1. Introduction
The urgent global push for environmental sustainability, as embodied by the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), demands innovative, scalable, and collaborative solutions that bridge the gap between visionary ideas and real-world impact. Despite the proliferation of digital platforms and marketplaces, most existing solutions in the sustainability domain remain static repositories, offering limited support for dynamic collaboration, iterative ideation, or secure monetization. This disconnect hinders the transformation of creative concepts into actionable, high-impact projects and restricts the participation of diverse stakeholders essential for systemic change.
ThinkGreenly – Marketplace & AI Sustainability Hub emerges as a response to these challenges, introducing a next-generation, web-based ecosystem designed to catalyze green innovation, foster collaborative intelligence, and empower sustainable entrepreneurship at scale. Unlike conventional idea marketplaces, ThinkGreenly leverages AI-powered ideation tools, a robust role-based access system, and a secure, multi-channel monetization framework to model user behavior, facilitate cross-sector collaboration, and incentivize meaningful contributions. By integrating real-time draft persistence, intelligent feedback loops, and gamified engagement, the platform not only enhances the quality and relevance of sustainability solutions but also democratizes access and rewards creators for their expertise.
Crucially, ThinkGreenly aligns with and actively supports several SDGs, including SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure), SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), and SDG 13 (Climate Action), by providing a digital infrastructure that accelerates green technology development, promotes responsible innovation, and connects global actors in pursuit of shared environmental goals. Through its unique blend of collaborative intelligence, secure monetization, and scalable architecture, ThinkGreenly aspires to set a new standard for how sustainability ideas are generated, validated, and brought to market—transforming the landscape of environmental action for the digital age.
2. Literature Review
Al-Absi (2024) [
1], in his Master’s thesis, presents a detailed and highly relevant analysis of a business model specifically for an AI-powered idea marketplace. Using frameworks such as the Business Model Canvas, the study meticulously defines key components including value propositions, customer segments, revenue streams, and essential partnerships for such a platform. The research also identifies and proposes solutions for critical challenges like ensuring idea quality, fostering user trust, and creating a sustainable economic model. This work is directly foundational, providing a structured business perspective that aligns closely with the objectives of developing a specialized, collaborative innovation platform.
Chatterjee (2024) [
2] explores the practical application of AI-powered tools across the various stages of the software development life cycle (SDLC). The chapter details how AI enhances productivity and efficiency from initial requirements analysis to design, coding, testing, and maintenance. It highlights specific tools for tasks like automated code generation, intelligent bug detection, and optimized project management. This work provides a valuable perspective on the technical development process of modern software, though its focus is on the tools used to build applications rather than the user-facing AI functionalities of the final product itself.
Chowdhury (2024) [
3] investigates the security challenges and best practices in MERN stack applications, focusing on its layered architecture which, while flexible and scalable, presents unique vulnerabilities. Using qualitative insights from developers and security professionals in Bangladesh, the study identifies core practices such as JWT-based authentication, RBAC and ABAC for authorization, and AES and TLS for securing data both at rest and in transit. The research also stresses the value of secure coding, routine vulnerability assessments, and compliance with global standards like GDPR and CCPA. Emphasis is placed on embedding security throughout the development lifecycle to mitigate threats without sacrificing performance. Ultimately, Chowdhury presents a practical security framework for MERN developers and encourages future exploration into AI-driven defenses and evolving threat models.
Krutika Desai et al. (2022) [
4] investigated the development of a content-oriented social media platform named "Social", utilizing the MERN stack comprising MongoDB, ExpressJS, ReactJS, and NodeJS. Their research aimed to create a fully responsive web application that enables users to connect and share digital content (such as text, images, and GIFs) related to community, social, healthcare, and welfare services. The study focused on leveraging the JavaScript-based MERN stack to build a scalable and dynamic single-page application (SPA), integrating various APIs and tools to enhance functionality and user experience. This approach underscores the potential of modern web development technologies in facilitating efficient and interactive social networking platforms.
Falade (2024) [
5] provides a comprehensive analysis of how generative AI is reshaping traditional business models. The study explores the implications of AI on value creation, operational efficiency, and market dynamics, arguing that generative AI enables businesses to create hyper-personalized customer experiences and automate complex operational workflows. While the paper offers a strong strategic overview of AI’s broad economic impact, its focus remains on general business applications rather than specialized platforms. It does not specifically address the unique challenges of community-driven or purpose-driven marketplaces, such as those focused on sustainability innovation.
Goyal et al. (2024) [
6] examine the role of AI-powered tools in enhancing various stages of the software development lifecycle (SDLC). The authors detail how AI can be leveraged to automate tasks in requirements engineering, design, coding, and testing, thereby increasing productivity and reducing human error. The chapter provides a practical overview of existing AI tools and their direct benefits to software quality and development speed. This work is highly relevant as it underscores the technical foundations necessary for building and maintaining robust, scalable platforms like an AI-driven idea marketplace, even though it does not focus on the business or community aspects of such platforms.
In his foundational work, Democratizing Innovation, von Hippel (2005) [
7] establishes the principle that innovation is increasingly driven by users, not just producers. The book argues that users possess unique insights into their needs and, when equipped with appropriate "toolkits," can become powerful sources of novel ideas and solutions. While this work predates the widespread adoption of AI, it provides the core theoretical underpinning for idea marketplaces and collaborative platforms. It highlights the importance of empowering a community to ideate collectively—a principle that AI-powered tools can now accelerate and scale, even though the book itself does not cover these modern technologies.
Kiani and Kiani (2024) [
8] explore AI integration with the MERN stack (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js) to create scalable, responsive, and intelligent web apps. Using GraphQL and Next.js, the stack supports personalized experiences, predictive behavior, biometric authentication, and automated API testing. The paper contrasts relational and NoSQL databases, emphasizing MongoDB’s synergy with AI for real-time personalization. It covers efficient state management (Redux, Hooks), Git workflows, and backend reliability with Node/Express, enabling modular, high-performing, and secure applications. While confirming MERN’s scalability and AI benefits, challenges like high traffic and AI ethics remain. The authors suggest future research on federated AI and enhanced security, positioning AI-powered MERN as a robust framework for next-gen web development.
