Submitted:
23 September 2024
Posted:
24 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
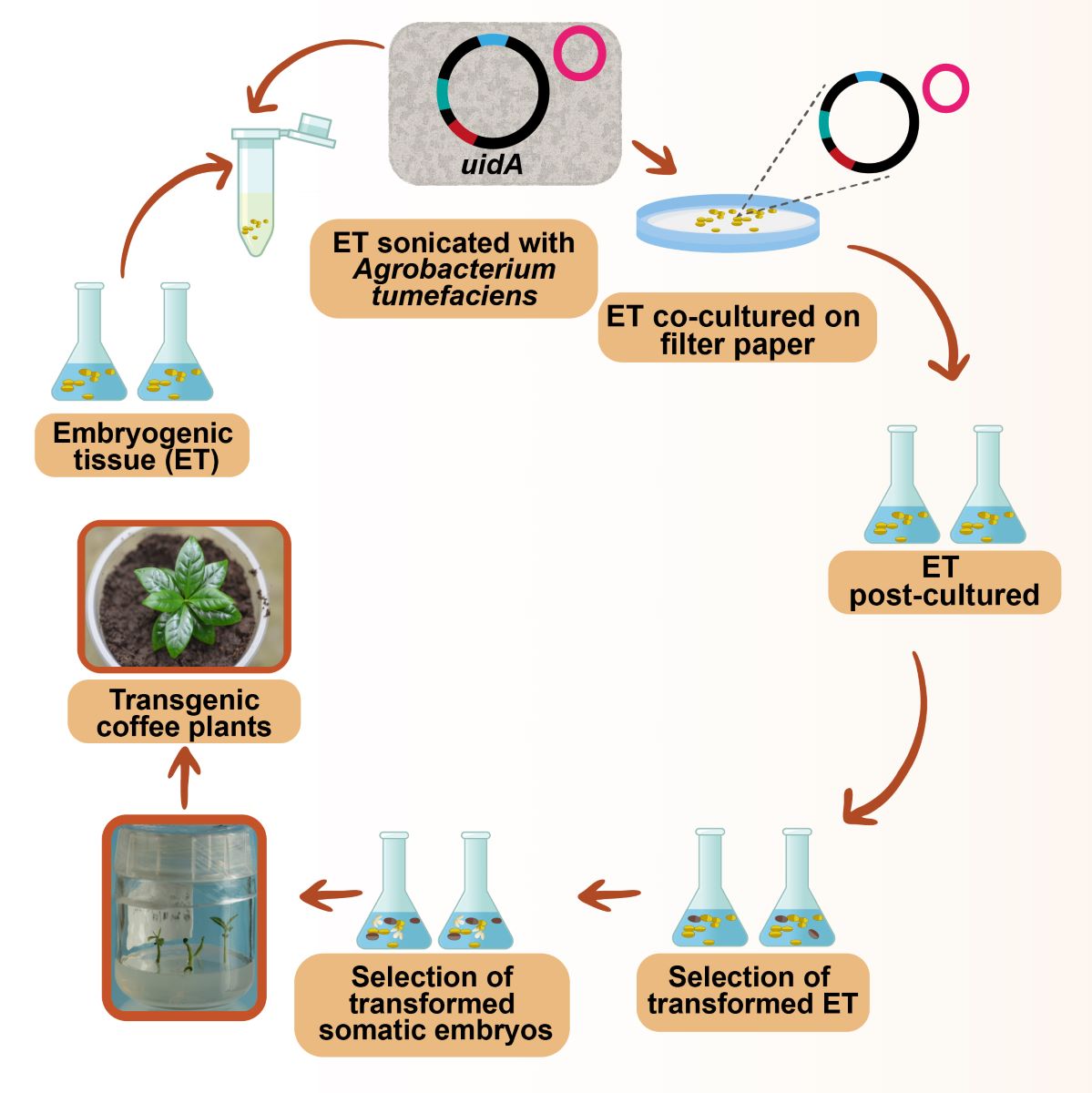
2.1. In Vitro Culture Conditions
2.2. Agrobacterium Tumefaciens Strains and Vectors
2.3. Agrobacterium Transformation
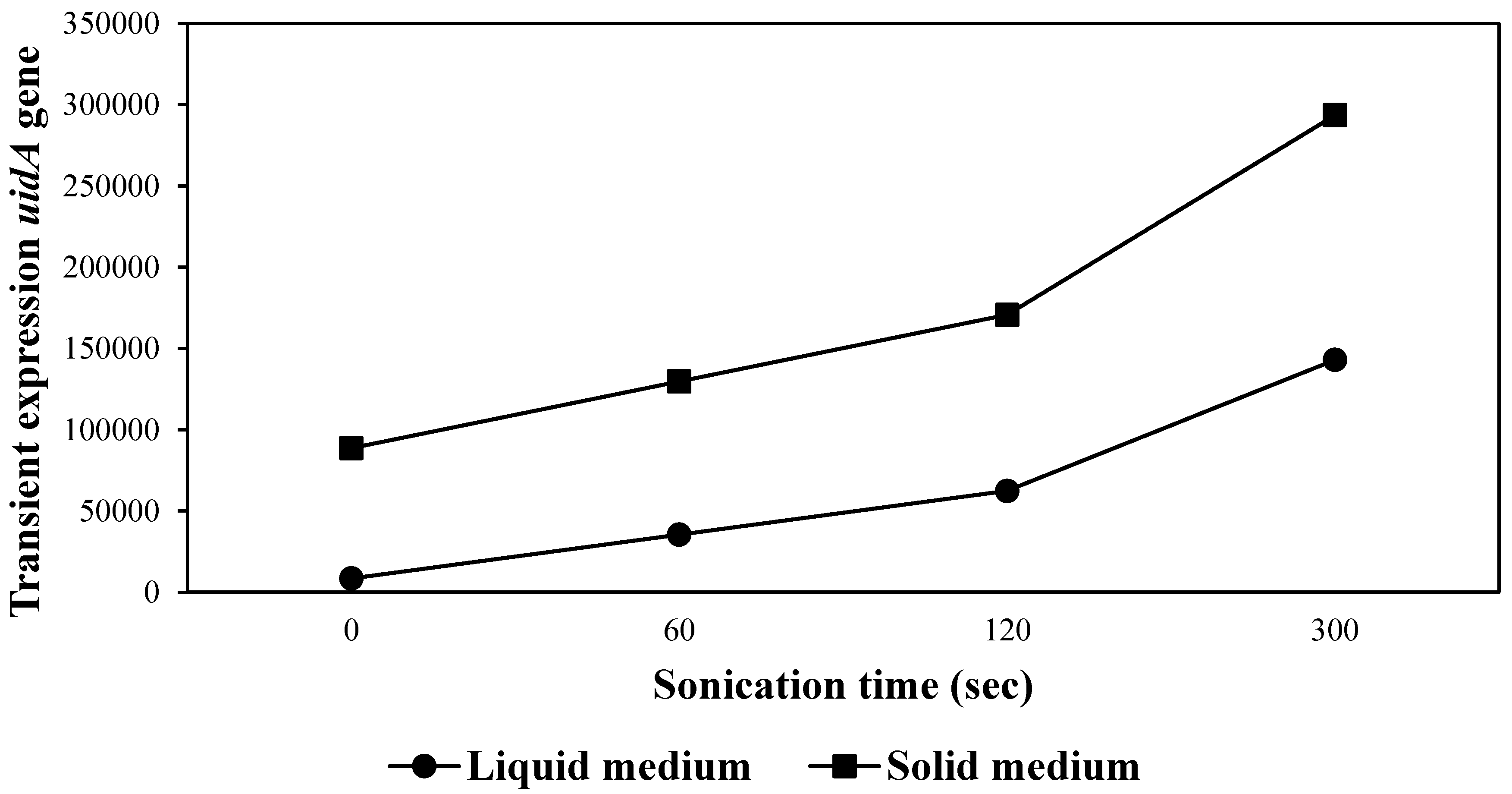
- Sonication time: Early ET of genotype BI.625 without pre-culturing was sonicated in a suspension of A. tumefaciens LBA4405 containing vector pC1301 for 0, 60, 120 and 300 sec. After 1 hr incubation in the suspension, the ET was co-cultured for four days in both solid and liquid differentiation media.
