Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
17 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
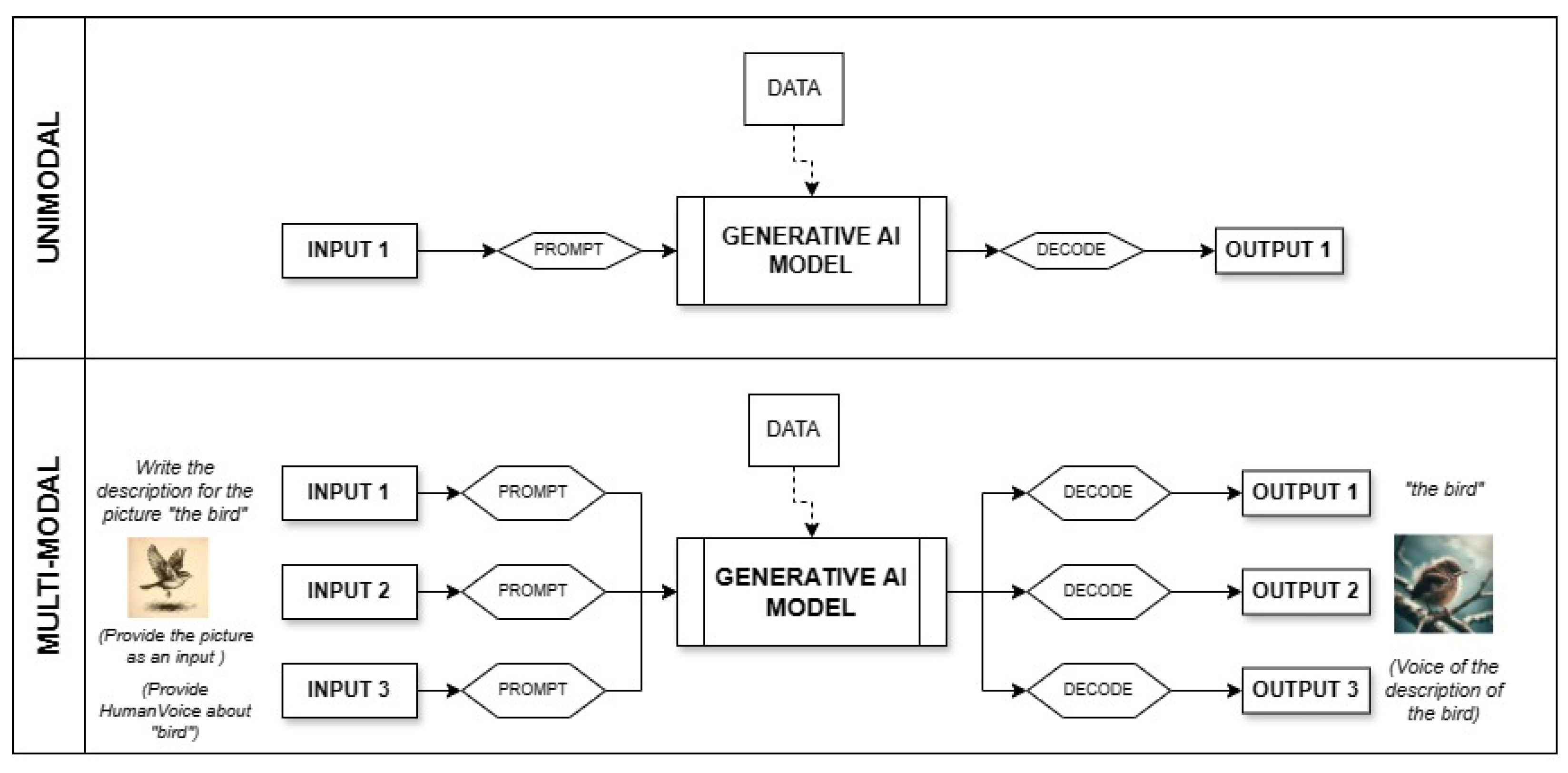
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. AI Serves as a Creative Catalyst for Multimodal Design Generation
| Aspect | Resume | Specific generative AI applications or technology - Source |
|---|---|---|
| Computational efficiency | AI enables rapid design generation, exploration, and iteration. |
1MidJourney - [10,11,12]; NS2-[13,14]; Dall-E3 - [15]. |
| Designers can quickly produce, evaluate, and refine multiple options, leading to more innovative and optimized solutions. | NLP4 and MMAIR5 - [16] NS-[17,18,19,20]; Dall-E - [21,22]; Dde6-GAN7 - [23]; CLIP8-[24]. |
|
| Generative AI tools for architecture need high computational power and complex algorithms. | NS-[18,25]; ChatGPT9-[26]; Bard AI10-[26]; Neural Canvas11 [27]. |
|
| Ensuring efficiency and accessibility for all firms is challenging due to large datasets, diverse inputs, and multiple design constraints. | NS – [18,25]; ChatGPT-[26]; Bard AI - [26]; NS-[16,17,18,19,20]; LLMs12-[28] |
|
| These demands can slow down processing and increase resource consumption. | NS-[18,25]; Neural Canvas [27]. | |
| Accuracy | Significant improvement in imaging accuracy ensures high-fidelity imaging for precise applications. | CGANs13-[29]; U-Net Arch14 - [29]. |
| Enhances reliability of multimodal communication and AI diagnostic processes. | GenAIVA15 and FER16 -[30]; ChatGPT-[31]; |
|
| Improves accuracy and transparency with visual explanations and textual analysis. | ChatGPT-[31]; | |
| Maintaining high accuracy while optimizing resource usage and ensuring adaptability across diverse contexts is challenging. | LangChain LLM-[32]; | |
| Ensuring consistent and reliable accuracy, generalizability, and efficient knowledge transfer in resource-limited environments is crucial. | 3DI17-[33]; MML18-[33]; GenAINet10-[34]. |
|
| Making visual explanations and textual analyses both accurate and comprehensible is challenging. | ChatGPT-[31]. | |
|
User Experience (UX) |
AI tools, like chatbots, improve adaptability, responsiveness, and user interaction by managing tasks and information efficiently. | ChatGPT-[35]; |
| Enhanced visualization and engagement build trust in AI systems | MidJourney-[36,37]; | |
| Integrating text, image, and voice modalities into one tool is technically complex. | NS - [38]. | |
| Generative AI tools require new skills and workflows, causing potential frustration and reduced productivity. | Dall-E-[36]; OpenAI-[39] | |
| Interoperability issues and variable AI output quality may need refinement. | MidJourney - [36]; Dall-E - [36]. |
|
| Limited customization can constrain designers' creativity. | NS - [38]. | |
| Building user trust is challenging due to past unreliable performance and data privacy and security concerns. | 20GAIS (IBM Watson) - [40] |
4.2. Blockchain Provides Methods of Verifying and Tracing the Authenticity of AI-Human Generative Design
4.3. Research Challenges, Limitations and Future Directions
| Aspect | Challenges | Addressing Challenges |
Proposed Solution | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Authenticity and traceability | Ensuring the authenticity and traceability of AI-generated images | Developing a blockchain-integrated framework that ensures the authenticity and traceability of the generative AI process. | A blockchain system can be used to store AI-generated images and their metadata as NFTs, ensuring secure and traceable data. | Scalability and performance of integrated systems in large-scale applications |
| Integration of technologies | Integrating multimodal generative AI and blockchain technologies seamlessly | Develop a structured framework for integration. | Combine multimodal generative AI and blockchain technology in a streamlined workflow for architectural design. | Interoperability between different generative AI tools and blockchain platforms |
