Submitted:
31 May 2024
Posted:
31 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Flat CDM Model
2.2. CDM Model with Free Spatial Curvature
2.3. Flat Constant wCDM model
2.4. Phenomenological Emergent Dark Energy (PEDE) Model
3. Data and Methodology
4. Analysis and Results
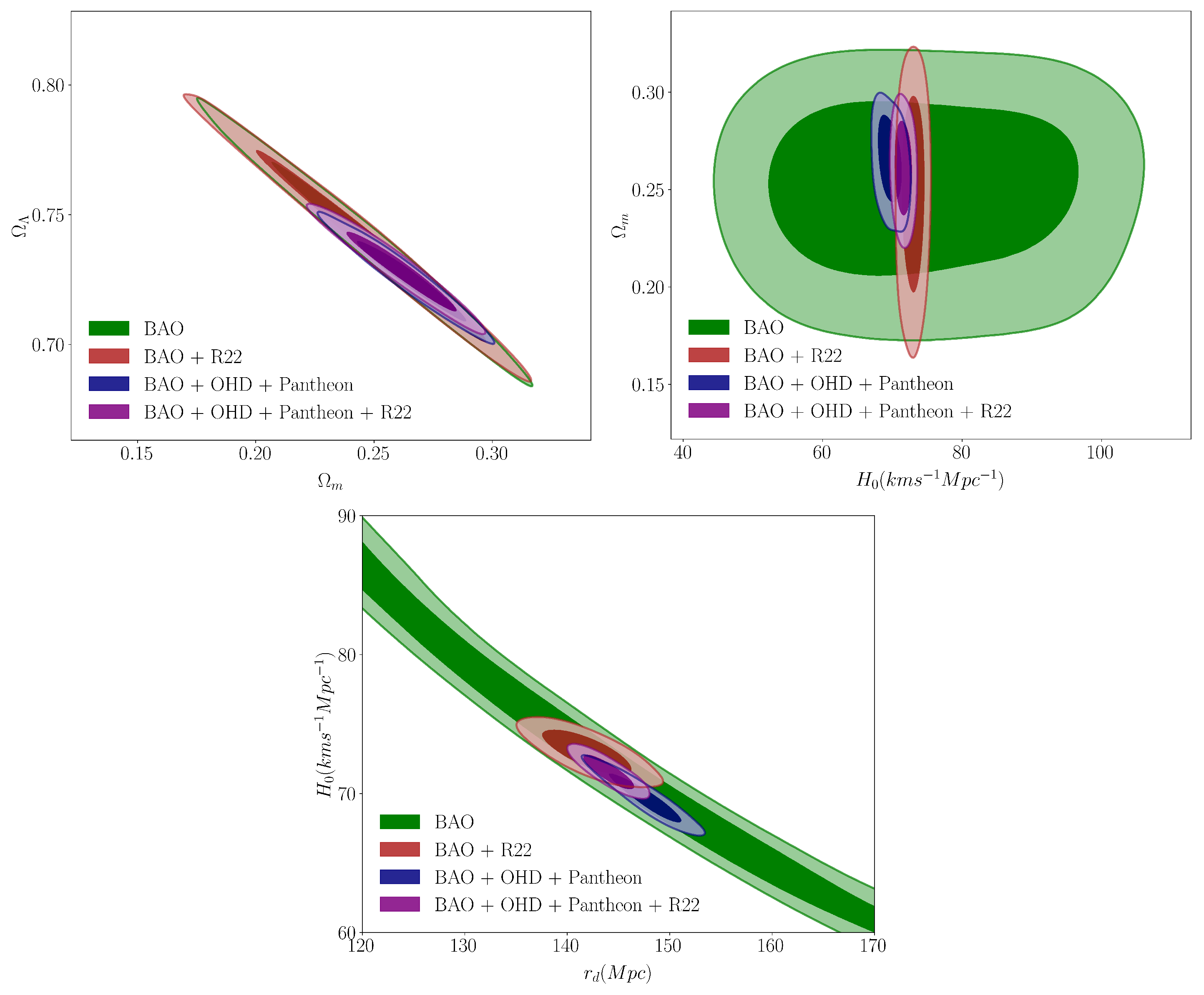
4.1. Flat CDM Model
| Parameter | BAO + R22 | BAO + OHD + Pantheon | BAO + OHD + Pantheon + R22 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (km s−1 Mpc−1) | 72.98 ± 1.07 | 69.65 ± 1.07 | 71.55 ± 0.78 |
| 0.248 ± 0.033 | 0.265 ± 0.014 | 0.261 ± 0.014 | |
| 0.738 ± 0.023 | 0.725 ± 0.010 | 0.728 ± 0.010 | |
| (Mpc) | 142.00 ± 2.76 | 147.71 ± 2.18 | 144.04 ± 1.58 |
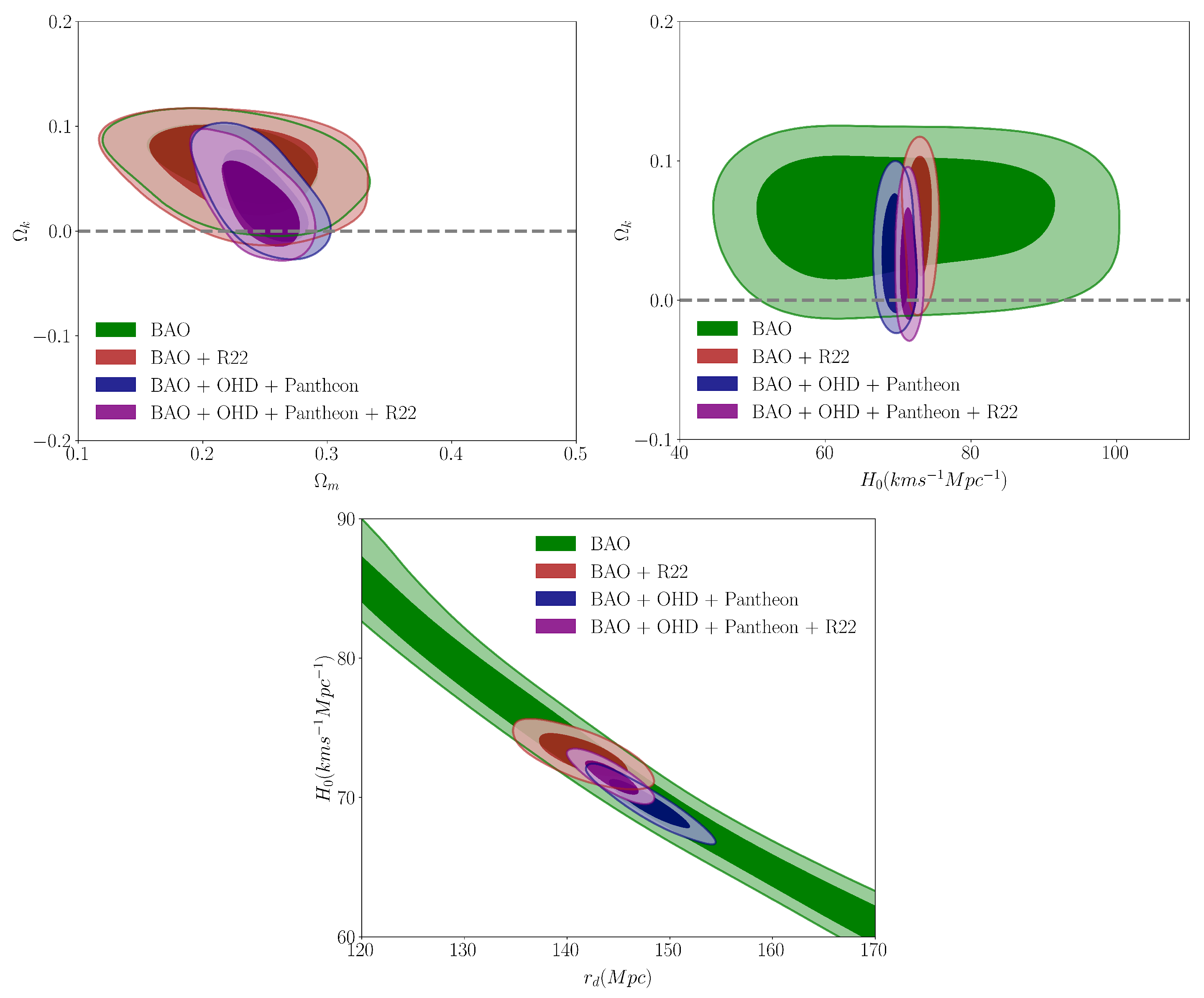
4.2. CDM Model with Free Curvature
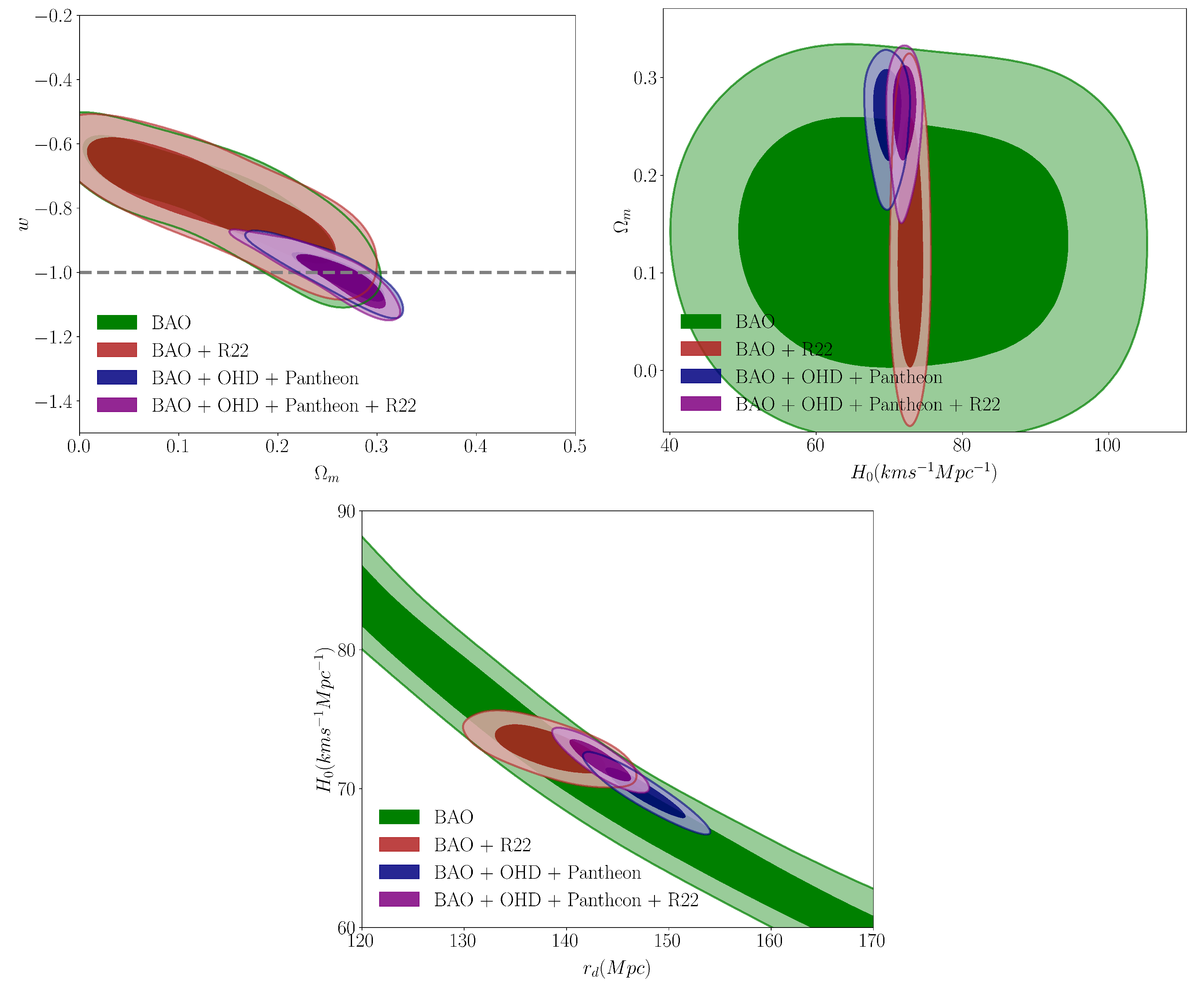
4.3. Flat wCDM Model
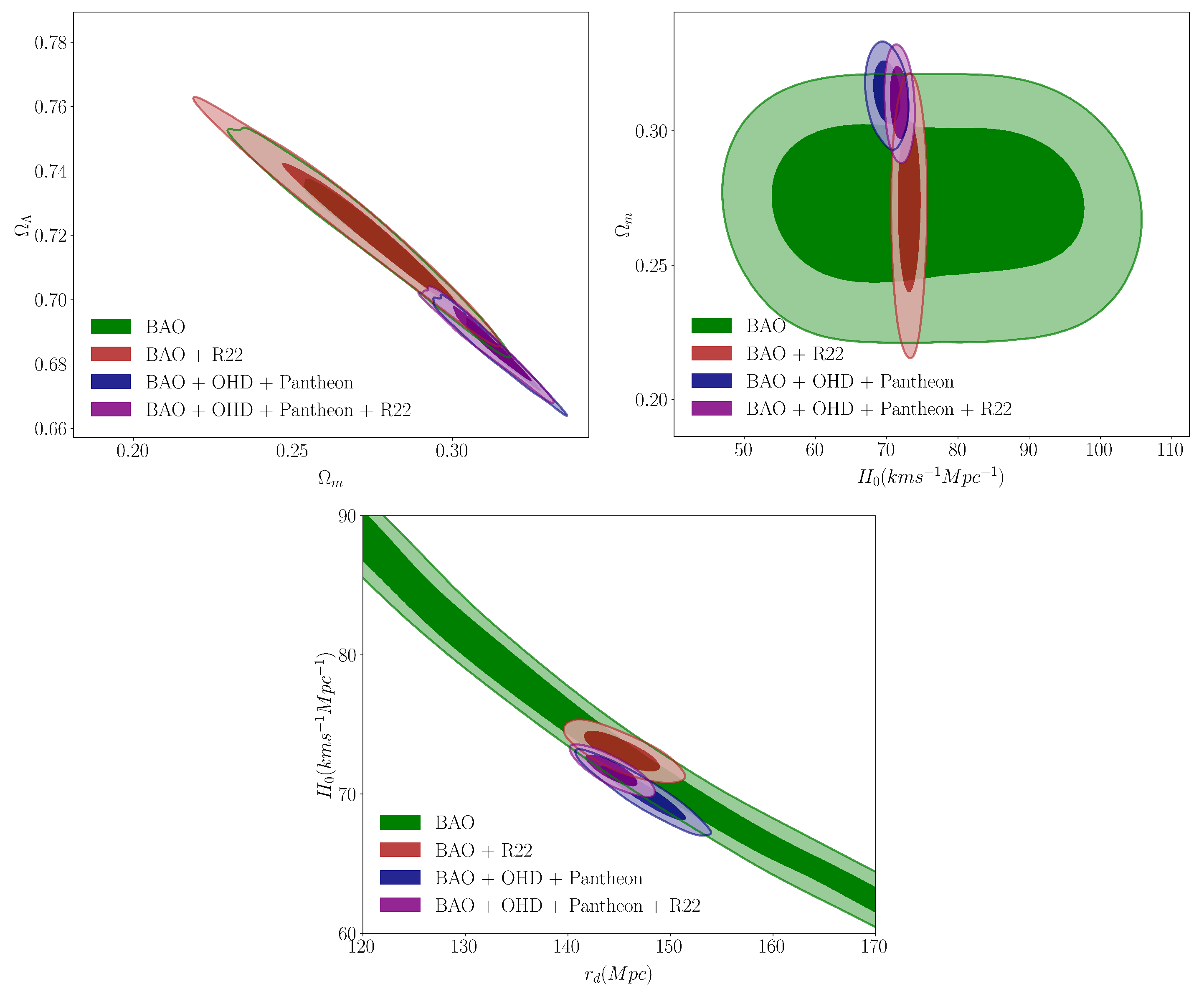
4.4. Phenomenological Emergent Dark Energy Model
5. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Planck Collaboration. Planck 2018 Results—VI. Cosmological Parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, A6, 641. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, C.L.; Larson, D.; Weil, J.L.; Jarosik, N.; Hinshaw, G.; Odegard, N.; Smith, K.M.; Hill, R.S.; Gold, B.; Halpern, M.; et al. Nine-year Wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe (WMAP) observations: Final maps and results. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2013, 208, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Challis, P.; Clocchiatti, A.; Diercks, A.; Garnavich, P.M.; Gillil, R.L.; Hogan, C.J.; Jha, S.; Kirshner, R.P.; et al. Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Macri, L.; Casertano, S.; Lampeitl, H.; Ferguson, H.C.; Filippenko, A.V.; Jha, S.W.; Li, W.; Chornock, R. A 3% solution: Determination of the Hubble constant with the Hubble space telescope and wide field camera 3. Astron. J. 2011, 730, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Macri, L.M.; Hoffmann, S.L.; Scolnic, D.; Casertano, S.; Filippenko, A.V.; Tucker, B.E.; Reid, M.J.; Jones, D.O.; Silverman, J.M.; et al. A 2.4% determination of the local value of the Hubble constant. Astron. J. 2016, 826, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Casertano, S.; Yuan, W.; Macri, L.M.; Scolnic, D. Large Magellanic Cloud Cepheid Standards Provide a 1% Foundation for the Determination of the Hubble Constant and Stronger Evidence for Physics beyond ΛCDM. Astron. J. 2019, 876, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Yuan, W.; Macri, L.M.; Scolnic, D.; Brout, D.; Casertano, S.; Jones, D.O.; Murakami, Y.; Anand, G. S.; Breuval, L.; et al. A Comprehensive Measurement of the Local Value of the Hubble Constant with 1 km/s/Mpc Uncertainty from the Hubble Space Telescope and the SH0ES Team. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2022, 934, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.G.; Wang, K. How the dark energy can reconcile Planck with local determination of the Hubble constant. Eur. Phys. J. 2016, 76, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Valentino, E.; Melchiorri, A.; Silk, J. Reconciling Planck with the local value of H0 in extended parameter space. Phys. Lett. B 2016, 761, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Huang, Q.G. Detecting the neutrinos mass hierarchy from cosmological data. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2018, 61, 039521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Pan, S.; Di Valentino, E.; Saridakis, E.N.; Chakraborty, S. Observational constraints on one-parameter dynamical dark-energy parametrizations and the H0 tension. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 043543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, V.; Smith, T.L.; Karwal, T.; Kamionkowsk, M. Early Dark Energy can Resolve the Hubble Tension. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 221301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagnozzi, S. New physics in light of the H0 tension: An alternative view. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 023518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Huang, Z.; Luo, X.; Miao, H.; Singh, N.K.; Huang, L. Can non-standard recombination resolve the Hubble tension? Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2020, 63, 290405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Nakama, T.; Wang, Y. A gigaparsec-scale local void and the Hubble tension. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2020, 63, 290403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.; Chen, Y.; Ratra, B. Baryon acoustic oscillation, Hubble parameter, and angular size measurement constraints on the Hubble constant, dark energy dynamics, and spatial curvature. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 488, 3844–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.B.; Raveri, M.; Pogosian, L.; Wang, Y.; Crittenden, R.G.; H.; ley, W.J.; Percival, W.J.; Beutler, F.; Brinkmann, J.; Chuang, C.; et al. Dynamical dark energy in light of the latest observations. Nat. Astron. 2017, 1, 627–632.
- Li, X.; Shafieloo, A. A Simple Phenomenological Emergent Dark Energy Model can Resolve the Hubble Tension. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 883, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Valentino, E. Investigating Cosmic Discordance. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 908, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haitao, M.; Zhiqi, H. The H0 Tension in Non-flat QCDM Cosmology. Astron. J. 2018, 868, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Millon, M.; Galan, A.; Courbin, F.; Treu, T.; Suyu, S. H.; Ding, X.; Birrer, S.; Chen, G. C.-F.; Shajib, A. J.; Sluse, D.; et al. An exploration of systematic uncertainties in the inference of H0 from time-delay cosmography. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 639, A101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.C.; Suyu, S.H.; Chen, G.C.