Submitted:
16 September 2024
Posted:
17 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Test Materials and Methods
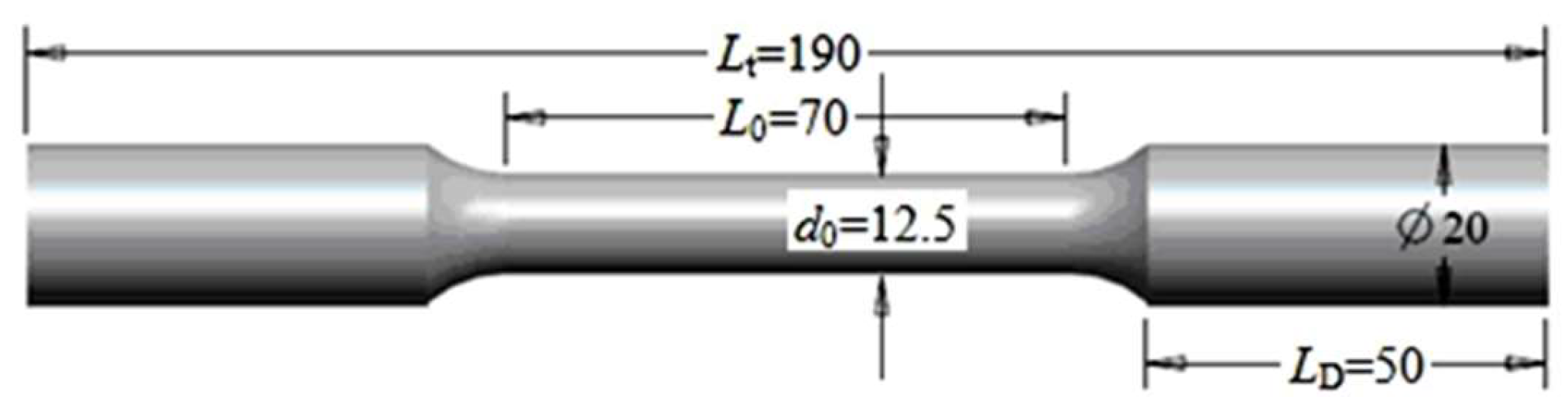
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Al-5Ti-1B-1RE Master Alloy Synthesized by Melt-Matching Method
2.2.2. Refinement Test Process
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Phase Analysis of Grain Refiner for Al-5Ti-1B-1RE Master Alloy
3.2. Calculation and Analysis of Thermodynamics
3.3. Crystallization Kinetics Analysis

3.4. Refinement Analysis of Different Grain Refiners
3.4.1. Analysis of Refining Effects of Different Grain Refiners
3.4.2. Analysis of Refining Properties of Different Grain Refiners
3.4.3. Analysis of Refinement Mechanism of Al-5Ti-1B-1RE Mater Alloy
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- When synthesizing a new Al-5Ti-1B-1RE master alloy grain refiner by melt matching method, the reaction generated by the second phase TiB2 and TiAl3 into the aluminium melt, Interaction with TiAl3 due to the presence of rare earths in the melt: 14Al+2TiAl3+ RE=Ti2Al20RE.
- (2)
- When the new Al-5Ti-1B-1RE master alloy grain refiner was synthesised by the melt-mixing method at synthesis temperature of 1103.15 K (830 °C), it was calculated that the magnitude of Gibbs free energy ΔG was ΔGTi2Al20RE<ΔGTiB2<ΔGAl3Ti.
- (3)
- When the temperature was appropriate, there was a certain degree of subcooling ΔT, the thermodynamic nucleation rate I1 and the kinetic nucleation rate I2 had an optimal fit, at which time the nucleation rate I reached the maximum value, and a “peak”appeared on the nucleation rate curve.
