Submitted:
28 August 2024
Posted:
29 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
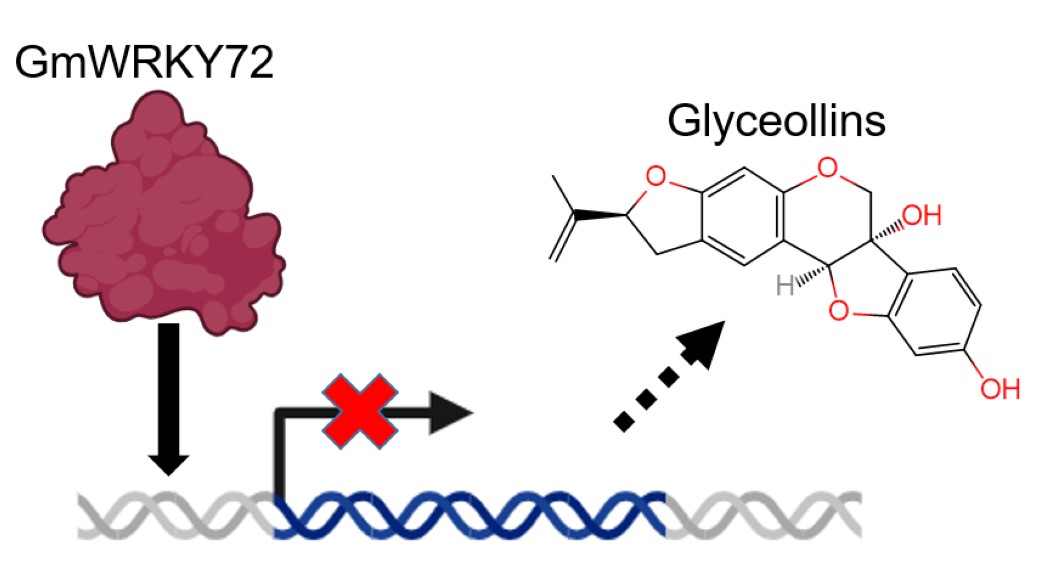
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
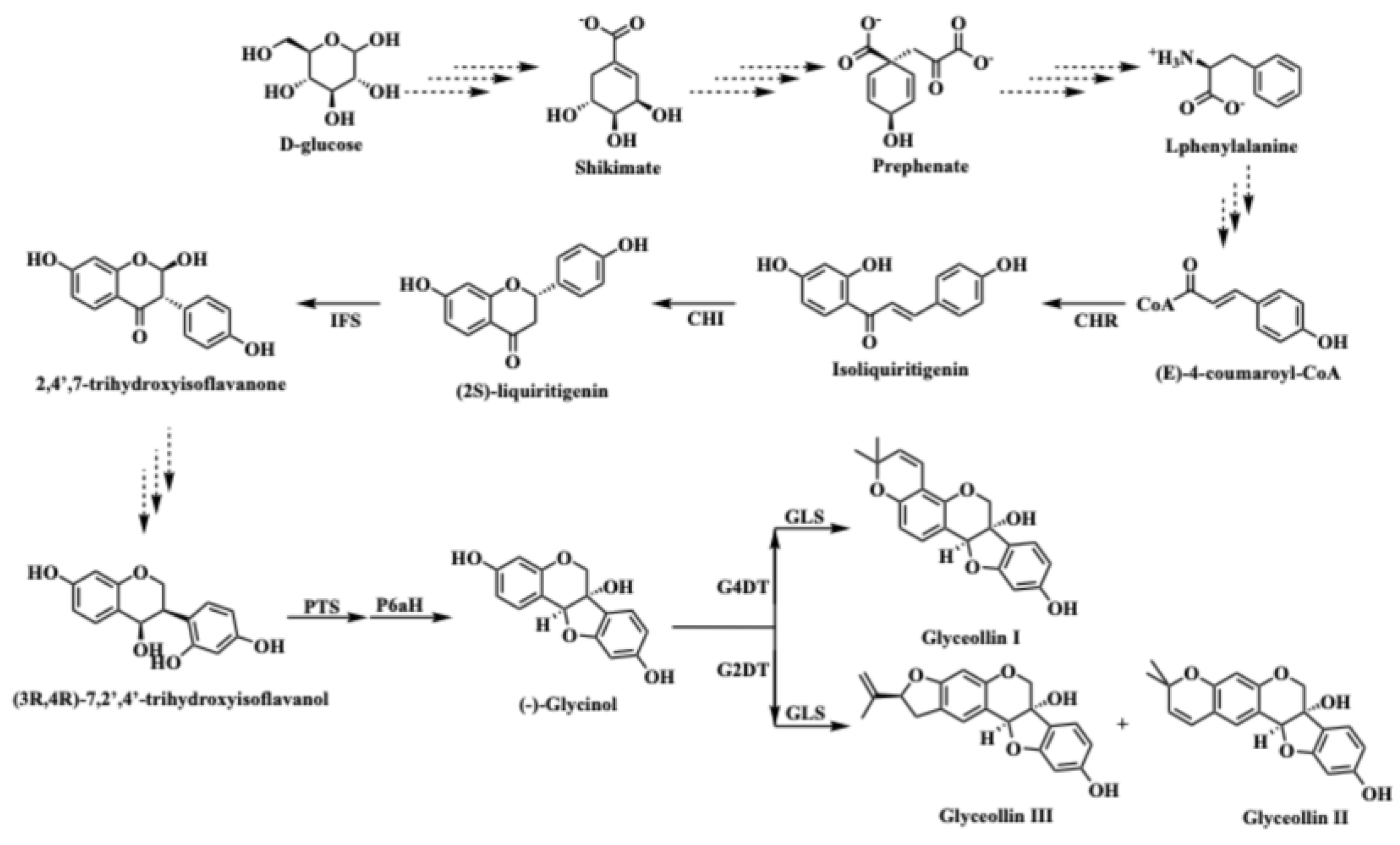
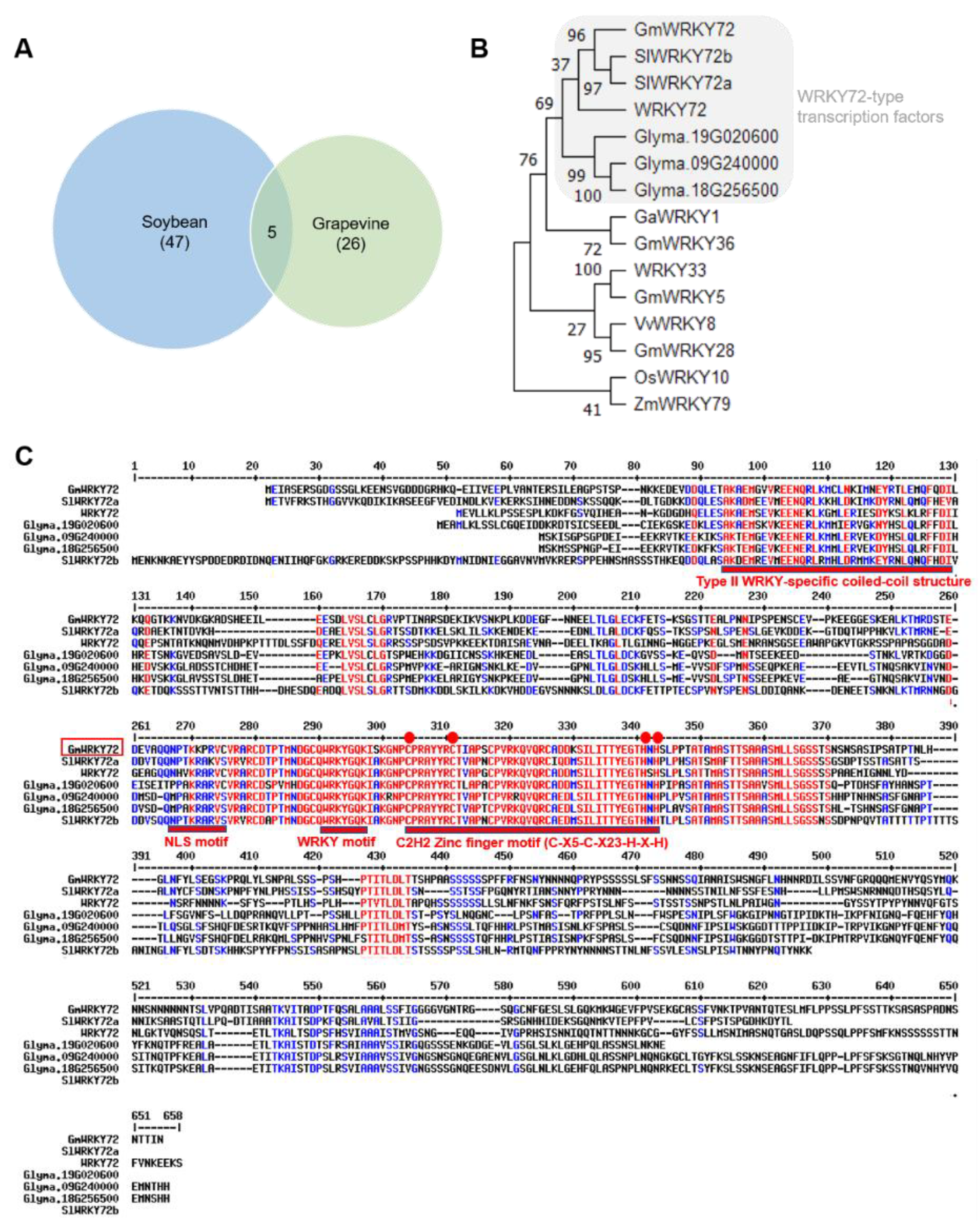
2.1. RNA-seq Identifies GmWRKY72 as a Candidate Regulator of Glyceollin Biosynthesis