| Data ownership and legal issues | Managing data ownership for AI-generated content | Addressing data ownership and regulatory issues by ensuring proper attribution and legal compliance through blockchain records. | Store AI-generated images and metadata in a blockchain system, ensuring data ownership and legal compliance through NFTs. | Comprehensive studies on legal and regulatory frameworks required to govern the use of AI and blockchain in architectural design |
|
User experience and interaction |
Improving design efficiency, accuracy, and user interaction | Utilizing detailed prompt engineering to ensure accurate and relevant AI-generated images that align with the intended architectural designs. | Use generative AI applications to create and refine architectural designs, ensuring user-friendly interaction and high-quality outputs. | User acceptance and trust in AI-generated designs and blockchain-based data management |
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davenport, T. H.; Mittal, N. How Generative AI Is Changing Creative Work, Harvard Business School Publishing, 2022. https://hbr.org/2022/11/how-generative-ai-is-changing-creative-work.
- Liu, Y.-C.; Liang, C. Design exploration predicts designer creativity: a deep learning approach, Cognitive Neurodynamics, 14(3), 2020, 291-300. 10.1007/s11571-020-09569-7. [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Fuge, M.; Brown, D. C. Design creativity, Artificial Intelligence for Engineering Design, Analysis and Manufacturing, 32(4), 2018, 363-364. 10.1017/S089006041800015X https://www.cambridge.org/core/article/design-creativity/F169FA985C16C17B2DEBBADDCB25C1A5.
- Dreith, B. How AI software will change architecture and design, Dezeen Limited, 2022. https://www.dezeen.com/2022/11/16/ai-design-architecture-product/.
- Litan, A. Why trust and security are essential for the future of generative AI, Gartner Inc., 2023. https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2023-04-20-why-trust-and-security-are-essential-for-the-future-of-generative-ai.
- Samuelson, P. Generative AI meets copyright, 381(6654), 2023, 158-161. [CrossRef]
- Fitriawijaya, A.; Taysheng, J. Multimodal Generative AI and NFT Metadata, Taipei, Taiwan, Release Date. 10.17632/d9zh352rf2.1.
- Golden, A.; Hsia, S.; Sun, F.; Acun, B.; Hosmer, B.; Lee, Y.; Devito, Z.; Johnson, J.; Wei, G.-Y.; Brooks, D. Generative AI Beyond LLMs: System Implications of Multimodal Generation, arXiv preprint arXiv:.14385, 2023. 10.48550/arXiv.2312.14385.
- Hariri, W. Unlocking the potential of ChatGPT: A comprehensive exploration of its applications, advantages, limitations, and future directions in natural language processing, arXiv preprint arXiv:.02017, 2023. 10.48550/arXiv.2304.02017.
- Del Castillo, A. P., AI: discovering the many faces of a faceless technology, ETUI aisbl, Brussels, Belgium, 2023 https://www.etui.org/sites/default/files/2023-05/AI-Guide-discovering%20the%20many%20faces%20of%20a%20faceless%20technology-2023.pdf.
- Ma, S. Y. Exploring ambiguity in generative AI images and its impact on collaborative design ideation, Master Student Thesis: Master, Industrial Engineering and Innovation Sciences, Eindhoven University of Technology, 2024 https://pure.tue.nl/ws/portalfiles/portal/320754968/MTP_thesis_report_Sherry_Ma.pdf.
- Jaruga-Rozdolska, A. Artificial intelligence as part of future practices in the architect's work: MidJourney generative tool as part of a process of creating an architectural form, Architectus, 3( 71), 2022, 95-104. [CrossRef]
- Meeran, A. AI and Architecture: Image-based Machine Learning for early-stage design conceptualization, 2021.
