Submitted:
24 February 2025
Posted:
25 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Bivalve microbiomes play a vital role in host health, supporting nutrient processing, immunity, and disease resistance. However, increasing hypoxia in Chilean coastal waters, driven by climate change and eutrophication, threatens to disrupt this microbial balance, potentially promoting pathogens and impairing essential functions. Mytilus chilensis, a key species in the region, is vulnerable to hypoxia-reoxygenation cycles, yet the effects on its microbiome remain poorly understood. This study investigates the impact of hypoxia on the structure and functional potential of the microbial communities residing in the gills and digestive glands of M. chilensis. Employing full-length 16S rRNA gene sequencing, we explored hypoxia's effects on microbial diversity and functional capacity. Our results revealed significant alterations in the microbial composition, with a shift towards facultative anaerobes thriving in low-oxygen environments. Notably, there was a decrease in dominant bacterial taxa like Rhodobacterales, while opportunistic pathogens such as Vibrio and Aeromonas exhibited increased abundance. Functional analysis indicated a decline in critical microbial functions associated with nutrient metabolism and immune support, potentially jeopardizing the health and survival of the host. This study sheds light on the intricate interactions between host-associated microbiota and environmental stressors, underlining the importance of managing the microbiome in the face of climate change and aquaculture practices.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design (Mussel Acclimatization, Hypoxia Challenge, and Sampling for Microbiological Analysis)
2.2. DNA Isolation and 16S Amplification
2.3. Library Preparation and Nanopore Sequencing
2.4. Data Processing and Taxonomic Assignment
2.5. Community Profiling and Statistical Testing
2.6. Data Processing and Heat-Tree Visualization of Microbial Communities
2.7. Linear Discriminant Analysis Effect Size (LEfSe) and Correlation Network Analysis
2.8. Prediction of Metagenomic Functional Potential
2.9. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. Alpha and Beta Diversity Analysis of M. chilensis Microbiota under Normoxia and Hypoxia
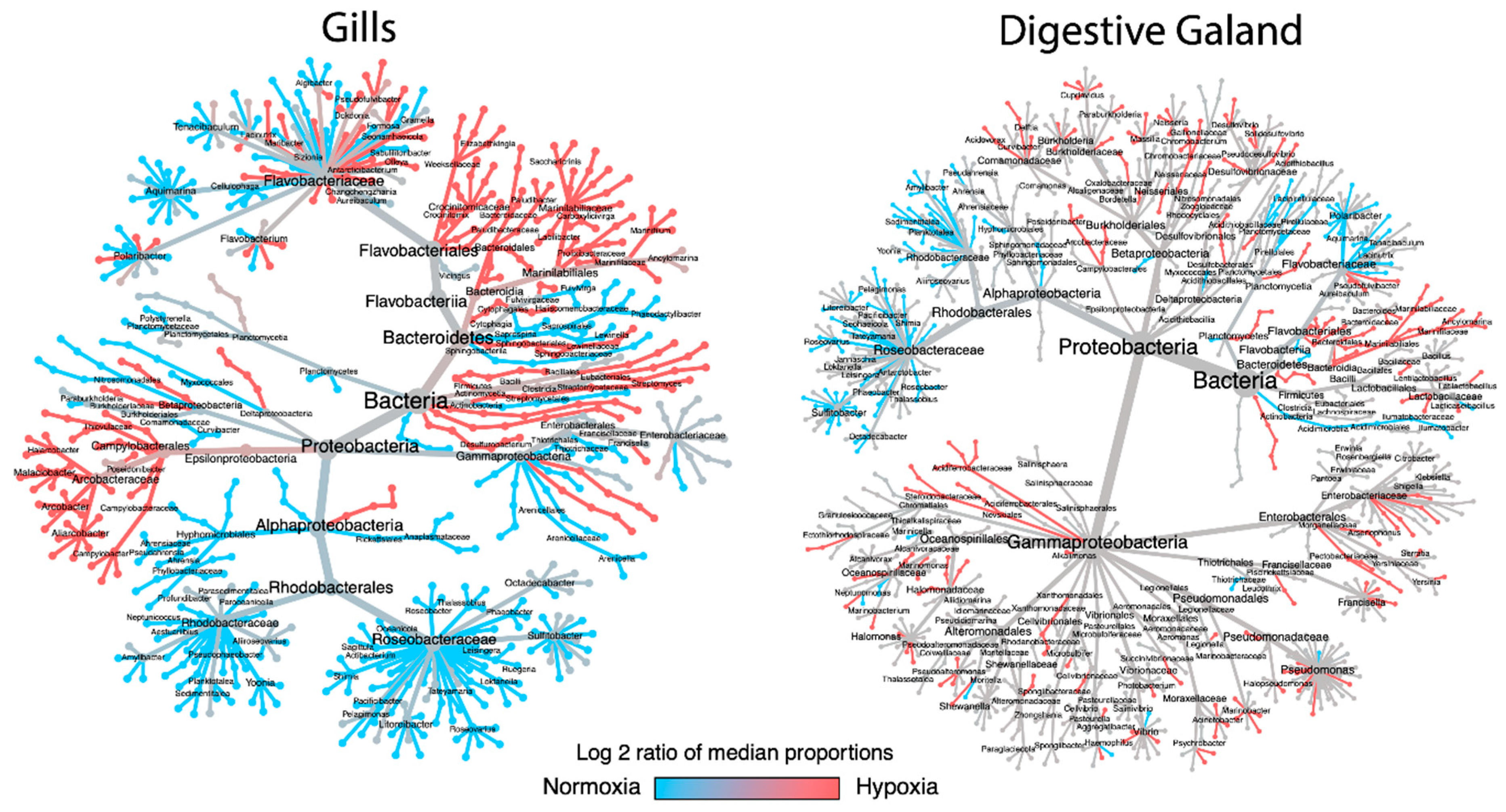
3.2. Taxonomic Shifts in the Microbiota of M. chilensis Under Normoxia and Hypoxia
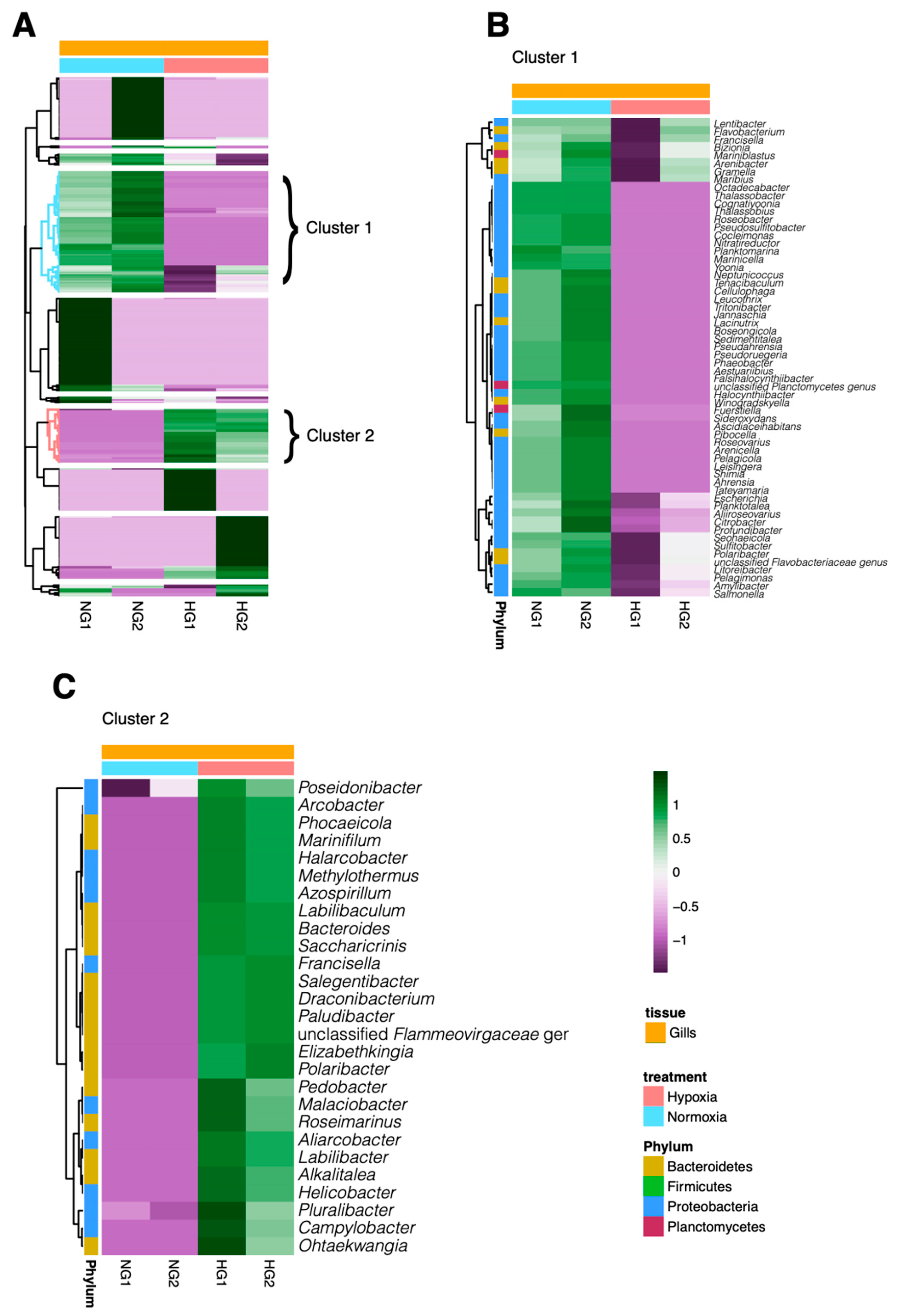
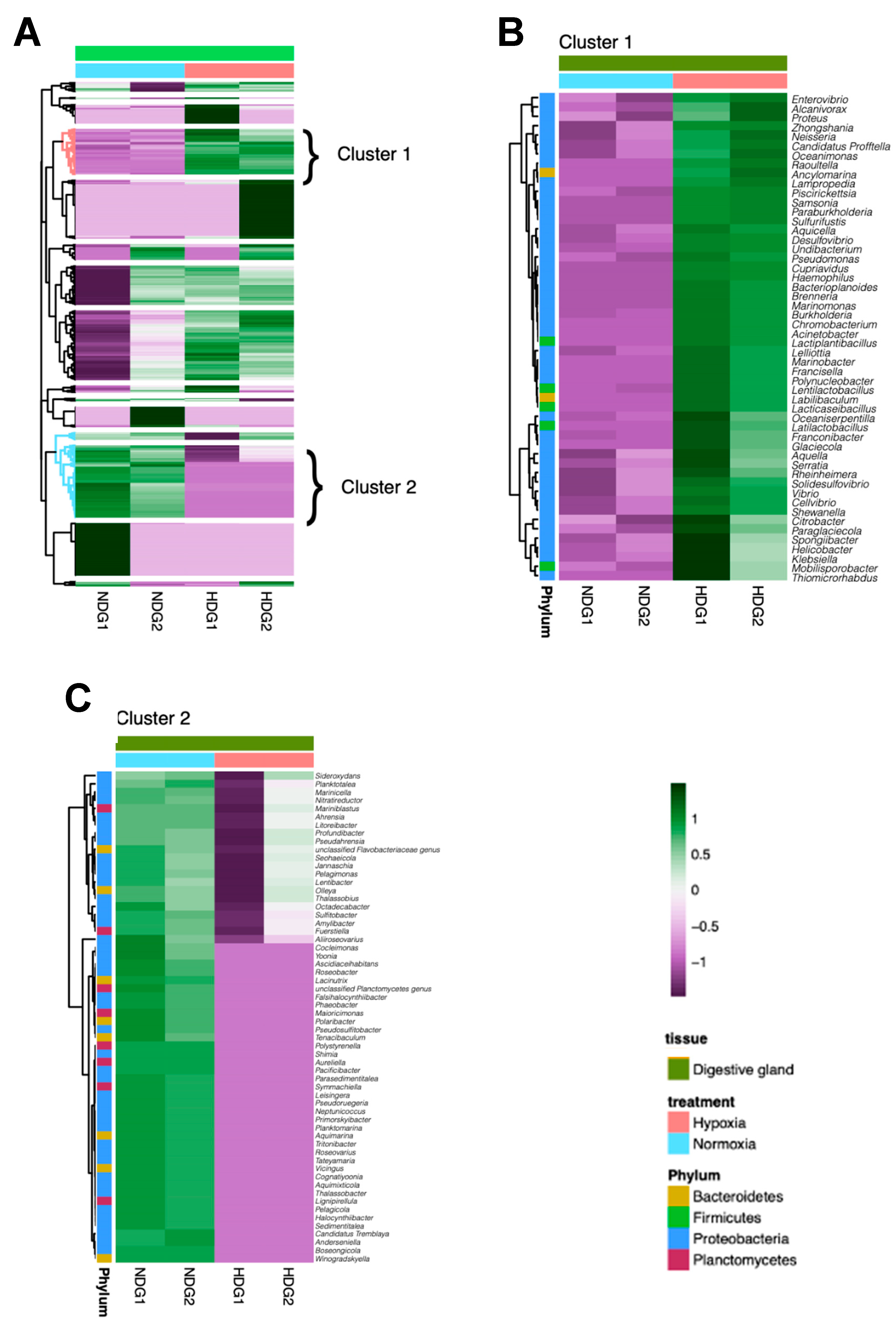
3.3. Analysis of Bacterial Genus Relative Abundance in the Microbiota of M. chilensis under Normoxia and Hypoxia
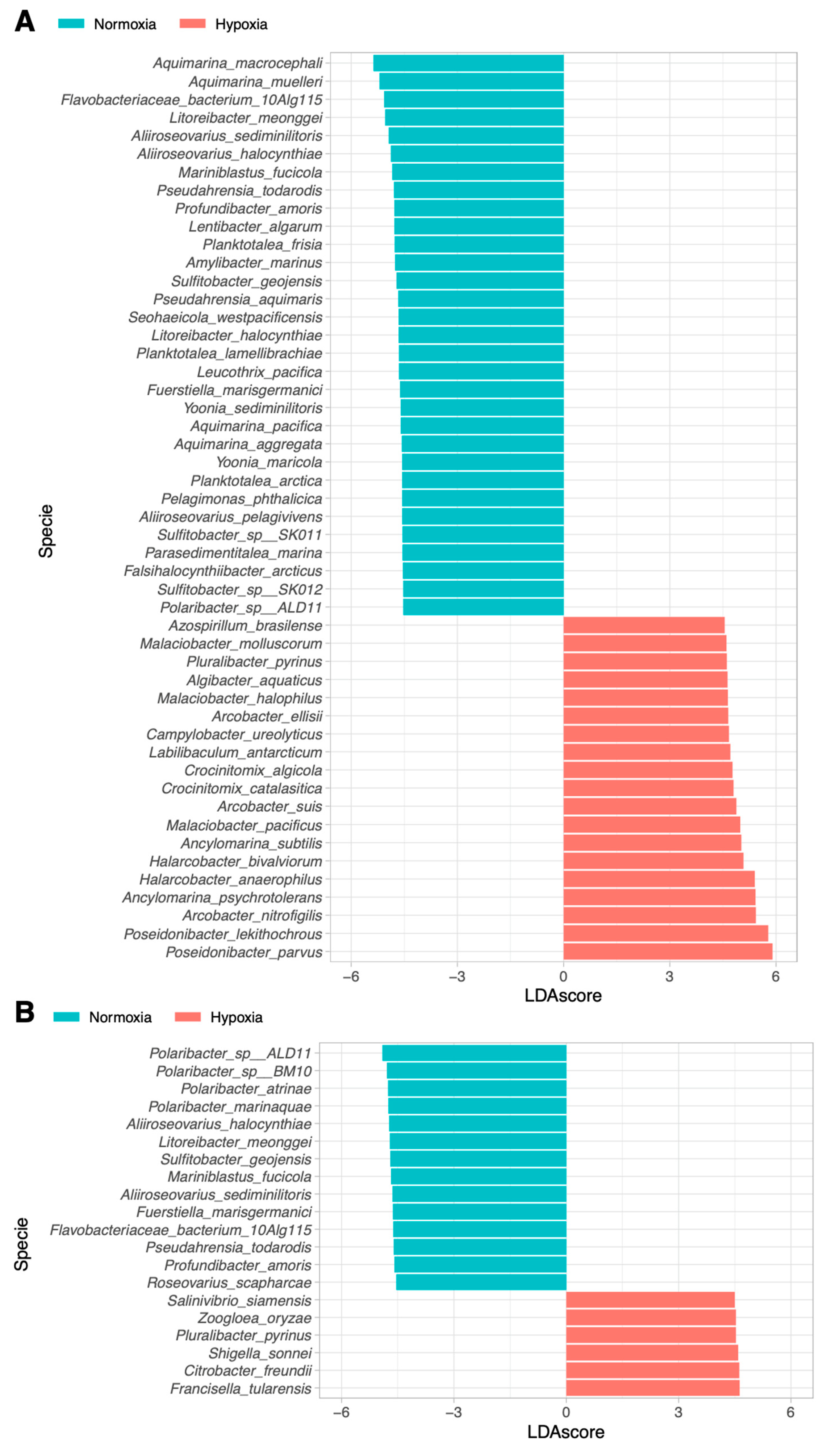
3.4. Linear Discriminant Analysis
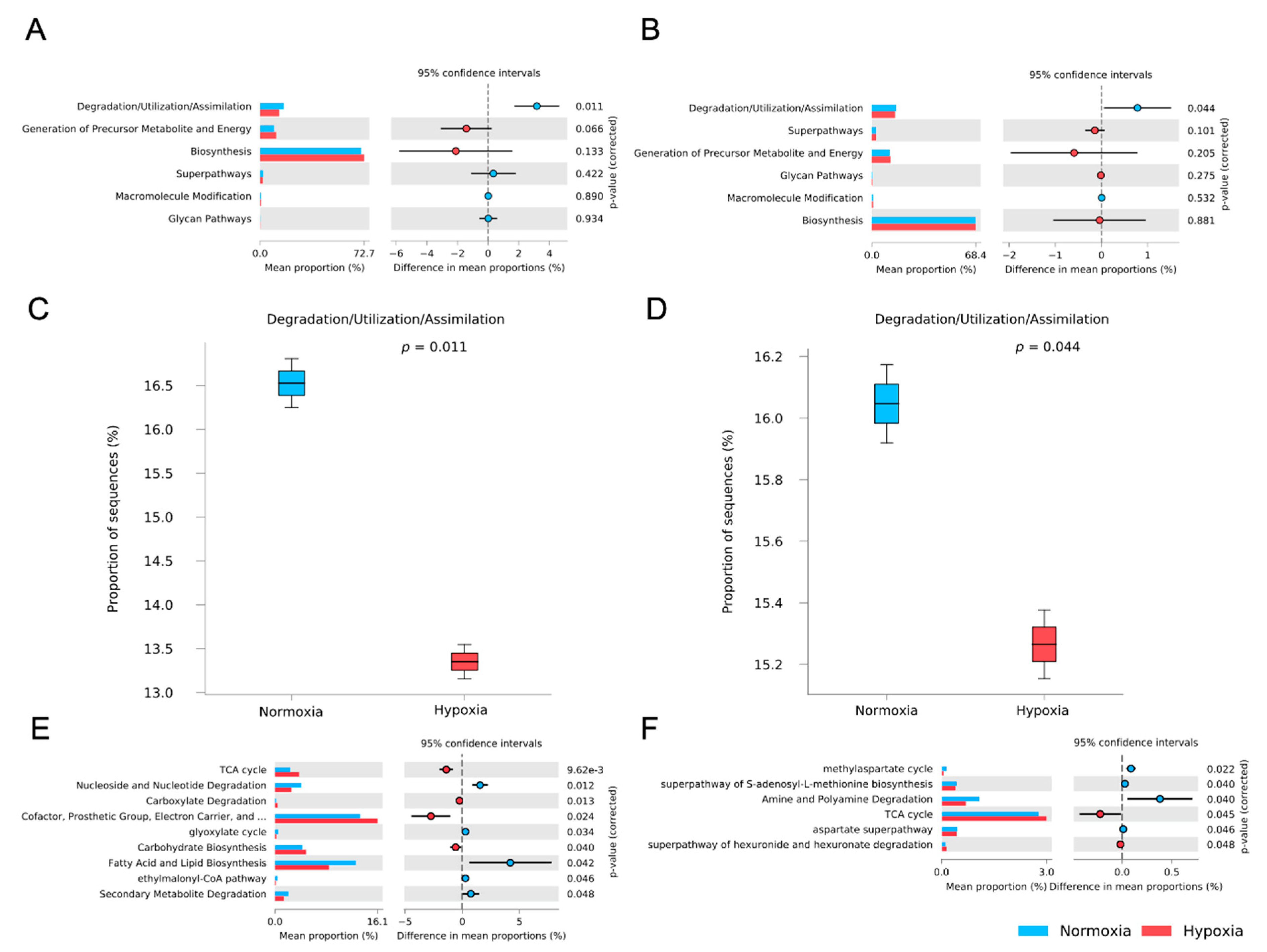
3.5. Functional Potential Prediction of the M. chilensis Microbiome Under Normoxia and Hypoxia
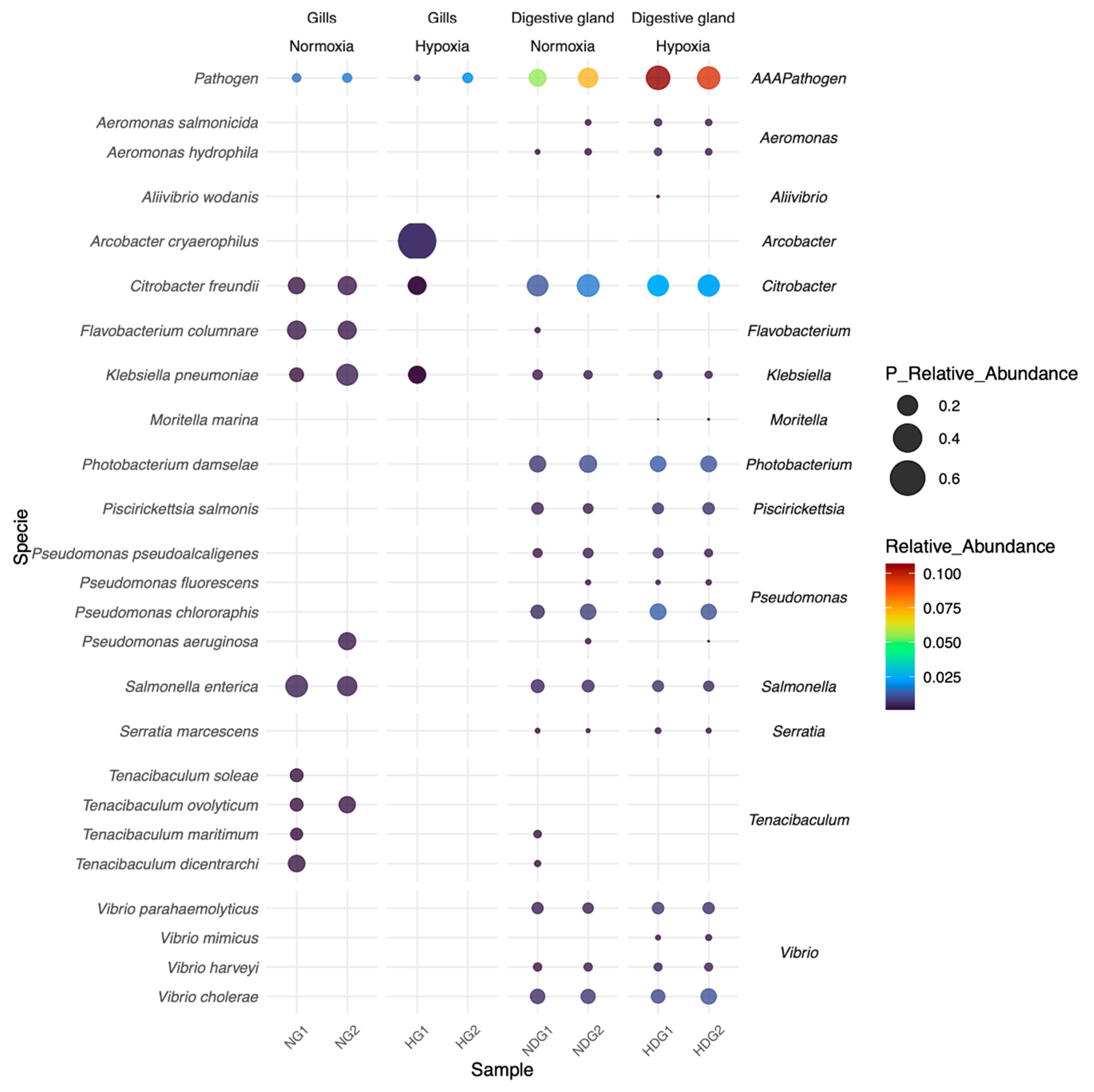
3.6. Dynamics of Bacterial Pathogens
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| °C | grados Celsius |
| ANID | Agencia Nacional de Investigación y Desarrollo |
| ANOSIM | Analysis of Similarities |
| CA | California |
| CEBB | Ethics Committee of the Universidad de Concepción |
| C.G.-E. | Cristian Gallardo Escárate |
| D.V.-M | Diego Valenzuela Miranda |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| FONDAP | Fondo de Financiamiento de Centros de Investigación en Áreas Prioritarias |
| INCAR | Interdisciplinary Center for Aquaculture Research |
| IPIAP | Instituto Público de Investigación de Acuicultura |
| LDA | linear discriminant analysis |
| LDOW | low dissolved oxygen water |
| LEfSe | Linear Discriminant Analysis Effect Size |
| log2 | logarithm base 2 |
| M. chilensis | Mytilus chilensis |
| MA | Massachusetts |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| mg/L | milligrams per liter |
| M.M.-R | Milton Montúfar Romero |
| M.F.M.-R | María Fernanda Morales-Rivera |
| n | sample size |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| OTUs | operational taxonomic units |
| PCoA | Principal Coordinates Analysis |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| pH | potential of hydrogen |
| PICRUSt2 | Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States |
| Q-score | Quality score |
| rRNA | ribosomal ribonucleic acid |
| SENESCYT | Secretaría de Educación Superior, Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación |
| SparCC | Sparse Correlations for Compositional Data |
| SRA | Sequence Read Archive |
| STAMP | Statistical Analysis of Metagenomic Profiles |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle |
| UK | United Kingdom |
| USA | United States of America |
| V.V.-M | Valentina Valenzuela-Muñoz |
References
- Fan, S.; Li, H.; Zhao, R. Effects of normoxic and hypoxic conditions on the immune response and gut microbiota of Bostrichthys sinensis. Aquaculture 2020, 525, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choumiline, K.; Pérez-Cruz, L.; Gray, A.; Bates, S.; Lyons, T. Scenarios of Deoxygenation of the Eastern Tropical North Pacific During the Past Millennium as a Window Into the Future of Oxygen Minimum Zones. Frontiers in Earth Science 2019, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.; Carstensen, J.; Vaquer-Sunyer, R.; Duarte, C. Ecosystem thresholds with hypoxia. Hydrobiologia 2009, 629, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading Dead Zones and Consequences for Marine Ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, A.; Peltzer, E.; Walz, P.; Brewer, P. Hypoxia by degrees: Establishing definitions for a changing ocean. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 2011, 58, 1212–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArley, T.; Hickey, A.; Herbert, N. Hyperoxia increases maximum oxygen consumption and aerobic scope of intertidal fish facing acutely high temperatures. Journal of Experimental Biology 2018, 221, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, S.; Moffitt, R.; Sauthoff, W.; Davis, C.; Hewett, K.; Hill, T. Paleoceanographic insights on recent oxygen minimum zone expansion: lessons for modern oceanography. PloS one 2015, 10, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, M.; Bagherzadeh, F.; Sharifpour, I.; Kazemi, R. Effect of hypoxia, normoxia and hyperoxia conditions on gill histopathology in two weight groups of beluga (Huso huso). Caspian Journal of Environmental Sciences 2013, 11, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Miranda, E.; Quiñones, R.; Aedo, G.; Valenzuela, A.; Mermoud, N.; Román, C.; Yañez, F. A major fish stranding caused by a natural hypoxic event in a shallow bay of the eastern South Pacific Ocean. Journal of Fish Biology 2010, 76, 1543–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Miranda, E.; Veas, R.; Anabalón, V.; Quiñones, R. Short-term alteration of biotic and abiotic components of the pelagic system in a shallow bay produced by a strong natural hypoxia event. PLoS One 2017, 12, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Miranda, E.; Veas, R.; Labra, F.; Salamanca, M.; Quiñones, R. Response of the epibenthic macrofaunal community to a strong upwelling-driven hypoxic event in a shallow bay of the southern Humboldt Current System. Marine Environmental Research 2012, 79, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labra, F.; Hernández-Miranda, E.; Quiñones, R. Dynamic relationships between body size, species richness, abundance, and energy use in a shallow marine epibenthic faunal community. Ecology and Evolution 2015, 5, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Yang, Y.; Pan, G. Oxygen micro-nanobubbles for mitigating eutrophication induced sediment pollution in freshwater bodies. Journal of Environmental Management 2023, 331, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Maza, L.; Farias, L. The intensification of coastal hypoxia off central Chile: Long term and high frequency variability. Frontiers in Earth Science 2023, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Shang, Y.; Chang, X.; Kong, H.; Zuberi, A.; Fang, J.; Liu, W.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, M.; et al. Effects of Ocean Acidification, Hypoxia, and Warming on the Gut Microbiota of the Thick Shell Mussel Mytilus coruscus Through 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing. Frontiers in Marine Science 2021, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreyeva, A.; Gostyukhina, O.; Kladchenko, E.; Afonnikov, D.; Rasskazov, D.; Lantushenko, A.; Vodiasova, E. Hypoxia exerts oxidative stress and changes in expression of antioxidant enzyme genes in gills of Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck, 1819). Marine Biology Research 2021, 17, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Shang, Y.; Clements, J.; Dupont, S.; Wang, T.; Wei, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Hu, M.; et al. Hypoxia aggravates the effects of ocean acidification on the physiological energetics of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2019, 149, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Lin, D.; Lu, W. Immune toxicity of TiO2 under hypoxia in the green-lipped mussel Perna viridis based on flow cytometric analysis of hemocyte parameters. Science of the Total Environment 2014, 470, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Cheung, S.; Shin, P.; Lu, W.; Li, J. Immune parameter changes of hemocytes in green-lipped mussel Perna viridis exposure to hypoxia and hyposalinity. Aquaculture 2012, 356, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falfushynska, H.; Piontkivska, H.; Sokolova, I. Effects of intermittent hypoxia on cell survival and inflammatory responses in the intertidal marine bivalves Mytilus edulis and Crassostrea gigas. Journal of Experimental Biology 2020, 223, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.; Falfushynska, H.; Timm, S.; Sokolova, I. Effects of hypoxia and reoxygenation on intermediary metabolite homeostasis of marine bivalves Mytilus edulis and Crassostrea gigas. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology 2020, 242, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, M.; Bulling, M. On the Importance of the Microbiome and Pathobiome in Coral Health and Disease. Frontiers in Marine Science 2017, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, G.; Rybakova, D.; Fischer, D.; Cernava, T.; Vergès, M.; Charles, T.; Chen, X.; Cocolin, L.; Eversole, K.; Corral, G.; et al. Microbiome definition re-visited: old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 2020, 8, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Wang, L.; Lai, Y.; Chiang, C. The utility of microbiome (microbiota) and exosomes in dentistry. Journal of Dental Sciences 2024, 19, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voolstra, C.; Ziegler, M. Adapting with Microbial Help: Microbiome Flexibility Facilitates Rapid Responses to Environmental Change. Bioessays 2020, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastelli, M.; Cani, P.; Knauf, C. The Gut Microbiome Influences Host Endocrine Functions. Endocrine Reviews 2019, 40, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soen, Y. Environmental disruption of host-microbe co-adaptation as a potential driving force in evolution. Frontiers in Genetics 2014, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Ley, R. The role of the microbiota in human genetic adaptation. Science 2020, 370, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, M.; Callahan, B. Pathogen resistance may be the principal evolutionary advantage provided by the microbiome. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2020, 375, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, F.; Osaili, T.; Obaid, R.; Naja, F.; Radwan, H.; Ismail, L.; Hasan, H.; Hashim, M.; Alam, I.; Sehar, B.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Time-Restricted Feeding/Eating: A Targeted Biomarker and Approach in Precision Nutrition. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semova, I.; Carten, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Mackey, L.; Knight, R.; Farber, S.; Rawls, J. Microbiota Regulate Intestinal Absorption and Metabolism of Fatty Acids in the Zebrafish. Cell Host & Microbe 2012, 12, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Wos-Oxley, M.; Catalano, S.; Hassan, M.; Li, X.; Qin, J.; Oxley, A. Host Species and Environment Shape the Gut Microbiota of Cohabiting Marine Bivalves. Microbial Ecology 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, T.; Rilling, J.; Larama, G.; Acuna, J.; Campos, M.; Inostroza, N.; Araya, M.; Altamirano, K.; Fujiyoshi, S.; Yarimizu, K.; et al. 16S rRNA-Based Analysis Reveals Differences in the Bacterial Community Present in Tissues of Choromytilus chorus (Mytilidae, Bivalvia) Grown in an Estuary and a Bay in Southern Chile. Diversity-Basel 2021, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguste, M.; Lasa, A.; Pallavicini, A.; Gualdi, S.; Vezzulli, L.; Canesi, L. Exposure to TiO2 nanoparticles induces shifts in the microbiota composition of Mytilus galloprovincialis hemolymph. Science of the Total Environment 2019, 670, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.; Clinton, S.; Hamp, T.; Oliver, J.; Ringwood, A. Potential impacts of hypoxia and a warming ocean on oyster microbiomes. Marine Environmental Research 2018, 139, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, N.; Liang, X.; Yoshida, A.; Osatomi, K.; Power, D.; Batista, F.; Yang, J. Elevated Seawater Temperatures Decrease Microbial Diversity in the Gut of Mytilus coruscus. Frontiers in Physiology 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ding, W.; Shao, A.; Liang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J. Characterization of Gut Microbiome in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in Response to Thermal Stress. Frontiers in Physiology 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Puente, B.; Pita, A.; Uribe, J.; Cuellar-Pinzon, J.; Guinez, R.; Presa, P. A biogeography-based management for Mytilus chilensis: The genetic hodgepodge of Los Lagos versus the pristine hybrid zone of the Magellanic ecotone. Aquatic Conservation-Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 2020, 30, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibañez, P.; Romalde, J.; Fuentes, D.; Figueras, A.; Figueroa, J. Health Status of Mytilus chilensis from Intensive Culture Areas in Chile Assessed by Molecular, Microbiological, and Histological Analyses. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, Q.; Tan, L.; Wang, L.; Wu, F.; Li, L.; Zhang, G. Host-microbiota interactions play a crucial role in oyster adaptation to rising seawater temperature in summer. Environmental Research 2023, 216, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.; Alderdice, R.; Cooney, C.; Kuhl, M.; Pernice, M.; Voolstra, C.; Suggett, D. Coral reef survival under accelerating ocean deoxygenation. Nature Climate Change 2020, 10, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmond, N.; Wing, S. Sub-lethal and lethal effects of chronic and extreme multiple stressors on a critical New Zealand bivalve under hypoxia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 2023, 703, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriarte, J.; Pantoja, S.; Daneri, G. Oceanographic Processes in Chilean Fjords of Patagonia: From small to large-scale studies. Progress in Oceanography 2014, 129, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yevenes, M.; Lagos, N.; Farías, L.; Vargas, C. Greenhouse gases, nutrients and the carbonate system in the Reloncaví Fjord (Northern Chilean Patagonia): Implications on aquaculture of the mussel, Mytilus chilensis, during an episodic volcanic eruption. Science of the Total Environment 2019, 669, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.; Vargas, C. Hypoxia in Chilean Patagonian Fjords. Progress in Oceanography 2014, 129, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linford, P.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Montes, I.; Dewitte, B.; Buchan, S.; Narváez, D.; Saldías, G.; Pinilla, E.; Garreaud, R.; Díaz, P.; et al. Recent Deoxygenation of Patagonian Fjord Subsurface Waters Connected to the Peru-Chile Undercurrent and Equatorial Subsurface Water Variability. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 2023, 37, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, P.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Basti, L.; Garreaud, R.; Pinilla, E.; Barrera, F.; Tello, A.; Schwerter, C.; Arenas-Uribe, S.; Soto-Riquelme, C.; et al. The impact of local and climate change drivers on the formation, dynamics, and potential recurrence of a massive fish-killing microalgal bloom in Patagonian fjord. Science of the Total Environment 2023, 865, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M.; Cifuentes, U.; Pizarro, O.; Djurfeldt, L.; Caceres, M. Seasonal hydrography and surface outflow in a fjord with a deep sill: the Reloncaví fjord, Chile. Ocean Science 2016, 12, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, W.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Ross, L.; Bravo, L.; Seguel, R.; Hernández, F. On the hydrography of Puyuhuapi Channel, Chilean Patagonia. Progress in Oceanography 2014, 129, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Santos, I.; Díaz, P.; Silva, N.; Garreaud, R.; Montero, P.; Henríquez-Castillo, C.; Barrera, F.; Linford, P.; Amaya, C.; Contreras, S.; et al. Oceanography time series reveals annual asynchrony input between oceanic and estuarine waters in Patagonian fjords. Science of the Total Environment 2021, 798, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, D.; León-Muñoz, J.; Garreaud, R.; Quinoñes, R.; Morey, F. Scientific warnings could help to reduce farmed salmon mortality due to harmful algal blooms. Marine Policy 2021, 132, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linford, P.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Montero, P.; Díaz, P.; Aracena, C.; Pinilla, E.; Barrera, F.; Castillo, M.; Alvera-Azcárate, A.; Alvarado, M.; et al. Oceanographic processes driving low-oxygen conditions inside Patagonian fjords. Biogeosciences 2024, 21, 1433–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, J.; Paredes, J.; Godoy, M.; Suarez, R.; Norambuena, L.; Vargas, V.; Fuenzalida, G.; Pinilla, E.; Artal, O.; Rojas, X.; et al. Disentangling the environmental processes responsible for the world’s largest farmed fish-killing harmful algal bloom: Chile, 2016. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 766, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, P.; Daneri, G.; González, H.; Iriarte, J.; Tapia, F.; Lizárraga, L.; Sanchez, N.; Pizarro, O. Seasonal variability of primary production in a fjord ecosystem of the Chilean Patagonia: Implications for the transfer of carbon within pelagic food webs. Continental Shelf Research 2011, 31, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneri, G.; Montero, P.; Lizárraga, L.; Torres, R.; Iriarte, J.L.; Jacob, B.; González, H.E.; Tapia, F.J. Primary Productivity and heterotrophic activity in an enclosed marine area of central Patagonia (Puyuhuapi channel; 44° S, 73° W). Biogeosciences Discuss. 