Submitted:
28 August 2024
Posted:
29 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
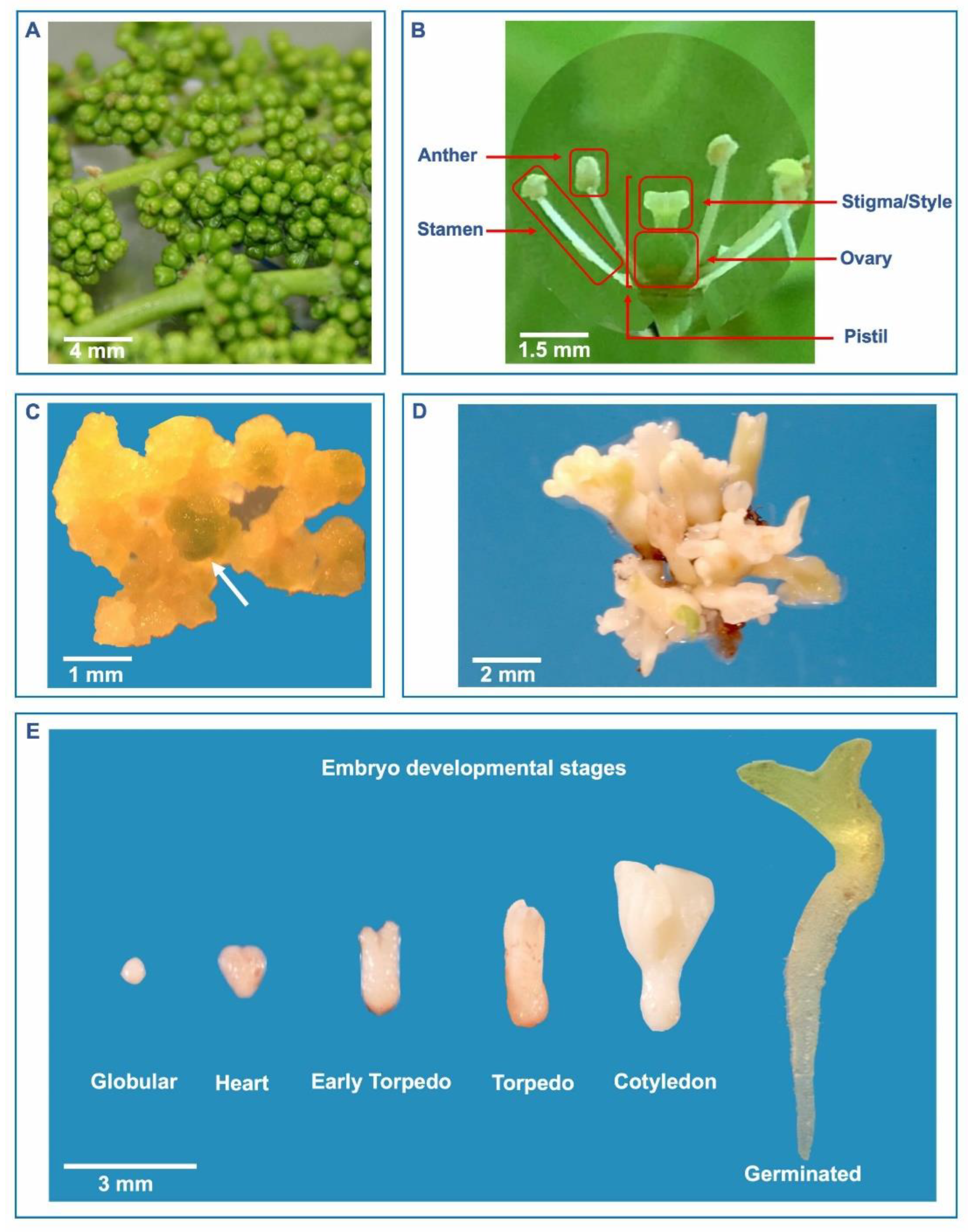
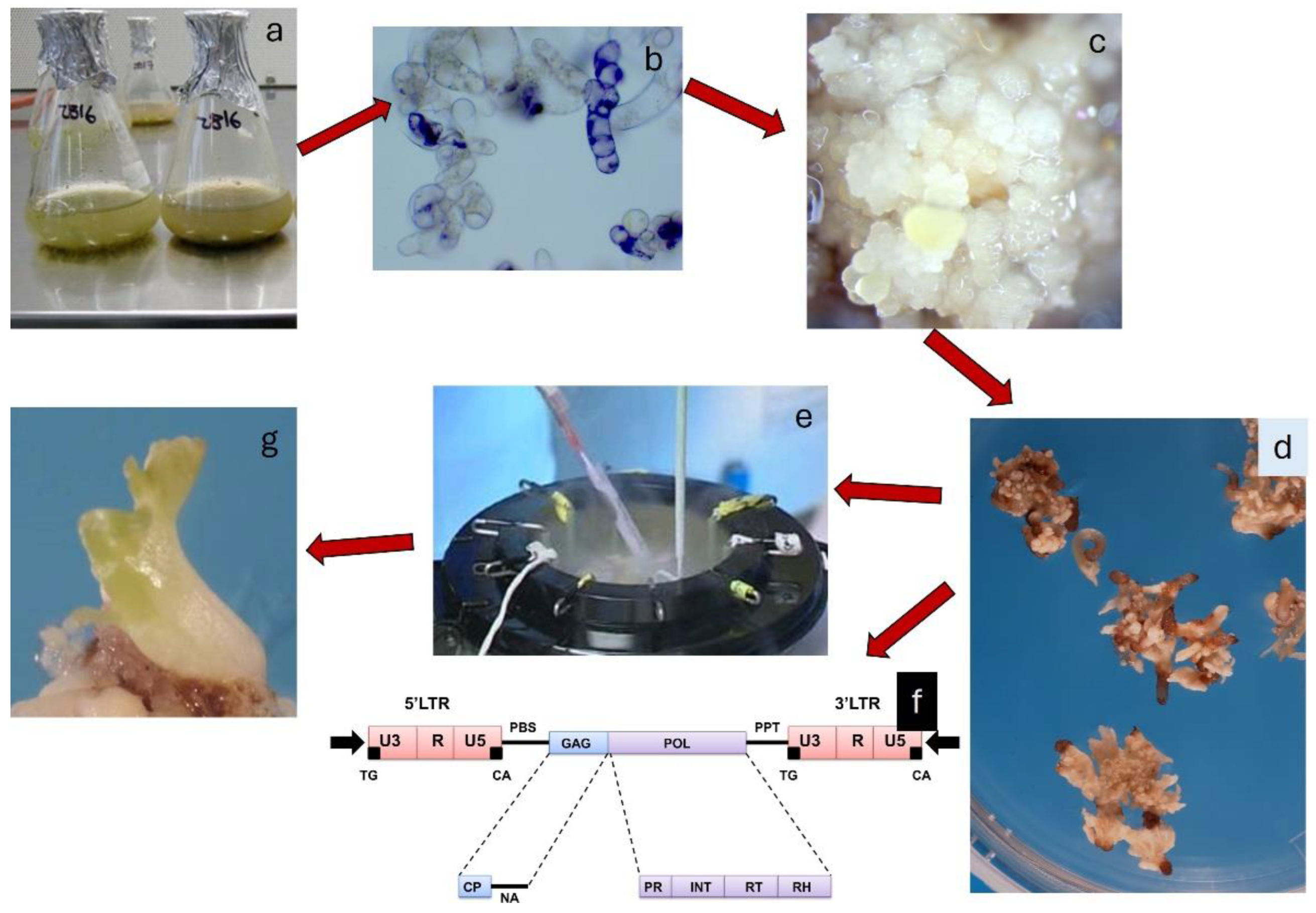
2. Explant Sources and Stages of Somatic Embryogenesis in Grapevine
3. Synchronisation of Somatic Embryo Production and Their Germination
4. Factors Affecting Somatic Embryogenesis in Grapevine
4.1. Genetic Control
4.2. Other Factors Controlling Somatic Embryogenesis
5. Applications of Somatic Embryogenesis and Embryogenic Cultures in Vitis
5.1. Somatic Embryogenesis for Germplasm Management
5.2. Somatic Embryogenesis as a Tool for Sanitation
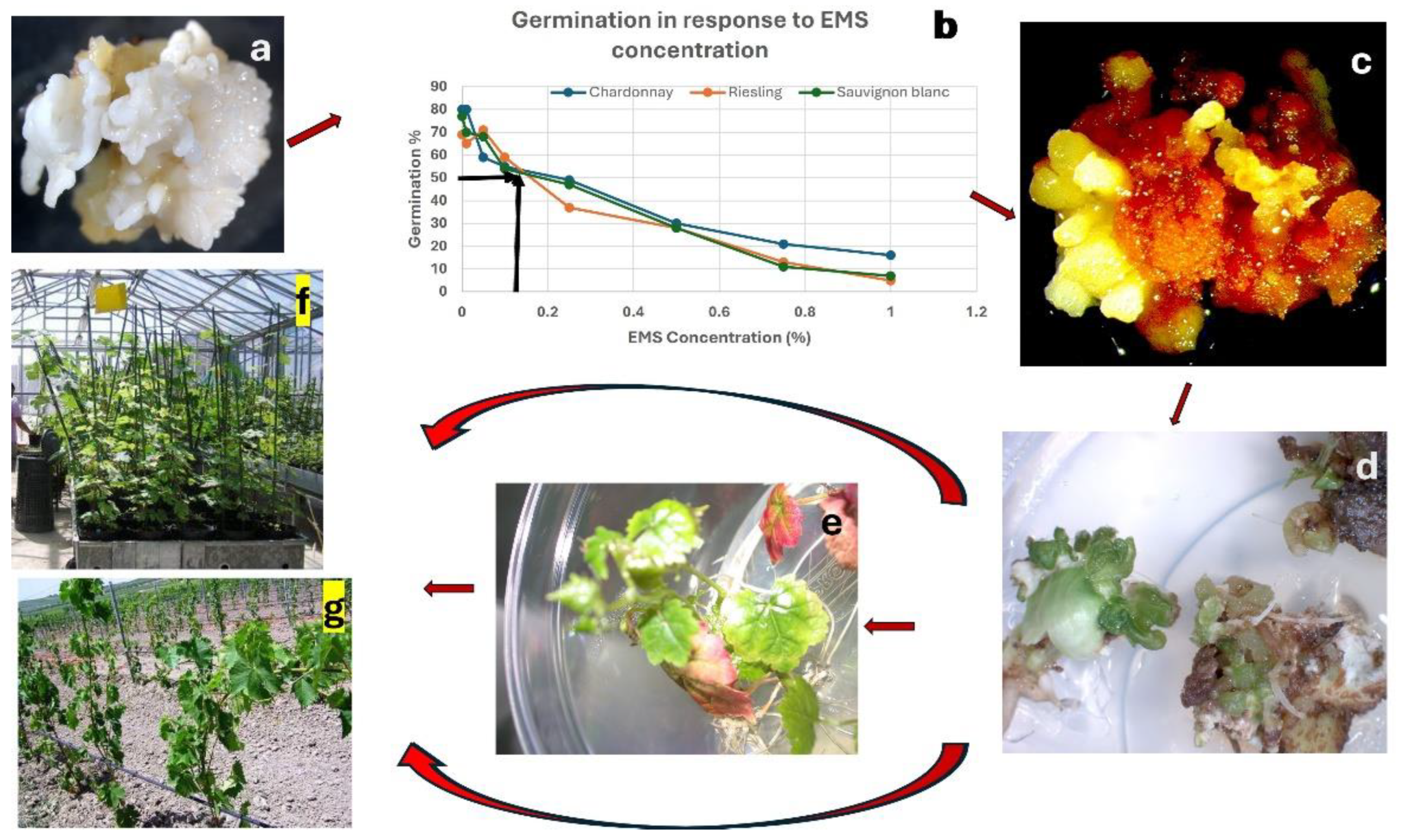
5.3. Induced Mutagenesis for Grapevine Improvement
5.4. Genetic Engineering
6. Genetic Stability of Plants Regenerated from Somatic Embryos
6.1. Somaclonal Variation
6.2. Chimerism in Grapevine and Segregation of Genotypes Through Somatic Embryogenesis
7. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, Y.H.; Tang, L.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, X.S. Plant cell totipotency: Insights into cellular reprogramming. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 2021, 63, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaün, C.; Lepiniec, L.; Dubreucq, B. Genetic and molecular control of somatic embryogenesis. Plants 2021, 10, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberlandt, G. Culturversuche mit isolierten Pflanzenzellen. In Plant Tissue Culture: 100 Years Since Gottlieb Haberlandt; Springer: 2003; pp. 1–24.
- Gautheret, R. Plant Tissue Culture: 100 Years since Gottlieb Haberlandt. New York: SpringWien 2003, 205-214.
- Haberlandt, G. Zelle und Elementarorgan. BioI. Zentralbl. 1925, 45, 257–272. [Google Scholar]
- Höxtermann, E. Cellular ‘elementary organisms’ in vitro. The early vision of Gottlieb Haberlandt and its realization. Physiologia Plantarum 1997, 100, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward, F.; Mapes, M.O.; Mears, K. Growth and organized development of cultured cells. II. Organization in cultures grown from freely suspended cells. American Journal of Botany 1958, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M. Historical review of research on plant cell dedifferentiation. Journal of Plant Research 2015, 128, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuchi, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Iwase, A.; Sugimoto, K. Plant regeneration: cellular