Submitted:
30 May 2024
Posted:
31 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
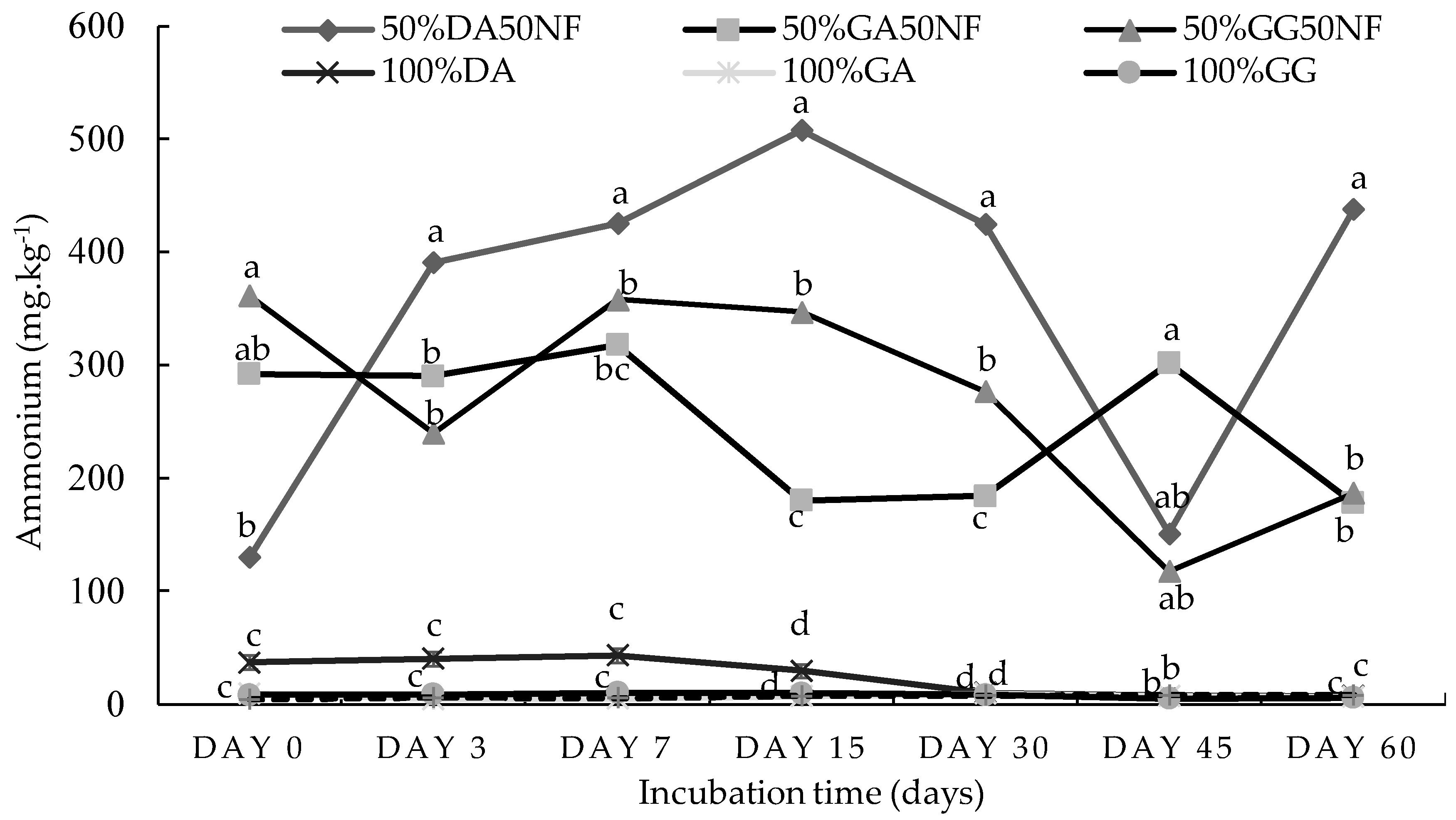
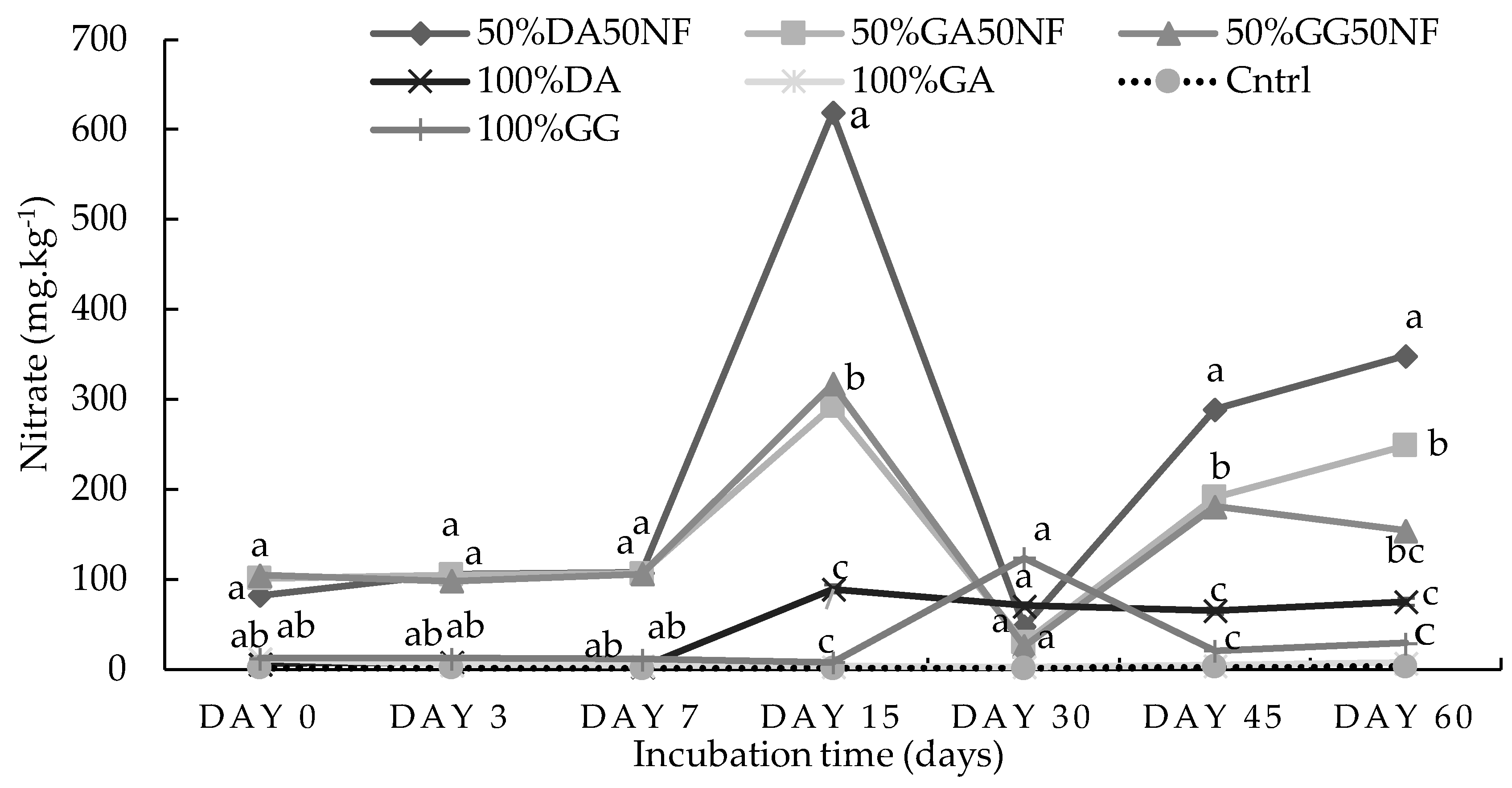
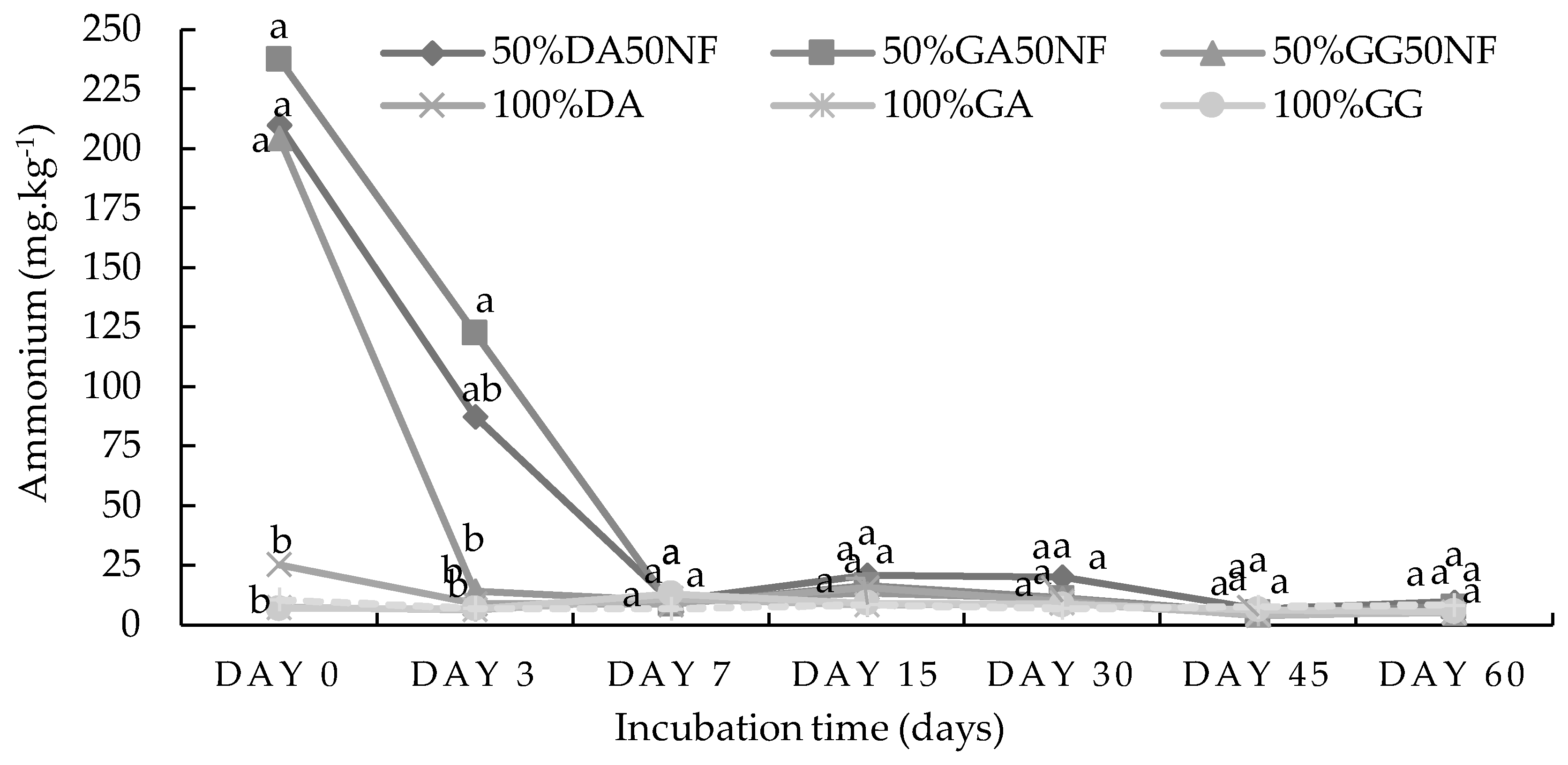
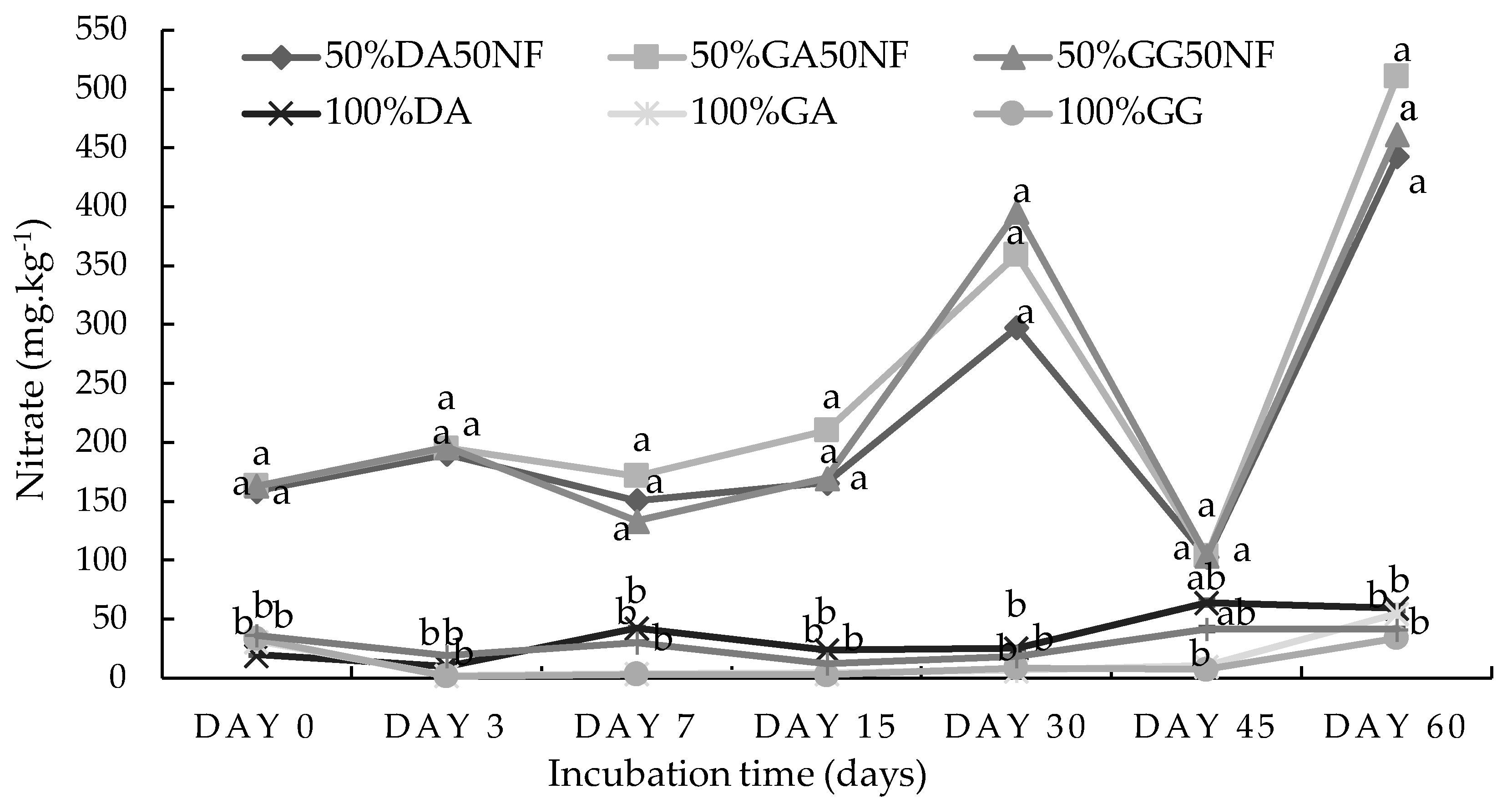
2.1. Incubation Study
2.1.1. Sandy Loam Soil from Pretoria
2.1.2. Loam Soil from Pretoria
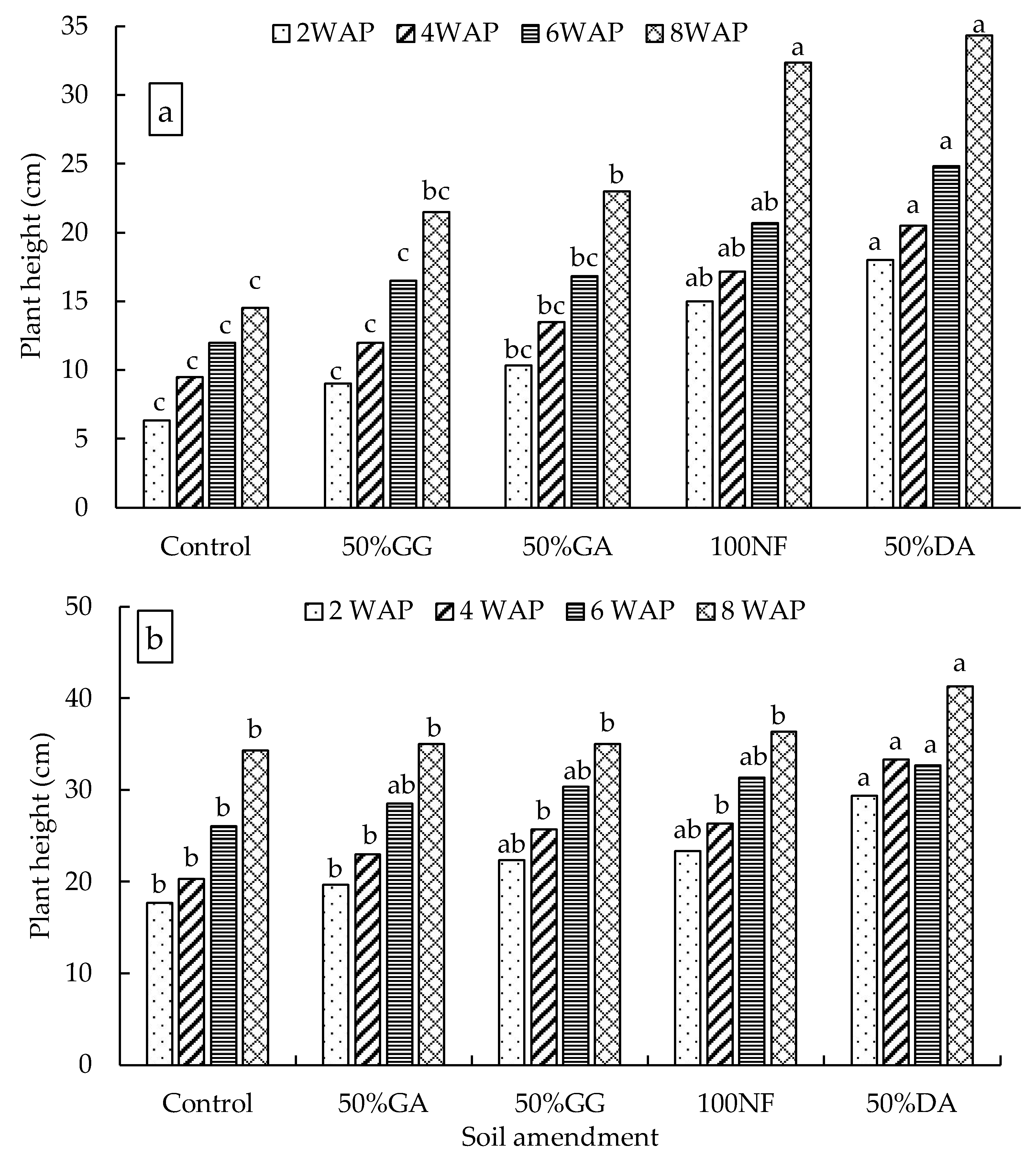
