Submitted:
10 September 2025
Posted:
11 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
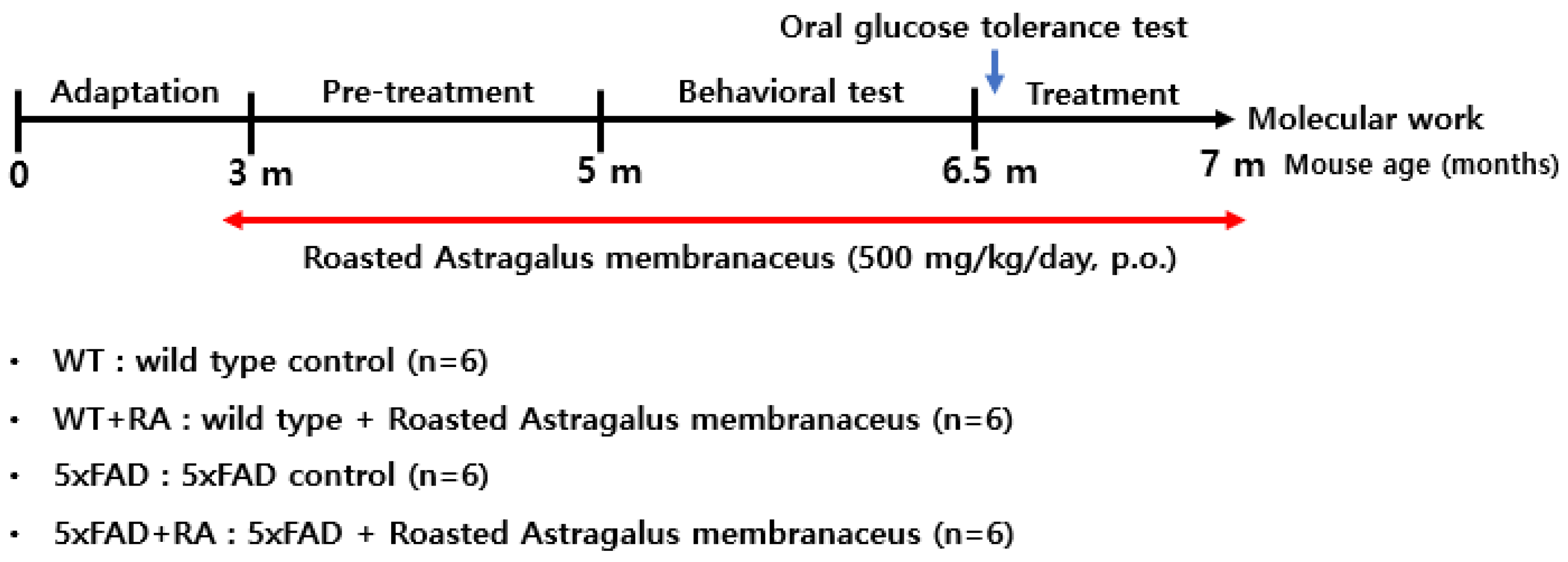
2.2. Animals and Experimental Groups
2.3. Metabolic Changes
2.4. Behavioral Measures
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
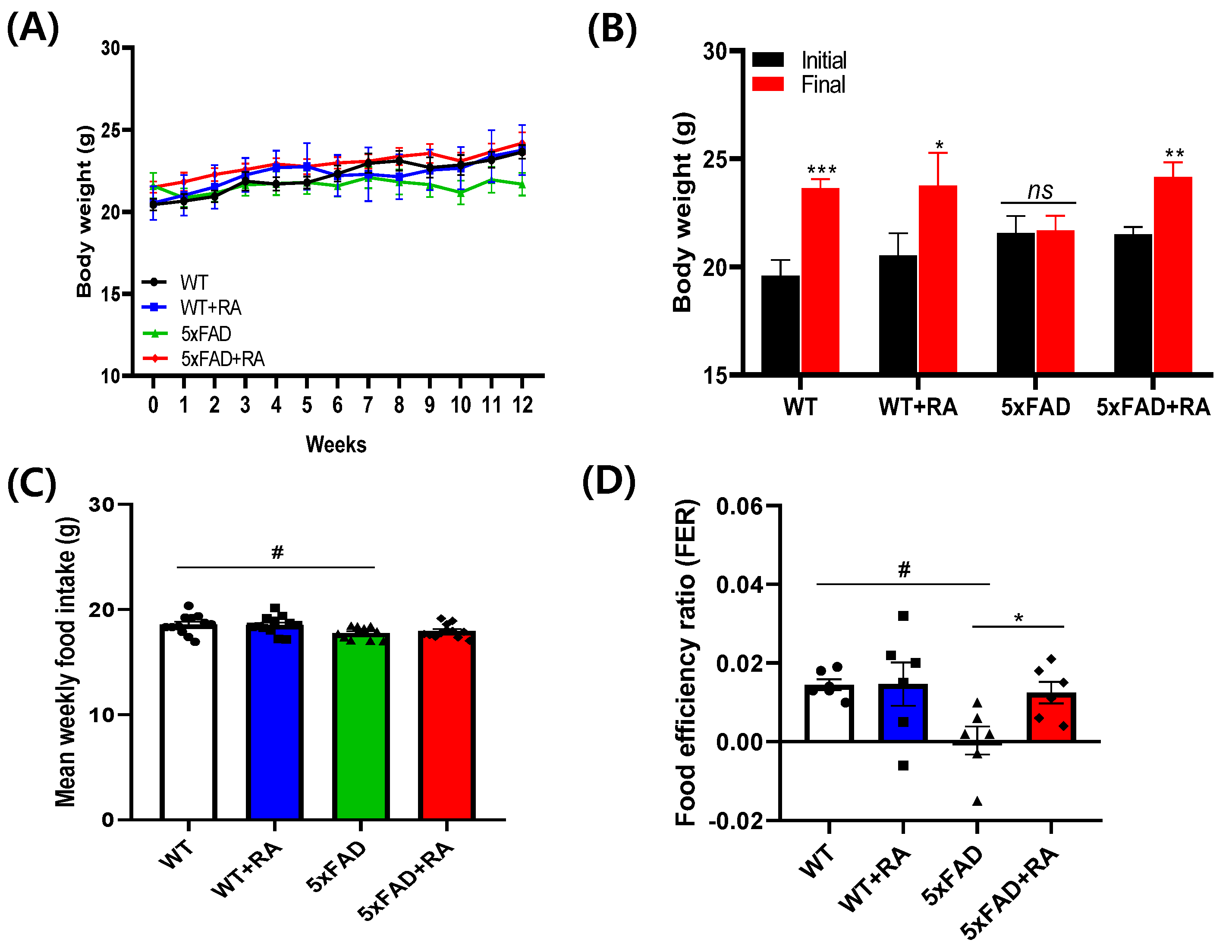
3.1. RA Increased Body Weight and Improved Food Efficiency Ratio of 5xFAD Mice
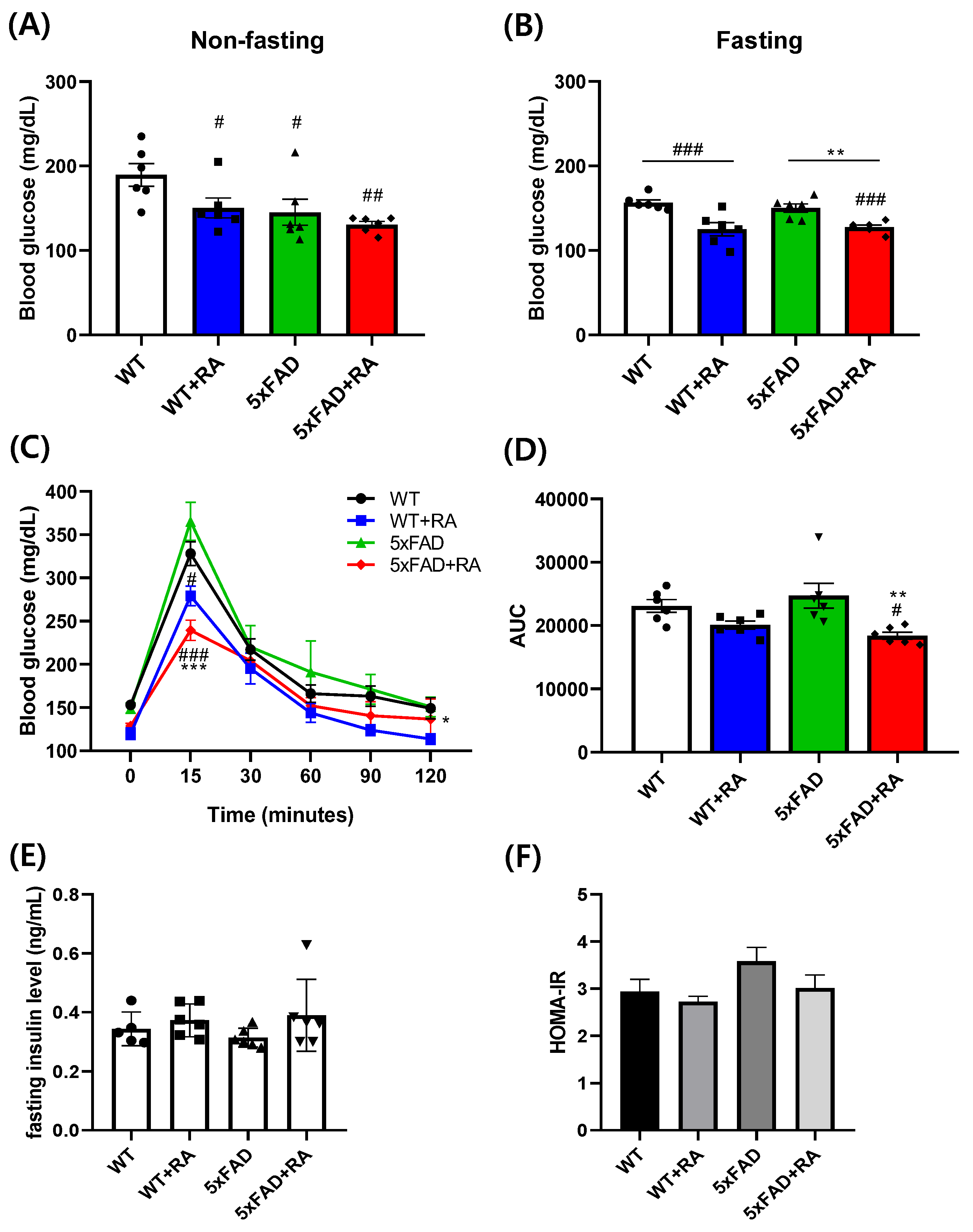
3.2. RA Reduced Fasting Blood Glucose and Improved Glucose Tolerance of 5xFAD Mice
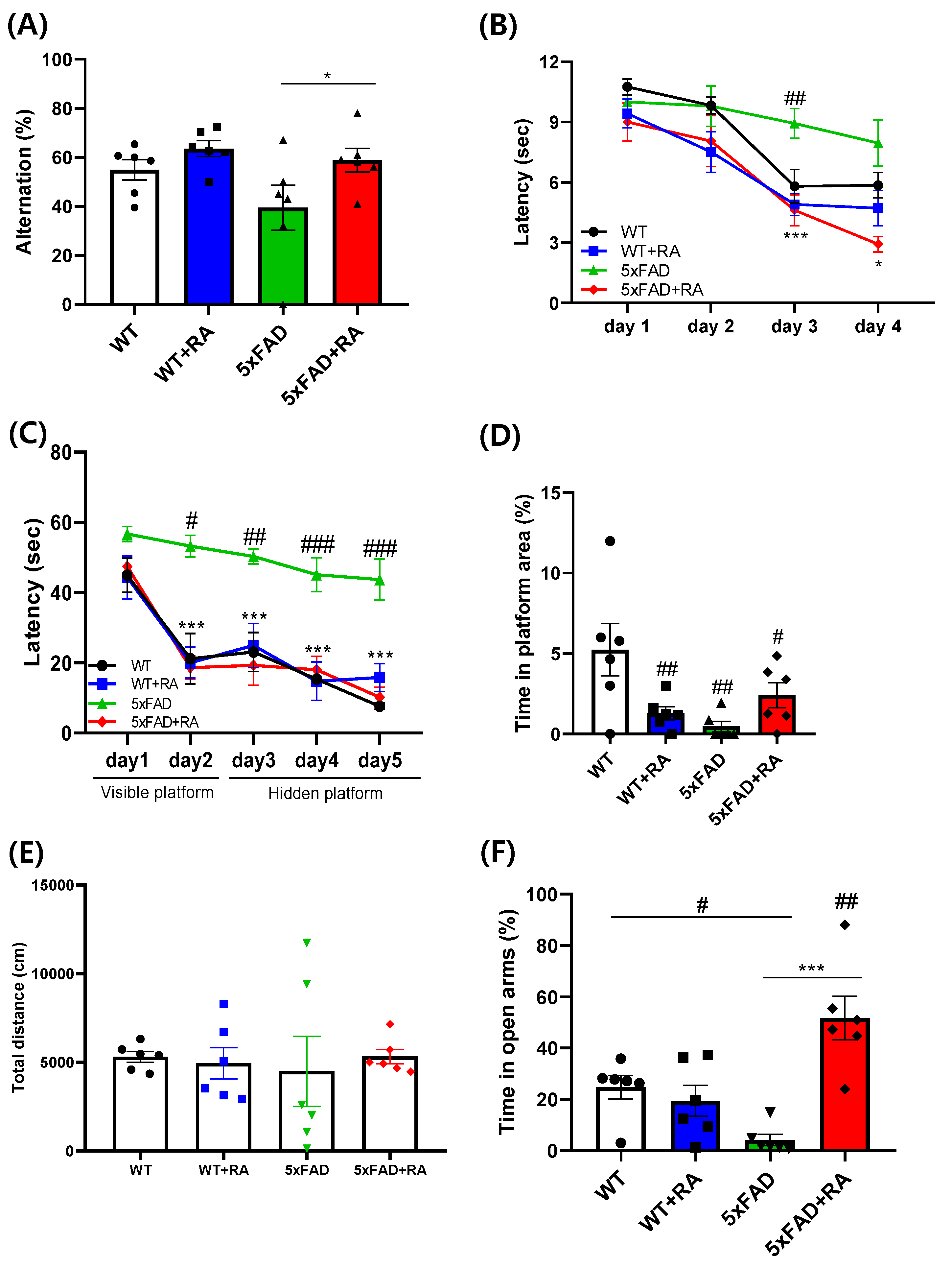
3.3. RA Improved Cognitive Deficits in 5xFAD Mice
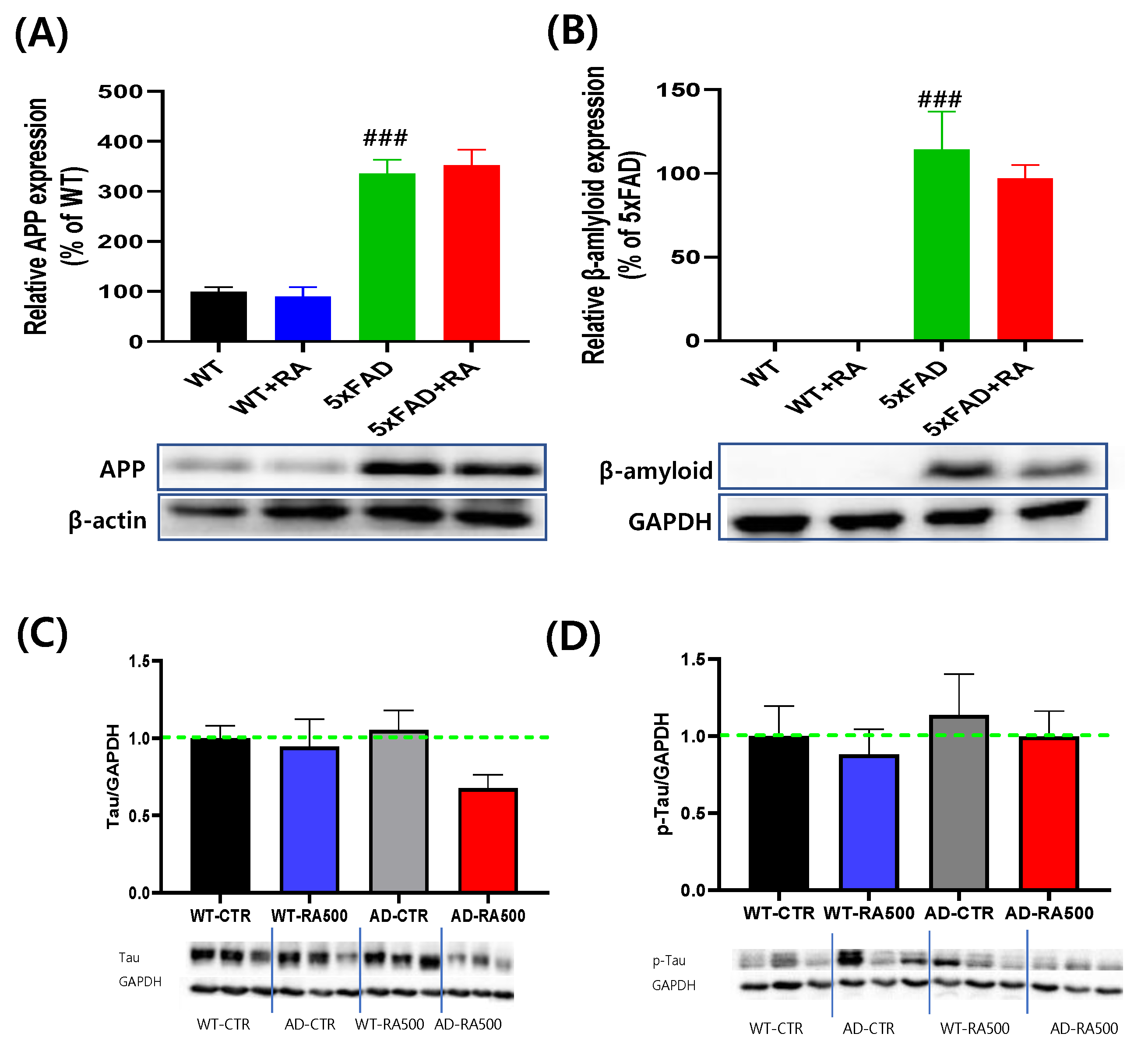
3.4. RA Didn’t Affect the Expression of Hippocampal β-Amyloid and p-Tau in 5xFAD Mice
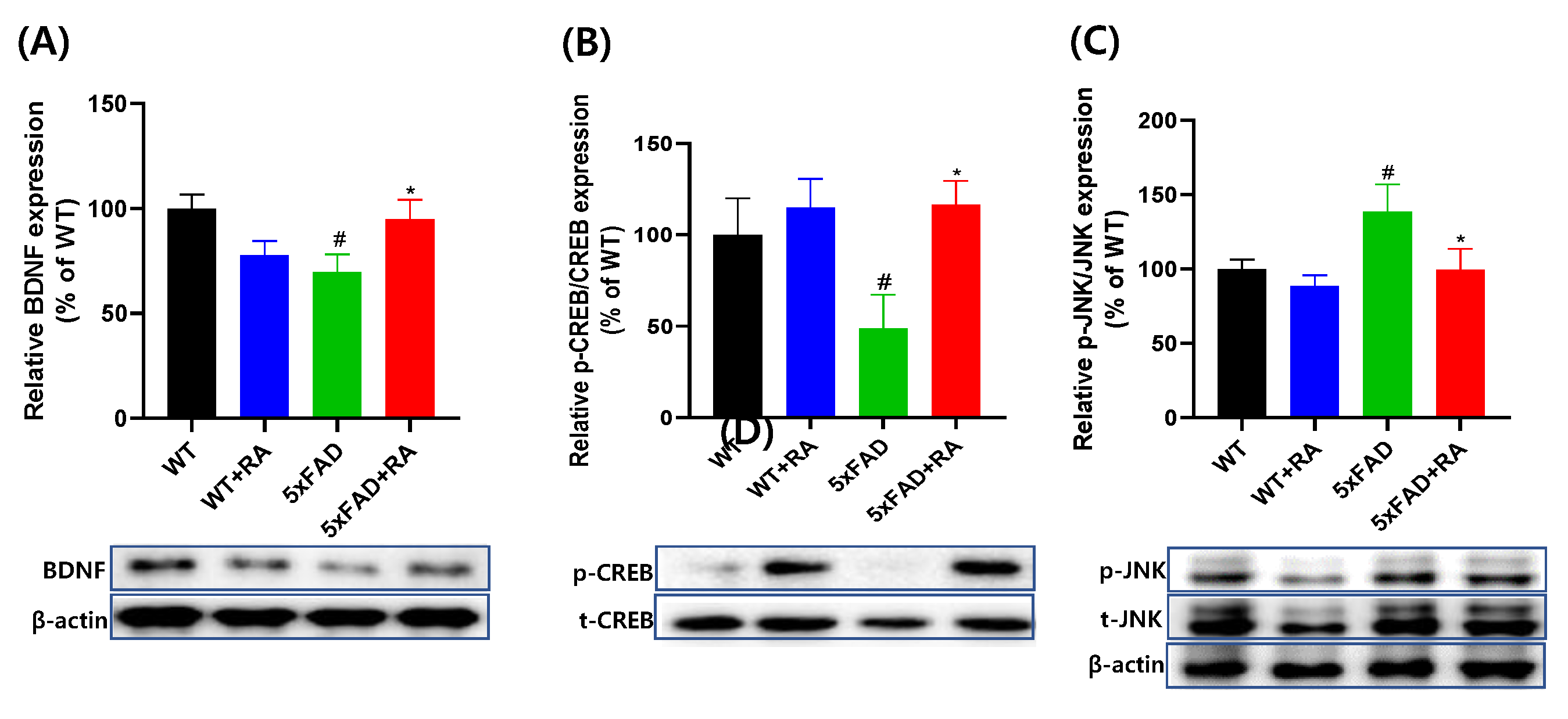
3.5. RA Normalized Altered Neurotrophic Signaling Pathways in 5xFAD Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| APP | Amyloid precursor protein |
| APS | Astragalus polysaccharides |
| AR | Astragali radix |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| CREB | cAMP-responsive element binding protein |
| EPM | Elevated plus maze |
| JNK | c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase |
| MWM | Morris water maze task |
| OFT | Open field task |
| RA | Roasted astragali radix |
| WT | Wild type |
| 5xFAD | Five familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations |
References
- Scheltens, P.; Blennow, K.; Breteler, M.M.; de Strooper, B.; Frisoni, G.B.; Salloway, S.; Van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2016, 388, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savelieff, M.G.; Lee, S.; Liu, Y.; Lim, M.H. Untangling amyloid-beta, tau, and metals in Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem Biol 2013, 8, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Halliwell, B. Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2019, 20, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampel, H.; Mesulam, M.M.; Cuello, A.C.; Farlow, M.R.; Giacobini, E.; Grossberg, G.T.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Vergallo, A.; Cavedo, E.; Snyder, P.J.; et al. The cholinergic system in the pathophysiology and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2018, 141, 1917–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.T.; Levinthal, D.J.; Kulich, S.M.; Chalovich, E.M.; DeFranco, D.B. Oxidative neuronal injury. The dark side of ERK1/2. Eur J Biochem 2004, 271, 2060–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qu, L.; Dong, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, E.