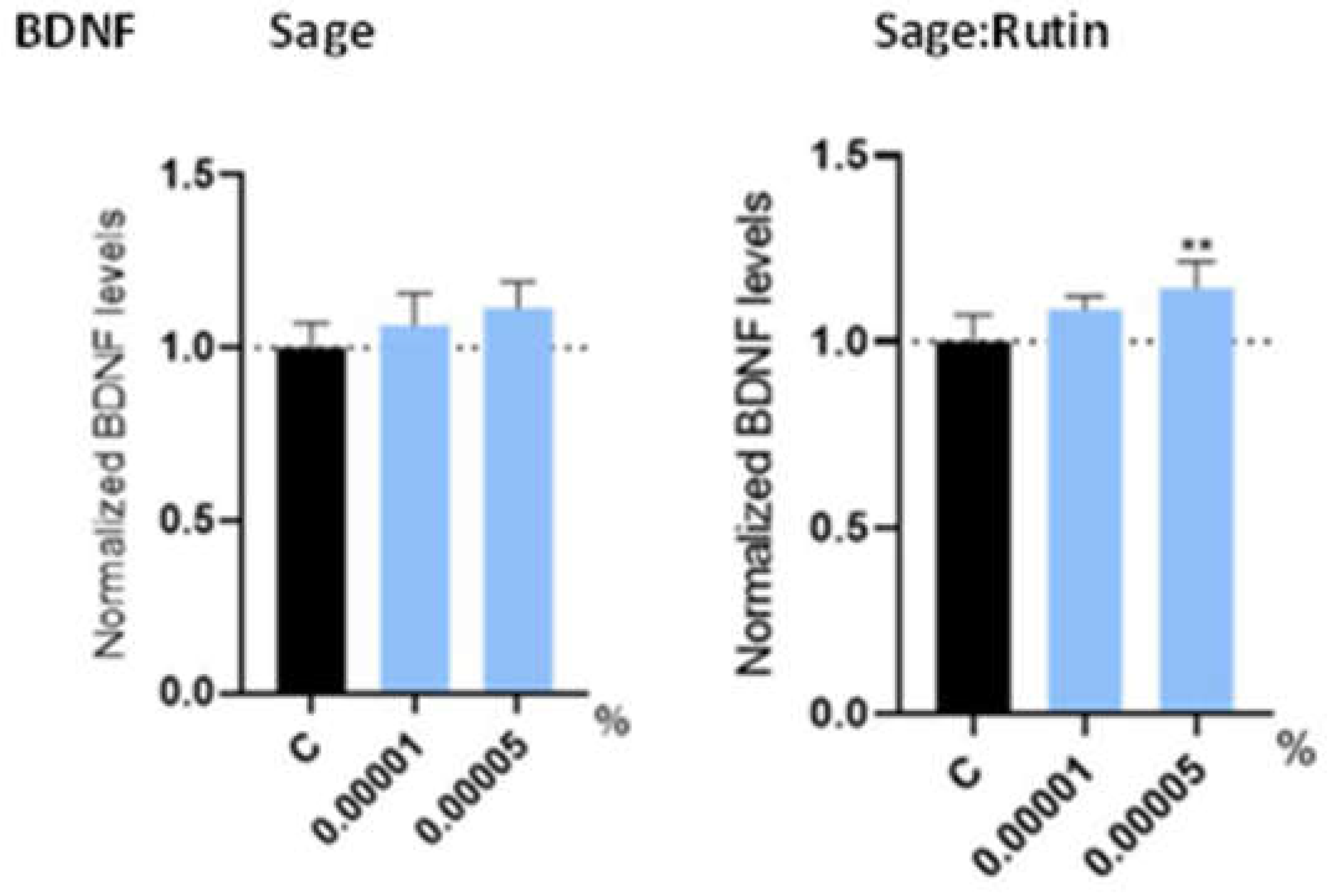
3.4. In vitro Results of Sage in combination with Rutin
3.5. Clinical Trial Results
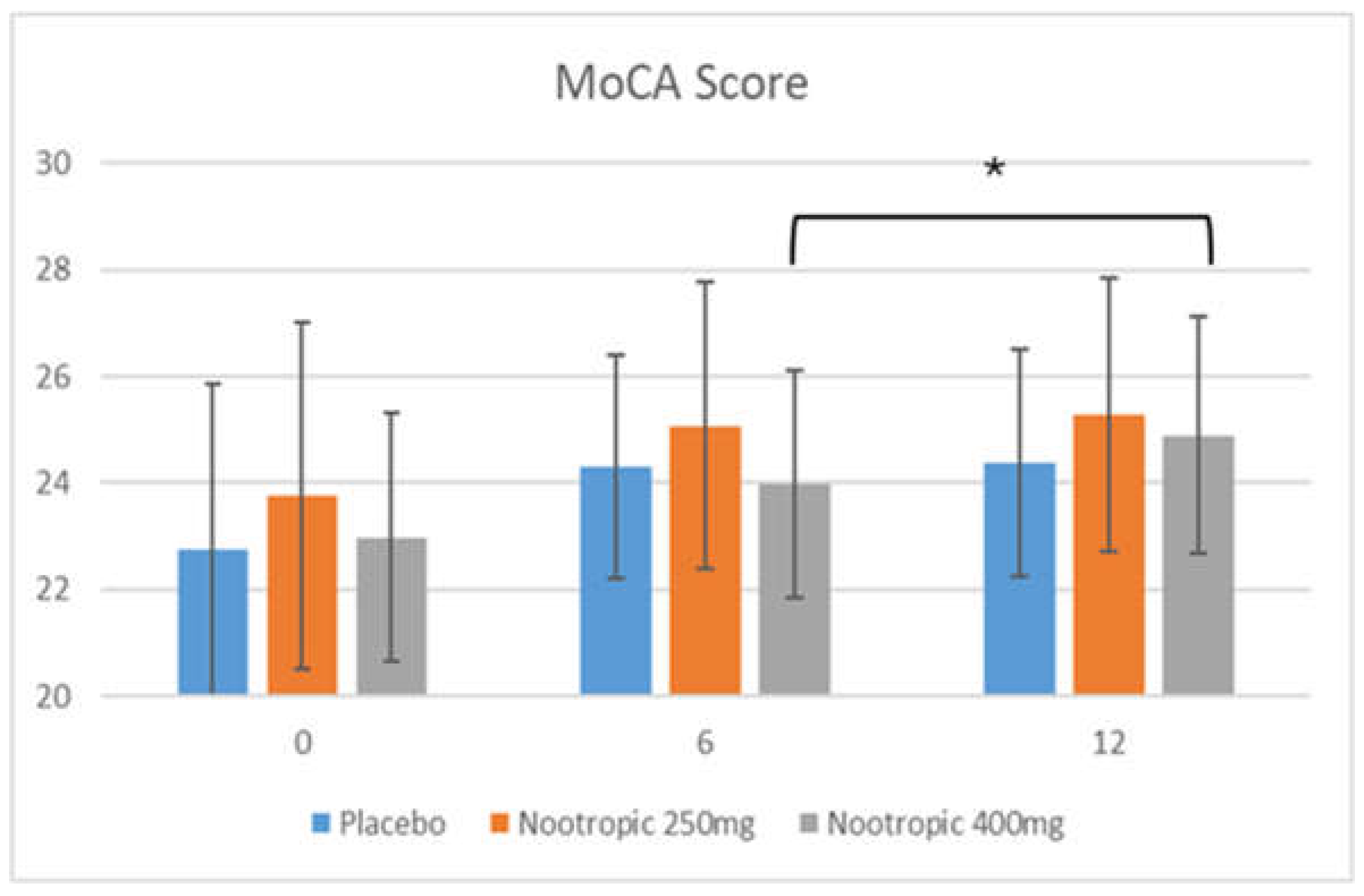
3.5.1. MoCA Test
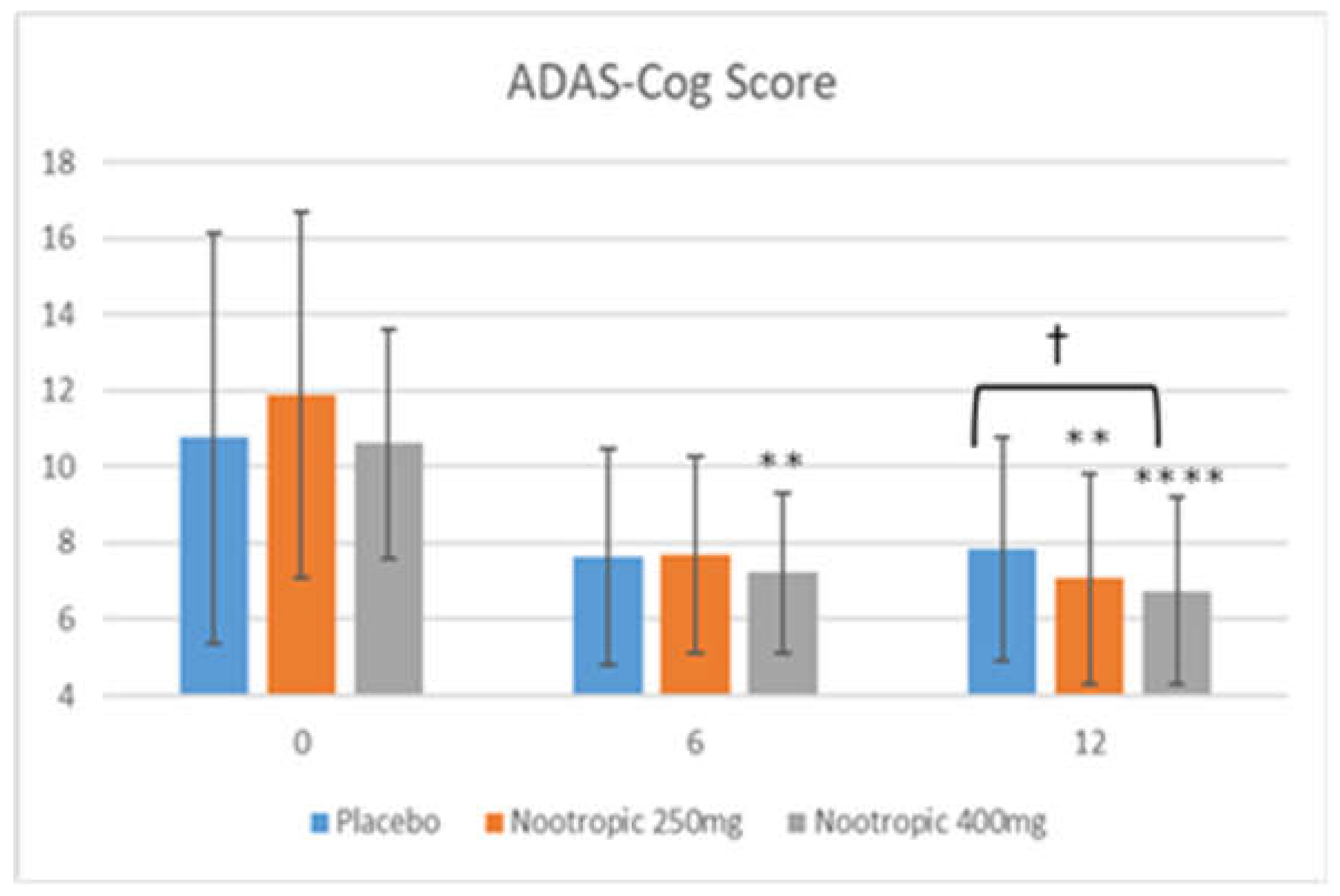
3.5.2. ADAS-Cog Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giurgea, C.; Salama, M. Nootropic Drugs. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. 1977, 1, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.; Kothari, S.; Kachhwaha, S. Nootropic Medicinal Plants: Therapeutic Alternatives for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Herb. Med. 2019, 17, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormehl, I.C.; Jordaan, B.; Oliver, D.W.; Croft, S. SPECT Monitoring of Improved Cerebral Blood Flow During Long-Term Treatment of Elderly Patients with Nootropic Drugs. Clin. Nucl. Med. 1999, 24, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malík, M.; Tlustoš, P. Nootropic Herbs, Shrubs, and Trees as Potential Cognitive Enhancers. Plants (Basel), 2023, 12, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamkaew, N.; Norman Scholfield, C.; Ingkaninan, K.; Taepavarapruk, N.; Chootip, K. Bacopa Monnieri Increases Cerebral Blood Flow in Rat Independent of Blood Pressure. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerendra Kumar, M.H.; Gupta, Y.K. Effect of Different Extracts of Centella Asiatica on Cognition and Markers of Oxidative Stress in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 79, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, D.W.; Jung, B.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.; Hwang, G.S.; Kang, K.S.; Lee, J.W. Ginsenoside Rb2 Suppresses the Glutamate-Mediated Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Cell Death in HT22 Cells. J. Ginseng. Res. 2019, 43, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonekura, L.; Martins, C.A.; Sampaio, G.R.; Monteiro, M.P.; César, L.A.M.; Mioto, B.M.; Mori, C.S.; Mendes, T.M.N.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Arçari, D.P.; et al. Bioavailability of Catechins from Guaraná (Paullinia cupana) and its Effect on Antioxidant Enzymes and other Oxidative Stress Markers in Healthy Human Subjects. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2970–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Murthy, V.; Ramassamy, C. Modulation of Hydrogen Peroxide and Acrolein-Induced Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunctions and Redox Regulated Pathways by the Bacopa monniera Extract: Potential Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 21, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Obara, Y.; Hirota, M.; Azumi, Y.; Kinugasa, S.; Inatomi, S.; et al. Nerve Growth Factor-Inducing Activity of Hericium Erinaceus In 1321n1 Human Astrocytoma Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumiyoshi, E.; Matsuzaki, K.; Sugimoto, N.; Tanabe, Y.; Hará, T.; Katakura, M.; et al. Sub-Chronic Consumption of Dark Chocolate Enhances Cognitive Function and Releases Nerve Growth Factors: a Parallel-Group Randomized Trial. Nutrients, 2019, 11, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decroix, L.; Tonoli, C.; Soares, D.D.; Tagougui, S.; Heyman, E.; Meeusen, R. Acute Cocoa Flavanol Improves Cerebral Oxygenation Without Enhancing Executive Function at Rest or After Exercise. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malík, M.; Tlustoš, P. Nootropics as Cognitive Enhancers: Types, Dosage and Side Effects of Smart Drugs. Nutrients. 2022, 14, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, S.; Ganeshpurkar, A.; Bansal, D.; Dubey, N. Protective Effect of Rutin on Impairment of Cognitive Functions Due to Antiepileptic Drugs on Zebrafish Model. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2015, 47, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Bekinschtein, P.; Cammarota, M.; Katche, C.; Slipczuk, L.; Rossato, J.I.; Goldin, A.; et al. BDNF is Essential to Promote Persistence of Long-Term Memory Storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States Am. 2008, 105, 2711–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enogieru, A.B.; Haylett, W.; Hiss, D.C.; Bardien, S.; Ekpo, O.E. Rutin as a Potent Antioxidant: Implications for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 624101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyenhuis, D.L.; Reckow, J. Office- And Bedside-Based Screening for Cognitive Impairment and the Dementias: Which Tools to Use, Interpreting the Results, and What are the Next Steps? Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2023, 39, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueper, J.K.; Speechley, M.; Montero-Odasso, M. The Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive Subscale (ADAS-Cog): Modifications and Responsiveness in Pre-Dementia Populations. a Narrative Review. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 63, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, F.; Tong, L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; He, H.; Xu, R.; Ma, Y.; Huang, C. Neuroprotective Effects of Anthocyanins and its Major Component Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside (C3G) in the Central Nervous System: an Outlined Review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 452, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafra-Stone, S.; Yasmin, T.; Bagchi, M.; Chatterjee, A.; Vinson, J.A.; Bagchi, D. Berry Anthocyanins as Novel Antioxidants in Human Health and Disease Prevention. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, T.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Lyu, X. Bilberry Anthocyanin Extract Promotes Intestinal Barrier Function and Inhibits Digestive Enzyme Activity by Regulating the Gut Microbiota in Aging Rats. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krikorian, R.; Shidler, M.D.; Nash, T.A.; Kalt, W.; Vinqvist-Tymchuk, M.R.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Joseph, J.A. Blueberry Supplementation Improves Memory in Older Adults. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3996–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.G.; Hamilton, D.A.; Joseph, J.A.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Dietary Blueberry Improves Cognition Among Older Adults in a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcnamara, R.K.; Kalt, W.; Shidler, M.D.; McDonald, J.; Summer, S.S.; Stein, A.L.; Stover, A.N.; Krikorian, R. Cognitive Response to Fish Oil, Blueberry, and Combined Supplementation in Older Adults with Subjective Cognitive Impairment. Neurobiol. Aging. 