- Basole, R. C.; Major, T. Generative AI for Visualization: Opportunities and Challenges, IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 44(2), 2024, 55-64. [CrossRef]
- Harreis, H.; Koullias, T.; Roberts, R.; Te, K. Generative AI: Unlocking the future of fashion, McKinsey Company, 2023. https://digital-humanai.io/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Generative-AI-Unlocking-the-future-of-fashion.pdf.
- Zhong, C.; Yi'an Shi, L. H. C.; Wang, L. AI-enhanced performative building design optimization and exploration, presented at the 29th International Conference on Computer-Aided Architectural Design Research in Asia, CAADRIA 2024, The Association for Computer-Aided Architectural Design Research in Asia (CAADRIA), 1(2024 Published. https://papers.cumincad.org/data/works/att/caadria2024_15.pdf.
- Bstieler, L.; Noble, C. H., The PDMA Handbook of Innovation and New Product Development, John Wiley & Sons, 2023.
- Li, C.; Zhang, T.; Du, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, H. Generative AI for Architectural Design: A Literature Review, arXiv preprint arXiv:.01335, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Cai, S.; Yang, W.; Wu, W.; Shen, H. Exploring Optimal Combinations: The Impact of Sequential Multimodal Inspirational Stimuli in Design Concepts on Creativity, presented at the Proceedings of the 2024 ACM Designing Interactive Systems Conference, IT University of Copenhagen, Denmark Association for Computing Machinery, 2024 Published, 2788–2801. [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, K. S., Can Artificial Intelligence Mark the Next Architectural Revolution? Design Exploration in the Realm of Generative Algorithms and Search Engines, Springer, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Paananen, V.; Oppenlaender, J.; Visuri, A. J. I. J. O. a. C. Using text-to-image generation for architectural design ideation, 2023, 14780771231222783. [CrossRef]
- Albaghajati, Z. M.; Bettaieb, D. M.; Malek, R. B. Exploring text-to-image application in architectural design: insights and implications, Architecture, Structures and Construction, 3(4), 2023, 475-497. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Marion, T.; Moghaddam, M. Dde-gan: Integrating a data-driven design evaluator into generative adversarial networks for desirable and diverse concept generation, Journal of Mechanical Design, 145(4), 2023, 041407. [CrossRef]
- Salem, A. A.; Mansour, Y.; Eldaly, H. Generative vs. Non-Generative AI: Analyzing the Effects of AI on the Architectural Design Process, Engineering Research Journal, 53(2), 2024, 119-128. [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Lu, X.; Fei, Y.; Gu, Y.; Huang, Y. Generative AI design for building structures, Automation in Construction, 157, 2024, 105187. [CrossRef]
- Rane, N.; Choudhary, S.; Rane, J. Integrating ChatGPT, Bard, and leading-edge generative artificial intelligence in architectural design and engineering: applications, framework, and challenges, SSRN Electronic Journal, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, C.; Fan, M.; Wang, Z. Neural Canvas: Supporting Scenic Design Prototyping by Integrating 3D Sketching and Generative AI, presented at the Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA Association for Computing Machinery, 2024 Published, Article 1056. [CrossRef]
- Makatura, L.; Michael Foshey; Bohan Wang; Felix Hähnlein; Pingchuan Ma; Bolei Deng; Megan Tjandrasuwita; Andrew Spielberg; Crystal Elaine Owens; Peter Yichen Chen; Allan Zhao; Amy Zhu; Wil J. Norton; Edward Gu; Joshua Jacob; Yifei Li; Adriana Schulz; Matusik., W. Large Language Models for Design and Manufacturing, An MIT Exploration of Generative AI, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, J.; Hassan, S. T.; Cheema, M. I. Application of conditional generative adversarial networks toward time-efficient and high-fidelity imaging via multimode fibers, in AI and Optical Data Sciences V, SPIE, 12903, 2024, 69-73. [CrossRef]
- F, G.; N, M.; Khan, J.; S. H, K. M. Envisioning the interactive convergence of Generative AI and Facial Expression Recognition, in 2024 IEEE 9th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT)), 2024, 1-5. 10.1109/I2CT61223.2024.10543745.
- Koga, S. Evaluating ChatGPT in pathology: towards multimodal AI in medical imaging, Journal of Clinical Pathology, 2024, jcp-2024-209483. [CrossRef]
- Micheal, A. A.; Prasanth, A.; Aswin, T.; Krisha, B. Advancing Educational Accessibility: The LangChain LLM Chatbot's Impact on Multimedia Syllabus-Based Learning, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Dollar, O. Deep Inverse Design, Discovery, and Optimization of Molecular Structure through 3D Invariant and Multimodal Machine Learning, 2023 http://hdl.handle.net/1773/50264.
- Zou, H.; Zhao, Q.; Bariah, L.; Tian, Y.; Bennis, M.; Lasaulce, S.; Debbah, M.; Bader, F. GenAINet: Enabling Wireless Collective Intelligence via Knowledge Transfer and Reasoning, arXiv preprint:2402.16631, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Zürcher, A. Developing a Chatbot for Internal Documents, Master, Business Information Technology, Haaga-Helia University of Applied Sciences, Finland, 2024 https://www.theseus.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/861594/Zurcher_Alexandre.pdf?sequence=2.
- Parati, I.; Zolotova, M. Using Future Thinking as a steering tool for Generative AI creative output: a case study aiming at rethink lighting in the next future, in Human Interaction & Emerging Technologies: Artificial Intelligence & Future Applications Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Human Interaction and Emerging Technologies, IHIET-AI 2024, April 25–27, 2024, Lausanne, Switzerland, Technology & Engineering, AHFE International Open Access), 2024. [CrossRef]
- Nistler, J.; Pojeta, T. J. V. T.-E. I. Graphical use of AI, 65(4), 2023, 54-56. https://www.vtei.cz/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/6575-casopis-VTEI-4-23-EN-AI.pdf.