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. A review of recent research progress on the astragalus genus. Molecules 2014, 19, 18850–18880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratkov, V.M.; Shkondrov, A.M.; Zdraveva, P.K.; Krasteva, I.N. Flavonoids from the Genus Astragalus: Phytochemistry and Biological Activity. Pharmacogn Rev 2016, 10, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.P.; Shen, J.G.; Xu, W.C.; Li, J.; Jiang, J.Q. Secondary metabolites of the genus Astragalus: structure and biological-activity update. Chem Biodivers 2013, 10, 1004–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, I.M.; Lima, F.O.V.; Fernandes, L.C.B.; Norrara, B.; Neta, F.I.; Alves, R.D.; Cavalcanti, J.; Lucena, E.E.S.; Cavalcante, J.S.; Rego, A.C.M.; et al. Astragaloside IV Supplementation Promotes A Neuroprotective Effect in Experimental Models of Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review. Curr Neuropharmacol 2019, 17, 648–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Chang, H.; Zhang, J.; Guo, G.; Shi, J.; Xu, H. Astragaloside IV Protects Rat Cardiomyocytes from Hypoxia-Induced Injury by Down-Regulation of miR-23a and miR-92a. Cell Physiol Biochem 2018, 49, 2240–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hou, X.; Xu, R.; Liu, C.; Tu, M. Research review on the pharmacological effects of astragaloside IV. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 2017, 31, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.K.L.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Fan, L.; Fraser, S.E.; Arfuso, F.; Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Focus on Formononetin: Anticancer Potential and Molecular Targets. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Zhao, K.; Huang, Q.; Shang, P. Structural features and biological activities of the polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus. Int J Biol Macromol 2014, 64, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Huang, G. The antiviral activity of polysaccharides and their derivatives. Int J Biol Macromol 2018, 115, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Gao, C.; Sun, X. Astragaloside IV Exerts Cognitive Benefits and Promotes Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Stroke Mice by Downregulating Interleukin-17 Expression via Wnt Pathway. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Liang, H.; Xiong, L. Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (Fabaceae): Bioactive Compounds and Potential Therapeutic Mechanisms Against Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 924429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sruthi, N.U.; Premjit, Y.; Pandiselvam, R.; Kothakota, A.; Ramesh, S.V. An overview of conventional and emerging techniques of roasting: Effect on food bioactive signatures. Food Chem 2021, 348, 129088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.J.; Kang, M.H.; Han, S.H.; Kim, G.S.; Kim, H.D.; Jang, G.Y. Roasted Astragalus membranaceus Inhibits Abeta25-35-Induced Oxidative Stress in Neuronal Cells by Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 and AKT/CREB/BDNF Pathways. Antioxidants (Basel) 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanoiu, A.; Pariente, J.; Booth, K.; Lobello, K.; Luscan, G.; Hua, L.; Lucas, P.; Styren, S.; Yang, L.; Li, D.; et al. Long-term safety and tolerability of bapineuzumab in patients with Alzheimer’s disease in two phase 3 extension studies. Alzheimers Res Ther 2016, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henley, D.B.; Sundell, K.L.; Sethuraman, G.; Dowsett, S.A.; May, P.C. Safety profile of semagacestat, a gamma-secretase inhibitor: IDENTITY trial findings. Curr Med Res Opin 2014, 30, 2021–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, M.F.; Mukai, Y.; Voss, T.; Kost, J.; Stone, J.; Furtek, C.; Mahoney, E.; Cummings, J.L.; Tariot, P.N.; Aisen, P.S.; et al. Further analyses of the safety of verubecestat in the phase 3 EPOCH trial of mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 2019, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decourt, B.; D’Souza, G.X.; Shi, J.; Ritter, A.; Suazo, J.; Sabbagh, M.N. The Cause of Alzheimer’s Disease: The Theory of Multipathology Convergence to Chronic Neuronal Stress. Aging Dis 2022, 13, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S. Natural Products in Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy: Would Old Therapeutic Approaches Fix the Broken Promise of Modern Medicines? Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padua, M.S.; Guil-Guerrero, J.L.; Lopes, P.A. Behaviour Hallmarks in Alzheimer’s Disease 5xFAD Mouse Model. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ma, P. Pharmacological effects of Astragalus polysaccharides in treating neurodegenerative diseases. Front Pharmacol 2024, 15, 1449101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zheng, L.; Lin, Z.; Hou, C.; Liu, W.; Yan, T.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Liu, Z. Study of pharmacokinetic profiles and characteristics of active components and their metabolites in rat plasma following oral administration of the water extract of Astragali radix using UPLC-MS/MS. J Ethnopharmacol 2015, 169, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Zhao, J.B.; Guo, L.; Yang, Y.L.; Hu, F.; Zhu, R.J.; Feng, S.L. Simultaneous determination of calycosin-7-O-beta-D-glucoside, ononin, calycosin, formononetin, astragaloside IV, and astragaloside II in rat plasma after oral administration of Radix Astragali extraction for their pharmacokinetic studies by ultra-pressure liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Cell Biochem Biophys 2014, 70, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Li, X.; Bai, X.X.; Gao, J.; Wang, C.Y. Calycosin improves cognitive function in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease by activating the protein kinase C pathway. Neural Regen Res 2017, 12, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, H.X.; Zhang, Y.B.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X.J.; Wu, S.L. Neuroprotective effect of formononetin in ameliorating learning and memory impairment in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2018, 82, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, D.; Mathura, V.; Ait-Ghezala, G.; Beaulieu-Abdelahad, D.; Patel, N.; Bachmeier, C.; Mullan, M. Flavonoids lower Alzheimer’s Abeta production via an NFkappaB dependent mechanism. Bioinformation 2011, 6, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.G.; Garrick, J.M.; Roque, P.J.; Pellacani, C. Mechanisms of Neuroprotection by Quercetin: Counteracting Oxidative Stress and More. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016, 2016, 2986796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Tan, X.; Reis, J.C.; Badr, M.Z.; Papasian, C.J.; Morrison, D.C.; Qureshi, N. Inhibition of nitric oxide in LPS-stimulated macrophages of young and senescent mice by delta-tocotrienol and quercetin. Lipids Health Dis 