2018, 64, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowtell, J.L.; Aboo-Bakkar, Z.; Conway, M.E.; Adlam, A.L.R.; Fulford, J. Enhanced Task-Related Brain Activation and Resting Perfusion in Healthy Older Adults After Chronic Blueberry Supplementation. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Manap, A.S.; Vijayabalan, S.; Madhavan, P.; Chia, Y.Y.; Arya, A.; Wong, E.H. , et al. Bacopa monnieri, a Neuroprotective Lead in Alzheimer Disease: a Review on its Properties, Mechanisms of Action, and Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Drug Target Insights. 2019, 13, 1177392819866412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Saoji, A.; Kumar, N.; Thawani, V.; Tiwari, M.; Thawani, M. Effect of Bacopa monnieri on Cognitive Functions in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Int. J. Collaborative Res. Intern. Med. Public Health. 2011, 3, 285–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Abichandani, L.G.; Thawani, V.; Gharpure, K.J.; Naidu, M.U.; Venkat-Ramana, G. Efficacy of Standardized Extract of Bacopa Monnieri (Bacognize®) on Cognitive Functions of Medical Students: a Six-Week, Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 4103423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, C.; Gregory, W.L.; Leo, M.; Kraemer, D.; Bone, K.; Oken, B. Effects of a Standardized Bacopa monnieri Extract o Cognitive Performance, Anxiety, and Depression in the Elderly: a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2008, 14, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stough, C.; Lloyd, J.; Clarke, J.; Downey, L.A.; Hutchison, C.W.; Rodgers, T.; et al. The Chronic Effects of an Extract of Bacopa monniera (Brahmi) on Cognitive Function in Healthy Human Subjects. Psychopharmacology. 2001, 156, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stough, C.; Downey, L.A.; Lloyd, J.; Silber, B.; Redman, S.; Hutchison, C.; et al. Examining the Nootropic Effects of a Special Extract of Bacopa monnieri on Human Cognitive Functioning: 90 Day Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Randomized Trial. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, A.; Stevens, J. Does Bacopa monnieri Improve Memory Performance in Older Persons? Results of a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2010, 16, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopresti, A.L. Salvia (Sage): a Review of its Potential Cognitive-Enhancing and Protective Effects. Drugs R.D. 2017, 17, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.; Pace, S.; Haskell, C.F.; Okello, E.J.; Milne, A.; Scholey, A. Effects of Cholinesterase Inhibiting Sage (Salvia Officinalis) on Mood, Anxiety and Performance on a Psychological Stressor Battery. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006, 31, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhondzadeh, S.; Noroozian, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Ohadinia, S.; Jamshidi, A.H.; Khani, M. Salvia Officinalis Extract in the Treatment of Patients with Mild to Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease: a Double Blind, Randomized and Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2003, 28, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholey, A.; Tildesley, N.T.J.; Ballard, C.; Wesnes, K.; Tasker, A.; Perry, E.K.; Kennedy, D. An Extract of Salvia (Sage) with Anticholinesterase Properties Improves Memory and Attention in Healthy Older Volunteers. Psychopharmacology. 2008, 198, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, E.; Kadoglou, N.P.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Valsami, G. Saffron: A Natural Product with Potential Pharmaceutical Applications. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 1634–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhondzadeh, S.; Sabet, M.S.; Harirchian, M.H.; Togha, M.; Cheraghmakani, H.; Razeghi, S.; et al. Saffron in the Treatment of Patients with Mild to Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease: a 16-Week, Randomized And Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhondzadeh, S.; Sabet, M.S.; Harirchian, M.H.; Togha, M.; Cheraghmakani, H.; Razeghi, S; et al. A 22-Week, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Trial of Crocus Sativus in the Treatment of Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease. Psychopharmacology. 2010, 207, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhnia, M.; Sabet, M.S.; Iranpour, N.; Gougol, A.; Yekehtaz, H.; Alimardani, R.; et al. Comparing the Efficacy and Safety of Crocus sativus L. with Memantine in Patients with Moderate to Severe Alzheimer’s Disease: a Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2014, 29, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolaki, M.; Karathanasi, E.; Lazarou, I.; Dovas, K.; Verykouki, E.; Karacostas, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Crocus sativus L. in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: One Year Single-Blind Randomized, with Parallel Groups, Clinical Trial. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2016, 54, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Braidy, N.; Orhan, I.E.; Badiee, A.; Daglia, M.; Nabavi, S.M. Rhodiola rosea L. and Alzheimer’s Disease: from Farm to Pharmacy. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jowko, E.; Sadowski, J.; Dlugolecka, B.; Gierczuk, D.; Opaszowski, B.; Cieslinski, I. Effects of Rhodiola rosea Supplementation on Mental Performance, Physical Capacity, and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Healthy Men. J. Sport Health. Sci. 2018, 7, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbinyan, V.; Kteyan, A.; Panossian, A.; Gabrielian, E.; Wikman, G.; Wagner, H. Rhodiola rosea in Stress Induced Fatigue--a Double Blind Cross-Over Study of a Standardized Extract Shr-5 with a Repeated Low-Dose Regimen on the Mental Performance of Healthy Physicians During Night Duty. Phytomedicine. 2000, 7, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cropley, M.; Banks, A.P.; Boyle, J. The Effects of Rhodiola rosea L. Extract on Anxiety, Stress, Cognition and Other Mood Symptoms. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fintelmann, V.; Gruenwald, J. Efficacy and Tolerability of a Rhodiola rosea Extract in Adults with Physical and Cognitive Deficiencies. Adv. Ther. 2007, 24, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, B.S.; Storzbach, D.M.; Kaye, J.A. The Efficacy of Ginkgo Biloba on Cognitive Function in Alzheimer Disease. Arch. Neurol. 1998, 55, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, E. The Risk-Benefit Profile of Commonly Used Herbal Therapies: Ginkgo, St. John’s Wort, Ginseng, Echinacea, Saw Palmetto, and Kava. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 136, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, C.S.; Zhang, A.L.; Cai, Y.; Xue, C.C. The Efficacy and Safety of Chinese Herbal Medicine for Mild Cognitive Impairment: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1341074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Tsai, W.H.; Chen, C.J.; Pan, T.M. Centella asiatica Extract Protects Against Amyloid Β1–40-Induced Neurotoxicity in Neuronal Cells by Activating the Antioxidative Defence System. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2016, 6, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanathorn, J.; Mator, L.; Muchimapura, S.; Tongun, T.; Pasuriwong, O.; Piyawatkul, N.; Yimtae, K.; Sripanidkulchai, B.; Singkhoraard, J. Positive Modulation of Cognition and Mood in the Healthy Elderly Volunteer Following the Administration of Centella asiatica. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 116, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekinschtein, P.; Cammarota, M.; Medina, J.H. BDNF and Memory Processing. Neuropharmacology. 2014, 76 Pt C, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Tsuji, M.; Oguchi, T.; Kasuga, K.; Kimura, A.; Futamura, A.; Sugimoto, A.; Kasai, H.; Kuroda, T.; Yano, S.; et al. Serum BDNF as a Potential Biomarker of Alzheimer’s Disease: Verification Through Assessment of Serum, Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Medial Temporal Lobe Atrophy. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 653267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, A.; Chernicki, B.; Ou, G.; Parmar, M.S. From Lab Bench to Hope: Emerging Gene Therapies in Clinical Trials for Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, N.; Ray, S.; Lomax, J.; Goertzen, S.; Komarnytsky, S.; Ho, C.T.; Munafo, J.P. Modulation of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Signaling Pathway by Culinary Sage (Salvia officinalis L. ). Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesulam, M.M. The Cholinergic Innervation of the Human Cerebral Cortex. Prog. Brain Res. 2004; 145, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, P.N.; Lodhi, A.; Rai, S.N.; Nandi, N.K.; Dumoga, S.; Yadav, P.; Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, S.K.; El-Shorbagi, A.A.; Chaudhary, S. Review of Pharmacotherapeutic Targets in Alzheimer’s Disease and its Management using Traditional Medicinal Plants. Degener. Neurol. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2024, 14, 47–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smach, M.A.; Hafsa, J.; Charfeddine, B.; Dridi, H.; Limem, K. Effects of Sage Extract on Memory Performance in Mice and Acetylcholinesterase Activity. Ann. Pharm. Fr. 2015, 73, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, A.; Mira, A.; Ashour, A.; Shimizu, K. Acetylcholine Esterase Inhibitors and Melanin Synthesis Inhibitors from Salvia officinalis. Phytomedicine. 