- Bagnato, V. P. Artificial Intelligence for Design: The Artificial Intelligence of Objects, Interdisciplinary Journal of Architecture and Built Environment, 2023, 30-35. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Valerio-Perna/publication/379573623_FORUM_AP_27_Venturing_into_the_Age_of_AI_Insights_and_Perspectives/links/660fb14db839e05a20bd9cfb/FORUM-A-P-27-Venturing-into-the-Age-of-AI-Insights-and-Perspectives.pdf#page=31.
- Schraml N, T. (2023, 2023 August-September) 'You've Got All the Weapons You Need. Now Fight!'. Database Trends & Applications [Article]. 32. Available: https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A766676216/AONE?u=anon~172811b0&sid=googleScholar&xid=b8f48060.
- Sharma, S. K.; Dwivedi, Y. K.; Metri, B.; Lal, B.; Elbanna, A., Transfer, Diffusion and Adoption of Next-Generation Digital Technologies: IFIP WG 8.6 International Working Conference on Transfer and Diffusion of IT, TDIT 2023, Nagpur, India, December 15–16, 2023, Proceedings, Part I, Springer Nature, 2023 https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-031-50192-0.
- Tomaževič, N.; Ravšelj, D.; Aristovnik, A. Artificial Intelligence for human-centric society: The future is here, in, European Liberal Forum), 2023. https://liberalforum.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Artificial-Intelligence-for-human-centric-society.pdf.
- Mcnamara, T. Artificial intelligence and the emergence of co-creativism in contemporary art, INSAM Journal of Contemporary Music, Art.
- Technology, (11), 2023, 12-38. https://www.ceeol.com/search/article-detail?id=1210421.
- Zhang, B.; Chen, G.; Ooi, B. C.; Shou, M. Z.; Tan, K. L.; Tung, A. K. H.; Xiao, X.; Yip, J. W. L.; Zhang, M. Managing Metaverse Data Tsunami: Actionable Insights, IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2024, 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Xue, W.; Jensen, H.; Rosas, F.; Shaw, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J. J. a. P. A. Pathway to Future Symbiotic Creativity, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Parra Pennefather, P. Prototyping with Generative AI, in Creative Prototyping with Generative AI: Augmenting Creative Workflows with Generative AI, Springer, 2023, 109-143. [CrossRef]
- Ioannıdıs, S.; Kontıs, A. P. The 4 Epochs of the Metaverse, Journal of Metaverse, 3(2), 2023, 152-165. [CrossRef]
- Kalpokas, I. J. P.; Criticism, S. Work of art in the Age of Its AI Reproduction, 2023, 01914537231184490. [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, I. Understanding the Influence of Artificial Intelligence Art on Transaction in the Art World, Master, School of Humanities, Social, Science, and Economics, International Hellenic University, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2024 https://repository.ihu.edu.gr/xmlui/bitstream/handle/11544/30356/Ion%20Rudolf.pdf?sequence=1.
- Gupta, R.; Pal, S. K. Introduction to Metaverse, Springer Books, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Popescu, A.-D. Non-fungible tokens (nft)–innovation beyond the craze, in 5th International Conference on Innovation in Business, Economics and Marketing Research, 32, 2021, 26-30. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/353973149_Non-Fungible_Tokens_NFT_-_Innovation_beyond_the_craze#fullTextFileContent.
- Sahu, B.; Chandramohan Jha, A. M. NFT Marketplaces: The Future of Digital Asset Trading, International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology (IJSRCSEIT), 9(3), 2023, 513-519. [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, H. Research on Blockchain Cross-Chain Model Based on "NFT + Cross-Chain Bridge", IEEE Access, 12, 2024, 77065-77078. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, Q.; Chen, S. Non-fungible token (NFT): Overview, evaluation, opportunities and challenges, arXiv preprint arXiv:.07447, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Moreaux, A. Visual content tracking, IPR management, & blockchain: from process abstraction to functional interoperability, Institut Polytechnique de Paris, 2023 https://theses.hal.science/tel-04418984/.