2011, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.P.; Yu, S.; Li, B.K.; Cui, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhang, L.D. Astragaloside IV, a Natural PPARgamma Agonist, Reduces Abeta Production in Alzheimer’s Disease Through Inhibition of BACE1. Mol Neurobiol 2017, 54, 2939–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.P.; Liu, Y.F.; Lin, H.J.; Hsu, C.C.; Cheng, B.C.; Liu, W.P.; Lin, M.T.; Hsu, S.F.; Chang, L.S.; Lin, K.C. Beneficial Effect of Astragaloside on Alzheimer’s Disease Condition Using Cultured Primary Cortical Cells Under beta-amyloid Exposure. Mol Neurobiol 2016, 53, 7329–7340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Jia, N.; Wang, W.; Jin, H.; Xu, J.; Hu, H. Protective effects of astragaloside IV against amyloid beta1-42 neurotoxicity by inhibiting the mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. PLoS One 2014, 9, e98866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yang, D.; Cheng, X.Y.; Yang, H.; Yang, X.H.; Liu, H.T.; Wang, R.; Zheng, P.; Yao, Y.; Li, J. Astragaloside IV Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment and Neuroinflammation in an Oligomeric Abeta Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model via Inhibition of Microglial Activation and NADPH Oxidase Expression. Biol Pharm Bull 2021, 44, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haiyan, H.; Rensong, Y.; Guoqin, J.; Xueli, Z.; Huaying, X.; Yanwu, X. Effect of Astragaloside IV on Neural Stem Cell Transplantation in Alzheimer’s Disease Rat Models. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016, 2016, 3106980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Zhu, G. Astragaloside IV prevents Abeta(1-42) oligomers-induced memory impairment and hippocampal cell apoptosis by promoting PPARgamma/BDNF signaling pathway. Brain Res 2020, 1747, 147041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, W.-c.; Wang, W.-p.; Tian, W.-y.; Zhang, X.-g. Optimization of extraction technology of Astragalus polysaccharides by response surface methodology and its effect on CD40. Carbohydrate Polymers 2009, 78, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Tsay, H.J.; Lu, M.K.; Lin, C.H.; Yeh, C.W.; Liu, H.K.; Shiao, Y.J. Astragalus membranaceus-Polysaccharides Ameliorates Obesity, Hepatic Steatosis, Neuroinflammation and Cognition Impairment without Affecting Amyloid Deposition in Metabolically Stressed APPswe/PS1dE9 Mice. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, S.; Kawauchi, S.; Balderrama-Gutierrez, G.; Kramar, E.A.; Matheos, D.P.; Phan, J.; Javonillo, D.I.; Tran, K.M.; Hingco, E.; da Cunha, C.; et al. Systematic phenotyping and characterization of the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Data 2021, 8, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oblak, A.L.; Lin, P.B.; Kotredes, K.P.; Pandey, R.S.; Garceau, D.; Williams, H.M.; Uyar, A.; O’Rourke, R.; O’Rourke, S.; Ingraham, C.; et al. Comprehensive Evaluation of the 5XFAD Mouse Model for Preclinical Testing Applications: A MODEL-AD Study. Front Aging Neurosci 2021, 13, 713726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, W.; Yang, J.; Ali, A.; Qin, H. Mechanism of Astragalus membranaceus Alleviating Acquired Hyperlipidemia Induced by High-Fat Diet through Regulating Lipid Metabolism. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Qin, J.; Hao, Y.; Liu, M.; Luo, J.; Luo, T.; Wei, L. Astragalus polysaccharide suppresses skeletal muscle myostatin expression in diabetes: involvement of ROS-ERK and NF-kappaB pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013, 2013, 782497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.A.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, D.H. Anti-stress effect of astragaloside IV in immobilized mice. J Ethnopharmacol 2014, 153, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Yoon, K.H.; Kim, K.S.; Shim, I. The Effects of Astragalus Membranaceus on Repeated Restraint Stress-induced Biochemical and Behavioral Responses. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 2009, 13, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elkader, H.A.E.; Abdou, H.M.; Khamiss, O.A.; Essawy, A.E. Anti-anxiety and antidepressant-like effects of astragaloside IV and saponins extracted from Astragalus spinosus against the bisphenol A-induced motor and cognitive impairments in a postnatal rat model of schizophrenia. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2021, 28, 35171–35187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu. X; Xu. W; Zhao. Z; Wu. X; Wang. S; Jian. C; Li. M; Li. K; Wang. Y; X., Q. Prophylactic Effects of Astragalus Polysaccharides on Depression-Like Behaviors in Rats With Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress: A Role of Gut-Microbiota–Brain Axis. Food Frontiers 2024, 6, 1343–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Alam, A.; San, C.Y.; Eguchi, S.; Chen, Q.; Lian, Q.; Ma, D. Molecular