Submitted:
16 August 2024
Posted:
19 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
WSAq Preparation
WSAq Preparation and Chemical Analysis
Animals
Object Location Memory Test (OLM)
Open Field Test (OF)
Forced Swim Test (FST)
Immunohistochemistry
Gene Expression Analysis
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
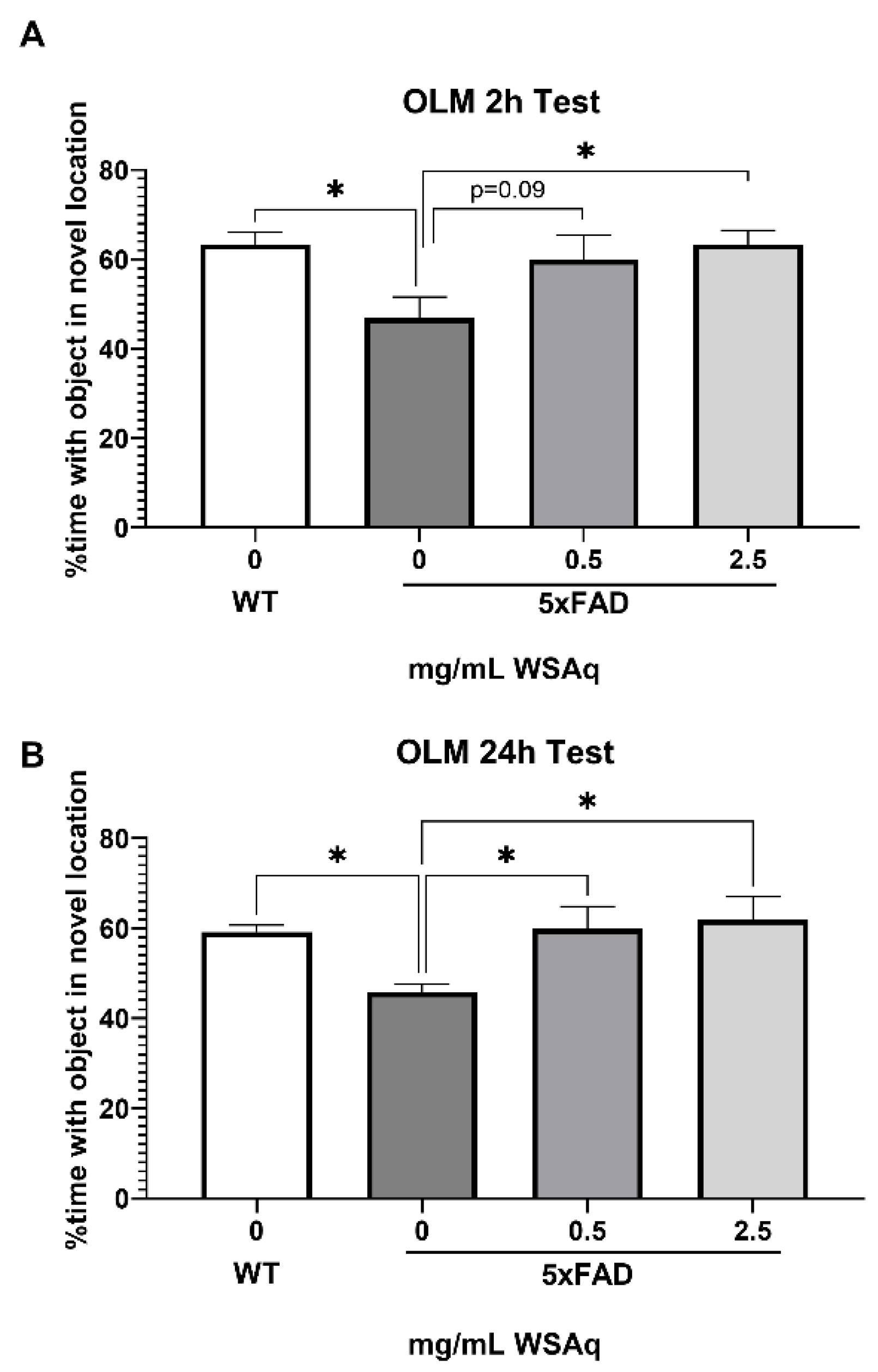
WSAq Improves Spatial Memory in 5xFAD Mice
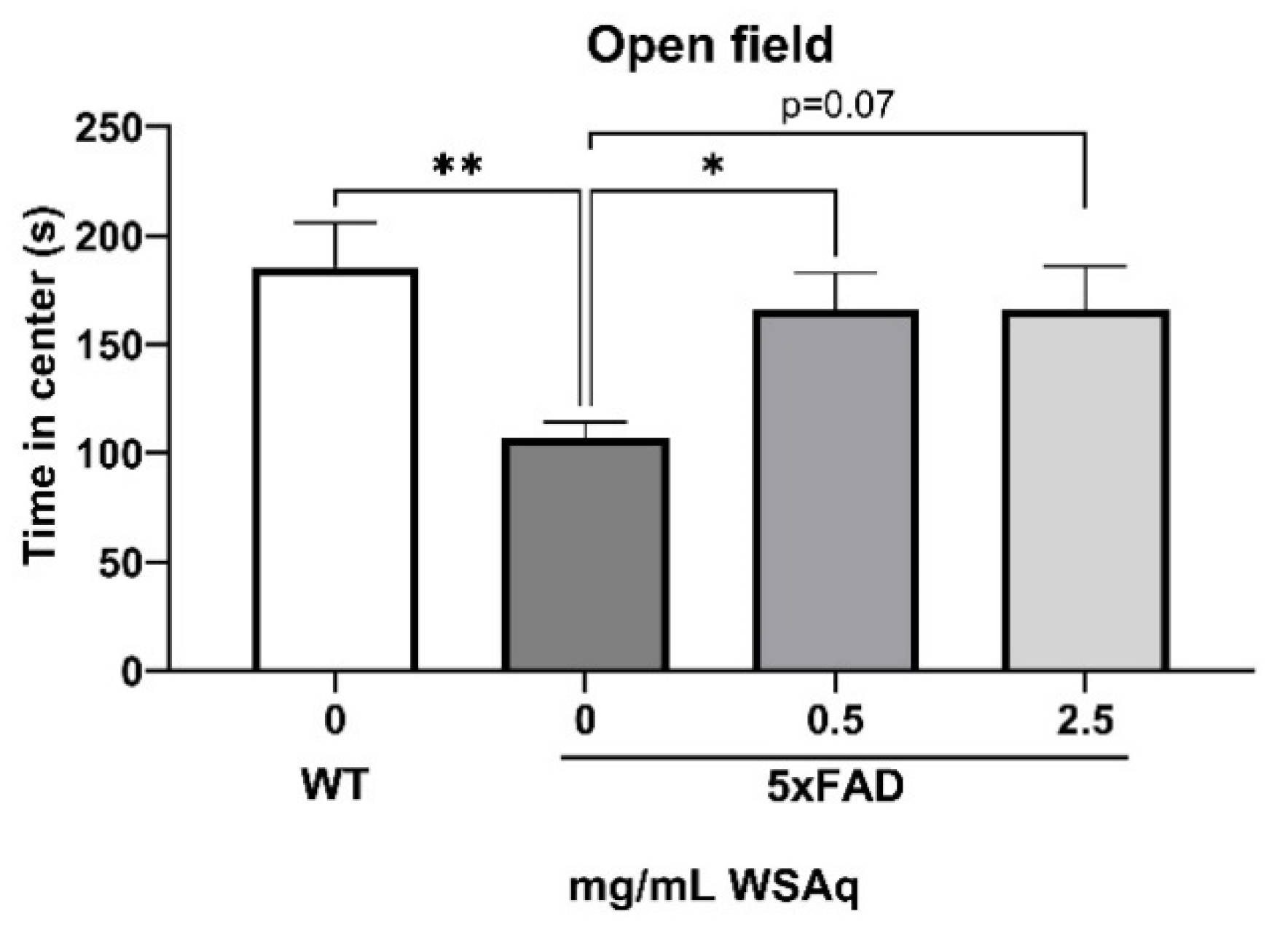
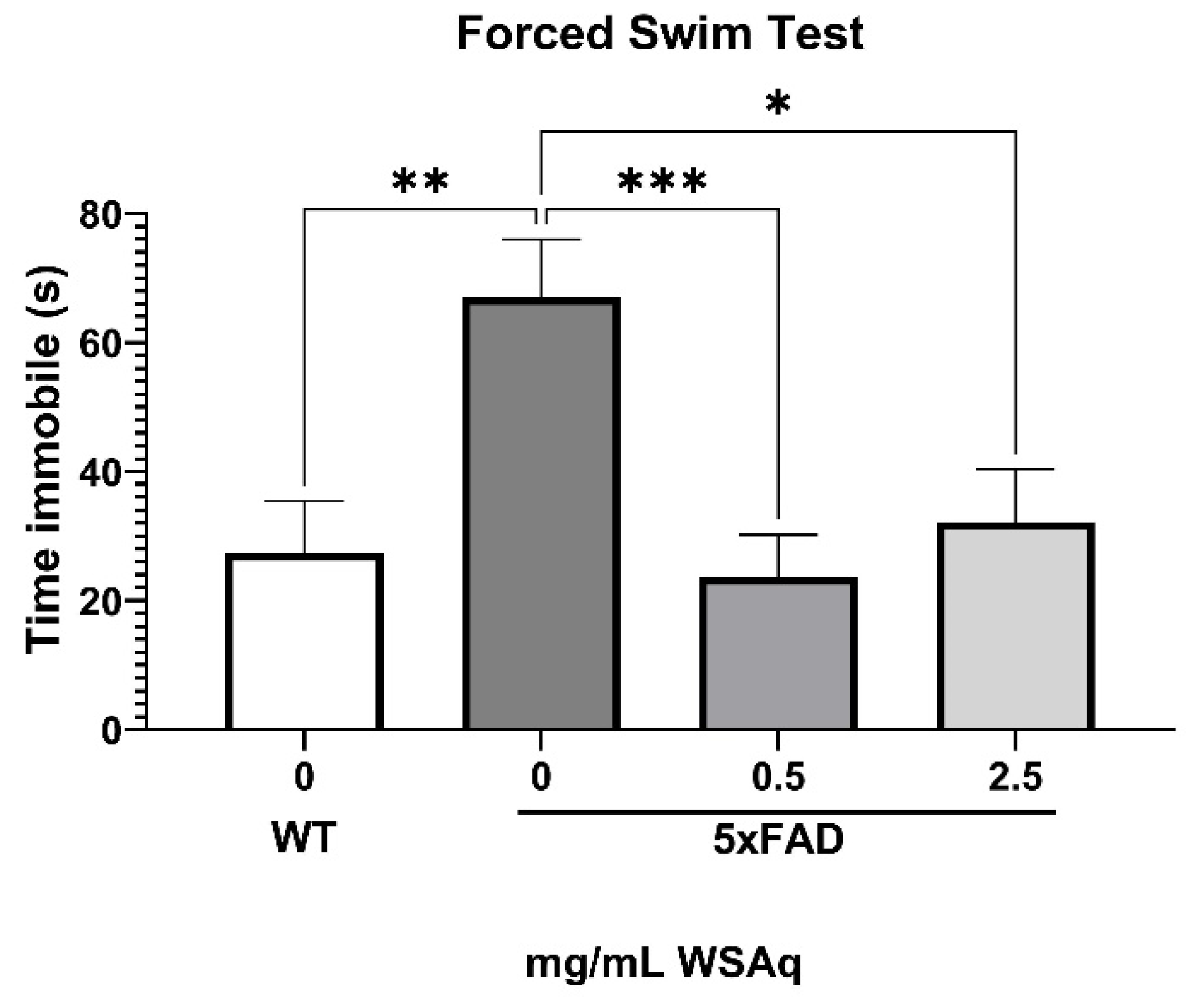
Anxiety-Related and Depressive-Like Behavior Is Reduced by WSAq in 5xFAD Mice
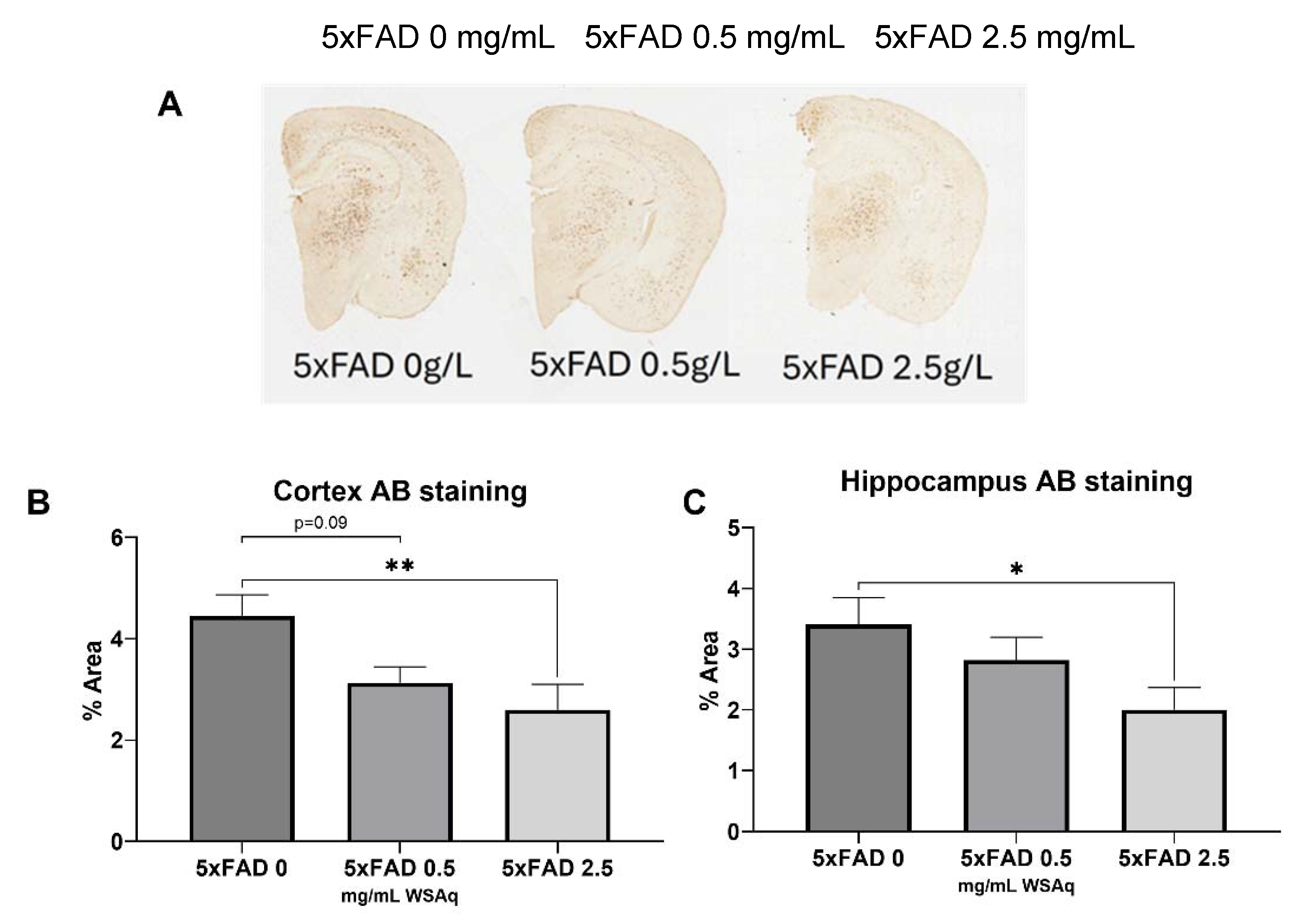
Aβ Plaque Burden is Reduced in WSAq-treated 5xFAD Mice
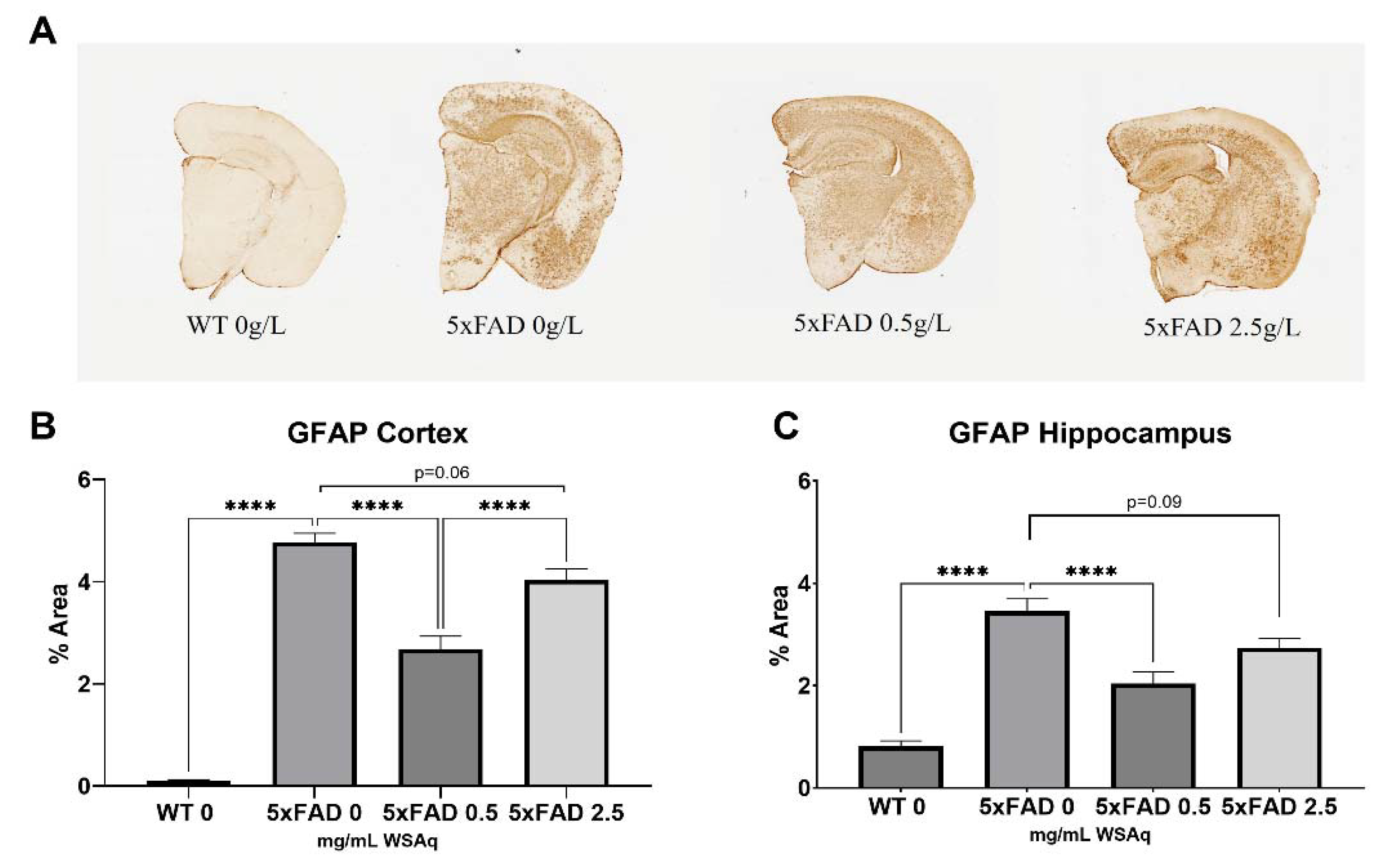
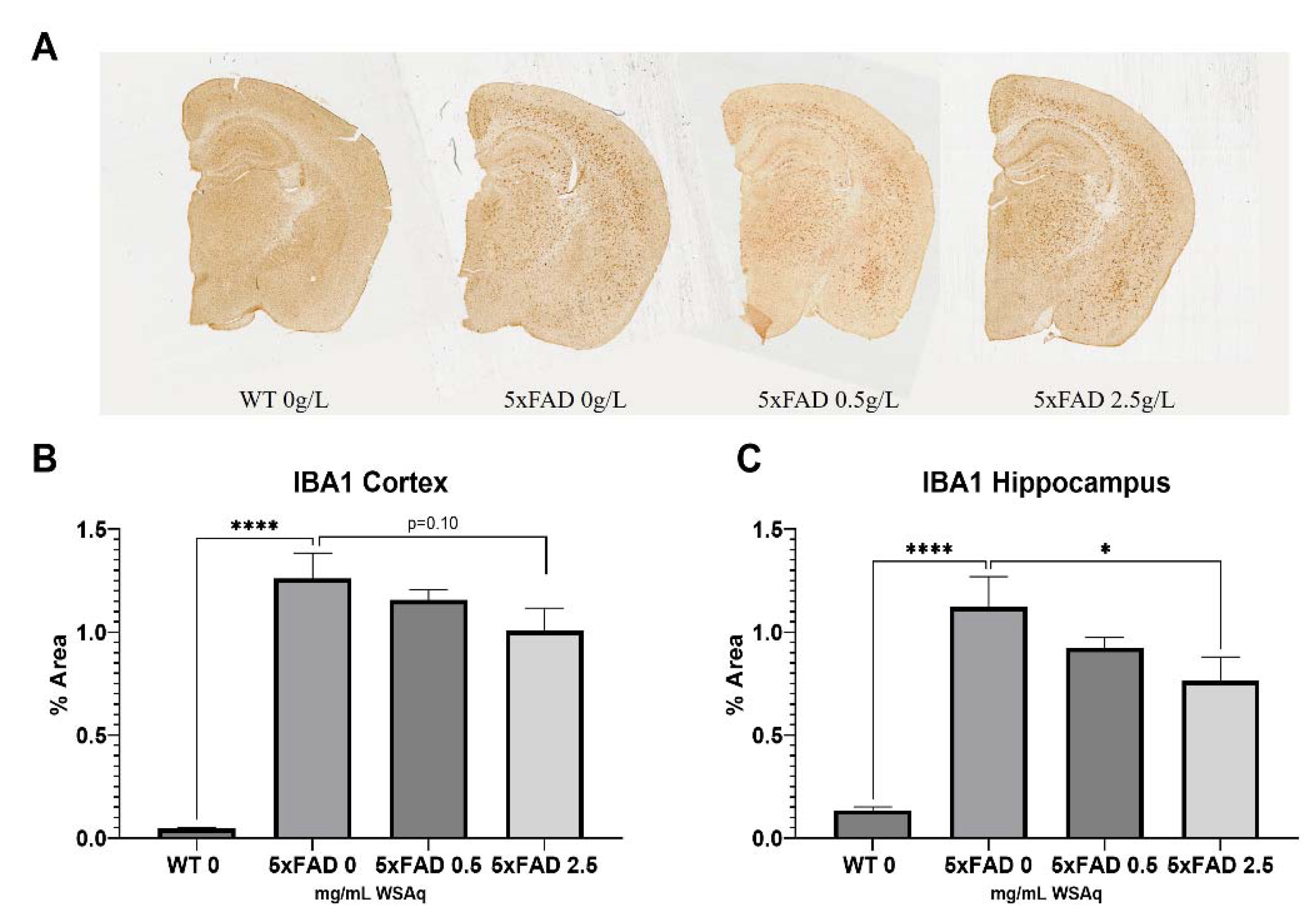
