Submitted:
23 May 2024
Posted:
24 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1.0. Introduction
2.0. Strategies for Support Modification
2.1. Support Doping
- Incipient Wetness Impregnation (IWI): This approach involves saturating the support material with a solution containing dopant precursors. Subsequent drying and calcination yield the doped support material, with dopant species dispersed on the support surface or integrated into its structure during calcination [73,74,75,76,77].
- Co-precipitation: In this method, the support material and dopant precursors are blended in a solution, and a precipitating agent is added to prompt the formation of dopant-incorporated support particles. The resulting mixture is then subjected to drying plus calcination to achieve the doped support material [78,79,80].
2.2. Support Coating
2.3. Support Promotion
- Stabilizing the support oxide
- Sticking the cobalt species on the support oxide by acting as an oxidic interface between support and Co particle
- Hydrogenation or dehydrogenation reactions- sometimes promoter elements either affect the hydrogenation or dehydrogenation reactions, hence shifting selectivity.
- Coke burning at the regeneration stage- promoters can lower the oxidative treatment temperature, this limits the clustering of supported Co species.
- Examine the influence of support reformation plus promoter addition on the fundamental FT activity by utilizing in-situ studies, hence preventing possible faults from catalyst deactivation.
- Exploring how support modification on the fundamental CH4 selectivity of FT cobalt catalyst happens without process parameters and mass- transport influence.
- Explore how CO adsorption and dissociation are affected by promoter addition and explore their relationships with variations in FT performance and selectivity towards higher hydrocarbons [57].
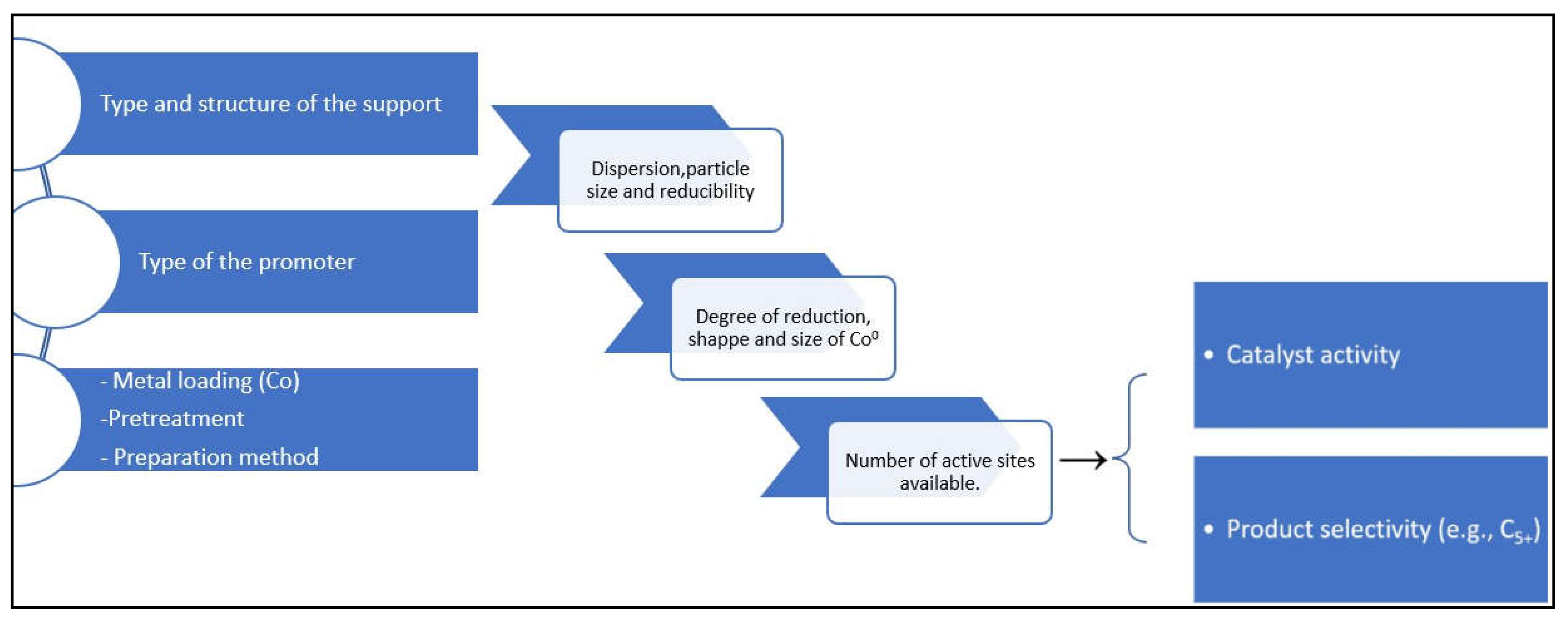
3.0. Support Modification for FTS
3.1. Effect of Support Modification on Catalyst Reduction for Fischer Tropsch Synthesis
| Sample | Reduction degree (DOR) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Co/Al | 39 | Garcilaso et_al, 2019 [144] |
| Co/Zr-Al | 40 | Garcilaso et_al, 2019 [144] |
| Co/Ce-Al | 35 | Garcilaso et_al, 2019 [144] |
| Co/Al | 42 | Barrientos, Garcilaso, Venezia, & Aho, 2017 [145] |
| Co/Zr-Al P | 44 | Barrientos et_al, 2017 [145] |
| Co/Zr-Al ME | 40 | Barrientos et_al, 2017 [145] |
| Co/MS | 98.28 | Wu, Yang, Suo, Qing, Yan, Wu, et al., 2015 [146] |
| Co/Zr-MS | 97.55 | Wu, Yang, Suo, Qing, Yan, Wu, et al., 2015 [146] |
| Co/TiZr-MS | 71.17 | Wu, Yang, Suo, Qing, Yan, Wu, et al., 2015 [146] |
| Co/Pt/SiO2 | 96 | Breejen et_al, 2011 [147] |
| Co/MnO/Pt/SiO2 | 94 | Breejen et_al, 2011 [147] |
3.2. Effect of Support Modification on Catalyst Particle Size for Fischer Tropsch Synthesis
3.3. Effect of Support Modification on Catalytic Activity and Product Selectivity for FTS
| Catalysts | Conversion (%) | Main Product | Selectivity (%) | Ref. |
| 12%Co/γ-Al2O3 | 45 | C5+ | 80 | Enger et al., 2011 [154] |
| 12%Co-0.5%Re/γ-Al2O3 | 45 | C5+ | 83.1 | Enger et al., 2011 [154] |
| 12%Co-0.5%Re/5%Mg-γ-Al2O3 | 45 | C5+ | 81.8 | Enger et al., 2011 [154] |
| 12%Co-0.5%Re/5%Zn-γ-Al2O3 | 45 | C5+ | 82.5 | Enger et al., 2011 [154] |
| 9.3%Co/TiO2 | 29.2 | C5+ | 85 | Eschemann, Oenema, & De Jong, 2016 [158] |
| 9.0%Co-0.12%Ag/TiO2 | 33.0 | C5+ | 89 | Eschemann, Oenema, & De Jong, 2016 [158] |
| 8.9%Co-0.11%Pt/TiO2 | 30.4 | C5+ | 83 | Eschemann, Oenema, & De Jong, 2016 [158] |
| 9.4%Co-0.25Re%/TiO2 | 33.1 | C5+ | 88 | Eschemann, Oenema, & De Jong, 2016 [158] |
| 15%Co/SiC | 71 | C5+ | 80 | Li, Wu, & Wu, 2017b [159] |
| 15%Co-5%Zr/SiC | 82 | C5+ | 81 | Li et al., 2017b [159] |
| 15%Co-5%Ca/SiC | 81 | C5+ | 82 | Li et al., 2017b [159] |
| 10%Co/SiO2 | 41.7 | C5+ | 82.5 | Wu, Yang, Suo, Qing, Yan, Wu, et al., 2015 [146] |
| 10%Co/TiO2-SiO2 | 85.9 | C5+ | 85.6 | Wu, Yang, Suo, Qing, Yan, Wu, et al., 2015 [146] |
| 10%Co/TiO2-ZrO2-SiO2 | 80.3 | C5+ | 75.4 | Wu, Yang, Suo, Qing, Yan, Wu, et al., 2015 [146] |
| 20%Co-0.1wt.%Pt/ZSM-5 | 26.8 | C12+ | 52.2 | Subramanian et al., 2016 [160] |
| 20%Co-0.1%Pt/ZSM-5 | 27 | C12+ | 52.0 | Subramanian et al., 2016 [160] |
| 20%Co-0.1wtPt/SiO2-ZSM-5 | 26.4 | C12+ | 60.5 | Subramanian et al., 2016 [160] |