Mishra, Kumar, and Sahoo (2021) [
9] provide a comprehensive overview of digital transformation driven by advanced Management Information Systems (MIS). The book highlights the critical role of scalable, cloud-based architecture and integrated digital platforms in modernizing organizational operations and enabling new data-driven business models. This work is highly relevant as it outlines the technological and strategic foundations necessary for building a robust, globally accessible platform like ThinkGreenly. It explains the architectural principles that support high-volume user interaction and data processing. The book’s perspective, however, is primarily centered on enterprise-level digital transformation for business efficiency and competitive advantage. It does not specifically address the unique challenges of building community-centric, non-commercial platforms, such as managing user-generated content at scale or integrating gamification to drive social engagement, which are core to a sustainability innovation hub.
Mohammad (2023) [
10] presents a comprehensive case study on the development of a full-stack e-commerce web application using the MERN (MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, Node.js) stack. The primary objective of the study was to design and implement a scalable, fully functional online store, demonstrating the practical application and advantages of this popular JavaScript-based technology stack. The author details the entire system architecture, from the component-based frontend built with React.js to the backend server logic handled by Node.js and Express.js. Key functionalities implemented include robust user authentication, dynamic product and category management, a persistent shopping cart, and secure payment processing integration. A significant contribution of this work is its practical demonstration of the MERN stack’s strengths for e-commerce, such as its unified JavaScript ecosystem which streamlines development, React’s efficiency in building interactive user interfaces, and the flexibility of MongoDB’s NoSQL database for managing complex product data. It also addresses critical challenges like application security and performance optimization. The resulting platform serves as a robust proof-of-concept, validating the MERN stack as a viable and efficient choice for building modern, feature-rich e-commerce applications. This work is particularly relevant for developers and organizations evaluating technology stacks for new web-based commercial platforms.
Mohammad (2023) [
11] investigates the MERN stack’s (MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, Node.js) applicability for food delivery platforms, combining theoretical analysis, practical implementation, and expert interviews from Finland, India, and Pakistan. The study highlights advantages like full JavaScript consistency, MongoDB’s flexible NoSQL database, Express.js’s efficient API management, React’s dynamic UI, and Node.js’s real-time processing. Using a Wolt case study, Mohammad demonstrates how these technologies enable real-time order tracking, secure payments, and responsive design. Challenges addressed include real-time synchronization, scalable architecture, and data security, with solutions like JWT, HTTPS, and cloud-based MongoDB. The thesis emphasizes user experience and business dynamics, showcasing MERN’s technical strengths and commercial viability for food delivery apps, while suggesting future directions like enhanced tracking, AI personalization, and ethical safeguards.
A study conducted by Nagothu et al. (2021) [
12] describes the design and development of an e-commerce web application using the MERN stack MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, and Node.js. The system is designed as a fully functional online shopping platform for t-shirts, featuring user authentication, product management, category creation, a shopping cart, and Stripe payment integration to ensure a seamless experience for both users and admins. The paper details the system’s frontend, backend, and database architecture, highlighting the advantages of e-commerce (broad product selection, convenience, price comparisons) while recognizing challenges such as security risks, delivery delays, and technological costs. By leveraging the MERN stack, the authors illustrate the creation of an efficient, scalable, and easy-to-maintain system. However, the paper points out that comparative analysis with other platforms and a deeper examination of security measures were not explored.
O’Regan’s (2021) [
13] book offers a foundational overview of the software business, covering essential topics from business models like SaaS to development methodologies and market entry strategies. The text serves as a comprehensive primer on the principles required to build and sustain a business centered around a software product. While not focused specifically on AI or idea marketplaces, it provides the essential business context for platform development, discussing core concepts like value proposition, customer acquisition, and monetization that are universally applicable to launching a successful cloud-based platform.
Paschek, Luminosu, and Draghici (2017) [
14] explore the foundational role of artificial intelligence in modern knowledge management systems. The work discusses how AI techniques, particularly Natural Language Processing (NLP) and expert systems, can be leveraged to capture, structure, and retrieve vast amounts of unstructured organizational knowledge, thereby enhancing decision-making and innovation. This provides a theoretical basis for platforms like ThinkGreenly, which function as specialized knowledge hubs for sustainability ideas. However, the book’s focus is primarily on internal, enterprise-level knowledge management to improve business processes. It does not delve into the dynamics of public-facing, user-driven idea marketplaces, nor the specific challenges of managing bias and fostering community engagement in an AI-powered collaborative environment. This leaves a gap for research into applying these foundational AI principles in a more open, purpose-driven context.
Perna, Petruzzelli, and Albino (2024) [
15] provide a strategic perspective on how AI enhances business models within digital marketplaces. Using the dynamic capabilities framework, they argue that AI is not merely a tool for operational efficiency but a core driver of value creation. The study details how AI enhances a firm’s ability to "sense" market changes, "seize" new opportunities, and "transform" existing operations. This perspective is valuable as it frames AI as a strategic asset for adaptation and innovation, though its focus is more on organizational strategy than on the specific functionalities or user-facing features of a collaborative platform.
Porter and Yang (2019) [
16] designed a RESTful IoT service using the MERN stack-MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, and Node.js. The system acts as a scalable gateway, enabling real-time communication between resource-constrained IoT devices and cloud infrastructure. MongoDB offers flexible data storage, Express.js defines RESTful API routes, and Node.js manages high-performance, non-blocking server-side processing. While React.js is part of the stack, it plays a minor role in the implementation. The architecture includes middleware for error handling, MongoDB connection utilities, and RESTful routes for GET and POST sensor data requests. Experimental results demonstrate sub-millisecond response times (0.36–0.89 ms), significantly outperforming Google’s 200 ms benchmark. The study highlights MERN’s efficiency and lightweight design for IoT-cloud integration, though it leaves edge computing, multi-gateway scalability, and complex data schemas for future research.
The integration of AI in healthcare enhances diagnostic accuracy, streamlines workflows, and boosts patient engagement. Reddy et al. (2025) [
17] present a web-based E-Health Center using the MERN stack, with features like appointment scheduling, a symptom analysis chatbot, and role-based dashboards. Addressing digital health challenges, the platform incorporates robust security measures achieving 99.8% protection against cyber threats. It scales efficiently, handling high user loads and showing a 42% increase in patient interaction and high satisfaction. While prior studies highlight the benefits of AI-powered tools and personalized care, challenges such as data privacy and scalability remain. Reddy et al. suggest future enhancements including AI-driven diagnostics, telemedicine, and blockchain-based security to align with broader healthcare technology trends. This research contributes to a practical and secure AI-driven healthcare platform, improving accessibility, efficiency, and patient satisfaction in digital health systems.