WSAq Reduces Astrocytic and Microglial Activation in 5xFAD Mice
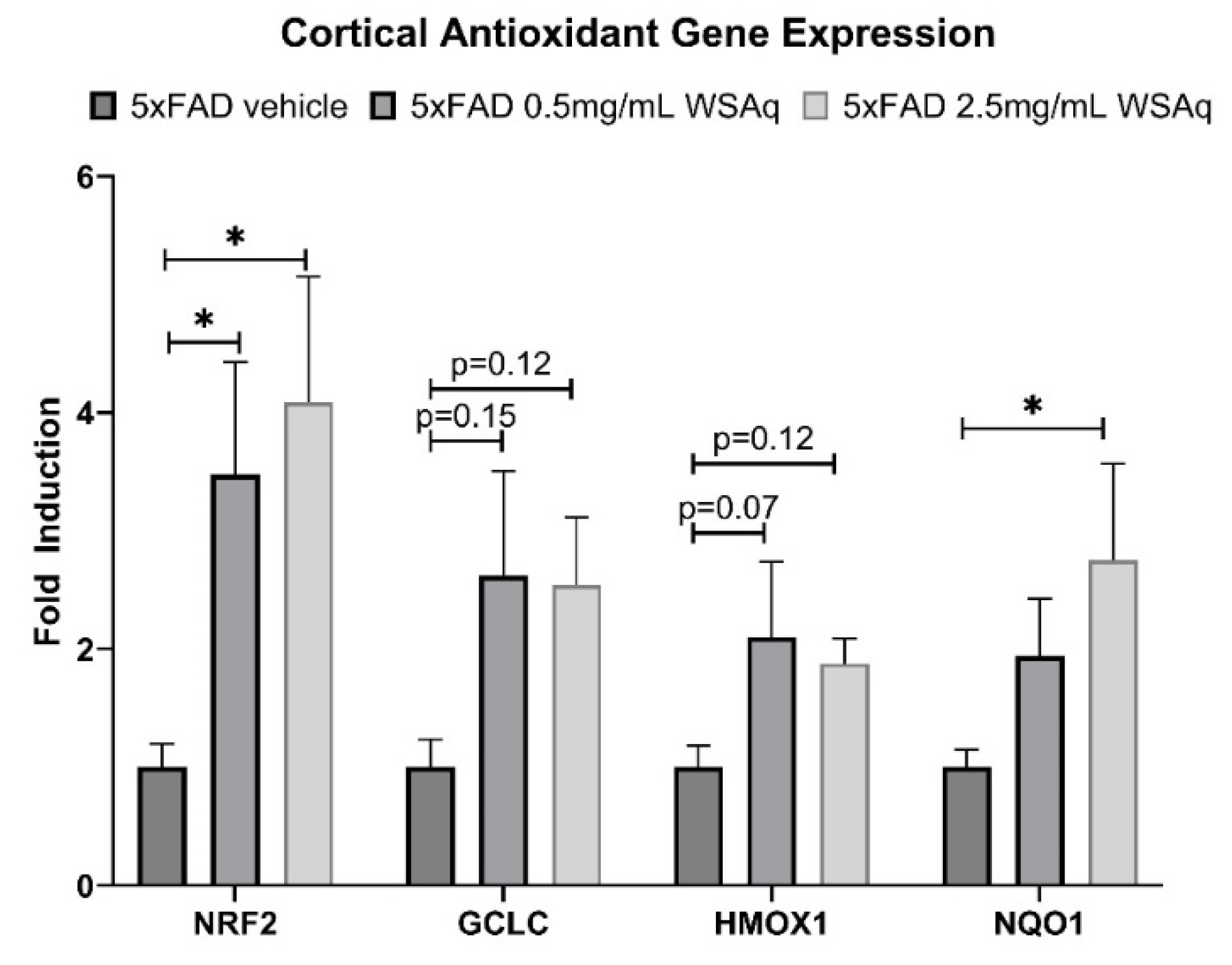
Antioxidant Response Genes Are Upregulated in 5xFAD Mice following WSAq Treatment
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 2023 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement, 2023. 19(4): p. 1598-1695.
- Lyketsos, C.G., et al., Neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement, 2011. 7(5): p. 532-9.
- Siddappaji, K.K. and S. Gopal, Molecular mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease and the impact of physical exercise with advancements in therapeutic approaches. AIMS Neurosci, 2021. 8(3): p. 357-389.
- Rostagno, A.A., Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Mol Sci, 2022. 24(1).