origins and molecular mechanisms. Development 2016, 143, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, A.; Bemer, M.; Boutilier, K. A transcriptional view on somatic embryogenesis. Regeneration 2017, 4, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Hernández, H.A.; Ledezma-Rodríguez, M.; Avilez-Montalvo, R.N.; Juárez-Gómez, Y.L.; Skeete, A.; Avilez-Montalvo, J.; De-la-Peña, C.; Loyola-Vargas, V.M. Signaling overview of plant somatic embryogenesis. Frontiers in Plant Science 2019, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyola-Vargas, V.M.; Ochoa-Alejo, N. Somatic embryogenesis. An overview. In Somatic Embryogenesis. Fundamental Aspects and Applications, Loyola-Vargas, V.M., Ochoa-Alejo, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Catalano, C.; Abbate, L.; Motisi, A.; Crucitti, D.; Cangelosi, V.; Pisciotta, A.; Di Lorenzo, R.; Carimi, F.; Carra, A. Autotetraploid emergence via somatic embryogenesis in Vitis vinifera induces marked morphological changes in shoots, mature leaves, and stomata. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Iaffaldano, B.; Qi, Y. CRISPR ribonucleoprotein-mediated genetic engineering in plants. Plant communications 2021, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carra, A.; Sajeva, M.; Abbate, L.; Siragusa, M.; Pathirana, R.; Carimi, F. Factors affecting somatic embryogenesis in eight Italian grapevine cultivars and the genetic stability of embryo-derived regenerants as assessed by molecular markers. Scientia Horticulturae 2016, 204, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, S.; De Pasquale, F.; Carimi, F.; Sajeva, M. Effect of 2, 4-D and 4-CPPU on somatic embryogenesis from stigma and style transverse thin cell layers of Citrus. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 2002, 68, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonga, J.M.; Klimaszewska, K.K.; von Aderkas, P. Recalcitrance in clonal propagation, in particular of conifers. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 2009, 100, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carimi, F.; Barizza, E.; Gardiman, M.; Lo Schiavo, F. Somatic embryogenesis from stigmas and styles of grapevine. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology-Plant 2005, 41, 249–252. [Google Scholar]
- Carimi, F.; De Pasquale, F. Micropropagation of Citrus. In Micropropagation of Woody Trees and Fruits; Forestry Sciences; 2003; pp. 589–619.