2016, 23, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merad, M.; Soufi, W.; Ghalem, S.; Boukli, F.; Baig, M.H.; Ahmad, K.; et al. Molecular Interaction of Acetylcholinesterase with Carnosic Acid Derivatives: a Neuroinformatics Study. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets. 2014, 13, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelo, F.; Días, C.; Martins, A.; Madeira, P.J.; Jorge, T.; Florencio, M.H.; et al. Molecular Recognition of Rosmarinic Acid from Salvia sclareoides Extracts by Acetylcholinesterase: a New Binding Site Detected by NMR Spectroscopy. Chemistry. 2013, 19, 6641–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Pace, S.; Haskell, C.; Okello, E.J.; Milne, A.; Scholey, A.B. Effects of Cholinesterase Inhibiting Sage (Salvia officinalis) on Mood, Anxiety and Performance on a Psychological Stressor Battery. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006, 31, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholey, A.B.; Tildesley, N.T.; Ballard, C.G.; Wesnes, K.A.; Tasker, A.; Perry, E.K.; et al. An Extract of Salvia (Sage) with Anticholinesterase Properties Improves Memory and Attention in Healthy Older Volunteers. Psychopharmacology. 2008, 198, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henneges, C.; Reed, C.; Chen, Y.F.; Dell’Agnello, G.; Lebrec, J. Describing the Sequence of Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients: Results from an Observational Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 52, 1065–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.D.; Lachmann, T.; Jaarsveld, S.; Riedel-Heller, S.G.; Rodriguez, F.S. Creativity Across the Lifespan: Changes with Age and with Dementia. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 160, Erratum In BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundman, M.; Petersen, R.C.; Ferris, S.H.; Thomas, R.G.; Aisen, P.S.; Bennett, D.A.; et al. Mild Cognitive Impairment can be Distinguished from Alzheimer Disease and Normal Aging for Clinical Trials. Arch Neurol. 2004, 61, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
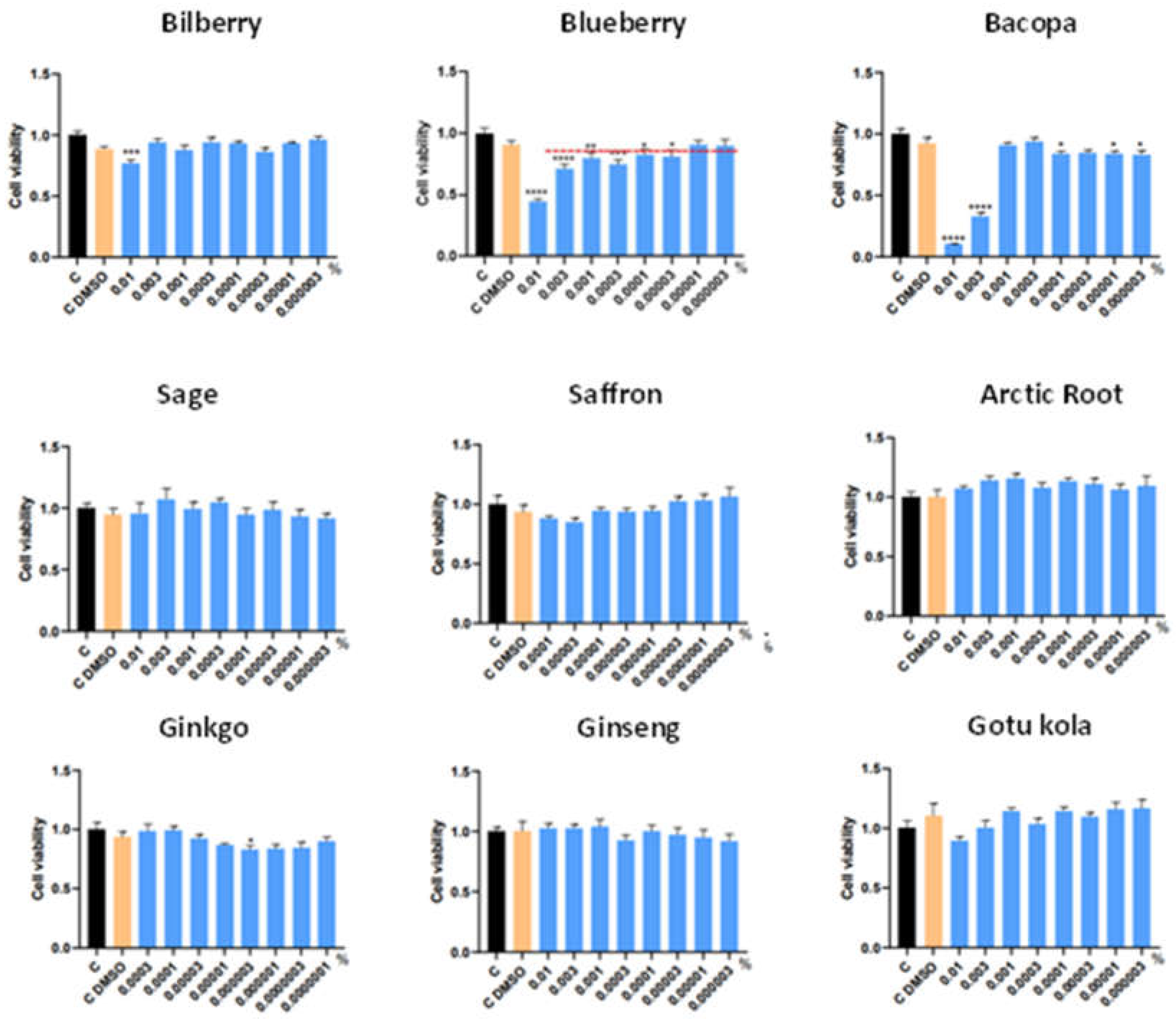
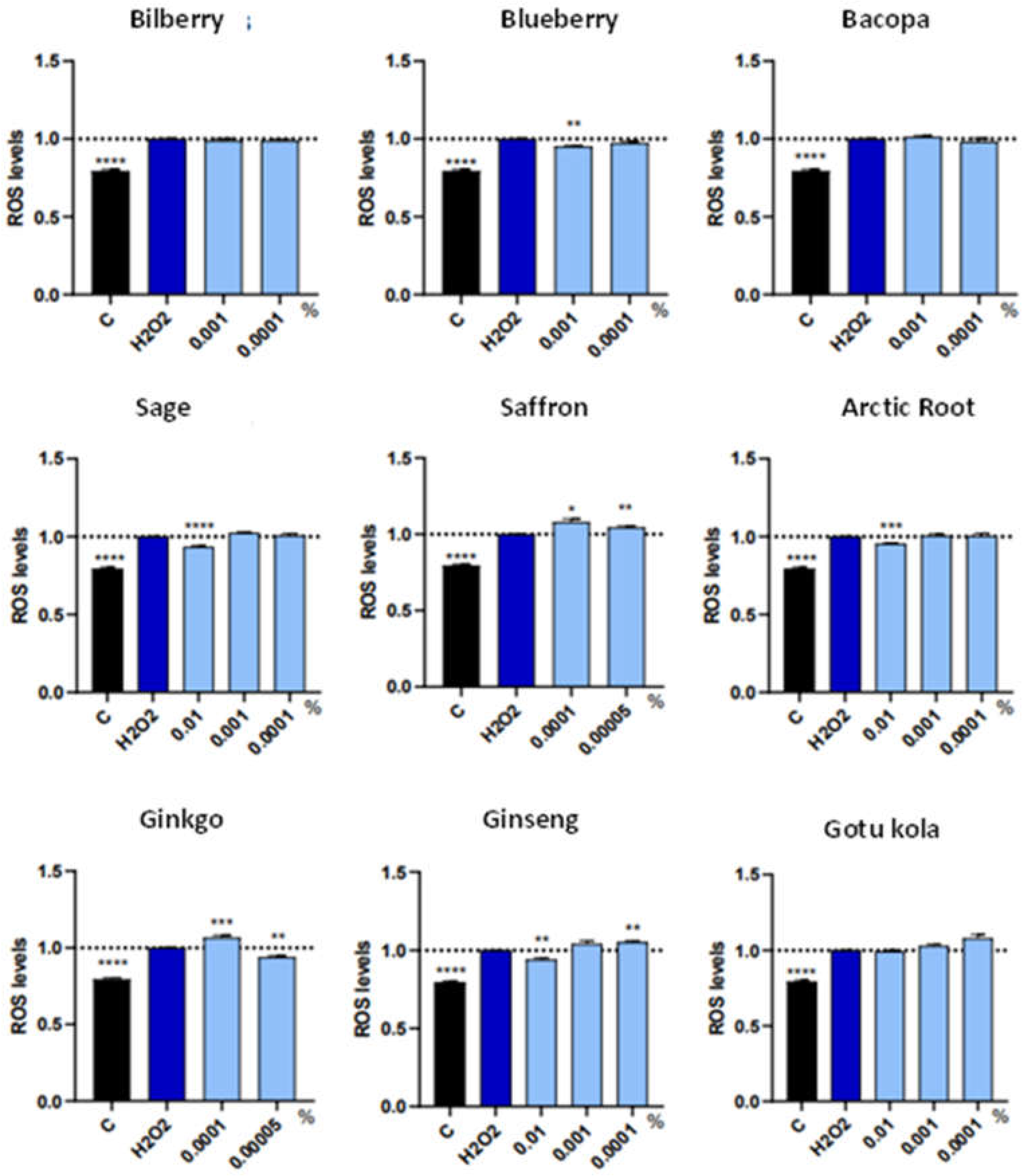
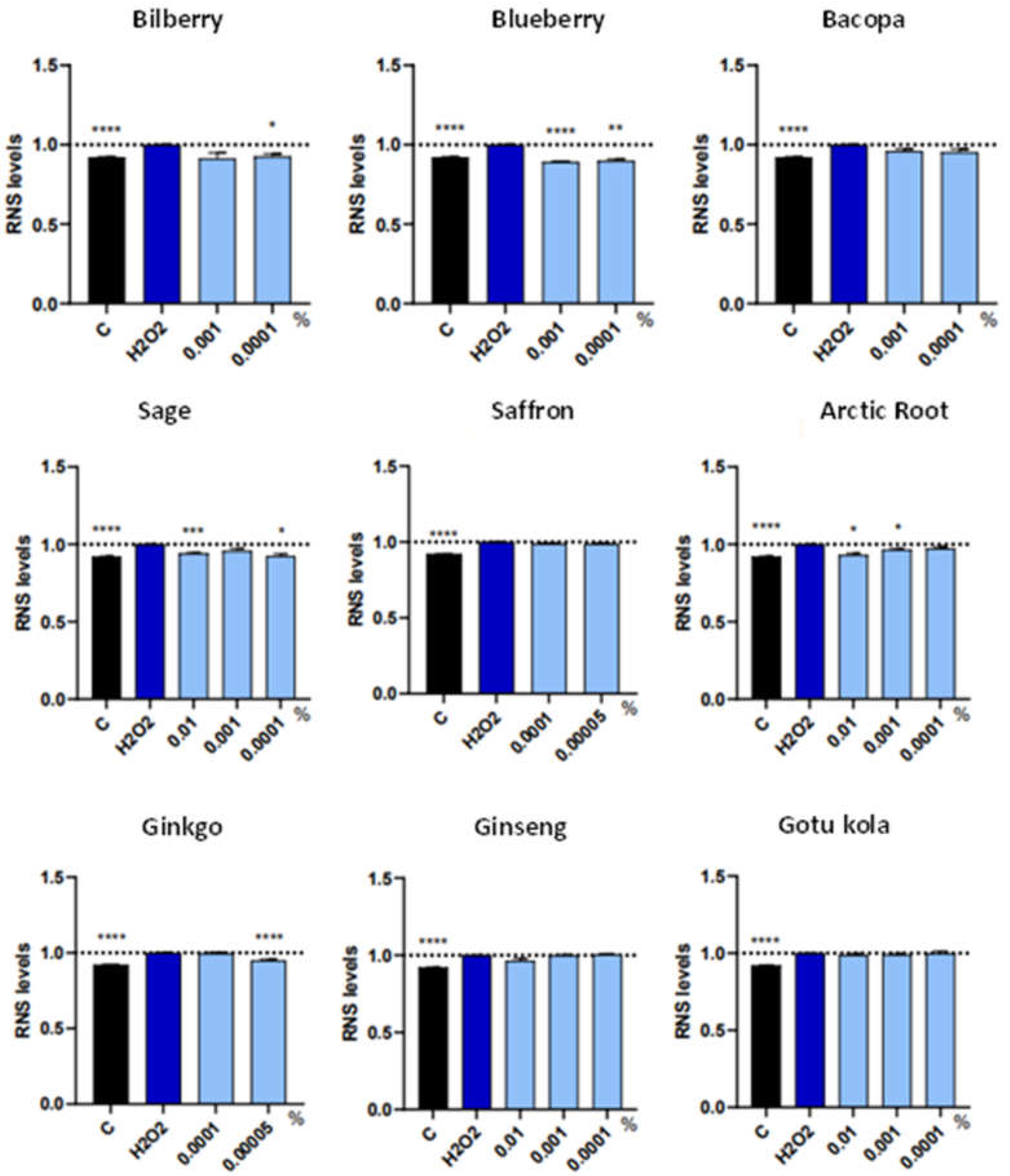
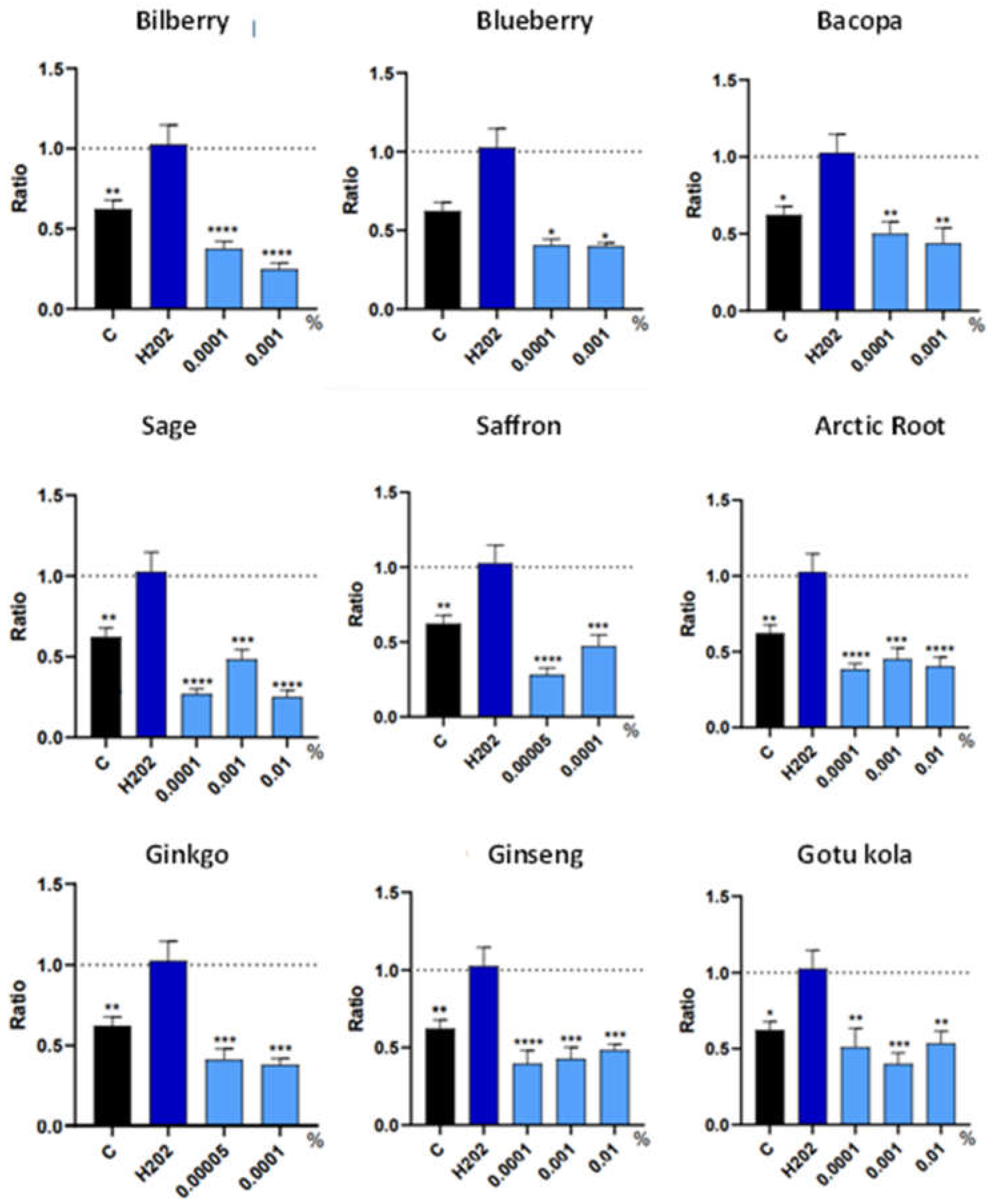
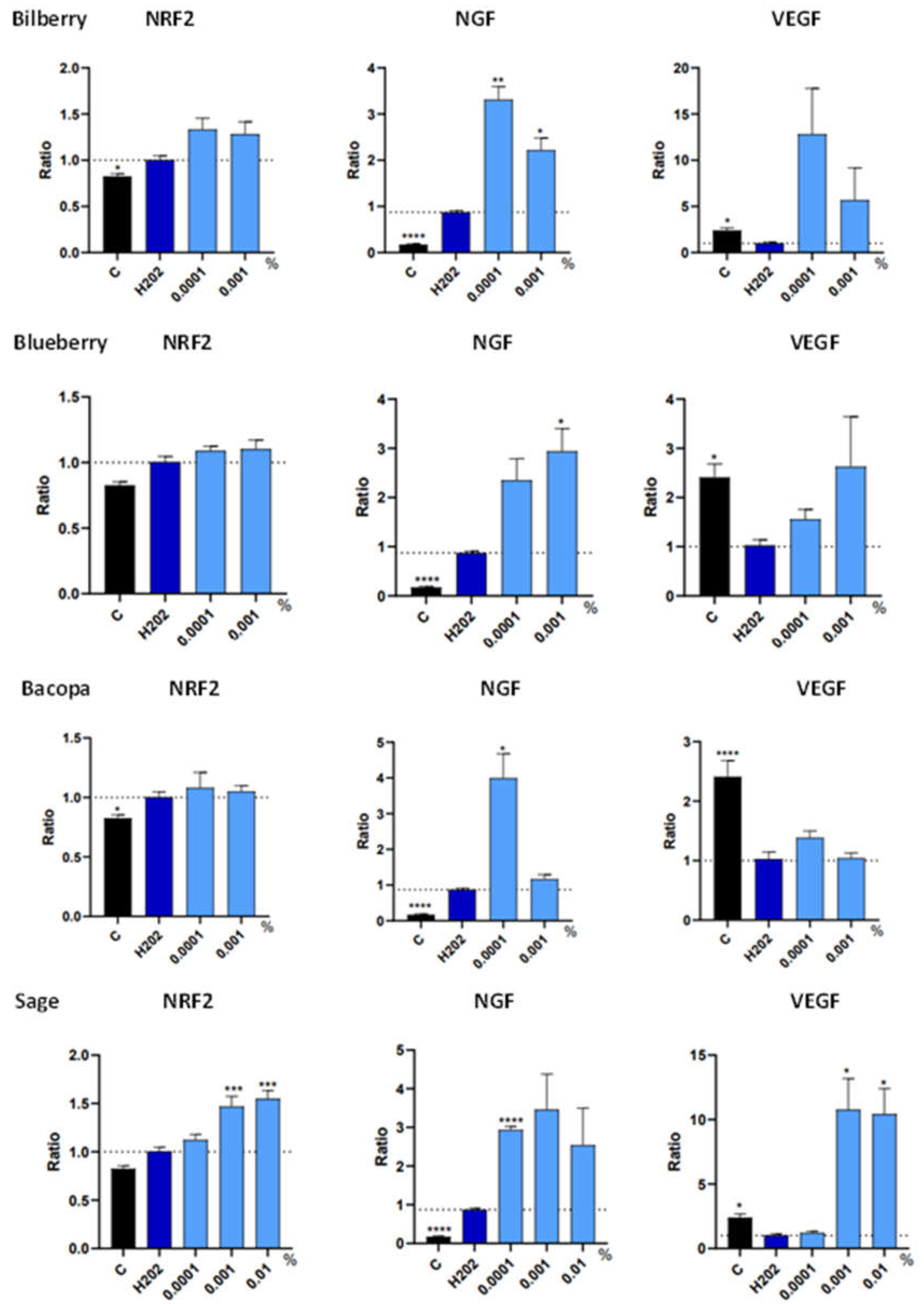
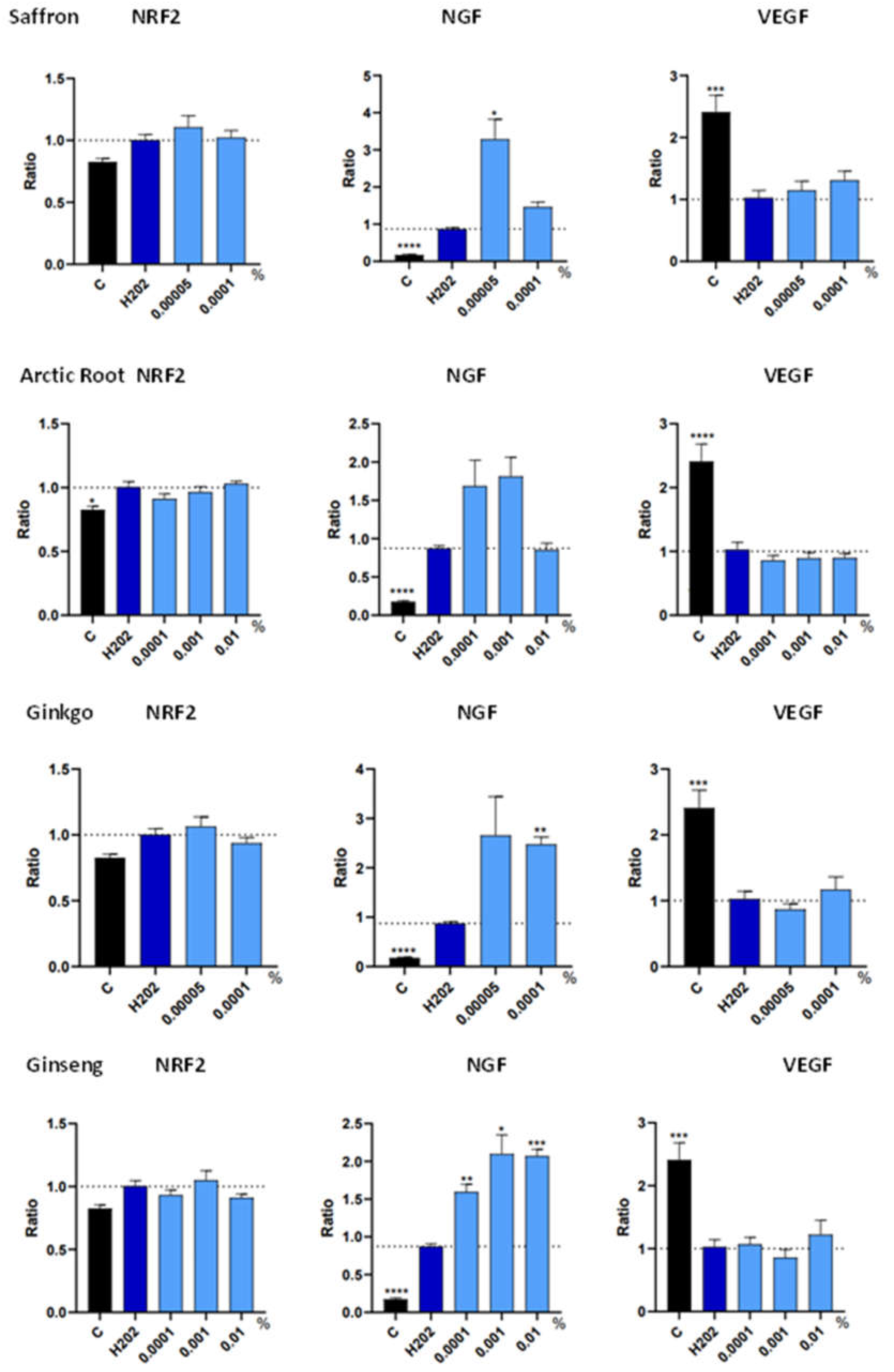
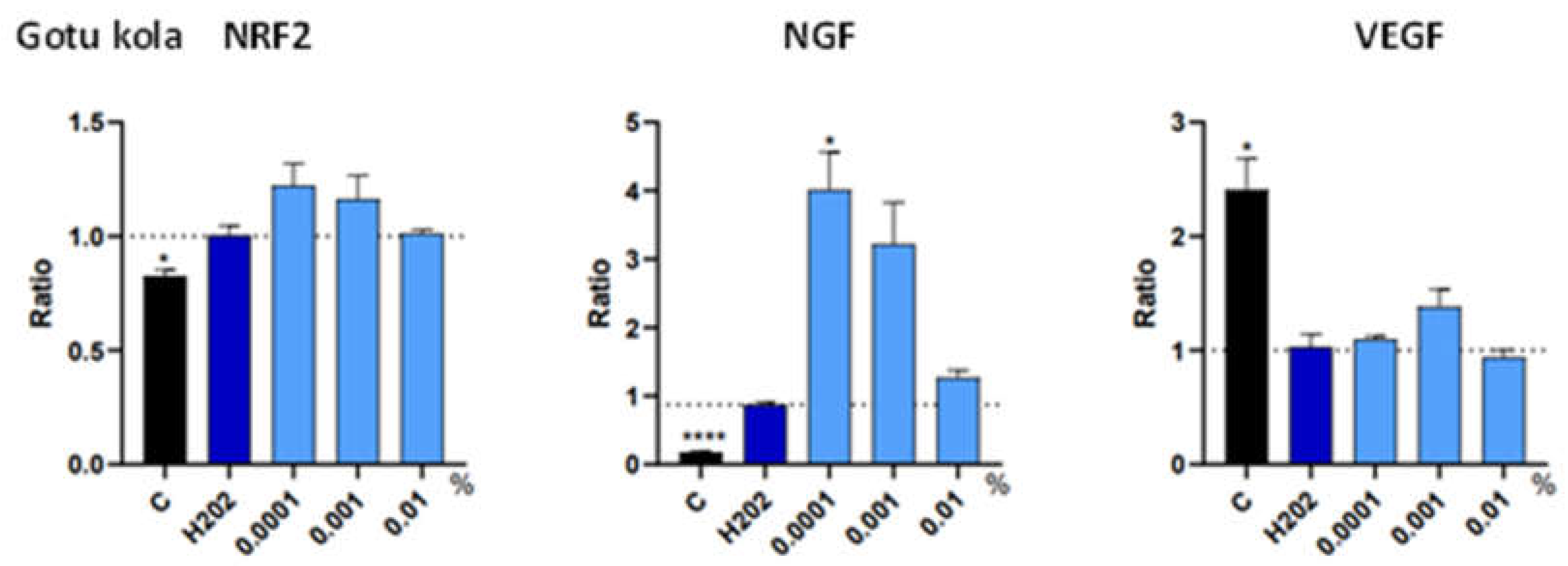
| Botanical Extract | ROS | RNS | NRF2 | NGF | VEGF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bilberry | NS | 0.0001% (*) | NS | 0.001% (*) 0.0001% (**) |
NS |
| Blueberry | 0.001% (*) | 0.001%(****) 0.0001% (**) |
NS | 0.001% (*) | NS |
| Bacopa | NS | NS | NS | 0.0001% (*) | NS |
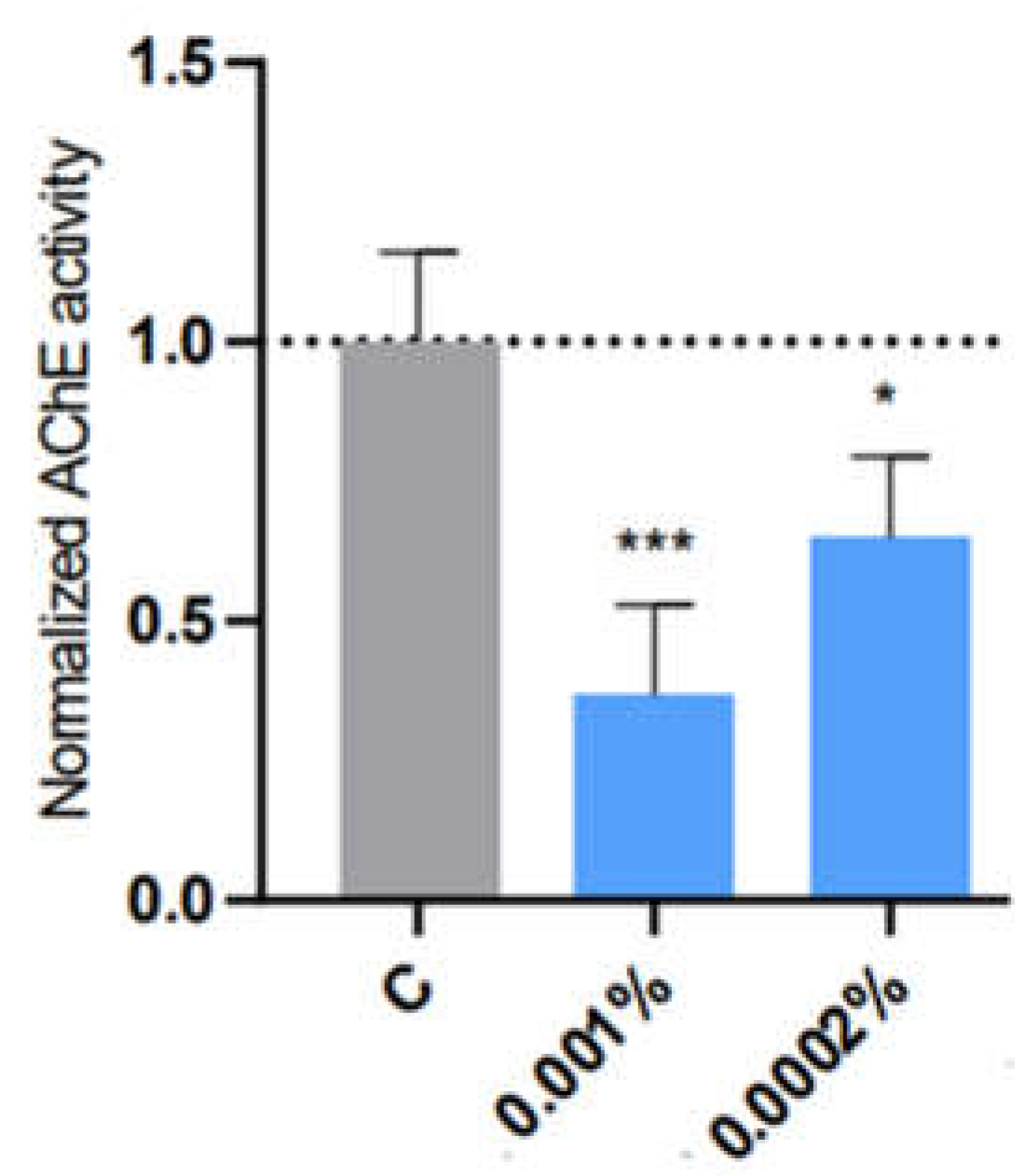
| Sage | 0.01% (****) | 0.01% (***) 0.0001% (*) |
0.001% (***) 0.01% (***) |
0.0001% (****) | 0.01% (*) 0.001% (*) |
| Saffron | P-ox: 0.0001% (*) 0.00005%(**) |
NS | NS | 0.00005% (*) | NS |
| Arctic Root | 0.01% (***) | 0.01% (*) 0.001% (*) |
NS | NS | NS |
| Ginkgo | P-ox: 0.0001%(***) A-ox: 0.00005%(**) |