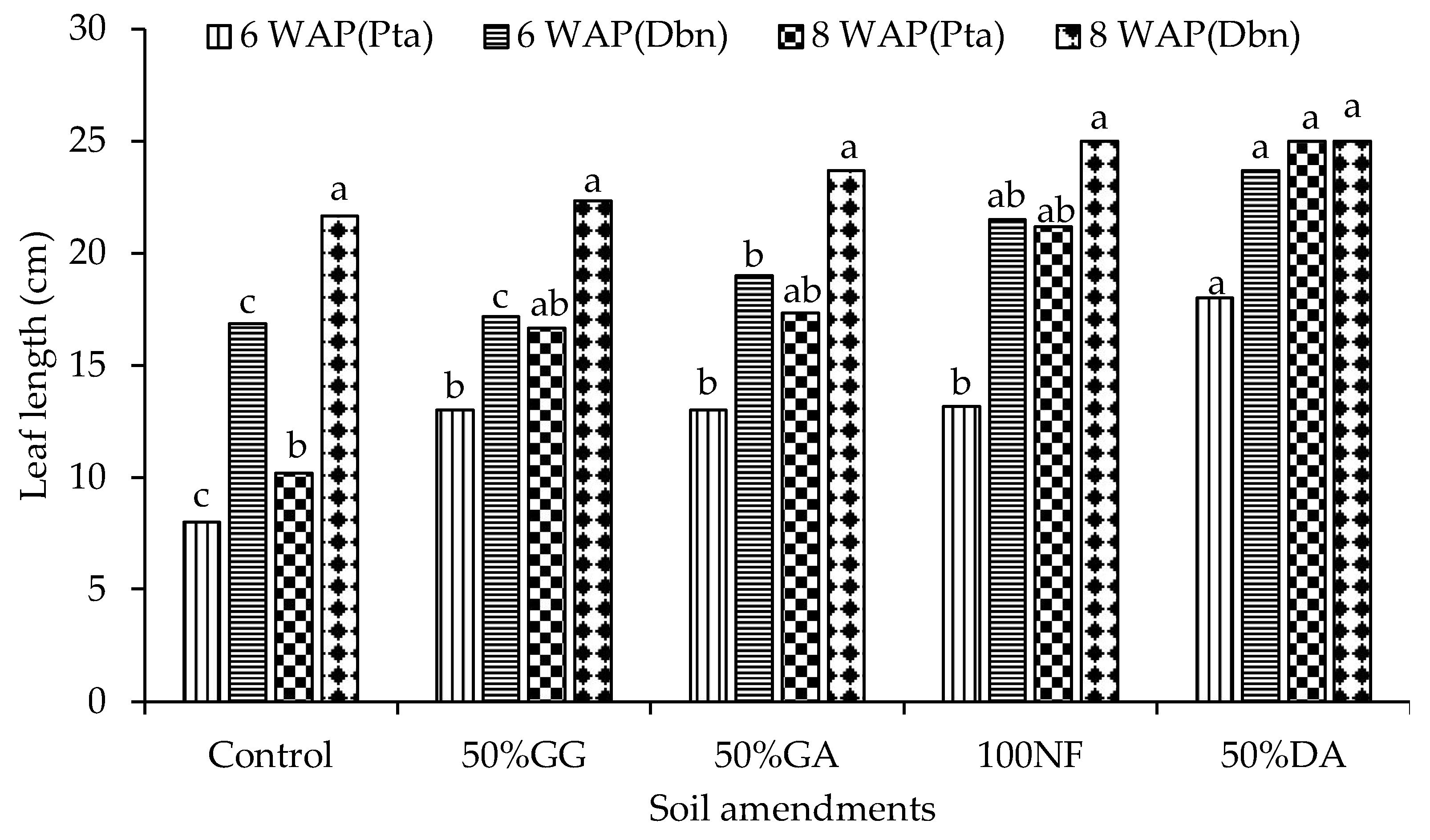
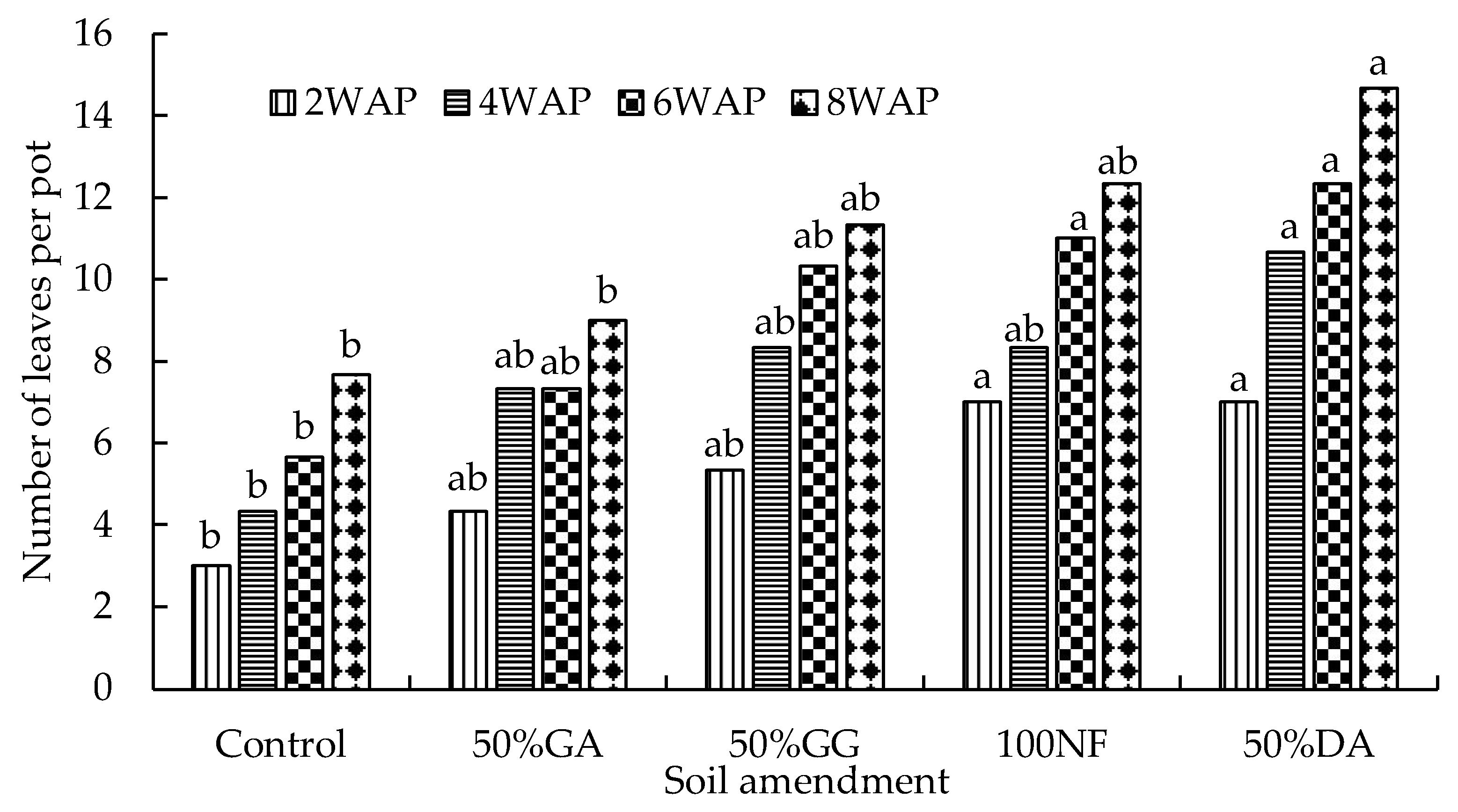
2.2. Glasshouse Experiment
3. Discussion
3.1. Nitrogen Mineralization of Organic-Inorganic Amendments
4.2. The Effect of the Organic-Inorganic Amendment on Plant Growth
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Incubation Study
| Sand | Silt | Clay | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling site | Very Coarse (mm) 2–1 |