- Martinelli, L.; Gribaudo, I. Somatic embryogenesis in grapevine. In Molecular Biology and Biotechnology of the Grapevine, Roubelakis-Angelakis, K.A., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht-Boston-London, 2001; pp. 327–351. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, J.L. Somatic embryogenesis: a model for early development in higher plants. The Plant Cell 1993, 5, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.D.; Conger, B. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from suspension cultures of switchgrass. Crop science 1999, 39, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, A.; Blervacq, A.-S.; Hendriks, T.; Slomianny, C.; Vasseur, J.; Hilbert, J.-L. Cell wall differentiation during early somatic embryogenesis in plants. II. Ultrastructural study and pectin immunolocalization on chicory embryos. Canadian Journal of Botany 2000, 78, 824–831. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, E.C. Structural and developmental patterns in somatic embryogenesis. In Vitro Embryogenesis in Plants, Thorpe, T.A., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, Boston, London, 1995; pp. 205–247. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, T.L. Gene expression during plant embryogenesis and germination: an overview. Plant Cell 1993, 5, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Kumar, P. Regulation of somatic embryogenesis in crops: a review. Agricultural Reviews 2013, 34, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ammirato, P.V. Organizational events during somatic embryogenesis. In Proceedings of the VIth International Congress on Plant Tissue and Cell Culture, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, USA; 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, O.; Aarrouf, J.; Nougarede, A. Ontogenesis, differentiation and precocious germination in anther-derived somatic embryos of grapevine (vitis vinifera L.): Embryonic organogenesis. Annals of Botany 1996, 78, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasankar, S.; Bondada, B.R.; Li, Z.J.; Gray, D.J. Comparative anatomy and morphology of Vitis vinifera (Vitaceae) somatic embryos from solid- and liquid-culture-derived proembryogenic masses. American Journal of Botany 2003, 90, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasankar, S.; Gray, D.J.; Litz, R.E. High-efficiency somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from suspension cultures of grapevine. Plant Cell Reports 1999, 18, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutos-Thevenot, P.; Goebel-Tourand, I.; Mauro, M.-C.; Jouanneau, J.-P.; Boulay, M.; Deloire, A.; Guern, J. Somatic embryogenesis from grapevine cells. I-Improvement of embryo development by changes in culture conditions. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 1992, 29, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutos-Thevenot, P.; Maes, O.; Jouenne, T.; Claude Mauro, M.; Boulay, M.; Deloire, A.; Guern, J. Extracellular protein patterns of grapevine cell suspensions in embryogenic and non-embryogenic situations. Plant Science 1992, 86, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlenko, V.A.; Kotikov, I.V.; Troshin, L.P. Plant regeneration from somatic embryos of interspecific hybrids of grapevine formed in liquid medium. Journal of Horticultural Science & Biotechnology 2005, 80, 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Vasanth, K.; Vivier, M.A. Improved cryopreservation procedure for long term storage of synchronised culture of grapevine. Biologia Plantarum 2011, 55, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.C.; Gafny, R.; Sahar, N.; Sela, I.; Mawassi, M.; Tanne, E.; Perl, A. Cryopreservation of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) embryogenic cell suspensions by encapsulation-dehydration and subsequent plant regeneration. Plant Science 2002, 162, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.C.; Mawassi, M.; Sahar, N.; Li, P.; Violeta, C.T.; Gafny, R.; Sela, I.; Tanne, E.; Perl, A. Cryopreservation of grapevine (Vitis spp.) embryogenic cell suspensions by encapsulation-vitrification. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture 2004, 77, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Furtado de Almeida, A.-A.; Costa, M.; Britto, D.; Valle, R.; Royaert, S.; Marelli, J.-P. Abnormalities in somatic embryogenesis caused by 2, 4-D: an overview. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 2019, 137, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acanda, Y.; Martínez, Ó.; Prado, M.J.; González, M.V.; Rey, M. Changes in abscisic acid metabolism in relation to the maturation of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L., cv. Mencía) somatic embryos. BMC Plant Biology 2020, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, L.; Gribaudo, I. Strategies for effective somatic embryogenesis in grapevine: an appraisal. In Grapevine Molecular Physiology & Biotechnology, Roubelakis-Angelakis, K.A., Ed.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, 2009; pp. 461–493. [Google Scholar]
- Bidabadi, S.S.; Jain, S.M. Cellular, Molecular, and Physiological Aspects of In Vitro Plant Regeneration. Plants (Basel) 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, M.J.; Grueiro, M.P.; González, M.V.; Testillano, P.S.; Domínguez, C.; López, M.; Rey, M. Efficient plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis from anthers and ovaries of six autochthonous grapevine cultivars from Galicia (Spain). Scientia Horticulturae 2010, 125, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, G.; Minuto, M.; Boccacci, P.; Perrone, I.; Vallania, R.; Gribaudo, I. Characterization of expression dynamics of WOX homeodomain transcription factors during somatic embryogenesis in Vitis vinifera. Journal of Experimental Botany 2011, 62, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, R.; Carimi, F. Studies on improving the efficiency of somatic embryogenesis in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) and optimising ethyl methanesulfonate treatment for mutation induction. Plants 2023, 12, 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carimi, F.; Pathirana, R.; Carra, A. Somatic embryogenesis and Agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation in Vitis In Somatic Embryogenesis and Genetic Transformation in Plants Aslam, J., Srivastave, P.S., Sharma, M.P., Eds.; Narosa Publishing House: New Delhi, 2013; pp. 199–218. [Google Scholar]
- Gribaudo, I.; Gambino, G.; Vallania, R. Somatic embryogenesis from grapevine anthers: The optimal developmental stage for collecting explants. American Journal of Enology and Viticulture 2004, 55, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, R.; Zok, A.; Pedryc, A.; Howard, S.; Kovács, L.G. Somatic embryogenesis in a broad spectrum of grape genotypes. Scientia Horticulturae 2009, 120, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriotti, L.; Limera, C.; Mezzetti, B.; Ricci, A.; Sabbadini, S. From induction to embryo proliferation: improved somatic embryogenesis protocol in grapevine for Italian cultivars and hybrid Vitis rootstocks. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 2022, 151, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellenbaum, P.; Jacques, A.; Maillot, P.; Bertsch, C.; Mazet, F.; Farine, S.; Walter, B. Characterization of VvSERK1, VvSERK2, VvSERK3 and VvL1L genes and their expression during somatic embryogenesis of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant cell reports 2008, 27, 1799–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillot, P.; Lebel, S.; Schellenbaum, P.; Jacques, A.; Walter, B. Differential regulation of SERK, LEC1-Like and Pathogenesis-Related genes during indirect secondary somatic embryogenesis in grapevine. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2009, 47, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutos-thevenot, P.; Jouenne, T.; Maes, O.; Guerbette, F.; Grosbois, M.; Le Caer, J.P.; Boulay, M.; Deloire, A.; Kader, J.C.; Guern, J. Four 9-kDa proteins excreted by somatic embryos of grapevine are isoforms of lipid-transfer proteins. European Journal of Biochemistry 1993, 217, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, J.; Lallemand, M.; Fleurat-Lessard, P.; Laquitaine, L.; Delrot, S.; Coutos-Thevenot, P.; Gomes, E. Overexpression of the VvLTP1 gene interferes with somatic embryo development in grapevine. Funct Plant Biol 2008, 35, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maës, O.; Coutos-Thévenot, P.; Jouenne, T.; Boulay, M.; Guern, J. Influence of extracellular proteins, proteases and protease inhibitors on grapevine somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 1997, 50, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.; Rama, J.; Taboada, L.; Martin, C.; Ibanez, M.; Segura, A.; Gonzalez-Benito, M.E. Improved somatic embryogenesis of grapevine (Vitis vinifera) with focus on induction parameters and efficient plant regeneration. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture 2009, 96, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Pedro, T.; Gammoudi, N.; Peiró, R.; Olmos, A.; Gisbert, C. Somatic embryogenesis from seeds in a broad range of Vitis vinifera L. varieties: rescue of true-to-type virus-free plants. BMC Plant Biology 2017, 17, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Tripathi, M.; Tiwari, R.; Baghel, B.; Ahuja, A. Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration via embryogenic suspensions of grape (Vitis vinifera L.). Asian J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci 2018, 20, S112–S125. [Google Scholar]
- Maillot, P.; Deglène-Benbrahim, L.; Walter, B. Efficient somatic embryogenesis from meristematic explants in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) cv. Chardonnay: an improved protocol. Trees 2016, 30, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillot, P.; Kieffer, F.; Walter, B. Somatic embryogenesis from stem nodal sections of grapevine. Vitis 2006, 45, 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Gambino, G.; Ruffa, P.; Vallania, R.; Gribaudo, I. Somatic embryogenesis from whole flowers, anthers and ovaries of grapevine (Vitis spp.). Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture 2007, 90, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, H.G.; Campos, M.C.; Pais, M.S.; Peixe, A. Use of morphometric parameters for tracking ovule and microspore evolution in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L., cv. “Aragonez”) and evaluation of their potential to improve in vitro somatic embryogenesis efficiency from gametophyte tissues. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Plant 2010, 46, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emons, M.C. Somatic embryogenesis: cell biological aspects. Acta Botanica Neerlandica 1994, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.R.; Kikkert, J.R.; Malnoy, M.A.; Wallace, P.G.; Barnard, J.; Reisch, B.I. Evaluation of transgenic 'Chardonnay' (Vitis vinifera) containing magainin genes for resistance to crown gall and powdery mildew. Transgenic Research 2006, 15, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiologia Plantarum 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, J.; Nitsch, C. Haploid plants from pollen grains. Science 1969, 163, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linsmaier, E.M.; Skoog, F. Organic growth factor requirements of tobacco tissue cultures. Physiologia Plantarum 1965, 18, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, G.; McCown, B.H. Commercially feasible micropropagation of mountain laurel, Kalmia latifolia, by use of shoot-tip culture. Proc. Int. Plant Prop. Soc. 1980, 30, 421–427. [Google Scholar]
- Chee, R.; Pool, R.; Bucher, D. A method for large scale in vitro propagation of Vitis. New York's Food and Life Sciences Bulletin 1984, 1-9.