mechanisms of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neuro-protection: Recent developments. Brain Res 2017, 1665, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, Y.; Nakasone, H.; Kasahara, R.; Fukuchi, M. Expression Profiles of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Splice Variants in the Hippocampus of Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mouse. Biol Pharm Bull 2024, 47, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Roy, A.; Raha, S.; Kundu, M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Pahan, K. Upregulation of BDNF and hippocampal functions by a hippocampal ligand of PPARalpha. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pins, B.; Cifuentes-Diaz, C.; Farah, A.T.; Lopez-Molina, L.; Montalban, E.; Sancho-Balsells, A.; Lopez, A.; Gines, S.; Delgado-Garcia, J.M.; Alberch, J.; et al. Conditional BDNF Delivery from Astrocytes Rescues Memory Deficits, Spine Density, and Synaptic Properties in the 5xFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer Disease. J Neurosci 2019, 39, 2441–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Gu, L.J.; Guo, J.Y. [Study on effect of astragali radix polysaccharides in improving learning and memory functions in aged rats and its mechanism]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2014, 39, 2071–2075. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wan, G.; Jiang, R.; Zou, L.; Wan, D.; Zhu, H.; Feng, S. Astragalus injection ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive decline via relieving acute neuroinflammation and BBB damage and upregulating the BDNF-CREB pathway in mice. Pharm Biol 2022, 60, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginet, V.; Puyal, J.; Magnin, G.; Clarke, P.G.; Truttmann, A.C. Limited role of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway in a neonatal rat model of cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. J Neurochem 2009, 108, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priori, E.C.; Musi, C.A.; Giani, A.; Colnaghi, L.; Milic, I.; Devitt, A.; Borsello, T.; Repici, M. JNK Activation Correlates with Cognitive Impairment and Alteration of the Post-Synaptic Element in the 5xFAD AD Mouse Model. Cells-Basel 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porte, B.; Marguerit, G.; Thomasseau, S.; Paquet, C.; Hugon, J. Dose-dependent