Submitted:
21 June 2024
Posted:
24 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Significance
1.2. Opioid Receptors
1.3. Exercise
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Brain Slice Preparation
2.3. Fast Scan Cyclic Voltammetry
2.4. Preparation of Brain Slices for Imaging and Confocal Microscopy
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
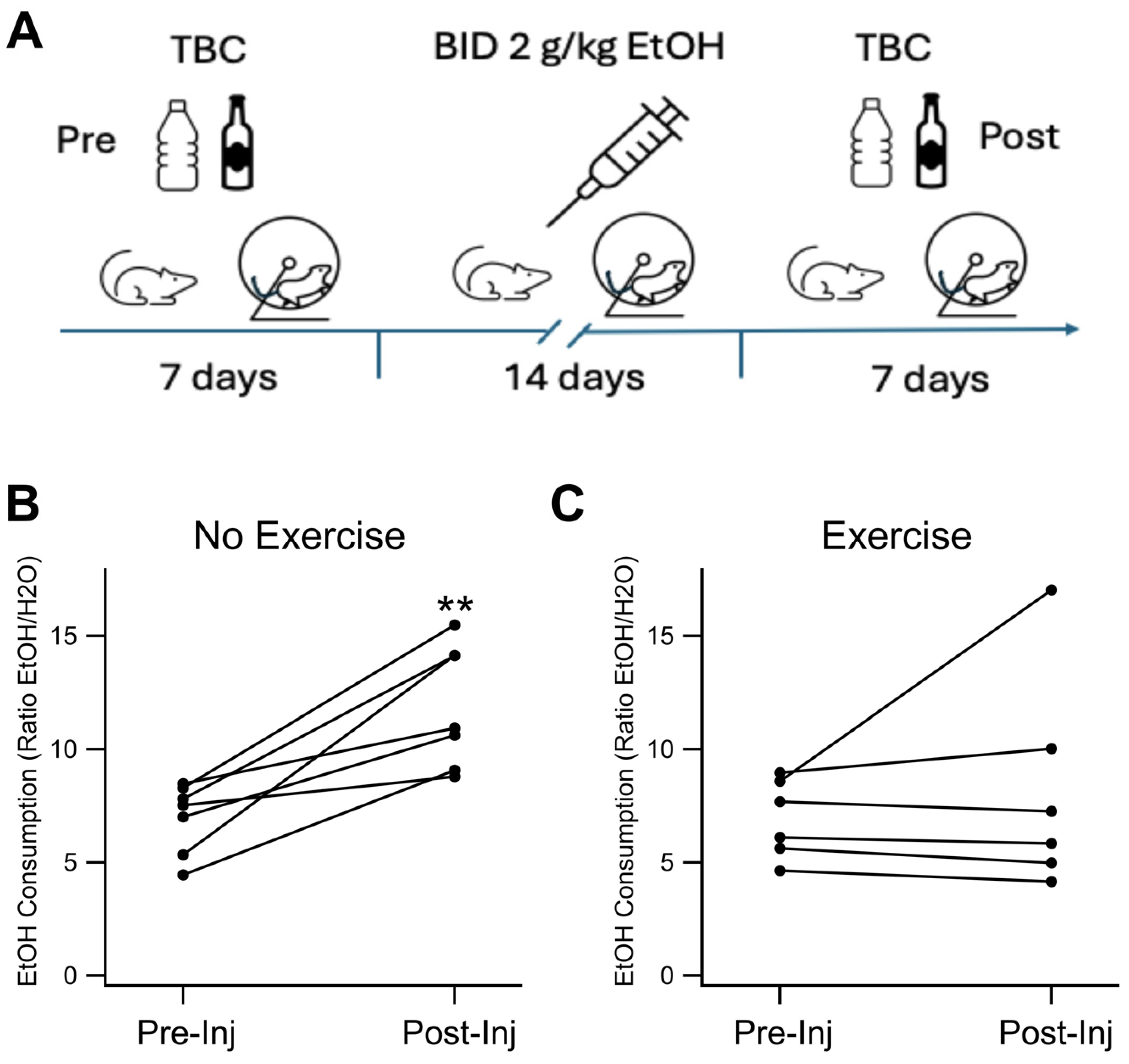
3.1. Effects of Exercise on EtOH Two Bottle Choice Behavior in EtOH-Dependent Mice
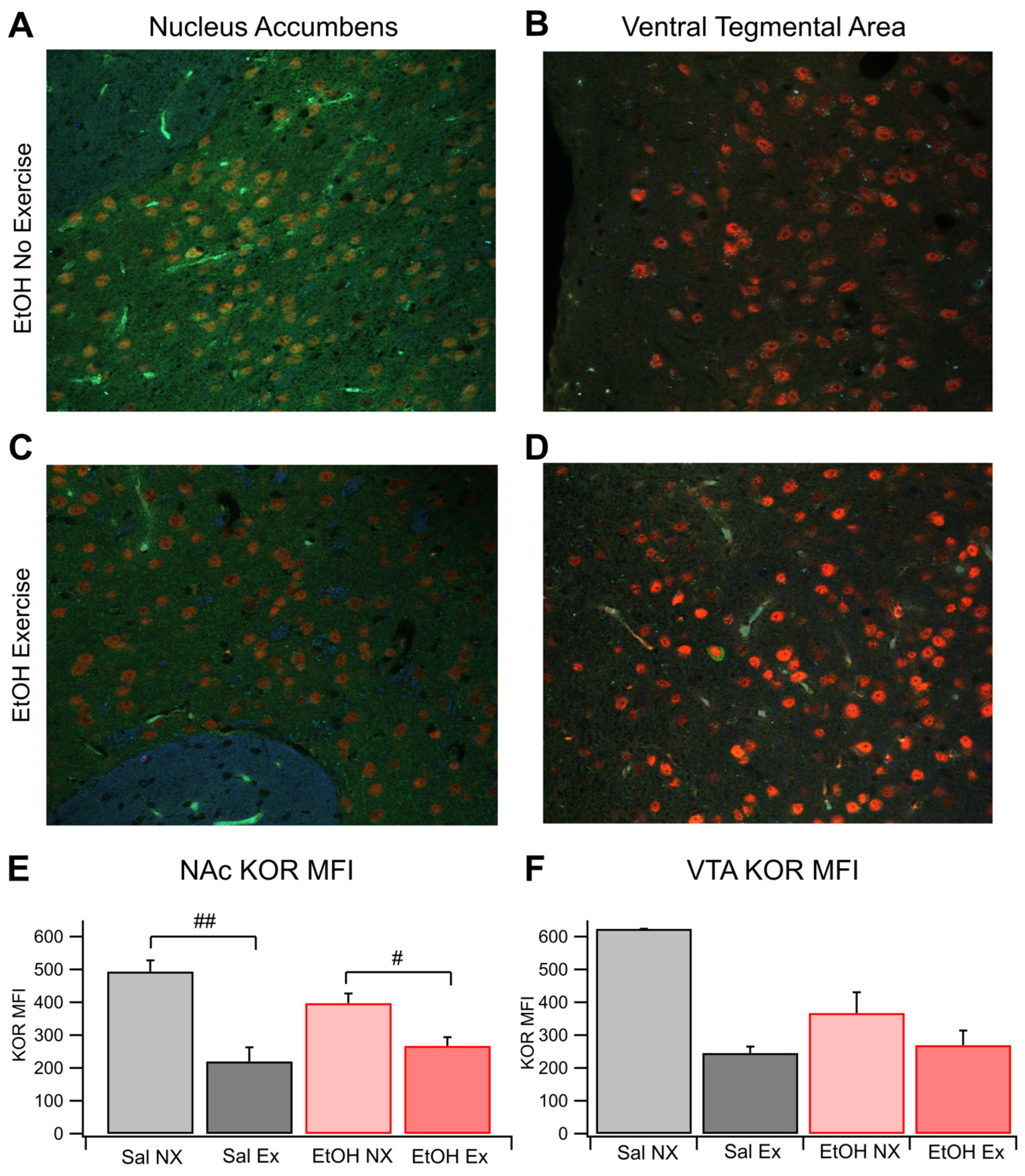
3.2. Immunohistochemical Analysis of KORs in the NAc and VTA
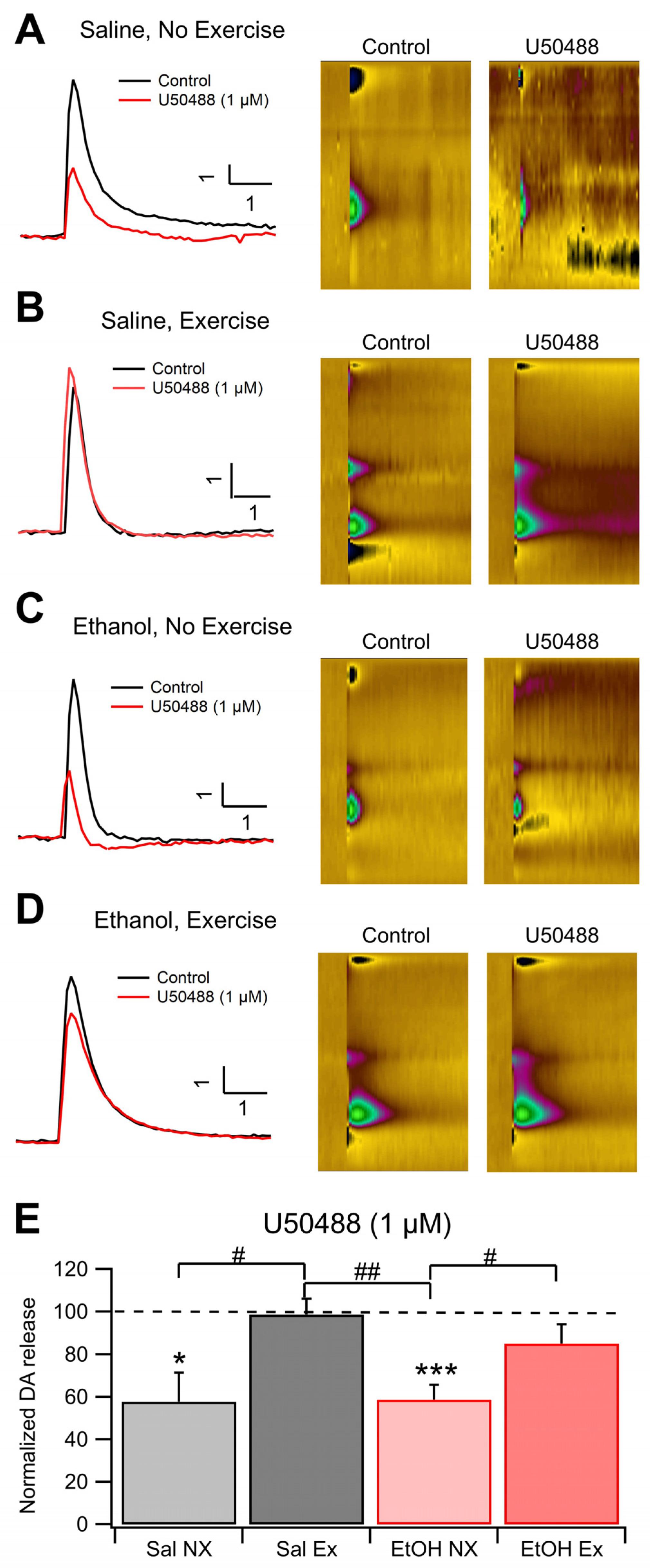
3.3. Role of KORs in Evoked DA Release and Chronic EtOH: Fast-Scan Cyclic Voltammetry
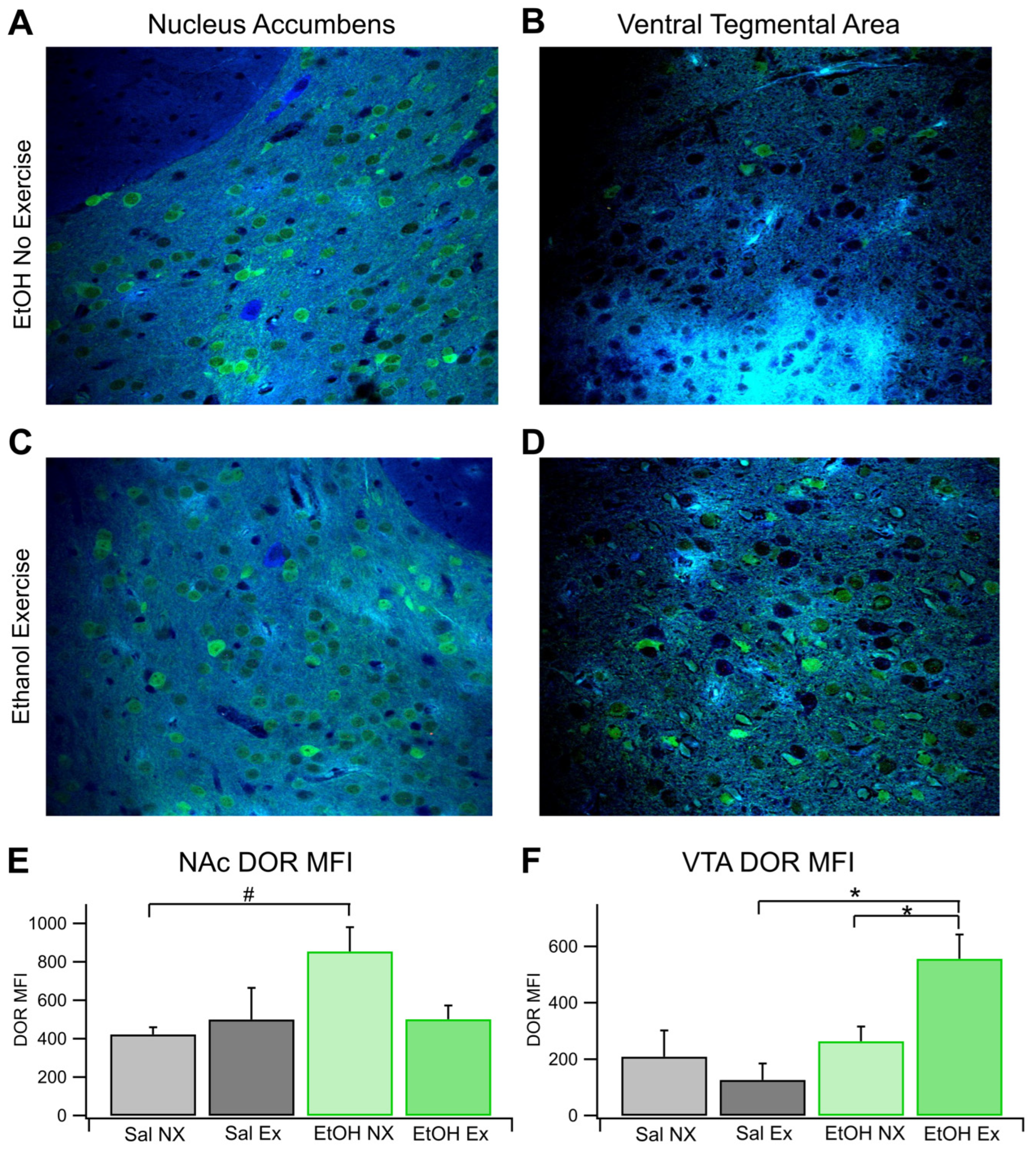
