Submitted:
01 September 2023
Posted:
04 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
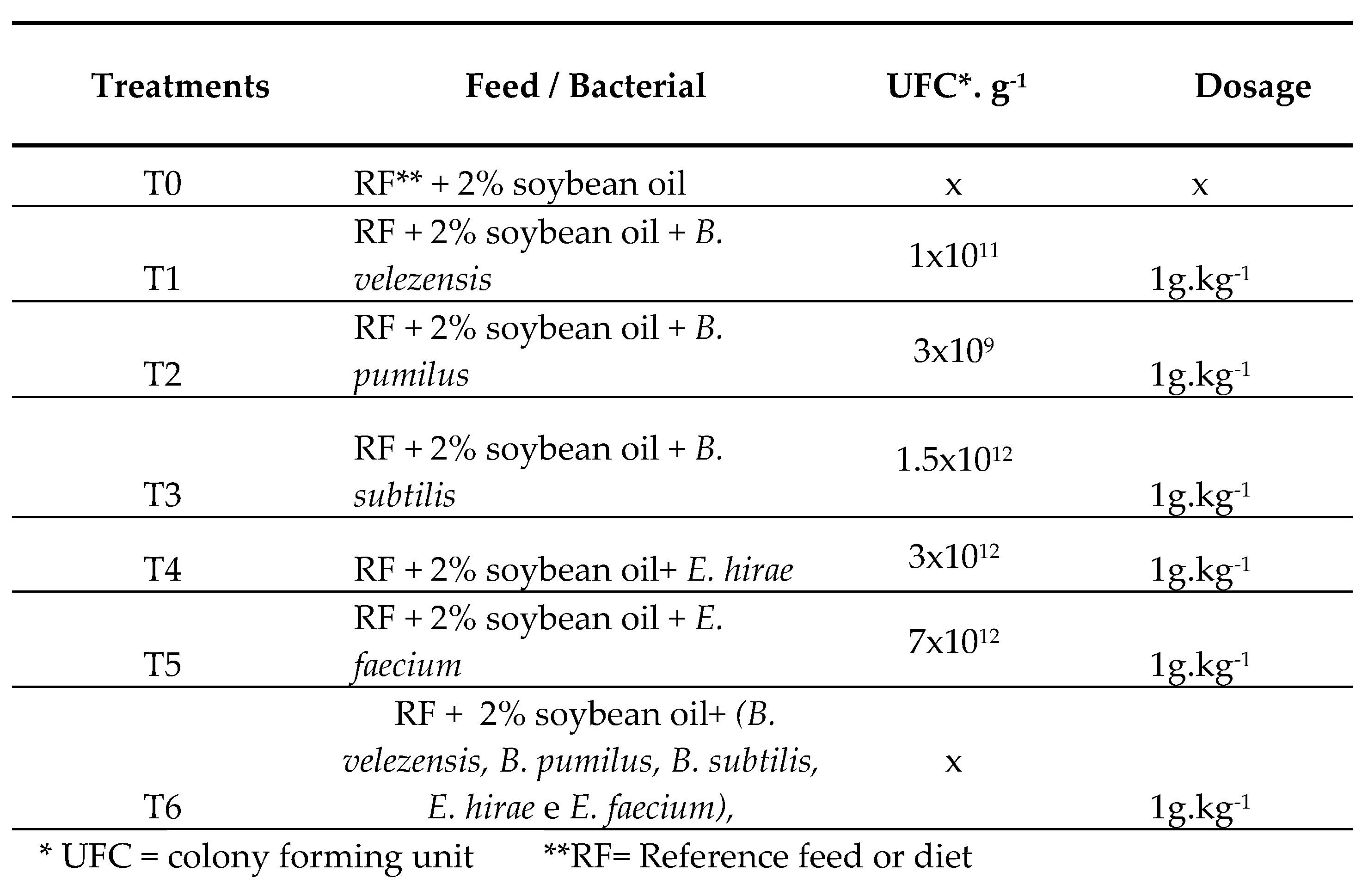
2.2. Potential probiotic bacteria identification
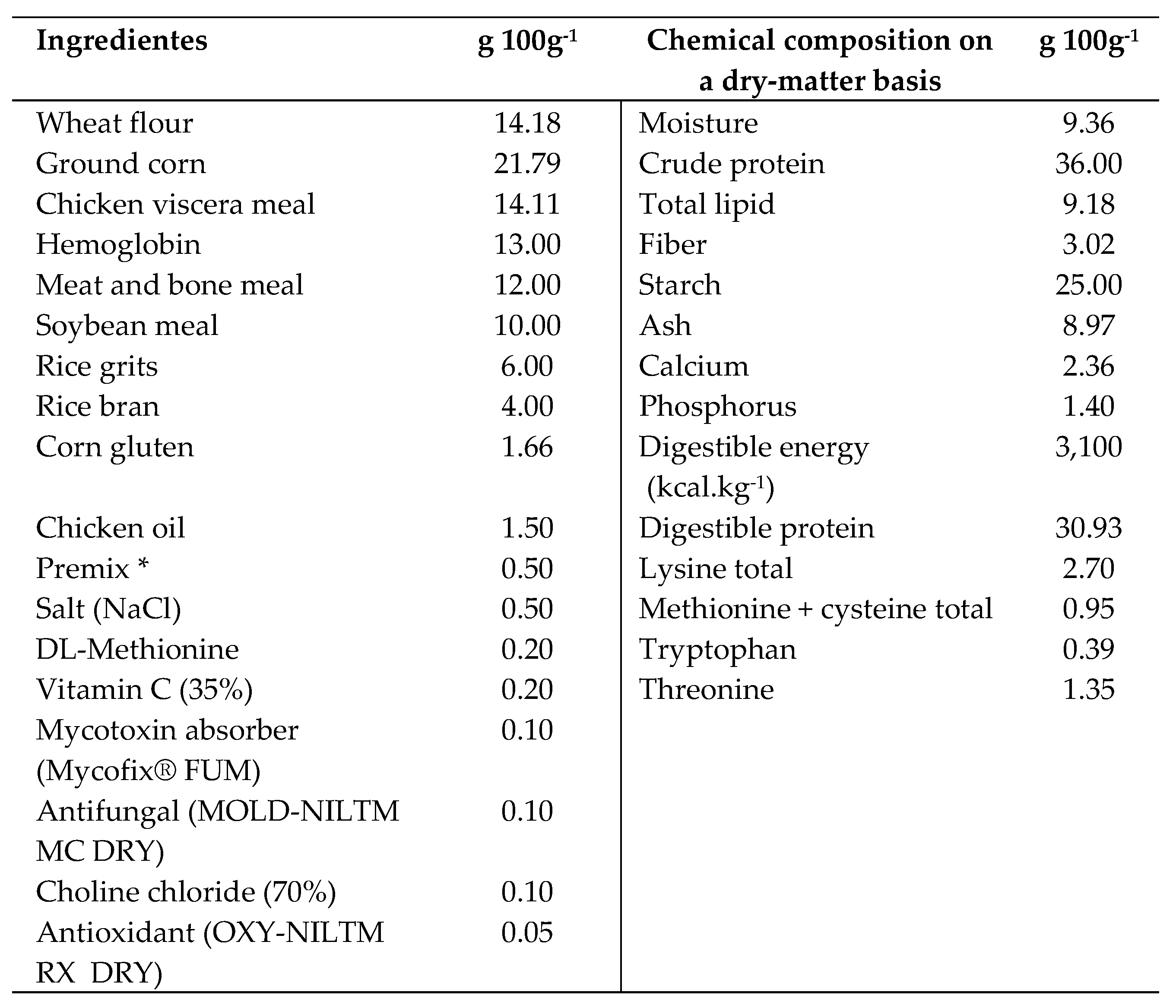
2.3. Experimental Diets
2.4. Experimental Design and Fish
2.5. Zootechnical performance
