Submitted:
20 August 2024
Posted:
21 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtaining Reproductive Fluids (OF and UF)
2.2. Derive and Culture Skin Fibroblasts for Use as Karyoplasts
2.3. In Vitro Oocyte Maturation (IVM)
2.4. Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SNCT) by handmade cloning (HMC)
2.4.1. Cytoplast Preparation
2.4.2. Triplets’ Formation and Fusion
2.4.3. Activation of Cloned Embryos
2.4.4. In Vitro Culture of Cloned Embryos in the WOW System
2.5. In Vitro Production of Parthenogenetic Embryos
2.6. Evaluation of ROS and GSH Levels in Parthenogenetic and Cloned Embryos
2.7. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of FO and FU on the In Vitro Development of Parthenogenetic Embryos
3.2. Effect of OF and UF on the In Vitro Development of Cloned Embryos
3.3. Effect of OF and UF on the Presence and Levels of ROS and GSH in Parthenogenetic Embryos
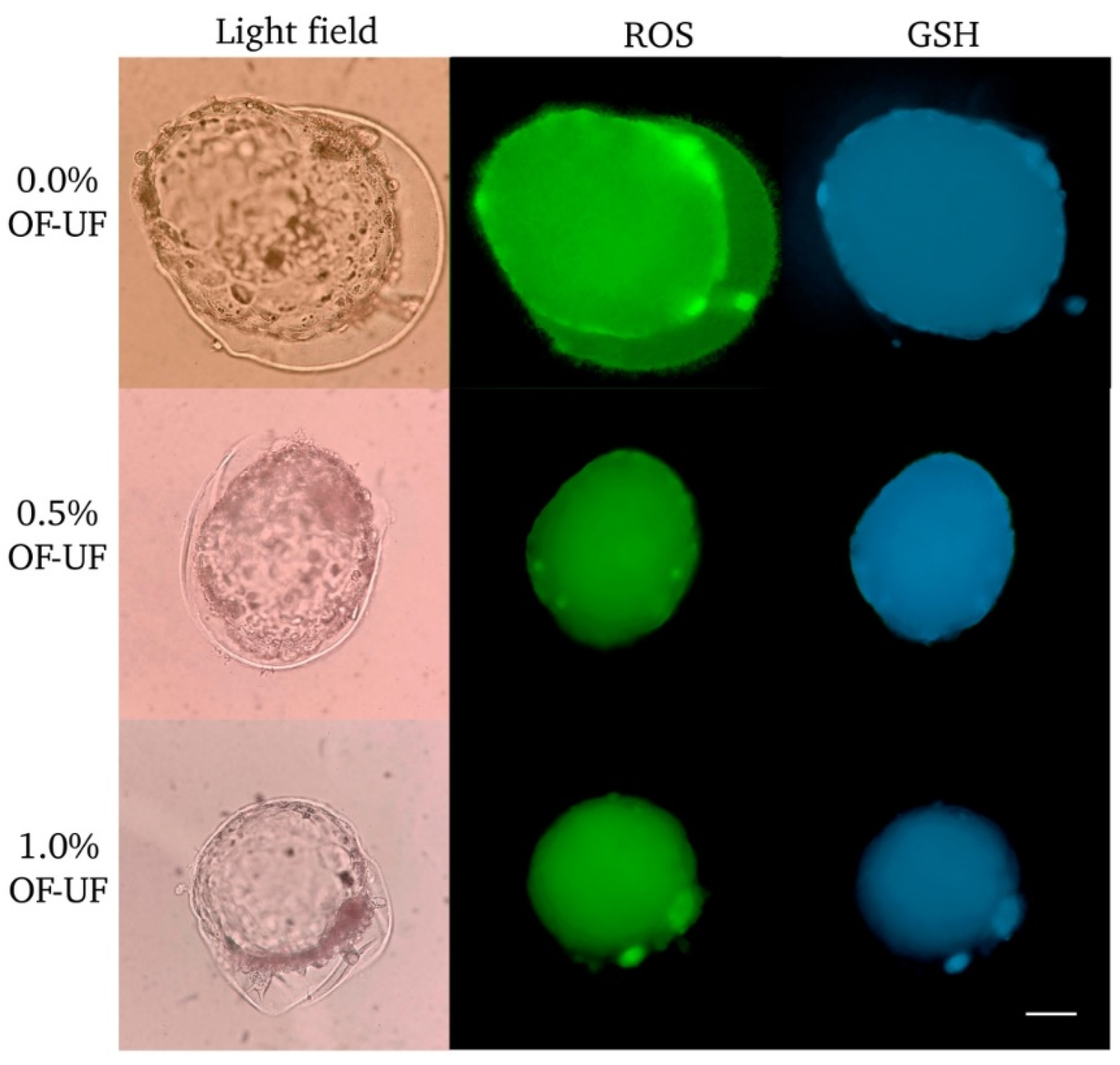