- Lu, W.; Wu, L. A blockchain-based deployment framework for protecting building design intellectual property rights in collaborative digital environments, Computers in Industry, 159, 2024, 104098. [CrossRef]
- Truong, V. T.; Le, L.; Niyato, D. Blockchain meets metaverse and digital asset management: A comprehensive survey, Ieee Access, 11, 2023, 26258-26288. [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Kietzmann, J.; Pitt, L.; Dabirian, A. The evolution of non-fungible tokens: Complexity and novelty of NFT use-cases, IT Professional, 24(1), 2022, 9-14. [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-H.; Rust, R. T. J. J. O. S. R. Artificial intelligence in service, 21(2), 2018, 155-172. [CrossRef]
- Morháč, D.; Valaštín, V.; Košťál, K.; Kotuliak, I. Cross-Chain Payments on Blockchain Networks: An Apartment Booking Use-Case, presented at the Proceedings of the 39th ACM/SIGAPP Symposium on Applied Computing, Avila, Spain Association for Computing Machinery, 2024 Published, 608–611. [CrossRef]
- Battah, A.; Madine, M.; Yaqoob, I.; Salah, K.; Hasan, H. R.; Jayaraman, R. Blockchain and NFTs for trusted ownership, trading, and access of AI models, IEEE Access, 10, 2022, 112230-112249. [CrossRef]
- Bhujel, S.; Rahulamathavan, Y. A survey: Security, transparency, and scalability issues of nft's and its marketplaces, Sensors, 22(22), 2022, 8833. [CrossRef]
- Khalil, U.; Uddin, M.; Malik, O. A.; Hong, O. W. A Novel NFT Solution for Assets Digitization and Authentication in Cyber-Physical Systems: Blueprint and Evaluation, IEEE Open Journal of the Computer Society, 5, 2024, 131-143. [CrossRef]
| Input | Output | |
|---|---|---|
| Image options | Selected images | |
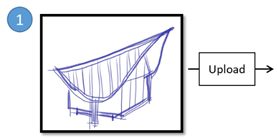 Design Intention: Micro Library is located in the rice field, with a building concept modern house with a pyramid roof Produce a hand sketch depicting the intended shape of the building to ensure alignment with the desired design. |
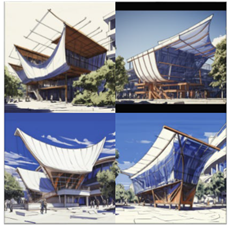 Prompt:https://s.mj.run/mzXZOLMb-Xw people walking, sunny day, architectural rendering --s 750 |
 09effa33-8139-42cc-8704-feeddebf8186 |