0.00005%(****) | NS | 0.0001% (**) | NS |
| Ginseng | 0.01% (**) 0.0001% (**) |
NS | NS | 0.0001% (**) 0.001% (*) 0.01% (***) |
NS |
| Gotu kola | NS | NS | NS | 0.0001% (*) | NS |
| MoCA subscores | Week 0 | Week 6 | Week 12 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short-term memory recall | Placebo: 1.64 +/- 1.40 Nootropic 250mg: 2.10 +/- 1.47 Nootropic 400mg: 1.67 +/- 1.04 |
Placebo: 1.90 +/- 1.26 Nootropic 250mg: 2.78 +/- 1.43* Nootropic 400mg: 1.77 +/- 1.48 |
Placebo: 2.14 +/- 1.27 Nootropic 250mg: 2.83 +/- 1.32***† Nootropic 400mg: 2.51 +/- 1.24*** |
| Visuospatial memory | Placebo: 2.76 +/- 0.37 Nootropic 250mg: 2.83 +/- 0.30 Nootropic 400mg: 2.87 +/- 0.23 |
Placebo: 2.88 +/- 0.22 *** Nootropic 250mg: 2.88 +/- 0.22** Nootropic 400mg: 2.92 +/- 0.14 |
Placebo: 2.98 +/- 1.05 *** Nootropic 250mg: 2.88 +/- 0.22*** Nootropic 400mg: 2.92 +/- 0.14*** |
| Executive function | Placebo: 3.55 +/- 0.99 Nootropic 250mg: 3.83 +/- 0.90 Nootropic 400mg: 3.44 +/- 0.97 |
Placebo: 4.26 +/- 0.74 *** Nootropic 250mg: 4.20 +/- 0.68*** Nootropic 400mg: 4.23 +/- 0.63*** |
Placebo: 4.00 +/- 0.71 *** Nootropic 250mg: 4.28 +/- 0.73*** Nootropic 400mg: 4.31 +/- 0.75*** |
| Attention, concentration | Placebo: 4.67 +/- 1.19 Nootropic 250mg: 4.70 +/- 1.16 Nootropic 400mg: 4.87 +/- 1.00 |
Placebo: 4.71 +/- 1.09 Nootropic 250mg: 4.70 +/- 1.06 Nootropic 400mg: 4.64 +/- 1.23 |
Placebo: 4.88 +/- 1.05 Nootropic 250mg: 4.93 +/- 0.95 Nootropic 400mg: 4.82 +/- 1.15 |
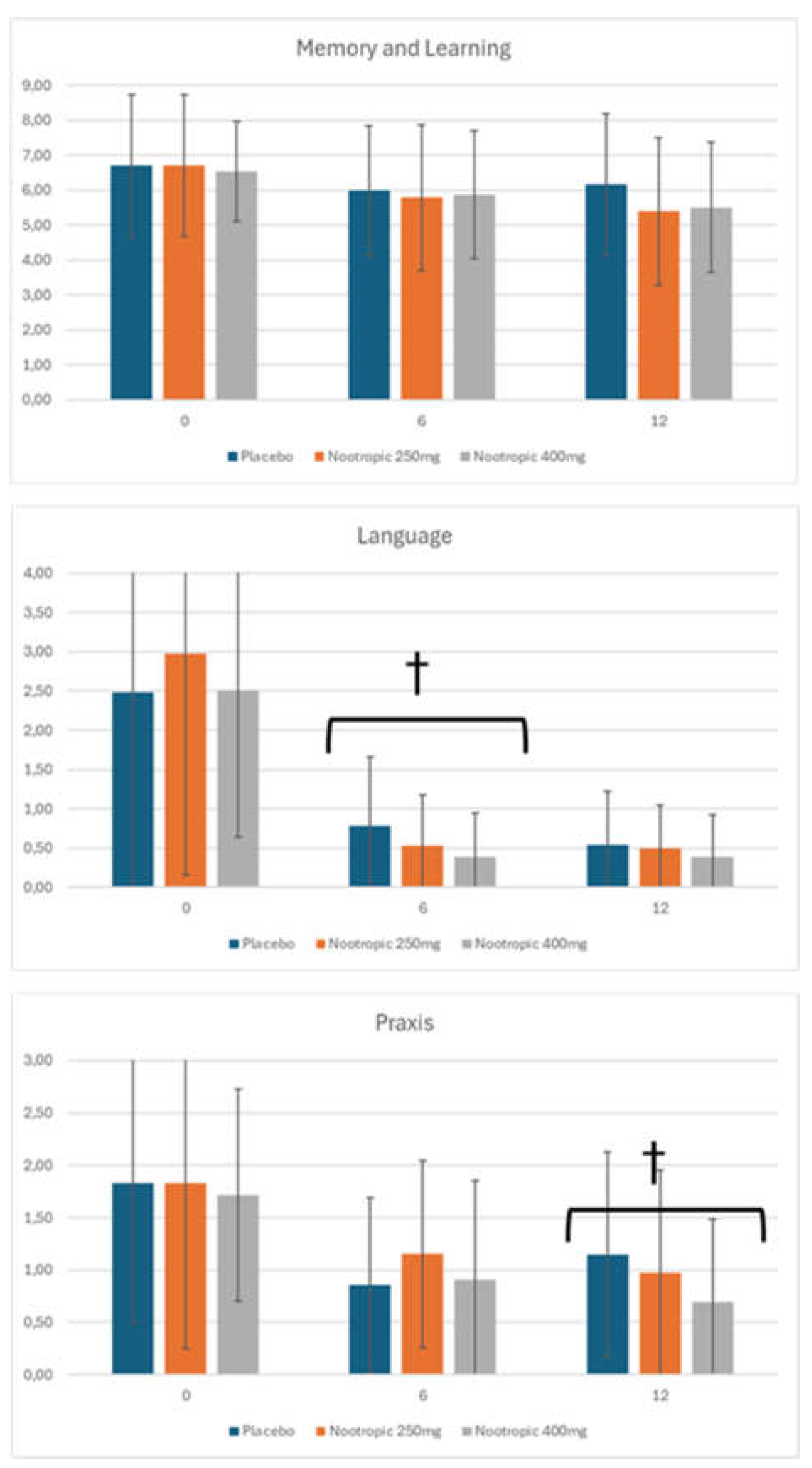
| Language | Placebo: 2.45 +/- 0.63 Nootropic 250mg: 2.55 +/- 0.56 Nootropic 400mg: 2.41 +/- 0.60 |
Placebo: 2.69 +/- 0.46 * Nootropic 250mg: 2.68 +/- 0.49* Nootropic 400mg: 2.46 +/- 0.55 |
Placebo: 2.60 +/- 0.52 Nootropic 250mg: 2.55 +/- 0.54 Nootropic 400mg: 2.44 +/- 0.64 |
| Abstract reasoning | Placebo: 1.71 +/- 0.42 Nootropic 250mg: 1.75 +/- 0.39 Nootropic 400mg: 1.77 +/- 0.36 |
Placebo: 1.88 +/- 0.21 *** Nootropic 250mg: 1.88 +/- 0.23*** Nootropic 400mg: 1.95 +/- 0.10*** |
Placebo: 1.81 +/- 0.31 Nootropic 250mg: 1.85 +/- 0.26 Nootropic 400mg: 1.92 +/- 0.14*** |
| Orientation in time and place | Placebo: 5.98 +/- 0.05 Nootropic 250mg: 5.88 +/- 0.22 Nootropic 400mg: 5.95 +/- 0.10 |
Placebo: 5.95 +/- 0.09 *** Nootropic 250mg: 5.98 +/- 0.05*** Nootropic 400mg: 6.00 +/- 0.00*** |
Placebo: 5.98 +/- 0.05*** Nootropic 250mg: 5.98 +/- 0.05*** Nootropic 400mg: 5.97 +/- 0.05*** |
| ADAS-Cog Item | Week 0 | Week 6 | Week 12 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Word Recall | Placebo: 4.28 +/- 1.05 Nootropic 250mg: 4.34 +/- 0.83 Nootropic 400mg: 4.41 +/- 0.78 |
Placebo: 3.91 +/- 1.07 Nootropic 250mg: 3.68 +/- 0.94* Nootropic 400mg: 3.82 +/- 0.99* |
Placebo: 4.06 +/- 0.93 Nootropic 250mg: 3.81 +/- 1.26††† Nootropic 400mg: 3.66 +/- 1.07**††† |
| Orientation | Placebo: 0.19 +/- 0.34 Nootropic 250mg: 0.53 +/- 0.17 Nootropic 400mg: 0.17 +/- 0.31 |
Placebo: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** Nootropic 250mg: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** Nootropic 400mg: 0.03 +/- 0.05*** |
Placebo: 0.02 +/- 0.05*** Nootropic 250mg: 0.05 +/- 0.09*** Nootropic 400mg: 0.03 +/- 0.05*** |
