Submitted:
23 May 2024
Posted:
23 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Fish Samplings
2.2. Fish Measurements and Preparation of Gut Samples
2.3. Environmental Characterization
2.4. DNA Extraction, Amplification and Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatic Analyses
3. Results
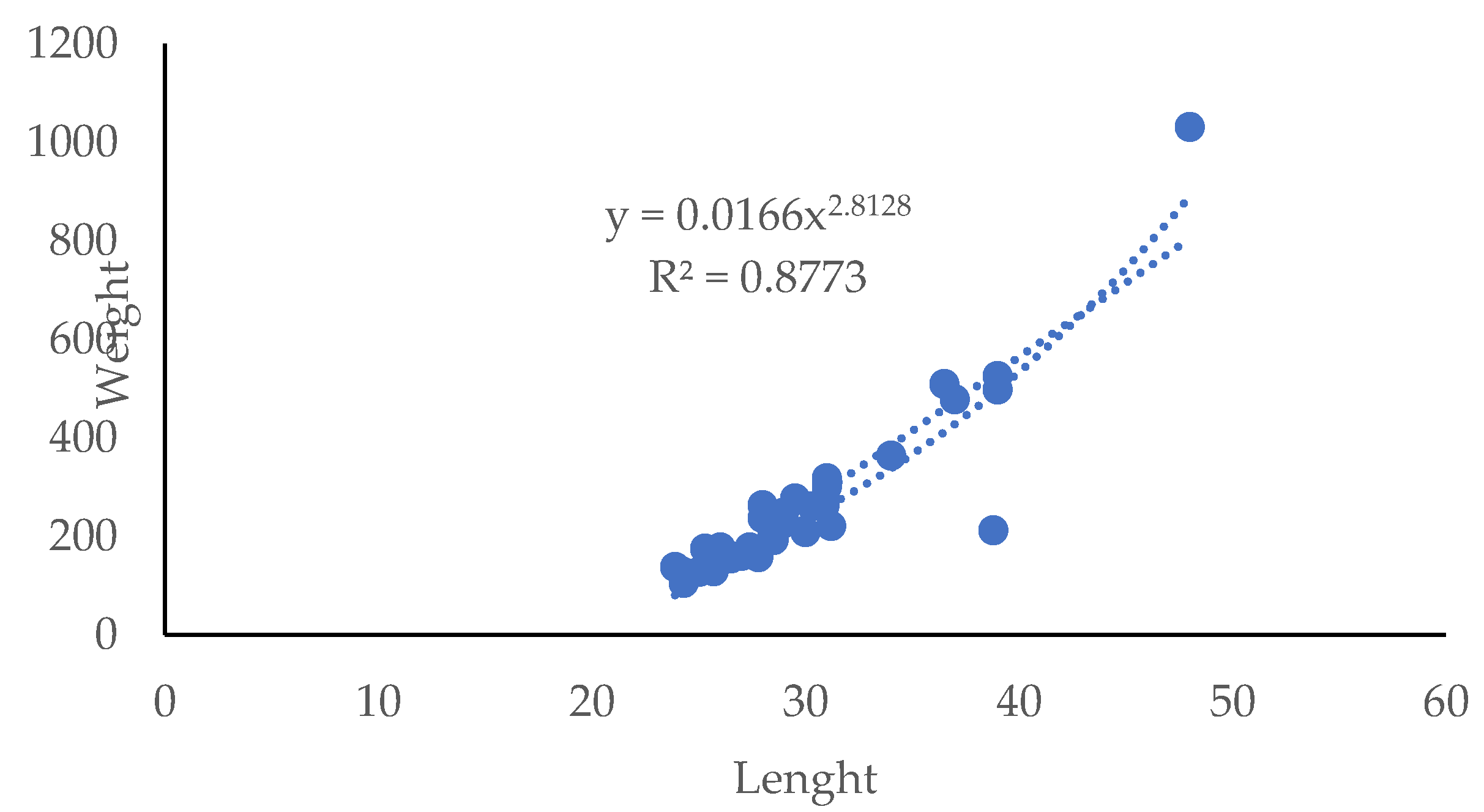
3.1. Fish Biometry
3.2. Aquatic Environmental Characterization
3.3. 16S rDNA Sequencing
3.3.1. Diversity Analysis
3.3.2. Composition of Intestinal Microbiota of Grey Mullets
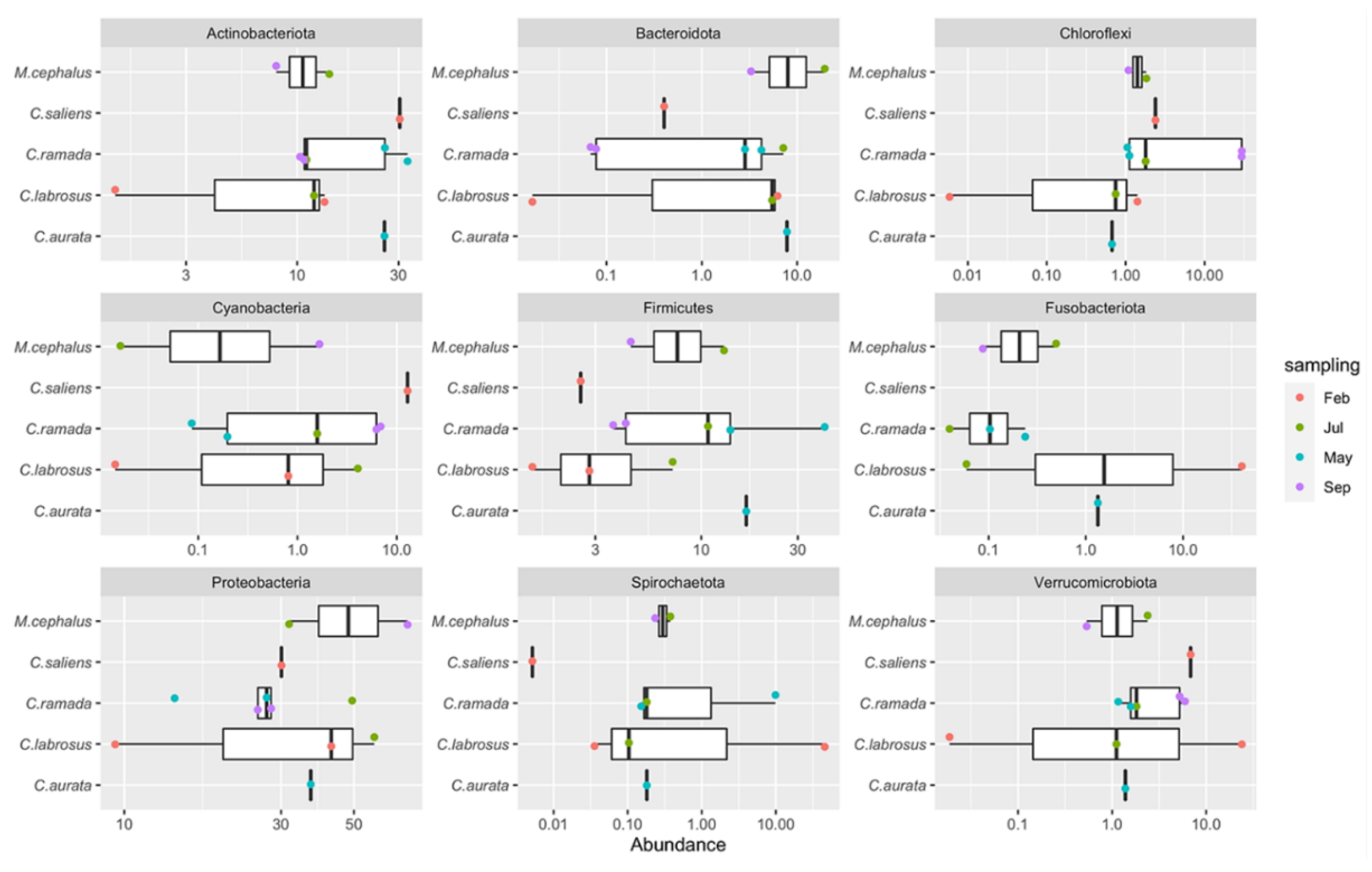
3.3.2.1. Phyla
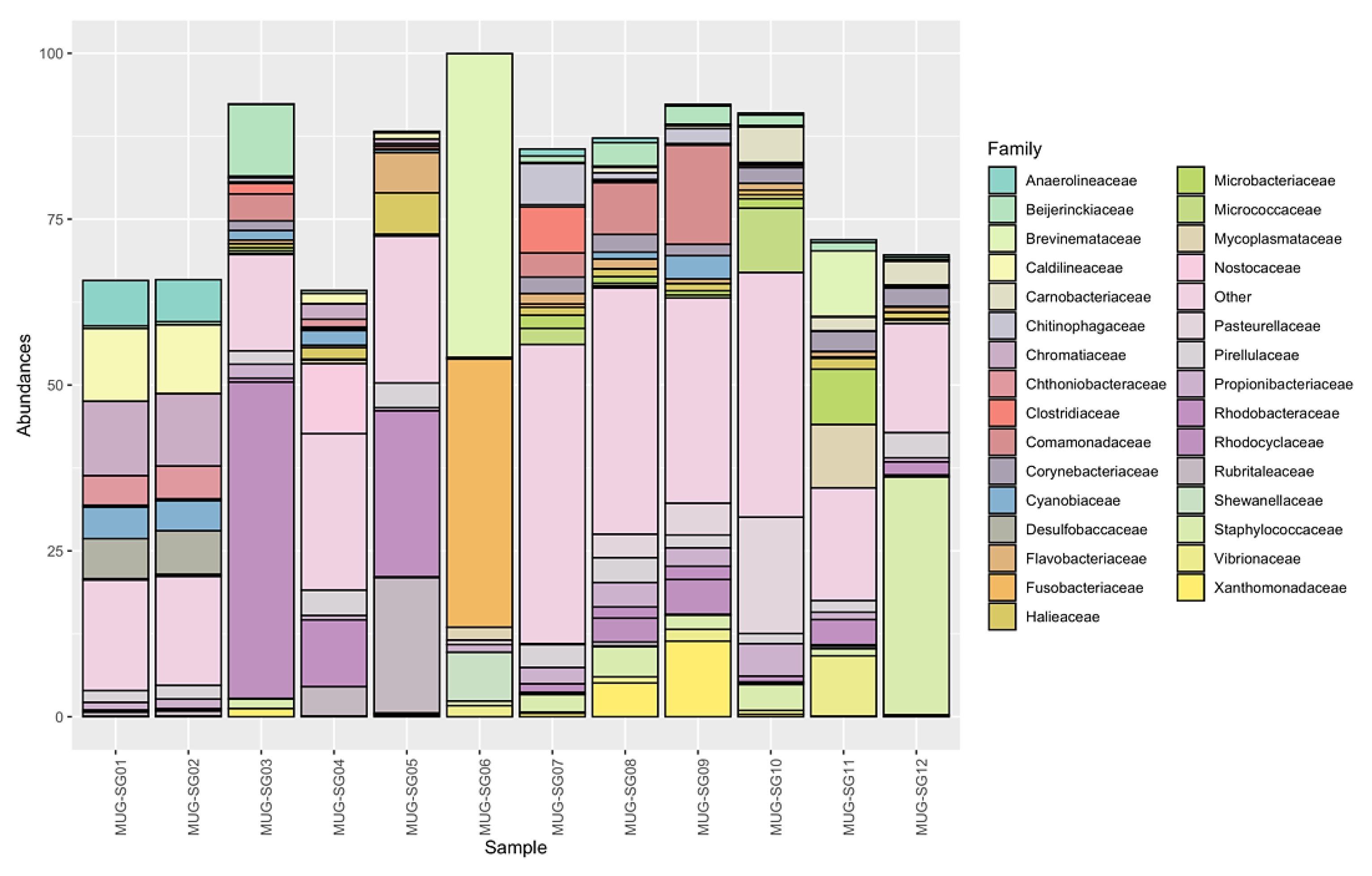
3.3.2.2. Families
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hai, N.V. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmann, K.K; Rasmussen, B. B.; Castex, M.; Gram, L.; Bentzon-Tilia, M. The aquaculture microbiome at the centre of business creation. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.; DiBattista, J.D.; Stat, M.; Bunce, M.; Boyce, M.C.; Fairclough, D.V.; Travers, M.J; Huggett, M.J. The Microbiome of the gastrointestinal tract of a range-shifting marine herbivorous fish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A. R.; Chao, R.; Ringø, E.; Zhou Z., G. Progress in fish gastrointestinal microbiota research. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, T.P.R.A.; Wynne, J.W.; Weyrich, L.S.; Oxley, A.P.A. A microbial sea of possibilities: current knowledge and prospects for an improved understanding of the fish microbiome. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1101–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, G.; Ray, A.K. Bacterial symbiosis in the fish gut and its role in health and metabolism. Symbiosis 2017, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denev, S.; Staykov, Y.; Moutafchieva, R.; Beev, G. . Microbial ecology of the gastrointestinal tract of fish and the poten-tial application of probiotics and prebiotics in finfish aquaculture. Int. Aquat. Res. 2009, 1, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Guerreiro, I.; Serra, C. R.; Enes, P.; Couto, A.; Salvador, A.; Costas, B.; Oliva-Teles, A. Effect of short chain fructooligo-saccharides (scFOS) on immunological status and gut microbiota of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) reared at two temperatures. Fish and Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 201649, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringø, E.; Zhou, Z.; Vecino, J. L.; Wadsworth, S.; Romero, J.; Krogdahl, Å.; Olsen, R.E.; Dimitroglou, A.; Foey, A.; Da-vies, F.; Owen, M.; Lauzon, H.L.; Martinsen, L.L.; De Schryver, P.; Bossier, P.; Sperstad, S.; Merrifield, D.L. Effect of die-tary components on the gut microbiota of aquatic animals. A never-ending story? Aquacul. Nutr. 2016, 22, 219–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullam, K.E.; Essinger, S.D.; Lozupone, C.A.; O'Connor, M.P.; Rosen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Kilham, S.S.; Russell, J. A. Envi-ronmental and ecological factors that shape the gut bacterial communities of fish: a meta-analysis. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 363–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzon, M. C.; Naya-Català, F.; Simó-Mirabet, P.; Picard-Sánchez, A.; Roig, F. J.; Calduch-Giner, J. A.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Sex, Age, and Bacteria: How the Intestinal Microbiota Is Modulated in a Protandrous Hermaphro-dite Fish. Front. Microbiol. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Floris, R.; Manca, S.; Fois, N. Microbial ecology of intestinal tract of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata Linnaeus, 1758) from two coastal lagoons of Sardinia (Italy). Trans. Water Bullet. 2013, 7, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, R.; Sanna, G.; Satta, C.; Piga, C.; Sanna, F.; Lugliè, A.; Fois, N. Intestinal Microbial Ecology and Fillet Metal Chemistry of Wild Grey Mullets Reflect the Variability of the Aquatic Environment in a Western Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon (Santa Giusta, Sardinia, Italy). Water 2021, 13, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikouli, E.; Meziti, A.; Antonopoulou, E.; Mente, E.; Kormas, K.A. Gut Bacterial Communities in Geographically Dis-tant Populations of Farmed Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) and Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Microorganisms 2018, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnecki, A.M.; Patterson, W.F.; Arias, C.R. Microbiota of wild-caught Red Snapper Lutjanus campechanus BMC. Microbi-ology 2016, 16, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukgehnaish, K.; Kumar, P.; Sivachandran, P.; Marimuthu, K.; Arshad, A.; Paray, B. A.; Arockiaraj, J. Gut microbiota metagenomics in aquaculture: factors influencing gut microbiome and its physiological role in fish. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1903–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashinskaya, E.N.; Belkova, N.L.; Izvekova, G.I.; Simonov, E.P.; Andree, K.B.; Glupov, V.V.; Baturina, O.A; Kabilov, M.R.; Solovyev, M.M. A comparative study on microbiota from the intestine of Prussian carp (Carassius gibelio) and their aquatic environmental compartments, using different molecular. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 948–961, The Society for Applied Microbiology methods. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehler, C. E.; Secombes, C. J.; Martin Samuel, A.M. Environmental and physiological factors shape the gut microbiota of Atlantic salmon parr (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2017, 467, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetti, D. Biology, Ecology and Culture of Grey Mullet (Mugilidae). In first ed.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 42–127.