2.6. Microbiology and Denaturant gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE).
2.7. Hematological analyses
2.8. Lysozyme activity
2.9. Phagocyte respiratory burst activity
2.10. Lactate test
2.11. Bromatological analysis
2.11. Data analysis
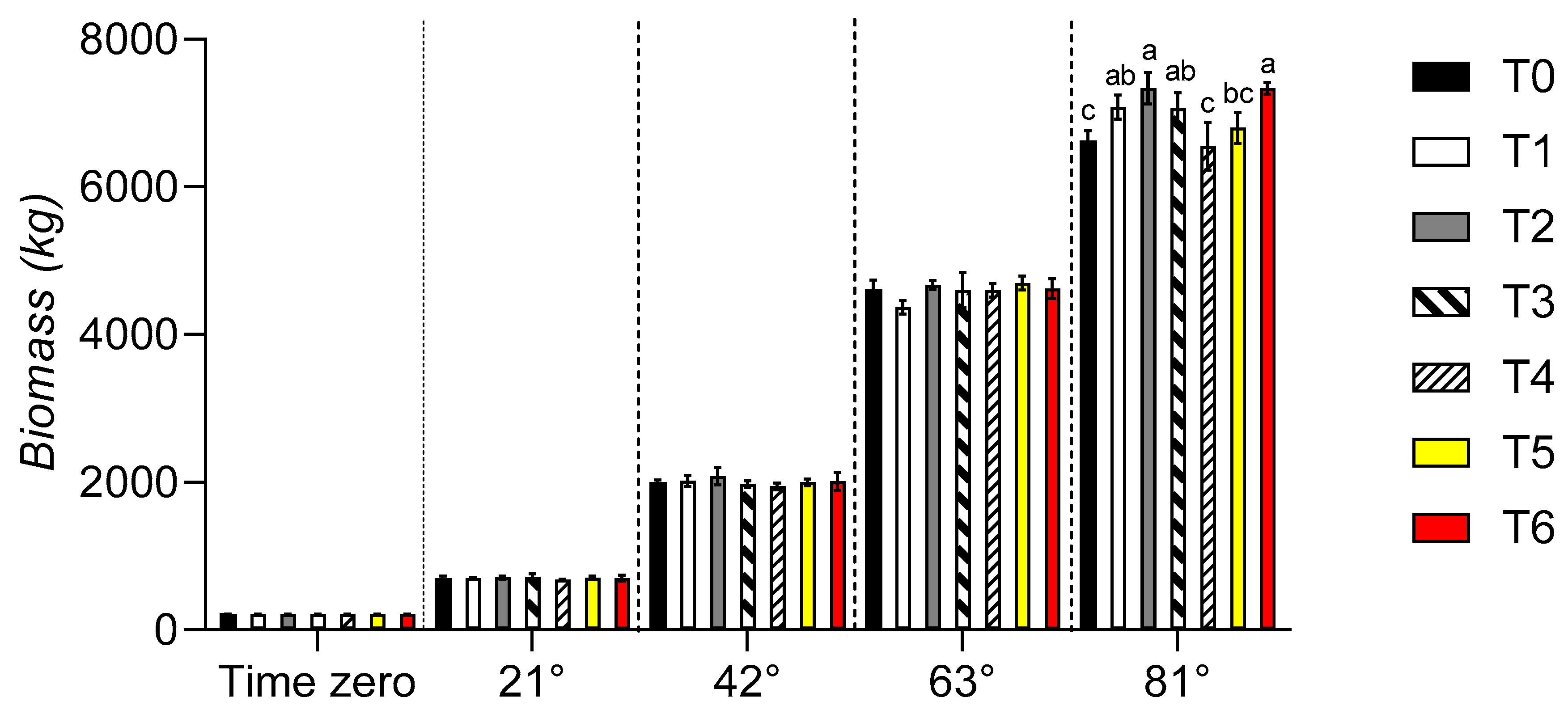
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial identification
3.2. Water quality