Coarse (mm) 1–0.5 |
Medium (mm) 0.5–0.25 |
Fine (mm) 0.25–0.1 |
Very fine (mm) 0.1–0.05 |
Coarse (mm) 0.05–0.02 |
Fine (mm) 0.02–0.002 |
Clay (mm) < 0.002 |
| Sandy loam | 4.00% | 2.00% | 17.20% | 37.50% | 15.60% | 5.60% | 8.70% | 9.40% |
| Loam | 3.90% | 3.00% | 9.70% | 10.20% | 11.00% | 12.00% | 25.90% | 24.30% |
| Soil Properties | Pretoria | Durban |
|---|---|---|
| Physical characterization | ||
| Textural class | Sandy loam | Loam |
| Clay % | 9.30% | 24.30% |
| Chemical characterization | ||
| pH in H20 (1:2.5) | 6.20 | 6.50 |
| Available P (mg/kg) | 3.11 | 19.97 |
| Total N (%) | 0.064 | 0.20 |
| Total C (%) | 0.59 | 2.30 |
| C:N ratio | 9.22 | 11.50 |
| Exchangeable bases | ||
| Ca (meq/100 g) | 220.00 | 436.00 |
| Mg (meq/100 g) | 156.70 | 301.00 |
| K (meq/100 g) | 73.40 | 212.70 |
| Na (meq/100 g) | 74.00 | 84.40 |
| CEC (meq/100 g) | 12.00 | 46.00 |
- T1 = control, (no amendments)
- T2 = 5 g of dry algae per kg of soil (100% DA),
- T3 = 136 g of ground agri-mat per kg of soil (100% GA),
- T4 = 61 g of ground grass per kg of soil (100% GG),
- T5 = 2.5 g of N using Lime Ammonium Nitrate (LAN) + 2.5 g of dry algae per kg of soil (50% DA50NF),
- T6 = 50% GA50NF
- T7 = 50% GG50NF
4.2. Glasshouse Experiment
- T1 = control,
- T2 = 2.5 g of dry algae (DA) per kg of soil + 75 kgN·ha-1 using LAN (50% DA),
- T3 = 68 g of ground agri-mat (GA) per kg of soil + 75 kgN·ha-1 using LAN (50% GA),
- T4 = 30.5 g of ground grass (GG) per kilogram of soil + 75 kgN·ha-1 using LAN (50% GG),
- T5 = 150 kgN·ha-1 using LAN (100NF).