- Koven, W.; Gisbert, E.; Meiri-Ashkenazi, I.; Nixon, O.; Israeli, D.; Tandler, A.; Soria, H.N.; Solovyev, M; , Rosenfeld, H. The effect of weaning diet type on grey mullet (Mugil cephalus) juvenile performance during the trophic shift from car-nivory to omnivory. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; D’Abramo, L.R.; Glencross, B.D.; Huyben, D.C.; Juarez, L.M.; Lockwood, G.S.; McNevin, A.A.; Tacon, A.G.J.; Teletchea, F.; Tomasso, J.R.; Tucker C., S.; Valenti W., C. Achieving sustainable aquaculture: Historical and current per-spectives and future needs and challenges. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2020, 51, 578–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, K.; Potts, T.; Freeman, S.; Israel, D.; Johansen, J.; Kletou, D.; Meland, M.; Pecorino, D.; Rebours, C.; Shorten, M.; Angel, D.L. The implications of aquaculture policy and regulation for the development of integrated multi-trophic aquaculture in Europe. Aquaculture 2015, 443, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Márquez, J.; Cerezo, I. M.; Figueroa, L. F.; Abdala-Díaz, R. T.; Arijo, S. First Evaluation of Associated Gut Micro-biota in Wild Thick-Lipped Grey Mullets (Chelon labrosus, Risso 1827). Fishes 2022, 7, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataudella, S.; Crosetti, D.; Massa, F. (eds). Mediterranean coastal lagoons: sustainable management and interactions among aq-uaculture, capture fisheries and the environment. Studies and Reviews; General Fisheries Commission for the Mediterranean. No 95. Rome, FAO, 2015; pp. 278.
- Caredda, M.; Addis, M.; Pes, M.; Fois, N.; Sanna, G.; Piredda, G.; Sanna, G. Physico-chemical, colorimetric, rheological parameters and chemometric discrimination of the origin of Mugil cephalus’ roes during the manufacturing process of Bottarga. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khemis, I.B.; Hamza, N.; Sadok, S. Nutritional quality of the fresh and processed grey mullets (Mugilidae) products: a short review including data concerning fish from freshwater. Aquat. Living Resour. 2019, 32, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallainc, D.; Concu, D.; Gimenez, G.; Papiol, G.G.; Loi, B.; Leggieri, F.; Brundu, G.; Chindris, A.; Sanna, G.; Fois, N.; An-tognarelli, F.; Rossini, P. Producing flat-head grey mullet Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus, 1758) fries in captivity from sexual-ly mature adults collected in Sardinian lagoons. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100844–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzato, M. Classic and modern valliculture. In The State of Italian Marine Fisheries and Aquaculture; Ministero delle Politiche Agricole, Alimentari e Forestali (MiPAAF); Cataudella, S., Spagnolo, M. (Eds.); Roma, Italy, 2011; pp. 237–238.
- Cataudella, S.; Tancioni, L.; Cannas, A. L’acquacoltura estensiva. In Acquacoltura Responsabile verso le Produzioni Acquat-iche del terzo Millennio; Cataudella, S., Bronzi, P. (Eds.); Unimar-Uniprom; Rome, Italy, 2001; pp. 283–306.
- Le, M.H.; Wang, D. Structure and membership of gut microbial communities in multiple fish cryptic species under po-tential migratory effects. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, S.; Yi, H.; Lai, H.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, X.; Huang, C.; Lin, L.; Xin, G.; Li, G. Intestinal mi-crobiota of the four omnivorous fishes revealed by 16S rRNA metabarcoding from the habitats of oyster reefs. Ecol. In-dic. 2023, 154, 110895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottiglia, M. Guide per il riconoscimento delle specie animali delle acque lagunari e costiere italiane - Pesci lagunari. Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (Roma), AQ/1/90, vol.1, 1980; pp.
