Submitted:
14 June 2024
Posted:
14 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of Bacillus spp.
3. Utilizing Bacillus in Shellfish and Finfish
3.1. Application of Bacillus in Fin fishes
3.1.1. Bacillus aerius
3.1.2. Bacillus aerophilus
3.1.3. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens
3.1.4. Bacillus altitudinis
3.1.5. Bacillus aryabhattai
3.1.6. Bacillus atrophaeus
3.1.7. Bacillus cereus
3.1.8. Bacillus circulans
3.1.9. Bacillus clausii
3.1.10. Bacillus coagulans
3.1.11. Bacillus flexus
3.1.12. Bacillus licheniformis
3.1.13. Bacillus megaterium
3.1.14. Bacillus methylotrophicus
3.1.15. Bacillus nealsonii
3.1.16. Bacillus pumilus
3.1.17. Bacillus sonorensis
3.1.18. Bacillus subtilis
3.1.19. Bacillus tequilensis
3.1.20. Bacillus thermoamylovorans
3.1.21. Bacillus thuringiensis
3.1.22. Bacillus silvestris
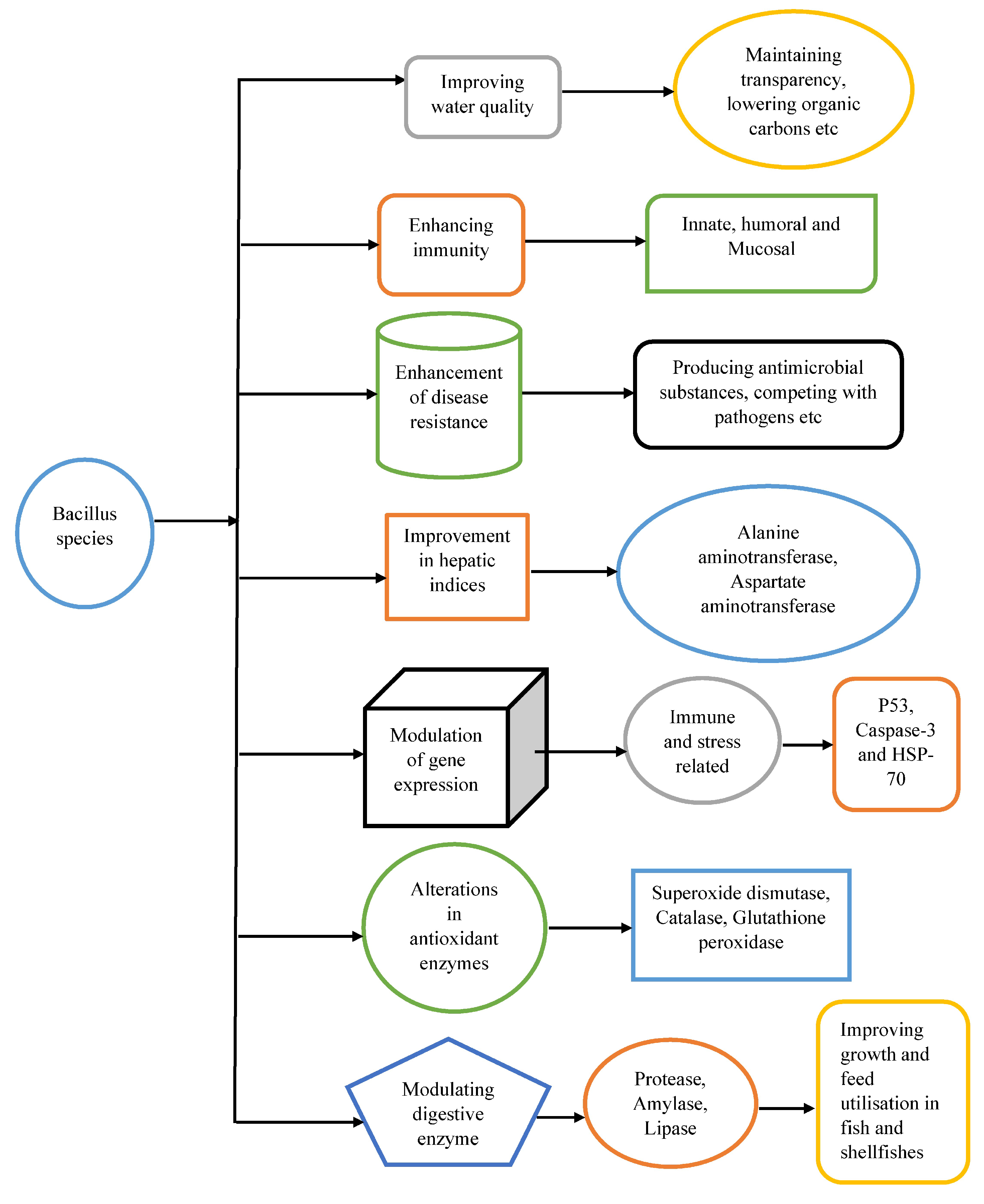
4. Effects of Bacillus spp on Fin Fish and Shellfish
4.1. Impact of Bacillus Species on Finfish
4.1.1. The Effects of Bacillus on Immunological Parameters and Disease Resistance in Finfish
4.1.2. Effects of Bacillus as a Growth Promoter in Fin Fishes
| Bacillus spp. | Fish species | Initial Weight | Application of Bacillus spp | Observation on Growth | Conclusion | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. subtilis | Oreochromis niloticus | 14.82 ± 0.42 g | Dietary application for 50 days | Fish given probiotics showed noticeably improved growth results as compared to the control group, and their digestive enzyme activity also increased noticeably | In tilapia housed in a biofloc system, B. subtilis efficiently increases fish output, immunity, and defense against LPS-induced damages | [168] |
| (a mix of B. subtilis and B. licheniformis) | Oreochromis niloticus | 53.01 ± 1.0 g | Dietary application for 50 days | All probiotic BS enriched groups showed improved weight gain, specific growth rate, and feed conversion ratio | Application of probiotic BS at 10 gkg-1 (BS10) may be taken into consideration to enhance tilapia farming growth | [169] |
| B. amyloliquefaciens and B. pumilus isolated from striped catfish (P. hypophthalmus) | (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) | 25.2 ± 1.3 g | dietary supplementation | Growth improvement in fish given a combination of probiotics | Thus, striped catfish health and growth rate can be enhanced by dietary supplementation of a blend of B. amyloliquefaciens and B. pumilus at 5 × 108 CFU g−1 | [170] |
| Two species of Bacillus (B. licheniformis and B. subtilis) | Asian Sea Bass, L. calcarifer | 1.5 ± 0.2 g | During 8 weeks of dietary supplementaion | Compared to Asian sea bass fed the basal food (control), those supplemented with probiotic Bacillus (B. licheniformis and B. subtilis) had noticeably improved growth. | Considering that the optimal outcome is obtained when 1 ×106 CFU g−1 of Bacillus is supplemented in the diet | [160] |
| (B. subtilis and B. licheniformis | Oreochromis niloticus | mean weight of around 150 g | 30 days of dietary supplementation | The fish fed with diets containing 0.04% and 0.08% of probiotics presented higher weight gain than the control group | The establishment of a beneficial microorganism population may improve host health | [102] |
| Mixed probiotic containing (B. licheniformis and B. subtilis and Ferroin solution) | kutum, (Rutilus frisii kutum) | 0.4 ± 0.1 g | 60 days of supplemented diets in ratios | Fish receiving diets supplemented with probiotics and Ferroin solution showed significantly better growth than those fed the basal diet (control) | These results indicate that the combination of probiotic and Ferroin solution represents an effective dietary supplement for growth performance | [171] |
| B. subtilis | grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella | 50 ± 2.5 g | 56 days dietary feeding | Significantly higher SGR and lower FCR than those fed the control diet | An optimum dose of B. subtilis Ch9 could induce digestive and potentially promote the digestion and absorption of nutrients, as well as improve the growth performance of grass carp significantly. | [152] |
| B. subtilis | Oreochromis niloticus | 16.5 ± 0.2 g | 21-d growth trial as feed additives | There was no discernible difference in growth performance when any probiotic-added diet was used | Given the short study period, these outcomes are not shocking | [99] |
| B. pumilus | Oreochromis niloticus | 3.62 ± 0.06 g | 84 days of dietary supplementation | The study showed fish fed a pro-enzyme diet had improved feed consumption and growth performance | Pro-enzyme supplementation enhanced the growth performance | [172] |
| B. circulans | Catla catla | 6.48 ± 0.43 g | Feeding of diets supplemented for 60 day | Compared to other treatments, C. catla given feed probiotic showed higher growth performance in terms of live weight gain and specific growth rate | The study's findings support the use of Bacillus circulans PB 7, a probiotic, for improved growth and appropriate nutrient use | [64] |
| B. licheniformis | triangular bream (Megalobrama terminalis) | 30.5 ± 0.5 g | 8-week feeding trial, | Fish fed B. licheniformis showed a considerably higher growth parameters | B. licheniformis, either by itself or in combination, can greatly enhance triangular bream growth performance | [173] |
| B. clausii | Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus | Average weight of 21 g | Dietary supplementation for 56 days | Fish fed B. clausii gained more weight than the control group | The growth performance and health benefits of the Japanese flounder were enhanced by B. clausii | [67] |
4.1.3. Bacillus spp Effects on Liver Health of Fin Fishes
4.1.4. Bacillus Species-Related Effects on Finfish Gene Expression
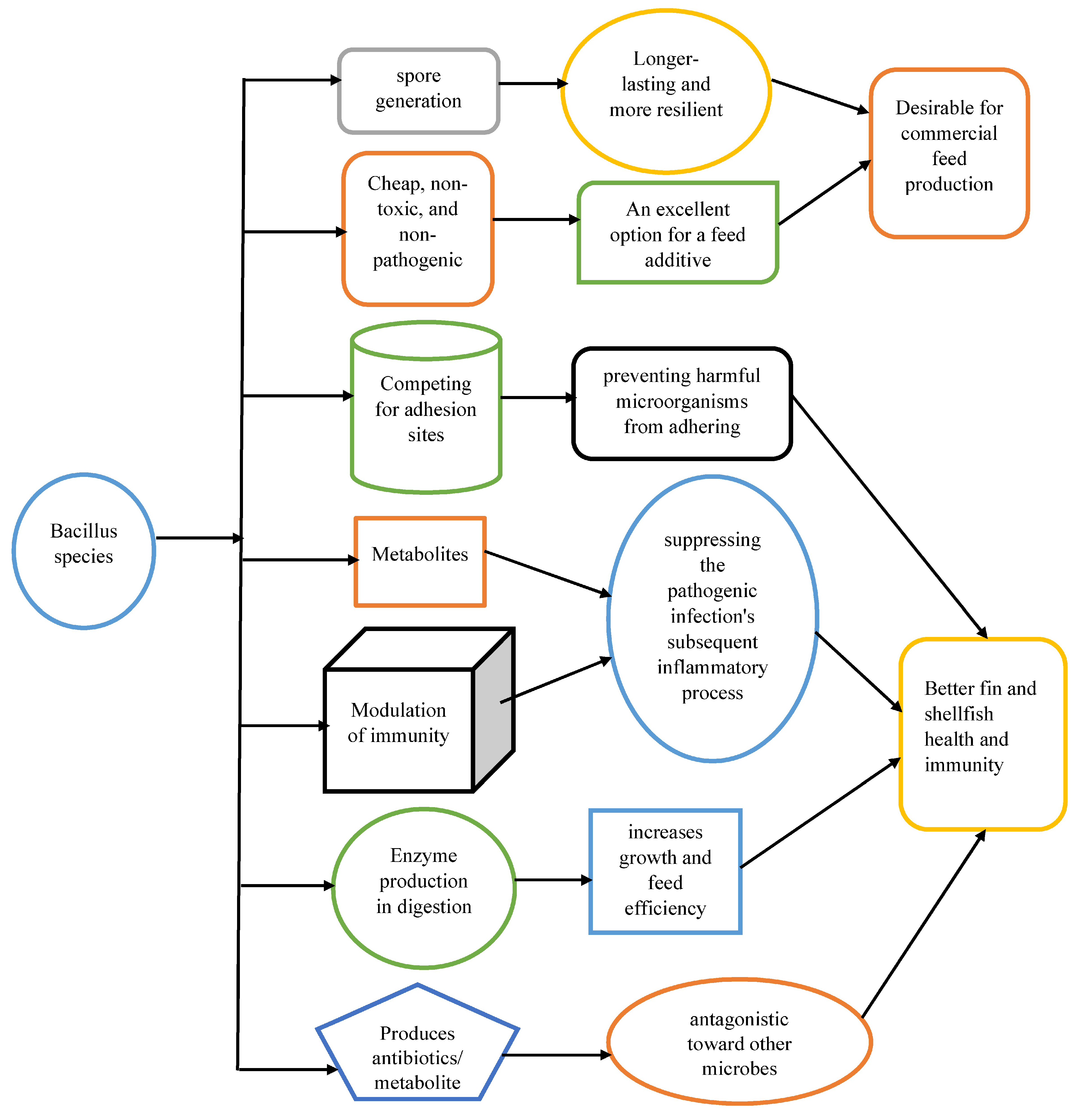
4.2. Effects of Bacillus spp on Shellfish
4.2.1. Enhancement of Immune Response Resistance to Diseases in Shell Fishes
4.2.2. Modifying Digestive Enzymes and Encouraging Shellfish Development
