Submitted:
03 June 2024
Posted:
03 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
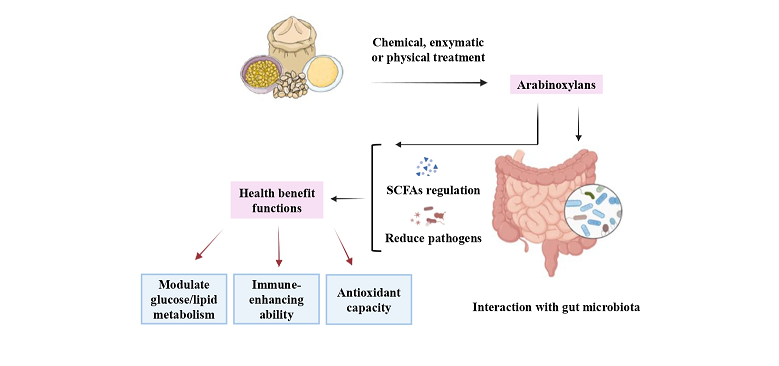
Keywords:
1. Introduction
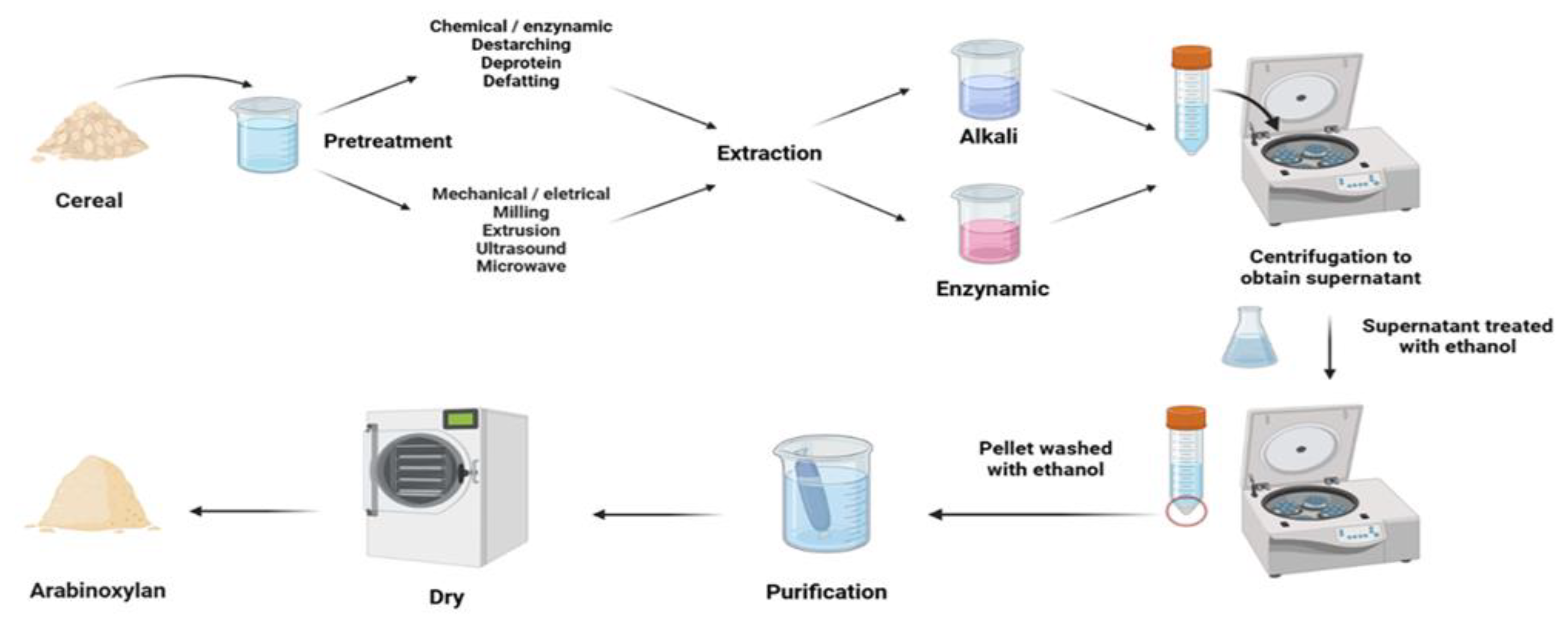
2. Materials and Methods
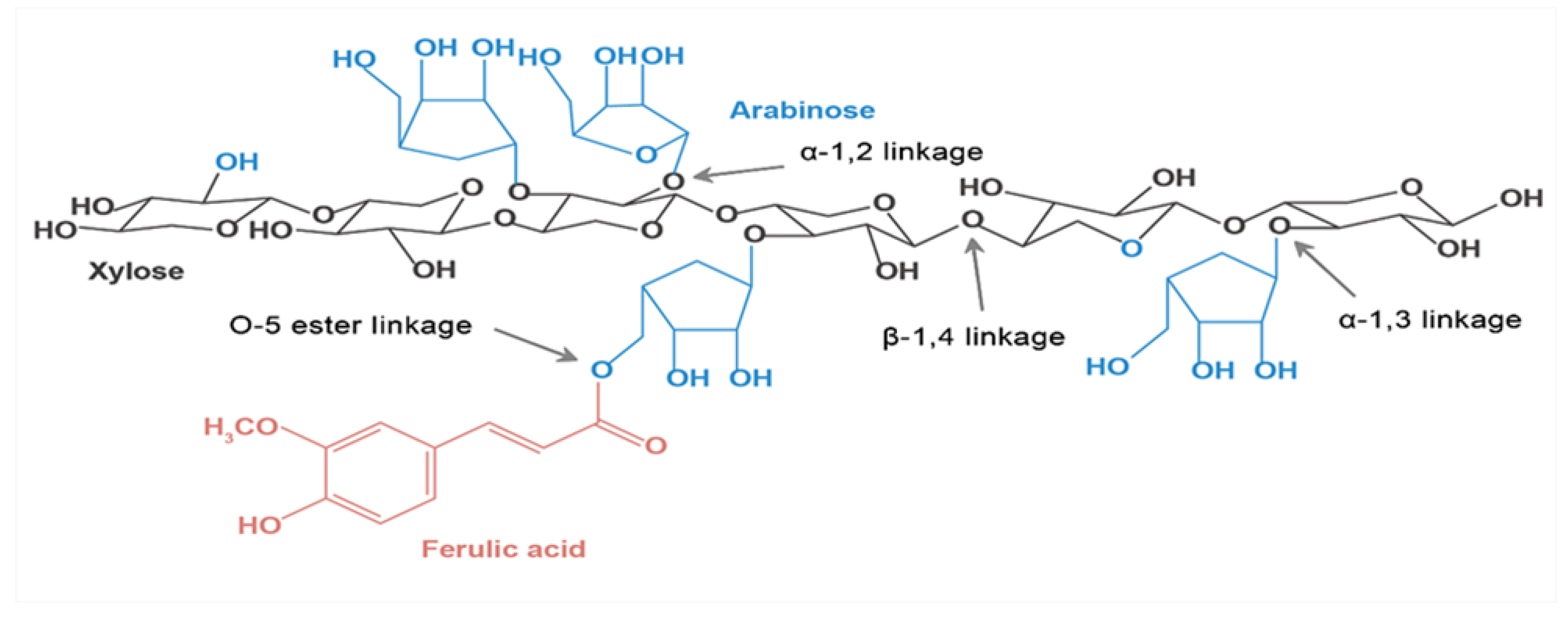
3. Structural Features
3.1. Monosaccharide Compositions and Branching Degree
3.2. Glycosidic Linkages
3.3. Combination of Phenolic Compounds
4. Effects of Different Treatments on WUAX Structure in Cereals
4.1. Alkali Extraction
4.2. Enzymatic Extraction
4.3. Microbial Fermentation
5. Technological Proprieties of Industrial Interest
5.1. Interaction with Gluten Protein
5.2. Effect on Physical Properties of Dough
5.3. Effect on Final Cereal Products
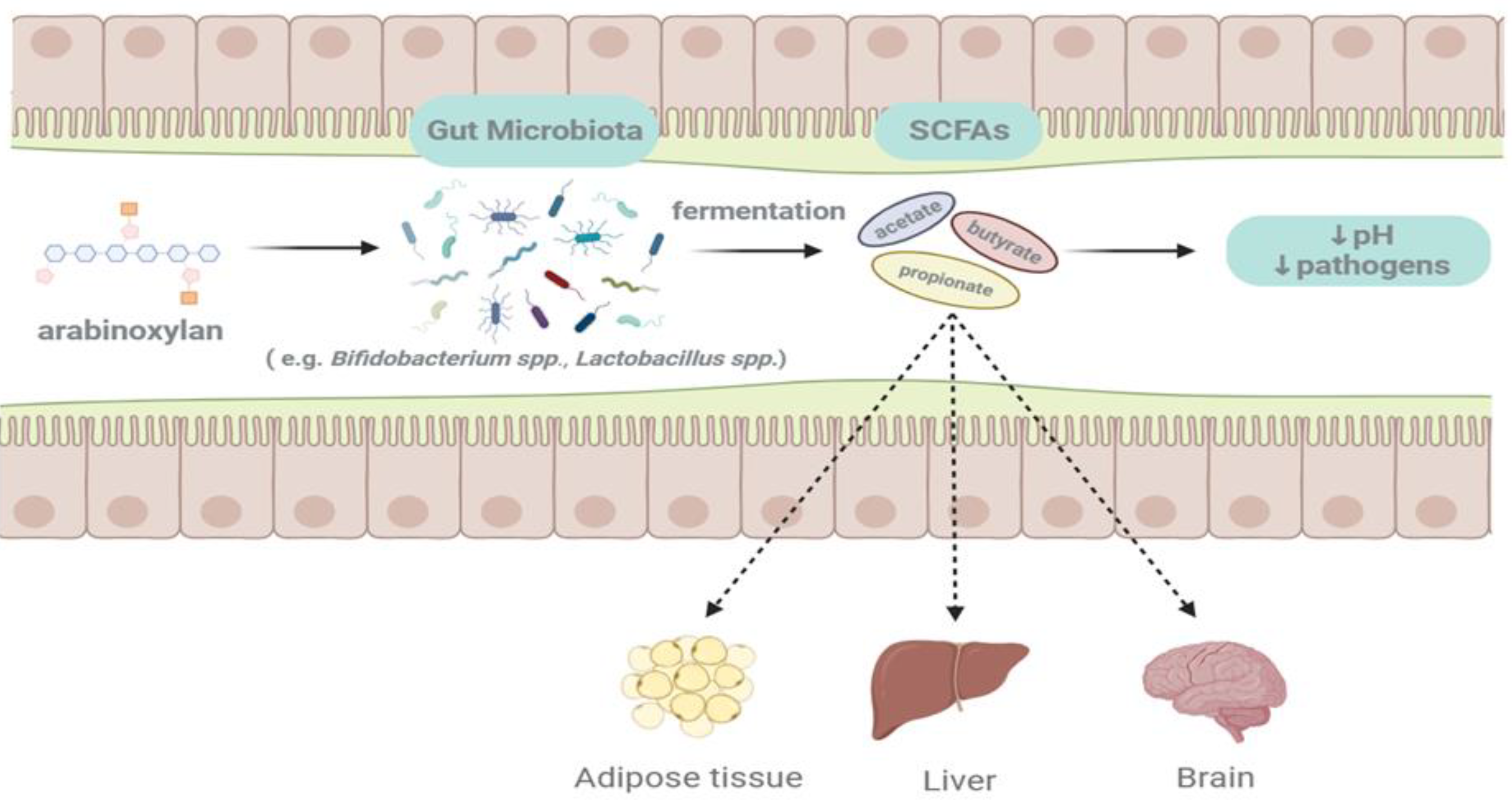
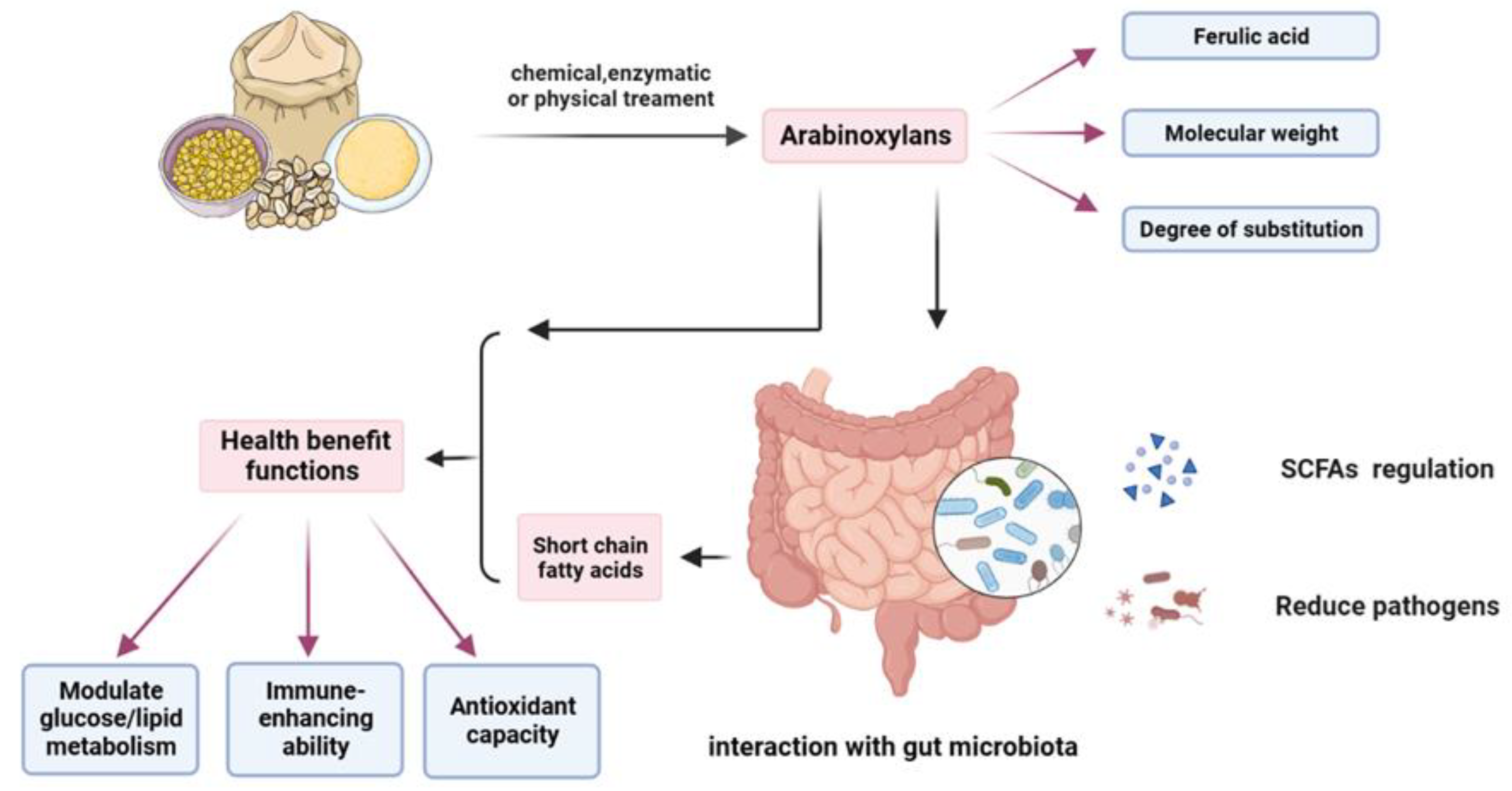
6. Biological Activities of AX from the Perspective of the Gut Health
6.1. Fermentability in the Human Gut
6.2. Improvement of Gut Health
6.3. Alleviation of Metabolic Syndrome by Enhancement of Gut Health
7. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J., Bai, J., Fan, M., Li, T., Li, Y., Qian, H., Wang, L., Zhang, H., Qi, X., & Rao, Z. (2020). Cereal-derived arabinoxylans: Structural features and structure–activity correlations. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 96(C), 157-165. [CrossRef]
- Bakken, T., Braaten, T., Olsen, A., Kyrø, C., Lund, E., & Skeie, G. (2016). Consumption of Whole-Grain Bread and Risk of Colorectal Cancer among Norwegian Women (the NOWAC Study). Nutrients, 8(1), 40. [CrossRef]
- Han, F., Wang, Y., Han, Y., Zhao, J., Han, F., Song, G., Jiang, P., & Miao, H. (2018). Effects of Whole-Grain Rice and Wheat on Composition of Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Rats. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 66(25), 6326-6335. [CrossRef]
- Ullah H, Esposito C, Piccinocchi R, De Lellis LF, Santarcangelo C, Minno AD, Baldi A, Buccato DG, Khan A, Piccinocchi G, Sacchi R, Daglia M. Postprandial Glycemic and Insulinemic Response by a Brewer's Spent Grain Extract-Based Food Supplement in Subjects with Slightly Impaired Glucose Tolerance: A Monocentric, Randomized, Cross-Over, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients. 2022 Sep 21;14(19):3916. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H., Yu, K.-W., Hong, H.-D., & Shin, K.-S. (2017). Effect of arabinoxylan- and rhamnogalacturonan I-rich polysaccharides isolated from young barley leaf on intestinal immunostimulatory activity. Journal of Functional Foods, 35, 384-390. [CrossRef]