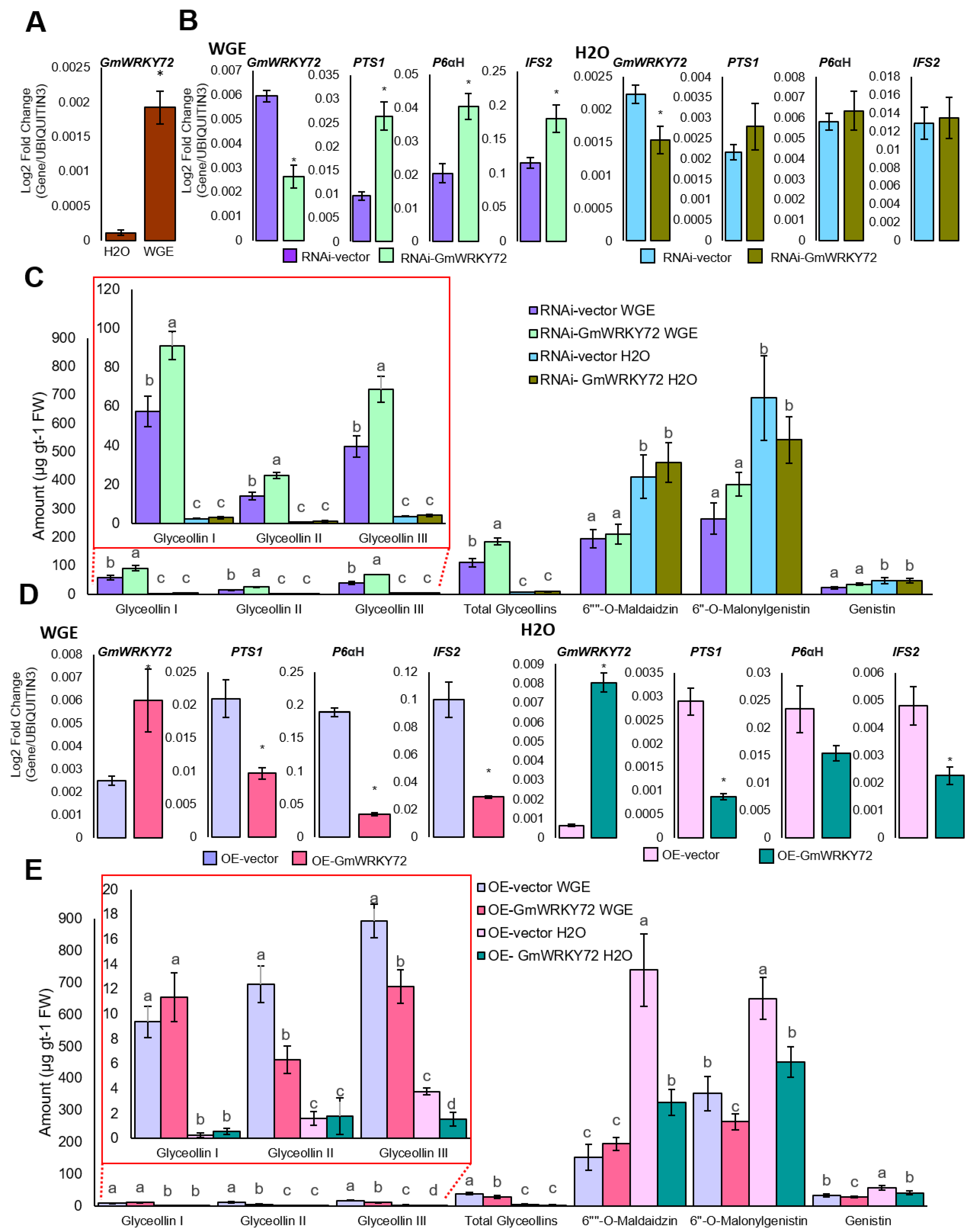
2.2. GmWRKY72 Negatively Regulates Glyceollin Biosynthesis
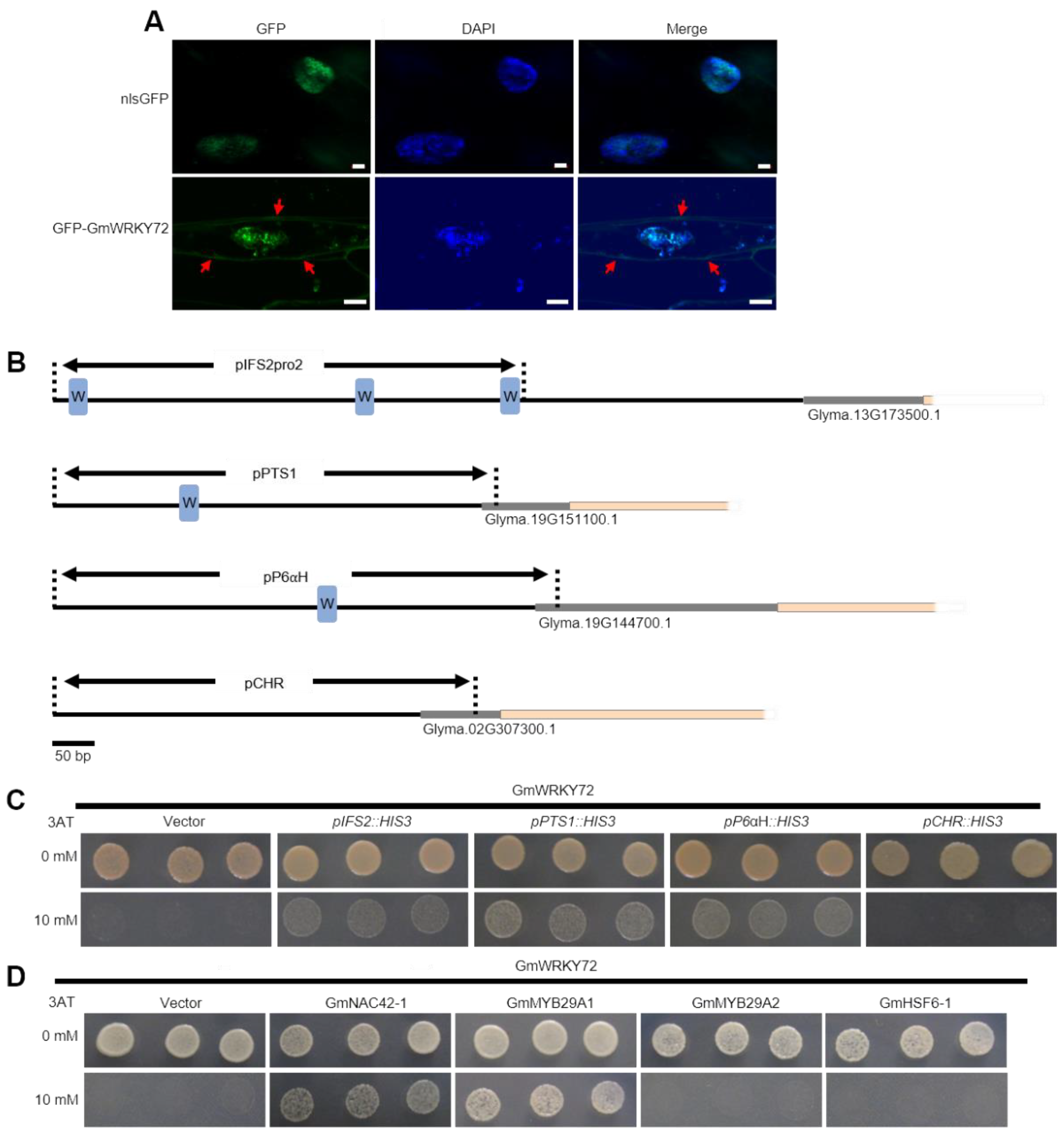
2.3. GmWRKY72 Localizes to the Nucleus and Directly Binds Glyceollin Transcription Factors and Biosynthesis Gene Promoters
3. Discussion
3.1. GmWRKY72 is a Negative Regulator of Glyceollin Biosynthesis in Soybean
3.2. Subfunctionalization among WRKY72-Type Transcription Factors
3.3. Growing Evidence of Phytoalexin Transcription Factor Complexes
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Cloning and Plasmid Constructs
4.3. Transcriptome Data Analysis
4.4. Hairy Root Transformation and Elicitation
4.5. Isoflavonoids Analyses
4.6. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Measurements
4.7. Subcellular Localization
4.8. Yeast Hybrid Assays
4.9. Statistical Analysis
4.10. Accession Numbers
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pruitt, R.N.; Locci, F.; Wanke, F.; Zhang, L.; Saile, S.C.; Joe, A.; Karelina, D.; Hua, C.; Fröhlich, K.; Wan, W.-L.J.N. The EDS1–PAD4–ADR1 node mediates Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity. 2021, 598, 495-499.