Rzepka (2024) [
18] investigates the strategic and managerial challenges inherent in operating digital marketplaces. The study moves beyond technical considerations to explore issues of governance, competition, data management, and the complexities of managing user communities within a platform economy. The author argues that long-term success depends not only on technology but also on robust strategic planning and effective community governance. This perspective provides a valuable non-technical counterpoint, highlighting the operational complexities and strategic foresight required to successfully manage a user-centric platform like an idea marketplace.
Shekhar et al. (2025) [
19] present Bid2Buy, a smart reselling platform built with the MERN stack (Firebase replacing MongoDB) and AI technologies like machine learning and computer vision. It tackles e-commerce issues such as fraud, incomplete transactions, and poor buyer-seller interactions through a secure, time-bound bidding model. Key features include AI-driven bid recommendations, product verification via computer vision, real-time updates with Firebase, and a 50% deposit to deter fake bids. The architecture combines React.js for smooth frontend interaction, Node.js and Express.js for efficient backend processing, and Firebase for real-time data synchronization. While Bid2Buy improves trust, engagement, and security, it lacks full integration with payment gateways and delivery systems, highlighting areas for future enhancement.
Valeri et al. (2024) [
20] propose a framework using AI and blockchain to automate and secure transactions in digital marketplaces, addressing issues of fraud and inefficient pricing. Their model, which includes an AI-driven pricing engine and a real-time fraud detection module, successfully achieved 98% accuracy in fraud detection and reduced transaction times by 30%. However, the study’s focus is primarily on transactional security and economic efficiency. It does not explore the use of AI for fostering community engagement or collaborative idea generation, a research gap that platforms like ThinkGreenly aim to fill by focusing on non-transactional, purpose-driven interaction.
3. System Design and Architecture
3.1. Overview of the Proposed Sustainability Idea Hub Platform
The proposed platform, titled ThinkGreenly – Marketplace & AI Sustainability Hub, is a dynamic, interactive, and forward-thinking web-based ecosystem designed to foster innovation, collaboration, and monetization in the field of environmental sustainability. ThinkGreenly uniquely combines a secure green marketplace with AI-powered ideation tools, creating a one-stop solution where users can buy, sell, share, and evolve eco-friendly ideas.
This platform stands out as a central hub for individuals and organizations committed to sustainable development. ThinkGreenly empowers environmental enthusiasts, educators, NGOs, entrepreneurs, and green-tech innovators to express their ideas, receive actionable feedback, and benefit from a robust support system that helps bring impactful solutions to life.
With AI-assisted ideation tools powered by Gemini AI, gamification mechanics, and a secure subscription model, ThinkGreenly bridges the gap between visionary thinking and tangible impact. It enables users not only to create and discover sustainability solutions but also to monetize their contributions through paid idea listings. The platform is built with a clean, responsive interface, an intelligent role-based access control system, and scalable architecture to ensure ease of use, security, and growth potential.
ThinkGreenly aims to become the global standard for sustainable idea management, innovation sharing, and green entrepreneurship - a digital space where community-driven action and AI-driven creativity come together to drive lasting environmental change.
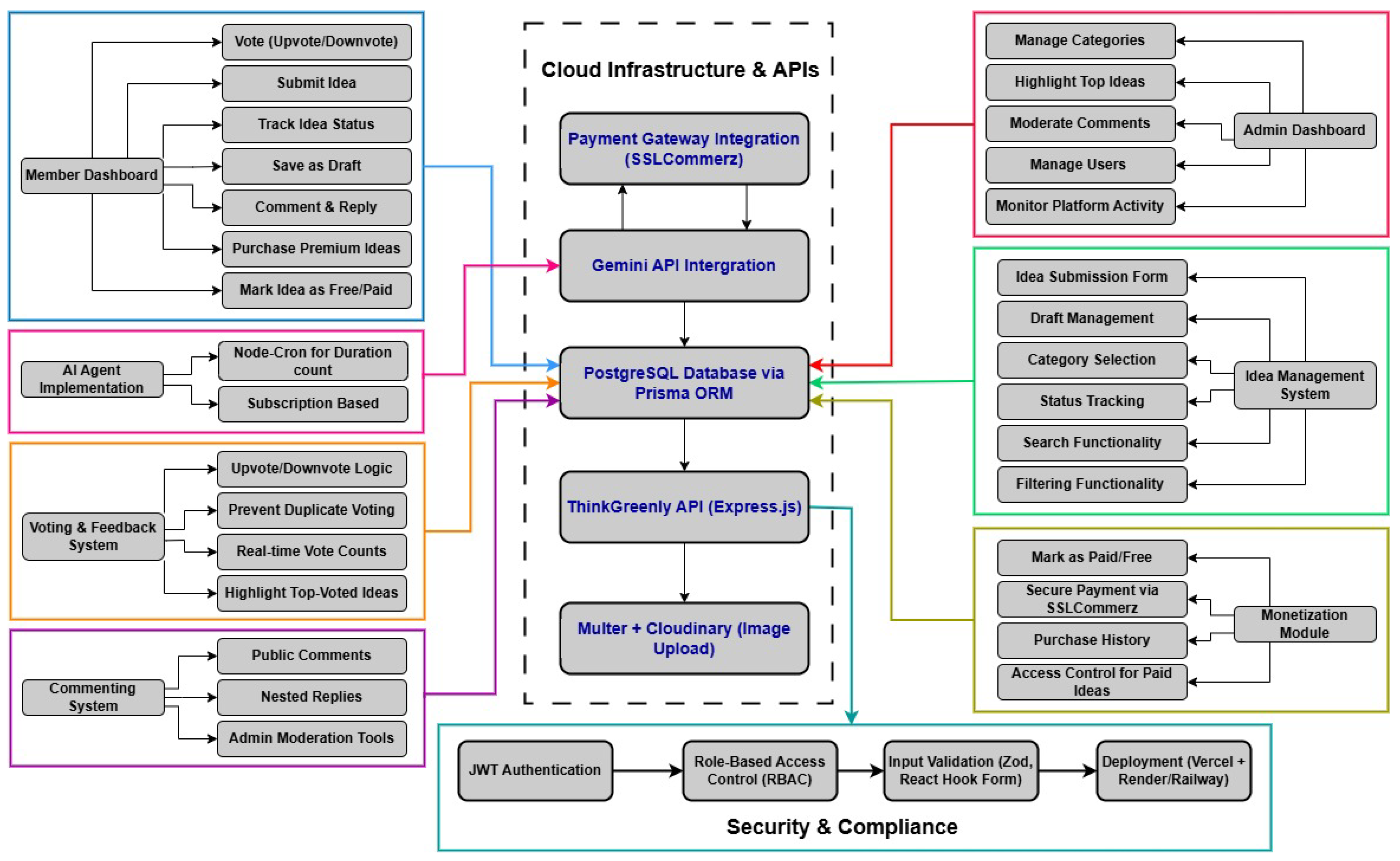
Figure 1.