- Kinney, J.W., et al., Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement (N Y), 2018. 4: p. 575-590.
- Heneka, M.T., et al., Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet Neurol, 2015. 14(4): p. 388-405.
- Al-Ghraiybah, N.F., et al., Glial Cell-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Mol Sci, 2022. 23(18).
- Leonoudakis, D., et al., Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Role of Natural Product Securinine in Activated Glial Cells: Implications for Parkinson's Disease. Mediators Inflamm, 2017. 2017: p. 8302636.
- Li, J., et al., Hydrocortisone Mitigates Alzheimer's-Related Cognitive Decline through Modulating Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation. Cells, 2023. 12(19).
- Lecca, D., et al., Role of chronic neuroinflammation in neuroplasticity and cognitive function: A hypothesis. Alzheimers Dement, 2022. 18(11): p. 2327-2340.
- Rao, J.S., et al., Neuroinflammation and synaptic loss. Neurochem Res, 2012. 37(5): p. 903-10.
- Guo, B., et al., Neuroinflammation mechanisms of neuromodulation therapies for anxiety and depression. Transl Psychiatry, 2023. 13(1): p. 5.
- Ly, M., et al., Neuroinflammation: A Modifiable Pathway Linking Obesity, Alzheimer's disease, and Depression. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry, 2023. 31(10): p. 853-866.
- Ionescu-Tucker, A. and C.W. Cotman, Emerging roles of oxidative stress in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging, 2021. 107: p. 86-95.
- Tonnies, E. and E. Trushina, Oxidative Stress, Synaptic Dysfunction, and Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis, 2017. 57(4): p. 1105-1121.