- Kyrø, C., Tjønneland, A., Overvad, K., Olsen, A., & Landberg, R. (2018). Higher Whole-Grain Intake Is Associated with Lower Risk of Type 2 Diabetes among Middle-Aged Men and Women: The Danish Diet, Cancer, and Health Cohort. The Journal of Nutrition, 148(9), 1434-1444. [CrossRef]
- Malin, S. K., Kullman, E. L., Scelsi, A. R., Godin, J.-P., Ross, A. B., & Kirwan, J. P. (2019). A Whole-Grain Diet Increases Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion Independent of Gut Hormones in Adults at Risk for Type 2 Diabetes. Molecular nutrition & food research, 63(7), 1800967. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H., Flint, A. J., Qi, Q., Dam, R. M. v., Sampson, L. A., Rimm, E. B., Holmes, M. D., Willett, W. C., Hu, F. B., & Sun, Q. (2015). Association Between Dietary Whole Grain Intake and Risk of Mortality: Two Large Prospective Studies in US Men and Women. JAMA Internal Medicine, 175(3), 373-384. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y., Wan, Q., Feng, J., Du, L., Li, K., & Zhou, Y. (2018). Whole grain diet reduces systemic inflammation: A meta-analysis of 9 randomized trials. Medicine, 97(43), e12995. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y., Yang, J., Du, L., Li, K., & Zhou, Y. (2019). Association of whole grain, refined grain, and cereal consumption with gastric cancer risk: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Food science & nutrition, 7(1), 256-265. [CrossRef]
- Saulnier, L., Sado, P.-E., Branlard, G., Charmet, G., & Guillon, F. (2007). Wheat arabinoxylans: Exploiting variation in amount and composition to develop enhanced varieties. Journal of Cereal Science, 46(3), 261-281. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M., Zhao, Z., Niu, M., Zhao, S., Jia, C., & Wu, Y. (2020). Thermomechanical behaviors and protein polymerization in bread dough modified by bran components and transglutaminase LWT, 133, 109894. [CrossRef]
- Frederix, S. A., Van hoeymissen, K. E., Courtin, C. M., & Delcour, J. A. (2004). Water-extractable and water-unextractable arabinoxylans affect gluten agglomeration behavior during wheat flour gluten-starch separation. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 52(26), 7950-7956. [CrossRef]