3.4. Effect of OF and UF on the Presence and Levels of ROS and GSH in Cloned Embryos
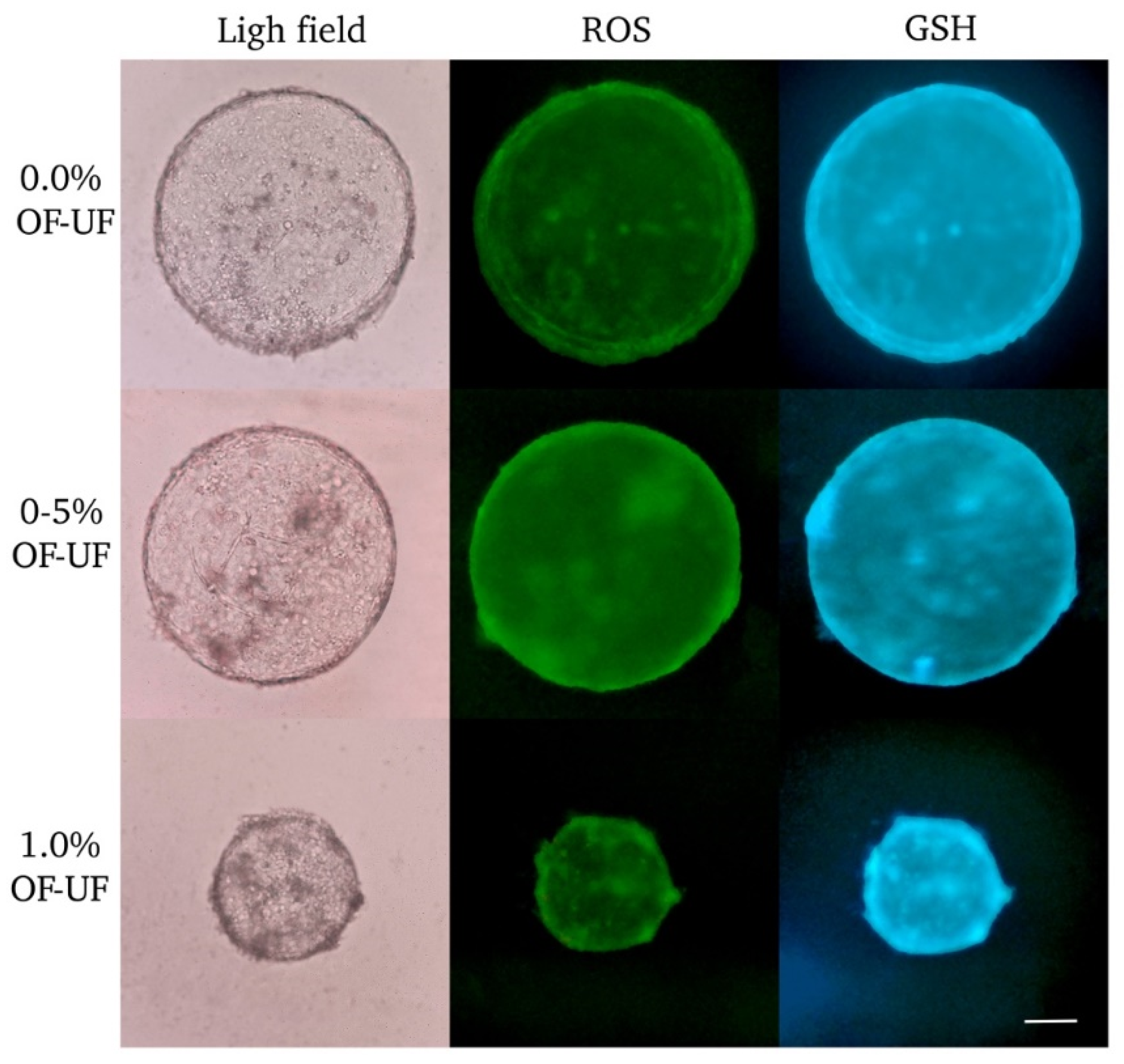
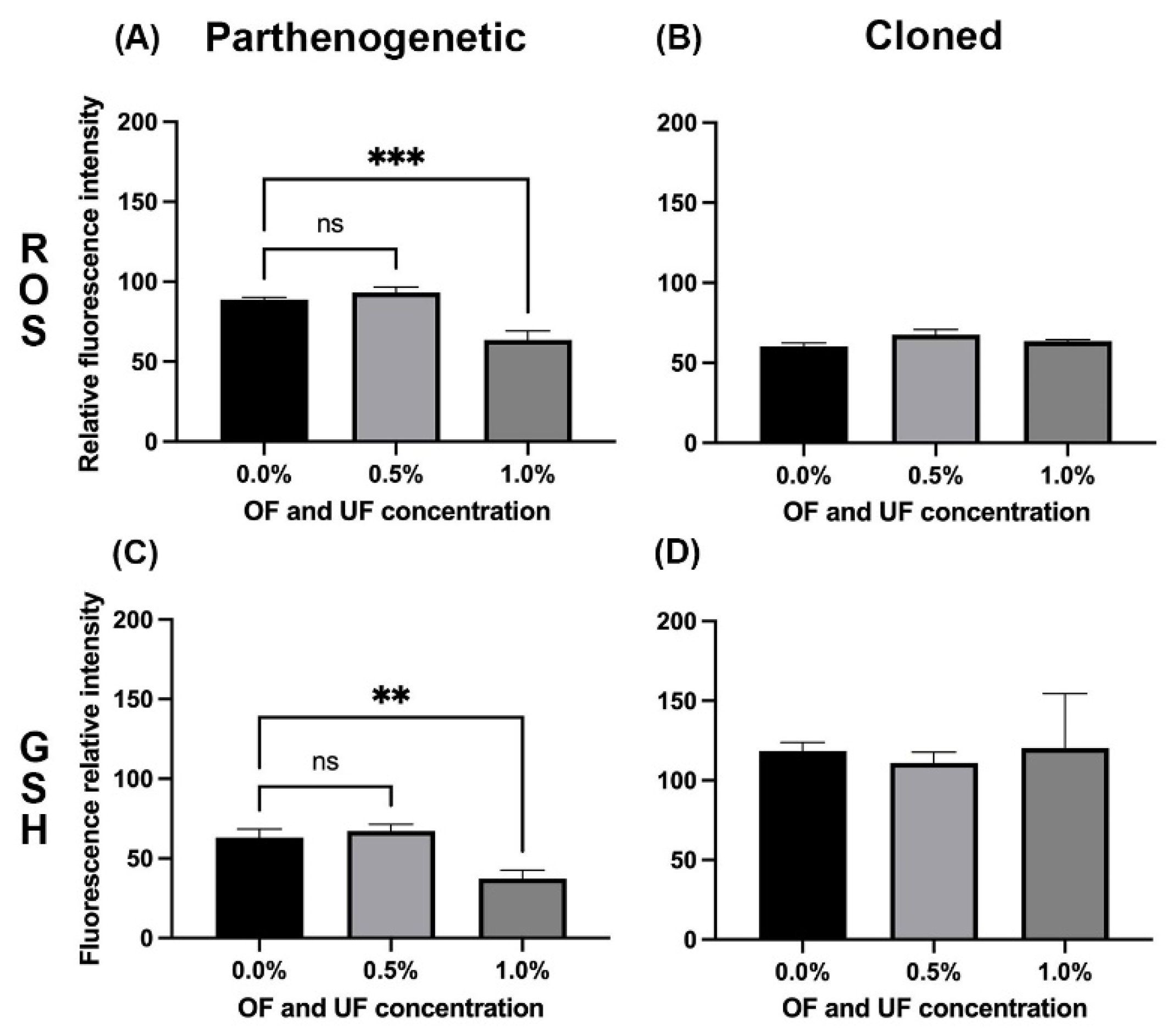
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Viana, J.H.M. Statistics of embryo production and transfer in domestic farm animals. In: Embryo Technology Newsletter, 2022; 2021, 40 https://www.iets.org/Portals/0/Documents/Public/Committees/DRC/IETS_Data_Retrieval_Report_2021.pdf [accessed on 10 April 2024].