- Co-culturing time: The ET of genotype BK.620 without pre-culturing was sonicated in a suspension of A. tumefaciens EHA105 containing vector pC1301 for 300 sec. After 1 hr incubation in the suspension, the ET was co-cultured in solid differentiation medium for 0–8 days.
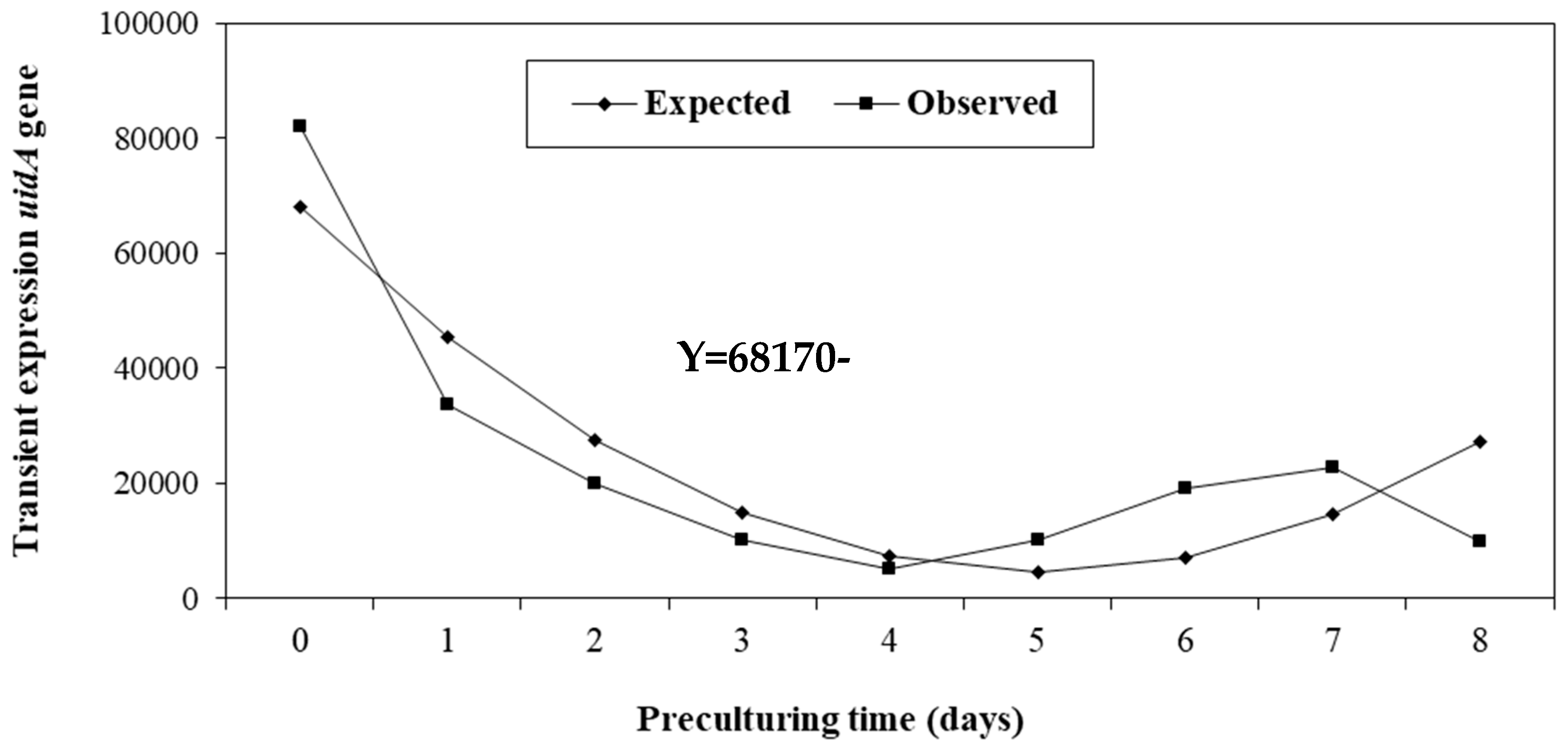
- Pre-culturing time: The ET of genotype BK.620 was pre-cultured in the dark in solid differentiation medium supplemented with 100 µM acetosyringone for 0–8 days, followed by sonication of embryogenic cells for 300 sec in a suspension of A. tumefaciens EHA105 containing vector pC2301. After 1 hr incubation in the suspension, the ET was co-cultured in a solid differentiation medium for four days.