- Rumpagaporn, P., Reuhs, B. L., Kaur, A., Patterson, J. A., Keshavarzian, A., & Hamaker, B. R. (2015). Structural features of soluble cereal arabinoxylan fibers associated with a slow rate of in vitro fermentation by human fecal microbiota. Carbohydrate Polymers, 130, 191-197. [CrossRef]
- Lin, S., Agger, J. W., Wilkens, C., & Meyer, A. S. (2021). Feruloylated Arabinoxylan and Oligosaccharides: Chemistry, Nutritional Functions, and Options for Enzymatic Modification. Annual review of food science and technology, 12, 331-354. [CrossRef]
- Döring, C., Hussein, M. A., Jekle, M., & Becker, T. (2017). On the assessments of arabinoxylan localization and enzymatic modifications for enhanced protein networking and its structural impact on rye dough and bread. Food Chemistry. [CrossRef]
- Fadel, A., Mahmoud, A. M., Ashworth, J. J., Li, W., Ng, Y. L., & Plunkett, A. (2018). Health-related effects and improving extractability of cereal arabinoxylans. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 109, 819-831. [CrossRef]
- Fry, S. C. (2004). Primary Cell Wall Metabolism: Tracking the Careers of Wall Polymers in Living Plant Cells. New Phytologist, 161(3), 641-675. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M. P., Kale, M. S., Hicks, K. B., & Hanah, K. (2017). Isolation, characterization and the functional properties of cellulosic arabinoxylan fiber isolated from agricultural processing by-products, agricultural residues and energy crops. Food Hydrocolloids, 63, 545-551. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z., Li, S., Fu, Y., Li, C., Chen, D., & Chen, H. (2019). Arabinoxylan structural characteristics, interaction with gut microbiota and potential health functions. Journal of Functional Foods, 54, 536-551. [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, N. K., & Turner, M. A. (2008). A simplified method for extracting water-extractable arabinoxylans from wheat flour. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 88(11), 1905-1910. [CrossRef]
- Izydorczyk, M. S., & Biliaderis, C. G. (1992). Influence of structure on the physicochemical properties of wheat arabinoxylan. Carbohydrate Polymers, 17(3), 237-247.