- Galli, C.; Lazzari, G. 25th Anniversary of cloning by somatic-cell nuclear transfer: Current applications of SCNT in advanced breeding and genome editing in livestock. Reproduction. 2021, 162, F23-F32. [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.A.; Pereira, A.F. Potential role of intraspecific and interspecific cloning in the conservation of wild mammals. Zygote. 2019, 27, 111-117. [CrossRef]
- Bolton, R.L.; Mooney, A.; Pettit, M.T.; Bolton, A.E.; Morgan, L.; Drake, G.J.; Appeltant, R.; Walker, S.L.; Gillis, J.D.; Hvilsom, C. Resurrecting biodiversity: advanced assisted reproductive technologies and biobanking. Reprod Fertil. 2022, 3, R121-R146. [CrossRef]
- Loi, P.; Palazzese, L.; Scapolo, P.A.; Fulka, J.; Fulka, H.; Czernik, M. 25th Anniversary of cloning by somatic-cell nuclear transfer: Scientific and technological approaches to improve SCNT efficiency in farm animals and pets. Reproduction. 2021, 162, F33-F43. [CrossRef]
- Kalds, P.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Cai, B.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Redesigning small ruminant genomes with CRISPR toolkit: Overview and perspectives. Theriogenology. 2020, 147, 25-33. [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Avendaño, J.R.; Ambríz-Garcia, D.A.; Cortez-Romero, C.; Trejo-Cordova, A.; Navarro-Maldonado, M.C.; Current state of the efficiency of sheep embryo production through somatic cell nuclear transfer. Small Rumin Res. 2022, 212, 106702. [CrossRef]
- Simmet, K.; Wolf, E.; Zakhartchenko, V.; Manipulating the Epigenome in Nuclear Transfer Cloning: Where, When and How. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 22, 236. [CrossRef]
- Sawai, K.; Takahashi, M.; Fujii, T.; Moriyasu, S.; Hirayama, H.; Minamihashi, A.; Hashizume, T.; Onoe, S. DNA methylation status of bovine blastocyst embryos obtained from various procedures. J Reprod Dev. 2011, 57, 236-41. [CrossRef]
- Beaujean, N.; Taylor, J.; Gardner, J.; Wilmut, I.; Meehan, R.; Young, L. Effect of limited DNA methylation reprogramming in the normal sheep embryo on somatic cell nuclear transfer. Biol Reprod, 2004, 71, 185–193. [CrossRef]
- Loi, P.; Clinton, M.; Vackova, I.; Fulka, J.; Jr, Feil, R.; Palmieri, C.; Della Salda, L.; Ptak, G. Placental abnormalities associated with post-natal mortality in sheep somatic cell clones. Theriogenology. 2006, 65, 1110-21. [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, C.; Loi, P.; Ptak, G.; Della Salda, L. Review paper: a review of the pathology of abnormal placentae of somatic cell nuclear transfer clone pregnancies in cattle, sheep, and mice. Vet Pathol. 2008, 45, 865-80. [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; You, S.; Cao, Y.; Li, C.; Wei, J.; Wang, D.; Qiao, J.; Zhao, X.; Hu, S.; Quan, R. Aberrant expression of miR-127, miR-21 and miR-16 in placentas of deceased cloned sheep. Res Vet Sci. 2016, 105, 200-4. [CrossRef]
- Nava-Trujillo, H.; Rivera, R.M. Review: Large offspring syndrome in ruminants: current status and prediction during pregnancy. Animal. 2023, 17, Suppl 1, 100740. [CrossRef]