- Age of ET: Transformation efficiency of the uidA gene was evaluated using early and differentiated ET of genotype BI.625 without pre-culturing, followed by sonication for 300 sec of embryogenic cells in a suspension of A. tumefaciens LBA4404 containing vector pC1301. After 1 hr incubation in the suspension, the ET was co-cultured in a solid differentiation medium for four days.
- Agrobacterium strain: A. tumefaciens strains LBA4404 and EHA105 were evaluated with the vector pC1301.
- Transformation vector: Vectors pC1301 and pC2301 previously introduced into strain LBA4404 were compared.
- Coffee genotype: The early ETs of genotypes BI.625 and BK.620 were co-cultured with A. tumefaciens strain LBA4404 containing the vector pC1301. The protocol described for evaluating the age of ET was followed to evaluate Agrobacterium strains, transformation vectors and coffee plant genotypes.
2.4. Stable Transformation
2.4.1. Development of Transgenic Somatic Embryos
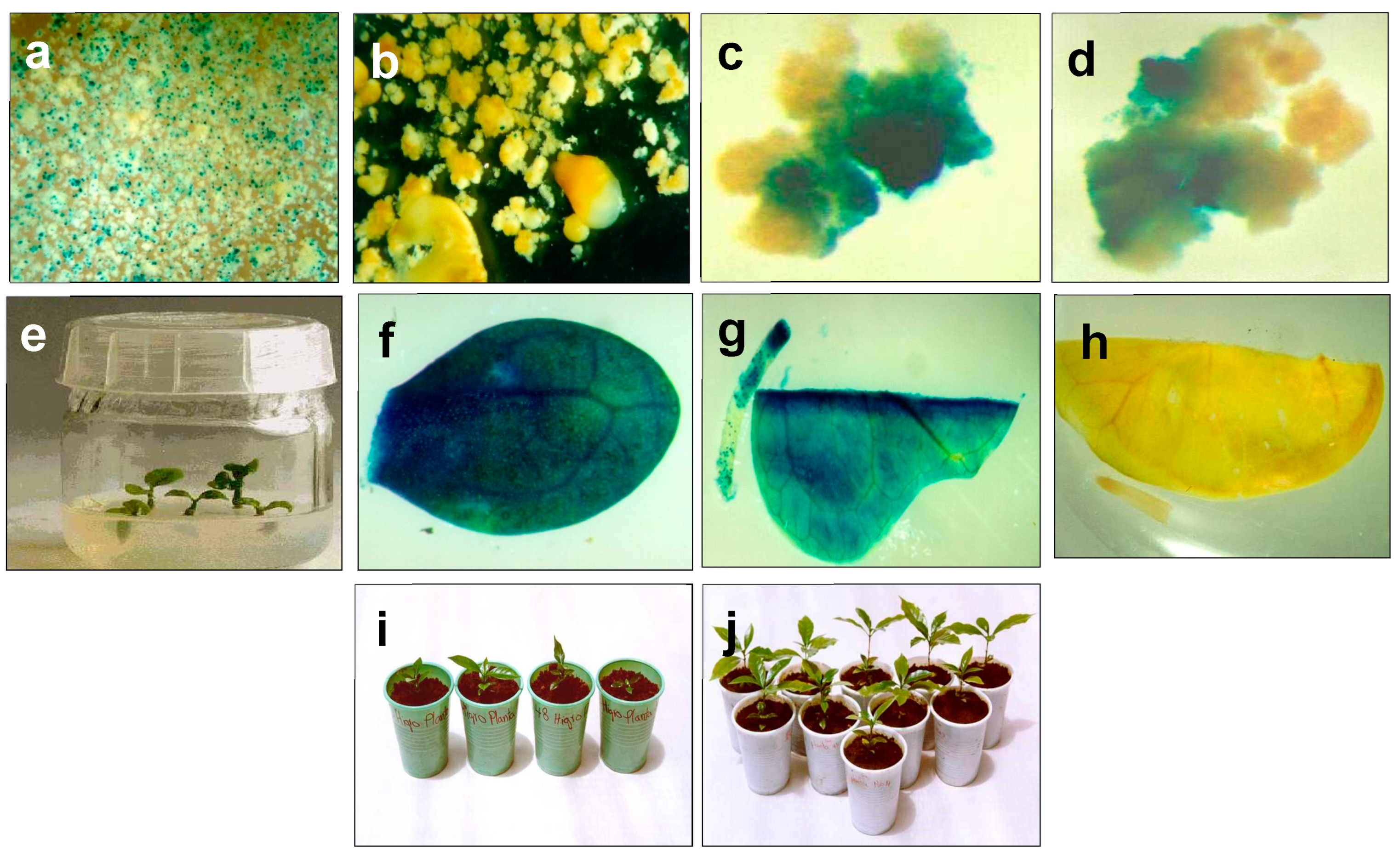
2.4.2. Histochemical GUS Assay
2.4.3. PCR and Southern Blot Analysis of Transgenic Plants
2.5. Experimental Design and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Age of ET
3.2. Pre-Culturing Time
3.3. Agrobacterium Strain, Transformation Vector and Coffee Genotype
3.4. Sonication Time and Co-Culturing Medium
3.5. Co-Culturing Time
3.6. Regeneration of Transgenic Plants and Molecular Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Statistics Division. 2024, http://faostat.fao.org [Accessed July 26, 2024].
- International Coffee Organization. Coffee Development Report 2022. 2022, www.ico.org/documents/cy2022-23/annual-review-2021-2022-e.pdf. [Accessed June 24, 2024].
- Davis, A.P.; Rakotonasolo, F. Six new species of coffee (Coffea) from northern Madagascar. Kew Bull. 2021, 76, 497–511. [CrossRef]
- International Coffee Organization. Coffee Market Report. www.ico.org/documents/cy2022-23/cmr-1222-e.pdf. 2023, [Accessed April 24, 2024].