- Kurt, G., Emmie, D., Danuta, B., Anna, F., Wioletta, D., Zoltan, B., Mariann, R., A, D. J., & M, C. C. (2008). Variation in the content of dietary fiber and components thereof in wheats in the HEALTHGRAIN Diversity Screen. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 56(21), 9740-9749. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., Smith, C., & Li, W. (2014). Extraction and modification technology of arabinoxylans from cereal by-products: A critical review. Food Research International, 65, 423-436. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y., Li, F., Wang, Y., Li, J., Teng, C., Wang, C., & Li, X. (2019). Effects of different MW water-extractable arabinoxylans on the physicochemical properties and structure of wheat gluten. Journal of food science and technology, 56(1), 340-349. [CrossRef]
- Izydorczyk, M. S., & Biliaderis, C. G. (1995). Cereal arabinoxylans: advances in structure and physicochemical properties. Carbohydrate Polymers, 28(1), 33-48. [CrossRef]
- Nishitsuji, Y., Whitney, K., Nakamura, K., Hayakawa, K., & Simsek, S. (2020b). Changes in structure and solubility of wheat arabinoxylan during the breadmaking process %J Food Hydrocolloids. 109(prepublish).
- Qin, J., Li, R., Raes, J., Arumugam, M., Burgdorf, K. S., Manichanh, C., Nielsen, T., Pons, N., Levenez, F., Yamada, T., Mende, D. R., Li, J., X, J., Li, S., Li, D., Cao, J., Wang, B., Liang, H., Zheng, H., Xie, Y., Tap, J., Lepag, P., Bertalan, M., Batto, J.-M., Consortium, M., & Wang, J. (2010). A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature, 464(7285), 59-65. [CrossRef]
- Emiliano, S. (2014). Microbiome, holobiont and the net of life. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 42(3), 485-494. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z., Zhang, H., He, L., Hou, Y., Che, Y., Liu, T., Xiong, S., Zhang, X., Luo, S., Liu, C., & Chen, T. (2023). Influence of structural features and feruloylation on fermentability and ability to modulate gut microbiota of arabinoxylan in in vitro fermentation. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13, 1113601. [CrossRef]
- Paesani, C., Sciarini, L. S., Moiraghi, M., Salvucci, E., Prado, S. B. R., & P, G. T. (2020). Human colonic in vitro fermentation of water-soluble arabinoxylans from hard and soft wheat alters Bifidobacterium abundance and short-chain fatty acids concentration. LWT, 134, 110253. [CrossRef]
- Valerie, V. C., Katrien, S., Emmie, D., Tom, V. d. W., Massimo, M., Willy, V., Yasmine, D., Okanlawon, O., Eddy, D., Johan, B., Bart, D. K., F, B. W., A, D. J., & M, C. C. (2008). Structurally different wheat-derived arabinoxylooligosaccharides have different prebiotic and fermentation properties in rats. The Journal of Nutrition, 138(12), 2348-2355. [CrossRef]
- Chateigner-Boutin. (2016). Developing Pericarp of Maize: A Model to Study Arabinoxylan Synthesis and Feruloylation. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 1476. [CrossRef]
- Broekaert, W. F., Courtin, C. M., Verbeke, K., Wiele, T. V. d., Verstraete, W., & Delcour, J. A. (2011). Prebiotic and other health-related effects of cereal-derived arabinoxylans, arabinoxylan-oligosaccharides, and xylooligosaccharides. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 51(2), 178-194. [CrossRef]
- Escarnot, E., Aguedo, M., Agneessens, R., Wathelet, B., & Paquot, M. (2011). Extraction and characterization of water-extractable and water-unextractable arabinoxylans from spelt bran: Study of the hydrolysis conditions for monosaccharides analysis. Journal of Cereal Science, 53(1), 45-52. [CrossRef]
- Niño-Medina, G., Carvajal-Millán, E., Rascon-Chu, A., Marquez-Escalante, J. A., Guerrero, V., & Salas-Muñoz, E. (2010). Feruloylated arabinoxylans and arabinoxylan gels: structure, sources and applications. Phytochemistry Reviews, 9(1), 111-120. [CrossRef]
- Buksa, K., Nowotna, A., Ziobro, R., & Praznik, W. (2014). Molecular properties of arabinoxylan fractions isolated from rye grain of different quality. Journal of Cereal Science, 60(2), 368-373. [CrossRef]
- Revanappa, S. B., Nandini, C. D., & Salimath, P. V. (2015). Structural variations of arabinoxylans extracted from different wheat ( Triticum aestivum ) cultivars in relation to chapati -quality. Food Hydrocolloids, 43, 736-742. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y., Cui, S. W., Gu, X., & Zhang, J. (2011). Isolation and structural characterization of water unextractable arabinoxylans from Chinese black-grained wheat bran. Carbohydrate Polymers, 85(3), 615-621. [CrossRef]
- Tian, L., Gruppen, H., & Schols, H. A. (2015). Characterization of (Glucurono)arabinoxylans from Oats Using Enzymatic Fingerprinting. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 63(50), 10822-10830. [CrossRef]
- Pang, J., Zhang, Y., Tong, X., Zhong, Y., Kong, F., Li, D., Liu, X., & Qiao, Y. (2023). Recent Developments in Molecular Characterization, Bioactivity, and Application of Arabinoxylans from Different Sources. Polymers, 15(1), 225. [CrossRef]
- Koegelenberg, D., & Chimphango, A. F. A. (2017). Effects of wheat-bran arabinoxylan as partial flour replacer on bread properties Food Chemistry, 221, 1606-1613. [CrossRef]
- Casas, G. A., Lærke, H. N., Knudsen, K. E. B., & Stein, H. H. (2018). Arabinoxylan is the main polysaccharide in fiber from rice coproducts, and increased concentration of fiber decreases in vitro digestibility of dry matter. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 247, 255-261. [CrossRef]
- Guo, R., Xu, Z., Wu, S., Li, X., Li, J., Hu, H., Wu, Y., & Ai, L. (2019). Molecular properties and structural characterization of an alkaline extractable arabinoxylan from hull-less barley bran. Carbohydrate Polymers, 218, 250-260. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Xie, J., Chen, T., Ma, D., Yao, T., Gu, F., Lim, J., Tuinstra, M. R., & Hamaker, B. R. (2021). High Arabinoxylan Fine Structure Specificity to Gut Bacteria Driven by Corn Genotypes but not Environment. Carbohydrate Polymers, 257, 117667. [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-Y. (2000). Structural characteristics of arabinoxylan in barley, malt, and beer. Food Chemistry, 70(2), 131-138. [CrossRef]