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahorana, P.C.; Biswas, D.R.; Datta, S.C. Mineralization of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulphur in soil as influenced by rock phosphate enriched compost and chemical fertilizers. J. Indian Soc. Soil Scie. 2015, 6, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soinne, H.; Keskinen, R.; Raty, M.; Kanerva, S.; Turtola, E.; Kaseva, J.; Nuutinen, V.; Simojoki, A.; Salo, T. Soil organic carbon and clay content as deciding factors for net nitrogen mineralization and cereal yields in boreal mineral soils. Euro J. Soil Scie 2020, 72, 1479–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Bahar, M.M.; Sarkar, B.; Bolan, N.; Donne, S. Fertilizer Value of Nutrient-Enriched Biochar and Response of Canola Crop. J. Soil Scie Plant Nutri 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.M. Nutrient status and growth of Maize plants as affected by green microalgae as soil additives. J. Biolog Scie 2001, 6, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, E.; Caliz, J.; Montserrat, G.; Garau, M.A.; Cruanas, R.; Vila, X.; Sierra, J. Air-drying, cooling and freezing for soil sample storage affects the activity and the microbial communities from Mediterranean soils. Geomicrobiol J 2012, 29, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Li, L.; Friman, V.P.; Guo, J.; Guo, S.; Shen, Q.; Ling, N. Organic amendments increase crop yields by improving microbe-mediated soil functioning of agroecosystems: A meta-analysis. Soil Bio. Biochem 2018, 124, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, M.I.; Wurster, C.M.; de Paula Silva, P.H.; Bass, A.M.; de Nys, R. Algal biochar–Production and properties. Biores Techno 2010, 102, 1886–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, M.K.; Khaliq, A. Nitrogen mineralization of a loam soil supplemented with organic-inorganic amendments under laboratory incubation. Front. Plant Scie 2016, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. Sustain Agric 2011, 2, 761–786. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.; van der Velde, M.; Bastos, A.C. A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst & Environ 2011, 144, 175–187. [Google Scholar]
- Souri, M.K. Effectiveness of chloride compared to 3,4 dimethylpyrazole phosphate on nitrification inhibition in soil. Comm. Soil Scie & Plant Anal 2010, 41, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar]
- Pansu, M.; Thuries, L.; Larre-Larrouy, M.C.; Bottner, P. Predicting N transformations from organic inputs in soil in relation to incubation time and biochemical composition. Soil Biol & Biochem 2003, 35, 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Chivenge, P.; Vanlauwe, B.; Six, J. Does the combined application of organic mineral nutrient sources influence maize productivity? A meta-analysis. Plant Soil 2011, 342, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. The response mechanisms of soil N moralization under biological soil crusts to temperature and moisture in temperate desert regions. Euro. J. Soil Biol 2014, 62, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulbry, W.; Westhead, E.K.; Pizarro, C.; Sikora, L. Recycling of manure nutrients: use of algal biomass from dairy manure treatment as a slow-release fertilizer. Biores Technol. 2005, 96, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, A.; Lopez-Pineiro, A.; Ramirez, M. Soil quality attributes of conservation management regimes in a semi-arid region of western Spain. Soil and Till Res 2007, 95, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, G.; Bengtson, P.; Månsson, K.F. Gross nitrogen mineralization-, immobilization-, and nitrification rates as a function of soil C/N ratio and microbial activity. Soil Biol & Biochem 2003, 35, 143–154. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, M.M.; Hina, M.; Khalique, A.; Khan, S.R. Mineralization of three organic manures used as nitrogen source in all soil incubated under laboratory conditions. Commun. Soil Scie & Plant Anal 2007, 38, 1691–1711. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, S.; Nikhil, K. Algae as a soil conditioner. Int J. Eng & Technical Res 2014, 2, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, R.; Chokshi, K.; Ghosh, T.; Trivedi, K.; Pancha, I.; Kubavat, D.; Mishra, S.; Ghosh, A. Lipid extracted microalgae biomass residue as a fertilizer substitute for Zea Mays L. Front. Plant Scie 2016, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gamal, M.A.H. Impact of algal addition to manure compost as affected by different moisture levels. Austral J. Basic & Applied Scie 2011, 5, 729–737. [Google Scholar]