2012, 2012, 5929–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montúfar-Romero, M.; Valenzuela-Muñoz, V.; Valenzuela-Miranda, D.; Gallardo-Escárate, C. Hypoxia in the Blue Mussel Mytilus chilensis Induces a Transcriptome Shift Associated with Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Metabolism, and Immune Response. Genes 2024, 15, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzigbli, L.; Sokolov, E.; Ponsuksili, S.; Sokolova, I. Tissue- and substrate-dependent mitochondrial responses to acute hypoxia-reoxygenation stress in a marine bivalve (Crassostrea gigas). Journal of Experimental Biology 2022, 225, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, E.; Markert, S.; Hinzke, T.; Hirschfeld, C.; Becher, D.; Ponsuksili, S.; Sokolova, I. Effects of hypoxia-reoxygenation stress on mitochondrial proteome and bioenergetics of the hypoxia-tolerant marine bivalve Crassostrea gigas. Journal of Proteomics 2019, 194, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, J.; Falfushynska, H.; Piontkivska, H.; Sokolova, I. Molecular Biomarkers of the Mitochondrial Quality Control Are Differently Affected by Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Stress in Marine Bivalves Crassostrea gigas and Mytilus edulis. Frontiers in Marine Science 2020, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, K.; Piontkivska, H.; Zettler, M.; Sokolov, E.; Hinzke, T.; Nair, A.; Sokolova, I. Transcriptional response of key metabolic and stress response genes of a nuculanid bivalve, Lembulus bicuspidatus from an oxygen minimum zone exposed to hypoxia-reoxygenation. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology B-Biochemistry & Molecular Biology 2021, 256, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falfushynska, H.; Sokolov, E.; Piontkivska, H.; Sokolova, I. The Role of Reversible Protein Phosphorylation in Regulation of the Mitochondrial Electron Transport System During Hypoxia and Reoxygenation Stress in Marine Bivalves. Frontiers in Marine Science 2020, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lu, Y.; Sun, M.; Shen, H.; Niu, D. Effects of acute hypoxia and reoxygenation on histological structure, antioxidant response, and apoptosis in razor clam Sinonovacula constricta. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2024, 145, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzigbli, L.; Ponsuksili, S.; Sokolova, I. Mitochondrial responses to constant and cyclic hypoxia depend on the oxidized fuel in a hypoxia-tolerant marine bivalve Crassostrea gigas. Scientific Reports 2024, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanina, A.; Sokolova, I. Effects of intermittent hypoxia on oxidative stress and protein degradation in molluscan mitochondria. Journal of Experimental Biology 2016, 219, 3794–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Hu, M.; Lan, X.; Waiho, K.; Lv, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y. Nano-titanium dioxide exacerbates the harmful effects of perfluorooctanoic acid on the health of mussels. Environmental International 2024, 187, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, M.; Mardones-Toledo, D.; Büchner-Miranda, J.; Salas-Yanquin, L.; Gray, M.; Cubillos, V.; Montory, J.; Chaparro, O. Food acquisition by the intertidal filter feeder bivalve Perumytilus purpuratus: Can the gill explain a differential performance between smaller individuals and the larger ones? Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 2024, 571, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.; Eom, H.; Nam, S.; Shin, Y.; Rhee, J. Chlorothalonil induces oxidative stress and reduces enzymatic activities of Na+/K+-ATPase and acetylcholinesterase in gill tissues of marine bivalves. Plos One 2019, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sforzini, S.; Moore, M.; Oliveri, C.; Volta, A.; Jha, A.; Banni, M.; Viarengo, A. Role of mTOR in autophagic and lysosomal reactions to environmental stressors in molluscs. Aquatic Toxicology 2018, 195, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otegui, M.; Fiori, S.; Menechella, A.; Dos Santos, E.; Gimenez, J. Histological characterization and morphological alterations in gill and digestive gland in non-native bivalve from the Province of Buenos Aires: Spatial and seasonal evaluation. Zoologischer Anzeiger 2024, 312, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, W.; Shin, Y.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Rhee, J. Microcystin-LR bioconcentration induces antioxidant responses in the digestive gland of two marine bivalves Crassostrea gigas and Mytilus edulis. Aquatic Toxicology 2017, 188, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkovic-Mitic, S.; Pavlovic, S.; Perendija, B.; Despotovic, S.; Gavric, J.; Gacic, Z.; Saicic, Z. Influence of some metal concentrations on the activity of antioxidant enzymes and concentrations of vitamin E and SH-groups in the digestive gland and gills of the freshwater bivalve Unio tumidus from the Serbian part of Sava River. Ecological Indicators 2013, 32, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Riisgård, H. Relationship between oxygen concentration, respiration and filtration rate in blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology 2018, 36, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, E.; Porter, F. A Strain Gauge Monitor (SGM) for Continuous Valve Gape Measurements in Bivalve Molluscs in Response to Laboratory Induced Diel-cycling Hypoxia and pH. Jove-Journal of Visualized Experiments 2018, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yang, M.; Fu, H.; Ge, X.; Zou, J. Altered intestinal microbiota induced by chronic hypoxia drives the effects on lipid metabolism and the immune response of oriental river prawn Macrobrachium nipponense. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Miranda, D.; Valenzuela-Muñoz, V.; Benavente, B.; Muñoz-Trorcoso, M.; Nuñez-Acuña, G.; Gallardo-Escárate, C. The Atlantic salmon microbiome infected with the sea louse Caligus rogercresseyi reveals tissue-specific functional dysbiosis. Aquaculture 2024, 580, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuffreda, L.; Rodríguez-Pérez, H.; Flores, C. Nanopore sequencing and its application to the study of microbial communities. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal 2021, 19, 1497–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonenfant, Q.; Noé, L.; Touzet, H. Porechop_ABI: discovering unknown adapters in Oxford Nanopore Technology sequencing reads for downstream trimming. Bioinformatics Advances 2023, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, K.; Wang, Q.; Nute, M.; Tyshaieva, A.; Reeves, E.; Soriano, S.; Wu, Q.; Graeber, E.; Finzer, P.; Mendling, W.; et al. Emu: species-level microbial community profiling of full-length 16S rRNA Oxford Nanopore sequencing data. Nature Methods 2022, 19, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. Journal of vegetation science 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckerman, A.; Childs, D.; Petchey, O. Data Management, Manipulation, and Exploration with dplyr; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 57–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Ewald, J.; Pang, Z.; Shiri, T.; Xia, J. MicrobiomeAnalyst 2.0: comprehensive statistical, functional and integrative analysis of microbiome data. Nucleic Acids Research 2023, 51, W310–W318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, Z.; Sharpton, T.; Grünwald, N. Metacoder: An R package for visualization and manipulation of community taxonomic diversity data. PLOS Computational Biology 2017, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.; Maffei, V.; Zaneveld, J.; Yurgel, S.; Brown, J.; Taylor, C.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nature Biotechnology 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Mai, J.; Cao, X.; Burberry, A.; Cominelli, F.; Zhang, L. ggpicrust2: an R package for PICRUSt2 predicted functional profile analysis and visualization. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspi, R.; Billington, R.; Ferrer, L.; Foerster, H.; Fulcher, C.; Keseler, I.; Kothari, A.; Krummenacker, M.; Latendresse, M.; Mueller, L.; et al. The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases. Nucleic Acids Research 2016, 44, D471–D480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.; Tyson, G.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R. STAMP: statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todgham, A.; Stillman, J. Physiological Responses to Shifts in Multiple Environmental Stressors: Relevance in a Changing World. Integrative and Comparative Biology 2013, 53, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earhart, M.; Blanchard, T.; Harman, A.; Schulte, P. Hypoxia and High Temperature as Interacting Stressors: Will Plasticity Promote Resilience of Fishes in a Changing World? Biological Bulletin 2022, 243, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, R.; Schul, M.; Bravo, L.; Altieri, A.; Meyer, J. Shifts in the coral microbiome in response to in situ experimental deoxygenation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2023, 89, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubé, C.; Ky, C.; Planes, S. Microbiome of the Black-Lipped Pearl Oyster Pinctada margaritifera, a Multi-Tissue Description With Functional Profiling. Frontiers in Microbiology 2019, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C. Unraveling Interactions between the Microbiome and the Host Immune System To Decipher Mechanisms of Disease. mSystems 2018, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavel, T.; Gomes-Neto, J.; Lagkouvardos, I.; Ramer-Tait, A. Deciphering interactions between the gut microbiota and the immune system via microbial cultivation and minimal microbiomes. Immunological Reviews 2017, 279, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiong, K.; Tu, Z.; Waiho, K.; Yang, C.