- Trape, S.; Harrison, I. J.; Diouf, P. S.; Durand, J. D. Redescription of Liza bandialensis (Teleostei: Mugilidae) with an iden-tification key to mullet species of Eastern Central Atlantic. C. R. Biol. 2012, 335(2), 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovda, M. B.; Lunestad, B. T.; Fontanillas, R.; Rosnes, J. T. Molecular characterisation of the intestinal microbiota of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2007, 272, Issues 1–4, Pages 581-588, ISSN 0044-8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrodenyte-Arbaciauskiene, V.; Sruoga, A.; Butkauskas, D.; Skrupskeli, K. Phylogenetic analysis of intestinal bacteria of freshwater salmon Salmo salar and sea trout Salmo trutta trutta and diet. Fish Sci. 2008, 74, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.D.H.; Parsons, T.R. A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis, 2nd ed. Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1972; p. 167.
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences form high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet.j. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: an R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS One 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofek, T.; Lalzar, M.; Laviad-Shitrit, S.; Izhaki, I.; Halpern, M. Comparative Study of Intestinal Microbiota Composition of Six Edible Fish Species. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 760266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floris, R.; Sanna, G.; Mura, L.; Fiori, M.; Culurgioni, J.; Diciotti, R.; Rizzo, C.; Lo Giudice, A.; Laganà, P.; Fois, N. Isola-tion and Identification of Bacteria with Surface and Antibacterial Activity from the Gut of Mediterranean Grey Mullets. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katselis, G.; Koukou, K.; Dimitriou, E.; Koutsikopoulos, C. Short-term seaward fish migration in the Messo-longhie-Etolikolagoons (Western Greek coast) in relation to climatic variables and the lunar cycle. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 73, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Wolfgang, K.; Konrad, J.; Domig, A. New view of the fish gut microbiome: Advances from next-generation sequencing. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 464–475, ISSN 0044-8486,. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerton, S.; Culloty, S.; Whooley, J.; Stanton, C.; Ross, RP. The Gut Microbiota of Marine Fish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadoin, E.; Durand, L.; Guillou, A.; Crochemore, S.; Bouvier, T.; Roque, E.; Dagorn, L.; Auguet, J.C.; Adingra, A.; Des-nues, C.; Bettarel, Y. Does the Composition of the Gut Bacteriome Change during the Growth of Tuna? Microorganisms 2021, 27, 9, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speirs, L. B. M.; Rice, D. T. F.; Petrovski, S.; Seviour, R. J. The Phylogeny, Biodiversity, and Ecology of the Chloroflexi in Activated Sludge. Front. Microbiol. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Li-Ying, W.; Zhou, Z.; Mbadinga, S. M.; Zhou, L.; Liu, J. F.; Yang, S.Z.; Gu, J. D.; Mu, B. Z. High Frequency of Thermodesulfovibrio spp. and Anaerolineaceae in Association with Methanoculleus spp. in a Long-Term Incubation of n-Alkanes-Degrading Methanogenic Enrichment Culture. Front. Microbiol. [CrossRef]
- Bovio, P.; Cabezas, A.; Etchebehere, C. Preliminary analysis of Chloroflexi populations in full-scale UASB methano-genic reactors. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achenbach, L.A.; Michaelidou, U.; Bruce, R.A.; Fryman, J.; Coates, J.D. Dechloromonas agitata gen. nov., sp. nov. and Dechlorosoma suillum gen. nov., sp. nov., two novel environmentally dominant (per)chlorate-reducing bacteria and their phylogenetic position. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, M.; Salamone, A.; Nerenberg, R. Kinetics of a chlorate-accumulating, perchlorate-reducing bacterium. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, F.; Motta, O.; Turano, M.; Proto, A.; Vigliotta, G. . Preferential Use of the Perchlorate over the Nitrate in the Respiratory Processes Mediated by the Bacterium Azospira sp. OGA 24. Water 2020, 12, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, P.K.; Martinelango, P.K.; Jackson, W.A.; Anderson, T.A.; Tian, K.; Tock, R.W.; Rajagopalan, S. The origin of naturally occurring perchlorate: the role of atmospheric processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumarathilaka, P.; Oze, C.; Indraratne, S.P.; Vinthanage, M. Perchlorate as an emerging contaminant in soil, water and food. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Lokesh, J.; Abdelhafiz, Y.; Siriyappagouder, P.; Pierre, R.; Sørensen, M.; Fernandes, J.M.O.; Kiron, V. Macroalga-Derived Alginate Oligosaccharide Alters Intestinal Bacteria of Atlantic Salmon. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; He, T.; Becker, S.; Zhang, G.; Li, D.; Ma, X. Butyrate: A Double-Edged Sword for Health? Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, Q.; Ringø, E.; Wu, X.; He, Y.; Yang, D. The influence of weight and gender on intestinal bacterial community of wild largemouth bronze gudgeon (Coreius guichenoti, 1874). BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.S.; Kanmani, P.; Yuvaraj, N.; Paari, K.; Pattukumar, V.; Arul, V. Purification and characterization of enterocin MC13 produced by a potential aquaculture probiont Enterococcus faecium MC13 isolated from the gut of Mugil cephalus. Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnevali, O.; Maradonna, F.; Gioacchini, G. Integrated control of fish metabolism, wellbeing and reproduction: The role of probiotic. Aquaculture 2017, 472, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronzi, P.; Rampacci, M.; Ugolini, R. L’acquacoltura intensiva. In Cataudella, S., Bronzi P. (Eds.), Aquacoltura responsabile verso le Produzioni Acquatiche del terzo Millennio. Unimar-Uniprom, Rome, Italy, 2001; pp. 348–349.
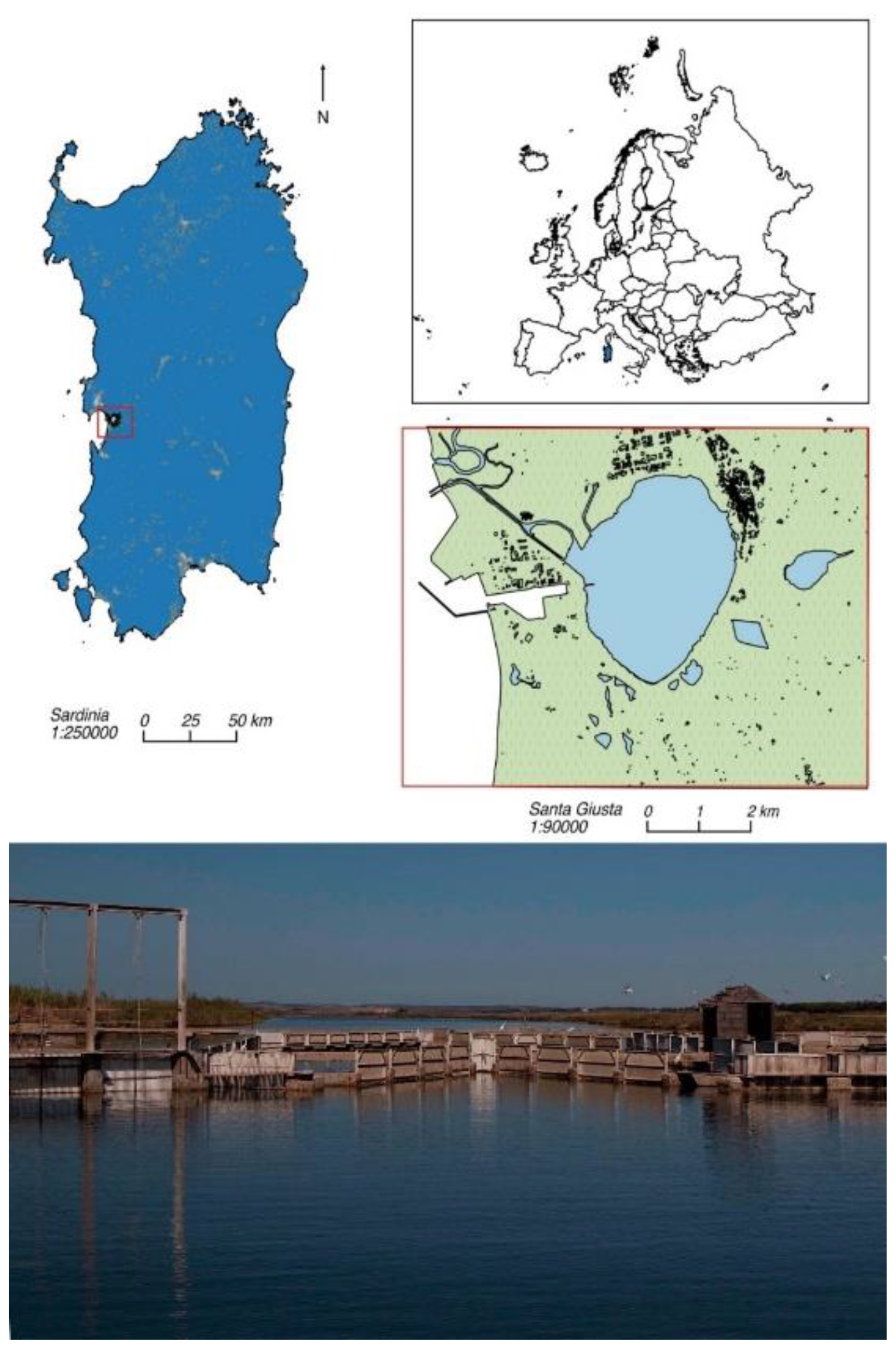


| Autumn | Winter | Summer | Spring | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total rains (mm) | 396.2a | 106.2a | 40.0b | 69.4b |
| Temperature (°C) | 14.53±4.22a | 12.59±2.19a | 26.83±2.03b | 19.65±1.38c |
| Salinity (psu) | 20.84±7.54a | 22.83±3.85a | 35.10±2.99b | 27.33±2.38ab |
| DO (mgL-1) | 9.57±1.85a | 10.03±1.07a | 5.78±0.67b | 7.01±0.73c |
| DIN (µM) | 4.91±0.75a | 2.60±1.32b | 3.48±1.71ab | 3.42±1.57ab |
| PO4 (µM) | 1.96±1.02a | 1.20±0.49b | 0.45±0.26c | 0.77±0.13bc |
| SiO4 (µM) | 296.73±38.53a | 63.61±71.38b | 96.01±52.21b | 32.01±8.06b |
| Chla (mg m-3) | 22.42±4.84a | 3.70±2.82b | 3.43±2.11b | 0.55±0.26c |
| Sample code | Season | Host species | Total counts | Observed ASVs | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N. fish) | ||||||
| MUG-SG01 | Autumn | C. ramada (3) | 26,486 | 457 | 5.02 | 0.98 |
| MUG-SG02 | Autumn | C. ramada (3) | 28,282 | 487 | 5.13 | 0.98 |
| MUG-SG03 | Autumn | M. cephalus (3) | 292,010 | 705 | 3.36 | 0.76 |
| MUG-SG04 | Winter | C. saliens (2) | 96,743 | 1,211 | 5.21 | 0.96 |
| MUG-SG05 | Winter | C. labrosus (3) | 78,504 | 984 | 5.45 | 0.98 |
| MUG-SG06 | Winter | C. labrosus (3) | 342,004 | 150 | 1.95 | 0.76 |
| MUG-SG07 | Summer | M. cephalus (3) | 345,355 | 1,081 | 5.99 | 0.99 |
| MUG-SG08 | Summer | C. ramada (3) | 291,064 | 1,343 | 5.93 | 0.99 |
| MUG-SG09 | Summer | C. labrosus (2) | 127,093 | 747 | 5 | 0.96 |
| MUG-SG10 | Spring | C. auratus (3) | 110,687 | 514 | 4.75 | 0.96 |
| MUG-SG11 | Spring | C. ramada (3) | 311,797 | 717 | 4.68 | 0.95 |
| MUG-SG12 | Spring | C. ramada (3) | 242,564 | 1,810 | 4.45 | 0.9 |
| Mean ±sd | 191,049 ± 124,210 | 850 ± 458 | 4.74 ± 1.12 | ± 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