- Driver, J.A.; Kuniyuki, A.H. In vitro propagation of Paradox walnut rootstock. HortScience 1984, 19, 507–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, M.; Martin, D.; Joly, D.; Demangeat, G.; This, P.; Masson, J.E. Medium-dependent response of grapevine somatic embryogenic cells. Plant Science 2001, 161, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elidemir, A.; Uzun, H.; Bayir, A. Effect of different medium and sucrose concentrations on germination of somatic embryos in grape. Acta Horticulturae 2007, 754, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.C.d.; Silva, A.L.L.d.; Schuck, M.R.; Purcino, M.; Tanno, G.N.; Biasi, L.A. Fox grape cv. Bordô (Vitis labrusca L.) and grapevine cv. Chardonnay (Vitis vinifera L.) cultivated in vitro under different carbohydrates, amino acids and 6-Benzylaminopurine levels. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology 2013, 56, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nookaraju, A.; Agrawal, D. Use of amino acids for a highly efficient somatic embryogenesis in grapevine 'Crimson Seedless'. Vitis 2013, 52, 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-M.; Wu, Y.-F.; Zhi, L.; Song, C.-B.; Wang, X.-P. Advancements in plant regeneration and genetic transformation of grapevine (Vitis spp.). Journal of Integrative Agriculture 2021, 20, 1407–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouamama, B.; Salem-Fnayou, A.B.; Jouira, H.B.; Ghorbel, A.; Mliki, A. Influence of the flower stage and culture medium on the induction of somatic embryogenesis from anther culture in Tunisian grapevine cultivars. J. Int. Sci. Vigne Vin 2007, 41, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carimi, F.; Pathirana, R.; Carra, A. Biotechnologies for germplasm management and improvement. In Grapevines – Varieties, Cultivation and Management, Szabo, P.V., Shojania, J., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, 2012; pp. 199–249. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Yu, Z.-Y.; Cheng, Z.-M.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, J.-M. In vitro explants regeneration of the grape ‘Wink’(Vitis vinifera L.‘Wink’). Journal of Plant Breeding and Crop Science 2011, 3, 276–282. [Google Scholar]
- López-Pérez, A.J.; Carreño, J.; Martínez-Cutillas, A.; Dabuza, M. High embryogenic ability and plant regeneration of table grapevine cultivars (Vitis vinifera L.) induced by activated charcoal. Vitis 2005, 44, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, F.-l.; Du, J.-c.; Lu, H.; He, Z.-q. Somatic embryogenesis and histological analysis from zygotic embryos in Vitis vinifera L.‘Moldova’. Forestry Studies in China 2008, 10, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.T.; Dhekney, S.A.; Dutt, M.; Gray, D.J. An improved protocol for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 2008, 93, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhekney, S.A.; Li, Z.T.; Gray, D.J. Factors influencing induction and maintenance of Vitis rotundifolia Michx. embryogenic cultures. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 2011, 105, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Lee, H.-R.; Pyee, J.; Cha, H.-C. Regeneration of grape (Vitis labruscana cv. Kyoho) by shoot-tip culture. Journal of Plant Biology 2001, 44, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasankar, S.; Van Aman, M.; Cordts, J.; Dhekney, S.; Li, Z.T.; Gray, D.J. Low temperature storage of suspension culture-derived grapevine somatic embryos and regeneration of plants. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology-Plant 2005, 41, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PlantGrape. 110 Richter. Available online: https://www.plantgrape.fr/en/varieties/rootstock-varieties/21 (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Ortiz, J.M.; Martin, J.P.; Borrego, J.; Chavez, J.; Rodriguez, I.; Munoz, G.; Cabello, F. Management and characterization of a Vitis germplasm bank in Spain. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Grape Genetics and Breeding, Vols 1 and 2 2003, 619-625.
- Popescu, C.F.; Crespan, M. Combining Microsatellite Markers and Ampelography for Better Management of Romanian Grapevine Germplasm Collections. Notulae Scientia Biologicae 2018, 10, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.B.; Dilli, Y.; Oncu-Oner, T.; Unal, A. Exploring genetic diversity and population structure of a large grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) germplasm collection in Turkiye. Front Plant Sci 2023, 14, 1121811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maul, E.; Töpfer, R.; Carka, F.; Cornea, V.; Crespan, M.; Dallakyan, M.; de Andrés Domínguez, T.; De Lorenzis, G.; Dejeu, L.; Goryslavets, S. Identification and characterization of grapevine genetic resources maintained in Eastern European Collections. Vitis 2015, 54, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Margaryan, K.; Maul, E.; Muradyan, Z.; Hovhannisyan, A.; Devejyan, H.; Melyan, G.; Aroutiounian, R. Armenian national grapevine collection: Conservation, characterization and prospects. In Proceedings of the BIO Web of Conferences; 2019; p. 01002. [Google Scholar]
- Akhalkatsi, M.; Ekhvaia, J.; Mosulishvili, M.; Nakhutsrishvili, G.; Abdaladze, O.; Batsatsashvili, K. Reasons and processes leading to the erosion of crop genetic diversity in mountainous regions of Georgia. Mountain Research and Development 2010, 30, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.d.C.; Luis, Z.G.; Scherwinski-Pereira, J.E. Short-term storage in vitro and large-scale propagation of grapevine genotypes. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2012, 47, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Pedro, T.; Muñoz, P.; Peiró, R.; Jiménez, C.; Olmos, A.; Gisbert, C. Evaluation of conditions for in vitro storage of commercial and minor grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) cultivars. The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology 2018, 93, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleweldt, G.; Harstlangenbucher, M. The effect of growth-inhibitors on long-term storage of in vitro cultures of grapevine. Vitis 1987, 26, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Alzubi, H.; Yepes, L.M.; Fuchs, M. In vitro storage of micropropagated grapevine rootstocks at low temperature. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Plant 2019, 55, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romadanova, N.V.; Aralbayeva, M.M.; Zemtsova, A.S.; Alexandrova, A.M.; Kazybayeva, S.Z.; Mikhailenko, N.V.; Kushnarenko, S.V.; Bettoni, J.C. In Vitro Collection for the Safe Storage of Grapevine Hybrids and Identification of the Presence of Plasmopara viticola Resistance Genes. Plants (Basel) 2024, 13, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruseva, R. Possibility for short-term in vitro conservation of grapevine explants by excluding growth regulators from the nutrient medium. Rasteniev"dni Nauki 1998, 35, 888–890. [Google Scholar]
- Ruseva, R. Decreasing the growth rate of in vitro grapevine plants by increasing the level of sucrose in the nutrient medium. Rasteniev"dni Nauki 1998, 35, 891–894. [Google Scholar]
- Ruseva, R. Study of the possibilities for in vitro storage of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) explants at low temperatures. Rasteniev"dni Nauki 2001, 38, 374–376. [Google Scholar]