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Fang, J.; Hu, M.; et al. Combined effect of salinity and hypoxia on digestive enzymes and intestinal microbiota in the oyster Crassostrea hongkongensis. Environmental Pollution 2023, 331, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemraj, D.; Falkenberg, L.; Cheung, K.; Man, L.; Carini, A.; Russell, B. Acidification and hypoxia drive physiological trade-offs in oysters and partial loss of nutrient cycling capacity in oyster holobiont. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 2023, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, B.; Espinosa, E. Bivalve immunity and response to infections: Are we looking at the right place? Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2016, 53, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.; Henríquez-Castillo, C.; Lohrmann, K.; Romero, M.; Ramajo, L.; Schmitt, P.; Brokordt, K. The Gill Microbiota of Argopecten purpuratus Scallop Is Dominated by Symbiotic Campylobacterota and Upwelling Intensification Differentially Affects Their Abundance. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dor-Roterman, Y.; Benayahu, Y.; Reshef, L.; Gophna, U. Host-Microbiome Interactions in a Changing Sea: The Gill Microbiome of an Invasive Oyster under Drastic Temperature Changes. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assié, A.; Borowski, C.; van der Heijden, K.; Raggi, L.; Geier, B.; Leisch, N.; Schimak, M.; Dubilier, N.; Petersen, J. A specific and widespread association between deep-sea Bathymodiolus mussels and a novel family of Epsilonproteobacteria. Environmental Microbiology Reports 2016, 8, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokmer, A.; Wegner, K. Hemolymph microbiome of Pacific oysters in response to temperature, temperature stress and infection. The International Society for Microbial Ecology Journal 2015, 9, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; Sadarangani, M.; Finlay, B. The role of the immune system in governing host-microbe interactions in the intestine. Nature Immunology 2013, 14, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.; Barnes, A. Bacterial diversity of the digestive gland of Sydney rock oysters, Saccostrea glomerata infected with the paramyxean parasite, Marteilia sydneyi. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2010, 109, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shade, A.; Handelsman, J. Beyond the Venn diagram: the hunt for a core microbiome. Environmental Microbiology 2012, 14, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Ramos, M.; Mansell, T. Leveraging quorum sensing to manipulate microbial dynamics. Current Opinion in Biomedical Engineering 2021, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Aceves, M.; Diggle, S.; Greenberg, E. Microbial Primer: LuxR- LuxI Quorum Sensing. Microbiology-SGM 2023, 169, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, A.; Shukla, A.; Patel, D. Quorum Sensing and Quorum Quenching: Two sides of the same coin. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 2023, 123, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.; Li, A.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Shin, P.; Wu, R.; Pointing, S.; Chiu, J. Interactive effects of hypoxia and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) on microbial community assembly in surface marine sediments. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2014, 85, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, F.; Umezawa, Y.; Kondo, R.; Wada, M. Effects of bottom-water hypoxia on sediment bacterial community composition in a seasonally hypoxic enclosed bay (Omura Bay, West Kyushu, Japan). FEMS Microbiology Ecology 2018, 94, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibel, B.; Häfker, N.; Trübenbach, K.; Zhang, J.; Tessier, S.; Pörtner, H.; Rosa, R.; Storey, K. Metabolic suppression during protracted exposure to hypoxia in the jumbo squid, Dosidicus gigas, living in an oxygen minimum zone. Journal of Experimental Biology 2014, 217, 2555–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Bäckhed, F. The gut microbiota - masters of host development and physiology. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2013, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlenz, C.; Gatlin, D. Interrelationships between fish nutrition and health. Aquaculture 2014, 431, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Dong, H.; Xia, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, H.; Yao, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S. The Diversity of Gut Microbiome is Associated With Favorable Responses to Anti-Programmed Death 1 Immunotherapy in Chinese Patients With NSCLC. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2019, 14, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenis, Y.; Elmetwally, M.; Maldonado-Estrada, J.; Bazer, F. Physiological importance of polyamines. Zygote 2017, 25, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, K.; Barone, S.; Soleimani, M. Polyamines and Their Metabolism: From the Maintenance of Physiological Homeostasis to the Mediation of Disease. Medical Sciences 2022, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.; Gardiner, M. Microbial Dysbiosis: Rethinking Disease in Marine Ecosystems. Frontiers in Microbiology 2016, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, M.; Ward, J. Gut Microbiomes of the Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea virginica) and the Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis): Temporal Variation and the Influence of Marine Aggregate-Associated Microbial Communities. mSphere 2019, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabal, N.; Mazón-Suástegui, J.; Vázquez-Juárez, R.; Asencio-Valle, F.; Morales-Bojórquez, E.; Romero, J. Molecular Analysis of Bacterial Microbiota Associated with Oysters (Crassostrea gigas and Crassostrea corteziensis) in Different Growth Phases at Two Cultivation Sites. Microbial Ecology 2012, 64, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, N.; Mazón-Suástegui, J.; Vázquez-Juárez, R.; Ascencio-Valle, F.; Romero, J. Changes in the composition and diversity of the bacterial microbiota associated with oysters (Crassostrea corteziensis, Crassostrea gigas and Crassostrea sikamea) during commercial production. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 2014, 88, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utermann, C.; Parrot, D.; Breusing, C.; Stuckas, H.; Staufenberger, T.; Blümel, M.; Labes, A.; Tasdemir, D. Combined genotyping, microbial diversity and metabolite profiling studies on farmed Mytilus spp. from Kiel Fjord. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ni, J.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Y.; Yan, Q. Comparative study on gastrointestinal microbiota of eight fish species with different feeding habits. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2014, 117, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguste, M.; Lasa, A.; Balbi, T.; Pallavicini, A.; Vezzulli, L.; Canesi, L. Impact of nanoplastics on hemolymph immune parameters and microbiota composition in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Marine Environmental Research 2020, 159, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibáñez, P.; Romalde, J.; Maldonado, J.; Fuentes, D.; Figueroa, J. First characterization of the gut microbiome associated with Mytilus chilensis collected at a mussel farm and from a natural environment in Chile. Aquaculture 2022, 548, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meer, D.; van den Thillart, G.; Witte, F.; de Bakker, M.; Besser, J.; Richardson, M.; Spaink, H.; Leito, J.; Bagowski, C. Gene expression profiling of the long-term adaptive response to hypoxia in the gills of adult zebrafish. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology 2005, 289, R1512–R1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Lin, H.; Lin, C. Effects of hypoxia on ionic regulation, glycogen utilization and antioxidative ability in the gills and liver of the aquatic air-breathing fish Trichogaster microlepis. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology 2015, 179, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lv, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Sui, Y.; Wang, Y. Effects of Ocean Acidification and Microplastics on Microflora Community Composition in the Digestive Tract of the Thick Shell Mussel Mytilus coruscus Through 16S RNA Gene Sequencing. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 2021, 107, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Yu, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H. Analysis of microbial abundance and community composition in esophagus and intestinal tract of wild veined rapa whelk (Rapana venosa) by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Journal of General and Applied Microbiology 2018, 64, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Wang, F.; Yu, Z.