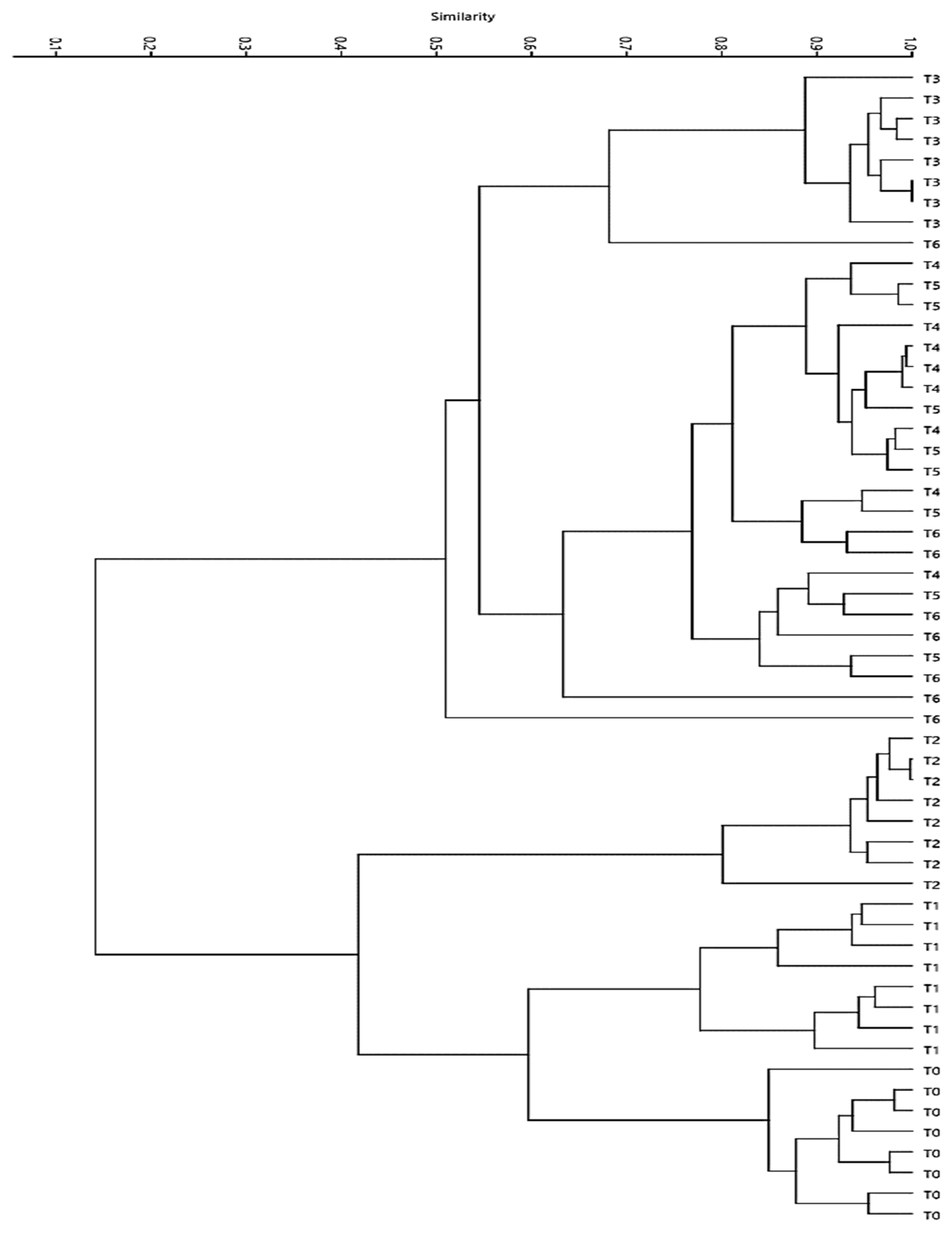
3.3. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE)
3.4. Hemogram, glycemy, lactate, lysozyme, respiratory burst
3.5. Bromatological analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 1. PeixeBR. Anuário 2023, /: Brazilian Association of Fish Culture - yearbook. Brazil, 2023; pp. 14. https, 2023.