- Tehrim, S.; SAJID, G.M. In vitro establishment, conservation and its implications for grape germplasm biodiversity. Romanian Biotechnological Letters 2011, 16, 6781–6789. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, N.A.; Gomaa, A.H.; Shahin, M.A.; El Homosany, A.A. In vitro storage and cryopreservation of some grape varieties. Journal of Horticultural Science & Ornamental Plants 2013, 5, 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, D. Effects of dehydration and exogenous growth regulators on dormancy, quiescence and germination of grape somatic embryos. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology 1989, 25, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Capriotti, L.; Ricci, A.; Molesini, B.; Mezzetti, B.; Pandolfini, T.; Piunti, I.; Sabbadini, S. Efficient protocol of de novo shoot organogenesis from somatic embryos for grapevine genetic transformation. Frontiers in Plant Science 2023, 14, 1172758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senaratna, T.; McKersie, B.D.; Bowley, S.R. Artificial seeds of alfalfa ( Medicago sativa L.). Induction of desiccation tolerance in somatic embryos. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology 1990, 26, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, O.; Dewitte, W.; Nougarède, A.; Van Onckelen, H. Precociously germinating somatic embryos of Vitis vinifera have lower ABA and IAA levels than their germinating zygotic counterparts. Physiologia Plantarum 1998, 102, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel-Tourand, I.; Mauro, M.-C.; Sossountzov, L.; Miginiac, E.; Deloire, A. Arrest of somatic embryo development in grapevine: histological characterization and the effect of ABA, BAP and zeatin in stimulating plantlet development. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 1993, 33, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-R.; Lambardi, M.; Engelmann, F.; Pathirana, R.; Panis, B.; Volk, G.M.; Wang, Q.-C. Advances in cryopreservation of in vitro-derived propagules: Technologies and explant sources. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 2021, 144, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochatt, S.; Lambardi, M.; Panis, B.; Pathirana, R.; Revilla, M.A.; Wang, Q.-C. Cryopreservation and In Vitro banking: a cool subject – Preface from the editors. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 2021, 144, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miaja, M.L.; Gambino, G.; Vallania, R.; Gribaudo, I. Cryopreservation of Vitis vinifera L. somatic embryos by vitrification or encapsulation-dehydration. Acta Horticulturae 2004, 663, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Amar, A.; Daldoul, S.; Allel, D.; Reustle, G.; Mliki, A. Reliable encapsulation-based cryopreservation protocol for safe storage and recovery of grapevine embryogenic cell cultures. Scientia horticulturae 2013, 157, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.C.; Tanne, E.; Arav, A.; Gafny, R. Cryopreservation of in vitro-grown shoot tips of grapevine by encapsulation-dehydration. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture 2000, 63, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussert, S.; Mauro, M.C.; Deloire, A.; Hamon, A.; Engelmann, F. Cryopreservation of grape embryogenic suspensions. 1. Influence of pretreatment, freezing and thawing conditions. Cryoletters 1991, 12, 287–298. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Benito, M.E.; Martin, C.; Vidal, J.R. Cryopreservation of embryogenic cell suspensions of the Spanish grapevine cultivars 'Albarino' and 'Tempranillo'. Vitis 2009, 48, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Oiyama, I. Cryopreservation of nucellar cells of navel orange (Citrus sinensis Osb. var. brasiliensis Tanaka) by vitrification. Plant Cell Reports 1990, 9, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, R. Cryopreserved grapevine: a new way to maintain high-health germplasm and cultivar imports with less rigorous quarantine; NZW 10-107; Plant and Food Research: New Zealand, June 2011 2011; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Pathirana, R.; Mathew, L.; Jibran, R.; Hunter, D.A.; Morgan, E.R. Cryopreservation and cryotherapy research on horticultural crops in New Zealand. Acta Horticulturae 2019, 1234, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, R.; McLachlan, A.; Hedderley, D.; Panis, B.; Carimi, F. Pre-treatment with salicylic acid improves plant regeneration after cryopreservation of grapevine (Vitis spp.) by droplet vitrification. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 2016, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carimi, F.; Carra, A.; Panis, B.; Pathirana, R. Strategies for conservation of endangered wild grapevine (Vitis vinifera L. subsp. sylvestris (C.C. Gmel.) Hegi). Acta Horticulturae 2016, 1115, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettoni, J.C.; Bonnart, R.; Shepherd, A.N.; Kretzschmar, A.A.; Volk, G.M. Modifications to a Vitis shoot tip cryopreservation procedure: Effect of shoot tip size and use of cryoplates. Cryoletters 2019, 40, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gribaudo, I.; Vallania, R.; Miaja, M.L.; Franks, T.; Thomas, M. Genotype influence on somatic embryogenesis in grapevine anther and leaf cultures. Acta Horticulturae 2000, 528, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikkert, J.R.; Striem, M.J.; Vidal, J.R.; Wallace, P.G.; Barnard, J.; Reisch, B.I. Long-term study of somatic embryogenests from anthers and ovaries of 12 grapevine (Vitis sp.) genotypes. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology-Plant 2005, 41, 232–239. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, M.; Gertz, C.; Masson, J.E. High efficiency initiation of regenerable embryogenic callus from anther filaments of 19-grapevine genotypes grown worldwide. Plant Science 2004, 167, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, T.; Botta, R.; Thomas, M.R.; Franks, J. Chimerism in grapevines: implications for cultivar identity, ancestry and genetic improvement. TAG Theoretical and Applied Genetics 2002, 104, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, G.; Moine, A.; Boccacci, P.; Perrone, I.; Pagliarani, C. Somatic embryogenesis is an effective strategy for dissecting chimerism phenomena in Vitis vinifera cv Nebbiolo. Plant Cell Reports 2021, 40, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, S.; Garrison, K.E.; Dangl, G.S.; Boursiquot, J.-M.; Meredith, C.P. Genetic Divergence and Chimerism within Ancient Asexually Propagated Winegrape Cultivars. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2002, 127, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, M.J.; Rodriguez, E.; Rey, L.; Gonzalez, M.V.; Santos, C.; Rey, M. Detection of somaclonal variants in somatic embryogenesis-regenerated plants of Vitis vinifera by flow cytometry and microsatellite markers. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture 2010, 103, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Reustle, G.; Zyprian, E. Detection of somaclonal variation in grapevine regenerants from protoplasts by RAPD-PCR. Vitis 1996, 35, 99–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gardiman, M.; Carimi, F.; Meneghetti, S.; Barizza, E.; Schiavo, F.l. Micropropagation and genetic stability of Vitis vinifera, cv Aglianico, plants obtained by somatic embryo-genesis. Italus Hortus 2009, 16, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Martelli, G. Where grapevine virology is heading to. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 19th Congress of ICVG, Santiago, Chile, April 9-12, 2018, 2018; pp. 10–15.
- Fuchs, M.; Lemaire, O. Novel approaches for viral disease management. In Grapevine Viruses: Molecular Biology, Diagnostics and Management, Meng, B., Martelli, G.P., Golino, D.A., Fuchs, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishers: 2017; pp. 599–621.
- Golino, D.; Fuchs, M.; Sim, S.; Farrar, K.; Martelli, G. Improvement of grapevine planting stock through sanitary selection and pathogen elimination. In Grapevine Viruses: Molecular Biology, Diagnostics and Management, Meng, B., Martelli, G.P., Golino, D.A., Fuchs, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishers: 2017; pp. 561–579.
