Submitted:
08 May 2024
Posted:
09 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical and Molecular Analysis
2.2. Functional Study Using Yeast Model
2.3. LIPT2 Sequence Alignment
2.4. LIPT2 Protein Structure Predictions
3. Results
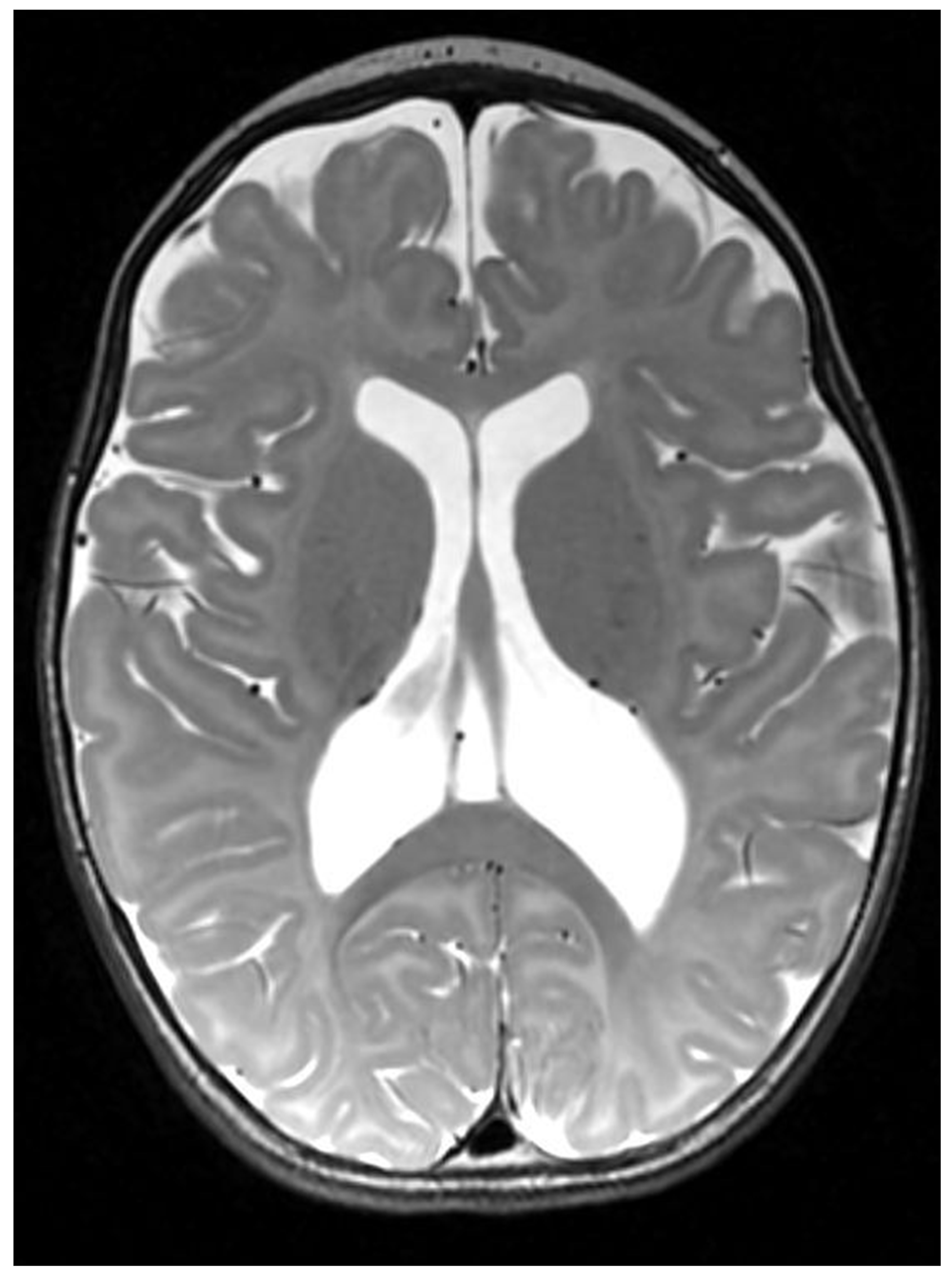
3.1. Clinical Case Report