- Calkins, M.J., et al., Impaired mitochondrial biogenesis, defective axonal transport of mitochondria, abnormal mitochondrial dynamics and synaptic degeneration in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Hum Mol Genet, 2011. 20(23): p. 4515-29.
- Amin, F.U., S.A. Shah, and M.O. Kim, Vanillic acid attenuates Aβ(1-42)-induced oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in mice. Sci Rep, 2017. 7: p. 40753. [CrossRef]
- Forman, H.J. and H. Zhang, Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2021. 20(9): p. 689-709. [CrossRef]
- Knight, E., et al., The Role of Dietary Antioxidants and Their Potential Mechanisms in Alzheimer's Disease Treatment. Metabolites, 2023. 13(3). [CrossRef]
- Pritam, P., et al., Antioxidants in Alzheimer's Disease: Current Therapeutic Significance and Future Prospects. Biology (Basel), 2022. 11(2). [CrossRef]
- Juszczyk, G., et al., Chronic Stress and Oxidative Stress as Common Factors of the Pathogenesis of Depression and Alzheimer's Disease: The Role of Antioxidants in Prevention and Treatment. Antioxidants (Basel), 2021. 10(9). [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.S. and S.H. Koh, Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: the roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl Neurodegener, 2020. 9(1): p. 42. [CrossRef]
- Rostami, J., et al., Crosstalk between astrocytes and microglia results in increased degradation of alpha-synuclein and amyloid-beta aggregates. J Neuroinflammation, 2021. 18(1): p. 124.