- Young, L.E.; Schnieke, A.E.; McCreath, K.J.; Wieckowski, S.; Konfortova, G.; Fernandes, K.; Ptak, G.; Kind, A. J.; Wilmut, I.; Loi, P.; Feil, R. Conservation of IGF2-H19 and IGF2R imprinting in sheep: effects of somatic cell nuclear transfer. Mech Dev. 2003, 120, 1433-42. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Pan, J.; Zhao, L.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, H. M.; Zhang, D. Discovery of DNA Methylation Status of Peg3, Cdkn1c and Gtl2 in Cloned and Natural Lambs. Prog Biochem Biophys. 2016, 43, 706-715. [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Tang, H.; Wei, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, P. TRIM28 regulates Igf2-H19 and Dlk1-Gtl2 imprinting by distinct mechanisms during sheep fibroblast proliferation. Gene. 2017, 637, 152-160. [CrossRef]
- Cajas, Y.N.; Cañón-Beltrán, K.; de la Blanca, M.G.M.; Sánchez, J.M.; Fernandez-Fuertes, B.; González, E.M.; Rizos, D. Role of reproductive fluids and extracellular vesicles in embryo–maternal interaction during early pregnancy in cattle. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2021, 34, 117-138. [CrossRef]
- Coy, P.; Romar, R.; Romero-Aguirregomezcorta, J. The embryo culture media in the era of epigenetics: is it time to go back to nature? Anim Reprod. 2022, 19, e20210132. [CrossRef]
- Lopera-Vasquez, R.; Hamdi, M.; Maillo, V.; Gutierrez-Adan, A.; Bermejo-Alvarez, P.; Ramírez, M.Á.; Yáñez-Mó, M.; Rizos, D. Effect of bovine oviductal extracellular vesicles on embryo development and quality in vitro. Reproduction. 2017, 153, 461-470. [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, M.; Lopera-Vasquez, R.; Maillo, V.; Sanchez-Calabuig, M.J.; Núnez, C.; Gutierrez-Adan, A.; Rizos, D. Bovine oviductal and uterine fluid support in vitro embryo development. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2018, 30, 935-945. [CrossRef]
- Barrera, A.D.; García, E.V.; Hamdi, M.; Sánchez-Calabuig, M.J.; López-Cardona, Á.P.; Balvís, N.F.; Rizos, D.; Gutiérrez-Adán, A. Embryo culture in presence of oviductal fluid induces DNA methylation changes in bovine blastocysts. Reproduction. 2017, 154, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Canovas, S.; Ivanova, E.; Romar, R.; García-Martínez, S.; Soriano-Úbeda, C.; García-Vázquez, F.A.; Saadeh, H.; Andrews, S.; Kelsey, G.; Coy, P. DNA methylation and gene expression changes derived from assisted reproductive technologies can be decreased by reproductive fluids. Elife. 2017, 6, e23670. [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Kim, J.; Lim, J.; Lee, E. Anthocyanin stimulates in vitro development of cloned pig embryos by increasing the intracellular glutathione level and inhibiting reactive oxygen species. Theriogenology. 2010, 74, 777-85. [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Xing, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y. Melatonin significantly improves the developmental competence of bovine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos. J Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 455-68. [CrossRef]
- [26] Nadri, P.; Ansari-Mahyari, S.; Jafarpour, F.; Mahdavi, A.H.; Tanhaei Vash, N.; Lachinani, L.; Dormiani, K.; Nasr-Esfahani, M. H. Melatonin accelerates the developmental competence and telomere elongation in ovine SCNT embryos. PLoS One. 2022, 17, e0267598. [CrossRef]
- Koo, O.J.; Jang, G.; Kwon, D.K.; Kang, J.T.; Kwon, O.S.; Park, H.J.; H. J.; Kang, S. K.; Lee, B. C. Electrical activation induces reactive oxygen species in porcine embryos. Theriogenology. 2008, 70, 1111-8. [CrossRef]