3.4. Immunohistochemical Analysis of DORs in the NAc and VTA
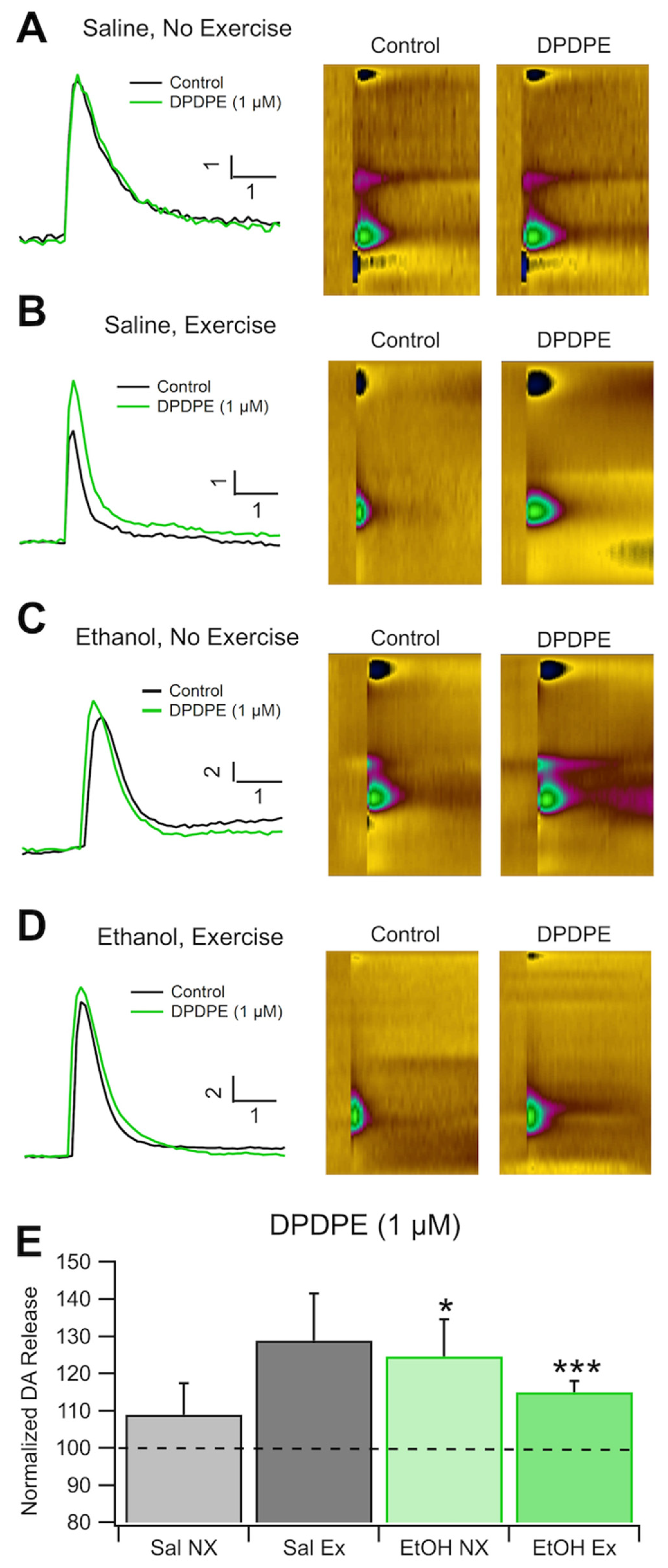
3.5. Role of DORs in Evoked DA Release and Chronic EtOH: Fast-Scan Cyclic Voltammetry
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Table 5.9A—Alcohol use disorder in past year: among people aged 12 or older; by age group and demographic characteristics, numbers in thousands, 2021 and 2022. 2022 [cited 2024 Feb 15]; Available from: https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt42728/NSDUHDetailedTabs2022/NSDUHDetailedTabs2022/NSDUHDetTabsSect5pe2022.htm#tab5.9a.
- National Survey on Drug Use and Health, S.A.a.M.H.S. Administration, Editor. 2022: https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt42728/NSDUHDetailedTabs2022/NSDUHDetailedTabs2022/NSDUHDetTabsSect5pe2022.htm#tab5.9a.