- Speers, A.B., et al., Effects of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) on Stress and the Stress- Related Neuropsychiatric Disorders Anxiety, Depression, and Insomnia. Curr Neuropharmacol, 2021. 19(9): p. 1468-1495. [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.M.A., et al., Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) root extract attenuates hepatic and cognitive deficits in thioacetamide-induced rat model of hepatic encephalopathy via induction of Nrf2/HO-1 and mitigation of NF-kappaB/MAPK signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021. 277: p. 114141.
- Lewis, J.E., et al., The effects of twenty-one nutrients and phytonutrients on cognitive function: A narrative review. J Clin Transl Res, 2021. 7(4): p. 575-620.
- Manchanda, S. and G. Kaur, Withania somnifera leaf alleviates cognitive dysfunction by enhancing hippocampal plasticity in high fat diet induced obesity model. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2017. 17(1): p. 136. [CrossRef]
- Lopresti, A.L., et al., An investigation into the stress-relieving and pharmacological actions of an ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) extract: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019. 98(37): p. e17186.
- Gannon, J.M., et al., Effects of a standardized extract of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) on depression and anxiety symptoms in persons with schizophrenia participating in a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Ann Clin Psychiatry, 2019. 31(2): p. 123-129.
- Dey, A., S.S. Chatterjee, and V. Kumar, Triethylene glycol-like effects of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal) root extract devoid of withanolides in stressed mice. Ayu, 2018. 39(4): p. 230-238. [CrossRef]
- Cabey, K., et al., Withania somnifera and Centella asiatica Extracts Ameliorate Behavioral Deficits in an In Vivo Drosophila melanogaster Model of Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants (Basel), 2022. 11(1). [CrossRef]
- Holvoet, H., et al., Withania somnifera Extracts Promote Resilience against Age-Related and Stress-Induced Behavioral Phenotypes in Drosophila melanogaster; a Possible Role of Other Compounds besides Withanolides. Nutrients, 2022. 14(19). [CrossRef]
- B6.Cg-Tg(APPSwFlLon,PSEN1*M146L*L286V)6799Vas/Mmjax. Available from: https://www.jax.org/strain/008730.
- Bilkei-Gorzo, A., Genetic mouse models of brain ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacol Ther, 2014. 142(2): p. 244-57.
- Luke C. Marney, J.C., Armando Alcazar Magana, Liping Yang, Natascha Techen, Md Nure Alam, Mikah Brandes, Amala Soumyanath, Jan F. Stevens, Claudia S. Maier, Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry quantification of phytochemicals in Withania somnifera using data-dependent acquisition, multiple-reaction-monitoring, and parallel-reaction-monitoring with an inclusion list. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2024. 12. [CrossRef]
- Marney, L.C., et al., Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry quantification of phytochemicals in Withania somnifera using data-dependent acquisition, multiple-reaction-monitoring, and parallel-reaction-monitoring with an inclusion list. Front Chem, 2024. 12: p. 1373535. [CrossRef]
- Seibenhener, M.L. and M.C. Wooten, Use of the Open Field Maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice. J Vis Exp, 2015(96): p. e52434.
- Yankelevitch-Yahav, R., et al., The forced swim test as a model of depressive-like behavior. J Vis Exp, 2015(97).
- Bhattacharyya, S., COMPARATIVE EFFECT OF WITHANIA SOMNIFERA AND PANAX GINSENG ON SWIM-STRESS INDUCED IMPAIRED ENERGY STATUS OF MICE Pharmacology online 2009.
- Pandit, S., et al., Effects of Withania somnifera Extract in Chronically Stressed Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 2024. 16(9). [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M., K. Nagabhushanam, and L. Mundkur, A standardized Ashwagandha root extract alleviates stress, anxiety, and improves quality of life in healthy adults by modulating stress hormones: Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Medicine (Baltimore), 2023. 102(41): p. e35521. [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, K., J. Kapoor, and S. Anishetty, A prospective, randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study of safety and efficacy of a high-concentration full-spectrum extract of ashwagandha root in reducing stress and anxiety in adults. Indian J Psychol Med, 2012. 34(3): p. 255-62. [CrossRef]
- Auddy, B., A Standardized Withania Somnifera Extract Significantly Reduces Stress-RelatedParameters in Chronically Stressed Humans: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Original Research, 2008.
- Ng, Q.X., et al., A systematic review of the clinical use of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) to ameliorate cognitive dysfunction. Phytotherapy Research, 2020. 34(3): p. 583-590. [CrossRef]
- Konar, A., et al., Protective role of Ashwagandha leaf extract and its component withanone on scopolamine-induced changes in the brain and brain-derived cells. PLoS One, 2011. 6(11): p. e27265. [CrossRef]
- Baitharu, I., et al., Withania somnifera root extract ameliorates hypobaric hypoxia induced memory impairment in rats. J Ethnopharmacol, 2013. 145(2): p. 431-41. [CrossRef]
- Kurapati, K.R., et al., Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) reverses beta-amyloid1-42 induced toxicity in human neuronal cells: implications in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND). PLoS One, 2013. 8(10): p. e77624.