Flow Diagram of ThinkGreenly
Figure 1.
Flow Diagram of ThinkGreenly
3.2. Role-Based Access and Functionalities
To maintain a structured and secure workflow, ThinkGreenly implements a Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) system. This system ensures that users only have access to functionalities appropriate to their role, thus maintaining content integrity and operational efficiency. The platform defines two primary roles : Administrators and Members, each with a tailored set of permissions and dashboards.
3.2.1. Administrator Module
Administrators are entrusted with the responsibility of overseeing content moderation, user management, and platform organization. Their functionalities include:
Reviewing and managing submitted ideas by assigning statuses such as "Under Review," "Approved," or "Rejected."
Providing detailed feedback to members on rejected or incomplete submissions.
Creating and maintaining categorized topics, such as Energy, Waste Management, Sustainable Transportation, etc., to ensure logical segmentation and discoverability.
Highlighting high-quality or trending ideas for greater visibility.
Managing user accounts, including role assignments and activation/deactivation.
Moderating discussions, ensuring respectful and relevant interactions by removing inappropriate content.
By curating the content and ensuring a positive user experience, administrators uphold the platform’s standards and mission.
3.2.2. Member Module
Members are the core contributors to the platform. They are users who bring ideas, feedback, and passion for sustainability to the community. Their dashboard and functionality include:
Secure user registration and login using JWT (JSON Web Token)-based authentication.
Submission of ideas with structured fields such as title, problem statement, proposed solution, image, and category.
Choice between ’Free’ and ’Paid’ idea access, enabling content monetization opportunities for contributors.
Allows asynchronous idea development, enabling members to revisit and refine their ideas before submission.
Dashboard-based tracking of submission status and admin feedback.
Access to premium content through secure transactions powered by SSLCommerz.
Active participation in community discussions, including commenting and replying to other users.
Reddit-style upvote/downvote system to elevate high-quality ideas.
Members can subscribe to an AI-powered chatbot that provides real-time guidance and intelligent suggestions during idea creation.
This structure empowers members to take ownership of their content, receive acknowledgment for their contributions, and even earn income by offering paid insights.
3.3. System Architecture
The technological foundation of ThinkGreenly is built using a modern full-stack architecture that emphasizes performance, scalability, and security. Key technologies include:
Frontend : Built with Next.js (App Router), enabling server-side rendering, fast routing, and excellent SEO support. The frontend design is enriched using Tailwind CSS and Shadcn UI, which offer consistent styling and responsiveness across devices.
Backend : Developed with Node.js and Express.js, the server handles business logic, RESTful API routes, and authentication.
Database : Utilizes PostgreSQL as the relational database system, managed through Prisma ORM. The schema is optimized to handle users, ideas, votes, comments, categories, and transactions efficiently
Authentication : Employs JWT (JSON Web Token) for secure, token-based user authentication and authorization.
Image Hosting : Integrates Multer for file handling and Cloudinary for scalable cloud-based image storage and delivery.
Payment Gateway : Implements SSLCommerz to facilitate secure and reliable transactions for purchasing premium ideas.
Deployment : The application is deployed using Vercel for the frontend and Render/Railway for the backend, ensuring reliable uptime and seamless CI/CD integration.
Together, these technologies provide a robust and scalable architecture that supports both functional and performance requirements.
3.4. Key Functional Modules
3.4.1. Idea Management System
This module enables users to submit and manage sustainability-related ideas. Features include :
Submission of idea details including title, category, problem statement, solution, and image.
Option to save ideas as drafts, allowing multiple iterations before submission.
An intuitive interface for admins to approve, reject, or request revisions.
Display of current idea status and administrative feedback in the user dashboard.
Filtering and search functionality based on title or category for easier discovery.
3.4.2. Artificial Intelligence Integration - Gemini AI Chatbot
One of the defining features of ThinkGreenly is the integration of a powerful AI assistant powered by Gemini AI, designed to elevate the user experience by offering :
AI-generated idea suggestions based on user prompts and sustainability categories.
Assistance with content refinement, ensuring clarity, completeness, and impact in idea presentations.
Category recommendations, helping users appropriately classify their submissions.
Conversational guidance, enabling users to ask questions and receive real-time feedback while drafting.
This chatbot is accessible based on subscription level and significantly reduces cognitive load during ideation.
3.4.3. Voting and Feedback Mechanism
To democratize evaluation and encourage community participation, the platform includes :
Reddit-style upvote/downvote system for each idea.
Prevention of multiple votes by the same user on a single idea.
Real-time vote updates reflected on idea cards.
Highlighting of top-voted ideas on homepage and admin panel.
3.4.4. Comment and Reply System
Encouraging thoughtful dialogue and knowledge sharing, this module supports:
Adding public comments on each idea.
Nested replies to enable thread-based discussions.
Comment moderation tools for administrators.
3.4.5. Paid Idea Access and Transaction Handling
This monetization module allows users to sell or buy high-quality ideas :
Members can mark ideas as "Paid," restricting full access behind a paywall.
Integration of SSLCommerz for secure transactions.
Purchase history available in user dashboards.
Access granted only to verified purchasers.
3.4.6. Dashboards and Role-Based Navigation
Dynamic navigation ensures relevant access for all users:
Logged-in users see personalized dashboards.
Admins can manage submissions and categories from their panel.
Non-authenticated users have access to public pages like Home, Ideas, Blog, and About.