- Watanabe, W.O. , Losordo, T. M., Fitzsimmons, K., Hanley, F. Tilapia production systems in the Americas: technological advances, trends, and challenges. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2002, 10, 465–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. , Lu, M. Tilapia polyculture: a global review. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, F. Stress and the welfare of cultured fish. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2004, 86, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Alafawany, M.; Patra, A.K.; Kar, I.; Tiwari, R.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Dhama, K.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R. The functionality of probiotics in aquaculture: an overview. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 117: 36-52, 2021. [CrossRef]
- 6- Hai, N. Van Research findings from the use of probiotics in tilapia aquaculture: A review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, D.C. , Leonardo, A. F.G., Tachibana, L., Corrêa, C.F., Bordon, I.C.A.C., Romagosa, E., Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T. Effect of incorporating probiotics into the diet of matrinxã (Brycon amazonicus) breeders. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2012, 28, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.M. , Mohamed, M.F., John, G. Effect of probiotics on the survival, growth and challenge infection in Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 647–656. 39. [CrossRef]
- Del'Duca, A. , Cesar, D.E., Diniz, C.G., Abreu, P.C. Evaluation of the presence and efficiency of potential probiotic bacteria in the gut of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) using the fluorescent in situ hybridization technique. Aquaculture. [CrossRef]
- Jatobá, A. , Vieira, F.D.N., Neto, C.B., Silva, B.C., Mouriño, J.L.P., Jerônimo, G.T., Dotta, G., Martins, M.L. Utilização de bactérias ácido-lácticas isoladas do trato intestinal de tilápia-do-nilo como probiótico. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2008, 43, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etyemez, M. , Balcazar, J. L. Isolation and characterization of bacteria with antibacterial properties from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 105, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, T. , Ruiz-Zarzuela, I. , de Blas, I., Balcázar, J.L. Probiotics in aquaculture: a current assessment. Rev. Aquac. 2014, 6, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcázar, J.L. , Decamp, O. , Vendrell, D., De Blas, I., Ruiz-Zarzuela, I. Health and nutritional properties of probiotics in fish and shellfish. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2006, 18, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchietti, S. , Fausto, A. M., Randelli, E., Carnevali, O., Taddei, A.R., Buonocore, F., Scapigliati, G., Abelli, L. Early treatment with Lactobacillus delbrueckii strain induces an increase in intestinal T-cells and granulocytes and modulates immune-related genes of larval Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirarat, N. , Pinpimai, K. , Endo, M., Katagiri, T., Ponpornpisit, A., Chansue, N., Maita, M. Modulation of intestinal morphology and immunity in nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 91, e92–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert, E. , Castillo, M., Skalli, A., Andree, K.B., Badiola, I. Bacillus cereus var. toyoi promotes growth, affects the histological organization and microbiota of the intestinal mucosa in rainbow trout fingerlings. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picchietti, S. , Mazzini, M. , Taddei, A.R., Renna, R., Fausto, A.M., Mulero, V., Carnevali, O., Cresci, A., Abelli, L. Effects of administration of probiotic strains on GALT of larval gilthead seabream: Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telli, G.S. , Ranzani-Paiva, M. J.T., Dias, D.C., Sussel, F.R., Ishikawa, C.M., Tachibana, L. Dietary administration of Bacillus subtilis on hematology and non-specific immunity of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus raised at different stocking densities. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 39, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakstad, O.G. , Nonstad, I., Faksness, L., Brandvik, P.J. Responses of microbial communities in arctic sea ice after contamination by crude petroleum oil. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Paniagua, S.T.; Reyes-Becerril, M.; Ascencio-Valle, F.; Esteban, M.A.; Clavijo, E.; Balebona, M. C.; Moriñigo, M.A. Modulation of the intestinal microbiota and immune system of farmed Sparus aurata by the administration of the yeast Debaryomyces hansenii L2 in conjunction with inulin. J. Aquac. Res. Develop. 2011, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzorati, M. , Wittebolle, L. , Boon,N., Daffonchio, D., Verstraet, W. How to get more out of molecular fingerprints: practical tools for microbial ecology. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar]
- Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T. , Pádua, S.B., Tavares-Dias, M., Egami, M.I. 2023. Methods for hematological analysis in fish, /: São Paulo, Brazil, 2023. 138 pp. https, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D. H; Austin, B. Innate immune responses in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) induced by probiotics. Fish Shellfish Immunology 2006, 21, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, Ø. , Lied, E., Lambertsen, G. Liver retention of fat and of fatty acids in cod (Gadus morhua) fed different oils. Aquaculture. [CrossRef]
- AOAC AOAC® PRE-PUBLICATION DRAFT AOAC® Standards Development AOAC INTERNATIONAL Methods Committee Guidelines for Validation of Microbiological Methods for Food and Environmental Surfaces, 2002.