| Bacillus spp. | Fish species | Initial Weight | Application of Bacillus spp | Observation on Growth | Conclusion | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. cereus | L. vannamei | 4.55 g | 28 days dietary administration | Findings demonstrated that following a 28-day probiotic feeding regimen, shrimp growth was enhanced in comparison to the control group | The study showed that probiotics might be used to enhance white shrimp growth | [237] |
| B. licheniformis | Haliotis discus hannai Ino | 4.17 ± 0.32 | 8-week culture experiment | In comparison to the control group, the supplemented diet group exhibited a significantly greater specific growth rate of shell length, food intake, and food conversion rate | The study suggests B. licheniformis diets enhanced abalones food intake and growth. | [238] |
| B. amyloliquefaciens | H. discus hannai | 4.28 ± 0.23 g | 8-week culture experiment | Diets supplemented with Bacillus showed significantly increased body weight, specific growth rate, and food conversion efficiency compared to the control group | The experimental meal that contained 105 CFU/g of B. amyloliquefaciens promoted abalone growth and food intake | [239] |
| B. subtilis | (L. vannamei) | 12.03 ± 2.76 g | 1 month feeding of supplemented diets | Effective enhancement of growth | A notable rise in growth metrics suggested that Bacillus was the best option | [209] |
| B. subtilis and B. licheniformis | (L. vannamei) | 1 ± 0.1 g | Dietary supplementation for a month | Shrimp's specific growth rate was much higher in the supplemented diet than in the (control) treatment, and the treated groups' ultimate growth was comparable | Shrimp growth parameters were effectively increased by the Bacilli probiotic combination | [240] |
| B. licheniformis | H. discus hannai | 4.91 ± 0.34 g | 70 days of beimg fed dietary supplemented diets | The abalone in the supplemented diet exhibited a considerably greater feed conversion efficiency and specific growth rate compared to the control group | Maximum growth benefits of the probiotic were noted | [241] |
| B. subtilis | (L. vannamei) | 0.67 ± 0.06g | Dietary application for 8 weeks | The final weight, weight gain, and digestive enzyme activity of the shrimp fed Bacillus diets were significantly higher than those of the untreated control group | B. subtilis treatment can enhance shrimp growth performance | [189] |
| B. cereus | (P. monodon) | 0.204 ± 0.004 g | Dietary appliacation for 90 days | The group that received a supplemented meals achieved a higher FCR of 1.27 ± 0.081, a maximum production of 10.45 ± 0.275 g, and an SGR of 4.40 ± 0.179%, according to the overall growth responses | B. cereus, a lyophilized probiotic, was effective in boosting shrimp growth when added to feed at a concentration of 0.4%/100 g | [191] |
| B. pumilus | (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) | 1.81 ± 0.01 g | 2 months dietary application | The experimental groups exhibited significantly increased final weight, weight gain rate (WGR), and specific growth rate (SGR) compared to the control group | Adding B. pumilus to feed at a dosage of 1 × 108 CFU/g would enhance M. rosenbergii's growth and digestive enzymes | [242] |
4.2.3. Enhancing Shrimp Culture Water Quality Factors
5. Pathogenic Bacillus in Fin and Shellfish
6. Fish and Shellfish Safety with Bacillus
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buchmann, K. Control of parasitic diseases in aquaculture. Parasitology 2022, 149, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsène, M.M.; Davares, A.K.; Andreevna, S.L.; Vladimirovich, E.A.; Carime, B.Z.; Marouf, R.; Khelifi, I. The use of probiotics in animal feeding for safe production and as potential alternatives to antibiotics. Vet. World 2021, 14, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanes, C.G. Animal agriculture: Livestock, poultry, and fish aquaculture. In Animals and Human Society; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 133–179. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.Y.; Tran, N.; Cheong, K.C.; Sulser, T.B.; Cohen, P.J.; Wiebe, K.; Nasr-Allah, A. M, The future of fish in Africa: Employment and investment opportunities. PloS ONE 2021, 16, e0261615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Kossack, C.; Montero, R.; Köllner, B.; Maisey, K. Chilean aquaculture and the new challenges: Pathogens, immune response, vaccination and fish diversification. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 98, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringø, E, Probiotics in shellfish aquaculture. Aquac. Fish. 2020, 5, 1–27. [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Alagawany, M.; Patra, A.K.; Kar, I.; Tiwari, R.; Dawood, M.A.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. The functionality of probiotics in aquaculture: An overview. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 117, 36–52. [Google Scholar]
- Luise, D.; Bosi, P.; Raff, L.; Amatucci, L.; Virdis, S.; Trevisi, P. Bacillus spp. probiotic strains as a potential tool for limiting the use of antibiotics, and improving the growth and health of pigs and chickens. Frontiers in Microbiology 2022, 13, 801827. [Google Scholar]
- Panase, A.; Thirabunyanon, M.; Promya, J. ; Chitmanat, C, Influences of Bacillus subtilis and fructooligosaccharide on growth performances, immune responses, and disease resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 2023, 9, 1094681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, A.; Hussain, Z.; Akram, A.M.; Alorabi, M.; Sarwar, N.; Rehman, R.A.; Alkafafy, M. Impact of Bacillus subtilis supplemented feed on growth and biochemical constituents in Labeo rohita fingerlings. Journal of King Saud University-Science 2021, 33, 101668. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.; Dominguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Saraiva, J.A. ; Franco, D, Main groups of microorganisms of relevance for food safety and stability: General aspects and overall description. In Innovative Technologies for Food Preservation. Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 53-107.