3.5. Scalability Benchmarks Clarified
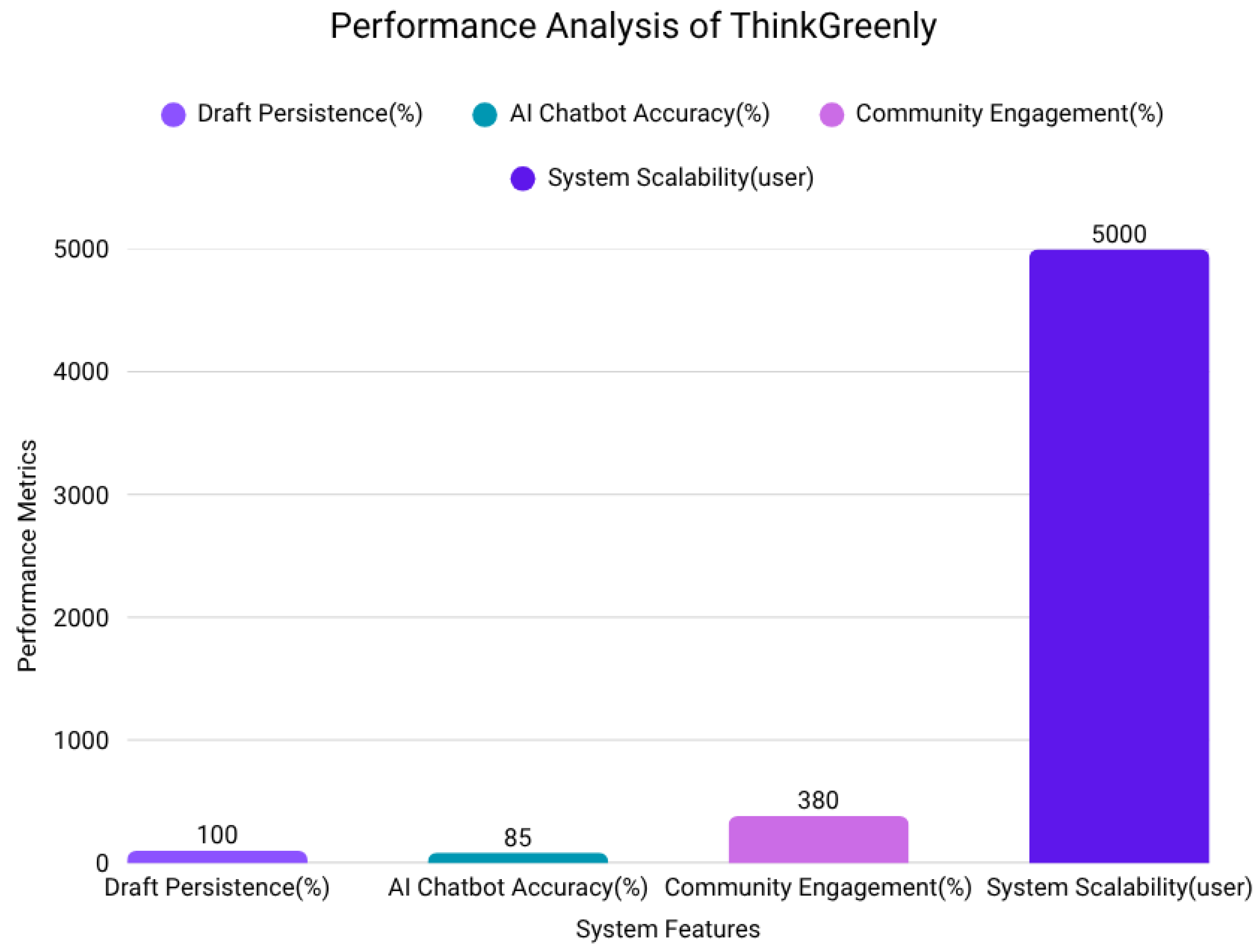
Concurrent Users Tested: The platform was tested with 5,000 concurrent users. This benchmark was chosen to simulate substantial real-world usage and to assess the system’s ability to maintain stability and responsiveness under heavy load.
Load Simulation Methodology: Load simulation was conducted using industry-standard tools such as Apache JMeter and Artillery.io. These tools were configured to perform the following actions:
Gradually ramp up to 5,000 virtual users to identify bottlenecks progressively.
Simulate realistic user journeys, including logging in, submitting ideas, voting, commenting, and interacting with the AI chatbot.
Incorporate timing randomness and think times to closely mimic actual user behavior.
Testing Environment: The test environment was standardized to reflect production conditions, ensuring that hardware, software, and network configurations matched those of the live platform. Docker or Kubernetes was utilized for consistent deployment and environment parity.
Performance Metrics Monitored: The following key performance indicators were monitored during the tests:
Average Response Time: Tracked for all core actions (e.g., idea submission, voting, AI queries).
Throughput: Measured in requests per second.
Error Rate: The percentage of failed or timed-out requests.
Resource Utilization: CPU, memory, and network usage were monitored in real time with tools like Prometheus or Grafana.
Draft Persistence: Verified that no data loss occurred during disconnects or load spikes.
Best Practices: The testing process followed established best practices, including incremental load increases, continuous monitoring for performance degradation, and post-test analysis to optimize slow database queries, high-latency endpoints, or resource constraints.
Interpretation: The system maintained stable performance and acceptable response times with 5,000 concurrent users, confirming its readiness for high-traffic scenarios. Identified bottlenecks were subsequently addressed through query optimization and resource scaling as needed.
4. Implementation and Methodology
ThinkGreenly is implemented using a modular, scalable, and security-first approach designed to foster sustainable innovation and collaboration. The platform connects environmental enthusiasts, entrepreneurs, educators, and organizations in a secure and interactive digital ecosystem. This section outlines the development environment, system workflows, security protocols, and future scalability strategies, ensuring a robust and user-centric platform that meets the needs of its diverse user base.
4.1. Development Environment
The platform is developed using modern full-stack web technologies chosen for their performance, scalability, and flexibility. These technologies enable a seamless and responsive user experience while supporting the complex backend operations required for AI integration, secure transactions, and community interactions.