| 20%Co-0.1wtPt/MOR | 40 | C12+ | 60.9 | Subramanian et al., 2016 [160] |
3.4. Effects of Preparation on Activity and Product Selectivity
5.0. Conclusions
6.0. Acknowledgements
References
- Johnson, G.R.; Werner, S.; Bell, A.T. An Investigation into the Effects of Mn Promotion on the Activity and Selectivity of Co/SiO2 for Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: Evidence for Enhanced CO Adsorption and Dissociation. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5888–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. Cheng et al., “Applied Catalysis A : General Sodium-promoted iron catalysts prepared on different supports for high temperature Fischer – Tropsch synthesis,” “Applied Catal. A, Gen., vol. 502, pp. 204–214, 2015.
- Mazurova, K.; Miyassarova, A.; Eliseev, O.; Stytsenko, V.; Glotov, A.; Stavitskaya, A. Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis Catalysts for Selective Production of Diesel Fraction. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Mahato, A.; Gupta, G.K.; Sahu, G.; Maity, S. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over Pd promoted cobalt based mesoporous supported catalyst. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. – Rev. d’IFP Energies Nouv. 2021, 76, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V. Vosoughi, A. K. Dalai, N. Abatzoglou, and Y. Hu, “Applied Catalysis A, General Performances of promoted cobalt catalysts supported on mesoporous alumina for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis,” Appl. Catal. A, Gen., vol. 547, no. May, pp. 155–163, 2017.
- Cano, L.; Blanco, A.G.; Lener, G.; Marchetti, S.; Sapag, K. Effect of the support and promoters in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis using supported Fe catalysts. Catal. Today 2017, 282, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillestad, M. Modeling the Fischer–Tropsch Product Distribution and Model Implementation. Chem. Prod. Process. Model. 2015, 10, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, E.; Scheper, C.; Wilson, J.; Vinkenburg, I.; Oosterbeek, H. Non-ASF Product Distributions Due to Secondary Reactions during Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. J. Catal. 1996, 158, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V. A. Online, K. D. Kruit, D. Vervloet, and F. Kapteijn, “Catalysis Science & Technology,” pp. 2210–2213, 2013.
- B. Todic, T. Olewski, N. Nikacevic, and D. B. Bukur, “Modeling of Fischer-Tropsch Product Distribution over Fe-based Catalyst,” vol. 32, no. 2007, pp. 793–798, 2013.
- Förtsch, D.; Pabst, K.; Groß-Hardt, E. The product distribution in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: An extension of the ASF model to describe common deviations. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 138, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzlaff, J.; Liu, Y.; Graffmann, C.; Gaube, J. Studies on product distributions of iron and cobalt catalyzed Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 1999, 186, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakov, A.Y.; Chu, W.; Fongarland, P. Advances in the Development of Novel Cobalt Fischer−Tropsch Catalysts for Synthesis of Long-Chain Hydrocarbons and Clean Fuels. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 1692–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. Pardo-tarifa, Cobalt catalyst supports for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. 2017.
- Duyckaerts, N.; Bartsch, M.; Trotuş, I.; Pfänder, N.; Lorke, A.; Schüth, F.; Prieto, G. Intermediate Product Regulation in Tandem Solid Catalysts with Multimodal Porosity for High-Yield Synthetic Fuel Production. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11480–11484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duyckaerts, N.; Trotuş, I.-T.; Swertz, A.-C.; Schueth, F.; Prieto, G. In Situ Hydrocracking of Fischer–Tropsch Hydrocarbons: CO-Prompted Diverging Reaction Pathways for Paraffin and α-Olefin Primary Products. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 4229–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Syngas et al., “Design of Cobalt Fischer − Tropsch Catalysts for the Combined Production of Liquid Fuels and Ole fi n Chemicals from Hydrogen- Rich Syngas,” 2021.