- Scalabrin, S.; Magris, G.; Liva, M.; Vitulo, N.; Vidotto, M.; Scaglione, D.; Del Terra, L.; Ruosi, M.R.; Navarini, L.; Pellegrino, G.; Mier y Teran, J.C.; Toniutti, L.; Suggi, F.; Cerutti, M.; Di Gaspero, G.; Morgante, M. A chromosome-scale assembly reveals chromosomal aberrations and exchanges generating genetic diversity in Coffea arabica germplasm. Nat Commun. 2024, 15, 463. [CrossRef]
- Federación Nacional de Cafeteros de Colombia. Estadísticas cafeteras. 2024, http://federaciondecafeteros.org/wp/estadisticascafeteras [Accessed April 24, 2024].
- Federación Nacional de Cafeteros de Colombia. Sistema de información cafetero de Colombia. 2024, http://sica.cafedecolombia.com [Accessed April 24, 2024].
- Molina, D.; Moncada, M.P.; Cortina, H.; Benavides, P. Searching for a coffee variety with antibiosis effect to Hypothenemus hampei Ferrari (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Euphytica. 2022, 218, 97. [CrossRef]
- Etienne, H.; Breton, D.; Breitler, J-C.; Bertrand, B.; Déchamp, E.; Awada, R.; Marraccini, P.; Léran, S.; Alpizar, E.; Campa, C.; Cuurtel, P.; Georget, F.; Ducos, J-P. Coffee somatic embryogenesis: How did research, experience gained and innovations promote the commercial propagation of elite clones from the two cultivated species?. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1630. [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Hernández, H.A.; Galaz-Ávalos, R.M.; Quintana-Escobar, A.O.; Pech-Hoil, R.; Collí-Rodríguez, A.M.; Salas-Peraza, I.Q.M. In vitro conversion of Coffea spp. somatic embryos in SETIS™ bioreactor system. Plants. 2023, 12, 3055. [CrossRef]
- Avila-Victor, C.M.; Ordaz-Chaparro, V.M.; Arjona-Suárez, E.d.J.; Iracheta-Donjuan, L.; Gómez-Merino, F.C.; Robledo-Paz, A.. In vitro mass propagation of coffee plants (Coffea arabica L. var. Colombia) through indirect somatic embryogenesis. Plants. 2023, 12, 1237. [CrossRef]
- Leroy, T.; Henry, A.M.; Royer, M.; Altosaar, I.; Frutos, R.; Duris, D.; Philippe, R. Genetically modified coffee plants expressing the Bacillus thuringiensis cry1Ac gene for resistance to leaf miner. Plant Cell Rep. 2000, 19, 382–389. [CrossRef]
- Perthuis, B.; Vassal, J.M.; Fenouillet, C.; Leroy, T. Cry1Ac insecticidal protein levels in genetically modified Coffea canephora Pierre coffee plants were negatively correlated with the growth speed in a field experiment. Euphytica. 2014, 202, 373–383. [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, É.V.; Bezerra, C.A.; Romero, J.V.; Valencia, J.W.; Valencia-Jiménez, A.; Pimenta, L.M., Barbosa, A.E.; Silva, M.C.; Meneguim, A.M.; Sá, M.E.; Engler, G.; de Almeida-Engler, J.; Fernandez, D.; Grossi-de-Sá, M.F. Seed-specific stable expression of the α-AI1 inhibitor in coffee grains and the in vivo implications for the development of the coffee berry borer. Trop. Plant Biol. 2015, 8, 98–107. [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Lozano, E.; Cabrera-Ponce, J.L.; Gómez-Lim, M.A.; Ibarra, J.E. Development of an efficient protocol to obtain transgenic coffee, Coffea arabica L., expressing the Cry10Aa toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5334. [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Lozano, E.; Cabrera-Ponce, J.L.; Noa-Carrazana, J.C.; Ibarra, J.E. Coffea arabica L. resistant to coffee berry borer (Hypothenemus hampei) mediated by expression of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry10Aa protein. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 765292. [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.E.; Wang, X.Y.; Escalona, M.; Yan, L.; Huang, L.F. Somatic embryogenesis of Arabica coffee in temporary immersion culture: Advances, limitations, and perspectives for mass propagation of selected genotypes. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 994578. [CrossRef]
- Salaün, C.; Lepiniec, L.; Dubreucq, B. Genetic and molecular control of somatic embryogenesis. Plants (Basel). 2021, 10, 1467. [CrossRef]
- Campos, N.A.; Panis, B.; Carpentier, S.C. Somatic embryogenesis in coffee: the evolution of biotechnology and the integration of omics technologies offer great opportunities. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1460. [CrossRef]
- Staritsky, G. Embroid formation in calllus tissues of Coffea. Acta Bot. Neerl. 1970, 19, 509–514.