- Pruitt, R.N.; Gust, A.A.; Nürnberger, T.J.N.p. Plant immunity unified. 2021, 7, 382-383. [CrossRef]
- Legein, M.; Smets, W.; Vandenheuvel, D.; Eilers, T.; Muyshondt, B.; Prinsen, E.; Samson, R.; Lebeer, S.J.F.i.m. Modes of action of microbial biocontrol in the phyllosphere. 2020, 11, 1619. [CrossRef]
- Saijo, Y.; Loo, E.P.i.; Yasuda, S.J.T.P.J. Pattern recognition receptors and signaling in plant–microbe interactions. 2018, 93, 592-613. [CrossRef]
- Lygin, A.V.; Zernova, O.V.; Hill, C.B.; Kholina, N.A.; Widholm, J.M.; Hartman, G.L.; Lozovaya, V.V.J.P. Glyceollin is an important component of soybean plant defense against Phytophthora sojae and Macrophomina phaseolina. 2013, 103, 984-994. [CrossRef]
- Lygin, A.V.; Li, S.; Vittal, R.; Widholm, J.M.; Hartman, G.L.; Lozovaya, V.V.J.P. The importance of phenolic metabolism to limit the growth of Phakopsora pachyrhizi. 2009, 99, 1412-1420. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Lin, J.; Johnson, A.; Morgan, R.L.; Zhong, W.; Ma, W.J.C.h.; microbe. Pseudomonas syringae type III effector HopZ1 targets a host enzyme to suppress isoflavone biosynthesis and promote infection in soybean. 2011, 9, 177-186. [CrossRef]
- Graham, T.L.; Graham, M.Y.; Subramanian, S.; Yu, O.J.P.p. RNAi silencing of genes for elicitation or biosynthesis of 5-deoxyisoflavonoids suppresses race-specific resistance and hypersensitive cell death in Phytophthora sojae infected tissues. 2007, 144, 728-740. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Li, N.; Dong, L.; Zhang, D.; Fan, S.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, P.; Zhang, S.J.F.i.p.s. Overexpression of soybean isoflavone reductase (GmIFR) enhances resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean. 2015, 6, 1024. [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.A.; Harris, B.; Lowery, M.; Infante, A.M.; Percifield, R.J.; Kovinich, N.J.P.P. Glyceollin transcription factor GmMYB29A2 regulates soybean resistance to Phytophthora sojae. 2020, 183, 530-546. [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.A.; Harris, B.; Lowery, M.; Coburn, K.; Infante, A.M.; Percifield, R.J.; Ammer, A.G.; Kovinich, N.J.B.g. The NAC family transcription factor GmNAC42–1 regulates biosynthesis of the anticancer and neuroprotective glyceollins in soybean. 2019, 20, 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Monsalvo, I.; Ly, M.; Jahan, M.A.; Wi, D.; Martirosyan, I.; Kovinich, N. RNA-Seq Dissects Incomplete Activation of Phytoalexin Biosynthesis by the Soybean Transcription Factors GmMYB29A2 and GmNAC42-1. Plants 2023, 12, 545. [CrossRef]
- Saga, H.; Ogawa, T.; Kai, K.; Suzuki, H.; Ogata, Y.; Sakurai, N.; Shibata, D.; Ohta, D.J.M.p.-m.i. Identification and characterization of ANAC042, a transcription factor family gene involved in the regulation of camalexin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. 2012, 25, 684-696.