neuroprotective effect of the JNK inhibitor Brimapitide in 5xFAD transgenic mice. Brain Res 2020, 1727, 146587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Han, X.; Xing, F.; Wu, H.; Shi, H.; Huang, F.; Xu, Q.; Wu, X. Total flavonoids of astragalus attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing the activation and inflammatory responses of microglia via JNK/AKT/NFkappaB signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2021, 80, 153385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Zhao, S.; Ren, C.; Ma, Z. Astragalus polysaccharide alleviates LPS-induced inflammation injury by regulating miR-127 in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2018, 32, 2058738418759180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Shao, C.; Li, W.; Wan, H.; He, Y.; Yang, J. Protective effects of Astragaloside IV against oxidative injury and apoptosis in cultured astrocytes by regulating Nrf2/JNK signaling. Exp Brain Res 2021, 239, 1827–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Qu, J.; Chen, B.; Dai, G.; Zhang, X.; Nie, K.; Mao, S.; Sun, H. Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behaviors and inflammatory response through regulating NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med 11 2361–2370.
- Liu, G.; Song, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Z. Astragalus injection protects cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and the expression of JNK3 after cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats. Behav Brain Funct 2013, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Feng, L.; Li, M. The Role of Traditional Chinese Medicine Natural Products in beta-Amyloid Deposition and Tau Protein Hyperphosphorylation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Drug Des Devel Ther 2023, 17, 3295–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Y.; Ouyang, H.T.; Yang, J.Y.; Huang, X.L.; Yang, T.; Duan, J.P.; Cheng, J.P.; Chen, Y.X.; Yang, Y.J.; Qiong, P. Subchronic toxicity studies of Radix Astragali extract in rats and dogs. J Ethnopharmacol 2007, 110, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Gao, C.; Chen, W.; Vong, C.T.; Yao, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Astragali Radix (Huangqi): A promising edible immunomodulatory herbal medicine. J Ethnopharmacol 2020, 258, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