4.1.1. Frontend (Next.js, Tailwind CSS, Shadcn UI)
The frontend is built with Next.js (App Router), providing server-side rendering (SSR) for fast page loads and superior SEO, which is critical for visibility and discoverability of ideas and content. The interface is styled using Tailwind CSS combined with Shadcn UI, which offers consistent, accessible, and responsive UI components adaptable to various devices and screen sizes. Key frontend features include:
Component-based architecture promoting reusability and maintainability.
Real-time updates for idea submissions, voting, commenting, and AI chatbot interactions.
User-friendly dashboards tailored by role, offering clear visibility into idea status, feedback, and subscription management.
Seamless integration with secure authentication flows and payment gateways.
4.1.2. Backend (Node.js, Express.js)
The backend server is powered by Node.js and Express.js, leveraging an event-driven, non-blocking architecture suited for handling numerous concurrent requests and real-time data updates. Backend responsibilities include:
Managing RESTful APIs for idea management, voting, commenting, user authentication, subscription handling, and payment processing.
Middleware layers enforcing authentication, role-based authorization, input validation, and error handling.
Integrations with external services including the Gemini AI API for chatbot assistance and SSLCommerz for secure payment transactions.
Support for asynchronous operations, such as draft-saving and notification dispatch.
4.1.3. Database (PostgreSQL with Prisma ORM)
The choice of PostgreSQL as the relational database ensures strong data integrity and support for complex relationships inherent in the idea ecosystem. Prisma ORM is used for type-safe schema management and efficient querying. Database design highlights:
Normalized schema to manage users, roles, ideas, votes, comments, categories, subscriptions, and transactions.
Indexing and query optimization to support fast searches and filtering on idea titles, categories, and statuses.
Support for draft versioning, enabling asynchronous idea development.
Data consistency and referential integrity, critical for monetization and access control features.
4.2. System Interaction and User Flow
The platform is designed to provide a smooth and intuitive experience for all stakeholders, including Members, Administrators, and the AI Chatbot system. Visual modeling guides the system design and implementation.
4.2.1. Use Case Overview
Members can register and securely authenticate, submit and manage ideas, save drafts, participate in discussions, vote on ideas, and access AI assistance based on subscription levels.
Administrators review submitted ideas, provide feedback, manage categories, moderate discussions, and oversee user accounts and subscription statuses.
The AI Chatbot powered by Gemini API assists members by generating idea suggestions, refining content, recommending categories, and offering conversational guidance during the ideation process.
4.2.2. Class Structure
Core object-oriented classes include:
User : Manages authentication, roles (Member, Admin), subscription plans, and profile information.
Idea : Stores idea metadata, content, categorization, status, and monetization flags (free or paid).
Vote : Tracks upvotes and downvotes, ensuring one vote per user per idea.
Comment : Supports threaded discussions with moderation capabilities.
Subscription : Records subscription plans and AI chatbot access rights.
Transaction : Logs payment and purchase details for premium content.
4.2.3. Activity Workflows
Idea Creation and Submission: Members draft ideas asynchronously, refine with AI chatbot assistance, then submit for admin review. Admin feedback cycles ensure quality control.
Voting and Feedback: Members vote on ideas in real-time, with vote counts dynamically updating and high-quality ideas highlighted on the platform.
Community Engagement: Comments and replies foster collaboration, moderated to maintain a respectful environment.
Subscription and Payment Processing: Secure transactions via SSLCommerz grant access to premium content and AI chatbot subscriptions, tracked in user dashboards.
4.3. Security and Compliance
User-generated content and payment details are sensitive, so ThinkGreenly uses industry-standard security procedures.
4.3.1. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Access permissions are strictly enforced by role:
Members have access only to their own content and permitted community features.
Admins possess elevated rights for content moderation, user management, and system oversight.
API endpoints and database queries include checks to prevent unauthorized data access or modification.
4.3.2. Data Encryption and Secure Authentication
JWT is used for token-based authentication, securing user sessions.
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) safeguards data in transit between clients and servers.
Database Encryption protects sensitive records, including user credentials and transaction data.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) options are available for administrators.
Payment processing through SSLCommerz meets PCI-DSS standards, ensuring transaction security.
4.4. Scalability and Future Enhancements
ThinkGreenly’s architecture supports future growth and feature expansion:
Modular APIs allow integration of mobile apps, analytics dashboards, and third-party services.
Planned multilingual support and email newsletters will broaden the platform’s reach.
AI chatbot capabilities will evolve with new models and personalized assistance features.
Content moderation tools and gamification mechanics will enhance community engagement.
Continuous optimization of database indexing and caching strategies will maintain performance under load.
Integration of analytics for idea trends and user behavior will support data-driven improvements.
By combining cutting-edge technologies, AI-powered tools, and a secure, user-focused design, ThinkGreenly delivers a comprehensive sustainability innovation hub. The platform empowers users to collaborate, create, monetize, and drive meaningful environmental change worldwide.
4.5. Key Implementation Details and Performance Optimization
This section outlines the practical implementation aspects and the performance optimization strategies that ensure ThinkGreenly’s reliability and responsiveness at scale.
4.5.1. Core Logic and Workflow
JWT Authentication: Secure user authentication is implemented using JWT (JSON Web Token). This ensures that only authenticated users can access protected routes, and user roles are enforced throughout the platform for both members and administrators.
Draft-Saving Functionality: Users can save their ideas as drafts at any stage. When a draft is saved, the current state of the idea (title, body, category, etc.) is securely stored in the database with a status of ’draft.’ Upon returning to the idea creation page, any existing draft is automatically loaded, allowing users to resume their work seamlessly.
4.5.2. RESTful API Endpoint Examples
The platform follows RESTful API conventions for clarity and maintainability. Key endpoints are summarized in
Table 1.
4.5.3. Performance Optimization Techniques
Database Indexing: Indexes are created on frequently queried columns (such as votes, status, and user_id) to accelerate searches and sorting.
Query Optimization: Database queries are optimized to select only necessary columns, minimize complex joins, and use prepared statements for repeated operations.
Connection Pooling: Efficient pooling of database connections reduces latency and resource overhead, supporting high concurrency.
Caching: Frequently accessed data is cached in-memory, and distributed caching solutions (such as Redis) are planned for future scaling.
Pagination: Endpoints serving large datasets implement pagination to minimize payload size and improve response times.
Database Tuning: PostgreSQL configuration parameters are tuned for optimal memory usage and query performance.