- Sondahl, M.R.; Sharp, W.R. High frecuency induction of somatic embryos in cultured leaf explants of Coffea arabica L. Z. Pflanzenphysiologie. 1977, 81, 395–408. [CrossRef]
- Molina, D.; Aponte, M.E.; Cortina, H.; Moreno, L.G. The effect of genotype and explant age on somatic embryogenesis of coffee. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2002, 71, 117–123. [CrossRef]
- Arimarsetiowati, R.; Daryono, B.S.; Astuti, Y.T.M.; Prastowo, E.; Semiarti, E. Regeneration and development of Coffea arabica L. plants through indirect somatic embryogenesis. Coffee Sci. 2023, 18, e182078. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.S.D.; Hartati, R.S.; Rubiyo, R.; Reflinur, R.; Purwito, A.; Sudarsono, S. Exploring indirect somatic embryogenesis and somaclonal variation for propagation of three Coffea arabica L. cultivars. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2024, 84, 15–27. [CrossRef]
- Avila-Victor, C.M.; Arjona-Suárez, E.d.J.; Iracheta-Donjuan, L.; Valdez-Carrasco, J.M.; Gómez-Merino, F.C.; Robledo-Paz, A. Callus type, growth regulators, and phytagel on indirect somatic embryogenesis of coffee (Coffea arabica L. var. Colombia). Plants. 2023, 12, 3570. [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.F.; Dechamp, E.; Champion, A.; Bertrand, B.; Combes, M-C.; Verdeil, J-L.; Lapeyre, F.; Lashermes, P.; Etienne, H. Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Coffea arabica L. is greatly enhanced by using established embryogenic callus cultures. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 92. [CrossRef]
- Shilo, S.; Tripathi, P.; Melamed-Bessudo, C.; Tzfadia, O.; Muth, T.R.; Levy, A.A. T-DNA-genome junctions form early after infection and are influenced by the chromatin state of the host genome. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006875. [CrossRef]
- Gelvin, S.B. Plant DNA repair and Agrobacterium T-DNA integration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8458. [CrossRef]
- Canche-Moo, R.L.R.; Ku-Gonzalez, A.; Burgeff, C.; Loyola-Vargas, V.M.; Rodriguez-Zapata, L.C.; Castaño, E. Genetic transformation of Coffea canephora by vacuum infiltration. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2006, 84, 373–377. [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Lin, L.; Luo, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Miao, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P. Recent progress in the regeneration and genetic transformation system of cucumber. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7180. [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.E.; Christie, P. J. The Agrobacterium Ti plasmids. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 10.1128/microbiolspec.plas-0010-2013. [CrossRef]
- Maciel, A.L.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Pasqual, M.; Carvalho, C.H. Large-scale, high-efficiency production of coffee somatic embryos. Crop. Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2016, 16, 102–107. [CrossRef]
- Parra-Vega, V.; Corral-Martínez, P.; Rivas-Sendra, A.; Seguí-Simarro, J.M. Induction of embryogenesis in Brassica napus microspores produces a callosic subintinal layer and abnormal cell walls with altered levels of callose and cellulose. Front Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1018. [CrossRef]
- Martínez, N.; Dávila, C.; Morales, J.; Castro, K.; Martínez, N.; López, H.; Villalobos, E. 6-benzylaminopurine induces somatic embryogenesis in the staminodia of new genotypes of Theobroma cacao L. from the Papaloapan Basin of Mexico and differs from that of T. bicolor Bonpl. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2024, 157, 64. [CrossRef]
- Udayabhanu, J.; Huang, T.; Xin, S.; Cheng, J.; Hua, Y.; Huang, H. Optimization of the transformation protocol for increased efficiency of genetic transformation in Hevea brasiliensis. Plants. 2022, 11, 1067. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, J.; Datta, S.; Mishra, S.P. Development of an efficient Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system for chickpea (Cicer arietinum). Biologia. 2017, 72, 153–160. [CrossRef]
- Sadhu, S.K.; Jogam, P.; Gande, K.; Banoth, R.; Suprasanna, P.; Peddaboina, V. Optimization of different factors for an Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation system using embryo axis explants of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). J. Plant Biotechnol. 2022, 49, 61–73. [CrossRef]
- Song, G-Q.; Han, X.; Wiersma, A.T.; Zong, X.; Awale, H.E.; Kelly, J.D. Induction of competent cells for Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated stable transformation of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). PLoS ONE. 2020, 15, e0229909. [CrossRef]
- Trick H.N.; Finer J.J. Sonication-assisted Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill] embryogenic suspension culture tissue. Plant Cell Rep. 1998, 17, 482–488. [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, K.; Vidya, N.; Appunu, C.; Gurusaravanan, P.; Arun, M. A simple and efficient genetic transformation system for soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) targeting apical meristem of modified half-seed explant. 3 Biotech. 2023, 13, 293. [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.L.; Paim Pinto, D.L.; Passos, A.B.; Marcelino-Guimaräes, F.C.; Bandini Rossi, A.; Krause, W.; de Carvalho, I.; Batista, D.; Rocha, D.; Otoni, W. Novel and efficient transformation of wild passion fruit (Passiflora cincinnata Mast.) using sonication-assisted Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant. 2021, 57, 380–386. [CrossRef]
- Mohanan, S.; Satyanarayana, K.V.; Sridevi, V.; Gowda, K.; Giridhar, P.; Chandrashekar, A., Ravishankar, G. Evaluating the effect and effectiveness of different constructs with a conserved sequence for silencing of Coffea canephora N-methyltransferases. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 399–409. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Hao, X.; Lv, K.; Xie, Y.; Xu, W. Establishment of an efficient callus transient transformation system for Vitis vinifera cv. 'Chardonnay'. Protoplasma. 2023, 261, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, A.; Pilavadi, T.; Venkatachalam, V.; Umapathy, D.; Arockiam, A.J.V.; Singarayar, M.S.; Lee, G-J.; Markandan, M. Bio-engineered As-Ag-TiO2 nanoparticles enhance the genetic transformation of Pisum sativum L. via proton-coupled electron transfer-dependent alternative protonation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 215, 118604. [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Guevara, C.; Vargas-Segura, C.; Villalta-Villalobos, J.; Pereira, L.F.P.; Gatica-Arias, A. A. simple and efficient agroinfiltration method in coffee leaves (Coffea arabica L.): Assessment of factors affecting transgene expression. 3 Biotech. 2018, 8, 471. [CrossRef]
- Mirzaee, M.H.; Emadpour, M. Advances in the transformation of Cyclamen persicum Mill. through direct regeneration based on an optimized kanamycin selection scheme. Mol. Biotechnol. 2024, 66, 311–320. [CrossRef]
- Nanasato, Y.; Konagaya, K.I.; Okuzaki, A.; Tsuda, M.; Tabei, Y. Improvement of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) by combination of vacuum infiltration and co-cultivation on filter paper wicks. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2013, 7, 267–276. [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Zheng, L.; Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, W. An, H. Co-culturing on dry filter paper significantly increased the efficiency of Agrobacterium-mediated transformations of maize immature embryos. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants. 2019, 25, 549–560. [CrossRef]
- Pavlichenko, V.V.; Protopopova, M.V. Simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Populus x berolinensis K. Koch. Methods Protoc. 2024, 7, 12. [CrossRef]
- Casarin, T.; Freitas, N.C.; Pinto, R.T.; Breitler J-C.; Zebral Rodrigues, L.A.; Marraccini, P.; Etienne, H.; Cardamone, L.E.; Carvalho, A.; Vilela, L. Multiplex CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of the phytoene desaturase gene in Coffea canephora. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17270. [CrossRef]
- Anwaar, S.; Jabeen, N.; Ahmad, K.S.; Shafique, S.; Irum, S.; Ismail, H.; Ullah, S.; Tahir, A.; Mehmood, N.; Gleason, M.L. Cloning of maize chitinase 1 gene and its expression in genetically transformed rice to confer resistance against rice blast caused by Pyricularia oryzae. PLoS ONE. 2024, 19, e0291939. [CrossRef]
- Molina, D.; Patino, L.; Quintero, M.; Cortes, J.; Bastos, S. Effects of the aspartic protease inhibitor from Lupinus bogotensis seeds on the growth and development of Hypothenemus hampei: an inhibitor showing high homologywith storage proteins. Phytochemistry. 2014, 98, 69–77. [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays tobacco tissues cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 472–497. [CrossRef]
- Jefferson R.A. Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1987, 5, 387–405. [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L.A. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15.