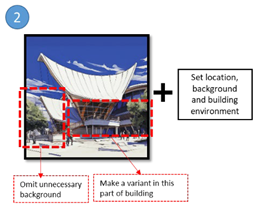 Modify the building and add the environment to adjust with design intention. |
 Prompt: modern stilt house building with long cube shape, with wooden material and perforated building facade |
 c4e63e2f-b027-4234-986b-ef2294080713 |
 Modify the building element |
 Prompt: trees and sky, --no building - Variations (Region) |
 8084c539-22e0-4cec-8163-84eba9190947 |
| Generative AI image linked to metadata in Firebase storage: | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Image Linked in Firebase storage: | |
| https://firebasestorage.googleapis.com/v0/b/genainft-ac24b.appspot.com/o/image%2F1.png?alt=media&token=0aab1e85-3c98-4e04-ac79-db175ab7c82e | |
| Metadata (.json file): | |
| { "attributes": [ { "username": "digicliffnotes", "user_id": "1084483399319822387", "job_id": "c4e63e2f-b027-4234-986b-ef2294080713", "creator_name": "Adam", "creation_date": "April 13th, 2024 11:26 pm", "creation_tool": "Midjourney", "prompt": "modern_stilt_house_building_with_long_cube_shape_with_wooden_material_and_perforated_building_facade", "image_link": "https://cdn.discordapp.com/attachments/1087237286707605535/1228727456182177862/digicliffnotes_modern_stilt_house_building_with_long_cube_shape_c4e63e2f-b027-4234-986b-ef2294080713.png? ex=662d189e&is=661aa39e&hm=e6931926dc71ae46f1f1966444fa2b5f344916e0a168a2b74e71688c1f69a478&" } ], "image":"https://firebasestorage.googleapis.com/v0/b/genainft-ac24b.appspot.com/o/image%2F1.png?alt=media&token=0aab1e85-3c98-4e04-ac79-db175ab7c82e", "name": "Design_option #1" } | |
| Link of metadata in Firebase storage : | |
| https://firebasestorage.googleapis.com/v0/b/genainft-ac24b.appspot.com/o/metadata%2F1.json?alt=media&token=c08b907d-b6f4-4653-9ceb-c8966e48e659 | |
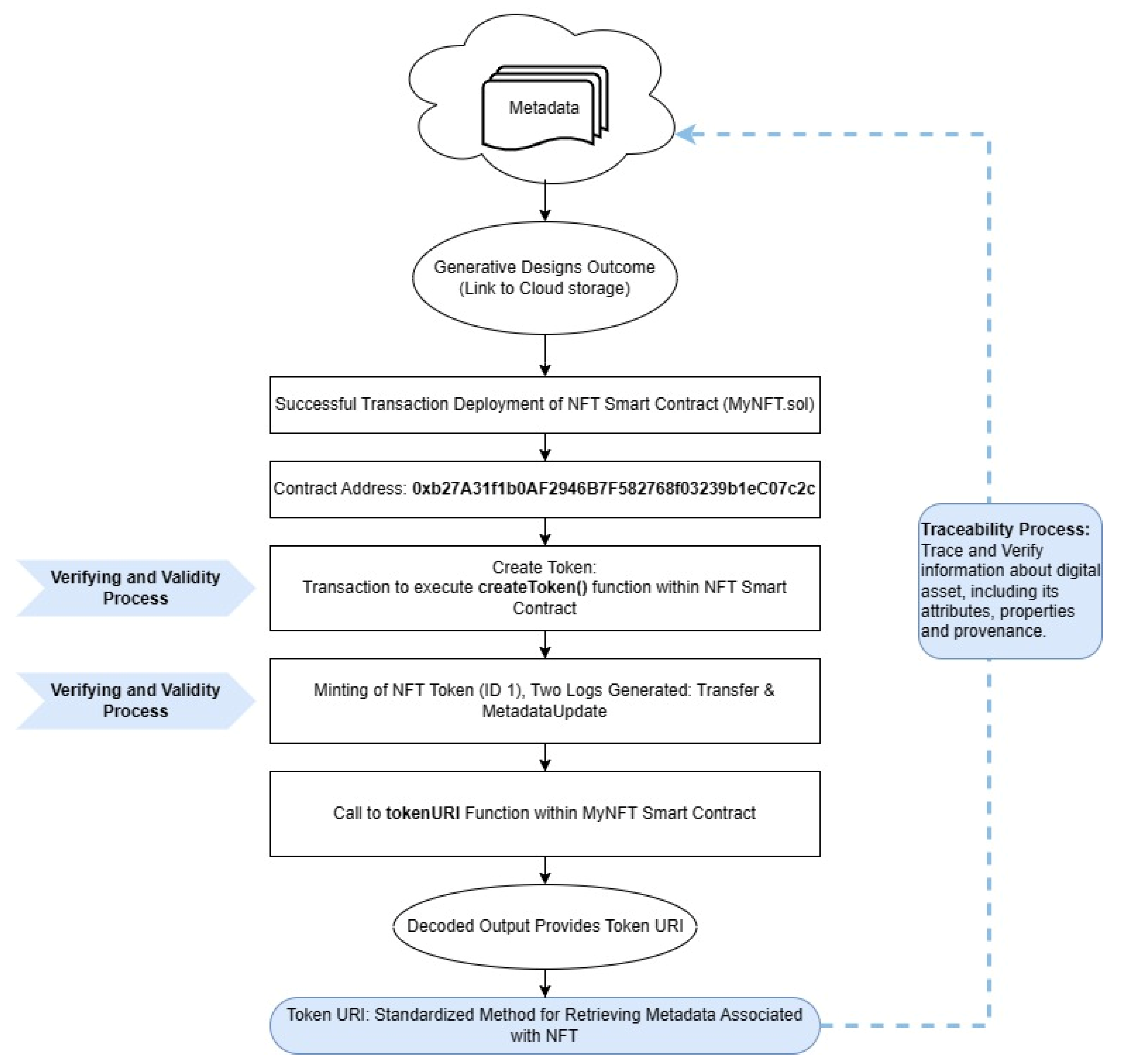
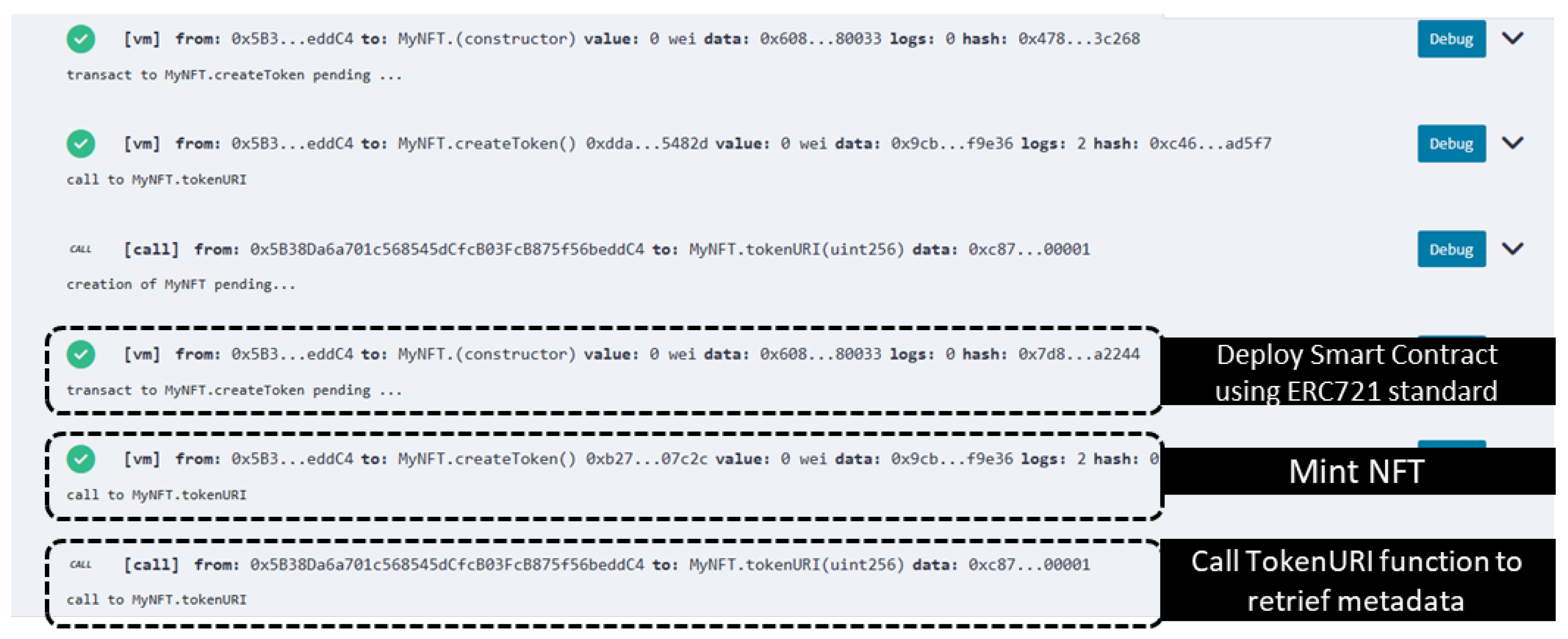
| Deploy and transaction the metadata using Smart Contract: | |
| The contract address: | 0xb27A31f1b0AF2946B7F582768f03239b1eC07c2c |
| Token address: | 0x5B38Da6a701c568545dCfcB03FcB875f56beddC4 |
| Token URI: | "https://firebasestorage.googleapis.com/v0/b/genainft-ac24b.appspot.com/o/metadata%2F1.json?alt=media" |
| Key points | Description |
|---|---|
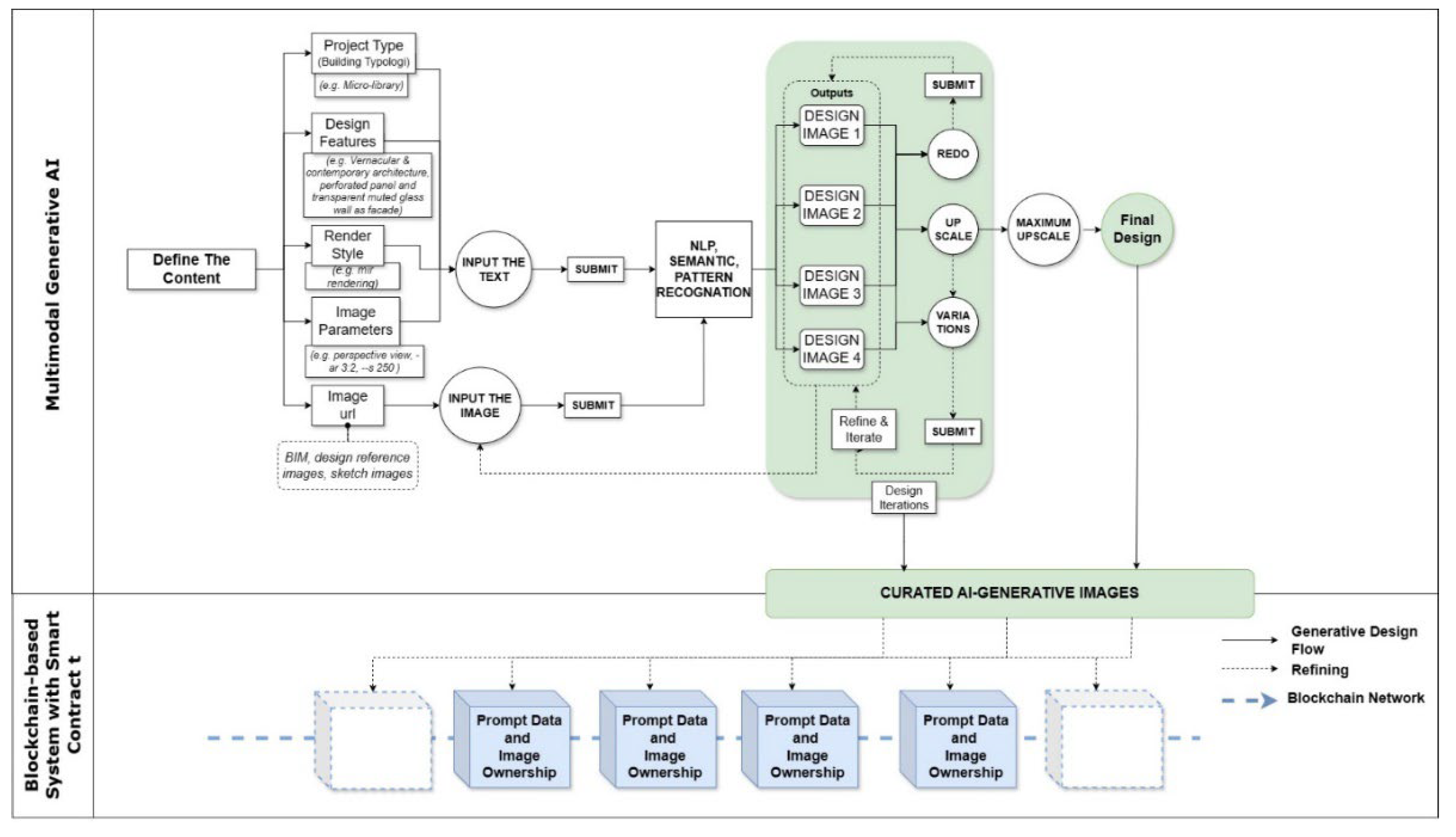