- Bezemer, G.L.; Bitter, J.H.; Kuipers, H.P.C.E.; Oosterbeek, H.; Holewijn, J.E.; Xu, X.; Kapteijn, F.; van Dillen, A.J.; de Jong, K.P. Cobalt Particle Size Effects in the Fischer−Tropsch Reaction Studied with Carbon Nanofiber Supported Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3956–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, A.; Prieto, G.; Rollán, J. Nanofibrous γ-Al2O3 as support for Co-based Fischer–Tropsch catalysts: Pondering the relevance of diffusional and dispersion effects on catalytic performance. J. Catal. 2009, 263, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, N.; van Steen, E.; Claeys, M. Structure sensitivity of the Fischer–Tropsch activity and selectivity on alumina supported cobalt catalysts. J. Catal. 2013, 299, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuxen, A.; Carenco, S.; Chintapalli, M.; Chuang, C.-H.; Escudero, C.; Pach, E.; Jiang, P.; Borondics, F.; Beberwyck, B.; Alivisatos, A.P.; et al. Size-Dependent Dissociation of Carbon Monoxide on Cobalt Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2273–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca, H.; Safonova, O.V.; Chambrey, S.; Fongarland, P.; Roussel, P.; Griboval-Constant, A.; Lacroix, M.; Khodakov, A.Y. Structure and catalytic performance of Pt-promoted alumina-supported cobalt catalysts under realistic conditions of Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. J. Catal. 2011, 277, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. Prieto, P. Concepción, R. Murciano, and A. Martínez, “The impact of pre-reduction thermal history on the metal surface topology and site-catalytic activity of Co = SiO 2 Fischer – Tropsch catalysts,” J. Catal., vol. 302, pp. 37–48, 2013.
- T. Jermwongratanachai et al., “Fischer – Tropsch synthesis : TPR and XANES analysis of the impact of simulated regeneration cycles on the reducibility of Co / alumina catalysts with different promoters ( Pt, Ru, Re, Ag, Au, Rh, Ir ),” Catal. Today, vol. 228, pp. 15–21, 2014.
- F. Morales and B. M. Weckhuysen, “Promotion Effects in Co-Based Fischer—Tropsch Catalysis,” ChemInform, vol. 38, no. 2, 2007.
- K. M. Cook, S. Poudyal, J. T. Miller, C. H. Bartholomew, and W. C. Hecker, “Applied Catalysis A : General Reducibility of alumina-supported cobalt Fischer – Tropsch catalysts : Effects of noble metal type, distribution, retention, chemical state, bonding, and influence on cobalt crystallite size,” “Applied Catal. A, Gen., vol. 449, pp. 69–80, 2012.
- Garbarino, G.; Cavattoni, T.; Riani, P.; Busca, G. Support effects in metal catalysis: a study of the behavior of unsupported and silica-supported cobalt catalysts in the hydrogenation of CO2 at atmospheric pressure. Catal. Today 2019, 345, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. K. Æ. B. J. Æ. J. T. Wolan, “Silica-Supported Cobalt Catalysts for Fischer – Tropsch Synthesis : Effects of Calcination Temperature and Support Surface Area on Cobalt Silicate Formation,” pp. 72–78, 2009.
- G. Okoye-chine, C. O. L. Mbuya, T. S. Ntelane, M. Moyo, and D. Hildebrandt, “The effect of silanol groups on the metal-support interactions in silica- supported cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalysts. A temperature programmed surface reaction,” J. Catal., vol. 381, pp. 121–129, 2020.
- Uchisawa, J.; Tango, T.; Caravella, A.; Hara, S.; Haneda, M.; Murakami, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Nanba, T.; Obuchi, A. Effects of the Extent of Silica Doping and the Mesopore Size of an Alumina Support on Activity as a Diesel Oxidation Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 7992–7998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Santra, A.; Goodman, D. Understanding silica-supported metal catalysts: Pd/silica as a case study. Catal. Today 2003, 85, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-X.; He, C.-H.; Zhu, M.-Q.; Wu, K.-J.; Lai, Y.-L. Silica-Supported Gold Catalyst Modified by Doping with Titania for Cyclohexane Oxidation. Catal. Lett. 2007, 118, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytter, E.; Eri, S.; Skagseth, T.H.; Schanke, D.; Bergene, E.; Myrstad, R.; Lindvåg, A. Catalyst Particle Size of Cobalt/Rhenium on Porous Alumina and the Effect on Fischer−Tropsch Catalytic Performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 9032–9036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Tropsch reaction over alumina-supported cobalt catalyst : activation using H 2 and CO Master ’ s Dissertation Report submitted in partial fulfilment of Magister Technologiae In Chemical Engineering In the FACULTY OF EGINEERING AND THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT Of the University of Johannesburg Compiled by Student Number Supervised by Co-Supervised by : Phathutshedzo Rodney Khangale : Prof Kalala Jalama : Prof Reinout Meijboom,” 2012.
- Rane, S.; Borg. ; Rytter, E.; Holmen, A. Relation between hydrocarbon selectivity and cobalt particle size for alumina supported cobalt Fischer–Tropsch catalysts. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2012, 437-438, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimura, K.; Miyazawa, T.; Hanaoka, T.; Hirata, S. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over alumina supported cobalt catalyst: Effect of promoter addition. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2015, 494, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, A.; Ghasemzadeh, K.; Khajavi, P.; Assa, F.; Abdi, M.; Babaluo, A.; Basile, A. Surface modification of α-alumina support in synthesis of silica membrane for hydrogen purification. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 18585–18591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.; Koch, B.; Ruiz, P.; Delmon, B. Influence of the Amount of Titania on the Texture and Structure of Titania Supported on Silica. J. Catal. 1996, 161, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Storsæter, B. Tøtdal, J. C. Walmsley, B. S. Tanem, and A. Holmen, “Characterization of alumina-, silica-, and titania-supported cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalysts,” J. Catal., vol. 236, no. 1, pp. 139–152, Nov. 2005.