- Noir, S.; Patheyron, S.; Combes, M.C.; Lashermes, P.; Chalhoub, B. Construction and characterisation of a BAC library for genome analysis of the allotetraploid coffee species (Coffea arabica L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 225–230. [CrossRef]
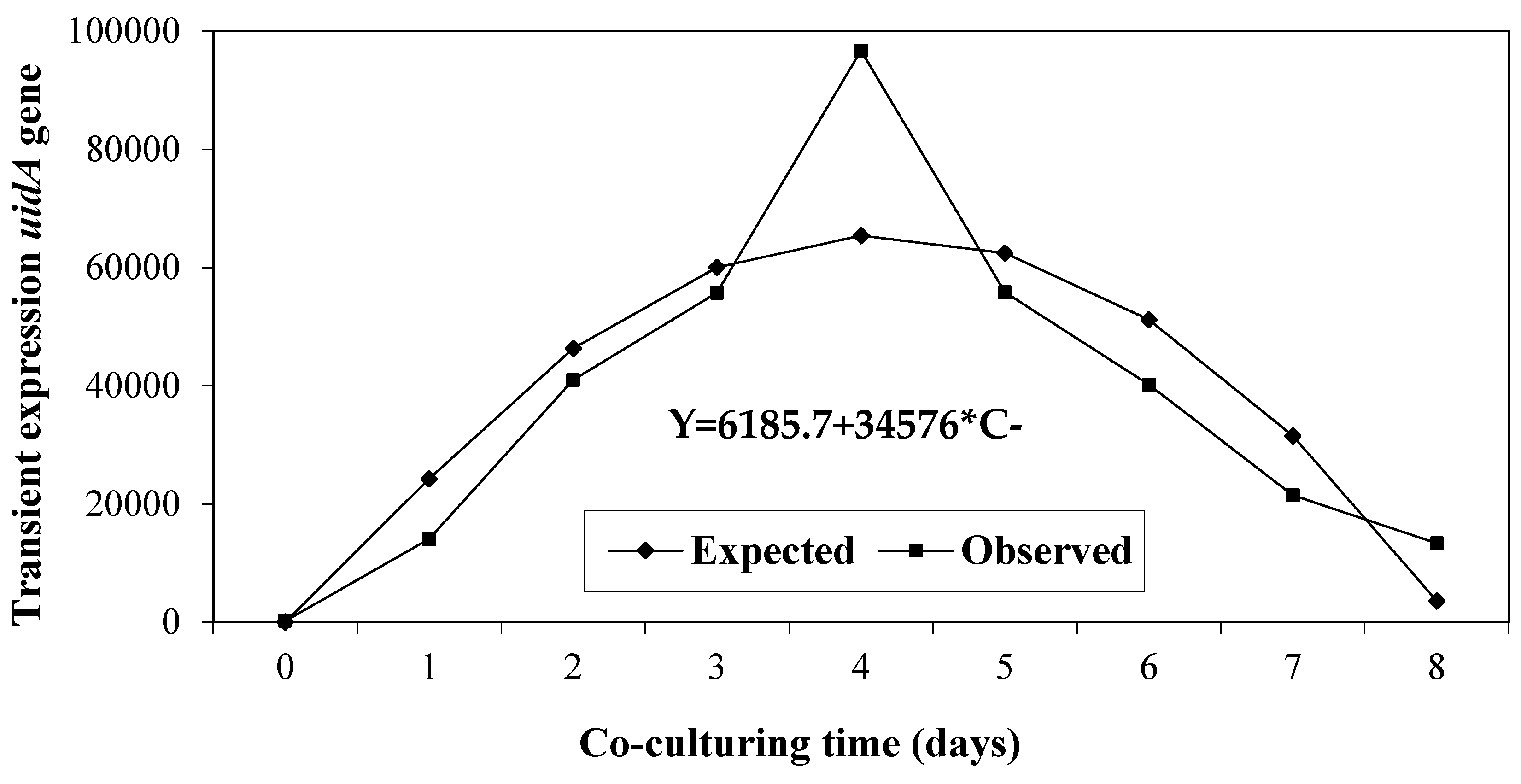
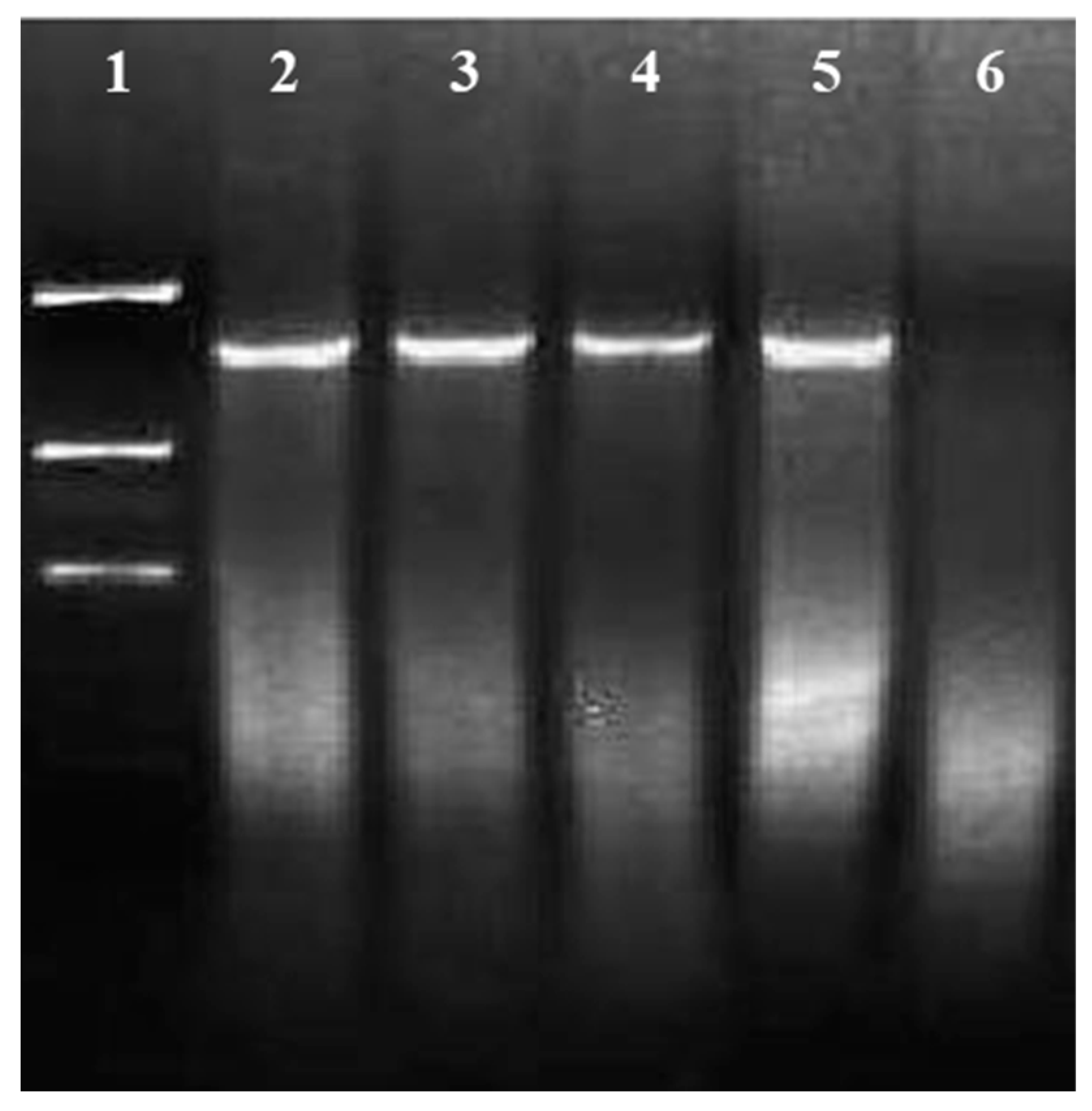