-F.; Rusu, C.E.; Millon, M.; Sluse, D.; Bonvin, V.; Fassnacht, C.D.; Taubenberger, S.; Auger, M.W.; et al. H0LiCOW—XIII. A 2.4 percent measurement of H0 from lensed quasars: 5.3σ tension between early- and late-Universe probes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 498, 1420–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooley, K.P.; Deller, A.T.; Gottlieb, O.; Nakar, E.; Hallinan, G.; Bourke, S.; Frail, D.A.; Horesh, A.; Corsi, A.; Hotokezaka, K. Superluminal motion of a relativistic jet in the neutron-star merger GW170817. Nature 2018, 561, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration and The Virgo Collaboration; The 1M2H Collaboration; The Dark Energy Camera GW-EM Collaboration and the DES Collaboration; The DLT40 Collaboration; The Las Cumbres Observatory Collaboration; The VINROUGE Collaboration; The MASTER Collaboration. A gravitational-wave standard siren measurement of the Hubble constant. Nature 2017, 551, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotokezaka, K.; Nakar, E.; Gottlieb, O.; Nissanke, S.; Masuda, K.; Hallinan, G.; Mooley, K. P.; Deller, A. T. A Hubble constant measurement from the superluminal motion of the jet in GW170817. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Wang, F.-Y. An 8 percent determination of the Hubble constant from localized fast radio bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc.: Lett. 2022, 515, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.W.; Ghosh, E.M.; Prochaska, J.X.; Bannister, K.W.; Bh, ari, S.; Day, C.K.; Deller, A.T.; Glowacki, M.; Gordon, A.C.; Heintz, K.E.; et al. A measurement of Hubble’s Constant using Fast Radio Bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 516, 4862–4881.