- Morales, F.; Desmit, E.; Degroot, F.; Visser, T.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Effects of manganese oxide promoter on the CO and H2 adsorption properties of titania-supported cobalt Fischer–Tropsch catalysts. J. Catal. 2007, 246, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fronzo, A.; Pirola, C.; Comazzi, A.; Galli, F.; Bianchi, C.; Di Michele, A.; Vivani, R.; Nocchetti, M.; Bastianini, M.; Boffito, D. Co-based hydrotalcites as new catalysts for the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis process. Fuel 2013, 119, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concepción, P.; López, C.; Martínez, A.; Puntes, V.F. Characterization and catalytic properties of cobalt supported on delaminated ITQ-6 and ITQ-2 zeolites for the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis reaction. J. Catal. 2004, 228, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartipi, S.; Alberts, M.; Meijerink, M.J.; Keller, T.C.; Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Towards Liquid Fuels from Biosyngas: Effect of Zeolite Structure in Hierarchical-Zeolite-Supported Cobalt Catalysts. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 1646–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-C.; Lee, S.; Cho, K.; Na, K.; Lee, C.; Ryoo, R. Mesoporous MFI Zeolite Nanosponge Supporting Cobalt Nanoparticles as a Fischer–Tropsch Catalyst with High Yield of Branched Hydrocarbons in the Gasoline Range. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3919–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomonik, I.G.; Gorshkov, A.S.; Mordkovich, V.Z. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over a Cobalt Catalyst Supported on Titania-Doped Silicon Carbide. Catal. Ind. 2020, 12, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Motchelaho, M.A.; Moyo, M.; Jewell, L.L.; Coville, N.J. Correlating the preparation and performance of cobalt catalysts supported on carbon nanotubes and carbon spheres in the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. J. Catal. 2011, 278, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Andrew, “Catalysis Science & Technology Fischer – Tropsch synthesis of hydrocarbons from,” pp. 2210–2229, 2014.
- C. G. Okoye-chine, M. Moyo, and D. Hildebrandt, “Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Fischer – Tropsch synthesis : The effect of hydrophobicity on silica-supported iron catalysts,” J. Ind. Eng. Chem., vol. 97, pp. 426–433, 2021.
- J. Jung, S. Woo, and D. Ju, “Fischer – Tropsch Synthesis over cobalt based catalyst supported on different mesoporous silica,” Catal. Today, vol. 185, no. 1, pp. 168–174, 2012.
- H. Du, M. Jiang, M. Zhao, X. Ma, and Z. Xu, “ScienceDirect Activity and selectivity enhancement of silica supported cobalt catalyst for alcohols production from syngas via Fischer-Tropsch synthesis,” Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, vol. 47, no. 7, pp. 4559–4567, 2021.
- H. Singleton, R. Oukaci, and J. G. Goodwin, “Fischer-Tropsch Activity for Non Promoted Cobalton-Alumina Catalysts,” vol. 1, no. 12, 2001.
- Bezemer, G.; Radstake, P.; Falke, U.; Oosterbeek, H.; Kuipers, H.; Vandillen, A.; Dejong, K. Investigation of promoter effects of manganese oxide on carbon nanofiber-supported cobalt catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. J. Catal. 2006, 237, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. H. Bartholomew, “Effects of Support and Dispersion on the CO Hydrogenation Activity / Selectivity Properties of Cobalt,” vol. 88, 1984.
- Z. Yu, Ø. Borg, D. Chen, C. Enger, V. Frøseth, and E. Rytter, “Carbon Nanofiber Supported Cobalt Catalysts for Fischer – Tropsch Synthesis with High Activity and Selectivity Carbon nanofiber supported cobalt catalysts for Fischer – Tropsch synthesis with high activity and selectivity,” no. June, pp. 1–6, 2006.
- Iglesia, E. Design, synthesis, and use of cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 1997, 161, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E. S. P. B. V, “Design of Fischer-Tropsch Catalysts by Pulse Surface Reaction Rate Analysis II. Selective Production of Liquid Fuel Fraction on Ruthenium / Alumina Catalyst Promoted by Rare Earth Oxides,” vol. 38, pp. 61–69, 1988.
- Bertole, C.J.; A Mims, C.; Kiss, G. Support and rhenium effects on the intrinsic site activity and methane selectivity of cobalt Fischer–Tropsch catalysts. J. Catal. 2004, 221, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. Jalama et al., “Applied Catalysis A : General A comparison of Au / Co / Al 2 O 3 and Au / Co / SiO 2 catalysts in the Fischer – Tropsch reaction,” vol. 395, pp. 1–9, 2011.
- Martínez, C. López, F. Márquez, and I. Díaz, “Fischer-Tropsch synthesis of hydrocarbons over mesoporous Co/SBA-15 catalysts: The influence of metal loading, cobalt precursor, and promoters,” J. Catal., vol. 220, no. 2, pp. 486–499, 2003.
- Ernst, S. Libs, P. Chaumette, and A. Kiennemann, “Preparation and characterization of Fischer – Tropsch active Co / SiO 2 catalysts,” vol. 186, pp. 145–168, 1999.
- Saib, A.; Claeys, M.; van Steen, E. Silica supported cobalt Fischer–Tropsch catalysts: effect of pore diameter of support. Catal. Today 2002, 71, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Z. Gholami, Z. Tišler, and V. Rubáš, “Recent advances in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis using cobalt-based catalysts : a review on supports, promoters, and reactors Recent advances in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis using,” Catal. Rev., vol. 63, no. 3, pp. 512–595, 2021.
- Fu, T.; Li, Z. Review of recent development in Co-based catalysts supported on carbon materials for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 135, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y. Chen, J. Wei, M. S. Duyar, V. V Ordomsky, A. Y. Khodakov, and J. Liu, “To cite this version : Chem Soc Rev,” 2022.
- Jiang, Z.-S.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Huang, C.-F.; Song, Y.-H.; Li, D.-P.; Liu, Z.-T.; Liu, Z.-W. Metal-support interactions regulated via carbon coating – A case study of Co/SiO2 for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Fuel 2018, 226, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cydric, A. Nzihou, P. Serp, K. Soulantica, and D. Pham, “Applied Catalysis A, General Cobalt catalysts on carbon-based materials for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis : a review,” Appl. Catal. A, Gen., vol. 609, no. 20, p. 117906, 2021. 20 November.