- Sipaúba-Tavares Limnologia aplicada a aquicultura. 1fst ed; FUNEP-UNESP: Jaboticabal SP, Brazil, 1995; 70p. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, D. , Vinothkanna A., Rai A.K., Vignesh V.S. Isolation of potential probiotic Bacillus spp. and assessment of their subcellular components to induce immune responses in Labeo rohita against Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immun 2015, 45, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazado, C.C. , Caipang C.M.A. Atlantic cod in the dynamic probiotics research in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2014, 424/425, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, J.O. Bacillus probiotic enzymes: external auxiliary apparatus to avoid digestive deficiencies, water pollution, diseases, and economic problems in marine cultivated animals In: Advances in Food and Nutrition Research. Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands 2017. pp. 15–35. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. , Wang, S. , Cai, Y., Guo, X., Cao, Z., Zhang, Y., Liu, S., Yuan, W., Zhu, W., Zheng, Y., Xie, Z., Guo, W., Zhou, Y. Dietary administration of Bacillus subtilis HAINUP40 enhances growth, digestive enzyme activities, innate immune responses and disease resistance of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M. , Pakzad, K. , Taheri-Mirghaed, A., Mirzargar, S., Shekarabi, S.P.H., Yosefi, P., Soleymani, N. Dietary application of the probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum 426951 Enhances immune status and growth of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) vaccinated against Yersinia ruckeri. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeer, S.; Vanderleyden, J.O.S.; Keersmaeckeret, S.C.J. Host interactions of probiotic bacterial surface molecules: comparison with commensals and pathogens. Nat. Ver. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowiak, P. , Slizewska, K. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on human health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.Z. , Yang, H. L., Ma, R.L., Lin, W.Y. Probiotic applications of two dominant gut Bacillus strains with antagonistic activity improved the growth performance and immune responses of grouper Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, M.C. , Dias, D. de C., Araujo, F. von A.P., Ishikawa, C.M., Tachibana, L. Probiotic Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus plantarum in diet of Nile tilapia. Bol. do Inst. Pesca 2019, 45, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L. , Sun, Y.Z., Ma, R.L., Ye, J.D. PCR-DGGE analysis of the autochthonous gut microbiota of grouper Epinephelus coioides following probiotic Bacillus clausii administration. Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S. , Zhang, Y. , Xu, L., Yang, Y., Marubashi, T., Zhou, Z., Yao, B. Effects of dietary Bacillus subtilis C-3102 on the production, intestinal cytokine expression and autochthonous bacteria of hybrid tilapia Oreochromis niloticus ♂×Oreochromis aureus ♀. Aquaculture, 2013, 412/413, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.A.; Weber, B.; Gonçalves, J.F.; Santos, G.A.; Rema, P.; Ozório, R.O.A. Dietary probiotic supplementation modulated gut microbiota and improved growth of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Bioch. Physiol. Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology 2013, 166, 302-307. [CrossRef]
- Forssten, S.D. , Ouwehand, A. C. Microbial ecology in health and disease simulating colonic survival of probiotics in single- strain products compared to multi-strain products. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2017, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Z. , Yang, H. L., Ma, R.L., Huang, K.P., Ye, J.D. Culture-independent characterization of the autochthonous gut microbiota of grouper Epinephelus coioides following the administration of probiotic Enterococcus faecium. Aquac. Int. 2012, 20, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakandakare, I.B.; Iwashita, M.K.P.; Dias, D.C.; Tachibana, L.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T.; Romagosa, E. Incorporation of probiotics in the diet for juvenile Nile tilapias: Hematological, immunological and microbiological parameters. Bol. do Inst. Pesca 2013, 39, 121–135. [Google Scholar]
- Mouriño, J.L.P. , Nascimento Vieira, F. , Jatobá, A.B., da Silva, B.C., Jesus, G.F.A., Seiffert, W.Q., Martins, M.L. Effect of dietary supplementation of inulin and W. cibaria on haemato-immunological parameters of hybrid surubim (Pseudoplatystoma sp). Aquac. Nutr. 2012, 18, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouriño, J.L.P. , Vieira, F. N., Jatobá, A., Silva, B.C., Pereira, G. V., Jesus, G.F.A., Ushizima, T.T., Seiffert, W.Q., Martins, M.L. Symbiotic supplementation on the hemato-immunological parameters and survival of the hybrid surubim after challenge with Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, Fletcher, Manning, M. J. Haematology of the turbot, Psetta maxima (L.): ultrastructural, cytochemical and morphological properties of peripheral blood leucocytes. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2003, 17, 77–84. [CrossRef]
- Tavares-Dias, M.; Moraes, F. R.; Onaka, E. M.; Rezende, P. C. B. Changes in blood parameters of hybrid tambacu fish parasitized by Dolops carvalhoi (Crustacea, Branchiura), a fish louse. Veterinarski Arhiv, /: http, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa, T. , Nakayasu, C. , Rieger, A.M., Barreda, D.R., Somamoto, T., Nakao, M. Phagocytosis by thrombocytes is a conserved innate immune mechanism in lower vertebrates. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passantino, L. , Cianciotta, A. , Patruno, R., Ribaud, M.R., Jirillo, E., Passantino, G.F. Do fish thrombocytes play an immunological role? Their cytoenzymatic profiles and function during an accidental piscine candidiasis in aquarium. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2005, 27, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, F.; Pádua, S. B. de; Ishikawa, M. M. Distúrbios morfológicos em células sanguíneas de peixes em cultivo: uma ferramenta prognóstica. In: Tavares-Dias, M. (Org.). Manejo e sanidade de peixes em cultivo, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Rosales, P. , Arijo, S. , Chabrillón, M., Alarcón, F.J., Tapia-Paniagua, S.T., Martínez-Manzanares, E., Balebona, M.C., Moriñigo, M.A. Effects of two closely related probiotics on respiratory burst activity of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis, Kaup) phagocytes, and protection against Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida. Aquaculture 2009, 293, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noffs, A.P. , Tachibana, L., Santos, A.A., Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T. Common snook fed in alternate and continuous regimens with diet supplemented with Bacillus subtilis probiotic. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2015, 50, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller, J.D. , Takahashi, L.S. Oxidative stress and fish immune system: phagocytosis and leukocyte respiratory burst activity. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2018, 90, 3403–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurabh, S. , Sahoo, P.K. Lysozyme: An important defense molecule of fish innate immune system. Aquac. Res. 2008, 39, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, B.A. Stress in fishes: a diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez Cruz, P. , Ibáñez, A.L., Monroy Hermosillo, O.A., Ramírez Saad, H.C. Use of Probiotics in Aquaculture ISRN Microbiol. 2012, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Varela, J.L. , Ruiz-Jarabo, I., Vargas-Chacoff, L., Arijo, S., León-Rubio, J.M., García- Millán, I., Martín del Río, M.P., Moriñigo, M.A., Mancera, J.M. Dietary administration of probiotic Pdp11 promotes growth and improves stress tolerance to high stocking density in gilthead seabream Sparus auratus. Aquaculture 2010, 309, 265–271. [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.A. , Batista, S. , Pires, M.A., Silva, A.P., Pereira, L.F., Saavedra, M.J., Ozório, R.O.A., Rema, P. Dietary probiotic supplementation improves growth and the intestinal morphology of Nile tilapia. Animal 2017, 11, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Flores, M. , Olvera-Novoa, M.A., Guzmán-Méndez, B.E., López-Madrid, W. Use of the bacteria Streptococcus faecium and Lactobacillus acidophilus, and the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as growth promoters in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2003, 216, 193–201. [CrossRef]
 |
 |
| Water quality parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21o day | 42o day | 63o day | 84o day | |