- Pesce, D.W.; Braatz, J.A.; Reid, M.J.; Riess, A.G.; Scolnic, D.; Condon, J.J.; Gao, F.; Henkel, C.; Impellizzeri, C.M.V.; Kuo, C.Y.; Lo, K.Y. The Megamaser Cosmology Project. XIII. Combined Hubble Constant Constraints. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 891, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.; Pesce, D.W.; Riess, A.G. An Improved Distance to NGC 4258 and Its Implications for the Hubble Constant. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 886, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.Y.; Braatz, J.A.; Lo, K.Y.; Reid, M.J.; Suyu, S.H.; Pesce, D.W.; Condon, J.J.; Henkel, C.; Impellizzeri, C.M.V. The Megamaser Cosmology Project. VI. Observations of NGC 6323. Astron. J. 2015, 800, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, W.L.; Madore, B.F.; Hatt, D.; Hoyt, T.J.; Jang, I.S.; Beaton, R.L.; Burns, C.R.; Lee, M.G.; Monson, A.J.; Neeley, J.R.; et al. The Carnegie-Chicago Hubble Program. VIII. An Independent Determination of the Hubble Constant Based on the Tip of the Red Giant Branch. Astron. J. 2019, 882, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, W.L.; Madore, B.F.; Hoyt, T.; Jang, I.S.; Beaton, R.; Lee, M.G.; Monson, A.; Neeley, J.; Jeffrey, R. Calibration of the Tip of the Red Giant Branch. Astron. J. 2020, 891, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, W.L. Measurements of the Hubble Constant: Tensions in Perspective. Astron. J. 2021, 919, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, G.E.; Watts, D.J.; Bennett, C.L.; Halpern, M.; Hinshaw, G.; Weil, J.L. Elucidating ΛCDM: Impact of Baryon Acoustic Oscillation Measurements on the Hubble Constant Discrepancy. Astron. J. 2021, 853, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M.; Amati, L.; Amendola, L.; Birrer, S.; Blakeslee, J.P.; Cantiello, M.; Cimatti, A.; Darling, J.; Valle, M.D.; Fishbach, M.; et al. Unveiling the Universe with emerging cosmological probes. Living Rev. Relativ. 2022, 25, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Ballard, W.; Palmese, A.; Magaña, I.; BenZvi, S.; Moon, J.; Ross, A.J.; Rossi, G.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Blum, R.; et al. A dark siren measurement of the Hubble constant with the LIGO/Virgo gravitational wave event GW190412 and DESI galaxies. arXiv 2023, 2311.13062.
- Alfradique, V.; Bom, C.R.; Palmese, A.; Teixeira, G.; Santana-Silva, L.; Drlica-Wagner, A.; Riley, A.H.; Rossi, G.; Martínez-Vázquez, C.E.; Sand, D.J.; et al. A dark siren measurement of the Hubble constant using gravitational wave events from the first three LIGO/Virgo observing runs and DELVE. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 528, 3249–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DESI Collaboration. DESI 2024 VI: Cosmological Constraints from the Measurements of Baryon Acoustic Oscillations. arXiv 2024, 2404.03002.
- DES Collaboration. Dark Energy Survey: A 2.1% measurement of the angular Baryonic Acoustic Oscillation scale at redshift zeff=0.85 from the final dataset. arXiv 2024, 2402.10696.