3.2. Molecular Analysis
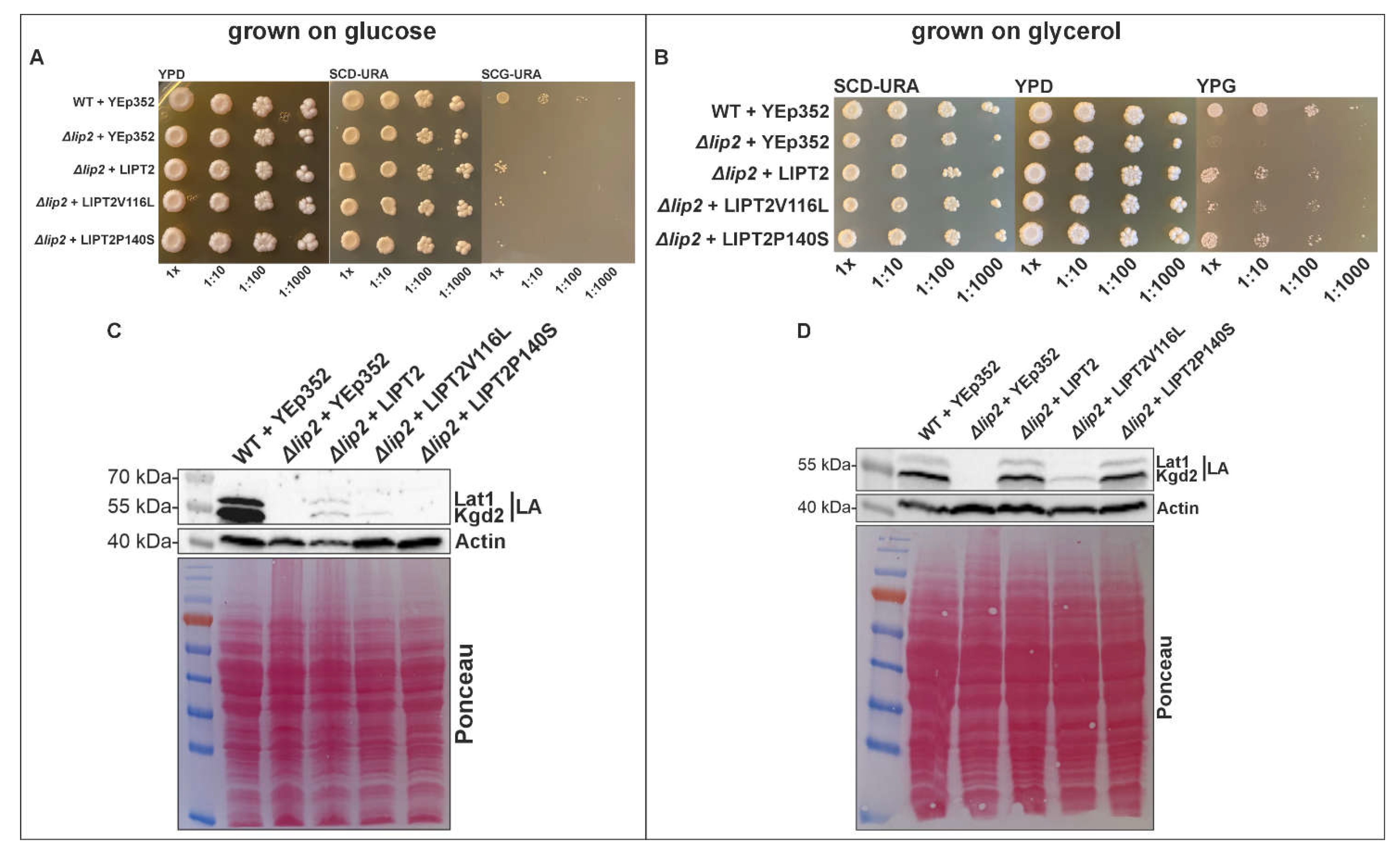
3.3. Functional Study Using Yeast Model System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Mayr JA, Feichtinger RG, Tort F, Ribes A, Sperl W. Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014 Jul;37(4):553-63.