- Rao, R. S. P., & Muralikrishna, G. (2007). Structural characteristics of water-soluble feruloyl arabinoxylans from rice ( Oryza sativa ) and ragi (finger millet, Eleusine coracana ): Variations upon malting. Food Chemistry, 104(3), 1160-1170. [CrossRef]
- Höije, A., Sandström, C., Roubroeks, J. P., Andersson, R., Gohil, S., & Gatenholm, P. (2006). Evidence of the presence of 2-O-β-d-xylopyranosyl-α-l-arabinofuranose side chains in barley husk arabinoxylan. Carbohydrate Research, 341(18), 2959-2966. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q., Xiao, X., Li, C., Kang, J., Liu, G., Douglas, G. H., & Wang, C. (2021). Catechin-grafted arabinoxylan conjugate: Preparation, structural characterization and property investigation. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 182, 796-805. [CrossRef]
- Anna, E., Zdenka, H., Eva, P., & Miloš, H. (1990). Structural features of a water-soluble l-arabino-d-xylan from rye bran. Carbohydrate Research, 198(1), 57-66. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., & Yang, C. (2016). Synthesis and properties of feruloyl corn bran arabinoxylan esters. International journal of cosmetic science, 38(3), 238-245. [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, M. F., Kroon, P. A., Williamson, G., & Garcia-Conesa, M. T. (2001). Esterase activity able to hydrolyze dietary antioxidant hydroxycinnamates is distributed along the intestine of mammals. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 49(11), 5679-5684. [CrossRef]
- Veenashri, B. R., & Muralikrishna, G. (2011a). In vitro anti-oxidant activity of xylo-oligosaccharides derived from cereal and millet brans – A comparative study. Food Chemistry, 126(3), 1475-1481. [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A., Aruldhas, J., Perumal, S. S., & Ekambaram, S. P. (2020). Phenolic acid bound arabinoxylans extracted from Little and Kodo millets modulate immune system mediators and pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 45(1), e13563. [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A., Ekambaram, S. P., Perumal, S. S., Aruldhas, J., & Erusappan, T. (2019). Chemical characterization and immunostimulatory activity of phenolic acid bound arabinoxylans derived from foxtail and barnyard millets. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 44(2), e13116. [CrossRef]
- Bijalwan, V., Ali, U., Kesarwani, A. K., Yadav, K., & Mazumder, K. (2016). Hydroxycinnamic acid bound arabinoxylans from millet brans-structural features and antioxidant activity. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 88, 296-305. [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Soto, F. E., Serna-Saldívar, S. O., Welti-Chanes, J., & Gutierrez-Uribe, J. A. (2015). Phenolic compounds, antioxidant capacity and gelling properties of glucoarabinoxylans from three types of sorghum brans. Journal of Cereal Science, 65, 277-284. [CrossRef]
- He, H.-J., Qiao, J., Liu, Y., Guo, Q., Ou, X., & Wang, X. (2021). Isolation, Structural, Functional, and Bioactive Properties of Cereal Arabinoxylan─A Critical Review. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 69(51), 15437-15457. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Liang, R., & Yang, C. (2017). Synthesis and antioxidant properties of caffeic acid corn bran arabinoxylan esters. International journal of cosmetic science, 39(4), 402-410. [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Soto, F. E., Serna-Saldívar, S. O., García-Lara, S., & Pérez-Carrillo, E. (2014). Hydroxycinnamic acids, sugar composition and antioxidant capacity of arabinoxylans extracted from different maize fiber sources. Food Hydrocolloids, 35, 471-475. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C., & Simsek, S. (2019). A novel combination of methods for the extraction and purification of arabinoxylan from byproducts of the cereal industry Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 13(2), 1049-1057. [CrossRef]
- Petit-Benvegnen, M. D., Saulnier, L., & Rouau, X. (1998). Solubilization of Arabinoxylans from Isolated Water-Unextractable Pentosans and Wheat Flour Doughs by Cell-Wall-Degrading Enzymes. Cereal Chemistry, 75(4), 551-556. [CrossRef]
- Ruthes, A. C., Martínez-Abad, A., Tan, H.-T., Bulone, V., & Vilaplana, F. (2017). Sequential fractionation of feruloylated hemicelluloses and oligosaccharides from wheat bran using subcritical water and xylanolytic enzymes. Green Chemistry, 19(8), 1919-1931. [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz-Turan, S., Jiménez-Quero, A., Menzel, C., Carvalho, D. M. d., Lindström, M. E., Sevastyanova, O., Moriana, R., & Vilaplana, F. (2020). Bio-based films from wheat bran feruloylated arabinoxylan: Effect of extraction technique, acetylation and feruloylation Carbohydrate Polymers, 250, 116916. [CrossRef]
- Hollmann, J., & Lindhauer, M. G. (2004). Pilot-scale isolation of glucuronoarabinoxylans from wheat bran. Carbohydrate Polymers, 59(2), 225-230. [CrossRef]
- Ruthes, A. C., Rudjito, R. C., Rencoret, J., Gutiérrez, A., Río, J. C. d., Jiménez-Quero, A., & Vilaplana, F. (2020). Comparative Recalcitrance and Extractability of Cell Wall Polysaccharides from Cereal (Wheat, Rye, and Barley) Brans Using Subcritical Water ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 8(18), 7192-7204. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S., Liu, X., Guo, Y., Wang, Q., Peng, D., & Cao, L. (2010). Comparison of the immunological activities of arabinoxylans from wheat bran with alkali and xylanase-aided extraction. Carbohydrate Polymers, 81(4), 784-789. [CrossRef]
- Kale, M. S., Yadav, M. P., Hicks, K. B., & Hanah, K. (2015). Concentration and shear rate dependence of solution viscosity for arabinoxylans from different sources. Food Hydrocolloids, 47, 178-183. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D. P., Maire, d. P. A., Anja, L., Anette, L., Anna, S., & Gunnar, W. (2021). Oxidation Level and Glycidyl Ether Structure Determine Thermal Processability and Thermomechanical Properties of Arabinoxylan-Derived Thermoplastics ACS APPLIED BIO MATERIALS, 4(4), 3133-3144. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Zheng, X., & Li, L. (2011). Molecular Characterization of Arabinoxylans from Hull-Less Barley Milling Fractions. Molecules, 16(4), 2743-2753. [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Y., Wang, Y. X., Zhang, T., Zhang, J. F., Pan, M., Huang, X. J., Yin, J. Y., & Nie, S. P. (2020). Structural characteristics and rheological properties of alkali-extracted arabinoxylan from dehulled barley kernel. Carbohydrate Polymers, 249, 116813. [CrossRef]