- (4)
- The mechanical properties of pure aluminum refined by Al-5Ti-1B-1RE master alloy were significantly better than those of pure aluminum added with equal amounts of domestic and imported Al-5Ti-1B wire master alloy. The tensile strength σb and elongation δ were increased by 11.94%, 8.29%, and 31.79%, 17.41%, respectively.
- (5)
- The refining mechanism of Al-5Ti-1B-1RE master alloy for industrial pure aluminum was a dual nucleation refining mechanism. Due to the addition of RE elements, the refining effect lasts longer.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, H.; Chakraborty, P.; Ponge, D.; Hickel, T.; Sun, B.; Wu, H.; Gault, T.; Raabel, D. Hydrogen trapping and embrittlement in high-strength Al alloys. Nature. 2022, 602, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Dong, C.; Chen, J.; Liu., L. Thermal Fatigue Crack Propagation Process and Mechanism of Multicomponent Al-7Si-0.3Mg Alloy. Crystals 2023, 13, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njuguna, B.; Li, J.; Tan, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, P. Grain refinement of primary silicon in hypereutectic Al-Si alloys by different P-containing compounds. China Foundry. 2021, 18, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Feng, L.; Wang, S.; Ji, G.; Addad, A.; Yang, H.; Nyberg, E.; Ji, S. On the exceptional creep resistance in a die-cast Gd-containing Mg alloy with Al addition. Acta Mater. 2022, 232, 117957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhou, T.; Xu, X.; Gao, Z.; Chen, Li. Refinement Mechanism Research of Al3Ni Phase in Ni-7050 Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 2013, 42, 0006–0013. [Google Scholar]
- Sotlz, U.; Sommer, F.; Sutttart, B. Phase Equilibrium of Aluminum-Rich AlTiB Alloys-Solubility of TiB2 in Aluminum Melts. Alum. 1995, 350–355. [Google Scholar]
- Birol, Y. Performance of Al–5Ti–1B and Al–3B grain refiners in investment casting of AlSi7Mg0.3 alloy with preheated ceramic moulds. Int J Cast Metal Res. 2013, 26, 283.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Si, N. Synthesis and Refinement Performance of the New Al-Ti-B-RE Master Alloy Grain Refiner. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2015, 44, 2970–2975. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Hong-Liang.; Yue, J.; Gao, Y.; Weng, K. Grain and dendrite refinement of A356 alloy with Al-Ti-C-RE master alloy. Rare Met. 2013, 32, 12–17. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Q.; Huang, T. Microstructure of Al-Ti-B-RE Master Alloy and Its Mechanism of Refining Pure Aluminum. J. Chin.Rare Earth Soc. 2007, 25, 597–602. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Liu, X. Ti transition zone on the interface between TiC and aluminum melt and its influence on melt viscosity. J. Mater Pro Tech. 2007, 182, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chai, L.; Ma, T.; Chen, Z. Synthesis of Al-5Ti-1B Refiner by Melt Recation Method. J. Mater Eng. 2017, 45, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Lv, J. Effect of Refinement and Modification on Microstructure, Properties and Eutectic Silicon Growth Mechanism of Cast A356 Aluminum Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2020, 49, 2665–2673. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Q.; Huang, T. Refining performance and long time efficiency of Al-Ti-B-RE master alloy. The Chin. J.Nonferrous Met. 2007, 17, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Lü, C.; Miao, H. Fabrication of a New Mg-50%Al4C3-6%Ce Master Alloy and Its Refinement Mechanism on AZ91D Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2013, 42, 0028–0031. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, G.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Weng, Y.; Song, T. Grain refinement effects of titanium added to commercial pure aluminum by electrolysis and by master alloys. Chin. J.Nonferrous Met. 2004, 14, 250–254. [Google Scholar]
- Nikitin, V.; Wan, Q.; Kandalova1, E.; Makarenko, A.; Yong, L. Preparation of Al-Ti-B grain refiner by SHS technology. Scripta Materialia, 2000, 42, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Song, T.; Weng, Y.; Zuo, X. Grain Refining of Aluminum Alloy with Titanium Added by Electrolysis and Structure and Properties of A-l Si Alloy Prepared with It. Light Alloy Fabrication Technology, 2005, 33, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Murty, B.; Kori, S. Venkateswarlu; Bhat, R.; Chakraborty, M. Manufacture of Al-Ti-B master alloys by the reaction of complex halide salts with molten aluminum. J. Mater Pro Tech. 1999, 89-90, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Xia, A. Development of Aluminum Boron and Aluminum Titanium Boron Master Alloys. Light Met. 1988, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Yang, G. Electrolytic production of aluminum alloy. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press. 2010.