- Chezem, W.R.; Memon, A.; Li, F.-S.; Weng, J.-K.; Clay, N.K.J.T.P.C. SG2-type R2R3-MYB transcription factor MYB15 controls defense-induced lignification and basal immunity in Arabidopsis. 2017, 29, 1907-1926. [CrossRef]
- Monsalvo, I.; Lin, J.; Kovinich, N.J.C.P.B. Phytoalexin Gene Regulation in Arabidopsis thaliana-On the Verge of a Paradigm Shift? 2024, 100367. [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; He, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Jia, N.J.H. Glyceollins from soybean: Their pharmacological effects and biosynthetic pathways. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Lecomte, S.; Efstathiou, T.; Ferriere, F.; Pakdel, F.J.N. An update on the effects of glyceollins on human health: possible anticancer effects and underlying mechanisms. 2019, 11, 79. [CrossRef]
- Bamji, S.F.; Corbitt, C.J.J.o.F.F. Glyceollins: Soybean phytoalexins that exhibit a wide range of health-promoting effects. 2017, 34, 98-105.
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Ou, Z.; Peng, Z.; Fu, C.; Zhao, C.; Yu, L.J.F.i.P.S. Salicylic acid-responsive factor TcWRKY33 positively regulates taxol biosynthesis in Taxus chinensis in direct and indirect ways. 2021, 12, 697476. [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, T.; Deepa, B.J.I.J.E.T.M.S. Phytoalexins: defend systems of plants and pharmacological potential—a systematic review. 2023, 7, 319-326. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Kovinich, N.J.P.R. Regulation of phytoalexin biosynthesis for agriculture and human health. 2021, 20, 483-505. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Ye, J.; Xu, F.J.P. Contemporary understanding of transcription factor regulation of terpenoid biosynthesis in plants. 2024, 259, 2. [CrossRef]
- Andreasson, E.; Jenkins, T.; Brodersen, P.; Thorgrimsen, S.; Petersen, N.H.; Zhu, S.; Qiu, J.L.; Micheelsen, P.; Rocher, A.; Petersen, M.J.T.E.j. The MAP kinase substrate MKS1 is a regulator of plant defense responses. 2005, 24, 2579-2589. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Qamar, S.A.; Chen, Z.; Mengiste, T.J.T.P.J. Arabidopsis WRKY33 transcription factor is required for resistance to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. 2006, 48, 592-605. [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Meng, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.J.T.P.C. Phosphorylation of a WRKY transcription factor by two pathogen-responsive MAPKs drives phytoalexin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. 2011, 23, 1639-1653. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.L.; Fiil, B.K.; Petersen, K.; Nielsen, H.B.; Botanga, C.J.; Thorgrimsen, S.; Palma, K.; Suarez-Rodriguez, M.C.; Sandbech-Clausen, S.; Lichota, J.J.T.E.j. Arabidopsis MAP kinase 4 regulates gene expression through transcription factor release in the nucleus. 2008, 27, 2214-2221. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Sang, T.; Wang, P.; Dai, S.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X.J.P.C. Differential phosphorylation of the transcription factor WRKY33 by the protein kinases CPK5/CPK6 and MPK3/MPK6 cooperatively regulates camalexin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. 2020, 32, 2621-2638.
- Verma, V.; Srivastava, A.K.; Gough, C.; Campanaro, A.; Srivastava, M.; Morrell, R.; Joyce, J.; Bailey, M.; Zhang, C.; Krysan, P.J.J.P.o.t.N.A.o.S. SUMO enables substrate selectivity by mitogen-activated protein kinases to regulate immunity in plants. 2021, 118, e2021351118. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Mu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Huang, T.; He, Y.; Dai, S.; Meng, X.J.T.P.C. Multilayered synergistic regulation of phytoalexin biosynthesis by ethylene, jasmonate, and MAPK signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. 2022, 34, 3066-3087. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-H.; Wang, J.-W.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.-Y.; Chen, X.-Y.J.P.p. Characterization of GaWRKY1, a cotton transcription factor that regulates the sesquiterpene synthase gene (+)-δ-cadinene synthase-A. 2004, 135, 507-515.
- Wang, L.; Fu, J.; Shen, Q.; Wang, Q.J.T.P.J. OsWRKY10 extensively activates multiple rice diterpenoid phytoalexin biosynthesis genes to enhance rice blast resistance. 2023, 115, 758-771. [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Liang, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.J.J.o.E.B. ZmWRKY79 positively regulates maize phytoalexin biosynthetic gene expression and is involved in stress response. 2018, 69, 497-510. [CrossRef]
- Schmutz, J.; Cannon, S.B.; Schlueter, J.; Ma, J.; Mitros, T.; Nelson, W.; Hyten, D.L.; Song, Q.; Thelen, J.J.; Cheng, J.J.n. Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. 2010, 463, 178-183. doi:10.1038/nature08670.