- Koob, G.F.; Volkow, N.D. Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, R.A. Dopamine and reward: The anhedonia hypothesis 30 years on. Neurotox. Res. 2008, 14, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Phillips, A. Independent modulation of basal and feeding-evoked dopamine efflux in the nucleus accumbens and medial prefrontal cortex by the central and basolateral amygdalar nuclei in the rat. Neuroscience 2003, 116, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Phillips, A.G. Modulation by Central and Basolateral Amygdalar Nuclei of Dopaminergic Correlates of Feeding to Satiety in the Rat Nucleus Accumbens and Medial Prefrontal Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 10958–10965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.G.; Ahn, S.; Howland, J.G. Amygdalar control of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system: parallel pathways to motivated behavior. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2003, 27, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ågmo, A.; Federman, I.; Navarro, V.; Padua, M.; Velazquez, G. Reward and reinforcement produced by drinking water: Role of opioids and dopamine receptor subtypes. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1993, 46, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ågmo, A.; Galvan, A.; Talamantes, B. Reward and reinforcement produced by drinking sucrose: Two processes that may depend on different neurotransmitters. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1995, 52, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, R.A. , Dopamine, learning and motivation. Nat Rev Neurosci 2004, 5, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestler, E.J. Psychogenomics: Opportunities for Understanding Addiction. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 8324–8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalivas, P.W., L. Churchill, and M.A. Klitenick, The circuitry mediating the translation of motivational stimuli into adaptive motor responses, in Limbic Motor Circuits and Neuropsychiatry, P.W. Kalivas and C.D. Barnes, Editors. 1993, CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton. p. 237-287.