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Lereclus, D.; Koehler, T.M. The Bacillus cereus group: Bacillus species with pathogenic potential. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahaddad, S.A.; Almalki, M.H.; Alghamdi, O.A.; Sohrab, S.S.; Yasir, M.; Azhar, E.I. ; Chouayekh, H, Bacillus Species as direct-fed microbial antibiotic alternatives for monogastric production. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, C.; Cock, I.E.; Chen, X. ; Feng, Y, Antimicrobial Bacillus: metabolites and their mode of action. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, U.D.; Lin, N.; Akhter, N.; Siddiqui, T.; Li, S. ; Wu, B, Overview of the latest developments in the role of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics in shrimp aquaculture. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 114, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Hong, B.; Luo, K.; Li, Y.; Fu, H. ; Wang, J, Isolation of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus pumilus with Anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus Activity and Identification of the Anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus Substance. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbuewu, I.P.; Mabelebele, M.; Sebola, N.A. ; Mbajiorgu, C, Bacillus probiotics as alternatives to in-feed antibiotics and its influence on growth, serum chemistry, antioxidant status, intestinal histomorphology, and lesion scores in disease-challenged broiler chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 876725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.K.; Roy, T.; Mondal, S. ; Ringø, E, Identification of gut-associated amylase, cellulase and protease-producing bacteria in three species of Indian major carps. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, D.Y. Microbial diversity in the intestine of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2013, 414, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jlidi, M.; Akremi, I.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Brabra, W.; Ali, M.B.; Ali, M. B, Probiotic properties of Bacillus strains isolated from the gastrointestinal tract against pathogenic Vibriosis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 884244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S. K, Multifaceted applications of probiotic Bacillus species in aquaculture with special reference to Bacillus subtilis. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 862–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaji, S.; Chaturvedi, P.; Suresh, K.; Reddy, G.S.N.; Dutt, C.B.S.; Wainwright, M. . & Bhargava, P. M.; Bacillus aerius sp. nov.; Bacillus aerophilus sp. nov.; Bacillus stratosphericus sp. nov. and Bacillus altitudinis sp. nov.; isolated from cryogenic tubes used for collecting air samples from high altitudes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap, C. A, The status of the species Bacillus aerius. Request for an Opinion. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2341–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeigler, D.R.; Perkins, J.B. The genus bacillus. In Practical handbook of microbiology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 249–278. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, D.; Banerjee, S.; Mukherjee, A. ; Ghosh, K, Selection and probiotic characterization of exoenzyme-producing bacteria isolated from the gut of Catla catla (Actinopterygii: Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae). Acta Ichthyologica et Piscatoria 2015.
- Meidong, R.; Khotchanalekha, K.; Doolgindachbaporn, S.; Nagasawa, T.; Nakao, M.; Sakai, K.; Tongpim, S. Evaluation of probiotic Bacillus aerius B81e isolated from healthy hybrid catfish on growth, disease resistance and innate immunity of Pla-mong Pangasius bocourti. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 73, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meidong, R.; Nakao, M.; Sakai, K. ; Tongpim, S, Lactobacillus paraplantarum L34b-2 derived from fermented food improves the growth, disease resistance and innate immunity in Pangasius bocourti. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Dutta, D.; Banerjee, S.; Ringø, E.; Breines, E.M.; Hareide, E. . & Ghosh, K, Potential probiotics from Indian major carp, Cirrhinus mrigala. Characterization, pathogen inhibitory activity, partial characterization of bacteriocin and production of exoenzymes. Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 108, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, D.; Souissi, S.; Ahamed, T. S, Effects of the potential probiotics Bacillus aerophilus KADR3 in inducing immunity and disease resistance in Labeo rohita. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 70, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priest, F.G.; Goodfellow, M.; Shute, L.A.; Berkeley, R.C.W. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens sp. nov. Nom. Rev. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1987, 37, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto, J, Studies on the production of bacterial amylase. I. Isolation of bacteria secreting potent amylases and their distribution. Nippon. Nogeikagaku Kaishi 1943, 19, 487–503.
- Liu, H.; Prajapati, V.; Prajapati, S.; Bais, H. ; Lu, J, Comparative genome analysis of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens focusing on phylogenomics, functional Traits, and prevalence of antimicrobial and virulence genes. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 724217. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, P.; Li, G.Y.; Yue, S.; Huang, J. . & Mo, Z. L, Isolation and characterization of Bacillus spp. M 001 for potential application in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) against V ibrio anguillarum. Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 374–381. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, P.; Zhu, W.; Mo, Z, The ability of marine Bacillus spp. isolated from fish gastrointestinal tract and culture pond sediment to inhibit growth of aquatic pathogenic bacteria. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2016, 15, 701–714. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, A.; Dutta, D.; Banerjee, S.; Ringø, E.; Breines, E.M.; Hareide, E. . & Ghosh, K, Culturable autochthonous gut bacteria in rohu, Labeo rohita. In vitro growth inhibition against pathogenic Aeromonas spp.; stability in gut, bio-safety and identification by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Symbiosis 2017, 73, 165–177. [Google Scholar]
- Kavitha, M.; Raja, M. ; Perumal, P, Evaluation of probiotic potential of Bacillus spp. isolated from the digestive tract of freshwater fish Labeo calbasu (Hamilton, 1822). Aquaculture Reports 2018, 11, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Halder U, Banerjee A, Chaudhry V, Varshney RK, Mantri S, Bandopadhyay R, Draft genome report of Bacillus altitudinis SORB11, isolated from the Indian sector of the Southern Ocean. Genome Announc 2017, 5, e00339-17.
- Shafi S, Kamili AN, Shah MA, Bandh SA, Dar R, Dynamics of bacterial class Bacilli in the deepest valley lake of Kashmir-the Manasbal Lake. Microb Pathog 2017, 104, 78–83. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay Kumar E, Srijana M, Kiran Kumar K, Harikrishna N, Reddy G, A novel serine alkaline protease from Bacillus altitudinis GVC11 and its application as a dehairing agent. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 2011, 34, 403–409. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao S, Lu Z, Zhang C, Lu F, Bie X, Purification, characterization, and heterologous expression of a thermostable β-1,3–1,4-glucanase from Bacillus altitudinis YC-9. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 169, 960–975. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Dutta, D.; Ghosh, K. Non-Starch Polysaccharide Degrading Gut Bacteria in Indian Major Carps and Exotic Carps. Jordan J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Ghosh, K.; Hazra, N, Evaluation of extracellular enzyme-producing autochthonous gut bacteria in walking catfish, Clarias batrachus (L. ). J. Fish. 2016, 4, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esakkiraj, P.; Usha, R.; Palavesam, A. ; Immanuel, G, Solid-state production of esterase using fish processing wastes by Bacillus altitudinis AP-MSU. Food Bioprod. Process. 2012, 90, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaji, S.; Chaturvedi, P.; Begum, Z.; Pindi, P.K.; Manorama, R.; Padmanaban, D.A. . & Narlikar, J. V, Janibacter hoylei sp. nov.; Bacillus isronensis sp. nov. and Bacillus aryabhattai sp. nov.; isolated from cryotubes used for collecting air from the upper atmosphere. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 2977–2986. [Google Scholar]
- Elarabi, N.I.; Abdelhadi, A.A.; Ahmed, R.H.; Saleh, I.; Arif, I.A.; Osman, G.; Ahmed, D. S, Bacillus aryabhattai FACU: A promising bacterial strain capable of manipulate the glyphosate herbicide residues. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsadek, M.M.; Zhu, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; Lin, L. . & Zhang, D, Beneficial effects of indigenous Bacillus spp. on growth, antioxidants, immunity and disease resistance of Rhynchocypris lagowskii. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2023, 141, 109047. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, A. ; Ghosh, K, Characterization and identification of gut-associated phytase-producing bacteria in some fresh water fish cultured in ponds. Acta Ichthyol. Et Piscat. 2012, 42, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sella, S.R.; Vandenberghe, L.P.; Soccol, C. R, Bacillus atrophaeus: main characteristics and biotechnological applications–a review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2015, 35, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, H.S.; Broomall, S.M.; McNew, L.A.; Daligault, H.; Chapman, C.; Bruce, D. ;... & Skowronski, E. W, Genomic signatures of strain selection and enhancement in Bacillus atrophaeus var. globigii, a historical biowarfare simulant. PLoS ONE.
- Wu, W.J. ; Chang, J, Effect of oxygen on the germination and culturability of Bacillus atrophaeus spores. Int. Microbiol. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Askarian, F.; Zhou, Z.; Olsen, R.E.; Sperstad, S.; Ringø, E, Culturable autochthonous gut bacteria in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L. ) fed diets with or without chitin. Characterization by 16S rRNA gene sequencing, ability to produce enzymes and in vitro growth inhibition of four fish pathogens. Aquaculture 2012, 326, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, N.A.; Vos, P. D. ; Bacillus. Bergey's manual of systematics of archaea and bacteria 2015, 1-163.