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Xue, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, L. Bacterial communities in gills and intestines of yesso scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) and its habitat waters in Changhai (Dalian, China). ISJ-Invertebrate Survival Journal 2017, 14, 340–351. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Sokolova, I.; Shang, Y.; Huang, W.; Khor, W.; Fang, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M. Effects of elevated temperature and different crystal structures of TiO2 nanoparticles on the gut microbiota of mussel Mytilus coruscus. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2024, 199, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; He, J.; He, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhao, B.; Mu, Y.; Lee, J.; Chu, Z. Effects of fulvic acid on growth performance and intestinal health of juvenile loath Paramisgurnus dabryanus (Sauvage). Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2017, 62, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, W.; Hu, G.; Qiu, L.; Meng, S.; Song, C.; Fan, L.; Zhao, Z.; Bing, X.; Chen, J. Gut microbiota analysis of juvenile genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by dietary supplementation of different resveratrol concentrations. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2018, 77, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liang, R.; Mo, J.; Yang, S.; Gu, N.; Wu, Z.; Babu, V.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Lin, L. Effects of brewer’s yeast hydrolysate on the growth performance and the intestinal bacterial diversity of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquaculture 2018, 484, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dishaw, L.; Flores-Torres, J.; Lax, S.; Gemayel, K.; Leigh, B.; Melillo, D.; Mueller, M.; Natale, L.; Zucchetti, I.; De Santis, R.; et al. The Gut of Geographically Disparate Ciona intestinalis Harbors a Core Microbiota. Plos One 2014, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, B.; Jiang, Q.; Ke, C. Changes in gut-associated flora and bacterial digestive enzymes during the development stages of abalone (Haliotis diversicolor). Aquaculture 2012, 338, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.; Judd, C.; Kuske, C.; Smith, C. Analysis of Stomach and Gut Microbiomes of the Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea virginica) from Coastal Louisiana, USA. Plos One 2012, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungrassamee, W.; Klanchui, A.; Maibunkaew, S.; Chaiyapechara, S.; Jiravanichpaisal, P.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Characterization of Intestinal Bacteria in Wild and Domesticated Adult Black Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Plos One 2014, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givens, C.; Burnett, K.; Burnett, L.; Hollibaugh, J. Microbial communities of the carapace, gut, and hemolymph of the Atlantic blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. Marine Biology 2013, 160, 2841–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, J.; Koo, H.; Dennis, L.; Kumar, R.; Ptacek, T.; Morrow, C.; Lefkowitz, E.; Powell, M.; Bej, A.; Watts, S. An abundance of Epsilonproteobacteria revealed in the gut microbiome of the laboratory cultured sea urchin, Lytechinus variegatus. Frontiers in Microbiology 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musella, M.; Wathsala, R.; Tavella, T.; Rampelli, S.; Barone, M.; Palladino, G.; Biagi, E.; Brigidi, P.; Turroni, S.; Franzellitti, S.; et al. Tissue-scale microbiota of the Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) and its relationship with the environment. Science of the Total Environment 2020, 717, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, T.; Baer, J.; Ward, J. Direct Comparison of Fecal and Gut Microbiota in the Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Discourages Fecal Sampling as a Proxy for Resident Gut Community. Microbial Ecology 2021, 81, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deegan, L.; Peterson, B.; Portier, R. Stable isotopes and cellulase activity as evidence for detritus as a food source for juvenile Gulf menhaden. Estuaries 1990, 13, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, L.; La Rosa, S.; Westereng, B.; Eijsink, V.; Pope, P.; Larsbrink, J. Polysaccharide degradation by the Bacteroidetes: mechanisms and nomenclature. Environmental Microbiology Reports 2021, 13, 559–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, U. Chitin, Characteristic, Sources, and Biomedical Application. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology 2020, 21, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, S.; Spohn, M.; Schäberle, T. Bioactive natural products from Bacteroidetes. Natural Product Reports 2022, 39, 1045–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Asoh, S.; Hiranuma, H.; Ohsawa, I.; Iio, K.; Satou, A.; Ishikura, M.; Ohta, S. Astaxanthin protects mitochondrial redox state and functional integrity against oxidative stress. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 2010, 21, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischbach, M.; Walsh, C. Antibiotics for Emerging Pathogens. Science 2009, 325, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, P.; Laxman, K.; Myint, M.; Dobretsov, S.; Richter, J.; Dutta, J. Bioinspired nanocoatings for biofouling prevention by photocatalytic redox reactions. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fimlaid, K.; Shen, A. Diverse mechanisms regulate sporulation sigma factor activity in the Firmicutes. Current Opinion in Microbiology 2015, 24, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesth, T.; Ozen, A.; Andersen, S.; Kaas, R.; Lukjancenko, O.; Bohlin, J.; Nookaew, I.; Wassenaar, T.; Ussery, D. Veillonella, Firmicutes: Microbes disguised as Gram negatives. Standards in Genomis Sciences 2013, 9, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Jiang, S.; Qian, D.; Duan, J. Modulation of microbially derived short-chain fatty acids on intestinal homeostasis, metabolism, and neuropsychiatric disorder. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2020, 104, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Sun, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. Assessment of the effect of Enteromorpha prolifera on bacterial community structures in aquaculture environment. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; He, H.; Wang, H.; Liang, Y.; Guo, C.; Shao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, M. Variations in Marine Bacterial and Archaeal Communities during an Ulva prolifera Green Tide in Coastal Qingdao Areas. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Gómez, B.; Richter, M.; Schüler, M.; Pinhassi, J.; Acinas, S.; González, J.; Pedrós-Alió, C. Ecology of marine Bacteroidetes: a comparative genomics approach. ISME Journal 2013, 7, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergauer, K.; Fernandez-Guerra, A.; Garcia, J.; Sprenger, R.; Stepanauskas, R.; Pachiadaki, M.; Jensen, O.; Herndl, G. Organic matter processing by microbial communities throughout the Atlantic water column as revealed by metaproteomics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America 2018, 115, E400–E408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, R. Ecosystem influences of natural and cultivated populations of suspension-feeding bivalve molluscs: A review. Journal of Shellfish Research 2004, 23, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zehr, J.; Jenkins, B.; Short, S.; Steward, G. Nitrogenase gene diversity and microbial community structure: a cross-system comparison. Environmental Microbiology 2003, 5, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Cai, C.; Yang, C.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Du, X.; Deng, Y. Effect of protein sources in formulated diets on the growth, immune response, and intestinal microflora of pearl oyster Pinctada fucata martensii. Aquaculture Reports 2020, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Parker, M.; Armbrust, E. Interactions between Diatoms and Bacteria. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 2012, 76, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchan, A.; LeCleir, G.; Gulvik, C.; González, J. Master recyclers: features and functions of bacteria associated with phytoplankton blooms. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2014, 12, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goecke, F.; Thiel, V.; Wiese, J.; Labes, A.; Imhoff, J. Algae as an important environment for bacteria - phylogenetic relationships among new bacterial species isolated from algae. Phycologia 2013, 52, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.; Whon, T.; Bae, J. Proteobacteria: microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends in Biotechnology 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryukhanov, A.; Korneeva, V.; Dinarieva, T.; Karnachuk, O.; Netrusov, A.; Pimenov, N. Components of antioxidant systems in the cells of aerotolerant sulfate-reducing bacteria of the genus Desulfovibrio (strains A2 and TomC) isolated from metal mining waste. Microbiology 2016, 85, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenborn, L.; Abdollahi, H.; Tee, W.; Dyall-Smith, M.; Janssen, P. A member of the delta subgroup of proteobacteria from a pyogenic liver abscess is a typical sulfate reducer of the genus Desulfovibrio. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2001, 39, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finster, K.; Kjeldsen, K. Desulfovibrio oceani subsp oceani sp nov., subsp nov and Desulfovibrio oceani subsp galateae subsp nov., novel sulfate-reducing bacteria isolated from the oxygen minimum zone off the coast of Peru. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek International Journal of General and Molecular Microbiology 2010, 97, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; He, Q.; Xavier, A.; Zhou, J.; Pereira, I.; Louro, R. Transcriptional response of Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough to oxidative stress mimicking environmental conditions. Archives of Microbiology 2008, 189, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramel, F.; Amrani, A.; Pieulle, L.; Lamrabet, O.; Voordouw, G.; Seddiki, N.; Brèthes, D.; Company, M.; Dolla, A.; Brasseur, G. Membrane-bound oxygen reductases of the anaerobic sulfate-reducing Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough: roles in oxygen defence and electron link with periplasmic hydrogen oxidation. Microbiology-SGM 2013, 159, 2663–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypionka, H. Oxygen respiration by Desulfovibrio species. Annual Review of Microbiology 2000, 54, 827–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, H.; Wimpenny, J. Effects of Oxygen on the Growth of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Journal of General Microbiology 1990, 136, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sánchez, R.; Rebollar, E.; Gutierrez-Rios, R.; Garciarrubio, A.; Juarez, K.; Segovia, L. Metagenomic analysis of carbohydrate-active enzymes and their contribution to marine sediment biodiversity. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology 2024, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppinger, M.; Baar, C.; Raddatz, G.; Huson, D.; Schuster, S. Comparative analysis of four Campylobacterales. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2004, 2, 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R. Molecular signatures (unique proteins and conserved indels) that are specific for the epsilon proteobacteria (Campylobacterales). BMC Genomics 2006, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Goethem, M.; Makhalanyane, T.; Cowan, D.; Valverde, A. Cyanobacteria and Alphaproteobacteria May Facilitate Cooperative Interactions in Niche Communities. Frontiers in microbiology 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cheung, S.; Koh, X.; Xia, X.; Jing, H.; Lee, P.; Kao, S.; Gan, J.; Dai, M.; Liu, H. Active degradation-nitrification microbial assemblages in the hypoxic zone in a subtropical estuary. Science of the total environment 2023, 904, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, D.; Vanwonterghem, I.; Rinke, C.; Parks, D.; Zhang, Y.; Takai, K.; Sievert, S.; Simon, J.; Campbell, B.; Hanson, T.; et al. Comparative Genomic Analysis of the Class Epsilonproteobacteria and Proposed Reclassification to Epsilonbacteraeota (phyl. nov.). Frontiers in Microbiology 2017, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On, S. Taxonomy of Campylobacter, Arcobacter, Helicobacter and related bacteria:: current status, future prospects and immediate concerns. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2001, 90, 1S–15S. [Google Scholar]
- Gazdag, O.; Takács, T.; Ködöböcz, L.; Krett, G.; Szili-Kovács, T. Alphaproteobacteria communities depend more on soil types than land managements. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica Section B-Soil and PlantActa Agriculturae Scandinavica Section B-Soil and Plant Science 2019, 69, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagagnan, S.; Guerin-Rechdaoui, S.; Marconi, A.; Rocher, V.; Giusti-Miller, S.; Moilleron, R.; Jusselme, M. Overview of microbial communities in the surface water of the Seine River to understand their response to climate change and human activities. Aquatic Ecology 2024, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, F.; Tan, J.; Yan, J.; Sun, H. Bacterial Community Composition in the Gut Content and Ambient Sediment of Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus Revealed by 16S rRNA Gene Pyrosequencing. Plos One 2014, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoma, S.; Vikram, S.; Jansson, J.; Ansorge, I.; Cowan, D.; Van de Peer, Y.; Makhalanyane, T. Agulhas Current properties shape microbial community diversity and potential functionality. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papale, M.; Rizzo, C.; Caruso, G.; Amalfitano, S.; Maimone, G.; Miserocchi, S.; La Ferla, R.; Aspholm, P.; Decembrini, F.; Azzaro, F.; et al. Ice Melt-Induced Variations of Structural and Functional Traits of the Aquatic Microbial Community along an Arctic River (Pasvik River, Norway). Water 2021, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshina, E.; Kosiakova, N.; Prokhorenko, I. Lipopolysaccharide from Rhodobacter capsulatus Counteracts the Effects of Toxic Lipopolysaccharides and Inhibits the Release of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in Human Whole Blood. Biologicheskie Membrany 2013, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Li, K.; Li, K. Acute effects of the environmental probiotics Rhodobacter sphaeroides on intestinal bacteria and transcriptome in shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2024, 145, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J. Thetidibacter halocola gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member within the family Roseobacteraceae isolated from seawater. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek International Jurnal of General and Molecular Microbiology 2023, 116, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedashkovskaya, O.; Otstavnykh, N.; Balabanova, L.; Bystritskaya, E.; Kim, S.; Zhukova, N.; Tekutyeva, L.; Isaeva, M. Rhodoalgimonas zhirmunskyi gen. nov., sp. nov., a Marine Alphaproteobacterium Isolated from the Pacific Red Alga Ahnfeltia tobuchiensis: Phenotypic Characterization and Pan-Genome Analysis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ren, W.; Zhong, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhou, P.; Xu, X. Thiosulfatihalobacter marinus gen. nov. sp. nov., a novel member of the family Roseobacteraceae, isolated from the West Pacific Ocean. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 2022, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Kaushik, A.; Kumar, D.; Bag, S. Foodborne Pathogenic Vibrios: Antimicrobial Resistance. Frontiers in Microbiology 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zago, V.; Veschetti, L.; Patuzzo, C.; Malerba, G.; Lleo, M. Resistome, Mobilome and Virulome Analysis of Shewanella algae and Vibrio spp. Strains Isolated in Italian Aquaculture Centers. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Ager-Wick, E.; Kumar, J.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I.; Peng, B.; Evensen, O.; Sorum, H.; Munang’andu, H. Aeromonas species isolated from aquatic organisms, insects, chicken, and humans in India show similar antimicrobial resistance profiles. Frontiers in Microbiology 2022, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.; Shum, H.; To, K.; Sridhar, S. Emerging Infections Due to Shewanella spp.: A Case Series of 128 Cases Over 10 Years. Frontiers in Medicine 2022, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z. Nosocomial peripancreatic infection associated with Shewanella xiamenensis. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2011, 60, 1387–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, A.; Di Palo, D.; Galano, A.; Becciani, S.; Montagnani, C.; Pecile, P.; Galli, L.; Rossolini, G. Intestinal carriage of Shewanella xiamenensis simulating carriage of OXA-48-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 2015, 82, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, J.; Abbott, S. The genus Shewanella: from the briny depths below to human pathogen. Critical Reviews in Microbiology 2014, 40, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-López, J.; Cabrero-Martínez, O.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Hernández-Cortez, C.; Pelcastre-Rodríguez, L.; Gonzalez-Avila, L.; Castro-Escarpulli, G. Horizontal Gene Transfer and Its Association with Antibiotic Resistance in the Genus Aeromonas spp. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerminiaux, N.; Cameron, A. Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in clinical environments. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 2019, 65, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, D. Shewanella infection in humans: Epidemiology, clinical features and pathogenicity. Virulence 2022, 13, 1515–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samreen; Ahmad, I. ; Malak, H.; Abulreesh, H. Environmental antimicrobial resistance and its drivers: a potential threat to public health. Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance 2021, 27, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavón, A.; Riquelme, D.; Jaña, V.; Iribarren, C.; Manzano, C.; Lopez-Joven, C.; Reyes-Cerpa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Pavez, L.; García, K. The High Risk of Bivalve Farming in Coastal Areas With Heavy Metal Pollution and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: A Chilean Perspective. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2022, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, B.; Baron, S.; Barraud, O. Aeromonas: the multifaceted middleman in the One Health world. Current Opinion in Microbiology 2022, 65, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.; LaMartina, E.; Lewis, J.; Dahl, A.; Nadig, N.; Szabo, A.; Newton, R.; Skwor, T. One Health and Global Health View of Antimicrobial Susceptibility through the “Eye” of Aeromonas: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2023, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Guo, M.; Yang, H.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhu, J.; Chen, L.; Du, H. blaKPC-24-Harboring Aeromonas veronii from the Hospital Sewage Samples in China. Microbiology Spectrum 2022, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilo, M.; Pereira, A.; Sousa-Santos, C.; Robalo, J.; Oliveira, M. Climatic Alterations Influence Bacterial Growth, Biofilm Production and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Aeromonas spp. Antibiotics-Basel 2021, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gufe, C.; Hodobo, T.; Mbonjani, B.; Majonga, O.; Marumure, J.; Musari, S.; Jongi, G.; Makaya, P.; Machakwa, J. Antimicrobial Profiling of Bacteria Isolated from Fish Sold at Informal Market in Mufakose, Zimbabwe. International Journal of Microbiology 2019, 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montezzi, L.; Campana, E.; Corrêa, L.; Justo, L.; Paschoal, R.; da Silva, I.; Souza, M.; Drolshagen, M.; Picao, R. Occurrence of carbapenemase-producing bacteria in coastal recreational waters. Internationa Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2015, 45, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Akter, S.; Ashrafudoulla, M.; Chowdhury, M.; Mahamud, A.; Park, S.; Ha, S. Insights into the mechanisms and key factors influencing biofilm formation by Aeromonas hydrophila in the food industry: A comprehensive review and bibliometric analysis. Food Research International 2024, 175, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherik, M.; Eves, R.; Guo, S.; Lloyd, C.; Klose, K.; Davies, P. Sugar-binding and split domain combinations in repeats-in-toxin adhesins from Vibrio cholerae and Aeromonas veronii mediate cell-surface recognition and hemolytic activities. mBio 2024, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, N. A review on pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and their mitigation through medicinal herbs in aquaculture. Heliyon 2023, 9, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ni, X.; Liu, Y.; Lu, C. Detection of three virulence genes alt, ahp and aerA in Aeromonas hydrophila and their relationship with actual virulence to zebrafish. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2011, 110, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hsu, G.; Hsu, B.; Yang, P.; Kuo, Y.; Wang, J.; Hussain, B.; Huang, S. Prevalence, virulence-gene profiles, antimicrobial resistance, and genetic diversity of human pathogenic Aeromonas spp. from shellfish and aquatic environments*. Environmental Pollution 2021, 287, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, F.; Marchandin, H.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Kodjo, A.; Lamy, B.; ColBVH, S.G. Multilocus genetics to reconstruct aeromonad evolution. BMC Microbiology 2012, 12, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, S.; De Silva, L.; Kumarage, P.; Heo, G. Occurrence of potential virulence determinants in Aeromonas spp. isolated from different aquatic environments. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2023, 134, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dien, L.; Ngo, T.; Nguyen, T.; Kayansamruaj, P.; Salin, K.; Mohan, C.; Rodkhum, C.; Dong, H. Non-antibiotic approaches to combat motile Aeromonas infections in aquaculture: Current state of knowledge and future perspectives. Reviews in Aquaculture 2022, 333–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Graf, J. Spatial and temporal population dynamics of a naturally occurring two-species microbial community inside the digestive tract of the medicinal leech. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2007, 73, 1984–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kari, Z.; Wee, W.; Sukri, S.; Harun, H.; Reduan, M.; Khoo, M.; Doan, H.; Goh, K.; Wei, L. Role of phytobiotics in relieving the impacts of Aeromonas hydrophila infection on aquatic animals: A mini-review. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 2022, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, E.; Calarco, J.; Davis, B.; Keenum, I.; Liguori, K.; Pruden, A.; Harwood, V. A Systematic Review of Culture-Based Methods for Monitoring Antibiotic-Resistant Acinetobacter, Aeromonas, and Pseudomonas as Environmentally Relevant Pathogens in Wastewater and Surface Water. Current Environmental Health Reports 2023, 10, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, R.; de Oliveira, W.; Correia, M.; Fontes, A.; Coelho, L. Aeromonas and Human Health Disorders: Clinical Approaches. Frontiers in Microbiology 2022, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, M.; Popowska, M. Insight into the mobilome of Aeromonas strains. Frontiers in Microbiology 2015, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Yu, T.; Yin, Z.; Wang, P.; Lu, X.; He, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, D.; Gao, B.; Mu, K. Uncovering the hidden threat: The widespread presence of chromosome-borne accessory genetic elements and novel antibiotic resistance genetic environments in Aeromonas. Virulence 2023, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekedar, H.; Kumru, S.; Blom, J.; Perkins, A.; Griffin, M.; Abdelhamed, H.; Karsi, A.; Lawrence, M. Comparative genomics of Aeromonas veronii: Identification of a pathotype impacting aquaculture globally. Plos One 2019, 14, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subirats, J.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Borrego, C.; Balcázar, J.; Simonet, P. Metagenomic analysis reveals that bacteriophages are reservoirs of antibiotic resistance genes. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2016, 48, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, B.; Cruciger, M.; Dacks, A.; Rio, R. Hitchhiking of host biology by beneficial symbionts enhances transmission. Scientific Reports 2014, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomar, L.; Graf, J. Investigation into the Physiologies of Aeromonas veronii in vitro and Inside the Digestive Tract of the Medicinal Leech Using RNA-seq. Biological Bulletin 2012, 223, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFall-Ngai, M. Negotiations between animals and bacteria: the ’diplomacy’ of the squid-vibrio symbiosis. Comparative Biochemist and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology 2000, 126, 471–480. [Google Scholar]
- Braschler, T.; Merino, S.; Tomás, J.; Graf, J. Complement resistance is essential for colonization of the digestive tract of Hirudo medicinalis by Aeromonas strains. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2003, 69, 4268–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltz, M.; LeVarge, B.; Graf, J. Identification of iron and heme utilization genes in Aeromonas and their role in the colonization of the leech digestive tract. Frontiers in Microbiology 2015, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bücker, R.; Krug, S.; Rosenthal, R.; Günzel, D.; Fromm, A.; Zeitz, M.; Chakraborty, T.; Fromm, M.; Epple, H.; Schulzke, J. Aerolysin From Aeromonas hydrophila Perturbs Tight Junction Integrity and Cell Lesion Repair in Intestinal Epithelial HT-29/B6 Cells. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2011, 204, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Graevenitz, A. The role of Aeromonas in diarrhea: A review. Infection 2007, 35, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J. Recent Advances in the Study of the Taxonomy, Pathogenicity, and Infectious Syndromes Associated with the Genus Aeromonas. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 1991, 4, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.; Graf, J. Bacterial symbioses of the medicinal leech Hirudo verbana. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch, K.; Gohritz, A.; Busch, K.; Spies, M.; Vogt, P. Hirudo medicinalis-leech applications in plastic and reconstructive microsurgery - A literature review. Handchirurgie Mikkrochirurgie Plastische Chirurgie 2007, 39, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaelli, P.; Theis, K.; Williams, J.; O’Connell, L.; Foster, J.; Eisthen, H. The skin microbiome facilitates adaptive tetrodotoxin production in poisonous newts. eLife 2020, 9, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Dashti, N.; Hynes, R.; Smith, D. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and soybean [Glycine max (L) Merr] growth and physiology at suboptimal root zone temperatures. Annals of Botany 1997, 79, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichty, K.; Loughran, R.; Ushijima, B.; Richards, G.; Boyd, E. Osmotic stress response of the coral and oyster pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus: acquisition of catabolism gene clusters for the compatible solute and signaling molecule myo-inositol. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2024, 90, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, A.; Kitting, C.; Rosson, R. Bacterial variability among individual penaeid shrimp digestive tracts. Crustaceana 1989, 56, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indergand, S.; Graf, J. Ingested blood contributes to the specificity of the symbiosis of Aeromonas veronii biovar sobria and Hirudo medicinalis, the medicinal leech. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2000, 66, 4735–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, J. Lessons from Digestive-Tract Symbioses Between Bacteria and Invertebrates. Annual Review of Microbiology 2016, 70, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, A.; Graf, J. Innate and procured immunity inside the digestive tract of the medicinal leech. ISJ-Invertebrate Survival Journal 2011, 8, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Nyholm, S.; Graf, J. Knowing your friends: invertebrate innate immunity fosters beneficial bacterial symbioses. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2012, 10, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardeni, J.; McClure, E.; Beka, L.; Graf, J. Host Matters: Medicinal Leech Digestive-Tract Symbionts and Their Pathogenic Potential. Frontiers in Microbiology 2016, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M.; Zaiden, N.; Teng, A.; Hu, Y.; Cao, B. Shewanella biofilm development and engineering for environmental and bioenergy applications. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 2020, 59, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, O.; Méjean, V.; Iobbi-Nivol, C. The Shewanella genus: ubiquitous organisms sustaining and preserving aquatic ecosystems. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 2020, 44, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, F. Insights on nitrate respiration by Shewanella. Frontiers in Marine Science 2015, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, A.; Silva, V.; Poeta, P.; Aonofriesei, F. Vibrio spp.: Life Strategies, Ecology, and Risks in a Changing Environment. Diversity-Basel 2022, 14, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visick, K.; Stabb, E.; Ruby, E. A lasting symbiosis: how Vibrio fischeri finds a squid partner and persists within its natural host. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2021, 19, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauge, T.; Mougin, J.; Ells, T.; Midelet, G. Sources and contamination routes of seafood with human pathogenic Vibrio spp.: A Farm-to-Fork approach. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety 2024, 23, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Alessiani, A.; Donatiello, A.; Didonna, A.; D’Attoli, L.; Faleo, S.; Occhiochiuso, G.; Carella, F.; Di Taranto, P.; Pace, L.; et al. Systematic Survey of Vibrio spp. and Salmonella spp. in Bivalve Shellfish in Apulia Region (Italy): Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, M.; Cubillejo, I.; Nag, D.; Withey, J. Advances in cholera research: from molecular biology to public health initiatives. Frontiers in Microbiology 2023, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubert, J.; Barja, J.; Romalde, J. New Insights into Pathogenic Vibrios Affecting Bivalves in Hatcheries: Present and Future Prospects. Frontiers in Microbiology 2017, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Balboa, S.; Romalde, J.; Figueras, M. Diversity and pathogenecity of Vibrio species in cultured bivalve molluscs. Environmental Microbiology Reports 2010, 2, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tercero-Alburo, J.; González-Márquez, H.; Bonilla-González, E.; Quiñones-Ramírez, E.; Vázquez-Salinas, C. Identification of capsule, biofilm, lateral flagellum, and type IV pili in Vibrio mimicus strains. Microbial Pathogenesis 2014, 76, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, D.; de Marín, C.; Marval, H.; Martínez, C. Identification of Bacteria of the Genus Vibrio Associated to Zones of Bivalve Mollusks Extraction, Sucre State, Venezuela. Revista Científica-Facultad de Ciencias Veterinarias 2012, 22, 459–467. [Google Scholar]
- Pruzzo, C.; Gallo, G.; Canesi, L. Persistence of vibrios in marine bivalves: the role of interactions with haemolymph components. Environmental Microbiology 2005, 7, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Qin, Z.; Feng, Y.; Geng, Y.; Huang, X.; Ouyang, P.; Chen, D.; Guo, H.; Deng, H.; Fang, J.; et al. Sialic acid catabolism contributes to Vibrio mimicus virulence. Aquaculture 2023, 574, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Manno, D.; Hawari, J. Psychrilyobacter atlanticus gen. nov., sp nov., a marine member of the phylum Fusobacteria that produces H2 and degrades nitramine explosives under low temperature conditions. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 2009, 59, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.; Rosenberg, R. Marine benthic hypoxia: A review of its ecological effects and the behavioral responses of benthic macrofauna. Oceanography and Marine Biology: an Annual Review 1995, 33, 245–303. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, A.; Jones, L.; Le Vay, L.; Christie, M.; Wilson, J.; Malham, S. A global review of the ecosystem services provided by bivalve aquaculture. Reviews in Aquaculture 2020, 12, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Koenen, M.; Bale, N.; Damsté, J.; Villanueva, L. The physiology and metabolic properties of a novel, low-abundance Psychrilyobacter species isolated from the anoxic Black Sea shed light on its ecological role. Environmental Microbiology Reports 2021, 13, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, S.; Bernatchez, L.; Audet, C.; Derôme, N. Network Analysis Highlights Complex Interactions between Pathogen, Host and Commensal Microbiota. Plos One 2013, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, M.; Nagano, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Hatada, Y.; Nogi, Y. Aquimarina macrocephali sp. nov., isolated from sediment adjacent to sperm whale carcasses. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 2010, 60, 2298–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Ramos, F. Antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture: Current knowledge and alternatives to tackle the problem. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2018, 52, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.; Alagawany, M.; Patra, A.; Kar, I.; Tiwari, R.; Dawood, M.; Dhama, K.; Abdel-Latif, H. The functionality of probiotics in aquaculture: An overview. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2021, 117, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.; Hazra, S.; Smolowitz, R.; Chistoserdov, A. Real-time PCR assay for Aquimarina macrocephali subsp homaria and its distribution in shell disease lesions of Homarus americanus, Milne-Edwards, 1837, and environmental samples. Journal of Microbiological Methods 2017, 139, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Choe, H.; Baik, K.; Seong, C. Aquimarina mytili sp nov., isolated from the gut microflora of a mussel, Mytilus coruscus, and emended description of Aquimarina macrocephali. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 2012, 62, 1974–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadeja, N.; Worrich, A. From gut to mud: dissemination of antimicrobial resistance between animal and agricultural niches. Environmental Microbiology 2022, 24, 3290–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subirats, J.; Triadó-Margarit, X.; Mandaric, L.; Acuña, V.; Balcázar, J.; Sabater, S.; Borrego, C. Wastewater pollution differently affects the antibiotic resistance gene pool and biofilm bacterial communities across streambed compartments. Molecular Ecology 2017, 26, 5567–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentzon-Tilia, M.; Sonnenschein, E.; Gram, L. Monitoring and managing microbes in aquaculture - Towards a sustainable industry. Microbial Biotechnology 2016, 9, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Chiarri, M.; Guo, X.; Tanguy, A.; He, Y.; Proestou, D. The use of -omic tools in the study of disease processes in marine bivalve mollusks. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 2015, 131, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habteweld, H.; Asfaw, T. Novel Dietary Approach with Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics to Mitigate Antimicrobial Resistance and Subsequent Out Marketplace of Antimicrobial Agents: A Review. Infection and Drug Resistance 2023, 16, 3191–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrieta, M.; Stiemsma, L.; Amenyogbe, N.; Brown, E.; Finlay, B. The intestinal microbiome in early life: health and disease. Frontiers in immunology 2014, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Montagnani, C.; Dantan, L.; Nicolas, N.; Travers, M.; Duperret, L.; Charrière, G.; Toulza, E.; Mitta, G.; Cosseau, C.; et al. Cross-talk and mutual shaping between the immune system and the microbiota during an oyster’s life. Philosophical Transactions of The Royal Society B-Biological Sciences 2024, 379, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majnik, A.; Lane, R. The relationship between early-life environment, the epigenome and the microbiota. Epigenomics 2015, 7, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, M.; Griffith, S.; Evans, S. Can selective breeding reduce the heavy metals content of pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas), and are there trade-offs with growth or survival? Journal of Shellfish Research 2005, 24, 979–986. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont, S.; Lokmer, A.; Corre, E.; Auguet, J.; Petton, B.; Toulza, E.; Montagnani, C.; Tanguy, G.; Pecqueur, D.; Salmeron, C.; et al. Oyster hemolymph is a complex and dynamic ecosystem hosting bacteria, protists and viruses. Animal Microbiome 2020, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