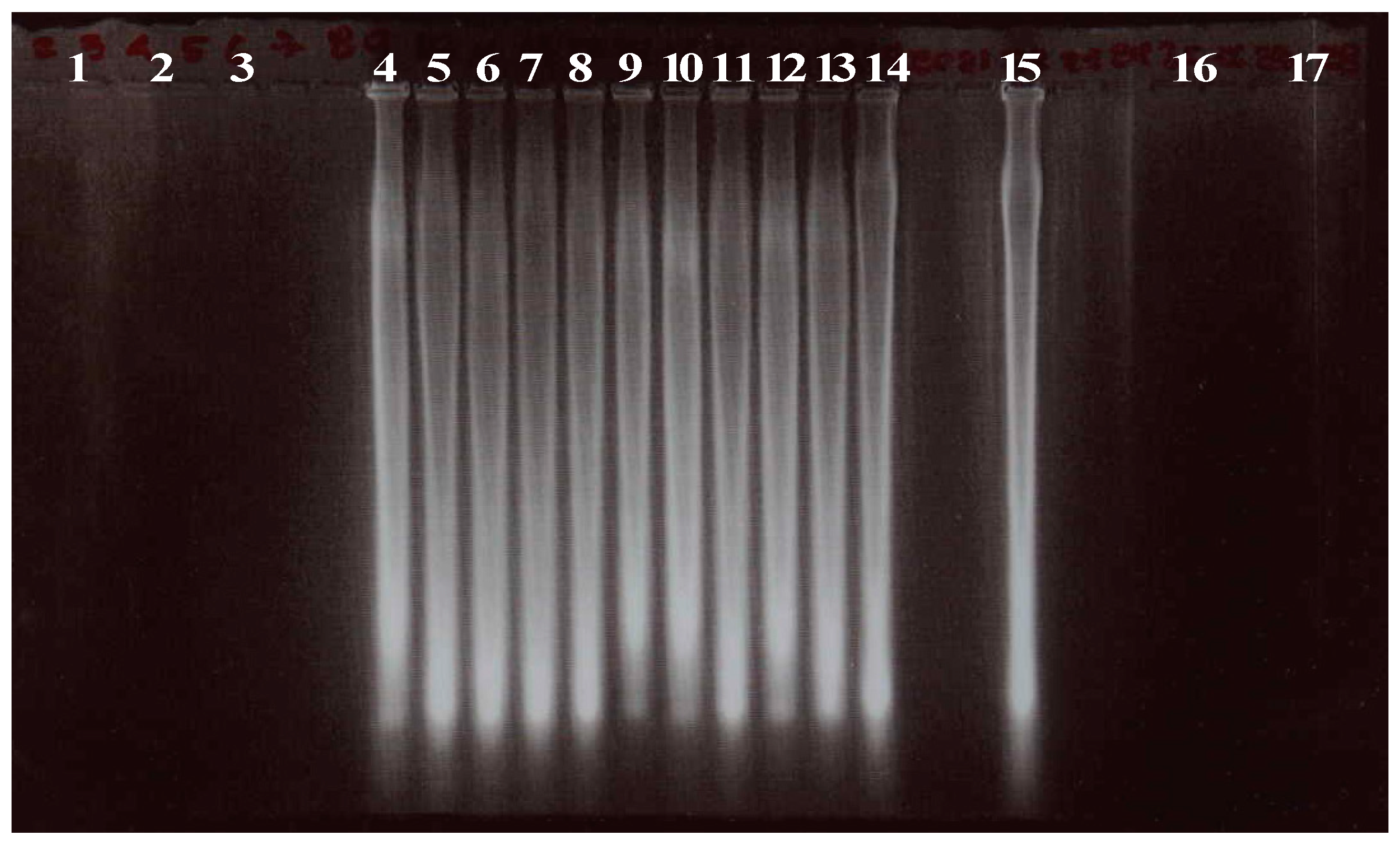
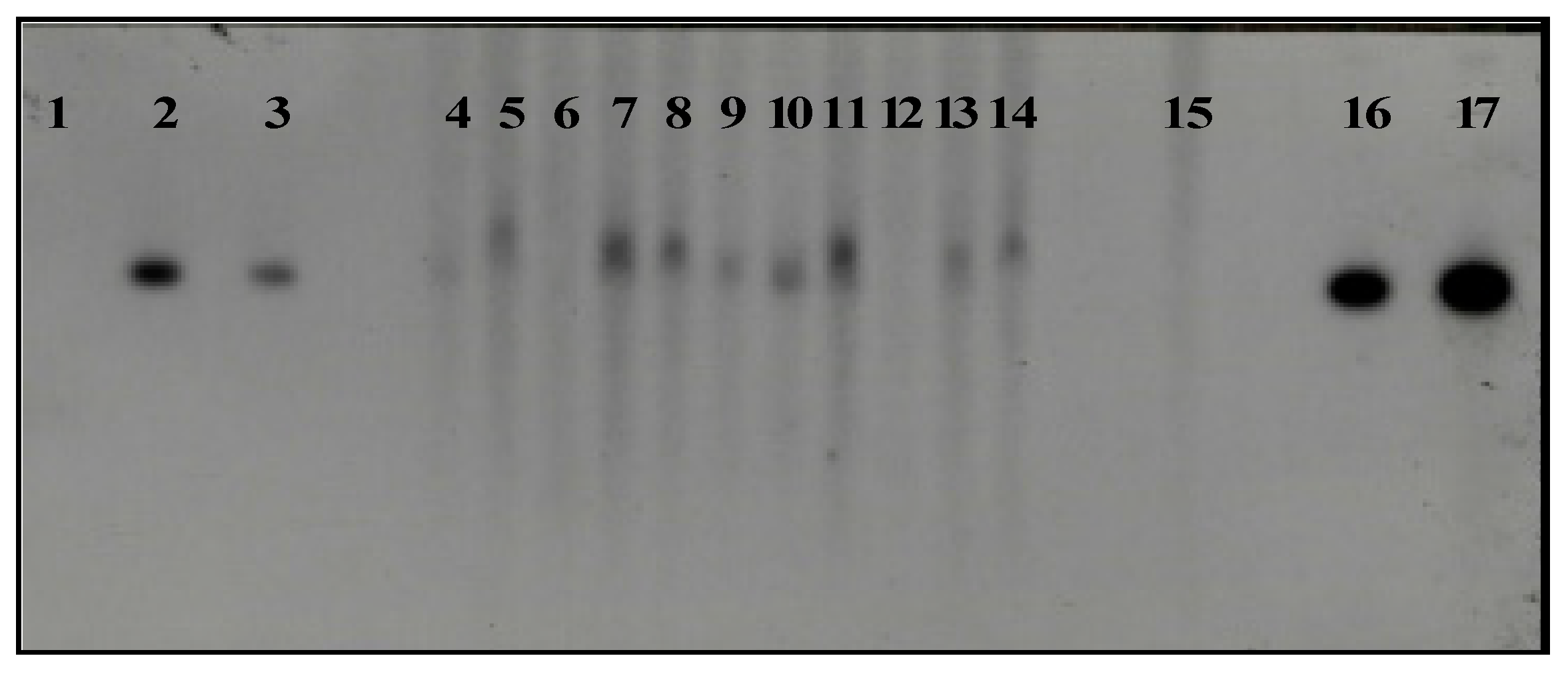

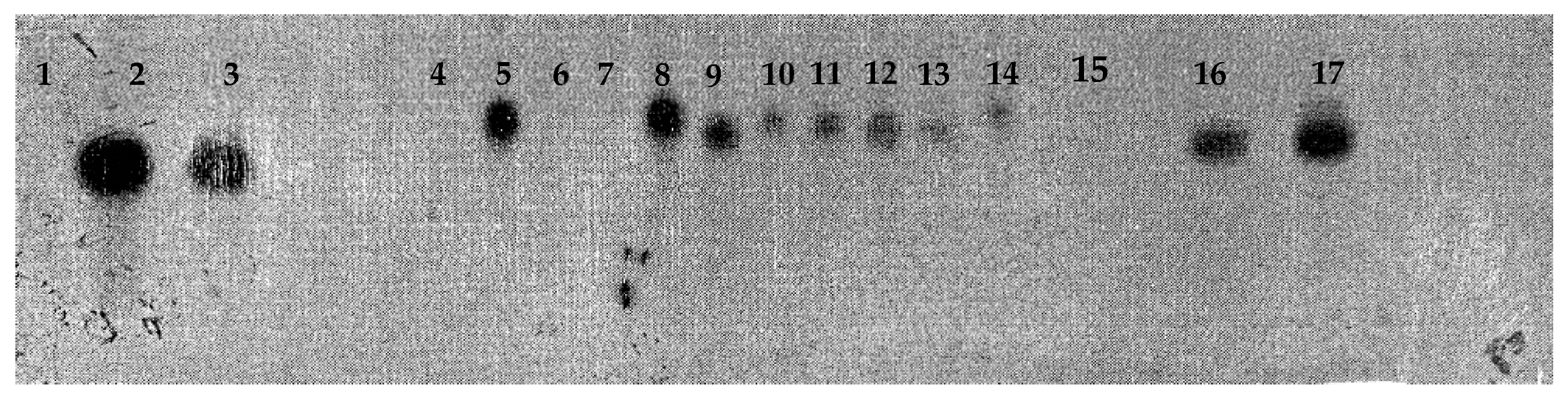
| Factor | Average transient expression of the uidA gene |
|---|---|
| Age of embryogenic tissue | |
| - Early - Differentiated |
229.535 ± 9.626 a 65.769 ± 5.340 b |
| A. tumefaciens strain | |
| - LBA4405 | 264.877 ± 12.176 a |
| - EHA105 | 99.759 ± 4.270 b |
| Co-culturing medium | |
| - Solid | 167.526 ± 80.923 a |
| - Liquid | 62.434 ± 54.765 b |
| Transformation vector | |
| - pC1301 | 164.199 ± 8.894 a |
| - pC2301 | 146.344 ± 9.150 b |
| Genotype | |
| - BK.620 | 172.437 ± 87.017 a |
| - BI.625 | 182.955 ± 87.810 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