- Scolnic, D.M.; Jones, D.O.; Rest, A.; Pan, Y.C.; Chornock, R.; Foley, R.J.; Huber, M.E.; Kessler, R.; Narayan, G.; Riess, A.G.; et al. The Complete Light-curve Sample of Spectroscopically Confirmed SNe Ia from Pan-STARRS1 and Cosmological Constraints from the Combined Pantheon Sample. Astron. J. 2018, 859, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, W.J.; Hobson, M.P.; Lasenby, A.N. POLYCHORD: Nested sampling for cosmology. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc.: Lett. 2015, 450, L61–L65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Han, Z.; Shuo, Y.; Siqi, L.; Tong-Jie, Z.; Yan-Chun, S. Four new observational H(z) data from luminous red galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey data release seven. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 14, 1221. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, J.; Verde, L.; Jimenez, R. Constraints on the redshift dependence of the dark energy potential. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M.; Cimatti, A.; Jimenez, R.; Pozzetti, L.; Zamorani, G.; Bolzonella, M.; Dunlop, J.; Lamareille, F.; Mignoli, M.; Pearce, H.; et al. Improved constraints on the expansion rate of the Universe up to z≈ 1.1 from the spectroscopic evolution of cosmic chronometers. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M.; Pozzetti, L.; Cimatti, A.; Jimenez, R.; Maraston, C.; Verde, L.; Thomas, D.; Citro, A.; Tojeiro, R.; Wilkinson, D. A 6 percent measurement of the Hubble parameter at z≈ 0.45: Direct evidence of the epoch of cosmic re-acceleration. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratsimbazafy, A.L.; Loubser, S.I.; Crawford, S.M.; Cress, C.M.; Bassett, B.A.; Nichol, R.C.; Väisänen, P. Age-dating luminous red galaxies observed with the Southern African Large Telescope. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 3239–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D.; Jimenez, R.; Verde, L.; Kamionkowski, M.; Stanford, S.A. Cosmic chronometers: Constraining the equation of state of dark energy. I: H(z) measurements. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2010, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, N.; Moresco, M.; Cimatti, A. Toward a Better Understanding of Cosmic Chronometers: A New Measurement of H(z) at z ≈ 0.7. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2022, 928, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Borghi, N.; Moresco, M.; Zhang, T.-J. New Observational H(z) Data from Full-spectrum Fitting of Cosmic Chronometers in the LEGA-C Survey. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2023, 265, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M. Raising the bar: New constraints on the Hubble parameter with cosmic chronometers at z ≈ 2. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc.: Lett. 2015, 450, L16–L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shafieloo, A. A Simple Phenomenological Emergent Dark Energy Model can Resolve the Hubble Tension. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 883, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, E.V. Probing gravitation, dark energy, and acceleration. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 023511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, M.; Polarski, D. Accelerating universes with scaling dark matter. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2001, 10, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, E.V. Exploring the Expansion History of the Universe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 091301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, R.; Loeb, A. Constraining Cosmological Parameters Based on Relative Galaxy Ages. Astrophys. J. 2002, 573, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano Torres, J.A. Testing Cosmic Acceleration from the Late-Time Universe. Astronomy 2023, 2, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazantzidis, L.; Perivolaropoulos, L. Evolution of the fσ8 tension with the Planck15/ΛCDM determination and implications for modified gravity theories. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 103503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, R.C.; Yadav, S.K.; Jesus, J.F.; Bernui, A. Cosmological parameter analyses using transversal BAO data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 497, 2133–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, R.C.; Bernui, A. BAO signatures in the 2-point angular correlations and the Hubble tension. Eur. Phys. J. C. 2020, 80, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, L.; Bernal, J.L.; Heavens, A.F.; Jimenez, R. The length of the low-redshift standard ruler. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, T.; Ruchika, Carvalho, J.C.; Alcaniz, J. Low-redshift estimates of the absolute scale of baryon acoustic oscillations. Eur. Phys. J. C 2023, 83, 495.