- Gambino, G.; Di Matteo, D.; Gribaudo, I. Elimination of Grapevine fanleaf virus from three Vitis vinifera cultivars by somatic embryogenesis. European Journal of Plant Pathology 2009, 123, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.-L.; Hao, X.-Y.; Cui, Z.-H.; Pathirana, R.; Volk, G.M.; Wang, Q.-C. Shoot tip cryotherapy for efficient eradication of grapevine leafroll-associated virus-3 from diseased grapevine in vitro plants. Annals of Applied Biology 2018, 173, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradamante, G.; Mittelsten Scheid, O.; Incarbone, M. Under siege: virus control in plant meristems and progeny. The Plant Cell 2021, 33, 2523–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, L.; Tiffin, H.; Erridge, Z.; McLachlan, A.; Hunter, D.; Pathirana, R. Efficiency of eradication of Raspberry bushy dwarf virus from infected raspberry (Rubus idaeus) by in vitro chemotherapy, thermotherapy and cryotherapy and their combinations. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 2021, 144, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettoni, J.C.; Dalla Costa, M.; Gardin, J.P.P.; Kretzschmar, A.A.; Pathirana, R. Cryotherapy: a new technique to obtain grapevine plants free of viruses. Revista Brasileira De Fruticultura 2016, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Cho, K.H.; Chun, J.A.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.C. Elimination ofGrapevine fleck virusfrom infected grapevines ‘Kyoho’ through meristem-tip culture of dormant buds. Journal of Plant Biotechnology 2017, 44, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayati, S.; Shams-Bakhsh, M.; Moieni, A. Elimination of Grapevine Virus A (GVA) by Cryotherapy and Electrotherapy. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology 2011, 13, 443–450. [Google Scholar]
- Markovic, Z.; Preiner, D.; Stupic, D.; Andabaka, Z.; Simon, S.; Voncina, D.; Maletic, E.; Kontic, J.K.; Chatelet, P.; Engelmann, F. Cryopreservation and cryotherapy of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Vitis 2015, 54, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Guta, I.C.; Buciumeanu, E.-C. Grapevine chemotherapy for elimination of multiple virus infection. Romanian Biotechnological Letters 2011, 16, 6535–6539. [Google Scholar]
- Skiada, F.G.; Maliogka, V.I.; Katis, N.I.; Eleftheriou, E.P. Elimination of Grapevine rupestris stem pitting-associated virus (GRSPaV) from two Vitis vinifera cultivars by in vitro chemotherapy. European Journal of Plant Pathology 2013, 135, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, R.; Fiore, N. Combined effect of thermotherapy and in vitro shoot culture on the Grapevine leafroll associated virus 2 Red Globe strain affecting 'Red Globe' vines. Journal of Food Agriculture & Environment 2009, 7, 274–277. [Google Scholar]
- Maliogka, V.I.; Skiada, F.G.; Eleftheriou, E.P.; Katis, N.I. Elimination of a new ampelovirus (GLRaV-Pr) and Grapevine rupestris stem pitting associated virus (GRSPaV) from two Vitis vinifera cultivars combining in vitro thermotherapy with shoot tip culture. Scientia Horticulturae 2009, 123, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Hoshino, Y. Histological examination of callogenesis and adventitious embryogenesis in immature ovary culture of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology 2000, 75, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, D.; Goussard, P. The ontogeny of somatic embryos from in vitro cultured grapevine anthers. South African Journal of Enology & Viticulture 1990, 11, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Goussard, P.G.; Wiid, J.; Kasdon, G.G.F. The Effectiveness of in vitro somatic embryogenesis in eliminating fanleaf virus and leafroll associated viruses from grapevines. South African Journal of Enology & Viticulture 1991, 12, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goussard, P.; Wiid, J. The elimination of fanleaf virus from grapevines using in vitro somatic embryogenesis combined with heat therapy. South Afrrican Journal of Enolology and Viticulture 1992, 13, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, G.; Bondaz, J.; Gribaudo, I. Detection and elimination of viruses in callus, somatic embryos and regenerated plantlets of grapevine. European Journal of Plant Pathology 2006, 114, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcsan, M.; Demian, E.; Varga, T.; Jaksa-Czotter, N.; Szegedi, E.; Olah, R.; Varallyay, E. Hts-based monitoring of the efficiency of somatic embryogenesis and meristem cultures used for virus elimination in grapevine. Plants 2020, 9, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.C.; Panis, B.; Engelmann, F.; Lambardi, M.; Valkonen, J.P.T. Cryotherapy of shoot tips: a technique for pathogen eradication to produce healthy planting materials and prepare healthy plant genetic resources for cryopreservation. Annals of Applied Biology 2009, 154, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Ren, J.; Tao, J. A SNP in the promoter region of theVvmybA1 gene is responsible for differences in grape berry color between two related bud sports of grape. Plant Growth Regulation 2017, 82, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, G.; Le Cunff, L.; Dereeper, A.; Legrand, D.; Sabot, F.; Bouchez, O.; Audeguin, L.; Boursiquot, J.-M.; This, P. Transposable elements are a major cause of somatic polymorphism in Vitis vinifera L. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e32973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- This, P.; Lacombe, T.; Thomas, M.R. Historical origins and genetic diversity of wine grapes. TRENDS in Genetics 2006, 22, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathirana, R. Mutations in plant evolution, crop domestication and breeding. Tropical Agricultural Research and Extension 2021, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahloowalia, B.S.; Maluszynski, M. Induced mutations - A new paradigm in plant breeding. Euphytica 2001, 118, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, R.; Deroles, S.; Hoeata, K.; Montefiori, M.; Tyson, J.; Wang, T.; Datson, P.M.; Hellens, R.P. Fast-tracking kiwifruit breeding through mutagenesis. Acta Horticulturae 2016, 1127, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluszynski, M.; Ahloowalia, B.S.; Sigurbjörnsson, B. Application of in vivo and in vitro mutation techniques for crop improvement. Euphytica 1995, 81, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, R. Plant mutation breeding in agriculture. CAB Reviews: Perspectives in Agriculture, Veterinary Science, Nutrition and Natural Resources 2011, 6, 1–20.
- Khawale, R.N.; Yerramilli, V.; Singh, S.K. Molecular marker-assisted selection of in vitro chemical mutagen-induced grapevine mutants. Current Science 2007, 92, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, N.; Safdar, I.; Naz, S. Effect of induced mutation for varietal improvement in some local grapevine cultivars. 2015.
- Krul, W.R.; Worley, J.F. Formation of adventitious embryos in callus cultures of 'Seyval', a French hybrid grape. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1977, 102, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, O.; Aarrouf, J.; Nougarede, A. Ontogenesis, differentiation and precocious germination in anther-derived somatic embryos of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.): Proembryogenesis. Annals of Botany 1996, 78, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhojwani, S.S.; Dantu, P.K. Somatic embryogenesis. In Plant Tissue Culture: An Introductory Text, Bhojwani, S.S., Dantu, P.K., Eds.; Springer India: India, 2013; pp. 75–92. [Google Scholar]
- Nagmani, R.; Becwar, M.; Wann, S. Single-cell origin and development of somatic embryos in Picea abies (L.) Karst.(Norway spruce) and P. glauca (Moench) Voss (white spruce). Plant Cell Reports 1987, 6, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toonen, M.A.; Hendriks, T.; Schmidt, E.D.; Verhoeven, H.A.; Van Kammen, A.; de Vries, S.C. Description of somatic-embryo-forming single cells in carrot suspension cultures employing video cell tracking. Planta 1994, 194, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoabi, M.; Lloyd, J.; Kossmann, J.; van der Vyver, C. Ethyl methanesulfonate mutagenesis and in vitro polyethylene glycol selection for drought tolerance in sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). Sugar Tech 2018, 20, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikam, A.A.; Devarumath, R.M.; Ahuja, A.; Babu, H.; Shitole, M.G.; Suprasanna, P. Radiation-induced in vitro mutagenesis system for salt tolerance and other agronomic characters in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). The Crop Journal 2015, 3, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patade, V.Y.; Suprasanna, P.; Bapat, V.A. Gamma irradiation of embryogenic callus cultures and in vitro selection for salt tolerance in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). Agricultural Sciences in China 2008, 7, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, R.; Carimi, F.; Carra, A.; Cheah, L.-H. Intergrating biotechnological advancements with induced mutagenesis: New opportunities for horticulture with special reference to Vitis vinifera. In Proceedings of the FAO/IAEA International Symposium on Induced Mutations in Plants., Vienna, Austria, 2008, 12-15 August 2008; p. 115. [Google Scholar]