- Priest, F. G, Aerobic Endospore-Forming. Bacillus 2013, 2, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, B.; Al-Zahrani, A.M. J, The effect of antimicrobial compounds on the gastrointestinal microflora of rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson. J. Fish Biol. 1988, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Sen, S.K.; Ray, A. K, Growth and survival of rohu, Labeo rohita (Hamilton) spawn fed diets supplemented with fish intestinal microflora. Acta Ichthyologica et piscatorial 2002, 1, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.K.; Bairagi, A.; Ghosh, K.S.; Sen, S. K, Optimization of fermentation conditions for cellulase production by Bacillus subtilis CY5 and Bacillus circulans TP3 isolated from fish gut. Acta Ichthyologica et Piscatoria 2007, 37, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Roy, R.N.; Sen, S.K.; Ray, A. K, Characterization of cellulase-producing bacteria from the digestive tract of tilapia, Oreochromis mossambica (Peters) and grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella (Valenciennes). Aquaculture Research 2006, 37, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, P.; Das Mohapatra, P. K, Effect of a probiotic bacterium Bacillus circulans PB7 in the formulated diets: on growth, nutritional quality and immunity of Catla catla (Ham. ). Fish physiology and biochemistry 2009, 35, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianiro, G.; Rizzatti, G.; Plomer, M.; Lopetuso, L.; Scaldaferri, F.; Franceschi, F. ; .. & Gasbarrini, A, Bacillus clausii for the treatment of acute diarrhea in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1074. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yang, H.L.; Xia, H.Q.; Ye, J.D.; Lu, K.L.; Hu, X. ; .. & Sun, Y.Z. Supplementation of heat-inactivated Bacillus clausii DE 5 in diets for grouper, Epinephelus coioides, improves feed utilization, intestinal and systemic immune responses and not growth performance. Aquaculture Nutrition 2018, 24, 821–831. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.D.; Wang, K.; Li, F.D.; Sun, Y.Z. Single or combined effects of fructo-and mannan oligosaccharide supplements and Bacillus clausii on the growth, feed utilization, body composition, digestive enzyme activity, innate immune response and lipid metabolism of the Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture nutrition 2011, 17, e902–e911. [Google Scholar]
- Jurenka, J.S. Bacillus coagulans. Alternative medicine review 2012, 17, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Breed, R.S.; Murray, E.G.D.; Smith, N.R. Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology. Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology; (7th Edition) (1957).
- Bhatnagar, A.; Raparia, S. ; Kumari, S, Influence of isolated Bacillus coagulans on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities of Catla catla. Journal of Nature Science and Sustainable Technology 2012, 6, 225. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J. Use of Bacillus coagulans as a Dietary Probiotic for the Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio. Journal of the World Aquaculture society 2014, 45, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obidi, O.F.; Soyinka, S.O.; Kamoru, T.A. Morphological, Biochemical and Molecular Characterisations of Bacteria Isolated from Water and Submerged Painted Boat Hulls in Badagry Lagoon, Lagos State, Nigeria. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management 2023, 27, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Dutta, D.; Ghosh, K. Evaluation of chitinolytic gut microbiota in some carps and optimization of culture conditions for chitinase production by the selected bacteria. The Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Food Sciences 2015, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Roy, M.; Kar, N.; RingØ, E. Gastrointestinal bacteria in rohu, Labeo rohita (Actinopterygii: Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae): scanning electron microscopy and bacteriological study. Acta Ichthyologica et Piscatoria 2010, 40, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Roy, T.; Ray, A.K. Characterization and identification of enzyme-producing bacteria isolated from the digestive tract of bata, Labeo bata. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society 2010, 41, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, G.; Ray, A.K.; Askarian, F.; Ringø, E. Characterisation and identification of enzyme-producing autochthonous bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract of two Indian air-breathing fish. Beneficial Microbes 2013, 4, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Mandal, S.; Khan, A.; Manna, S.K.; Ghosh, K. Distribution of extracellular enzyme-producing bacteria in the digestive tracts of 4 brackish water fish species. Turkish Journal of Zoology 2014, 38, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Banerjee, S.; Moon, U.M.; Khan, H.A.; Dutta, D. Evaluation of gut associated extracellular enzyme-producing and pathogen inhibitory microbial community as potential probiotics in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Int. J. Aquac. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán-Moreno, J.; García-Ortega, L.F.; Torres-Saucedo, L.; Rivas-Noriega, P.; Ramírez-Santoyo, R.M.; Sánchez-Calderón, L. ;... & Vidales-Rodríguez, L. E, Bacillus megaterium HgT21: A Promising Metal Multiresistant Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria for Soil Biorestoration. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022; 10. [Google Scholar]
- David, F.; Hebeisen, M.; Schade, G.; Franco-Lara, E.; Di Berardino, M. Viability and membrane potential analysis of Bacillus megaterium cells by impedance flow cytometry. Biotechnology and bioengineering 2012, 109, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.J.; Smullen, R.; Barnes, A. C, Dietary soybean protein concentrate-induced intestinal disorder in marine farmed Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar is associated with alterations in gut microbiota. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Yadav, A.N.; Saxena, R.; Rai, P.K.; Paul, D.; Tomar, R. S Novel, methanotrophic and methanogenic bacterial communities from diverse ecosystems and their impact on environment. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Carrias, A.; Williams, M.A.; Capps, N.; Dan, B.C.; Newton, J.C. ;... & Liles, M. R, Identification of Bacillus strains for biological control of catfish pathogens. 2012.
- Mukherjee, A.; Ghosh, K. Antagonism against fish pathogens by cellular components and verification of probiotic properties in autochthonous bacteria isolated from the gut of an I ndian major carp, Catla catla (Hamilton). Aquaculture Research 2016, 47, 2243–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Torrez, J.A.; Monroy-Dosta, M.D.C.; Hernández-Hernández, L.H.; Castro-Mejía, J.; Bustos-Martínez, J.A.; Hamdan-Partida, A. Presumptive probiotic isolated from Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1792), cultivated in Mexico. Int. J. Aquatic Sci. 2018, 9, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswaran, K.; Kempf, M.; Chen, F.; Satomi, M.; Nicholson, W. ; Kern, R, Bacillus nealsonii sp. nov.; isolated from a spacecraft-assembly facility, whose spores are γ-radiation resistant. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 2003, 53, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zammuto, V.; Fuchs, F.M.; Fiebrandt, M.; Stapelmann, K.; Ulrich, N.J.; Maugeri, T.L. ; .. & Moeller, R, Comparing spore resistance of Bacillus strains isolated from hydrothermal vents and spacecraft assembly facilities to environmental stressors and decontamination treatments. Astrobiology 2018, 18, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, S.; Ergün, S.; Yıgıt, M. Effects of dietary FARMARIN® XP supplement on immunological responses and disease resistance of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2018, 496, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Gong, L.; Liu, Y.; Lai, Q.; Li, G. ; Shao, Z, Bacillus pumilus group comparative genomics: toward pangenome features, diversity, and marine environmental adaptation. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 571212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrzyński, J.; Jakubowska, Z.; Dybek, B. Potential of Bacillus pumilus to directly promote plant growth. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1069053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, K.; Sen, S.K.; Ray, A.K. Characterization of Bacilli isolated from the gut of rohu, Labeo rohita, fingerlings and its significance in digestion. J. Appl. Aquac. 2002, 12, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Sun, Y.Z.; Hu, X.; Ye, J.D.; Lu, K.L.; Hu, L.H.; Zhang, J.J. Bacillus pumilus SE5 originated PG and LTA tuned the intestinal TLRs/MyD88 signaling and microbiota in grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hisnawi, A.; Ringø, E.; Davies, S.J.; Waines, P.; Bradley, G.; Merrifield, D.L. First report on the autochthonous gut microbiota of brown trout (S almo trutta Linnaeus). Aquac. Res. 2015, 46, 2962–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.Z.Z.V.; Zhou, Z.; Vecino, J.G.; Wadsworth, S.; Romero, J.; Krogdahl, Å. . & Merrifield, D.L. Effect of dietary components on the gut microbiota of aquatic animals. A never-ending story? Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 219–282. [Google Scholar]
- Fritze, D. Taxonomy of the genus Bacillus and related genera: the aerobic endospore-forming bacteria. Phytopathology 2004, 94, 1245–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adimpong, D.B.; Sørensen, K.I.; Nielsen, D.S.; Thorsen, L.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Derkx, P.M.; Jespersen, L. Draft whole-genome sequence of Bacillus sonorensis strain L12, a source of nonribosomal lipopeptides. Genome Announc. 2013, 1, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, D.; Ghosh, K. Screening of extracellular enzyme-producing and pathogen inhibitory gut bacteria as putative probiotics in mrigal, Cirrhinus mrigala (Hamilton, 1822). International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies 2015, 2, 310–318. [Google Scholar]
- EL-Mongy, M.; Hamouda, R.; Ali, S.; Sedeek, E.; Mahmoud, E. Antibacterial, antioxidant and anticancer of fermentation by Bacillus subtilis on bagasse and wheat bran. Curr. Chem. Lett. 2022, 11, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, S.; Carrias, A.A.; Williams, M.A.; Liles, M.R.; Terhune, J.S.; Davis, D.A. Effects of Bacillus subtilis strains on growth, immune parameters, and Streptococcus iniae susceptibility in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2017, 48, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Hamidoghli, A.; Choi, W.; Park, Y.; Jang, W.J.; Kong, I.S.; Bai, S.C. Effects of Bacillus subtilis WB60 and Lactococcus lactis on growth, immune responses, histology and gene expression in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Microorganisms v, 8(1).