- Pogosian, L.; Zhao, G.-B.; Jedamzik, K. Recombination-independent Determination of the Sound Horizon and the Hubble Constant from BAO. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 904, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the Dimension of a Model. Ann. Statist. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Observable | Measurement | Error | Year | Dataset Survey | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.30 | 7.92 | 0.15 | 2024 | DESI BGS | [38] | |
| 0.51 | 13.62 | 0.25 | 2024 | DESI LRG | [38] | |
| 0.51 | 20.98 | 0.61 | 2024 | DESI LRG | [38] | |
| 0.71 | 16.84 | 0.32 | 2024 | DESI LRG | [38] | |
| 0.71 | 20.08 | 0.60 | 2024 | DESI LRG | [38] | |
| 0.85 | 19.51 | 0.41 | 2024 | DES Year 6 | [39] | |
| 0.93 | 21.73 | 0.28 | 2024 | DESI LRG+ELG | [38] | |
| 0.93 | 17.87 | 0.35 | 2024 | DESI LRG+ELG | [38] | |
| 1.32 | 27.80 | 0.69 | 2024 | DESI ELG | [38] | |
| 1.32 | 13.82 | 0.42 | 2024 | DESI ELG | [38] | |
| 1.49 | 26.09 | 0.67 | 2024 | DESI QSO | [38] | |
| 2.33 | 39.71 | 0.94 | 2024 | DESI Lya QSO | [38] | |
| 2.33 | 8.52 | 0.17 | 2024 | DESI Lya QSO | [38] |
| z | Method | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.07 | 69 | 19.6 | Full-spectrum fitting | [42] |
| 0.09 | 69 | 12 | Full-spectrum fitting | [43] |
| 0.12 | 68.6 | 26.2 | Full-spectrum fitting | [42] |
| 0.17 | 83 | 8 | Full-spectrum fitting | [43] |
| 0.179 | 75 | 4 | Calibrated D4000 | [44] |
| 0.199 | 75 | 5 | Calibrated D4000 | [44] |
| 0.20 | 72.9 | 29.6 | Full-spectrum fitting | [42] |
| 0.27 | 77 | 14 | Full-spectrum fitting | [43] |
| 0.28 | 88.8 | 36.6 | Full-spectrum fitting | [42] |
| 0.352 | 83 | 14 | Calibrated D4000 | [44] |
| 0.38 | 83 | 13.5 | Calibrated D4000 | [45] |
| 0.4 | 95 | 17 | Full-spectrum fitting | [43] |
| 0.4004 | 77 | 10.2 | Calibrated D4000 | [45] |
| 0.425 | 87.1 | 11.2 | Calibrated D4000 | [45] |
| 0.445 | 92.8 | 12.9 | Calibrated D4000 | [45] |
| 0.47 | 89.0 | 49.6 | Full-spectrum fitting | [46] |
| 0.4783 | 80.9 | 9 | Calibrated D4000 | [45] |
| 0.48 | 97 | 62 | Full-spectrum fitting | [47] |
| 0.593 | 104 | 13 | Calibrated D4000 | [44] |
| 0.68 | 92 | 8 | Calibrated D4000 | [44] |
| 0.75 | 98.8 | 33.6 | Lick indices | [48] |
| 0.781 | 105 | 12 | Calibrated D4000 | [44] |
| 0.80 | 113.1 | 28.5 | Full-spectrum fitting | [49] |
| 0.875 | 125 | 17 | Calibrated D4000 | [44] |
| 0.88 | 90 | 40 | Full-spectrum fitting | [47] |
| 0.9 | 117 | 23 | Full-spectrum fitting | [43] |
| 1.037 | 154 | 20 | Calibrated D4000 | [44] |
| 1.3 | 168 | 17 | Full-spectrum fitting | [43] |
| 1.363 | 160 | 33.6 | Calibrated D4000 | [50] |
| 1.43 | 177 | 18 | Full-spectrum fitting | [43] |
| 1.53 | 140 | 14 | Full-spectrum fitting | [43] |
| 1.75 | 202 | 40 | Full-spectrum fitting | [43] |
| 1.965 | 186.5 | 50.4 | Calibrated D4000 | [50] |
| Parameter | BAO + R22 | BAO + OHD + Pantheon | BAO + OHD + Pantheon + R22 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (km s Mpc−1) | 73.05 ± 0.94 | 69.54 ± 1.15 | 71.45 ± 0.79 |
| 0.226 ± 0.043 | 0.248 ± 0.020 | 0.244 ± 0.020 | |
| 0.696 ± 0.032 | 0.707 ± 0.020 | 0.716 ± 0.020 | |
| 0.061 ± 0.031 | 0.032 ± 0.028 | 0.025 ± 0.026 | |
| (Mpc) | 141.50 ± 2.76 | 147.94 ± 2.54 | 144.34 ± 1.65 |
| Parameter | BAO + R22 | BAO + OHD + Pantheon | BAO + OHD + Pantheon + R22 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (km s−1 Mpc−1) | 72.83 ± 1.12 | 69.72 ± 1.14 | 72.02 ± 0.95 |
| 0.130 ± 0.087 | 0.261 ± 0.032 | 0.262 ± 0.033 | |
| 0.827 ± 0.073 | 0.727 ± 0.023 | 0.727 ± 0.023 | |
| w | -0.766 ± 0.121 | -1.006 ± 0.049 | -1.016 ± 0.056 |
| (Mpc) | 138.30 ± 3.36 | 147.64 ± 2.50 | 143.31 ± 1.82 |
| Parameter | BAO + R22 | BAO + OHD + Pantheon | BAO + OHD + Pantheon + R22 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (km s−1 Mpc−1) | 73.05 ± 0.96 | 70.06 ± 1.26 | 71.75 ± 0.80 |
| 0.272 ± 0.018 | 0.313 ± 0.007 | 0.310 ± 0.008 | |
| 0.722 ± 0.014 | 0.684 ± 0.007 | 0.687 ± 0.007 | |
| (Mpc) | 145.27 ± 2.54 | 147.39 ± 2.50 | 145.28 ± 1.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