- Kuboyama, T., C. Tohda, and K. Komatsu, Effects of Ashwagandha (roots of Withania somnifera) on neurodegenerative diseases. Biol Pharm Bull, 2014. 37(6): p. 892-7. [CrossRef]
- Mikulska, P., et al., Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)-Current Research on the Health-Promoting Activities: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceutics, 2023. 15(4). [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, N., et al., Withania somnifera reverses Alzheimer's disease pathology by enhancing low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2012. 109(9): p. 3510-5.
- Atluri, V.S.R., et al., Inhibition of Amyloid-Beta Production, Associated Neuroinflammation, and Histone Deacetylase 2-Mediated Epigenetic Modifications Prevent Neuropathology in Alzheimer's Disease in vitro Model. Front Aging Neurosci, 2019. 11: p. 342.
- Tiwari, S., et al., Withaferin A Suppresses Beta Amyloid in APP Expressing Cells: Studies for Tat and Cocaine Associated Neurological Dysfunctions. Front Aging Neurosci, 2018. 10: p. 291. [CrossRef]
- Budd Haeberlein, S., et al., Two Randomized Phase 3 Studies of Aducanumab in Early Alzheimer's Disease. J Prev Alzheimers Dis, 2022. 9(2): p. 197-210. [CrossRef]
- Swanson, C.J., et al., A randomized, double-blind, phase 2b proof-of-concept clinical trial in early Alzheimer's disease with lecanemab, an anti-Aβ protofibril antibody. Alzheimers Res Ther, 2021. 13(1): p. 80.
- Söderberg, L., et al., Lecanemab, Aducanumab, and Gantenerumab - Binding Profiles to Different Forms of Amyloid-Beta Might Explain Efficacy and Side Effects in Clinical Trials for Alzheimer's Disease. Neurotherapeutics, 2023. 20(1): p. 195-206.
- Paul, S., et al., Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal (Ashwagandha): A comprehensive review on ethnopharmacology, pharmacotherapeutics, biomedicinal and toxicological aspects. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021. 143: p. 112175. [CrossRef]
- Grunz-Borgmann, E., et al., Ashwagandha attenuates TNF-alpha- and LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation and CCL2 and CCL5 gene expression in NRK-52E cells. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2015. 15: p. 434.
- Maitra, R., et al., Inhibition of NFkappaB by the natural product Withaferin A in cellular models of Cystic Fibrosis inflammation. J Inflamm (Lond), 2009. 6: p. 15.
- KrishnaRaju, A.V., et al., Efficacy and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ashwagandha Sustained-Release Formulation on Depression and Anxiety Induced by Chronic Unpredictable Stress: in vivo and in vitro Studies. J Exp Pharmacol, 2023. 15: p. 291-305. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T. and G. Kaur, Withania somnifera as a potential candidate to ameliorate high fat diet-induced anxiety and neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation, 2017. 14(1): p. 201. [CrossRef]
- Abomosallam, M., et al., Neuroprotective effect of Withania somnifera leaves extract nanoemulsion against penconazole-induced neurotoxicity in albino rats via modulating TGF-beta1/Smad2 signaling pathway. Inflammopharmacology, 2024. 32(3): p. 1903-1928.
- Gomez Afonso, A., et al., Effects of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) on Hematological and Biochemical Markers, Hormonal Behavior, and Oxidant Response in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review. Curr Nutr Rep, 2023. 12(3): p. 465-477. [CrossRef]
- Du, B., Y. Zhang, and X. Bi, Editorial: Neuroinflammation and affective/cognitive impairment: The role of white matter and glial cells. Front Aging Neurosci, 2022. 14: p. 1115180. [CrossRef]
- Lubarska, M., et al., Liver Dangers of Herbal Products: A Case Report of Ashwagandha-Induced Liver Injury. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2023. 20(5). [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.Y., et al., Withania somnifera and Its Withanolides Attenuate Oxidative and Inflammatory Responses and Up-Regulate Antioxidant Responses in BV-2 Microglial Cells. Neuromolecular Med, 2016. 18(3): p. 241-52. [CrossRef]
- Sankar, S.R., et al., The neuroprotective effect of Withania somnifera root extract in MPTP-intoxicated mice: an analysis of behavioral and biochemical variables. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2007. 12(4): p. 473-81.
- Afewerky, H.K., et al., Sodium-calcium exchanger isoform-3 targeted Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal therapeutic intervention ameliorates cognition in the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Sci Rep, 2022. 12(1): p. 1537.
- Kuchewar, V.V., M.A. Borkar, and M.A. Nisargandha, Evaluation of antioxidant potential of Rasayana drugs in healthy human volunteers. Ayu, 2014. 35(1): p. 46-9. [CrossRef]
- Adrian L. Lopresti, S.J.S., Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) for the treatment and enhancement of mental and physical conditions: A systematic review of human trials. Journal of Herbal Medicine, 2021. 28. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S., D. Phaneuf, and J.P. Julien, Withaferin-A Treatment Alleviates TAR DNA-Binding Protein-43 Pathology and Improves Cognitive Function in a Mouse Model of FTLD. Neurotherapeutics, 2021. 18(1): p. 286-296. [CrossRef]
- Tohda, C. and E. Joyashiki, Sominone enhances neurite outgrowth and spatial memory mediated by the neurotrophic factor receptor, RET. Br J Pharmacol, 2009. 157(8): p. 1427-40. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