- Deluao, J.C.; Winstanley, Y.; Robker, R.L.; Pacella-Ince, L.; Gonzalez, M.B.; McPherson, N.O. Oxidative stress and reproductive function: Reactive oxygen species in the mammalian pre-implantation embryo. Reproduction. 2022, 164, F95-F108. [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, L.C.; Coy, P.; Avilés, M.; Gadea, J.; Romar, R. Glycosidase determination in bovine oviducal fluid at the follicular and luteal phases of the oestrous cycle. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2008, 20, 808-17. [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Maldonado, M.C.; Hernández-Martínez, S.; Vázquez-Avendaño, J.R.; Martínez-Ibarra, J.L.; Zavala-Vega, N.L.; Vargas-Miranda, B.; Rivera-Rebolledo J.A.; Ambríz-García D.A. Deriva de células epiteliales de tejido de piel descongelado de Ovis canadensis mexicana para la formación de un banco de germoplasma. Acta Zool. Mex. (n.s.). 2015, 31, 275-282. [CrossRef]
- Ward, F. A., Lonergan, P., Enright, B. P., Boland, M. P. (2000) Factor affecting recovery and quality of oocytes for bovine embryo production in vitro using ovum pick-up technology, Theriogenology, 54(3): 433-446. [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Avendaño, J.R.; Hernández-Martínez, S.; Hernández-Pichardo, J.E.; Rivera-Rebolledo, J.A.; Ambríz-García, D.A.; Navarro-Maldonado, M.C. Efecto del uso de medio secuencial humano en la producción de blastocistos de hembra Ovis canadensis mexicana por clonación manual. Acta Zool. Mex. (n.s.). 2017, 33, 328-338. [CrossRef]
- Hernández Martínez, S.; Hernández Pichardo, J.E.; Vazquez Avendaño, J.R.; Ambríz García, D.A.; Navarro Maldonado, M.C. Developmental dynamics of cloned Mexican bighorn sheep embryos using morphological quality standards. Vet Med Sci, 2020, 6, 382–392. [CrossRef]
- Vajta, G.; Lewis, I.M.; Hyttel, P.; Thouas, G.A.; Trounson, A.O. Somatic cell cloning without micromanipulators. Cloning. 2001, 3, 89-95. [CrossRef]
- Vajta, G.; Korösi, T.; Du, Y.; Nakata, K.; Ieda, S.; Kuwayama, M.; Nagy.; Z.P. The Well-of-the-Well system: an efficient approach to improve embryo development. Reprod Biomed Online. 2008, 17, 73-81. [CrossRef]
- Nina, M.; Ayala, C.; Susaño, R. Fluido uterino de llama (Lama glama), como medio para potenciar el desarrollo embrionario de vacas (Bos taurus) en cultivos in vitro. RIIARn. 2021, 8, 138-145. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Song, E.S.; Kim, E.S.; Cong, P.Q.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.I.; Yi, Y.J.; Park, C.S. Effects of Oviductal Fluid, Culture Media and Zona Pellucida Removal on the Development of Porcine Embryos by Nuclear Transfer. Asian-australas J Anim Sci. 2009, 22, 962-968. [CrossRef]
- Velazquez, M.A.; Parrilla, I.; Van Soom, A.; Verberckmoes, S.; Kues, W.; Niemann, H. Sampling techniques for oviductal and uterine luminal fluid in cattle. Theriogenology. 2010, 73, 758-67. [CrossRef]
- Itze-Mayrhofer, C.; Brem, G. Quantitative proteomic strategies to study reproduction in farm animals: Female reproductive fluids. J Proteomics. 2020, 225, 103884. [CrossRef]
- Cebrian-Serrano, A.; Salvador, I.; García-Roselló, E.; Pericuesta, E.; Pérez-Cerezales, S.; Gutierrez-Adán, A.; Coy, P.; Silvestre, M. A. Effect of the bovine oviductal fluid on in vitro fertilization, development and gene expression of in vitro-produced bovine blastocysts. Reprod Domest Anim. 2013, 48, 331-8. [CrossRef]