- Iqbal, S.; Davies, T.E.; Morgan, D.J.; Karim, K.; Hayward, J.S.; Bartley, J.K.; Taylor, S.H.; Hutchings, G.J. Fischer Tropsch synthesis using cobalt based carbon catalysts. Catal. Today 2015, 275, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesia, E.; Reyes, S.C.; Madon, R.J. Transport-enhanced $alpha;-olefin readsorption pathways in Ru-catalyzed hydrocarbon synthesis. J. Catal. 1991, 129, 238–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. S. Catalysts, J. Bao, J. He, Y. Zhang, Y. Yoneyama, and N. Tsubaki, “A Core / Shell Catalyst Produces a Spatially Confined Effect and Shape Selectivity in a Consecutive Reaction,” pp. 353–356, 2008.
- Khodakov, A.Y.; Griboval-Constant, A.; Bechara, R.; Zholobenko, V.L. Pore Size Effects in Fischer Tropsch Synthesis over Cobalt-Supported Mesoporous Silicas. J. Catal. 2002, 206, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Horlyck, J.; Finn, M.T.; Mesa, M.G.; Voutchkova-Kostal, A. Electronic Effects of Support Doping on Hydrotalcite-Supported Iridium N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 24705–24713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaseneva, P.; An, N.; Finn, M.; Tidemann, N.; Jose, N.; Voutchkova-Kostal, A.; Lapkin, A. Continuous synthesis of doped layered double hydroxides in a meso-scale flow reactor. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V. K. Yadav and T. Das, “Reaction Chemistry & Engineering the FeMnO δ / MgO – Al 2 O 3 catalyst used for the,” pp. 2298–2312, 2022.
- Kraum, M.; Baerns, M. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: the influence of various cobalt compounds applied in the preparation of supported cobalt catalysts on their performance. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 1999, 186, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y. Lee, B. Kim, H. Park, S. Ahn, K. Kim, and H. Roh, “Customized Ni – MgO – Al 2 O 3 catalyst for carbon dioxide reforming of coke oven gas : Optimization of preparation method and co-precipitation pH,” vol. 42, no. September, 2020.
- Nakanishi, M.; Uddin, A.; Kato, Y.; Nishina, Y.; Hapipi, A.M. Effects of preparation method on the properties of cobalt supported β-zeolite catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Catal. Today 2017, 291, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Arsalanfar, A. A. Mirzaei, H. R. Bozorgzadeh, and A. Samimi, “CHEMISTRY A Review of Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis on the Cobalt Based Catalysts,” 2014.
- Mohammadi, H.; Nekobahr, E.; Akhtari, J.; Saeedi, M.; Akbari, J.; Fathi, F. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles by co-precipitation method coated with biocompatible compounds and evaluation of in-vitro cytotoxicity. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirichenko, G. W. Graham, W. Chun, and R. W. Mccabe, Effect of coprecipitation conditions on the surface area, phase composition, and reducibility of CeO2-ZrO2-Y2O3 materials for automotive three-Way catalysts, vol. 118. Elsevier Masson SAS, 1998.
- M. Kipnis, E. Volnina, I. Belostotsky, R. Galkin, and N. Zhilyaeva, “Effective Cu / ZnO / Al 2 O 3 Catalyst for Methanol Production : Synthesis, Activation, Catalytic Performance, and Regeneration.
- Dubey, R.; Rajesh, Y.; More, M. Synthesis and Characterization of SiO2 Nanoparticles via Sol-gel Method for Industrial Applications. Mater. Today: Proc. 2015, 2, 3575–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Parashar, V. Kumar, and S. Ranbir, “Metal oxides nanoparticles via sol – gel method : a review on synthesis, characterization and applications,” J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 3729–3749, 2020.
- Bokov, D.; Jalil, A.T.; Chupradit, S.; Suksatan, W.; Ansari, M.J.; Shewael, I.H.; Valiev, G.H.; Kianfar, E. Nanomaterial by Sol-Gel Method: Synthesis and Application. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Elam, J.W.; Stair, P.C. Synthesis and Stabilization of Supported Metal Catalysts by Atomic Layer Deposition. Accounts Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, M.J.; Mackus, A.J.M.; Verheijen, M.A.; van der Marel, C.; Kessels, W.M.M. Supported Core/Shell Bimetallic Nanoparticles Synthesis by Atomic Layer Deposition. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 2973–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Zhang, Z. Lou, M. Zhou, and H. Wei, “Accepted Article.
- G. Vinothkumar, S. Rengaraj, P. Arunkumar, S. W. Cha, and K. S. Babu, “and La 3 + ) - Doped Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles for Enhanced Multienzyme-Mimetic and Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity,” 2019.
- Ichinose and, H. Senzu, “A Surface Sol - Gel Process of TiO 2 and Other Metal Oxide Films with Molecular,” vol. 4756, no. 10, pp. 1296–1298, 1997.
- Yan, W.; Mahurin, S.M.; Overbury, S.H.; Dai, S. Nanoengineering catalyst supports via layer-by-layer surface functionalization. Top. Catal. 2006, 39, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Ersen, O.; Chu, W.; Dintzer, T.; Petit, P.; Petit, C. Anchoring and promotion effects of metal oxides on silica supported catalytic gold nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 482, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savost’yanov, A.P.; Yakovenko, R.E.; Sulima, S.I.; Bakun, V.G.; Narochnyi, G.B.; Chernyshev, V.M.; Mitchenko, S.A. The impact of Al 2 O 3 promoter on an efficiency of C 5+ hydrocarbons formation over Co/SiO 2 catalysts via Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Catal. Today 2017, 279, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.-P.; Ding, Y.-J.; Lin, L.-W. Fischer−Tropsch Synthesis over Activated-Carbon-Supported Cobalt Catalysts: Effect of Co Loading and Promoters on Catalyst Performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 2391–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y. Huang, W. Li, J. Ren, and X. Qu, “Accepted Article.
- B. Wang, F. Liu, Y. Wu, Y. Chen, B. Weng, and C. M. Li, “Sensors and Actuators B : Chemical Synthesis of catalytically active multielement-doped carbon dots and application for colorimetric detection of glucose,” Sensors Actuators B. Chem., vol. 255, pp. 2601–2607, 2018.
- M. Gao, X. Lu, M. Chi, S. Chen, and C. Wang, “INORGANIC CHEMISTRY FRONTIERS nano fi bers and their sensitive colorimetric detection of sul fi te and L -cysteine †,” pp. 1862–1869, 2017.