- Song, H.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.J.P.S. WRKY transcription factors: Understanding the functional divergence. 2023, 334, 111770. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, B.; Chen, Z.J.J.o.E.B. Functional analysis of structurally related soybean GmWRKY58 and GmWRKY76 in plant growth and development. 2016, 67, 4727-4742. [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Liu, M.; Chen, Q.; Lai, Y.; He, C.J.J.o.E.B. Differential expression of a WRKY gene between wild and cultivated soybeans correlates to seed size. 2017, 68, 2717-2729. [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.-Y.; Du, Y.-T.; Ma, J.; Min, D.-H.; Jin, L.-G.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Ma, Y.-Z.; Xu, Z.-S.J.I.J.o.M.S. The WRKY transcription factor GmWRKY12 confers drought and salt tolerance in soybean. 2018, 19, 4087. [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Cai, Z.; Nian, H.; Ma, Q.J.F.i.P.S. GmWRKY21, a soybean WRKY transcription factor gene, enhances the tolerance to aluminum stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. 2022, 13, 833326. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Cui, R.; Xu, H.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, D.J.P.S. GmWRKY46, a WRKY transcription factor, negatively regulates phosphorus tolerance primarily through modifying root morphology in soybean. 2022, 315, 111148. [CrossRef]
- Bencke-Malato, M.; Cabreira, C.; Wiebke-Strohm, B.; Bücker-Neto, L.; Mancini, E.; Osorio, M.B.; Homrich, M.S.; Turchetto-Zolet, A.C.; De Carvalho, M.C.; Stolf, R.J.B.p.b. Genome-wide annotation of the soybean WRKY family and functional characterization of genes involved in response to Phakopsora pachyrhizi infection. 2014, 14, 1-18.
- Lin, J.; Wi, D.; Ly, M.; Jahan, M.A.; Pullano, S.; Martirosyan, I.; Kovinich, N.J.J. Soybean Hairy Root Transformation for the Analysis of Gene Function. 2023, e65485. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chi, Y.; Fan, B.; Chen, Z.J.S.r. Characterization of soybean WRKY gene family and identification of soybean WRKY genes that promote resistance to soybean cyst nematode. 2017, 7, 17804. [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Yan, Q.; Gan, S.; Xue, D.; Wang, H.; Xing, H.; Zhao, J.; Guo, N.J.B.P.B. GmWRKY40, a member of the WRKY transcription factor genes identified from Glycine max L., enhanced the resistance to Phytophthora sojae. 2019, 19, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Vannozzi, A.; Wong, D.C.J.; Höll, J.; Hmmam, I.; Matus, J.T.; Bogs, J.; Ziegler, T.; Dry, I.; Barcaccia, G.; Lucchin, M. Combinatorial regulation of stilbene synthase genes by WRKY and MYB transcription factors in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Cell Physiology 2018, 59, 1043-1059. [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, K.K.; Atamian, H.S.; Kaloshian, I.; Eulgem, T.J.T.P.J. WRKY72-type transcription factors contribute to basal immunity in tomato and Arabidopsis as well as gene-for-gene resistance mediated by the tomato R gene Mi-1. 2010, 63, 229-240.
- Rinerson, C.I.; Rabara, R.C.; Tripathi, P.; Shen, Q.J.; Rushton, P.J.J.B.p.b. The evolution of WRKY transcription factors. 2015, 15, 1-18. [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Devi, R.; Verma, B.; Hussain, S.; Arora, P.; Tabassum, R.; Gupta, S.J.P. WRKY transcription factors: Evolution, regulation, and functional diversity in plants. 2023, 260, 331-348. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Tian, A.G.; Zou, H.F.; Xie, Z.M.; Lei, G.; Huang, J.; Wang, C.M.; Wang, H.W.; Zhang, J.S.; Chen, S.Y.J.P.b.j. Soybean WRKY-type transcription factor genes, GmWRKY13, GmWRKY21, and GmWRKY54, confer differential tolerance to abiotic stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. 2008, 6, 486-503.
- Tao, H.; Miao, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, M.; Xia, C.; Zeng, W.; Sun, B.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, C. WRKY33-mediated indolic glucosinolate metabolic pathway confers resistance against Alternaria brassicicola in Arabidopsis and Brassica crops. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 2022, 64, 1007-1019.