- Booker, SJ. Unraveling the pathway of lipoic acid biosynthesis. Chem Biol. 2004 Jan;11(1):10-2.
- Pietikäinen LP, Rahman MT, Hiltunen JK, Dieckmann CL, Kastaniotis AJ. Genetic dissection of the mitochondrial lipoylation pathway in yeast. BMC Biol. 2021 Jan 25;19(1):14.
- Soreze Y, Boutron A, Habarou F, Barnerias C, Nonnenmacher L, Delpech H, Mamoune A, Chrétien D, Hubert L, Bole-Feysot C, Nitschke P, Correia I, Sardet C, Boddaert N, Hamel Y, Delahodde A, Ottolenghi C, de Lonlay P. Mutations in human lipoyltransferase gene LIPT1 cause a Leigh disease with secondary deficiency for pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013 Dec 17;8:192.
- Tort F, Ferrer-Cortès X, Thió M, Navarro-Sastre A, Matalonga L, Quintana E, Bujan N, Arias A, García-Villoria J, Acquaviva C, Vianey-Saban C, Artuch R, García-Cazorla À, Briones P, Ribes A. Mutations in the lipoyltransferase LIPT1 gene cause a fatal disease associated with a specific lipoylation defect of the 2-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes. Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Apr 1;23(7):1907-15.
- Baker PR 2nd, Friederich MW, Swanson MA, Shaikh T, Bhattacharya K, Scharer GH, Aicher J, Creadon-Swindell G, Geiger E, MacLean KN, Lee WT, Deshpande C, Freckmann ML, Shih LY, Wasserstein M, Rasmussen MB, Lund AM, Procopis P, Cameron JM, Robinson BH, Brown GK, Brown RM, Compton AG, Dieckmann CL, Collard R, Coughlin CR 2nd, Spector E, Wempe MF, Van Hove JL. Variant non ketotic hyperglycinemia is caused by mutations in LIAS, BOLA3 and the novel gene GLRX5. Brain. 2014 Feb;137(Pt 2):366-79.
- Wongkittichote P, Chhay C, Zerafati-Jahromi G, Weisenberg JL, Mian A, Jensen LT, Grange DK. Novel LIAS variants in a patient with epilepsy and profound developmental disabilities. Mol Genet Metab. 2023 Mar;138(3):107373.
- Habarou F, Hamel Y, Haack TB, Feichtinger RG, Lebigot E, Marquardt I, Busiah K, Laroche C, Madrange M, Grisel C, Pontoizeau C, Eisermann M, Boutron A, Chrétien D, Chadefaux-Vekemans B, Barouki R, Bole-Feysot C, Nitschke P, Goudin N, Boddaert N, Nemazanyy I, Delahodde A, Kölker S, Rodenburg RJ, Korenke GC, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Prokisch H, Rotig A, Ottolenghi C, Mayr JA, de Lonlay P. Biallelic Mutations in LIPT2 Cause a Mitochondrial Lipoylation Defect Associated with Severe Neonatal Encephalopathy. Am J Hum Genet. 2017 Aug 3;101(2):283-290.
- Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, McWilliam H, Remmert M, Söding J, Thompson JD, Higgins DG. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol. 2011 Oct 11;7:539.