- Takoudjou, M. A.-P., Gudipati, M., Bargui, K. B., & Germain, K. (2021). Purification and structural characterization of calcium hydroxide isolated arabinoxylans derived from bran, spent grain and sorghum grains. Journal of Cereal Science, 100, 103266. [CrossRef]
- Yan, J., Jia, X., Feng, L., Yadav, M., Li, X., & Yin, L. (2019). Rheological and emulsifying properties of arabinoxylans from various cereal brans Journal of Cereal Science, 90(C), 102844. [CrossRef]
- Li, S., Chen, H., Cheng, W., Yang, K., Cai, L., He, L., Du, L., Liu, Y., Liu, A., Zeng, Z., & Li, C. (2021). Impact of arabinoxylan on characteristics, stability and lipid oxidation of oil-in-water emulsions: Arabinoxylan from wheat bran, corn bran, rice bran, and rye bran Food Chemistry, 358, 129813. [CrossRef]
- Pihlajaniemi, V., Mattila, O., Koitto, T., Nikinmaa, M., Heiniö, R.-L., Sorsamäki, L., Siika-aho, M., & Nordlund, E. (2020). Production of syrup rich in arabinoxylan oligomers and antioxidants from wheat bran by alkaline pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis, and applicability in baking Journal of Cereal Science, 95, 103043. [CrossRef]
- Gruppen, H., Kormelink, F. J. M., & Voragen, A. G. J. (1993). Water-unextractable Cell Wall Material from Wheat Flour. 3. A Structural Model for Arabinoxylans. Journal of Cereal Science, 18(2), 111-128. [CrossRef]
- Buksa, K., Nowotna, A., & Ziobro, R. (2016). Application of cross-linked and hydrolyzed arabinoxylans in baking of model rye bread Food Chemistry, 192, 991-996. [CrossRef]
- Aguedo, M., Fougnies, C., Dermience, M., & Richel, A. (2014). Extraction by three processes of arabinoxylans from wheat bran and characterization of the fractions obtained. Carbohydrate Polymers, 105, 317-324. [CrossRef]
- Denisse, B., Renata, N., Michaela, W., Sylvia, G., Matilde, B., Kitti, T., Sandor, T., Stefano, D. A., & Regine, S. (2017). Optimization of Arabinoxylan Isolation from Rye Bran by Adapting Extraction Solvent and Use of Enzymes. Journal of food science, 82(11), 2562-2568. [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S., Karlsson, E. N., & Adlercreutz, P. (2017). Extraction of soluble arabinoxylan from enzymatically pretreated wheat bran and production of short xylo-oligosaccharides and arabinoxylo-oligosaccharides from arabinoxylan by glycoside hydrolase family 10 and 11 endoxylanases. Journal of Biotechnology, 260, 53-61. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S., Li, W., Smith, C. J., & Musa, H. (2015). Cereal-derived arabinoxylans as biological response modifiers: extraction, molecular features, and immune-stimulating properties. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 55(8), 1035-1052. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Sun, B., Liu, Y., & Zhang, H. (2014). Optimisation of ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction of arabinoxylan from wheat bran. Food Chemistry, 150, 482-488. [CrossRef]
- Ordaz-Ortiz, J. J., & Saulnier, L. (2005). Structural variability of arabinoxylans from wheat flour. Comparison of water-extractable and xylanase-extractable arabinoxylans. Journal of Cereal Science, 42(1), 119-125. [CrossRef]
- Ma, F., Li, X., Yin, J., Ma, L., & Li, D. (2020). Optimisation of double-enzymatic extraction of arabinoxylan from fresh corn fibre. Journal of food science and technology, 57(12), 4649-4659. [CrossRef]
- Clemens, D., Mario, J., & Thomas, B. (2016). Technological and Analytical Methods for Arabinoxylan Quantification from Cereals. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 56(6), 999-1011. [CrossRef]
- Benamrouche, S., Crônier, D., Debeire, P., & Chabbert, B. (2002). A Chemical and Histological Study on the Effect of (1→4)-β-endo-xylanase Treatment on Wheat Bran. Journal of Cereal Science, 36(2), 253-260. [CrossRef]
- Dornez, E., Gebruers, K., Delcour, J. A., & Courtin, C. M. (2009). Grain-associated xylanases: occurrence, variability, and implications for cereal processing. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 20(11), 495-510. [CrossRef]
- Courtin, C. M., & Delcour, J. A. (2002). Arabinoxylans and Endoxylanases in Wheat Flour Bread-making. Journal of Cereal Science, 35(3), 225-243. [CrossRef]
- Verwimp, T., Craeyveld, V. V., Courtin, C. M., & Delcour, J. A. (2007). Variability in the structure of rye flour alkali-extractable arabinoxylans. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 55(5), 1985-1992. [CrossRef]
- Kale, M. S., Yadav, M. P., Chau, H. K., & Hotchkiss, A. T. (2018). Molecular and functional properties of a xylanase hydrolysate of corn bran arabinoxylan. Carbohydrate Polymers, 181, 119-123. [CrossRef]
- Li, W., Zhang, S., & Smith, C. (2015). The molecular structure features-immune stimulatory activity of arabinoxylans derived from the pentosan faction of wheat flour. Journal of Cereal Science, 62, 81-86. [CrossRef]
- Yuwang, P., Sulaeva, I., Hell, J., Henniges, U., Böhmdorfer, S., Rosenau, T., Chitsomboon, B., & Tongta, S. (2017). Phenolic compounds and antioxidant properties of arabinoxylan hydrolysates from defatted rice bran. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 98(1), 140-146. [CrossRef]
- Maes, C., Vangeneugden, B., & Delcour, J. A. (2004). Relative activity of two endoxylanases towards water-unextractable arabinoxylans in wheat bran. Journal of Cereal Science, 39(2), 181-186. [CrossRef]
- Marilù, D., Mattia, Q., Giovanni, R., Grazia, F. M., Milena, B., Tiziana, S., Federica, M., Daniela, E., Franca, C., & Cristina, C. M. (2017). Evaluation of microbial consortia and chemical changes in spontaneous maize bran fermentation. . AMB Express, 7(1), 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Hell, J., Donaldson, L., Michlmayr, H., Kraler, M., Kneifel, W., Potthast, A., Rosenau, T., & Böhmdorfer, S. (2015). Effect of pretreatment on arabinoxylan distribution in wheat bran. Carbohydrate Polymers, 121, 18-26. [CrossRef]