- M. P. C. Van Etten, M. E. De Laat, E. J. M. Hensen, and I. A. W. Filot, “Unraveling the Role of Metal − Support Interactions on the Structure Sensitivity of Fischer − Tropsch Synthesis,” 2023.
- Y. Zhang et al., “Ru/TiO 2 Catalysts with Size-Dependent Metal/Support Interaction for Tunable Reactivity in Fischer − Tropsch Synthesis,” 2020.
- Q. Cheng, Y. Liu, S. Lyu, Y. Tian, Q. Ma, and X. Li, “Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering Manipulating metal-support interactions of metal catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis,” Chinese J. Chem. Eng., vol. 35, pp. 220–230, 2021.
- Macheli, L.; Carleschi, E.; Doyle, B.P.; Leteba, G.; van Steen, E. Tuning catalytic performance in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis by metal-support interactions. J. Catal. 2020, 395, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, R.; Giorgio, S.; Henry, C.R.; Louis, C. Alternative Methods for the Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles Supported on TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 7634–7642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. A. Calzada et al., “Applied Catalysis B : Environmental Au-Ru / TiO 2 prepared by deposition-precipitation with urea : Relevant synthesis parameters to obtain bimetallic particles,” Appl. Catal. B Environ., vol. 264, no. January 2019, p. 118503, 2020.
- Manawi, Y.M.; Ihsanullah; Samara, A. ; Al-Ansari, T.; Atieh, M.A. A Review of Carbon Nanomaterials’ Synthesis via the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Method. Materials 2018, 11, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. Dahmen, “Chemical Vapor Deposition,” vol. 2, 2002.
- Yang, N.; Bent, S.F. Investigation of inherent differences between oxide supports in heterogeneous catalysis in the absence of structural variations. J. Catal. 2017, 351, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, P.; Duan, X.; Gu, L.; Fu, G.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, N. Interfacing with silica boosts the catalysis of copper. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L. C. Almeida et al., “Fischer-tropsch catalyst deposition on metallic structured supports,” Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal., vol. 167, pp. 79–84, 2007.
- Shimura, K.; Miyazawa, T.; Hanaoka, T.; Hirata, S. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over TiO2 supported cobalt catalyst: Effect of TiO2 crystal phase and metal ion loading. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2013, 460-461, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N. C. Shiba, X. Liu, H. Mao, X. Qian, D. Hildebrandt, and Y. Yao, “Effect of Ru-promotion on the catalytic performance of a cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst activated in syngas or H 2,” Fuel, vol. 320, no. December 2021, p. 123939, 2022.
- Tucker, C.L.; Ragoo, Y.; Mathe, S.; Macheli, L.; Bordoloi, A.; Rocha, T.C.; Govender, S.; Kooyman, P.J.; van Steen, E. Manganese promotion of a cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalyst to improve operation at high conversion. J. Catal. 2022, 411, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasu, M.; Marquart, W.; Kooyman, P.J.; Drivas, C.; Isaacs, M.A.; Mayer, A.J.; Dann, S.E.; Kondrat, S.A.; Claeys, M.; Fischer, N. Empowering Catalyst Supports: A New Concept for Catalyst Design Demonstrated in the Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 6862–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukkathanyawat, H.; Tungkamani, S.; Phongaksorn, M.; Rattana, T.; Narataruksa, P.; Yoosuk, B. Promoter Effect on the Physico-chemical Properties of Cobalt Based Catalyst for CO Hydrogenation. Energy Procedia 2015, 79, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Koppen, L.M.; Dugulan, A.I.; Hensen, E.J.; Bezemer, G.L. Tuning stability of titania-supported Fischer-Tropsch catalysts: impact of surface area and noble metal promotion. Catal. Today 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, F.; Khodakov, A.Y. Promotion of Cobalt Fischer-Tropsch Catalysts with Noble Metals: a Review. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. – Rev. d’IFP Energies Nouv. 2008, 64, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. O. Eschemann, J. Oenema, and K. P. De Jong, “Effects of noble metal promotion for Co / TiO 2 Fischer-Tropsch catalysts,” Catal. Today, vol. 261, pp. 60–66, 2016.
- M. De Beer, A. Kunene, D. Nabaho, M. Claeys, and E. Van Steen, “Technical and economic aspects of promotion of cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalysts by noble metals-a review,” J. South. African Inst. Min. Metall., vol. 114, no. 2, pp. 157–165, 2014.
- W. Ma, G. Jacobs, R. A. Keogh, D. B. Bukur, and B. H. Davis, “Applied Catalysis A : General Fischer – Tropsch synthesis : Effect of Pd, Pt, Re, and Ru noble metal promoters on the activity and selectivity of a 25 % Co / Al 2 O 3 catalyst,” “Applied Catal. A, Gen., vol. 437–438, pp. 1–9, 2012.
- H. Xiong, M. A. Motchelaho, M. Moyo, L. L. Jewell, and N. J. Coville, “Effect of Group I alkali metal promoters on Fe / CNT catalysts in Fischer – Tropsch synthesis,” FUEL, vol. 150, pp. 687–696, 2015.
- Y. Yang, H. Zhang, H. Ma, W. Qian, Q. Sun, and W. Ying, “Effect of alkalis ( Li, Na, and K ) on precipitated iron-based catalysts for high-temperature Fischer-Tropsch synthesis,” Fuel, vol. 326, no. June, p. 125090, 2022.
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J. Synergistic Effect of Alkali Na and K Promoter on Fe-Co-Cu-Al Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Light Hydrocarbons. Catalysts 2021, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.R.; Bell, A.T. Effects of Lewis acidity of metal oxide promoters on the activity and selectivity of Co-based Fischer–Tropsch synthesis catalysts. J. Catal. 2016, 338, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Saheli, A. Reza, R. Azim, M. Michal, and D. Vaclav, “Effect of Synthetic Route and Metal Oxide Promoter on Cobalt-Based Catalysts for Fischer – Tropsch Synthesis,” Catal. Letters, vol. 148, no. 11, pp. 3557–3569, 2018.
- Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Hou, B. Cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Effect of the catalyst granule thermal conductivity on the catalytic performance. Mol. Catal. 2021, 502, 111395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Li, C. Zhang, X. Cheng, M. Qing, J. Xu, and B. Wu, “Applied Catalysis A : General Effects of alkaline-earth metals on the structure, adsorption and catalytic behavior of iron-based Fischer – Tropsch synthesis catalysts,” “Applied Catal. A, Gen., vol. 464–465, pp. 10–19, 2013.
- H. Ma, Y. Yang, H. Fu, H. Zhang, W. Qian, and Q. Sun, “Effect of alkaline-earth metals ( Mg, Ca, Sr, and Ba ) on precipitated iron-based catalysts for high-temperature Fischer-Tropsch synthesis of light olefins,” Fuel, vol. 357, no. PA, p. 129605, 2024.
- M. Z. Leguizam et al., “Fischer – Tropsch Synthesis : Effect of the Promoter ’ s Ionic Charge and Valence Level Energy on Activity,” pp. 408–426, 2021.
- Horáček, J. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, the effect of promoters, catalyst support, and reaction conditions selection. Monatshefte Fuer Chemie/chemical Mon. 2020, 151, 649–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y. Suo, Y. Yao, Y. Zhang, S. Xing, and Z. Yuan, “Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Recent advances in cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts,” J. Ind. Eng. Chem., vol. 115, pp. 92–119, 2022.
- H. Wu, Y. Yang, H. Suo, M. Qing, L. Yan, and B. Wu, “Journal of Molecular Catalysis A : Chemical Effects of ZrO 2 promoter on physic-chemical properties and activity of Co / TiO 2 – SiO 2 Fischer – Tropsch catalysts,” vol. 396, pp. 108–119, 2015.
- C. Lu, Y. Lin, and I. Wang, “Naphthalene hydrogenation over Pt / TiO 2 – ZrO 2 and the behavior of strong metal – support interaction ( SMSI ),” vol. 198, pp. 223–234, 2000.
- M. Ruppert and T. Paryjczak, “Pt / ZrO 2 / TiO 2 catalysts for selective hydrogenation of crotonaldehyde : Tuning the SMSI effect for optimum performance,” vol. 320, pp. 80–90, 2007.
- Damyanova, S.; Grange, P.; Delmon, B. Surface Characterization of Zirconia-Coated Alumina and Silica Carriers. J. Catal. 1997, 168, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- s2.0-S002195178571113X-main.pdf.”.
- E. Iglesia, “Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis on Cobalt Catalysts: Structural Requirements and Reaction Pathways,” vol. 107, pp. 153–162, 1997.
- Corma and, F. V Melo, “Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis 130 A. Corma, F.V. Melo, S.Mendioroz and J.L.G. Fierro (Editors) 9 2000 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved. 1097,” pp. 1097–1102, 2000.
- F. Tropsch and L. U. Okonye, “Sustainable Energy & Fuels Contributing to energy sustainability : a review of mesoporous material supported catalysts for,” pp. 79–107, 2021.
- Vosoughi, V.; Badoga, S.; Dalai, A.K.; Abatzoglou, N. Modification of mesoporous alumina as a support for cobalt-based catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 162, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Lualdi, Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Cobalt-based Catalysts for BTL Applications. 2012.
- Jacobs, G.; Das, T.K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Racoillet, G.; Davis, B.H. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: support, loading, and promoter effects on the reducibility of cobalt catalysts. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2002, 233, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- et al. , “Fischer-Tropsch synthesis over γ-alumina-supported cobalt catalysts: Effect of support variables,” J. Catal., vol. 248, no. 1, pp. 89–100, May 2007.
- Cai, Z.; Li, J.; Liew, K.; Hu, J. Effect of La2O3-dopping on the Al2O3 supported cobalt catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2010, 330, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Z. Li, J. Wu, and L. Wu, “Effect of Zr, Ca and Mn as promoters on the Co/SiC catalysts for the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis,” React. Kinet. Mech. Catal., vol. 122, no. 2, pp. 887–900, 2017.
- Jacobs, G.; Das, T.K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Racoillet, G.; Davis, B.H. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: support, loading, and promoter effects on the reducibility of cobalt catalysts. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2002, 233, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. A. Iloy and K. Jalama, “E ff ect of Operating Temperature, Pressure and Silica-Supported Cobalt Catalyst in CO 2,” 2019.
- V. Garcilaso, J. Barrientos, L. F. Bobadilla, O. H. Laguna, and M. Boutonnet, “Promoting effect of CeO 2, ZrO 2 and Ce / Zr mixed oxides on Co / g -Al 2 O 3 catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis,” vol. 132, pp. 1141–1150, 2019.
- J. Barrientos, V. Garcilaso, B. Venezia, and A. Aho, “Fischer – Tropsch Synthesis Over Zr-Promoted Co / γ-Al 2 O 3 Catalysts,” Top. Catal., vol. 60, no. 17, pp. 1285–1298, 2017.
- Wu, H.; Yang, Y.; Suo, H.; Qing, M.; Yan, L.; Wu, B.; Xu, J.; Xiang, H.; Li, Y. Effects of ZrO 2 promoter on physic-chemical properties and activity of Co/TiO 2 –SiO 2 Fischer–Tropsch catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2015, 396, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breejen, J.P.D.; Frey, A.M.; Yang, J.; Holmen, A.; van Schooneveld, M.M.; de Groot, F.M.F.; Stephan, O.; Bitter, J.H.; de Jong, K.P. A Highly Active and Selective Manganese Oxide Promoted Cobalt-on-Silica Fischer–Tropsch Catalyst. Top. Catal. 2011, 54, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. Morales et al., “In Situ X-ray Absorption of Co / Mn / TiO 2 Catalysts for Fischer - Tropsch Synthesis,” pp. 16201–16207, 2004.
- Monshi, A.; Foroughi, M.R.; Monshi, M.R. Modified Scherrer Equation to Estimate More Accurately Nano-Crystallite Size Using XRD. World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 2012, 02, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. R. Moradi, “Promotion of Co = SiO 2 Fischer – Tropsch catalysts with zirconium,” vol. 4, pp. 27–32, 2003.
- L. Bezemer, Cobalt supported on carbon nanofibers as catalysts for the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis.