- Soleilhavoup, C.; Riou, C.; Tsikis, G.; Labas, V.; Harichaux, G.; Kohnke, P.; Reynaud, K.; de Graaf, S.P.; Gerard, N.; Druart, X. Proteomes of the Female Genital Tract During the Oestrous Cycle. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016, 15, 93-108. [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.M.; Ramadoss, J.; Magness, R.R. Proteomic profile of uterine luminal fluid from early pregnant ewes. J Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3878-85. [CrossRef]
- Soto-Heras, S.; Paramio, M.T. Impact of oxidative stress on oocyte competence for in vitro embryo production programs. Res Vet Sci. 2020, 132, 342-350. [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.H.; Li, Y.H.; Jiao, L.H.; Wang, X.N.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.H. Extracellular and intracellular factors affecting nuclear and cytoplasmic maturation of porcine oocytes collected from different sizes of follicles. Zygote. 2002, 10, 253-60. [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; George, A.; Saha, A.P.; Sharma, R.; Manik, R.S.; Chauhan, M.S.; Palta, P.; Singla, S.K. Effect of cytoplasmic volume on developmental competence of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryos produced through hand-made cloning. Cell Reprogram. 2011, 13, 257-62. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Luo, C.; Deng, K.; Wu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, J.; Lu, F.; Shi, D. Cytoplasmic volume of recipient oocytes affects the nucleus reprogramming and the developmental competence of HMC buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryos. J Vet Med Sci. 2018, 80, 1291-1300. [CrossRef]
- Raja, A.K.; Sahare, A.A.; Jyotsana, B.; Priya, D.; Palta, P.; Chauhan, M.S.; Manik, R.S.; Singla, S.K. Reducing the cytoplasmic volume during hand-made cloning adversely affects the developmental competence and quality, and alters relative abundance of mRNA transcripts and epigenetic status of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryos. Anim Reprod Sci. 2019, 208, 106136. [CrossRef]
- Averill-Bates, D.A. The antioxidant glutathione. Vitam Horm. 2023, 121, 109-141. [CrossRef]
| OF-UF (%) | No. | Cleavage | 4 to 16- cells | Morula | Blastocysts | Fragmented |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 140 | 81.6 ± 3.6a (116) | 31.8 ± 4.9a (40) | 52.7 ± 8.1a (62) | 44.9 ± 7.5a (50) | 18.6 ± 8.6a (14) |
| 0.5 | 132 | 81.1 ± 4.0a (107) | 45.4 ± 6.5a (49) | 46 ± 6.7a (52) | 35.7 ± 5.7a (34) | 10.3 ± 4.8a (6) |
| 1.0 | 129 | 71.5 ± 6.1a (95) | 37.6 ± 10.9a (31) | 54.9 ± 12.6a (55) | 28 ± 4.0a (28) | 9.3 ± 3.9a (9) |
| 2.0 | 55 | 67.3 ± 12.5a (41) | 100b (41) | 0b | 0b | 0a |
| OF-UF (%) |
No. | Cleavage | 4 to 16- cells |
Morula | Blastocysts |
Fragmented |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 78 | 97.1 ± 2.9a (76) | 27.9 ± 8.0a (20) | 47.3 ± 9.2a (37) | 28.1 ± 5.5a (21) | 24.8 ± 3.7a (19) |
| 0.5 | 76 | 99.1 ± 0.9a (75) | 36.8 ± 9.4a (28) | 45.1 ± 6.5a (34) | 21.2 ± 4.1a (15) | 18.1 ± 4.7a (13) |
| 1.0 | 66 | 100a (66) | 62.1 ± 7.0a (41) | 27.1 ± 7.0b (18) | 7.7 ± 3.0b (5) | 10.9 ± 4.0a (7) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