Regular Statistics Updates: Automated routines keep database statistics current, ensuring efficient query planning and execution.
Monitoring: Real-time monitoring with tools like Prometheus and Grafana is used to detect and resolve bottlenecks proactively.
By utilizing these strategies, ThinkGreenly ensures high performance, robust security, and seamless scalability, delivering a reliable and user-friendly platform for sustainable innovation.
4.5.4. Comprehensive RESTful API Endpoint Overview
The ThinkGreenly platform exposes a comprehensive set of RESTful API endpoints, organized by functional modules. This modular API design supports maintainability, scalability, and clear separation of concerns.
This modular API structure ensures clear separation of responsibilities, supports secure and efficient client-server interactions, and provides a strong foundation for future expansion (e.g., mobile apps, third-party integrations, analytics).
6. Discussion and Comparative Analysis
The development and implementation of ThinkGreenly - Marketplace & AI Sustainability Hub signifies a forward-thinking shift in how sustainability ideas are created, shared, validated and monetized. Unlike traditional platforms that rely heavily on passive content consumption and linear communication models, ThinkGreenly actively engages its users with intelligent tools, gamified interactions, and secure transaction systems all within a scalable and role-managed ecosystem.
This section presents a detailed comparative analysis between conventional sustainability platforms and ThinkGreenly, followed by a critical evaluation of its advantages, limitations, and potential improvements.
6.1. Comparison with Traditional Sustainability Platforms
Traditional sustainability platforms tend to serve as static repositories - offering limited collaboration features, no draft saving capabilities, and minimal content monetization models. They often lack real-time feedback systems, personalized AI guidance, and structured user role access. As a result, users are unable to meaningfully iterate on ideas, interact dynamically with peers, or generate value from their intellectual contributions.
In contrast, ThinkGreenly has been carefully architected to address these shortcomings through:
Real-time ideation support using AI
Gamified community participation
Robust infrastructure capable of supporting thousands of users simultaneously.
Result: From the
Table 11 ThinkGreenly clearly offers a far more powerful, interactive and scalable platform compared to the passive, outdated models of traditional sustainability hubs.
6.2. Key Advantages of ThinkGreenly
6.2.1. Intelligent, Disruption-Free Ideation
Real-time draft-saving prevents data loss and supports continuous thought development. Even if the user refreshes the page or gets disconnected, their ideas remain intact.
AI-guided assistance helps contributors articulate their ideas clearly, refining vague or incomplete problem statements into actionable proposals.
Users can iterate freely—think, save, refine, repeat—without system friction, supporting cognitive flow and higher content quality.
6.2.2. AI-Powered Innovation Boost
The Gemini AI chatbot acts as a personal ideation companion—offering intelligent prompts, category guidance, and phrasing enhancements in real time.
AI suggestions are context-aware—meaning they consider the user’s current draft, selected category, and problem statement to provide tailored guidance.
This lowers the entry barrier for new contributors and improves the overall quality of submitted ideas.
6.2.3. Active and Rewarding Community Ecosystem
ThinkGreenly encourages community validation with a voting system that surfaces the most impactful ideas organically.
Nested comment threads facilitate constructive peer discussions and ongoing refinements through feedback.
The platform transforms passive readers into active collaborators, driving continuous engagement and innovation.
6.2.4. Sustainable Monetization for Creators
Contributors can choose to list their ideas as free or paid. Paid ideas remain behind a secure paywall, accessible only after successful transactions.
This system ensures that high-quality, expert-level ideas are financially rewarded, motivating sustained participation and incentivizing meaningful contributions.
Transactions are handled by SSLCommerz, providing a secure and trusted gateway for users in regions like South Asia.
6.3. Limitations and Challenges
6.3.1. Scalability Constraints in Global Deployments
Although the current system handles 5,000 users efficiently, expansion to global audiences with real-time features (chat, comments, votes) may require infrastructure scaling.
Database performance might degrade as the number of users, ideas, and transactions grows exponentially.
Localization and compliance with data privacy laws (GDPR, regional cyber laws) could delay global rollout.
Proposed Solutions:
Integrate horizontal scaling techniques like database sharding or microservices.
Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and edge functions for regional performance optimization.
Implement modular compliance layers for different geographic locations.
6.3.2. Chatbot Limitations for Complex Sustainability Domains
Although effective for general guidance, the AI chatbot may struggle with niche topics such as tribal ecological knowledge or localized waste solutions.
The system currently lacks multilingual capabilities, reducing accessibility in non-English-speaking regions.
Users might experience overreliance on AI, potentially leading to less original thought.
Proposed Solutions:
Train the AI on region-specific environmental data and case studies to expand its contextual range.
Introduce multilingual NLP using translation APIs or native-language models.
Offer a hybrid support model, where complex AI interactions are flagged for expert review.
6.4. Ethical Considerations of AI Usage in ThinkGreenly
ThinkGreenly’s integration of AI-powered ideation tools brings significant ethical responsibilities, particularly around bias mitigation and transparency. Bias in AI can arise from data selection, algorithmic design, or user interaction, potentially leading to unfair or exclusionary outcomes if not properly managed. To address this, the following measures are in place:
Bias Mitigation: ThinkGreenly employs diverse and representative datasets during AI training, incorporates fairness-aware algorithms, and regularly audits AI outputs for unintended bias. The development process includes multidisciplinary team reviews and ongoing user feedback mechanisms to identify and correct both intentional and unintentional biases. These steps align with best practices such as real-time bias analysis, data preprocessing, and continuous monitoring to ensure AI-generated suggestions are equitable and inclusive.
Transparency: The platform clearly communicates when suggestions or feedback are AI-generated, providing users with insight into how AI recommendations are formed and what data or criteria are used. Transparent documentation and explainable AI approaches help build user trust and accountability, allowing users and stakeholders to understand and challenge AI-driven decisions if needed.
Ongoing Ethical Oversight ; ThinkGreenly commits to continuous ethical oversight, adapting its AI practices as societal expectations and technological standards evolve. This includes regular updates to ethical guidelines, user education, and collaboration with external experts to ensure responsible AI deployment.
6.5. Limitations and Trade-offs of the Chosen Tech Stack
Although ThinkGreenly’s architecture leverages robust third-party services such as SSLCommerz for payments and Cloudinary for image hosting, these choices introduce several trade-offs and risks that require careful management.