| Word Recognition | Placebo: 1.45 +/- 0.79 Nootropic 250mg: 1.31 +/- 0.77 Nootropic 400mg: 1.28 +/- 0.69 |
Placebo: 1.63 +/- 1.16 Nootropic 250mg: 1.59 +/- 0.95* Nootropic 400mg: 1.56 +/- 0.11 |
Placebo: 1.45 +/- 1.10 Nootropic 250mg: 1.18 +/- 0.88 Nootropic 400mg: 1.23 +/- 0.79 |
| Remembering Test Instructions | Placebo: 0.69 +/- 0.72 Nootropic 250mg: 0.78 +/- 0.85 Nootropic 400mg: 0.59 +/- 0.69 |
Placebo: 0.37 +/- 0.55 Nootropic 250mg: 0.63 +/- 0.81 Nootropic 400mg: 0.46 +/- 0.64 |
Placebo: 0.57 +/- 0.71 Nootropic 250mg: 0.55 +/- 0.81 Nootropic 400mg: 0.53 +/- 0.72 |
| Commands | Placebo: 0.19 +/- 0.34 Nootropic 250mg: 0.35 +/- 0.52 Nootropic 400mg: 0.15 +/- 0.25 |
Placebo: 0.26 +/- 0.41 Nootropic 250mg: 0.10 +/- 0.18*† Nootropic 400mg: 0.10 +/- 0.18† |
Placebo: 0.12 +/- 0.21 Nootropic 250mg: 0.05 +/- 0.10** Nootropic 400mg: 0.21 +/- 0.33* |
| Spoken Language Ability | Placebo: 0.29 +/- 0.48 Nootropic 250mg: 0.35 +/- 0.58 Nootropic 400mg: 0.37 +/- 0.57 |
Placebo: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** Nootropic 250mg: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** Nootropic 400mg: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** |
Placebo: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** Nootropic 250mg: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** Nootropic 400mg: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** |
| Word-finding Difficulty | Placebo: 0.66 +/- 0.96 Nootropic 250mg: 0.65 +/- 0.88 Nootropic 400mg: 0.73 +/- 0.93 |
Placebo: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** Nootropic 250mg: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** Nootropic 400mg: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** |
Placebo: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** Nootropic 250mg: 0.05 +/- 0.1*** Nootropic 400mg: 0.03 +/- 0.05*** |
| Comprehension | Placebo: 0.36 +/- 0.56 Nootropic 250mg: 0.48 +/- 0.76 Nootropic 400mg: 0.44 +/- 0.64 |
Placebo: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** Nootropic 250mg: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** Nootropic 400mg: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** |
Placebo: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** Nootropic 250mg: 0.03 +/- 0.05*** Nootropic 400mg: 0.00 +/- 0.00*** |
| Naming objects/ fingers | Placebo: 0.95 +/- 1.09 Nootropic 250mg: 1.15 +/- 1.01 Nootropic 400mg: 0.88 +/- 0.81 |
Placebo: 0.50 +/- 0.69*** Nootropic 250mg: 0.43 +/- 0.60*** Nootropic 400mg: 0.30 +/-0.48*** |
Placebo: 0.40 +/- 0.58*** Nootropic 250mg: 0.39 +/- 0.48*** Nootropic 400mg: 0.18 +/- 0.31*** |
| Constructional Praxis | Placebo: 1.31 +/- 0.95 Nootropic 250mg: 1.30 +/- 1.11 Nootropic 400mg: 1.39 +/- 0.71 |
Placebo: 0.55 +/- 0.69*** Nootropic 250mg: 0.73 +/- 0.65*** Nootropic 400mg: 0.50 +/- 0.58*** |
Placebo: 0.62 +/- 0.68*** Nootropic 250mg: 0.47 +/- 0.65*** Nootropic 400mg: 0.41 +/- 0.55***• |
| Ideational Praxis | Placebo: 0.48 +/- 0.68 Nootropic 250mg: 0.53 +/- 0.76 Nootropic 400mg: 0.37 +/- 0.55 |
Placebo: 0.29 +/- 0.44 Nootropic 250mg: 0.43 +/- 0.55 Nootropic 400mg: 0.45 +/- 0.59 |
Placebo: 0.55 +/- 0.63 Nootropic 250mg: 0.53 +/- 0.64 Nootropic 400mg: 0.31 +/- 0.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