- Romanova, E.; Spirina, E.; Romanov, V.; Lyubomirova, V.; Shadyeva, L. Effects of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis on catfish in industrial aquaculture. In E3S Web of Conferences. EDP Sci. 2020, 175, 02013. [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana, L.; Telli, G.S.; Dias, D.D.C.; Goncalves, G.S.; Guimaraes, M.C.; Ishikawa, C.M. . & Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T. Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis in diets for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Effects on growth performance, gut microbiota modulation and innate immunology. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, N.; Tao, Y.; Xu, L. . & Ringø, E. Effects of dietary 60 g kg− 1 dried distiller's grains in least-cost practical diets on production and gut allochthonous bacterial composition of cage-cultured fish: comparison among fish species with different natural food habits. Aquac. Nutr. 2013, 19, 765–772. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Ringø, E.; Du, Z.; Zhou, Z. Protein replacement in practical diets altered gut allochthonous bacteria of cultured cyprinid species with different food habits. Aquac. Int. 2015, 23, 913–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Ringø, E.; Ghosh, K. Extracellular tannase-producing bacteria detected in the digestive tracts of freshwater fishes (Actinopterygii: Cyprinidae and Cichlidae), 2016.
- Das, P.; Ghosh, K. Evaluation of phytase-producing ability by a fish gut bacterium, Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 13, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Ghosh, K. Improvement of nutritive value of sesame oil cake in formulated diets for rohu, Labeo rohita (Hamilton) after bio-processing through solid state fermentation by a phytase-producing fish gut bacterium. Int. J. Aquat. Biol. 2015, 3, 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, Z.; Krumholz, L.; Aktas, D.F.; Hasan, F.; Khattak, M.; Shah, A.A. Degradation of polyester polyurethane by a newly isolated soil bacterium, Bacillus subtilis strain MZA-75. Biodegradation 2013, 24, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, E.M.; Krawczyk, A.O.; Klaus, V.; de Jong, A.; Boekhorst, J.; Eijlander, R.T. . & Wells-Bennik, M.H. Bacillus thermoamylovorans spores with very-high-level heat resistance germinate poorly in rich medium despite the presence of ger clusters but efficiently upon exposure to calcium-dipicolinic acid. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7791–7801. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choonut, A.; Prasertsan, P.; Klomklao, S.; Sangkharak, K. Bacillus thermoamylovorans-related strain isolated from high temperature sites as potential producers of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate (mcl-PHA). Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 3044–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyman, A.; Huyben, D.; Lundh, T.; Dicksved, J. Effects of microbe-and mussel-based diets on the gut microbiota in Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus). Aquac. Rep. 2017, 5, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Griko, N.; Junker, M.; Bulla, L.A. Bacillus thuringiensis: a genomics and proteomics perspective. Bioeng. Bugs 2010, 1, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, S.B.; Cladera-Olivera, F.; Daroit, D.J.; Brandelli, A. Cellulase-producing Bacillus strains isolated from the intestine of Amazon basin fish. Aquac. Res. 2011, 42, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthi, S.; Ruckmani, A.; Pukall, R.; Chakrabarti, T. Psychrobacillus gen. nov. and proposal for reclassification of Bacillus insolitus Larkin & Stokes, 1967, B. psychrotolerans Abd-El Rahman et al.; 2002 and B. psychrodurans Abd-El Rahman et al.; 2002 as Psychrobacillus insolitus comb. nov.; Psychrobacillus Psychrotolerans Comb. Nov. Psychrobacillus Psychrodurans Comb. Nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 33, 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthi, S.; Chakrabarti, T.; Stackebrandt, E. Re-examination of the taxonomic position of Bacillus silvestris Rheims et al. 1999 and proposal to transfer it to Solibacillus gen. nov. as Solibacillus Silvestris Comb. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheims, H.; Frühling, A.; Schumann, P.; Rohde, M.; Stackebrandt, E. Bacillus silvestris sp. nov.; a new member of the genus Bacillus That Contain. Lysine Its Cell Wall. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1999, 49, 795–802. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.M.E.; Selim, D.A.; Basuony, H.A.; Sabic, E.M.; Saleh, A.A.; Ebeid, T.A. Effect of dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis spores on growth performance, oxidative status, and digestive enzyme activities in Japanese quail birds. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Chaklader, M.R.; Shukry, M.; Ahmed, H.A.; Khallaf, M.A. A multispecies probiotic modulates growth, digestive enzymes, immunity, hepatic antioxidant activity, and disease resistance of Pangasianodon hypophthalmus fingerlings. Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.N.; Banerjee, G. Recent studies on probiotics as beneficial mediator in aquaculture: a review. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2020, 81, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puvanasundram, P.; Chong, C.M.; Sabri, S.; Yusoff, M.S.; Karim, M. Multi-strain probiotics: Functions, effectiveness and formulations for aquaculture applications. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdkeattipol, K.; Chuchird, N.; Chonudomkul, D.; Yongmanitchai, W.; Pichitkul, P. Effect of partial replacement of fish meal by Bacillus sp-fermented soybean meal on growth performance, immunity, hepatopancreas microbiota and disease resistance in pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). J. Fish. Environ. 2021, 45, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar, F.; Neubauer, P.; Gimpel, M. Bioactive secondary metabolites from Bacillus subtilis: a comprehensive review. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2038–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, A.; Abunna, F. Maintenance of fish health in aquaculture: review of epidemiological approaches for prevention and control of infectious disease of fish. Veterinary medicine international 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, V.N.; Shane, A.L. Group B streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae). Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen-Ivey, C.R.; Figueras, M.J.; McGarey, D.; Liles, M.R. Virulence factors of Aeromonas hydrophila: in the wake of reclassification. Frontiers in microbiology 2016, 1337. [Google Scholar]
- Vivas, R.; Barbosa, A.A.T.; Dolabela, S.S.; Jain, S. Multidrug-resistant bacteria and alternative methods to control them: an overview. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 890–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, T.M.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Khusro, A.; Zidan, B.R.M.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B. . & Koirala, N. Antibiotic resistance in microbes: History, mechanisms, therapeutic strategies and future prospects. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1750–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, K.U.; Knirsch, C.; Anderson, A.S. The role of vaccines in preventing bacterial antimicrobial resistance. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A.; Singh, R. Probiotics in aquaculture: a promising emerging alternative approach. Symbiosis 2019, 77, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Yilmaz, E.; Dawood, M.A.; Ringø, E.; Ahmadifar, E.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics used to control vibriosis in fish: A review. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipe, H.; Temperton, B.; Lange, A.; Bass, D.; Tyler, C.R. Probiotics and competitive exclusion of pathogens in shrimp aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 324–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.T.; Casciaro, M.; Gangemi, S.; Buquicchio, R. Immunosenescence in aging: between immune cells depletion and cytokines up-regulation. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2017, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattaraj, S.; Ganguly, A.; Mandal, A.; Das Mohapatra, P.K. A review of the role of probiotics for the control of viral diseases in aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 2513–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Pan, L.; Gong, L.; Yang, Y.; He, H.; Li, Y. . & Xia, L. Interaction of a novel Bacillus velezensis (BvL03) against Aeromonas hydrophila in vitro and in vivo in grass carp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8987–8999. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iqtedar, M.; Aslam, M.; Akhyar, M.; Shehzaad, A.; Abdullah, R.; Kaleem, A. Extracellular biosynthesis, characterization, optimization of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using Bacillus mojavensis BTCB15 and its antimicrobial activity against multidrug resistant pathogens. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, S.; Diep, D.B.; Evensen, Ø.; Munang’andu, H.M. Garvicin KS, a Broad-Spectrum Bacteriocin Protects Zebrafish Larvae against Lactococcus garvieae Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, S.; Ergun, S.; Yigit, M.; Çelik, E.Ş. Effect of combination of dietary Bacillus subtilis and trans-cinnamic acid on innate immune responses and resistance of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss to Yersinia ruckeri. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, M.; Gao, F.; Lu, M.; Chen, G. Effects of dietary probiotic supplementation on the growth, gut health and disease resistance of juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Anim. Nutr. 2020, 6, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Tang, J.W.; Yao, X.H.; Wu, Y.F.; Wang, X.; Feng, J. Improvement of the Nutritional Quality of Cottonseed Meal by Bacillus subtilis and the Addition of Papain. International Journal of Agriculture & Biology 2012, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.X.; Feng, X.; Xie, L.L.; Peng, X.Y.; Yuan, J.; Chen, X.X. Effect of probiotic Bacillus subtilis Ch9 for grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella (Valenciennes, 1844), on growth performance, digestive enzyme activities and intestinal microflora. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2012, 28, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.H.; Rahimnejad, S.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, K.J. Evaluations of Bacillus spp. as dietary additives on growth performance, innate immunity and disease resistance of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) against Streptococcus iniae and as water additives. Aquaculture 2013, 402, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telli, G.S.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T.; de Carla Dias, D.; Sussel, F.R.; Ishikawa, C.M.; Tachibana, L. Dietary administration of Bacillus subtilis on hematology and non-specific immunity of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus raised at different stocking densities. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 39, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.M.; Ahmed, Y.A.G.; Ghareeb, A.A.A.; Mohamed, M.F. Studies on Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, as potential probiotics, on the immune response and resistance of Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus) to challenge infections. Fish & shellfish immunology.
- Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Guo, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Y. . & Zhou, Y. Dietary administration of Bacillus subtilis HAINUP40 enhances growth, digestive enzyme activities, innate immune responses and disease resistance of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 326–333. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Q.; Xu, H.; Mai, K.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Effects of dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis and fructooligosaccharide on growth performance, survival, non-specific immune response and disease resistance of juvenile large yellow croaker, Larimichthys crocea. Aquaculture, 2011; 317, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Reda, R.M.; Selim, K.M. Evaluation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens on the growth performance, intestinal morphology, hematology and body composition of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Int. 2015, 23, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobi, N.; Malaikozhundan, B.; Sekar, V.; Shanthi, S.; Vaseeharan, B.; Jayakumar, R.; Nazar, A.K. GFP tagged Vibrio parahaemolyticus Dahv2 infection and the protective effects of the probiotic Bacillus licheniformis Dahb1 on the growth, immune and antioxidant responses in Pangasius hypophthalmus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 52, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorian, T.J.; Jamali, H.; Farsani, H.G.; Darvishi, P.; Hasanpour, S.; Bagheri, T.; Roozbehfar, R. Effects of probiotic bacteria Bacillus on growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, and hematological parameters of Asian sea bass, Lates calcarifer (Bloch). Probiotics and antimicrobial proteins 2019, 11, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.Z.; Yang, H.L.; Ma, R.L.; Lin, W.Y. Probiotic applications of two dominant gut Bacillus strains with antagonistic activity improved the growth performance and immune responses of grouper Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.F.A.; Petrillo, T.R.; Yunis-Aguinaga, J.; Marcusso, P.F.; Claudiano, G.D.S.; Moraes, F.R.D.; Moraes, J.R. Efectos del probiótico Bacillus amyloliquefaciens en el crecimiento, hematología y morfometría intestinal en tilapias del Nilo criadas en balsa jaula. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2015, 43, 963–971. [Google Scholar]
- Sahandi, J.; Jafarian, H.; Roozbehfar, R.; Babaei, S.; Dehestani, M. The use of two enrichment forms (Brachionus plicatilis enrichment and rearing water enrichment) with probiotic bacilli spore on growth and survival of Silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix), 2012.
- Wang, Y.; Chi, L.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, D.; Xiao, Z. . & Li, J. Effects of stocking density on the growth and immunity of Atlantic salmon salmo salar reared in recirculating aquaculture system (RAS). J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 350–360. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, A.K.; Sahu, N.P.; Saharan, N.; Dash, G. Effect of dietary supplementation of chromium on growth and biochemical parameters of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) fingerlings. Indian J. Fish. 2014, 61, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Van Doan, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Khanongnuch, C.; Kanpiengjai, A.; Unban, K.; Srichaiyo, S. Host-associated probiotics boosted mucosal and serum immunity, disease resistance and growth performance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2018, 491, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Li, W. Effect of dietary probiotic, Bacillus coagulans, on growth performance, chemical composition, and meat quality of Guangxi Yellow chicken. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, G.; Adorian, T.J.; Rafiee, G. Beneficial effects of Bacillus subtilis on water quality, growth, immune responses, endotoxemia and protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced damages in Oreochromis niloticus under biofloc technology system. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1476–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarike, E.D.; Cai, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, L.; Jian, J. . & Kuebutornye, F.K. Effects of a commercial probiotic BS containing Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis on growth, immune response and disease resistance in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thy, H.T.T.; Tri, N.N.; Quy, O.M.; Fotedar, R.; Kannika, K.; Unajak, S.; Areechon, N. Effects of the dietary supplementation of mixed probiotic spores of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 54A, and Bacillus pumilus 47B on growth, innate immunity and stress responses of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 391–399. [Google Scholar]
- Azarin, H.; Aramli, M.S.; Imanpour, M.R.; Rajabpour, M. Effect of a probiotic containing Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis and ferroin solution on growth performance, body composition and haematological parameters in Kutum (Rutilus frisii kutum) fry. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2015, 7, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.S.; Mohammady, E.Y.; Soaudy, M.R.; Elashry, M.A.; Moustafa, M.M.; Wassel, M.A. . & Elsaied, H.E. Synergistic effects of Bacillus pumilus and exogenous protease on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) growth, gut microbes, immune response and gene expression fed plant protein diet. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 275, 114892. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.N.; Li, X.F.; Xu, W.N.; Zhang, D.D.; Lu, K.L.; Wang, L.N. . & Liu, W.B. Combined effects of dietary fructooligosaccharide and Bacillus licheniformis on growth performance, body composition, intestinal enzymes activities and gut histology of triangular bream (Megalobrama terminalis). Aquac. Nutr. 2015, 21, 755–766. [Google Scholar]
- Kunjiappan, S.; Bhattacharjee, C.; Chowdhury, R. In vitro antioxidant and hepatoprotective potential of Azolla microphylla phytochemically synthesized gold nanoparticles on acetaminophen–induced hepatocyte damage in Cyprinus carpio L. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. -Anim. 2015, 51, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi-Arpanahi, D.; Soltani, E.; Jafaryan, H.; Soltani, M.; Naderi-Samani, M.; Campa-Córdova, A.I. Efficacy of two commercial and indigenous probiotics, Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis on growth performance, immuno-physiology and resistance response of juvenile white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2018, 496, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, D.; Vahdatpour, T.; Nikpiran, H.; Jafargholipour, M.A.; Vahdatpour, S. Effects of probiotic, prebiotic and synbiotic intake on blood enzymes and performance of Japanese quails (Coturnix japonica). Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 81, 870. [Google Scholar]
- Chimela, W.; Mesua, N.; Abdulraheem, B.A. Aspartate transaminase (AST) activity in selected tissues & organs of Clarias Gariepinus exposed to different levels of paraquat. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2014, 4, 2161–0525. [Google Scholar]
- Hassaan, M.S.; Soltan, M.A.; Jarmołowicz, S.; Abdo, H.S. Combined effects of dietary malic acid and B acillus subtilis on growth, gut microbiota and blood parameters of N ile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutthi, N.; Thaimuangphol, W.; Rodmongkoldee, M.; Leelapatra, W.; Panase, P. Growth performances, survival rate, and biochemical parameters of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) reared in water treated with probiotic. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 27, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, A.; Banerjee, G.; Dan, S.K.; Ghosh, K.; Ray, A.K. Evaluation of in vivo probiotic efficiency of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens in Labeo rohita challenged by pathogenic strain of Aeromonas hydrophila MTCC 1739. Probiotics and antimicrobial proteins 2018, 10, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Benedito-Palos, L.; Estensoro, I.; Petropoulos, Y.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Browdy, C.L.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Effects of dietary NEXT ENHANCE® 150 on growth performance and expression of immune and intestinal integrity related genes in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L. ). Fish & shellfish immunology 2015, 44, 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.; Tang, J.; Cai, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Abarike, E.D. . & Afriyie, G. In vivo assessment of the probiotic potentials of three host-associated Bacillus species on growth performance, health status and disease resistance of Oreochromis niloticus against Streptococcus agalactiae. Aquaculture 2020, 527, 735440. [Google Scholar]
- Ghalwash, H.R.; Salah, A.S.; El-Nokrashy, A.M.; Abozeid, A.M.; Zaki, V.H.; Mohamed, R.A. Dietary supplementation with Bacillus species improves growth, intestinal histomorphology, innate immunity, antioxidative status and expression of growth and appetite-regulating genes of Nile tilapia fingerlings. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 1378–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, M.A.; Gioacchini, G.; Decamp, O.; Makridis, P.; Bracciatelli, C.; Carnevali, O. Application of multi-species of Bacillus in sea bream larviculture. Aquaculture 2010, 305, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Midhun, S.J.; Neethu, S.; Arun, D.; Vysakh, A.; Divya, L.; Radhakrishnan, E.K.; Jyothis, M. Dietary supplementation of Bacillus licheniformis HGA8B improves growth parameters, enzymatic profile and gene expression of Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 2019, 505, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos-Vidal, E.; Sanz-Milián, B.; Teles, M.; Reyes-Cerpa, S.; Mancera, J.M.; Tort, L.; Reyes-Lopez, F.E. The gene expression profile of the glucocorticoid receptor 1 (gr1) but not gr2 is modulated in mucosal tissues of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) exposed to acute air-exposure stress. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 977719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Liu, H.; Yu, L.; Zha, J.; Wang, G. Probiotic potential of Bacillus velezensis JW: antimicrobial activity against fish pathogenic bacteria and immune enhancement effects on Carassius auratus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 78, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.Z.; Xia, H.Q.; Yang, H.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Zou, W.C. TLR2 signaling may play a key role in the probiotic modulation of intestinal microbiota in grouper Epinephelus coioides. Aquaculture 2014, 430, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zokaeifar, H.; Balcázar, J.L.; Saad, C.R.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Sijam, K.; Arshad, A.; Nejat, N. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on the growth performance, digestive enzymes, immune gene expression and disease resistance of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keysami, M.A.; Mohammadpour, M.; Saad, C.R. Probiotic activity of Bacillus subtilis in juvenile freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man) at different methods of administration to the feed. Aquac. Int. 2012, 20, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NavinChandran, M.; Iyapparaj, P.; Moovendhan, S.; Ramasubburayan, R.; Prakash, S.; Immanuel, G.; Palavesam, A. Influence of probiotic bacterium Bacillus cereus isolated from the gut of wild shrimp Penaeus monodon in turn as a potent growth promoter and immune enhancer in P. monodon. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, P.C.; Song, X.L.; Chen, G.F.; Xu, H.; Huang, J. Dietary supplementation of probiotic Bacillus PC465 isolated from the gut of Fenneropenaeus chinensis improves the health status and resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei against white spot syndrome virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laranja, J. Amorphous poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB)-accumulating Bacillus spp. as biocontrol agents in crustacean culture (Doctoral dissertation, Ghent University), 2017.