- Kuksova, V.B.; Piven, N.M.; Gleba, Y.Y. Somaclonal variation and in vitro induced mutagenesis in grapevine. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 1997, 49, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Cao, Z.Y.; An, L.Z.; Wang, Y.M.; Fang, X.W. In vitro tetraploid induction via colchicine treatment from diploid somatic embryos in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Euphytica 2006, 152, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriotti, L.; Sabbadini, S.; Limera, C.; Navacchi, O.; Mezzetti, B. Somaclonal variation and induced mutagenesis in several grapevine cultivars. Acta Horticulturae 2022, 1359, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baduel, P.; Colot, V. The epiallelic potential of transposable elements and its evolutionary significance in plants. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B 2021, 376, 20200123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, B. The significance of responses of the genome to challenge. Science 1984, 226, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, B. Controlling elements and the gene. In Proceedings of the Cold Spring Harbor symposia on quantitative biology; 1956; pp. 197–216. [Google Scholar]
- Lijavetzky, D.; Ruiz-García, L.; Cabezas, J.A.; De Andrés, M.T.; Bravo, G.; Ibáñez, A.; Carreño, J.; Cabello, F.; Ibáñez, J.; Martínez-Zapater, J.M. Molecular genetics of berry colour variation in table grape. Molecular Genetics and Genomics 2006, 276, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Goto-Yamamoto, N.; Hirochika, H. Retrotransposon-induced mutations in grape skin color. Science 2004, 304, 982–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjak, A.; Forneck, A.; Casacuberta, J.M. Genome-Wide Analysis of the “Cut-and-Paste” Transposons of Grapevine. PLOS ONE 2008, 3, e3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Cao, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Leng, X.; Peng, Y.; Wang, N.; et al. The complete reference genome for grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) genetics and breeding. Horticulture Research 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, L.; Gribaudo, I.; Bertoldi, D.; Candioli, E.; Poletti, V. High efficiency somatic embryogenesis and plant germination in grapevine cultivars Chardonnay and Brachetto a grappolo lungo. Vitis 2001, 40, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Vivier, M.A.; Pretorius, I.S. Genetic improvement of grapevine: tailoring grape varieties for the third millennium - a review. South African Journal for Enology and Viticulture 2000, 21, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, G.; Chialva, C.; Miras, S.; Lijavetzky, D. New technologies and strategies for grapevine breeding through genetic transformation. Frontiers in Plant Science 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccacci, P.; Mela, A.; Pavez Mina, C.; Chitarra, W.; Perrone, I.; Gribaudo, I.; Gambino, G. Cultivar-specific gene modulation in Vitis vinifera: analysis of the promoters regulating the expression of WOX transcription factors. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 45670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, F.; Moine, A.; Nerva, L.; Pagliarani, C.; Perrone, I.; Boccacci, P.; Gribaudo, I.; Chitarra, W.; Gambino, G. Grapevine virome and production of healthy plants by somatic embryogenesis. Microbial Biotechnology 2022, 15, 1357–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Maltese, F.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolic constituents of grapevine and grape-derived products. Phytochem Rev 2010, 9, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacio-Bielsa, A.; González-Abolafio, R.; Álvarez, B.; Lastra, B.; Cambra, M.A.; Salcedo, C.I.; López, M.M.; Penyalver, R. Chromosomal and Ti plasmid characterization of tumorigenic strains of three Agrobacterium species isolated from grapevine tumours. Plant Pathology 2009, 58, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, A. Biological control of crown gall on grapevine and root colonization by nonpathogenic Rhizobium vitis strain ARK-1. Microbes and environments 2013, 28, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldo, A.R.; Cavallini, E.; Jia, Y.; Moss, S.M.; McDavid, D.A.; Hooper, L.C.; Robinson, S.P.; Tornielli, G.B.; Zenoni, S.; Ford, C.M. A grapevine anthocyanin acyltransferase, transcriptionally regulated by VvMYBA, can produce most acylated anthocyanins present in grape skins. Plant Physiology 2015, 169, 1897–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capriotti, L.; Baraldi, E.; Mezzetti, B.; Limera, C.; Sabbadini, S. Biotechnological approaches: gene overexpression, gene silencing, and genome editing to control fungal and oomycete diseases in grapevine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dry, I.; Riaz, S.; Fuchs, M.; Sosnowski, M.; Thomas, M. Scion breeding for resistance to biotic stresses. In The Grape Genome, Cantu, D., Walker, M., Eds.; Springer, Cham.: 2019; pp. 319–347.
- Paul, N.C.; Park, S.-W.; Liu, H.; Choi, S.; Ma, J.; MacCready, J.S.; Chilvers, M.I.; Sang, H. Plant and fungal genome editing to enhance plant disease resistance using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Frontiers in Plant Science 2021, 12, 700925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Duan, W.; Fan, P.; Li, S.; Liang, Z. Optimizing the CRISPR/Cas9 system for genome editing in grape by using grape promoters. Horticulture Research 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tu, M.; Wang, Y.; Yin, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Gu, Y.; Li, Z.; Xi, Z.; Wang, X. Whole-genome sequencing reveals rare off-target mutations in CRISPR/Cas9-edited grapevine. Horticulture research 2021, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, D.-Y.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Y.-Q. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis of VvMLO3 results in enhanced resistance to powdery mildew in grapevine (Vitis vinifera). Horticulture research 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.; Kikkert, J.; Wallace, P.; Reisch, B. High-efficiency biolistic co-transformation and regeneration of 'Chardonnay' (Vitis vinifera L.) containing npt-II and antimicrobial peptide genes. Plant Cell Reports 2003, 22, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhekney, S.A.; Li, Z.T.; Gray, D.J. Grapevines engineered to express cisgenic Vitis vinifera thaumatin-like protein exhibit fungal disease resistance. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology-Plant 2011, 47, 458–466. [Google Scholar]
- Dal Bosco, D.; Sinski, I.; Ritschel, P.S.; Camargo, U.A.; Fajardo, T.V.; Harakava, R.; Quecini, V. Expression of disease resistance in genetically modified grapevines correlates with the contents of viral sequences in the T-DNA and global genome methylation. Transgenic Research 2018, 27, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmer, C.; Djennane, S.; Ackerer, L.; Hleibieh, K.; Marmonier, A.; Gersch, S.; Garcia, S.; Vigne, E.; Komar, V.; Perrin, M. Nanobody-mediated resistance to Grapevine fanleaf virus in plants. Plant Biotechnology Journal 2018, 16, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Agüero, C.B.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Walker, M.A.; Lu, J. Overexpression of a thaumatin-like protein gene from Vitis amurensis improves downy mildew resistance in Vitis vinifera grapevine. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Karn, A.; Reisch, B.; Nguyen, A.; Sun, Y.; Bao, Y.; Campbell, M.S.; Church, D.; Williams, S.; Xu, X.; et al. Haplotyping the Vitis collinear core genome with rhAmpSeq improves marker transferability in a diverse genus. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillaumie, S.; Mzid, R.; Méchin, V.; Léon, C.; Hichri, I.; Destrac-Irvine, A.; Trossat-Magnin, C.; Delrot, S.; Lauvergeat, V. The grapevine transcription factor WRKY2 influences the lignin pathway and xylem development in tobacco. Plant molecular biology 2010, 72, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgetti, L.; RUFFINI CASTIGLIONE, M.; TURRINI, A.; ronchi Vittoria, N.; Chiara, G. Cytogenetic and histological approach for early detection of “mantled” somaclonal variants of oil palm regenerated by somatic embryogenesis: first results on the characterization of regeneration system. Caryologia 2011, 64, 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Ronchi, V.N. Cytogenetics of plant cell cultures. In Developments in Crop Science, Bhojwani, S.S., Ed.; Elsevier: 1990; Volume 19, pp. 276–300.