- Bao, K. Liew, and J. Li, “Journal of Molecular Catalysis A : Chemical Fischer – Tropsch synthesis on CaO-promoted Co / Al 2 O 3 catalysts,” vol. 0, pp. 47–51, 2009.
- S. C. Reyes, R. J. Madon, and S. L. Soled, “Selectivity Control and Catalyst Design in the Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis : Sites, Pellets, and Reactors,” vol. 39, 1993.
- Enger, B.C.; Fossan. -L.; Borg,.; Rytter, E.; Holmen, A. Modified alumina as catalyst support for cobalt in the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. J. Catal. 2011, 284, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Nurunnabi and S. Q. Turn, “Pore size effects on Ru / SiO 2 catalysts with Mn and Zr promoters for Fischer – Tropsch synthesis,” Fuel Process. Technol., vol. 130, pp. 155–164, 2015.
- F. Gu, “La, Mn and Zn promoted microporous iron catalysts with high productivity and stability,” pp. 147–159, 2016.
- Dinse, M. Aigner, M. Ulbrich, G. R. Johnson, and A. T. Bell, “Effects of Mn promotion on the activity and selectivity of Co / SiO 2 for Fischer – Tropsch Synthesis,” vol. 288, pp. 104–114, 2012.
- Eschemann, T.O.; Oenema, J.; de Jong, K.P. Effects of noble metal promotion for Co/TiO2 Fischer-Tropsch catalysts. Catal. Today 2016, 261, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Z. Li, J. Wu, and L. Wu, “Effect of Zr, Ca and Mn as promoters on the Co / SiC catalysts for the Fischer – Tropsch synthesis,” React. Kinet. Mech. Catal., vol. 122, no. 2, pp. 887–900, 2017.
- Subramanian, V.; Zholobenko, V.L.; Cheng, K.; Lancelot, C.; Heyte, S.; Thuriot, J.; Paul, S.; Ordomsky, V.V.; Khodakov, A.Y. The Role of Steric Effects and Acidity in the Direct Synthesis of iso-Paraffins from Syngas on Cobalt Zeolite Catalysts. ChemCatChem 2015, 8, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-H.; Bae, J.W.; Prasad, P.S.S.; Park, S.-J.; Woo, K.-J.; Jun, K.-W. Effect of Preparation Method of Fe–based Fischer–Tropsch Catalyst on their Light Olefin Production. Catal. Lett. 2009, 130, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gac, W.; Zawadzki, W.; Greluk, M.; Słowik, G.; Rotko, M.; Kuśmierz, M. The Effects of Ce and W Promoters on the Performance of Alumina-Supported Nickel Catalysts in CO2 Methanation Reaction. Catalysts 2021, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. Zhai, G. Sun, Q. Zhu, and D. Ma, “Fischer-tropsch synthesis nanostructured catalysts: Understanding structural characteristics and catalytic reaction,” Nanotechnol. Rev., vol. 2, no. 5, pp. 547–576, 2013.
- Macheli, L.; Roy, A.; Carleschi, E.; Doyle, B.P.; van Steen, E. Surface modification of Co3O4 nanocubes with TEOS for an improved performance in the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Catal. Today 2018, 343, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. Petersen, M. Claeys, P. J. Kooyman, and E. Van Steen, “Cobalt-Based Fischer – Tropsch Synthesis : A Kinetic Inverse Model System,” 2019.
- Sun, K.; Tan, M.; Bai, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, P.; Gong, N.; Zhang, T.; Yang, G.; Tan, Y. Design and synthesis of spherical-platelike ternary copper-cobalt-manganese catalysts for direct conversion of syngas to ethanol and higher alcohols. J. Catal. 2019, 378, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Göbel et al., “Structural evolution of bimetallic Co-Cu catalysts in CO hydrogenation to higher alcohols at high pressure,” vol. 383, pp. 33–41, 2020.
- L. Zhao, W. Li, J. Zhou, X. Mu, and K. Fang, “ScienceDirect One-step synthesis of Cu e Co alloy / Mn 2 O 3 e Al 2 O 3 composites and their application in higher alcohol synthesis from syngas,” Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, vol. 42, no. 27, pp. 17414–17424, 2017.
- Z. Zhao et al., “Tuning the Fischer – Tropsch reaction over Co x Mn y La / AC catalysts toward alcohols : Effects of La promotion,” J. Catal., vol. 361, pp. 156–167, 2018.
- Z. Zhao et al., “Ziang Zhao, †, ‡, ¶ Wei Lu, †, ¶ Ruoou Yang, ‡, ∥ Hejun Zhu, *, † Wenda Dong, † Fanfei Sun, ‡, ∥ Zheng Jiang, *, ∥ Yuan Lyu, † Tao Liu, † Hong Du, † and Yunjie Ding *, †, § †,” 2018.
- Z. Shi, H. Yang, P. Gao, X. Chen, H. Liu, and L. Zhong, “Effect of alkali metals on the performance of CoCu / TiO 2 catalysts for CO 2 hydrogenation to long - chain hydrocarbons,” Chinese J. Catal., vol. 39, no. 8, pp. 1294–1302, 2018.
- Pei, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, H.; Du, H. One-step production of C1–C18 alcohols via Fischer-Tropsch reaction over activated carbon-supported cobalt catalysts: Promotional effect of modification by SiO2. Chin. J. Catal. 2015, 36, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. C. Ribeiro et al., “Tailoring the product selectivity of Co / SiO 2 Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts by lanthanide doping,” Catal. Today, vol. 343, no. October 2018, pp. 80–90, 2020.
- Y. Dai, F. Yu, Z. Li, Y. An, T. Lin, and Y. Yang, “Effect of Sodium on the Structure-Performance Relationship of Co / SiO 2 for Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis,” 2017.
| Effect on the support and/or catalyst | Promoter elements | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of promotion | Mode | Activity | Selectivity | Stability | |
| Structural | Support stabilization | ✓ | ✓ | Mg, Zr, Nb, Rh, Si, Re, Pt, La | |
| Increasing metal dispersion | ✓ | ✓ | Mn, Zr, Ti, Cr, Pd, Ce, Re, Ru, Th | ||
| Electronic | Metal catalyst alloying | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Ni, Re, Pt, Ir, Cu, Pd |
| Synergistic | Water-gas Shift | ✓ | ✓ | Ce, Cu, Mn, B | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