| Framework for integration | Combines Generative AI and blockchain for architectural design using a hypothesis scenario framework to outline the design process flow and real-life applications. |
| Generative AI design process | Involves initial sketches, prompt engineering, and iterative refinement to generate accurate AI outputs. Key elements include building typology, site details, materials, spatial layout, and rendering style. |
| Features of Generative AI | Utilises variants, upscale, blends, remixes, and prompts to provide multiple design possibilities. AI models are trained on large datasets to identify artistic trends and stylistic components. |
| Data ownership and legal aspects | Emphasizes the importance of data ownership in AI training datasets, impacting legal, moral, and regulatory implications. It includes rights to usage, modification, distribution, and monetization of AI-generated outputs. |
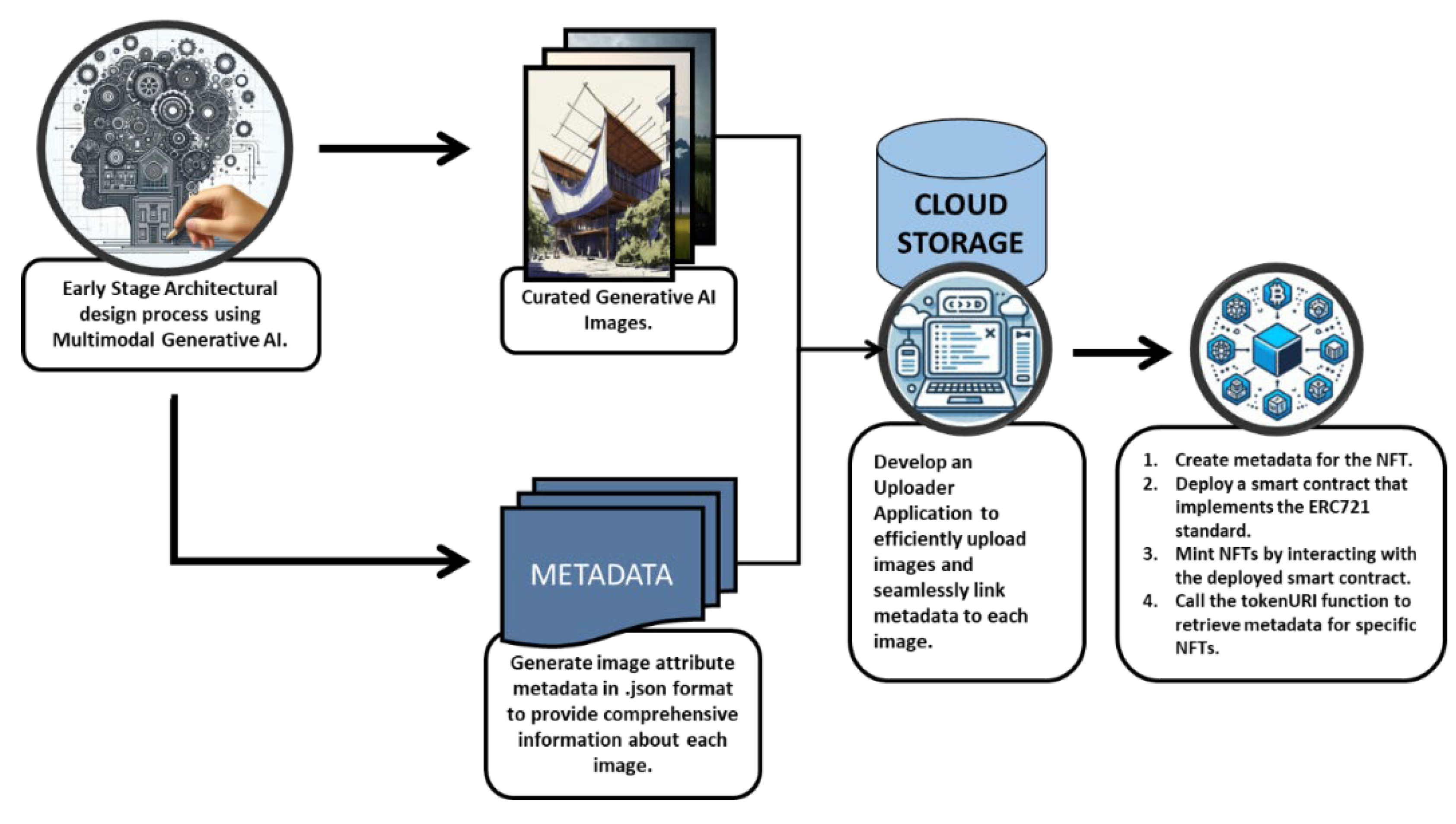
| Blockchain for data storage | Uses blockchain to store prompt data and AI-generated images as NFTs, ensuring secure data ownership. The process includes generating images, producing metadata, storing data in Google Firebase, and converting metadata into NFT format. |
| Results and implementation | Showcases the outcomes of the generative design process, with metadata linked to final images. Provides examples of metadata, storage links, and smart contract details for NFT deployment, demonstrating the practical application of the method. |
| Uni-modal | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Output (Generated image by Generative AI) | ||
| Image Options | Selected Image | ||
|
Design objective |
Design iteration: Find the reference building with writing the prompt to develop the building shape suitable with the design intention |
 Job ID: 7c006bd2-07ad-4e8d-b9ef-47f00abc4732 |
 Job ID: f918bc31-bcff-4a1c-a49a-d98959652c05 |
| Image | - | ||
| Prompts | Create a prompt as a trigger to draw the environment: ["micro library, incorporating vernacular and contemporary architecture, combination of perforated metal panel and transparent muted glass wall as facade, mir rendering, perpspective view, located in the rice field near the village in taiwan, natural light"] |