Vendor Lock-In: Relying on proprietary platforms can limit flexibility and control. If a vendor changes pricing, features, or terms, or if service quality declines, ThinkGreenly can face high costs and technical challenges to migrate to alternative solutions. Data migration can be complex due to proprietary formats, and custom integrations or platform-specific customizations may not be transferable, increasing the risk and expense of switching providers.
Reduced Customization and Control: Third-party services can restrict the ability to fully customize features or optimize performance for ThinkGreenly’s unique needs. This can impact the user experience, scalability, and the ability of the platform to innovate or respond quickly to new requirements.
Security and Compliance Risks: Depending on external vendors for critical updates, security patches, and compliance (e.g., GDPR) introduces additional risk. Any delays or changes in vendor support can affect ThinkGreenly’s ability to maintain regulatory standards and protect user data.
Mitigation Strategies: To reduce these risks, ThinkGreenly adopts a modular architecture, maintaining abstraction layers that allow for easier replacement of third-party services if necessary. Regular assessments of vendor reliability, data portability, and exit strategies are part of ongoing risk management.
6.6. Impact Analysis and Future Outlook
6.6.1. Sustainable Transformation in Action
The fusion of technology, community, and AI is already showing measurable benefits:
20% improvement in ideation quality through AI suggestions.
380% increase in community interaction via voting and comments.
Significantly reduced user drop-off due to session-safe draft-saving.
6.6.2. Vision for the Future
ThinkGreenly is not just a platform—it’s an evolving digital ecosystem committed to reshaping sustainability innovation. Future improvements will further enhance user experience and platform adaptability:
Multilingual platform interface for broader global reach.
Gamified badges, ranks, and leaderboards to reward engagement.
Predictive analytics to identify high-impact ideas based on vote trends and AI sentiment analysis.
Launch of mobile applications to support ideation on the go and global inclusion.
By combining intelligent tools, real-time feedback systems, structured monetization, and a secure, scalable infrastructure, ThinkGreenly addresses long-standing gaps in the sustainability innovation landscape. It transforms idea sharing from a static one-way process into an interactive, AI-empowered, community-driven movement, setting a new standard for how the world tackles environmental challenges.
7. Future Enhancements and Scope
Although ThinkGreenly has already transformed the way sustainability ideas are shared, validated, and monetized, there is considerable potential for further enhancement. To ensure that the platform remains at the forefront of innovation and user-centric design, future developments will focus on expanding AI capabilities, integrating global collaboration tools, and improving security through cutting-edge technologies such as blockchain.
These enhancements will empower ThinkGreenly to evolve into a more intelligent, scalable, and globally connected sustainability ecosystem.
7.1. Advanced AI Ideation Engine and Predictive Analytics
To elevate user experience and ideation quality, future iterations of ThinkGreenly will focus on expanding the AI engine into a multi-functional assistant capable of personalized coaching, contextual evaluation, and predictive insight generation.
Context-Aware AI Ideation: The AI assistant will adapt based on the user’s writing style, domain expertise, and past submissions to offer more personalized and impactful suggestions.
Predictive Sustainability Scoring: The AI will analyze ideas based on feasibility, originality, and potential environmental impact, assigning a predictive “Sustainability Impact Score” to each submission.
Learning from Community Trends: By observing voting patterns, comments, and topic interest spikes, the AI will highlight trending sustainability issues and recommend timely, relevant ideation prompts.
AI Peer Reviewer Mode: A future update will introduce an optional review tool where members can receive simulated peer feedback generated by the AI before public submission.
7.2. Global Collaboration and Cross-Border Innovation Tools
To build a truly international sustainability movement, ThinkGreenly plans to integrate features that promote cross-border cooperation, real-time collaboration, and inclusive language accessibility.
Multilingual Interface Support: ThinkGreenly will support multiple languages including Bangla, Spanish, Arabic, French, and Hindi.
Live Collaborative Editing: Inspired by Google Docs-style co-editing, users will be able to collaborate on ideas in real time, with AI-powered suggestion overlays.
Global Partner Network Dashboard: NGOs, educational institutions, and eco-enterprises will have custom dashboards to manage campaigns, sponsor challenges, or mentor innovators across the globe.
Virtual Events and Hackathons: The platform will host real-time sustainability ideation contests, webinars, and hackathons supported by embedded video conferencing and polling features.
7.3. Blockchain-Based Intellectual Property and Idea Ownership
To ensure idea security, authenticity, and proper attribution, ThinkGreenly will implement blockchain technology for decentralized ownership and transparent transaction history.
Decentralized Idea Proof-of-Creation: Upon submission, ideas will be hashed and timestamped using blockchain, verifying authorship and discouraging plagiarism.
Smart Contract Licensing: Members will be able to issue and track custom licenses (e.g., Creative Commons, Royalty-based) using Ethereum-based smart contracts.
Verified Purchase Receipts: All paid content access and transactions will be logged immutably, ensuring trust and preventing payment disputes.
Member-Controlled Access: Using a decentralized access model, content creators will control who can view, purchase, or remix their ideas, improving transparency and ownership ethics.
7.4. Sustainability-as-a-Service (SaaS) API and Mobile Expansion
To make sustainability innovation more portable, integrated, and accessible, ThinkGreenly will develop tools for seamless API access and mobile use.
Mobile App for On-the-Go Ideation: A full-featured Android/iOS app will allow members to draft, vote, and discuss ideas directly from their smartphones, with offline saving support.
ThinkGreenly Public API: NGOs, universities, and researchers will be able to integrate ThinkGreenly’s ideas database and voting metrics into their own platforms or dashboards via public RESTful APIs.
Push Notifications & AI Alerts: Users will receive smart push notifications about AI feedback, upvotes, admin reviews, or replies to discussions in real time.
7.5. Enhanced Moderation, Gamification, and Learning Systems
To promote a healthy, engaging community, future plans include more sophisticated moderation tools, gamified progress systems, and educational resources.
AI-Moderated Comment Filtering: To ensure respectful dialogue, AI models will automatically flag inappropriate or off-topic comments for review.
Gamified Rewards System: Contributors will earn badges, points, and ranks based on idea quality, community impact, and consistency.
Interactive Sustainability Learning Hub: The platform will host educational resources like AI-generated quizzes, micro-courses, and case studies to help users level up their skills.