- Adilah, R.N.; Chiu, S.T.; Hu, S.Y.; Ballantyne, R.; Happy, N.; Cheng, A.C.; Liu, C.H. Improvement in the probiotic efficacy of Bacillus subtilis E20-stimulates growth and health status of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei via encapsulation in alginate and coated with chitosan. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 125, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Tan, B.; Lao, Y.; Duan, Z.; Sun, W.; Dong, X. Isolation of a putative probiotic strain S12 and its effect on growth performance, non-specific immunity and disease-resistance of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Son, M.A.; Elshopakey, G.E.; Rezk, S.; Eldessouki, E.A.; Elbahnaswy, S. Dietary mixed Bacillus strains promoted the growth indices, enzymatic profile, intestinal immunity, and liver and intestinal histomorphology of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 27, 101385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.S.; Soltan, M.A.; Ghonemy, M.M.R. Effect of synbiotics between Bacillus licheniformis and yeast extract on growth, hematological and biochemical indices of the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C De, B.; Meena, D.K.; Behera, B.K.; Das, P.; Das Mohapatra, P.K.; Sharma, A.P. Probiotics in fish and shellfish culture: immunomodulatory and ecophysiological responses. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 40, 921–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullian, M.; Thompson, F.; Rodriguez, J. Selection of probiotic bacteria and study of their immunostimulatory effect in Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2004, 233, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.; Espinosa, Y.; Echeverría, F.; Cárdenas, G.; Román, R.; Stern, S. Exposure to probiotics and β-1, 3/1, 6-glucans in larviculture modifies the immune response of Penaeus vannamei juveniles and both the survival to White Spot Syndrome Virus challenge and pond culture. Aquaculture 2007, 273, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcázar, J.L.; Rojas-Luna, T.; Cunningham, D.P. Effect of the addition of four potential probiotic strains on the survival of pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) following immersion challenge with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2007, 96, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, A.T.; Maita, M.; Futami, K.; Endo, M.; Katagiri, T. Effects of a probiotic bacterial Lactobacillus rhamnosus dietary supplement on the crowding stress response of juvenile Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Fish. Sci. 2011, 77, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezuela, R.; Fumanal, M.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; Meseguer, J.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; Esteban, M.Á. Changes in intestinal morphology and microbiota caused by dietary administration of inulin and Bacillus subtilis in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) specimens. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, D.K.; Das, P.; Kumar, S.; Mandal, S.C.; Prusty, A.K.; Singh, S.K. . & Mukherjee, S.C. Beta-glucan: an ideal immunostimulant in aquaculture (a review). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 39, 431–457. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Sun, Y.Z.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Z. Probiotics as means of diseases control in aquaculture, a review of current knowledge and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K. Functionality of probiotics on the resistance capacity of shrimp against white spot syndrome virus (WSSV). 2023, Fish & shellfish immunology 2023, 108942. [Google Scholar]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Swelum, A.A.; Ghanima, M.M.A.; Shukry, M.; Omar, A.A.; Taha, A.E. . & Abd El-Hack, M.E. Shrimp production, the most important diseases that threaten it, and the role of probiotics in confronting these diseases: a review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 144, 126–140. [Google Scholar]
- Rengpipat, S.; Phianphak, W.; Piyatiratitivorakul, S.; Menasveta, P. Effects of a probiotic bacterium on black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon survival and growth. Aquaculture 1998, 167, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewcharoen, W.; Srisapoome, P. Probiotic effects of Bacillus spp. from Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) on water quality and shrimp growth, immune responses, and resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus (AHPND strains). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, D.Y.; Ho, P.L.; Huang, S.Y.; Cheng, S.C.; Shiu, Y.L.; Chiu, C.S.; Liu, C.H. Enhancement of immunity and disease resistance in the white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, by the probiotic, Bacillus subtilis E20. Fish & shellfish immunology 2009, 26, 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Tan, B.; Mai, K. Dietary probiotic Bacillus OJ and isomaltooligosaccharides influence the intestine microbial populations, immune responses and resistance to white spot syndrome virus in shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2009, 291, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.J.; Liu, K.F.; Cheng, S.H.; Chang, C.I.; Lay, J.J.; Hsu, Y.O. . & Chen, T.I. Selection of probiotic bacteria for use in shrimp larviculture. Aquac. Res. 2009, 40, 609–618. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.Y.; Fu, L.L.; Li, W.F.; Zhu, Y.R. Effect of dietary supplementation with Bacillus subtilis on the growth, performance, immune response and antioxidant activities of the shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Khalil, R.H.; Nour, A.M.; Elkhayat, B.K.; Khalifa, E.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. Effects of Bacillus subtilis-fermented rice bran on water quality, performance, antioxidants/oxidants, and immunity biomarkers of White leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) reared at different salinities with zero water exchange. J. Appl. Aquac. 2022, 34, 332–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Hamidoghli, A.; Choi, W.; Bae, J.; Jang, W.J.; Lee, S.; Bai, S.C. Evaluation of potential probiotics Bacillus subtilis WB60, Pediococcus pentosaceus, and Lactococcus lactis on growth performance, immune response, gut histology and immune-related genes in whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepaamorndech, S.; Chantarasakha, K.; Kingcha, Y.; Chaiyapechara, S.; Phromson, M.; Sriariyanun, M. . & Visessanguan, W. Effects of Bacillus aryabhattai TBRC8450 on vibriosis resistance and immune enhancement in Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 86, 4–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.F.; Chiu, C.H.; Shiu, Y.L.; Cheng, W.; Liu, C.H. Effects of the probiotic, Bacillus subtilis E20, on the survival, development, stress tolerance, and immune status of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei larvae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmos, J.; Acosta, M.; Mendoza, G.; Pitones, V. Bacillus subtilis, an ideal probiotic bacterium to shrimp and fish aquaculture that increase feed digestibility, prevent microbial diseases, and avoid water pollution. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Hong-biao, Yong-quan Su, Yong Mao, Xin-xin You, Shao-xiong Ding, and Jun Wang. "Dietary supplementation with Bacillus can improve the growth and survival of the kuruma shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicus in high-temperature environments." Aquaculture international 2014, 22, 607–617.
- Zokaeifar, H.; Babaei, N.; Saad, C.R.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Sijam, K.; Balcazar, J.L. Administration of Bacillus subtilis strains in the rearing water enhances the water quality, growth performance, immune response, and resistance against Vibrio harveyi infection in juvenile white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat Hoseini Madani, N.; Adorian, T.J.; Ghafari Farsani, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H. The effects of dietary probiotic Bacilli (Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis) on growth performance, feed efficiency, body composition and immune parameters of whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) postlarvae. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1926–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimrat, S.; Khaopong, W.; Sangsong, J.; Boonthai, T.; Vuthiphandchai, V. Improvement of growth performance, water quality and disease resistance against Vibrio harveyi of postlarval whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) by administration of mixed microencapsulated Bacillus probiotics. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suguna, P.; Binuramesh, C.; Abirami, P.; Saranya, V.; Poornima, K.; Rajeswari, V.; Shenbagarathai, R. Immunostimulation by poly-β hydroxybutyrate–hydroxyvalerate (PHB–HV) from Bacillus thuringiensis in Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.A.; Bakhiet, E.K.; Ali, S.G.; Hussien, H.R. Production and characterization of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) produced by Bacillus sp. isolated from Egypt. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 6, 046–051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranja, J.L.Q.; Ludevese-Pascual, G.L.; Amar, E.C.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P.; De Schryver, P. Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) accumulating Bacillus spp. improve the survival, growth and robustness of Penaeus monodon () postlarvae. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 173, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yuan, W.; Wang, S.; Guo, W.; Li, A.; Wu, Y. . & Zhou, Y. In vitro screening of putative probiotics and their dual beneficial effects: to white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) postlarvae and to the rearing water. Aquaculture 2019, 498, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Monier, M.N.; Kabary, H.; Elfeky, A.; Saadony, S.; El-Hamed, N.N.A.; Eissa, M.E.; Eissa, E.S.H. The effects of Bacillus species probiotics (Bacillus subtilis and B. licheniformis) on the water quality, immune responses, and resistance of whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) against Fusarium solani infection. Aquaculture International 2023, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Dawood, M.A.; Koshio, S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Van Doan, H. Probiotic application for sustainable aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.J.; Liu, Q.Q.; Liao, S.; Fang, H.H.; Yin, P.; Xie, S.W. . & Niu, J. Effects of dietary mixed probiotics on growth, non-specific immunity, intestinal morphology and microbiota of juvenile pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 90, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Lamba, R. Antimicrobial ability and growth promoting effects of feed supplemented with probiotic bacterium isolated from gut microflora of Cirrhinus mrigala. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraja, T.; Banerjee, S.; Yusoff, F.; Shariff, M.; Khatoon, H. A holistic approach for selection of Bacillus spp. as a bioremediator for shrimp postlarvae culture. Turk. J. Biol. 2013, 37, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimrat, S.; Suksawat, S.; Boonthai, T.; Vuthiphandchai, V. Potential Bacillus probiotics enhance bacterial numbers, water quality and growth during early development of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 159, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachruddin, M.; Sholichah, M.; Istiqomah, S.; Supriyanto, A. Effect of probiotic culture water on growth, mortality, and feed conversion ratio of Vaname shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei Boone). In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: 2018; Vol. 137, p. 0120. [Google Scholar]
- Kongnum, K.; Hongpattarakere, T. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum isolated from digestive tract of wild shrimp on growth and survival of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) challenged with Vibrio harveyi. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamilarasu, A.; Ahilan, B.; Gopalakannan, A.; Somu Sunder Lingam, R. Evaluation of probiotic potential of Bacillus strains on growth performance and physiological responses in Penaeus vannamei. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 3124–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynar, P.; Beyatli, Y. Determination of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate production by Bacillus spp. isolated from the intestines of various fishes. Fish. Sci. 2009, 75, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, K.; Liu, J.Y.; Ling, F.; Liu, X.L.; Lu, L.; Xia, L.; Wang, G.X. Effects of dietary administration of Shewanella haliotis D4, Bacillus cereus D7 and Aeromonas bivalvium D15, single or combined, on the growth, innate immunity and disease resistance of shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2014, 428, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Han, Y.; Wu, F.; Liu, Y. Effects of a probiotic (Bacillus licheniformis) on the growth, immunity, and disease resistance of Haliotis discus hannai Ino. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 76, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaolong, Gao, Ke Caihuan, Zhang Mo, Li Xian, Wu Fucun, and Liu Ying. "Effects of the probiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens on the growth, immunity, and disease resistance of Haliotis discus hannai." Fish & shellfish immunology 2019, 94, 617–627.