||
| Multimodal | |||
| Design objective | Design iteration: Combine the building to get wider range design options using blend |
 Job ID: f4e81d0e-b2e2-4057-8ee3-42a59f97551c seed 2798360210 |
 Job ID: 8ede5825-a45c-452b-ba8e-bb22e6c2d14a seed 2798360210 |
| Image |
 
|
||
| Prompts | No prompt | ||
| Aspect | Resume | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Authenticity, certification and ownership | NFTs provide a robust method for certifying the authenticity of digital assets through blockchain technology. | [10,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] |
| Blockchain's immutable nature ensures that the ownership records of NFTs remain tamper-proof and verifiable, thus guaranteeing the authenticity of AI-generated content. | [47,48,49] | |
| Proving ownership and authenticity in a decentralized NFT market can be complex. | [50,51] | |
| Ensuring the security of blockchain and NFTs against hacking, fraud, and other malicious activities is a significant concern that can impact the reliability of authenticity and ownership records. | [42,46,47] | |
| Integration in the creative process | NFTs facilitate creating, owning, and distributing collaborative AI-human creations. This integration supports a new dimension of creativity where digital assets are co-created by humans and AI. | [42,44,48] |
| Interoperability issues between different blockchain platforms can hinder seamless integration and data exchange. | [52,53,54] | |
| Complexity integrating NFT-based. | [55,56,57] | |
| Scalability and traceability process | Blockchain-based NFTs simplify the registration, verification, and tracing of financial transactions related to digital assets, thus enhancing these transactions' overall security and transparency. | [43,46,49,58,59] |
| NFTs offer a transparent and secure means to track and verify ownership of digital assets. | [60,61] | |
| Implementing blockchain solutions on a large scale can be complex and costly, limiting their practicality for verifying and tracking digital assets. | [55,56,62] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