- Jakovetić, T. S., Nataša, Š., Jelena, J., Ivana, G., Sanja, G., Nikola, Đ., Vukašinović, S. M., Jian, H., Nevena, L., & Zorica, K. J. (2020). Upgrading of valuable food component contents and anti-nutritional factors depletion by solid-state fermentation: A way to valorize wheat bran for nutrition Journal of Cereal Science, 99, 103159. [CrossRef]
- Kiszonas, A. M., Fuerst, E. P., Luthria, D., & Morris, C. F. (2015). Arabinoxylan content and characterisation throughout the bread-baking process. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 50(8), 1911-1921. [CrossRef]
- Nishitsuji, Y., Whitney, K., Nakamura, K., Hayakawa, K., & Simsek, S. (2020a). Changes in structure and solubility of wheat arabinoxylan during the breadmaking process. Food Hydrocolloids, 109, 106129. [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K. M., Strain, C. R., Johnson, C., Patangia, D., Stanton, C., Koc, F., Gil-Martinez, J., O’Riordan, P., Sahin, A. W., Ross, R. P., & Arendt, E. K. (2021). Extraction and characterisation of arabinoxylan from brewers spent grain and investigation of microbiome modulation potential. . European journal of nutrition, 60(8), 4393-4411. [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Ramirez, J. G., Vasquez-Lara, F., Vasquez-Lara, F., Scholar, S. o., Sanchez-Estrada, A., Troncoso-Rojas, R., Heredia-Olea, E., & Islas-Rubio, A. R. (2022). Arabinoxylans Release from Brewers’ Spent Grain Using Extrusion and Solid-State Fermentation with Fusarium oxysporum and the Antioxidant Capacity of the Extracts Foods, 11(10), 1415. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M., Vliet, T. v., & Hamer, R. J. (2004). How gluten properties are affected by pentosans. Journal of Cereal Science, 39(3), 395-402. [CrossRef]
- Si, X., Li, T., Zhang, Y., Zhang, W., Qian, H., Li, Y., Zhang, H., Qi, X., & Wang, L. (2021). Interactions between gluten and water-unextractable arabinoxylan during the thermal treatment. Food Chemistry, 345, 128785. [CrossRef]
- Verjans, P., Dornez, E., Delcour, J. A., & Courtin, C. M. (2010). Selectivity for water-unextractable arabinoxylan and inhibition sensitivity govern the strong bread improving potential of an acidophilic GH11 Aureobasidium pullulans xylanase. Food Chemistry, 123(2), 331-337. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z., Liu, L., Yang, W., Ding, L., Awais, M., Wang, L., & Zhou, S. (2018). Improving the physicochemical properties of whole wheat model dough by modifying the water-unextractable solids. Food Chemistry, 259, 18-24. [CrossRef]
- Sun, J., Si, X., Li, T., Zhao, J., Qian, H., Li, Y., Zhang, H., Qi, X., & Wang, L. (2022). The Influence of Water-Unextractable Arabinoxylan and Its Hydrolysates on the Aggregation and Structure of Gluten Proteins. Frontiers in Nutrition, 9, 877135. [CrossRef]
- Arif, S., Ahmed, M., Chaudhry, Q., & Hasnain, A. (2018). Effects of water extractable and unextractable pentosans on dough and bread properties of hard wheat cultivars. LWT, 97, 736-742. [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Ramírez, J., Garzon, R., Serna-Saldivar, S. O., & Rosell, C. M. (2020). Exploring the potential of arabinoxylan as structuring agent in model systems for gluten-free yeast-leavened breads Journal of Cereal Science, 95, 103080. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Boven, A. v., Mulder, J., Grandia, J., Chen, X. D., Boom, R. M., & Schutyser, M. A. I. (2019). Arabinoxylans-enriched fractions: From dry fractionation of wheat bran to the investigation on bread baking performance Journal of Cereal Science, 87, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Yang, M., Yue, Y., Liu, L., Tong, L., Wang, L., Ashraf, J., Li, N., Zhou, X., & Zhou, S. (2021). Investigation of combined effects of xylanase and glucose oxidase in whole wheat buns making based on reconstituted model dough system. LWT, 135, 110261. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A., Yadav, M. P., Singh, B., Bhinder, S., Simon, S., & Singh, N. (2019). Isolation and characterization of arabinoxylans from wheat bran and study of their contribution to wheat flour dough rheology Carbohydrate Polymers, 221, 166-173. [CrossRef]
- Pavlovich-Abril, A., Rouzaud-Sández, O., Carvajal-Millán, E., Navarro, R. E., Robles-Sánchez, R. M., & Barrón-Hoyos, J. M. (2016). Molecular characterization of water extractable arabinoxylans isolated from wheat fine bran and their effect on dough viscosity LWT - Food Science and Technology, 74, 484-492. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X. N., Yang, S., & Zhu, K. X. (2018). Impact of arabinoxylan with different MW on the thermo-mechanical, rheological, water mobility and microstructural characteristics of wheat dough International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 53(9), 2150-2158. [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J. R., Lawrence, G. J., Larroque, O., Li, Z., Laidlaw, H. K., Morell, M. K., & Rahman, S. (2011). A survey of β-glucan and arabinoxylan content in wheat. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 91(7), 1298-1303. [CrossRef]
- Janssen, F., Wouters, A. G. B., Meeus, Y., Moldenaers, P., Vermant, J., & Delcour, J. A. (2020). The role of non-starch polysaccharides in determining the air-water interfacial properties of wheat, rye, and oat dough liquor constituents Food Hydrocolloids, 105(C), 105771. [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, G., Shivhare, U. S., & Banerjee, U. C. (2013). Effect of Xylanase on Quality Attributes of Whole-wheat bread. Journal of Food Quality, 36(3), 172-180. [CrossRef]
- Mendis, M., Leclerc, E., & Simsek, S. (2016). Arabinoxylans, gut microbiota and immunity Carbohydrate Polymers, 139, 159-166. [CrossRef]
- Damen, B., Verspreet, J., Pollet, A., Broekaert, W. F., Delcour, J. A., & Courtin, C. M. (2011). Prebiotic effects and intestinal fermentation of cereal arabinoxylans and arabinoxylan oligosaccharides in rats depend strongly on their structural properties and joint presence. . Molecular nutrition & food research, 55(12), 1862-1874. [CrossRef]