| Oxigen (mg L−1) | 5.90±0.365 | 6.11±0.737 | 6.60±2.60 | 4.13±0.12 |
| pH | 7.25±0.071 | 7.61±0.127 | 7.49±082 | 7.24±0.06 |
| Temperature (oC) | 26.43±1.150 | 28.05±0.810 | 30.57±1.25 | 32.67±0.58 |
| Ammonia (mg L−1) | 0.25±0.00 | 0.25±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 | 1.00±0.00 |
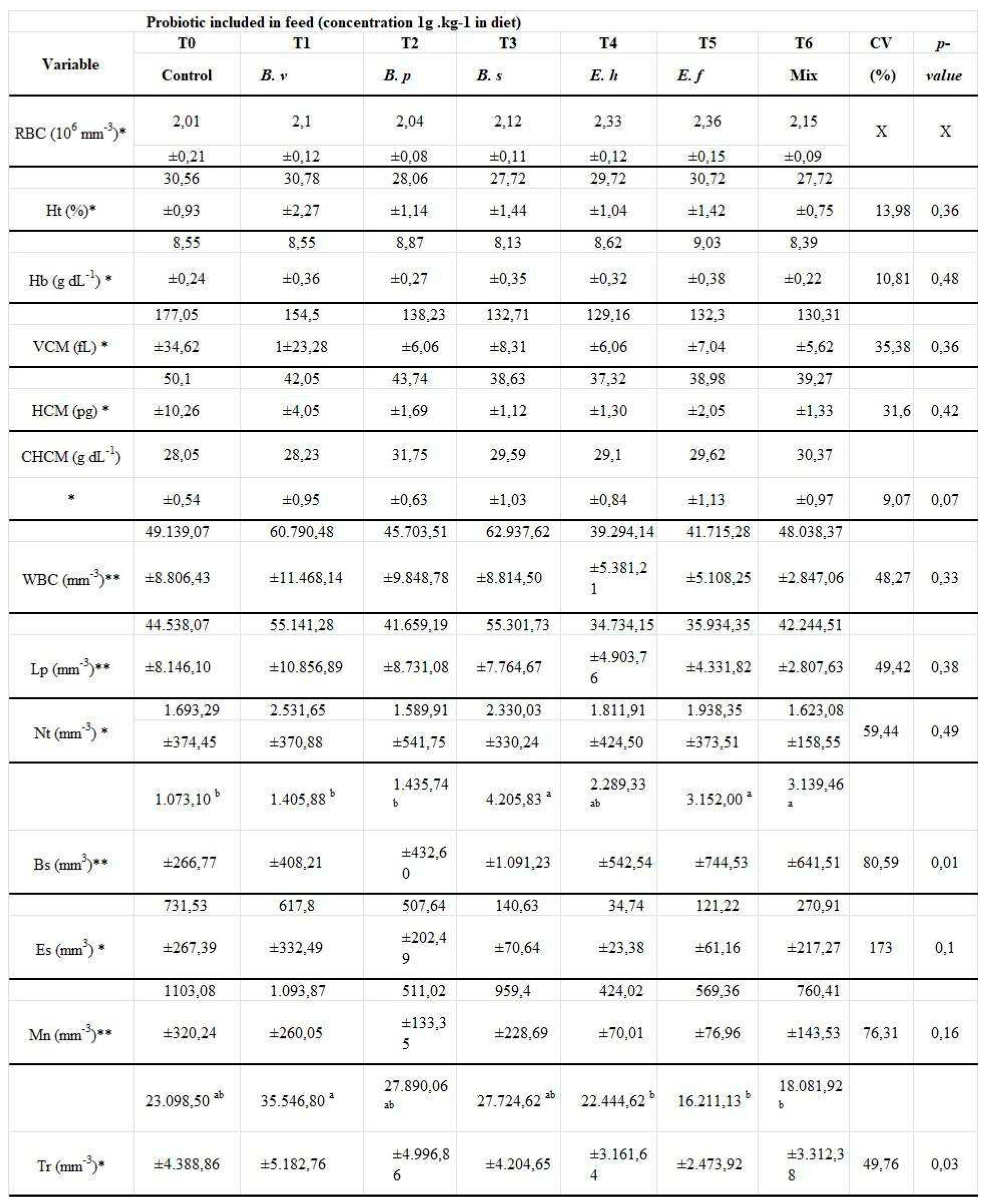
| Variable | TO | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | CV | P-value |
| control | B.v | B.p | B.s | E.h | E.f | mix | % | ||
| Wg (g) | 88.57 | 92.66 | 94.30 | 91.91 | 88.92 | 90.99 | 92.71 | 3.85 | 0.4300 |
| ± 3.33 | ± 3.06 | ± 2.64 | ± 1.35 | ± 5.78 | ± 4.08 | ± 2.76 | |||
| TS (%) | 90.80 | 92.90 | 94.60 | 93.30 | 89.60 | 90.80 | 96.30 | 4.40 | 0.1243 |
| ± 0.72 | ± 1.44 | ± 2.60 | ± 1.91 | ± 5.77 | ± 1.91 | ± 2.17 | |||
| AFRC (5) | 1.10c | 1.14ab | 1.10c | 1.13b | 1.16a | 1.13b | 1.11c | 1.08 | 0.0004 |
| ± 0,01 | ± 0.01 | ± 0.02 | ± 0.02 | ± 0.01 | ± 0.01 | ± 0.02 | |||
| SGR (%dia−1) | 4.37 | 4.43 | 4.42 | 4.36 | 4.37 | 4.40 | 4.43 | 0.53 | 0.2854 |
| ± 0.06 | ± 0.03 | ± 0.01 | ± 0.01 | ± 0.08 | ± 0.05 | ± 0.06 | |||
| PET (%) | 2.45a | 2.38b | 2.46a | 2.39b | 2.34c | 2.39b | 2.44a | 0.56 | 0.0006 |
| ± 0.01 | ± 0.02 | ± 0.05 | ± 0.04 | ± 0.01 | ± 0.01 | ± 0.03 |
| Probiotics included in feed (concentration 1g.kg-1 of diet) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | T0 Control |
T1 B. velezensis |
T2 B. pumilus |
T3 B. subtilis |
T4 E. hirae |
T5 E. faecium |
T6 MIX | CV (%) | P-value |
| H | 2.59abc ± 0.08 |
2.47bc ± 0.14 |
2.69ab ± 0.33 |
2.57abc ± 0.10 |
2.76a ± 0.25 |
2.38c ± 0.16 |
2.54abc ± 0.15 |
7.92 | 0.0108 |
| R | 16.13c ± 2.12 |
16.5c ± 2.12 |
21.25b ± 4.76 |
29.00a ± 1.58 |
27.88a ± 1.83 |
21.13b ± 5.55 |
21.63b ± 2.18 |
||
| 15.9 | <.0001 | ||||||||
| Rr | 49.19c ± 15.27 |
51.2c ± 13.00 |
90.55b ± 37.69 |
134.96a ± 14.83 |
124.86a ± 16.46 |
76.34bc ± 37.35 |
75.58bc ± 14.95 |
29.43 | <.0001 |
 |
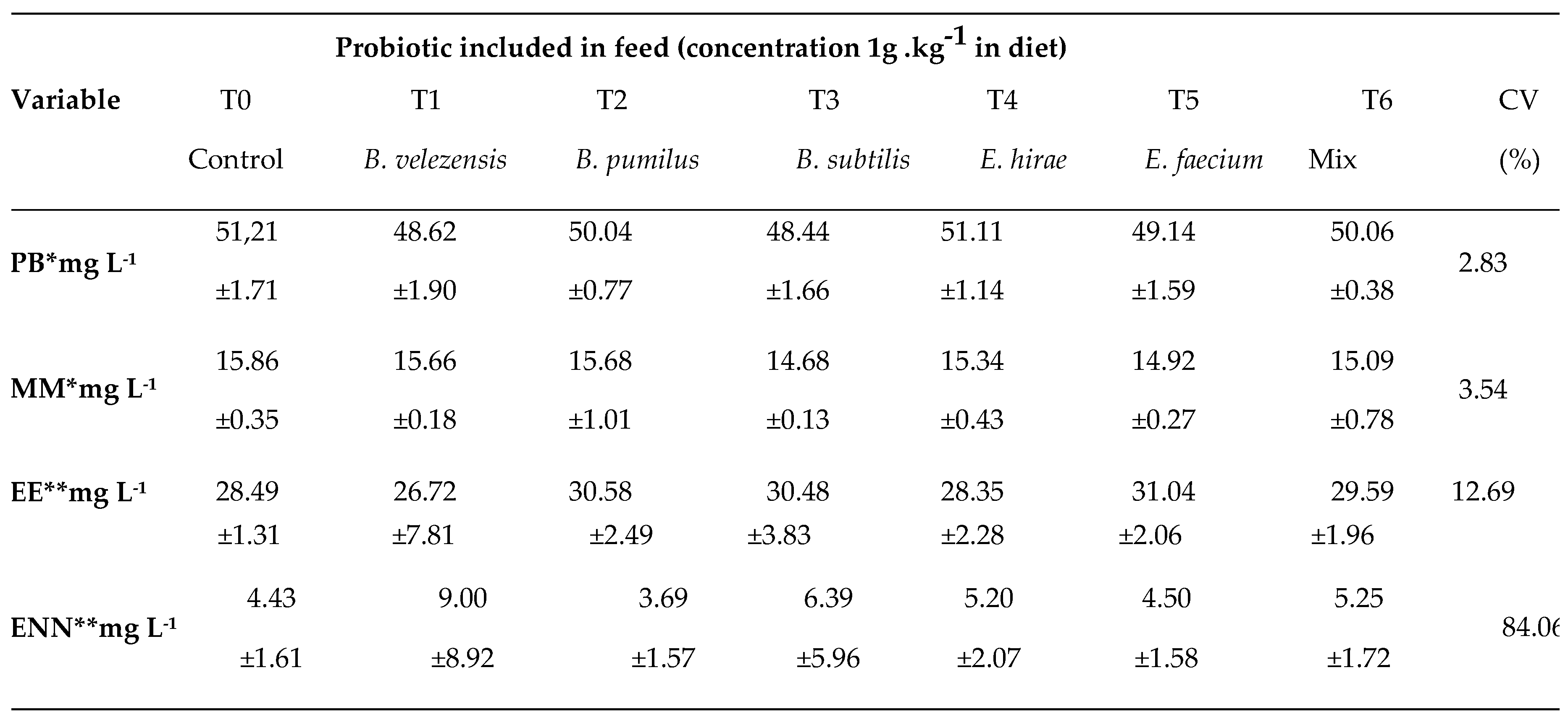
| Probiotic included in feed (concentration 1g .kg−1 in diet) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | CV | |
| Control | B. velezensis | B. pumilus | B. subtilis | E. hirae | E. faecium | Mix | (%) | P-value | |
| Blood glucose* | 53.78 | 49.33 | 44.67 | 48.78 | 45.00 | 42.11 | 43.78 | 18.06 | 0,07 |
| mg dL−1 | ±10.56 | ±5.00 | ±11.39 | ±8.72 | ±7.19 | ±7.56 | ±6.98 | ||
| 19.76 | 16.82 | 20.71 | 21.86 | 16.70 | 18.36 | 18.08 | |||
| Lactate* mmol L−1 | ±4.05 | ±5.17 | ±5.45 | ±4.84 | ±3.76 | ±8.51 | ±9.09 | 32.60 | 0,49 |
| 819.17 | 934.07 | 688.89 | 717.04 | 1,002.59 | 783.75 | 804.,07 | |||
| Lysozyme* | ±224.68 | ±623.04 | ±181.13 | ±275.74 | ±639.82 | ±206.78 | ±375.48 | 49.75 | 0,67 |
| mg L−1 | |||||||||
| Respiratory Burst** | 0.473 | 0.481 | 0.469 | 0.428 | 0.482 | 0.500 | 0.527 | ||
| Positive NBT cells (%) | ±0.09 | ±0.19 | ±0.09 | ±0.14 | ±0.07 | ±0.17 | ±0.06 | 26.74 | 0,67 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