- Giorgetti, L.; Vergara, M.; Evangelista, M.; Lo Schiavo, F.; Terzi, M.; Nuti Ronchi, V. On the occurrence of somatic meiosis in embryogenic carrot cell cultures. Molecular and General Genetics MGG 1995, 246, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchi, V.N.; Giorgetti, L.; Tonelli, M.; Martini, G. Ploidy reduction and genome segregation in cultured carrot cell lines. I. Prophase chromosome reduction. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 1992, 30, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.C.; Eckhoff, P.; Wood, L.; Paterson, A.H. A proposal to use gamete cycling in vitro to improve crops and livestock. Nature Biotechnology 2013, 31, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, G.N.; Frei, U.K.; Lübberstedt, T. Accelerating plant breeding. Trends in Plant Science 2013, 18, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.M.; Isenegger, D.; Dutta, S.; Sahab, S.; Kay, P.; Aboobucker, S.I.; Biswas, E.; Heerschap, S.; Nikolau, B.J.; Dong, L. Overcoming roadblocks for in vitro nurseries in plants: induction of meiosis. Frontiers in Plant Science 2023, 14, 1204813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Yamaguchi, H. Arrangement and association of somatic chromosomes induced by chloramphenicol in barley. Chromosoma 1973, 43, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Geng, Y.; Chen, Z. Inducing somatic meiosis-like reduction at high frequency by caffeine in root-tip cells of Vicia faba. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis 2000, 452, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ryabova, D.; Diedhiou, J.; Hucl, P.; Randhawa, H.; Marillia, E.; Foroud, N.; Eudes, F.; Kathiria, P. Trichostatin A increases embryo and green plant regeneration in wheat. Plant Cell Reports 2017, 36, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Soriano, M.; Cordewener, J.; Muiño, J.M.; Riksen, T.; Fukuoka, H.; Angenent, G.C.; Boutilier, K. The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin a promotes totipotency in the male gametophyte. The Plant Cell 2014, 26, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.M.; Enns, J.L.; Nelson, K.L.; Brost, J.M.; Orr, T.D.; Ferrie, A.M.R. Improving the efficiency of wheat microspore culture methodology: evaluation of pretreatments, gradients, and epigenetic chemicals. Plant Cell, Tissue, and Organ Culture 2019, 139, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouamama-Gzara, B.; Selmi, I.; Chebil, S.; Melki, I.; Mliki, A.; Ghorbel, A.; Carra, A.; Carimi, F.; Mahfoudhi, N. Elimination of Grapevine leafroll associated virus-3, Grapevine rupestris stem pitting associated virus and Grapevine virus A from a Tunisian cultivar by somatic embryogenesis and characterization of the somaclones using ampelographic descriptors. The Plant Pathology Journal 2017, 33, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butiuc-Keul, A.; Coste, A. Biotechnologies and strategies for grapevine improvement. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljuaid, B.S.; Ismail, I.A.; Attia, A.O.; El Dessoky, S.D. Genetic stability of in vitro propagated grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) cv. Al-Bayadi. Journal of Agriculture and Crops 2022, 8, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baránek, M.; Raddová, J.; Krizan, B.; Pidra, M. Genetic changes in grapevine genomes after stress induced by in vitro cultivation, thermotherapy and virus infection, as revealed by AFLP. Genetics and Molecular Biology 2009, 32, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crăciunaş, C.; Coste, A.; Oltean, B.; Farago, M.; Iliescu, M.; Iuoras, R.; Butiuc-Keul, A. Genetic stability of several cultivars of grapevine cultivated in vitro. Acta Horticulturae 2007, 812, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribaudo, I.; Marinoni, D.T.; Gambino, G.; Mannini, F.; Akkak, A.; Botta, R. Assessment of genetic fidelity in regenerants from two Vitis vinifera cultivars. In Ix International Conference on Grape Genetics and Breeding, Peterlunger, E., DiGaspero, G., Cipriani, G., Eds.; Acta Horticulturae; 2009; Volume 827, pp. 131–135.
- Schellenbaum, P.; Mohler, V.; Wenzel, G.; Walter, B. Variation in DNA methylation patterns of grapevine somaclones (Vitis vinifera L.). BMC Plant Biology 2008, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, P.; Kumar, N. Application of molecular markers for the assessment of genetic fidelity of in vitro raised plants: current status and future prospects. In Molecular Marker Techniques: A Potential Approach of Crop Improvement, Kumar, N., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 233–256. [Google Scholar]
- Nybom, H.; Weising, K.; Rotter, B. DNA fingerprinting in botany: past, present, future. Investigative Genetics 2014, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, V.; Matus, J.T.; Pinto-Carnide, O.; Carrasco, D.; Arroyo-García, R.; Castro, I. Genetic analysis of a white-to-red berry skin color reversion and its transcriptomic and metabolic consequences in grapevine (Vitis vinifera cv.‘Moscatel Galego’). BMC Genomics 2019, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sichel, V.; Sarah, G.; Girollet, N.; Laucou, V.; Roux, C.; Roques, M.; Mournet, P.; Cunff, L.L.; Bert, P.F.; This, P.; et al. Chimeras in Merlot grapevine revealed by phased assembly. BMC Genomics 2023, 24, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsch, C.; Kieffer, F.; Maillot, P.; Farine, S.; Butterlin, G.; Merdinoglu, D.; Walter, B. Genetic chimerism of Vitis vinifera cv. Chardonnay 96 is maintained through organogenesis but not somatic embryogenesis. BMC Plant Biology 2005, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forneck, A. Plant breeding: clonality—a concept for stability and variability during vegetative propagation. In Progress in Botany: Genetics Physiology Systematics Ecology, Esser, K., Lüttge, U., Beyschlag, W., Murata, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005; Volume 66, pp. 164–183. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuelli, F.; Lorenzi, S.; Grzeskowiak, L.; Catalano, V.; Stefanini, M.; Troggio, M.; Myles, S.; Martinez-Zapater, J.M.; Zyprian, E.; Moreira, F.M. Genetic diversity and population structure assessed by SSR and SNP markers in a large germplasm collection of grape. BMC plant biology 2013, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
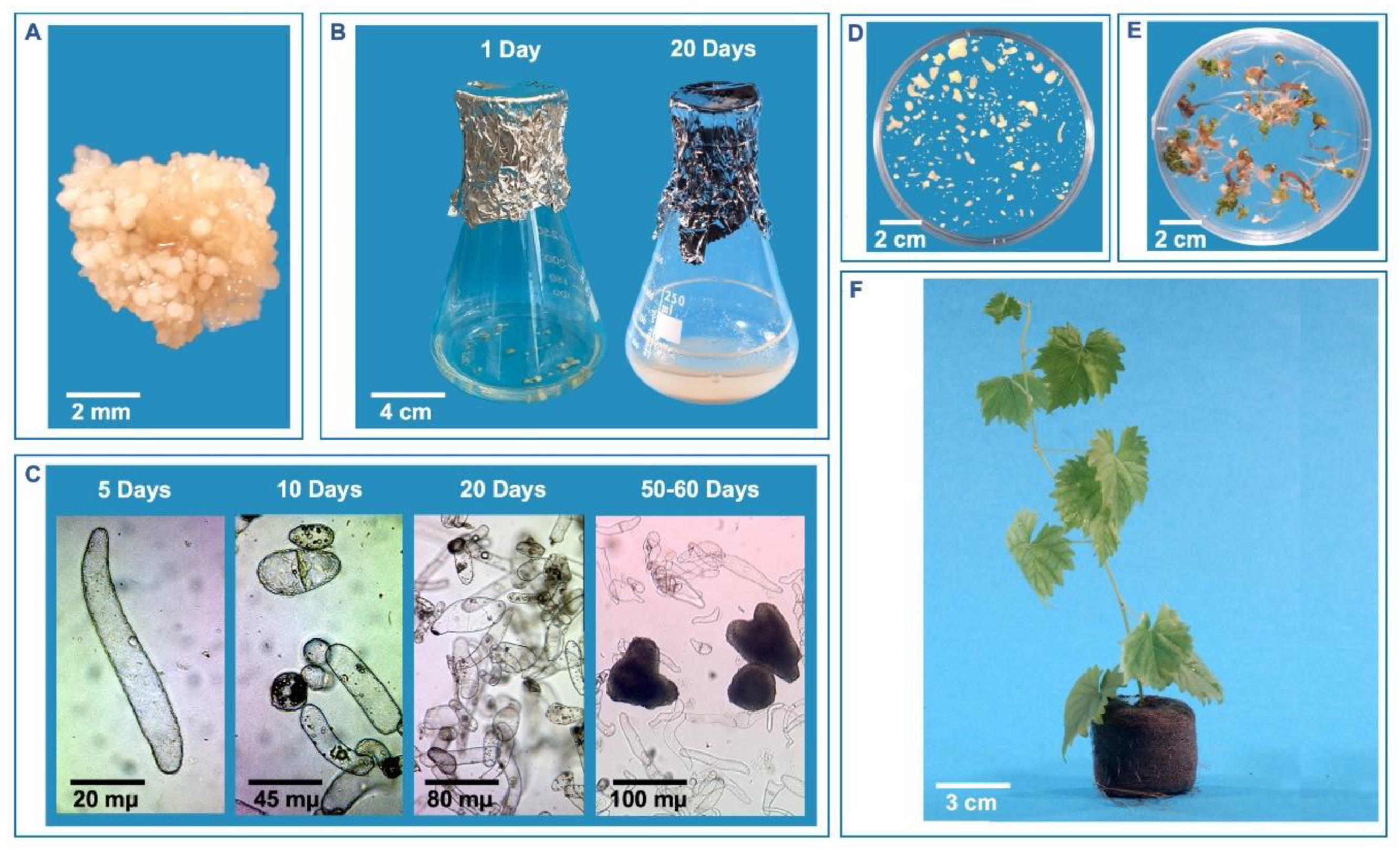

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