- Mgolozeli, S.; Nciizah, A.D.; Wakindiki, I.I.; Mudau, F.N.; Onwona-Agyeman, S. Investigation of Infiltration and Runoff Rate on Agri-Mats Using a Laboratory Rainfall Simulation Study. Commun. Soil Scie & Plant Anal 2023, 54, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Mgolozeli, S.; Nciizah, A.D.; Wakindiki, I.I.C.; Mudau, F.N. Innovative pro-smallholder farmers’ permanent mulch for better soil quality and food security under conservation agriculture. Agron 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mgolozeli, S.; Nciizah, A.D.; Wakindiki, I.I.; Onwona-Agyeman, S. Agri-mat and grass mulch effect on crop biomass yield in sandy loam and loam soils. Land Degr & Dev. 2024, 35, 2884–2896. [Google Scholar]
- Bechtold, J.S.; Naiman, R.J. Soil texture and nitrogen mineralization potential across a riparian toposequence in a semi-arid savana. Soil Biol & Biochem 2006, 38, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Hassink, J.; Bouwman, L.A.; Zwart, K.B.; Brussard, L. Relationships between habitable pore space, soil biota and mineralization rates in grassland soils. Soil Biol & Biochem 1993, 25, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Matus, F.J.; Lusk, C.H.; Maire, C.R. Effects of soil texture, Carbon inputs rates, and litter quality on free organic matter and nitrogen mineralization in Chilean Rain Forest and Agricultural soils. Commun. Soil Scie & Plant Anal 2007, 39, 187–201. [Google Scholar]
- Marti, E.; Caliz, J.; Montserrat, G.; Garau, M.A.; Cruanas, R.; Vila, X.; Sierra, J. Air-drying, cooling and freezing for soil sample storage affects the activity and the microbial communities from Mediterranean soils. Geomicrobiol. J 2012, 29, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndung’u, M.; Ngatia, L.W.; Onwonga, R.N.; Mucheru-Muna, M.W.; Fu, R.; Moriasi, D.N.; Ngetich, K.F. The influence of organic and inorganic nutrients inputs on soil organic carbon functional groups content and maize yields. Heliy 2021, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Li, M.; Mgelwa, A.S.; Hu, Y. Divergent mineralization of exogenous organic substrates and their priming effects depending on soil types. Biol & Fertil. Soils 2023, 59, 87–101. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Sarkar, B.; Bolan, N.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Churchman, G.J. Decomposition of soil organic matter as affected by clay types, pedogenic oxides and plant residue addition rates. J. Hazard Mat 2019, 374, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Probert, M.E.; Delve, R.J.; Kimani, S.K.; Dimes, J.P. Modelling nitrogen mineralization from manures: representing quality aspects by varying C: N ratio of sub-pools. Soil Biol & Biochem 2005, 37, 279–287. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, S.; Xu, H.; Ji, M.; Jiang, Y. Characteristics of soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, and C/N ratio in Chinese apple orchards. 2013, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malobane, M.E. Using the organic carbon fractions of the van soest method to determine compounds responsible for C and N mineralization from sludge amended soils. MSc Dissertation, University of Pretoria, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbaz, M.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Heitkamp, F. Decrease of soil organic stabilization with increasing inputs: Mechanisms and controls. Geoderma 2017, 304, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masunga, R.H.; Uzokwe, V.N.; Mlay, P.D.; Odeh, I.; Singh, A.; Buchan, D.; De Neve, S. Nitrogen mineralization dynamics of different valuable organic amendments commonly used in agriculture. Appl. Soil Ecol 2016, 101, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundijo, D.S.; Adetunji, M.T.; Azeez, J.O.; Arowolo, T.A. Effect of organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil organic carbon, Ph, Ammonium-nitrogen, Nitrate-nitrogen and some exchangeable cations. Int. J Environ Scie 2014, 3, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, S.; Al-Shankiti, A. Sustainable food production in marginal lands–Case of GDLA member countries. Int. Soil & Water Conserv Res 2013, 1, 24–38. [Google Scholar]
- Onwona-Agyeman, S.; Fuke, M.; Kabawata, Y.; Yamada, M.; Tanahashi, M. Compressed biomass as mulching in No-till farming. J. Arid Land Stud. 2015, 25, 253–256. [Google Scholar]
- Onwona-Agyeman, S.; Nakamura, S.; Kabawata, Y.; Yamad, M.; Sabi, E.B.; Tanahashi, M. Utilization of forestry residues in erosion control and soil moisture conservation. J. Arid Land Stud. 2012, 2, 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- Obalum, S.E.; Chibuike, G.U. Air drying effect on soil reaction and phosphorus extractability from upland-lowland tropical soils as related to other colloidal stability. Appl. Ecol and Environ Res. 2016, 15, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