- Lan, Y.; Zhu, Z. Master Alloys for Aluminum Alloys and Their Current Status. Light Met. 2004, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Yang, G.; Gu, S. Electrolytic production of aluminum based alloys. Special casting & nonferrous alloys. 2001, 102–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Li, P.; Zuo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, X. Research Progress of Al-Ti-B Grain Refiner: Mechanism Analysis and Second Phases Controlling. Mater Rev B: Rev Papers. 2020, 34, 09152–09163. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, Q.; Chen, Z.; Ma, Q.; Cai, D. Research progress of grain refinement behavior of Al-Ti-B in Al-Si alloys. Nonferrous Met. Mater. Eng. 2022, 43, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wang., K.; Cui, C.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Gu, C. The microstructure and formation mechanism of core-shell-like TiAl3/Ti2Al20Ce in melt-spun Al-Ti-B-Re grain refiner. Mater. Lett. 2012, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Cui, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Y. Microstructure of Al-5Ti-1B-1RE nanoribbon and its refining efficiency on as-cast A356 alloys. J. Rare Earths. 2013, 31, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; He, J.; Zhao, J. Mechanism of grain refinement in Al-Cu alloy by adding trace La and Al-5Ti-1B. Acta Phys. Sin. 2023, 72, 086401–086408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Tan, Y. Metallography and heat treatment. Beijing: China Machine Press.2007.
- Huang, Z. Composition optimization, microstructure and properties research of cast AlSi7Cu2Mg alloy. Taiyuan: Master's thesis from North China University. 2009.
- Wang, Z.; Si, N. The Effect of the Morphology and Distribution of the Second Phases of Al-Ti-B-RE Master Alloys on Refining Commercially Pure Aluminum. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2015, 44, 1494–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Bian, X. Master alloy for microstructure refinement of aluminum alloy. Changsha: Central South University Press. 2012.
- Ye, D.; Hu, J. Practical Handbook of the Thermodynamic Data for Inorganic Substances. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2002.
- Wang, Z. Fundamentals of Materials Science. Beijing: China Machine Press. 2023.
- Cai, Xun. Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press. 2017.
- Chen, X.; Geng, H.; Li, Y. Quantitative metallographic analysis of modification level of hypoeutectic Al-Si alloys. Acta Metall Sin. 2005, 41, 891–896. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yang, L.; Peng, L.; Ding, W. Strengthening-Toughening of High-Strength Al-Zn Cast Aluminum Alloys: Research Progress and Prospects. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2023, 52, 3954–3970. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Pan, F.; Chen, X.; Tang, A.; Peng, J. Research and Development of Purification Technologies of Aluminum Alloy Melt. Mater Rev. 2009, 23, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Huang, D.; Jiang, H. Research progress of aluminum alloys for automobiles. Heat Treat Met. 2006, 31, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Y.; Guo, P.; Zhang, J. The Effect of Rare-earth on the Refining Property of the Al-Ti-B-RE Master Alloys. Foundry Tech. 2005, 26, 774–775. [Google Scholar]







| Alloying Element | Ti | B | RE | Fe | Si | Cu | Ni | Al | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal composition | 5.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.10 | Bal | |
| Actual measurement value | 5.06 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.05 | Bal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