- Jumper J, Evans R, Pritzel A, Green T, Figurnov M, Ronneberger O, Tunyasuvunakool K, Bates R, Žídek A, Potapenko A, Bridgland A, Meyer C, Kohl SAA, Ballard AJ, Cowie A, Romera-Paredes B, Nikolov S, Jain R, Adler J, Back T, Petersen S, Reiman D, Clancy E, Zielinski M, Steinegger M, Pacholska M, Berghammer T, Bodenstein S, Silver D, Vinyals O, Senior AW, Kavukcuoglu K, Kohli P, Hassabis D. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature. 2021 Aug;596(7873):583-589.
- Ortigoza-Escobar JD. A Proposed Diagnostic Algorithm for Inborn Errors of Metabolism Presenting With Movements Disorders. Front Neurol. 2020 Nov 13;11:582160.
- Zea Vera A, Gropman AL. Surgical treatment of movement disorders in neurometabolic conditions. Front Neurol. 2023 Jun 2;14:1205339.
- Gropman AL. Neuroimaging in mitochondrial disorders. Neurotherapeutics. 2013 Apr;10(2):273-85.
- Set KK, Sen K, Huq AHM, Agarwal R. Mitochondrial Disorders of the Nervous System: A Review. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2019 Apr;58(4):381-394.
- Brown GK. Congenital brain malformations in mitochondrial disease. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2005;28(3):393-401.
- Ah Mew N, Loewenstein JB, Kadom N, Lichter-Konecki U, Gropman AL, Martin JM, Vanderver A. MRI features of 4 female patients with pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 alpha deficiency. Pediatr Neurol. 2011 Jul;45(1):57-9.
| Name of the primer | Sequence 5´-3´ |
|---|---|
| LIPT2_G346T_Forward | CGCTTGCGCATGCACTTAGCGTCGCTGG |
| LIPT2_G346T_Reverse | CCAGCGACGCTAAGTGCATGCGCAAGCG |
| LIPT2_C418T_Forward | CGCGCGGCCCTCGCCCTACACTGGC |
| LIPT2_C418T_Reverse | GCCAGTGTAGGGCGAGGGCCGCGCG |
| Patient 1 (Habaro et al.) | Patient 2 (Habaro et al.) | Patient 3 (Habaro et al.) | Proband | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | French/Ivory Coast | German | German | Chinese/Vietnamese |
| Clinical Presentation | Truncal hypotonia, spastic tetraplegia and dystonia, epileptic encephalopathy | Severe hypotonia, developmental delay | Severe hypotonia, developmental delay, epilepsy | Severe generalized dystonia, global developmental delay, feeding difficulties and failure to thrive |
| MRI Findings | Supra-tentorial cortical atrophy with ventricular dilatation, bi-frontal white matter abnormalities, and delayed myelination | Enlarged lateral ventricles and formation of cysts in the cortex and white matter of the whole cerebral structures | Periventricular cystic changes | Cortical malformations including ventricular colpocephaly, polymicrogyria and possible subependymal heterotopia |
| Biochemical characteristics | Hyperlactatemia with a high lactate/pyruvate ratio moderate hyperglycinemia, increased alanine and decreased branched-chain amino acids |
Lactic acidosis up to 17 mmol/L at birth | Lactic acidosis 3.7 mmol/L at birth and increased to values between 8 and 10 Elevation of alanine and proline, moderate increase of glycine, and decrease of branched-chain amino acids |
Lactic acidosis upto 6.1 mmol/L, normal plasma amino acid |
| Molecular Variants | c.89T>C and c.377T>G in trans | c.314T>G (p.Leu105Arg) and c.377T>G (p.Leu126Arg) in trans | c.314T>G (p.Leu105Arg) and c.377T>G (p.Leu126Arg) in trans | c.346 G>T (p.V116L) and c.418C>T (p.P140S) in trans |
| Outcome | Alive with no episodes of metabolic decompensation | Died within first month of life | Died within first month of life | Alive with severe dystonia but no episodes of metabolic decompensation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