- Rose, D. J., Patterson, J. A., & Hamaker, B. R. (2010). Structural differences among alkali-soluble arabinoxylans from maize (Zea mays), rice (Oryza sativa), and wheat (Triticum aestivum) brans influence human fecal fermentation profiles. . Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 58(1), 493-499. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H., Reuhs, B. L., Cantu-Jungles, T. M., Tuncil, Y. E., Kaur, A., Terekhov, A., Martens, E. C., & Hamaker, B. R. (2022). Corn arabinoxylan has a repeating structure of subunits of high branch complexity with slow gut microbiota fermentation Carbohydrate Polymers, 289, 119435. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T., Long, W., Zhang, C., Liu, S., Zhao, L., & Hamaker, B. R. (2017). Fiber-utilizing capacity varies in Prevotella- versus Bacteroides-dominated gut microbiota. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 2594. [CrossRef]
- Yao, T., Deemer, D. G., Chen, M.-H., Reuhs, B. L., Hamaker, B. R., & Lindemann, S. R. (2023). Differences in fine arabinoxylan structures govern microbial selection and competition among human gut microbiota. Carbohydrate Polymers, 316, 121039. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, A. L., Carvajal-Millan, E., Canett-Romero, R., Prakash, S., Rascón-Chu, A., López-Franco, Y. L., Lizardi-Mendoza, J., & Micard, V. (2022). Arabinoxylans-Based Oral Insulin Delivery System Targeting the Colon: Simulation in a Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem and Evaluation in Diabetic Rats. Pharmaceuticals, 15(9), 1062. [CrossRef]
- Emily, S., Sok Cheon, P., Shaoyu, W., Peter, S. M., Thomas, J., Soo Liang, O., Terry, G., Garth, H., & Emad, E.-O. (2021). The effects and benefits of arabinoxylans on human gut microbiota – A narrative review. Food Bioscience, 101267. [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A. M., Possemiers, S., Druart, C., Wiele, T. V. d., Backer, F. D., Cani, P. D., Larondelle, Y., & Delzenne, N. M. (2011). Prebiotic effects of wheat arabinoxylan related to the increase in bifidobacteria, Roseburia and Bacteroides/Prevotella in diet-induced obese mice. . PloS one, 6(6), e20944. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N. K., Deehan, E. C., Zhang, Z., Jin, M., Baskota, N., Perez-Muñoz, M. E., Cole, J., Tuncil, Y. E., Seethaler, B., Wang, T., Laville, M., Delzenne, N. M., Bischoff, S. C., Hamaker, B. R., Martínez, I., Knights, D., Bakal, J. A., Prado, C. M., & Walter, J. (2020). Gut microbiota modulation with long-chain corn bran arabinoxylan in adults with overweight and obesity is linked to an individualized temporal increase in fecal propionate. . Microbiome, 8(1), 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Truchado, P., Hernandez-Sanabria, E., Salden, B. N., Abbeele, P. V. d., Vilchez-Vargas, R., Jauregui, R., Pieper, D. H., Possemiers, S., & Wiele, T. V. d. (2017). Long chain arabinoxylans shift the mucosa-associated microbiota in the proximal colon of the simulator of the human intestinal microbial ecosystem (M-SHIME) Journal of Functional Foods, 32, 226-237. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L. (2013). The gut microbiota and obesity: from correlation to causality. . Nature reviews. Microbiology, 11(9), 639-647. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L., Zhang, F., Ding, X., Wu, G., Lam, Y. Y., Wang, X., Fu, H., Xue, X., Lu, C., Ma, J., Yu, L., Xu, C., Ren, Z., Xu, Y., Xu, S., Shen, H., Zhu, X., Shi, Y., Shen, Q., Dong, W., Liu, R., Ling, Y., Zeng, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, Q., Wang, J., Wang, L., Wu, Y., Zeng, B., Wei, H., Zhang, M., Peng, Y., & Zhang, C. (2018). Gut bacteria selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes. Science, 359(6380), 1151-1156. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H., Cheng, J., Zhou, S., Chen, D., Qin, W., Li, C., Li, H., Lin, D., Zhang, Q., Liu, Y., Liu, A., & Luo, Y. (2021). Arabinoxylan combined with different glucans improve lipid metabolism disorder by regulating bile acid and gut microbiota in mice fed with high-fat diet International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 168, 279-288. [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.-T., Zhong, K., Liu, L., Qiu, J., Guo, L., Zhou, X., Cao, L., & Zhou, S. (2014). Effects of dietary wheat bran arabinoxylans on cholesterol metabolism of hypercholesterolemic hamsters Carbohydrate Polymers, 112, 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Luo, S., He, L., Zhang, H., Li, Z., Liu, C., & Chen, T. (2022). Arabinoxylan from rice bran protects mice against high-fat diet-induced obesity and metabolic inflammation by modulating gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids. . Food & function, 13(14), 7707-7719. [CrossRef]
- Li, S., Sun, Y., Hu, X., Qin, W., Li, C., Liu, Y., Liu, A., Zhao, Y., Wu, D., Lin, D., Zhang, Q., Chen, D., & Chen, H. (2019). Effect of arabinoxylan on colonic bacterial metabolites and mucosal barrier in high-fat diet-induced rats. Food science & nutrition, 7(9), 3052-3061. [CrossRef]
| Source | Extraction | MW/kDa | A/X | Reference |
| Wheat bran | NaOH | 351.7 | 0.83 | [67] |
| Wheat bran | NaOH and Ca (OH)2 | 437 | 1.14 | [68] |
| Wheat bran | NaOH | 694 | 0.95 | [49] |
| Wheat bran | NaOH | 770 | 0.51 | [61] |
| Wheat bran | NaOH | 163 | 0.77 | [69] |
| Barley bran | NaOH | 298.36 | 0.58 | [44] |
| Barley endosperm | NaOH | 877.1 | 0.76 | [70] |
| Peeled barley seeds | Ba (OH)2 | 1360 | 0.60 | [71] |
| Sorghum seeds | Ca (OH)2 | 223.9 | 1.09 | [72] |
| Red sorghum bran | NaOH | 356 | 1.1 | [73] |
| White sorghum bran | NaOH | 136.2 | 1.08 | [73] |
| Oat grain | NaOH | 100 | 0.11 | [40] |
| Corn bran | NaOH | 360 | 0.47 | [14] |
| Corn bran | NaOH | 590 | 0.51 | [61] |
| Corn bran | NaOH and Ca (OH)2 | 233.3 | 0.76 | [74] |
| Rye bran | Ba (OH)2 | 381 | 0.6 | [39] |
| Rye bran | NaOH and Ca (OH)2 | 234.9 | 0.72 | [74] |
| Source | Extraction | MW/kDa | A/X | Reference |
| Wheat bran | Xylanase | / | 0.44 | [80] |
| Wheat bran | Endo-xylanase | 1-25 (85.7%) 25-700(14.3%) |
0.81 | [91] |
| Wheat bran | Endo-xylanase | 12.5 | 0.73 | [78] |
| Wheat bran | Endo-xylanase | 420 | 1.14 | [14] |
| Corn bran | Xylanase | 51.6- 132 | / | [90] |
| Corn bran | Endo-xylanase | 43 | 0.54 | [14] |
| Rice bran | Endo-xylanase | 23 | 0.97 | [14] |
| Rice bran | Xylanase | 57.9 | 0.29 | [92] |
| Rice bran | Xylanase | 41.4 | 0.3 | [92] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