- Jiang, J.; Xi, H.; Dai, Z.; Lecourieux, F.; Yuan, L.; Liu, X.; Patra, B.; Wei, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, L.J.J.o.E.B. VvWRKY8 represses stilbene synthase genes through direct interaction with VvMYB14 to control resveratrol biosynthesis in grapevine. 2019, 70, 715-729. [CrossRef]
- Javed, T.; Gao, S.-J.J.T.i.G. WRKY transcription factors in plant defense. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Graham, M.Y.; Yu, O.; Graham, T.L.J.P.P. RNA interference of soybean isoflavone synthase genes leads to silencing in tissues distal to the transformation site and to enhanced susceptibility to Phytophthora sojae. 2005, 137, 1345-1353. [CrossRef]
- Ayers, A.R.; Ebel, J.r.; Finelli, F.; Berger, N.; Albersheim, P.J.P.p. Host-pathogen interactions: IX. Quantitative assays of elicitor activity and characterization of the elicitor present in the extracellular medium of cultures of Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae. 1976, 57, 751-759.
- Glawischnig, E.J.P. Camalexin. 2007, 68, 401-406.
- Liu, F.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Wen, J.; Yi, B.; Shen, J.; Ma, C.; Fu, T.; Tu, J.J.P.B.J. Interactions of WRKY 15 and WRKY 33 transcription factors and their roles in the resistance of oilseed rape to Sclerotinia infection. 2018, 16, 911-925.
- Ramos, R.N.; Martin, G.B.; Pombo, M.A.; Rosli, H.G.J.P.m.b. WRKY22 and WRKY25 transcription factors are positive regulators of defense responses in Nicotiana benthamiana. 2021, 105, 65-82. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Mosher, S.L.; Fan, B.; Klessig, D.F.; Chen, Z.J.B.p.B. Functional analysis of Arabidopsis WRKY25 transcription factor in plant defense against Pseudomonas syringae. 2007, 7, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.-H.; Lai, Z.-B.; Zheng, Z.-Y.; Vinod, K.; Fan, B.-F.; Chen, Z.-X.J.M.p. Stress-and pathogen-induced Arabidopsis WRKY48 is a transcriptional activator that represses plant basal defense. 2008, 1, 459-470. [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Durán, R.; Macho, A.P.; Boutrot, F.; Segonzac, C.; Somssich, I.E.; Zipfel, C.J.e. The transcriptional regulator BZR1 mediates trade-off between plant innate immunity and growth. 2013, 2, e00983. [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Leib, K.; Zhao, P.; Kogel, K.-H.; Langen, G.J.M.g.; genomics. Phylogenetic analysis of barley WRKY proteins and characterization of HvWRKY1 and-2 as repressors of the pathogen-inducible gene HvGER4c. 2014, 289, 1331-1345. [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Zhang, L.; Fan, R.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Qi, T.; Zhao, L.; Yu, D.; Shen, Q.-H.J.J.o.G.; Genomics. HvMPK4 phosphorylates HvWRKY1 to enhance its suppression of barley immunity to powdery mildew fungus. 2024, 51, 313-325. [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, L.; Tong, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Huang, S.; Zhang, J.J.I. SAPK10-mediated phosphorylation on WRKY72 releases its suppression on jasmonic acid biosynthesis and bacterial blight resistance. 2019, 16, 499-510. [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.W.-K.; Abeysinghe, J.K.; Kamali, M. Regulating the Regulators: The Control of Transcription Factors in Plant Defense Signaling. 2018, 19, 3737. [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, S.; Mori, M.; Sugano, S.; Takatsuji, H.J.P.; Physiology, C. Transcription factor WRKY62 plays a role in pathogen defense and hypoxia-responsive gene expression in rice. 2016, 57, 2541-2551. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Luo, Q.; Yao, Q.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Duan, D.J.P.S. VqNAC44 enhances stilbene synthesis and disease resistance in Chinese wild grape by interacting with VqMYB15. 2024, 341, 111994. [CrossRef]
- Farrell, K.; Jahan, M.A.; Kovinich, N.J.M. Distinct mechanisms of biotic and chemical elicitors enable additive elicitation of the anticancer phytoalexin glyceollin I. 2017, 22, 1261. [CrossRef]
| Soybean gene name | Grapevine gene name | TF family | Soybean gene ID | Grapevine gene ID | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GmNAC42-1 | VviNAC36 | NAC/S6 | Glyma.02G284300 | VIT_12s0028g00860 | [11] |
| GmNAC42-2 | VviNAC36 | NAC/S6 | Glyma.14G030700 | VIT_12s0028g00860 | - |
| GmHSF6-1 | VviHsfB3a | HSF/A | Glyma.03G135800 | VIT_08s0007g08750 | [12] |
| GmMYB215 | VviMYB15 | R2R3-MYB/S2 | Glyma.10G180800 | VIT_05s0049g01020 | - |
| GmWRKY72 | VviWRKY53 | WRKY/llb | Glyma.17G097900 | VIT_17s0000g05810 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