- Sánchez-Ortiz, A.C.; Angulo, C.; Luna-González, A.; Álvarez-Ruiz, P.; Mazón-Suástegui, J.M.; Campa-Córdova, Á.I. Effect of mixed-Bacillus spp isolated from pustulose ark Anadara tuberculosa on growth, survival, viral prevalence and immune-related gene expression in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 59, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaolong, G.; Caihuan, K.; Fucun, W.; Xian, L.; Ying, L. Effects of Bacillus lincheniformis feeding frequency on the growth, digestion and immunity of Haliotis discus hannai. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 96, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhu, J.; Hu, J.; Dong, X.; Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Miao, S. Effects of dietary Bacillus pumilus on growth performance, innate immunity and digestive enzymes of giant freshwater prawns (Macrobrachium rosenbergii). Aquac. Nutr. 2019, 25, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmin, G.; Kathiresan, K.; Purushothaman, A. Effect of probiotics on bacterial population and health status of shrimp in culture pond ecosystem, 2001.
- Matias, H.B.; Yusoff, F.M.; Shariff, M.; Azhar, O. Effects of commercial microbial products on water quality in tropical shrimp culture ponds. Asian Fish. Sci. 2002, 15, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Xu, Z.R.; Xia, M.S. The effectiveness of commercial probiotics in northern white shrimp Penaeus vannamei ponds. Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.V.; Reddy, A.V.K.; Babu, B.S.; Lakshmi, T.V. Applications of Bacillus sp in aquaculture waste water treatment. Int JS Res Sci. Tech 2018, 4, 1806–1812. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Xiaojuan, Yu Xu, Haochang Su, Wujie Xu, Guoliang Wen, Chuangwen Xu, Keng Yang, Song Zhang, and Yucheng Cao. "Effect of a Bacillus Probiotic Compound on Penaeus vannamei Survival, Water Quality, and Microbial Communities." Fishes 2023, 8, 362.
- Phung, L.T.; Phung, N.K.; Phuong, T.T.M.; Nicolas, M.; Vincent, M.; Sandra, A.; Philippe, D.S.J. Effect of Bacillus sp. as probiotic on the treatment of environment in brackish water shrimp aquaculture. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: 2020; Volume 991, p. 012052.
- Decamp, O.; Moriarty, D.J.; Lavens, P. Probiotics for shrimp larviculture: review of field data from Asia and Latin America. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujeeb Rahiman, K.M.; Jesmi, Y.; Thomas, A.P.; Mohamed Hatha, A.A. Probiotic effect of Bacillus NL110 and Vibrio NE17 on the survival, growth performance and immune response of Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man). Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, e120–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva-Maia, E.; Alves-Modesto, G.; Otavio-Brito, L.; Vasconcelos-Gesteira, T.C.; Olivera, A. Effect of a commercial probiotic on bacterial and phytoplankton concentration in intensive shrimp farming (Litopenaeus vannamei) recirculation systems. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2013, 41, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.X.; Zhao, S.M.; Peng, N.; Xu, C.P.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.X. Effects of a probiotic (B acillus subtilis FY99-01) on the bacterial community structure and composition of shrimp (L itopenaeus vannamei, B oone) culture water assessed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and high-throughput sequencing. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, H.G.; Thuy, B.T.P.; Lin, C.; Vo, D.V.N.; Tran, H.T.; Bahari, M.B.; Vu, C.T. The nitrogen cycle and mitigation strategies for nitrogen loss during organic waste composting: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilya, D.; Devi, W.M. Bacillus probiotics and bioremediation: an aquaculture perspective. In Bacilli in Agrobiotechnology: Plant Stress Tolerance, Bioremediation, and Bioprospecting; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sineva, E.V.; Andreeva-Kovalevskaya, Z.I.; Shadrin, A.M.; Gerasimov, Y.L.; Ternovsky, V.I.; Teplova, V.V. . & Solonin, A.S. Expression of Bacillus cereus hemolysin II in Bacillus subtilis renders the bacteria pathogenic for the crustacean Daphnia magna. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 299, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Velmurugan, S.; Palanikumar, P.; Velayuthani, P.; Donio, M.B.S.; Babu, M.M.; Lelin, C. . & Citarasu, T. Bacterial white patch disease caused by Bacillus cereus, a new emerging disease in semi-intensive culture of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2015, 444, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Hendriksen, N.B.; Hansen, B.M.; Johansen, J.E. Occurrence and pathogenic potential of Bacillus cereus group bacteria in a sandy loam. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2006, 89, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreeva, Z.I.; Nesterenko, V.F.; Fomkina, M.G.; Ternovsky, V.I.; Suzina, N.E.; Bakulina, A.Y. . & Sineva, E.V. The properties of Bacillus cereus hemolysin II pores depend on environmental conditions. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 253–263. [Google Scholar]
- Elshaghabee, F.M.; Rokana, N.; Gulhane, R.D.; Sharma, C.; Panwar, H. Bacillus as potential probiotics: status, concerns, and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Forssten, S.; Hibberd, A.A.; Lyra, A.; Stahl, B. Probiotic approach to prevent antibiotic resistance. Ann. Med. 2016, 48, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogoju, S.; Nahashon, S. Recent advances in probiotic application in animal health and nutrition: A review. Agriculture 2022, 12, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anokyewaa, M.A.; Amoah, K.; Li, Y.; Lu, Y.; Kuebutornye, F.K.; Asiedu, B.; Seidu, I. Prevalence of virulence genes and antibiotic susceptibility of Bacillus used in commercial aquaculture probiotics in China. Aquaculture Reports 2021, 21, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, A.L.; Boyte, M.E.; Elkins, C.A.; Goldman, V.S.; Heimbach, J.; Madden, E. ;... & Smith, A. Considerations for determining safety of probiotics: A USP perspective. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 2022, 105266. [Google Scholar]
- Doan, H.V.; Soltani, E.; Ingelbrecht, J.; Soltani, M. Medicinal herbs and plants: Potential treatment of monogenean infections in fish. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 260–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anadón, A.; Ares, I.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Martínez, M.A. Probiotics: safety and toxicity considerations. In Nutraceuticals; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 1081–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, S.A.; Schoeni, J.L.; Vegge, C.; Pane, M.; Stahl, B.; Bradley, M. ;... & Sanders, M.E. Improving end-user trust in the quality of commercial probiotic products. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 739. [Google Scholar]
- James, G.; Das, B.C.; Jose, S.; VJ, R.K. Bacillus as an aquaculture friendly microbe. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 323–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathipa, M.G.; Thantsha, M.S. Probiotic engineering: towards development of robust probiotic strains with enhanced functional properties and for targeted control of enteric pathogens. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Bacillus probiotic for Finfishes aquaculture | ||
|---|---|---|
| Brand | Manufacturer | Comments |
| Naturalle Bacillus subtilis | Wuhan Nature´s Favour Bioengineering Co.; Ltd, Wuhan City, China http://www.wuhannature.com | Bacillus subtilis (2x1010 CFU/g). |
| Biozyme | Bio-Pharmachemie Joint-Venture Company, Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam http://www.biopharmachemie.com | Bacillus subtilis and Saccaromyces cerevisiae. |
| Fubon B. subtilis | Angel Yeast Co.; Ltd. Hubei, China http://www.angelyeast.com | Bacillus subtilis (≥ 20 billion CFU/g). |
| Bioron | American Pharma International, India http://www.americanpharmainternational.com | Each kg contains: B. subtilis (4.5x108 CFU), B. licheniformis, B. megaterium, Lactobacillus lactis, L. helveticus, Nitrosomonas sp. Nitrobacter sp. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Aspergillus oryzae. |
| Lactomin | American Pharma International, India http://www.americanpharmainternational.com | Each kg contains: B. subtilis (45,000 million CFU), B. licheniformis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, L. sporogenes and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
| Bacillus probiotic for shellfishes aquaculture | ||
| Brand | Composition | Dose |
| Aqua photo | Bacillus subtilis and Rhodopseudomonas | 50–70 ml/100 dec. Control unwanted gas, sediment and increase growth of plankton |
| Bio-zyme | Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 500 g/100 kg feed |
| Eco marine | Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus pumilis, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus megaterium | 3–4 tablet/acre |
| Golden Bac | Yeast,Bacillus subtilis, Lactobacillus sp. | 1.5–2 kg/acre |
| pH fixer | Bacillus sp. | 1–2 kg/acre |
| Procon-PS | Bacillus sp. Rhodococcus, and Rhodobacter | 5 L/hac (l m depth) |
| Super Biotic | Bacillus sp. | 1–2 kg/acre |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