- Kalivas, P.W.; Volkow, N.D. The Neural Basis of Addiction: A Pathology of Motivation and Choice. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkhanis, A.; Holleran, K.M.; Jones, S.R. Dynorphin/Kappa Opioid Receptor Signaling in Preclinical Models of Alcohol, Drug, and Food Addiction. Int Rev Neurobiol 2017, 136, 53–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Attali, B., D. Saya, and Z. Vogel, Kappa-opiate agonists inhibit adenylate cyclase and produce heterologous desensitization in rat spinal cord. Journal of Neurochemistry 1989, 52, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, D.J.; Grandy, D.K.; A Lester, H.; Davidson, N.; Chavkin, C. Kappa-opioid receptors couple to inwardly rectifying potassium channels when coexpressed by Xenopus oocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konkoy, C.; Childers, S.R. Dynorphin-Selective Inhibition Of Adenylyl Cyclase In Guinea-Pig Cerebellum Membranes. Mol Pharmacol 1989, 36, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prather, P.L. , et al., Properties of a kappa-opioid receptor expressed in CHO cells: interaction with multiple G-proteins is not specific for any individual G alpha subunit and is similar to that of other opioid receptors. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1995, 29, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallent, M.; Dichter, M.; Bell, G.; Reisine, T. The cloned kappa opioid receptor couples to an N-type calcium current in undifferentiated PC-12 cells. Neuroscience 1994, 63, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, D.J.; Grandy, D.K.; A Lester, H.; Davidson, N.; Chavkin, C. Kappa-opioid receptors couple to inwardly rectifying potassium channels when coexpressed by Xenopus oocytes. Molecular Pharmacology 1995, 47, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konkoy, C.S.; S. R. Childers, Dynorphin-selective inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in guinea pig cerebellum membranes. Molecular Pharmacology 1989, 36, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spanagel, R.; Herz, A.; Shippenberg, T.S. Opposing tonically active endogenous opioid systems modulate the mesolimbic dopaminergic pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2046–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prather, P.L. , et al., Properties of a kappa-opioid receptor expressed in CHO cells: interaction with multiple G-proteins is not specific for any individual G alpha subunit and is similar to that of other opioid receptors. Molecular Brain Research 1995, 29, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.M.; Valdez, G.R.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Bakalkin, G. Targeting dynorphin/kappa opioid receptor systems to treat alcohol abuse and dependence. Alcohol 2012, 46, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarman, S.K.; Haney, A.M.; Valdez, G.R. Kappa opioid regulation of depressive-like behavior during acute withdrawal and protracted abstinence from ethanol. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0205016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillett, K.; Harshberger, E.; Valdez, G.R. Protracted withdrawal from ethanol and enhanced responsiveness stress: Regulation via the dynorphin/kappa opioid receptor system. Alcohol 2013, 47, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakwar, E. , et al., Exercise and mental illness: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC). Journal of Clininical Psychiatry 2012, 73, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirohi, S.; Bakalkin, G.; Walker, B.M. Alcohol-induced plasticity in the dynorphin/kappa-opioid receptor system. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 5, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanagel, R.; Herz, A.; Shippenberg, T.S. Opposing tonically active endogenous opioid systems modulate the mesolimbic dopaminergic pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2046–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.I.; Lopez, M.F.; Griffin, W.C.; Haun, H.L.; Bloodgood, D.W.; Pati, D.; Boyt, K.M.; Kash, T.L.; Becker, H.C. Dynorphin-kappa opioid receptor activity in the central amygdala modulates binge-like alcohol drinking in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 44, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- I Chefer, V.; Bäckman, C.M.; Gigante, E.D.; Shippenberg, T.S. Kappa Opioid Receptors on Dopaminergic Neurons Are Necessary for Kappa-Mediated Place Aversion. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, N.; Murakawa, K.; Takada, K.; Oi, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Nagase, H.; Cools, A.; Koshikawa, N. Interactions among mu- and delta-opioid receptors, especially putative delta1- and delta2-opioid receptors, promote dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Neuroscience 2005, 135, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakawa, K.; Hirose, N.; Takada, K.; Suzuki, T.; Nagase, H.; Cools, A.R.; Koshikawa, N. Deltorphin II enhances extracellular levels of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens via opioid receptor-independent mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 491, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Koide, S.; Hirose, N.; Takada, K.; Tomiyama, K.; Koshikawa, N.; Cools, A. Fentanyl increases dopamine release in rat nucleus accumbens: involvement of mesolimbic mu- and delta-2-opioid receptors. Neuroscience 1999, 92, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okutsu, H.; Watanabe, S.; Takahashi, I.; Aono, Y.; Saigusa, T.; Koshikawa, N.; Cools, A.R. Endomorphin-2 and Endomorphin-1 Promote the Extracellular Amount of Accumbal Dopamine via Nonopioid and Mu-Opioid Receptors, Respectively. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 31, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonci, A.; Williams, J.T. A Common Mechanism Mediates Long-Term Changes in Synaptic Transmission after Chronic Cocaine and Morphine. Neuron 1996, 16, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.; North, R. Opioids excite dopamine neurons by hyperpolarization of local interneurons. J. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffensen, S.C.; Stobbs, S.H.; Colago, E.E.; Lee, R.-S.; Koob, G.F.; Gallegos, R.A.; Henriksen, S.J. Contingent and non-contingent effects of heroin on mu-opioid receptor-containing ventral tegmental area GABA neurons. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 202, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devine, D.; Wise, R. Self-administration of morphine, DAMGO, and DPDPE into the ventral tegmental area of rats. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 1978–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shippenberg, T.; Zapata, A.; Chefer, V. Dynorphin and the pathophysiology of drug addiction. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 116, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunillasdotter, V.; Andréasson, S.; Hallgren, M.; Jirwe, M. Exercise as treatment for alcohol use disorder: A qualitative study. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2022, 41, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droste, S.K.; Schweizer, M.C.; Ulbricht, S.; Reul, J.M.H.M. Long-Term Voluntary Exercise and the Mouse Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenocortical Axis: Impact of Concurrent Treatment with the Antidepressant Drug Tianeptine. J. Neuroendocr. 2006, 18, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, B.N.; Foley, T.E.; Le, T.V.; Strong, P.V.; Loughridge, A.B.; Day, H.E.; Fleshner, M. Long-term voluntary wheel running is rewarding and produces plasticity in the mesolimbic reward pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 217, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Zhou, C. Impact of Physical Exercise on Substance Use Disorders: A Meta-Analysis. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e110728–e110728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza-Gardner, A.K.; Barry, A.E. Examining physical activity levels and alcohol consumption: are people who drink more active? Am J Health Promot 2012, 26, e95–e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza-Gardner, A.K. and A.E. Barry, Examining physical activity levels and alcohol consumption: are people who drink more active? Am J Health Promot 2012, 26, e95–e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, D. , et al., Cocaine dependence and d2 receptor availability in the functional subdivisions of the striatum: relationship with cocaine-seeking behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 1190–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, D.; Grant, K.A.; Gage, H.D.; Mach, R.H.; Kaplan, J.R.; Prioleau, O.; Nader, S.H.; Buchheimer, N.; Ehrenkaufer, R.L.; Nader, M.A. Social dominance in monkeys: dopamine D2 receptors and cocaine self-administration. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voisey, J.; Swagell, C.D.; Hughes, I.P.; van Daal, A.; Noble, E.P.; Lawford, B.R.; Young, R.M.; Morris, C.P. A DRD2 and ANKK1 haplotype is associated with nicotine dependence. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 196, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arida, R.M.; da Silva, S.G.; de Almeida, A.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Zavala-Tecuapetla, C.; Brand, S.; Rocha, L. Differential effects of exercise on brain opioid receptor binding and activation in rats. J. Neurochem. 2014, 132, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.M.; Valdez, G.R.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Bakalkin, G. Targeting dynorphin/kappa opioid receptor systems to treat alcohol abuse and dependence. Alcohol 2012, 46, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, A.; Cavallo, D.; Goldberg, A.; de Laat, B.; Nabulsi, N.; Huang, Y.; Krishnan-Sarin, S.; Morris, E.D. PET imaging reveals lower kappa opioid receptor availability in alcoholics but no effect of age. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2539–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H., S. Roh, and D.J. Kim, Alcohol-induced blackout. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2009, 6, 2783–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorgason, J.T.; España, R.A.; Jones, S.R. Demon Voltammetry and Analysis software: Analysis of cocaine-induced alterations in dopamine signaling using multiple kinetic measures. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 202, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuppa, G.; Tambalo, S.; Pfarr, S.; Sommer, W.H.; Bifone, A. Aberrant insular cortex connectivity in abstinent alcohol-dependent rats is reversed by dopamine D3 receptor blockade. Addict. Biol. 2019, 25, e12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.C.; Williams, S.B.; Pistorius, S.S.; Park, H.J.; Woodward, T.J.; Payne, A.J.; Obray, J.D.; Shin, S.I.; Mabey, J.K.; Steffensen, S.C. Ventral Tegmental Area GABA Neurons Are Resistant to GABA(A) Receptor-Mediated Inhibition During Ethanol Withdrawal. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.B.; Yorgason, J.T.; Nelson, A.C.; Lewis, N.; Nufer, T.M.; Edwards, J.G.; Steffensen, S.C. Glutamate Transmission to Ventral Tegmental Area GABA Neurons Is Altered by Acute and Chronic Ethanol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 2186–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Gallegos, R.; Lee, R.S.; Criado, J.R.; Henriksen, S.J.; Steffensen, S.C. Adaptive responses of gamma-aminobutyric acid neurons in the ventral tegmental area to chronic ethanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999, 291, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow, K.H.; Bradley, K.D.; Allison, D.W.; Taylor, S.R.; Yorgason, J.T.; Hansen, D.M.; Walton, C.H.; Sudweeks, S.N.; Steffensen, S.C. Acute and Chronic Ethanol Modulate Dopamine D2-Subtype Receptor Responses in Ventral Tegmental Area GABA Neurons. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bills, K.B.; Otteson, D.Z.; Jones, G.C.; Brundage, J.N.; Baldwin, E.K.; Small, C.A.; Kim, H.Y.; Yorgason, J.T.; Blotter, J.D.; Steffensen, S.C. Mechanical Stimulation Alters Chronic Ethanol-Induced Changes to VTA GABA Neurons, NAc DA Release and Measures of Withdrawal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bills, K.B.; Clarke, T.; Major, G.H.; Jacobson, C.B.; Blotter, J.D.; Feland, J.B.; Steffensen, S.C. Targeted Subcutaneous Vibration With Single-Neuron Electrophysiology As a Novel Method for Understanding the Central Effects of Peripheral Vibrational Therapy in a Rodent Model. Dose-Response 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bills, K.B.; Obray, J.; Clarke, T.; Parsons, M.; Brundage, J.; Yang, C.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Yorgason, J.T.; Blotter, J.D.; Steffensen, S.C. Mechanical stimulation of cervical vertebrae modulates the discharge activity of ventral tegmental area neurons and dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Brain Stimul. 2019, 13, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.C.; Small, C.A.; Otteson, D.Z.; Hafen, C.W.; Breinholt, J.T.; Flora, P.D.; Burris, M.D.; Sant, D.W.; Ruchti, T.R.; Yorgason, J.T.; et al. Whole-Body Vibration Prevents Neuronal, Neurochemical, and Behavioral Effects of Morphine Withdrawal in a Rat Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.I.; Lopez, M.F.; Becker, H.C. Stress-Induced Enhancement of Ethanol Intake in C57BL/6J Mice with a History of Chronic Ethanol Exposure: Involvement of Kappa Opioid Receptors. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melchior, J.R.; Jones, S.R. Chronic ethanol exposure increases inhibition of optically targeted phasic dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens core and medial shell ex vivo. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 85, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Preez, A. , et al., The type of stress matters: repeated injection and permanent social isolation stress in male mice have a differential effect on anxiety- and depressive-like behaviours, and associated biological alterations. Translational Psychiatry 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drude, S.; Geißler, A.; Olfe, J.; Starke, A.; Domanska, G.; Schuett, C.; Kiank-Nussbaum, C. Side effects of control treatment can conceal experimental data when studying stress responses to injection and psychological stress in mice. Lab Anim. 2011, 40, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaisher-Grinberg, S.; Persaud, S.D.; Loh, H.H.; Wei, L.-N. Stress-induced epigenetic regulation of κ-opioid receptor gene involves transcription factor c-Myc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2012, 109, 9167–9172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirayama, Y.; Ishida, H.; Iwata, M.; Hazama, G.; Kawahara, R.; Duman, R.S. Stress increases dynorphin immunoreactivity in limbic brain regions and dynorphin antagonism produces antidepressant-like effects. J. Neurochem. 2004, 90, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F. Alcoholism: Allostasis and Beyond. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2003, 27, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F. Neurobiological substrates for the dark side of compulsivity in addiction. Neuropharmacology 2008, 56, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, G.F. Brain stress systems in the amygdala and addiction. Brain Res. 2009, 1293, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F. The role of CRF and CRF-related peptides in the dark side of addiction. Brain Res. 2009, 1314, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, M.D.; Lochner, M.A.; Bemis, K.G.; Hymson, D.L. Chronic ethanol alters the receptor binding characteristics of the delta opioid receptor ligand, DAla2DLeu5 enkephalin in mouse brain. Life Sci. 1983, 33, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alongkronrusmee, D.; Chiang, T.; Van Rijn, R.M. Delta Opioid Pharmacology in Relation to Alcohol Behaviors. 2016, Springer International Publishing. 199-225.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




